Altered Effective Connectivity of the Attentional Network in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy with EEG Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
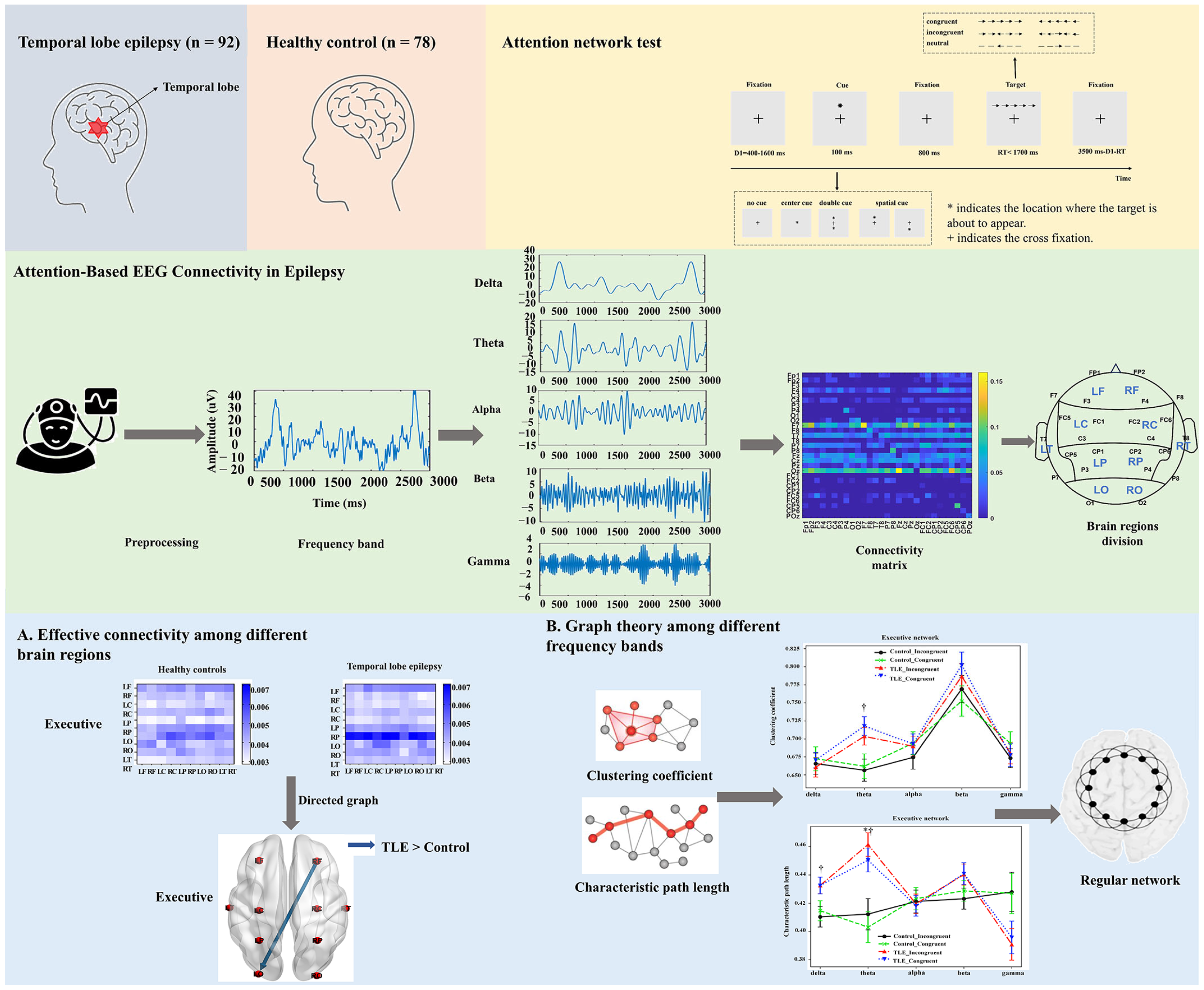
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
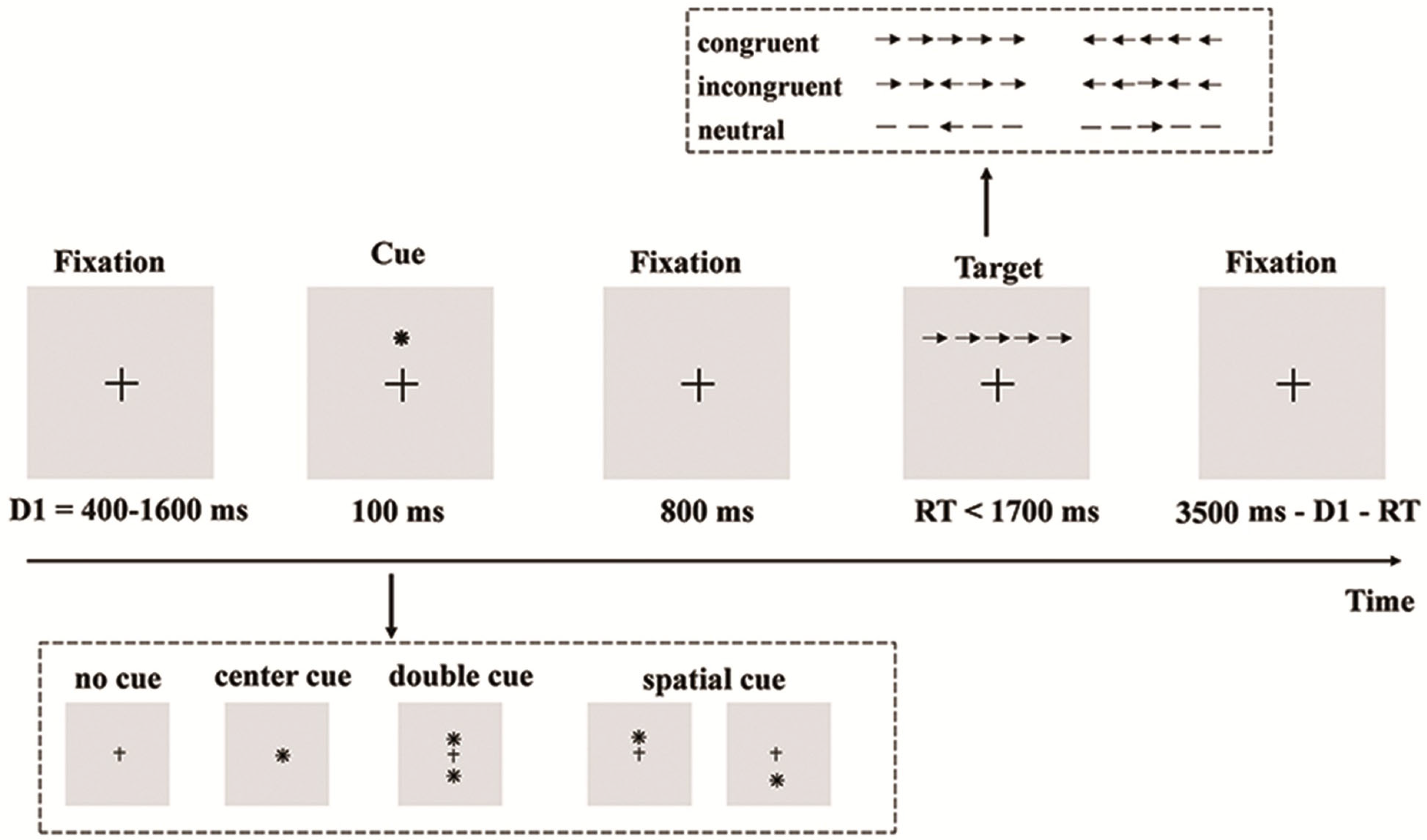
2.2. Behavioral Task Paradigms
2.3. EEG Recording and Preprocessing
2.4. Effective Connectivity Computation
2.5. Effective Connectivity Among the Brain Regions
2.6. Graphic Theoretical Metrics Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics
3.2. Behavioral Characteristics
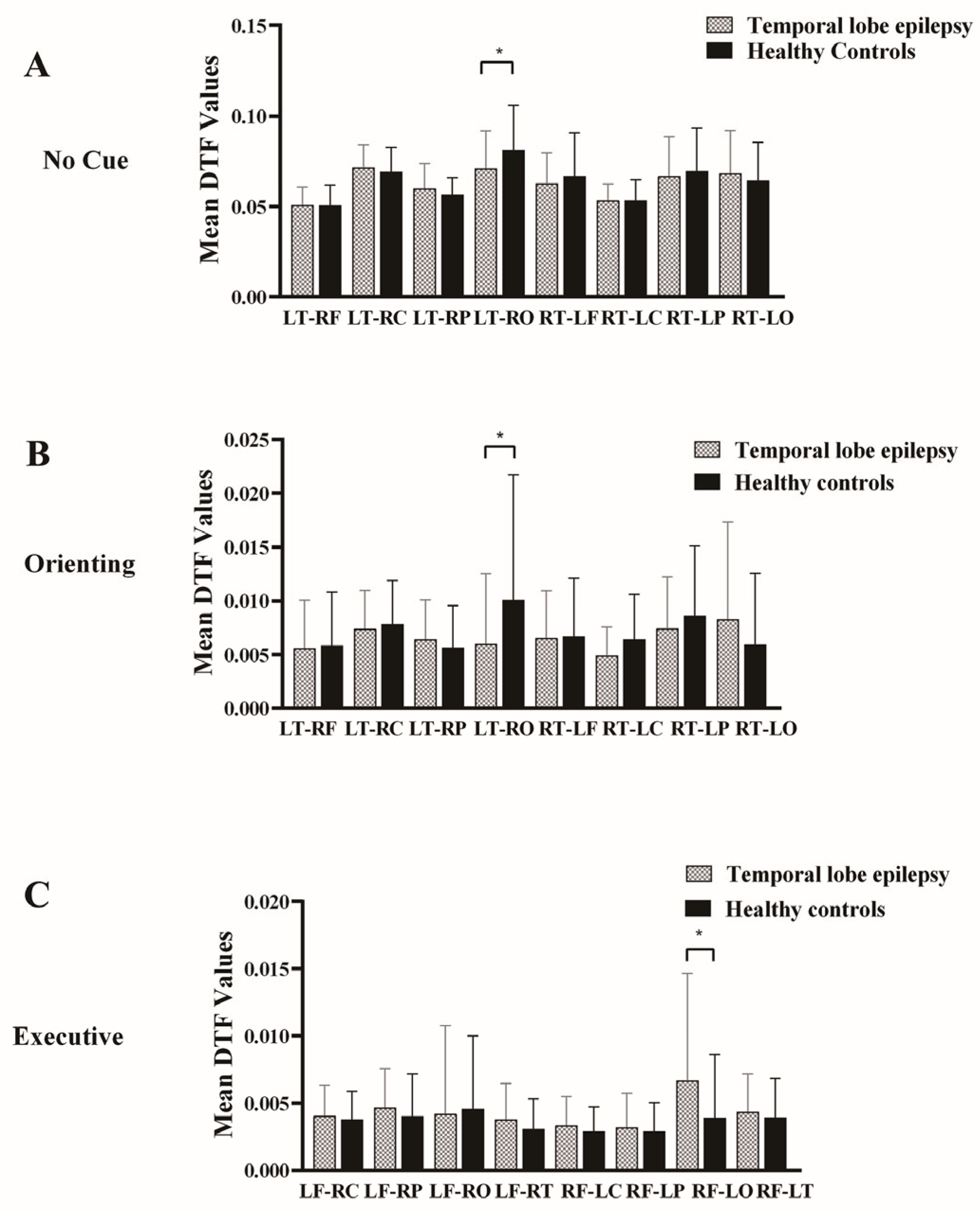
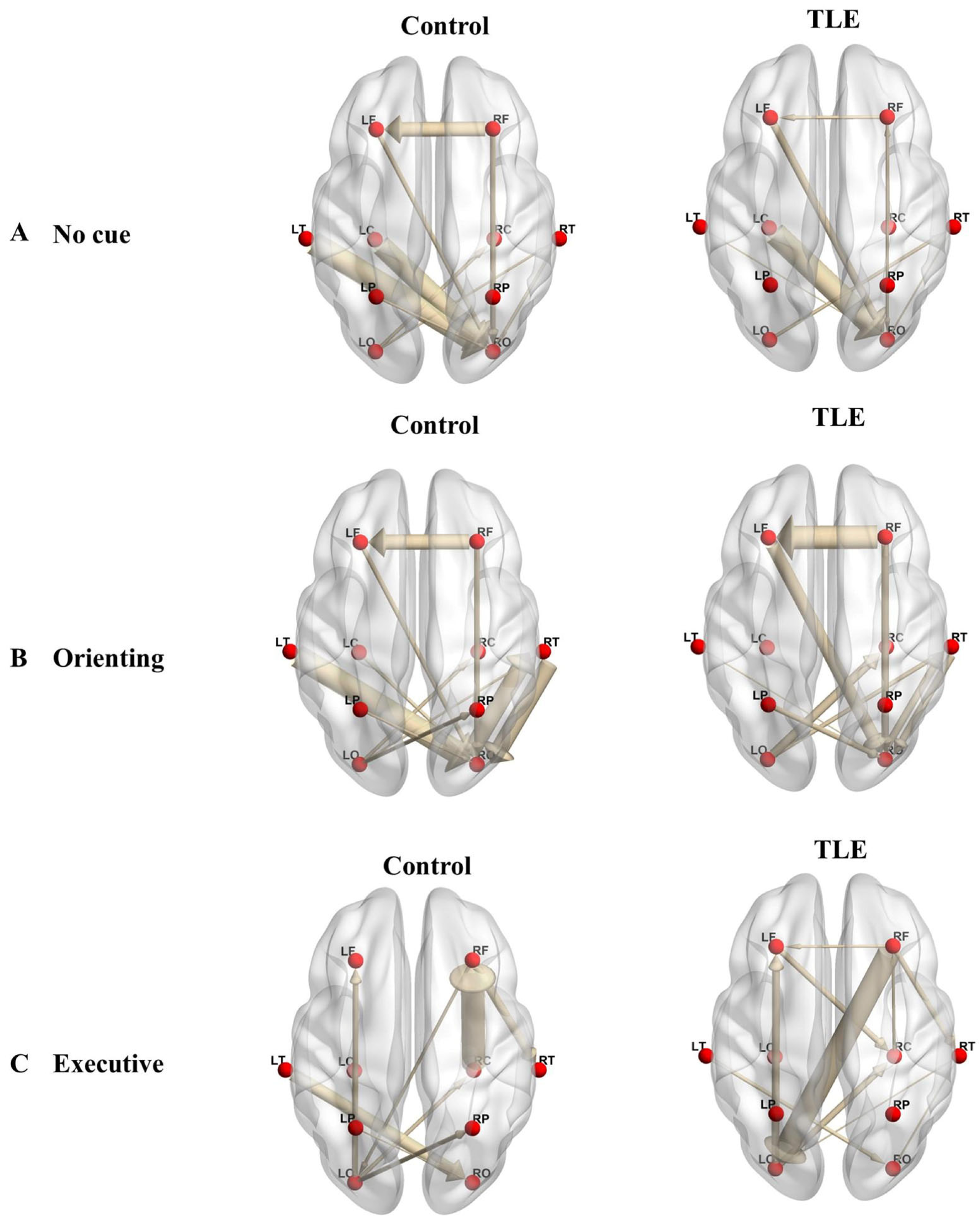
3.3. Effective Connectivity
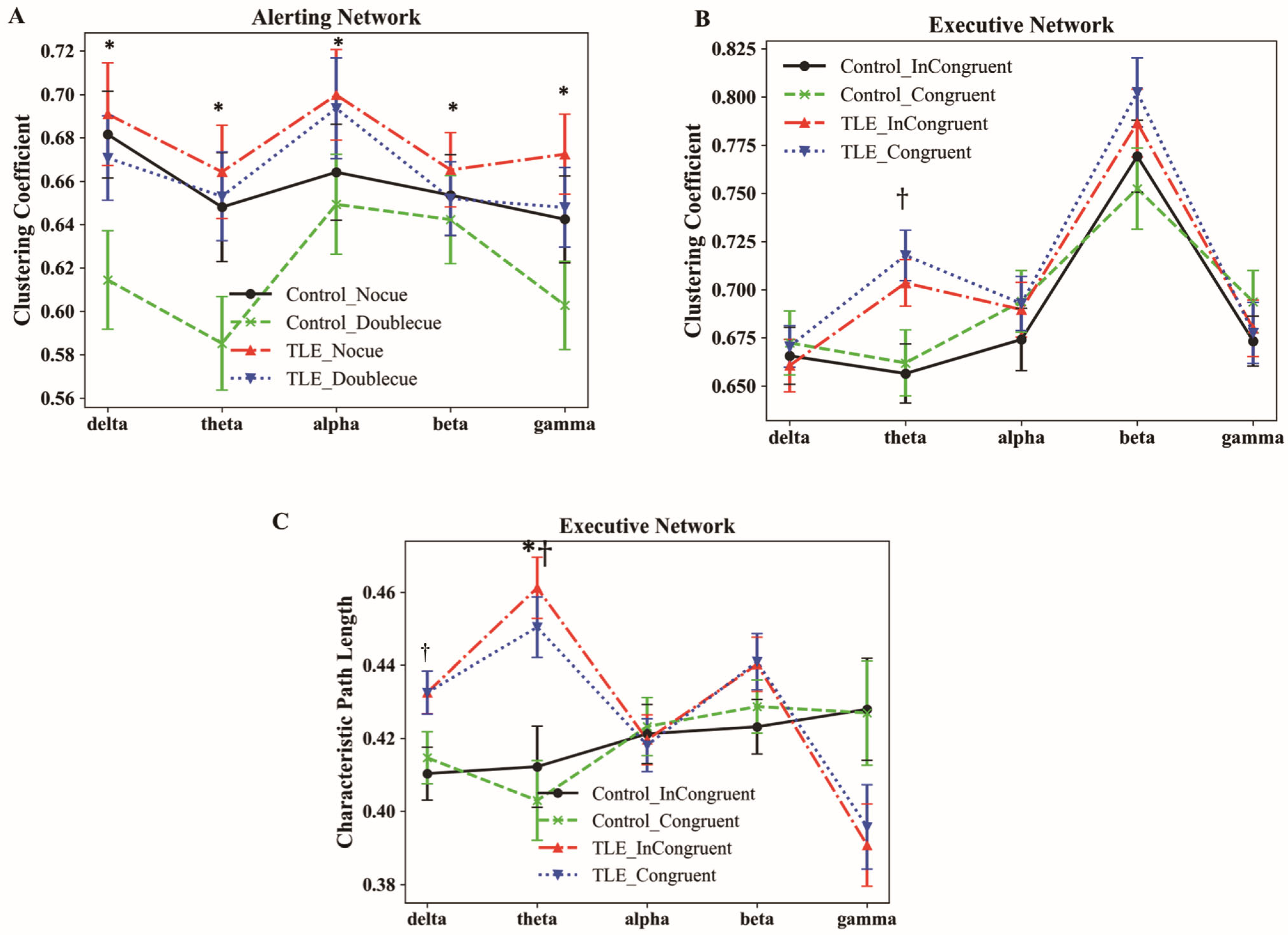
3.4. Characteristics of Graphic Theoretical Metrics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TLE | Temporal lobe epilepsy |
| ANT | Attention networks test |
| fMRI | Functional magnetic resonance imaging |
| EEG | Electroencephalography |
| HC | Healthy control |
| FIR | Finite impulse response |
| CAR | common average reference |
| ICA | Independent component analysis |
| EMG | Electromyogram |
| ECG | Electrocardiogram |
| GC | Granger causality |
| PDC | Partial directed coherence |
| DTF | Direct transfer function |
| MVAR | Multivariate autoregressive |
| BIC | Bayesian information criterion |
| CSD | Current source density |
| CC | Clustering coefficient |
| CPL | Characteristic path length |
| BCT | Brain Connectivity Toolbox |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| MRT | mean reaction time |
References
- Begley, C.; Wagner, R.G.; Abraham, A.; Beghi, E.; Newton, C.; Kwon, C.S.; Labiner, D.; Winkler, A. The global cost of epilepsy: A systematic review and extrapolation. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 892–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermann, B.P.; Seidenberg, M.; Dow, C.; Jones, J.; Rutecki, P.; Bhattacharya, A.; Bell, B. Cognitive prognosis in chronic temporal lobe epilepsy. Ann. Neurol. 2006, 60, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouse, M.A.; Ramanan, S.; Halai, A.D.; Volfart, A.; Garrard, P.; Patterson, K.; Rowe, J.B.; Ralph, M.A.L. The impact of bilateral versus unilateral anterior temporal lobe damage on face recognition, person knowledge and semantic memory. Cereb. Cortex 2024, 34, bhae336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caciagli, L.; Paquola, C.; He, X.; Vollmar, C.; Centeno, M.; Wandschneider, B.; Braun, U.; Trimmel, K.; Vos, S.B.; Sidhu, M.K.; et al. Disorganization of language and working memory systems in frontal versus temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain 2023, 146, 935–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, M.; Barekatain, M.; Doust, H.T.N.; Molavi, H.; Nouri, R.K.; Moradi, A.R.; Mehvari, J.; Zare, M. Cognitive impairments in patients with intractable temporal lobe epilepsy. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2011, 16, 1466–1472. [Google Scholar]
- Pozuelos, J.P.; Paz-Alonso, P.M.; Castillo, A.; Fuentes, L.J.; Rueda, M.R. Development of attention networks and their interactions in childhood. Dev. Psychol. 2014, 50, 2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmstaedter, C.; Kockelmann, E. Cognitive outcomes in patients with chronic temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 2006, 47, 96–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannest, J.; Szaflarski, J.P.; Eaton, K.P.; Henkel, D.M.; Morita, D.; Glauser, T.A.; Byars, A.W.; Patel, K.; Holland, S.K. Functional magnetic resonance imaging reveals changes in language localization in children with benign childhood epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes. J. Child. Neurol. 2013, 28, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Fan, J.; Dong, Y.; Wang, C.-Q.; Lee, T.M.; Posner, M.I. Selective impairment of attentional networks of orienting and executive control in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2005, 78, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Huang, D.; Chen, Z.; Ye, W.; Lv, Z.; Zheng, J. Temporal lobe epilepsy: Decreased thalamic resting-state functional connectivity and their relationships with alertness performance. Epilepsy Behav. 2015, 44, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Qin, B.; Dang, C.; Ye, W.; Chen, Z.; Yu, L. Alertness network in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy: A fMRI study. Epilepsy Res. 2012, 100, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, S.; Zhang, H.; Huang, K.; Wei, X.; Yang, K.; Wang, Q.; Feng, L. Impaired orienting function detected through eye movements in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1290959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rzezak, P.; Fuentes, D.; Guimarães, C.A.; Thome-Souza, S.; Kuczynski, E.; Guerreiro, M.; Valente, K.D. Executive dysfunction in children and adolescents with temporal lobe epilepsy: Is the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test enough? Epilepsy Behav. 2009, 15, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Pan, L.; Du, X.; Hou, Y.; Li, X.; Song, Y. Functional brain network mechanism of executive control dysfunction in temporal lobe epilepsy. BMC Neurol. 2020, 20, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Byrne, J.; Worden, M.S.; Guise, K.G.; McCandliss, B.D.; Fossella, J.; Posner, M.I. The relation of brain oscillations to attentional networks. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 6197–6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djordjević, Z.; Jovanović, A.; Perović, A. Brain connectivity measure—The direct transfer function—Advantages and weak points. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 10th Jubilee International Symposium on Intelligent Systems and Informatics, Subotica, Serbia, 20–22 September 2012; pp. 93–97. [Google Scholar]
- Babiloni, F.; Cincotti, F.; Babiloni, C.; Carducci, F.; Mattia, D.; Astolfi, L.; Basilisco, A.; Rossini, P.M.; Ding, L.; Ni, Y. Estimation of the cortical functional connectivity with the multimodal integration of high-resolution EEG and fMRI data by directed transfer function. Neuroimage 2005, 24, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, M.J.; Blinowska, K.J. A new method of the description of the information flow in the brain structures. Biol. Cybern. 1991, 65, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niso, G.; Bruña, R.; Pereda, E.; Gutiérrez, R.; Bajo, R.; Maestú, F.; Del-Pozo, F. HERMES: Towards an integrated toolbox to characterize functional and effective brain connectivity. Neuroinformatics 2013, 11, 405–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, L.E.; Karwowski, W. A graph theory-based modeling of functional brain connectivity based on eeg: A systematic review in the context of neuroergonomics. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 155103–155135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, F.; Burle, B.; Spieser, L.; Carbonnell, L.; Meckler, C.; Casini, L.; Hasbroucq, T. Linking EEG signals, brain functions and mental operations: Advantages of the Laplacian transformation. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2015, 97, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burle, B.; Spieser, L.; Roger, C.; Casini, L.; Hasbroucq, T.; Vidal, F. Spatial and temporal resolutions of EEG: Is it really black and white? A scalp current density view. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2015, 97, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsuradi, H.; Park, W.; Eid, M. Assessment of EEG-based functional connectivity in response to haptic delay. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 961101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Pan, L.; Du, X.; Li, X.; Hou, Y.; Bao, J.; Song, Y. Theta oscillation and functional connectivity alterations related to executive control in temporal lobe epilepsy with comorbid depression. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2020, 131, 1599–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, C.; Liu, J.; Cui, M.; Wu, W.; Hao, F.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Pan, L.; Deng, M.; et al. Alterations in functional connectivity of executive control network reveal influence of indoor toluene on cognition at low concentration. Build. Environ. 2023, 232, 110031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, C.; Pan, L.; Wang, J.; Cui, M.; Yu, P.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J. The Effect of Low-Level Indoor Exposure Toluene on Orienting Network. Indoor Air 2023, 2023, 3836418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Zhan, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Cui, M.; Zhang, X.; Su, X.; Pan, L.; Deng, M.; Zhao, L. Alternations in neural oscillation related to attention network reveal influence of indoor toluene on cognition at low concentration. Indoor Air 2022, 32, e13067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Xiang, Y.; Yuan, Z. Linking brain activation to topological organization in the frontal lobe as a synergistic indicator to characterize the difference between various cognitive processes of executive functions. Neurophotonics 2019, 6, 025008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Wang, J.; He, Y. BrainNet Viewer: A Network Visualization Tool for Human Brain Connectomics. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullmore, E.; Sporns, O. Complex brain networks: Graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Diessen, E.; Zweiphenning, W.J.E.M.; Jansen, F.E.; Stam, C.J.; Braun, K.P.J.; Otte, W.M. Brain Network Organization in Focal Epilepsy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e0114606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latora, V.; Marchiori, M. Efficient behavior of small-world networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 198701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paldino, M.J.; Zhang, W.; Chu, Z.D.; Golriz, F. Metrics of brain network architecture capture the impact of disease in children with epilepsy. NeuroImage Clin. 2017, 13, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Li, B.; Xi, P.; Liu, Y.; Li, F.; Lang, Y.; Tang, R.; Ma, N.; He, J. Time-Varying Functional Connectivity of Rat Brain during Bipedal Walking on Unexpected Terrain. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2023, 4, 0017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinov, M.; Sporns, O. Complex network measures of brain connectivity: Uses and interpretations. Neuroimage 2010, 52, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessitore, A.; Amboni, M.; Esposito, F.; Russo, A.; Picillo, M.; Marcuccio, L.; Pellecchia, M.T.; Vitale, C.; Cirillo, M.; Tedeschi, G. Resting-state brain connectivity in patients with Parkinson’s disease and freezing of gait. Park. Relat. D 2012, 18, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvao-Carmona, A.; González-Rosa, J.J.; Hidalgo-Muñoz, A.R.; Páramo, D.; Benítez, M.L.; Izquierdo, G.; Vázquez-Marrufo, M. Disentangling the attention network test: Behavioral, event related potentials, and neural source analyses. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Zheng, J.; Dang, C. The functional magnetic resonance imaging investigation of the alerting network in patient with temporal lobe epilepsy. J. Apoplexy Nerv. Dis. 2011, 28, 927–930. [Google Scholar]
- Posner, M.I.; Petersen, S.E. The attention system of the human brain. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1990, 13, 25–42. [Google Scholar]
- Bettus, G.; Wendling, F.; Guye, M.; Valton, L.; Regis, J.; Chauvel, P.; Bartolomei, F. Enhanced EEG functional connectivity in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2008, 81, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérard, M.; Bayot, M.; Derambure, P.; Dujardin, K.; Defebvre, L.; Betrouni, N.; Delval, A. EEG-based functional connectivity and executive control in patients with Parkinson’s disease and freezing of gait. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2022, 137, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonazi, B.K.; Keller, S.S.; Fallon, N.; Adams, V.; Das, K.; Marson, A.G.; Sluming, V. Resting-state functional brain networks in adults with a new diagnosis of focal epilepsy. Brain Bebav. 2019, 9, e01168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajpoot, K.; Riaz, A.; Majeed, W.; Rajpoot, N. Functional Connectivity Alterations in Epilepsy from Resting-State Functional MRI. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posner, M.I.; Sheese, B.E.; Odludas, Y.; Tang, Y. Analyzing and shaping human attentional networks. Neural Netw. 2006, 19, 1422–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Liu, J.; Qin, L.; Ye, W.; Zheng, J. Aberrant executive control networks and default mode network in patients with right-sided temporal lobe epilepsy: A functional and effective connectivity study. Int. J. Neurosci. 2020, 130, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, N.F.; Lemieux, L.; Kitchen, N.D.; Fish, D.R.; Shorvon, S.D. Extrahippocampal temporal lobe atrophy in temporal lobe epilepsy and mesial temporal sclerosis. Brain 2001, 124, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, B.C.; Chen, Z.; He, Y.; Evans, A.C.; Bernasconi, N. Graph-theoretical analysis reveals disrupted small-world organization of cortical thickness correlation networks in temporal lobe epilepsy. Cereb. Cortex 2011, 21, 2147–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Group | TLE Patients (n = 92) | HC (n = 78) | Statistical Value t-Value/χ2-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex a | Female/Male | 39/53 | 44/34 | 3.320 | 0.068 |
| Age ± SD (years) b | 30.80 ± 12.82 | 27.41 ± 10.55 | 1.857 | 0.065 | |
| Education level a | Elementary school | 6 | 2 | 4.254 | 0.373 |
| Junior high school | 19 | 12 | |||
| High school or vocational school | 26 | 22 | |||
| Associate degree | 20 | 15 | |||
| College degree or higher | 21 | 27 | |||
| Household registration a | Urban/Rural | 57/35 | 55/23 | 0.241 | 0.241 |
| Marital status a | Married/Unmarried | 48/44 | 40/38 | 0.013 | 0.908 |
| Duration of illness ± SD (years) | 7.53 ± 9.05 | — | — | ||
| Duration of episodes ± SD (minutes) | 2.12 ± 1.71 | — | — |
| MRT (Millisecond) | Accuracy Rate | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TLE Patients | HC Group | p-Value | TLE Patients | HC Group | p-Value | |
| No cue | 645.45 ± 112.59 | 573.36 ± 83.27 | <0.001 | 0.970 ± 0.070 | 0.988 ± 0.015 | 0.539 |
| Double cue | 609.71 ± 122.31 | 529.36 ± 82.55 | <0.001 | 0.971 ± 0.068 | 0.985 ± 0.020 | 0.914 |
| Center cue | 614.41 ± 119.66 | 538.71 ± 85.13 | <0.001 | 0.970 ± 0.067 | 0.980 ± 0.019 | 0.796 |
| Spatial cue | 575.84 ± 134.61 | 483.75 ± 86.71 | <0.001 | 0.977 ± 0.550 | 0.990 ± 0.016 | 0.181 |
| Congruent | 585.47 ± 124.91 | 504.92 ± 82.66 | <0.001 | 0.987 ± 0.050 | 0.997 ± 0.008 | 0.085 |
| Incongruent | 687.36 ± 148.68 | 586.27 ± 90.94 | <0.001 | 0.943 ± 0.130 | 0.968 ± 0.033 | 0.847 |
| Alerting network | 35.73 ± 30.35 | 44.00 ± 23.44 | 0.047 | - | - | - |
| Orienting network | 38.56 ± 34.08 | 54.95 ± 24.60 | 0.001 | - | - | - |
| Executive network | 101.88 ± 61.52 | 81.35 ± 32.35 | 0.018 | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, X.; Yang, H.; Dang, R.; Hu, B.; Feng, L.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Q. Altered Effective Connectivity of the Attentional Network in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy with EEG Data. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040387
Wei X, Yang H, Dang R, Hu B, Feng L, Xie Y, Wang Q. Altered Effective Connectivity of the Attentional Network in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy with EEG Data. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(4):387. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040387
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Xiaojie, Haojun Yang, Ruochen Dang, Bingliang Hu, Li Feng, Yuanyuan Xie, and Quan Wang. 2025. "Altered Effective Connectivity of the Attentional Network in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy with EEG Data" Bioengineering 12, no. 4: 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040387
APA StyleWei, X., Yang, H., Dang, R., Hu, B., Feng, L., Xie, Y., & Wang, Q. (2025). Altered Effective Connectivity of the Attentional Network in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy with EEG Data. Bioengineering, 12(4), 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040387







