Augmenting Screw Technique to Prevent TLIF Cage Subsidence: A Biomechanical In Vitro Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
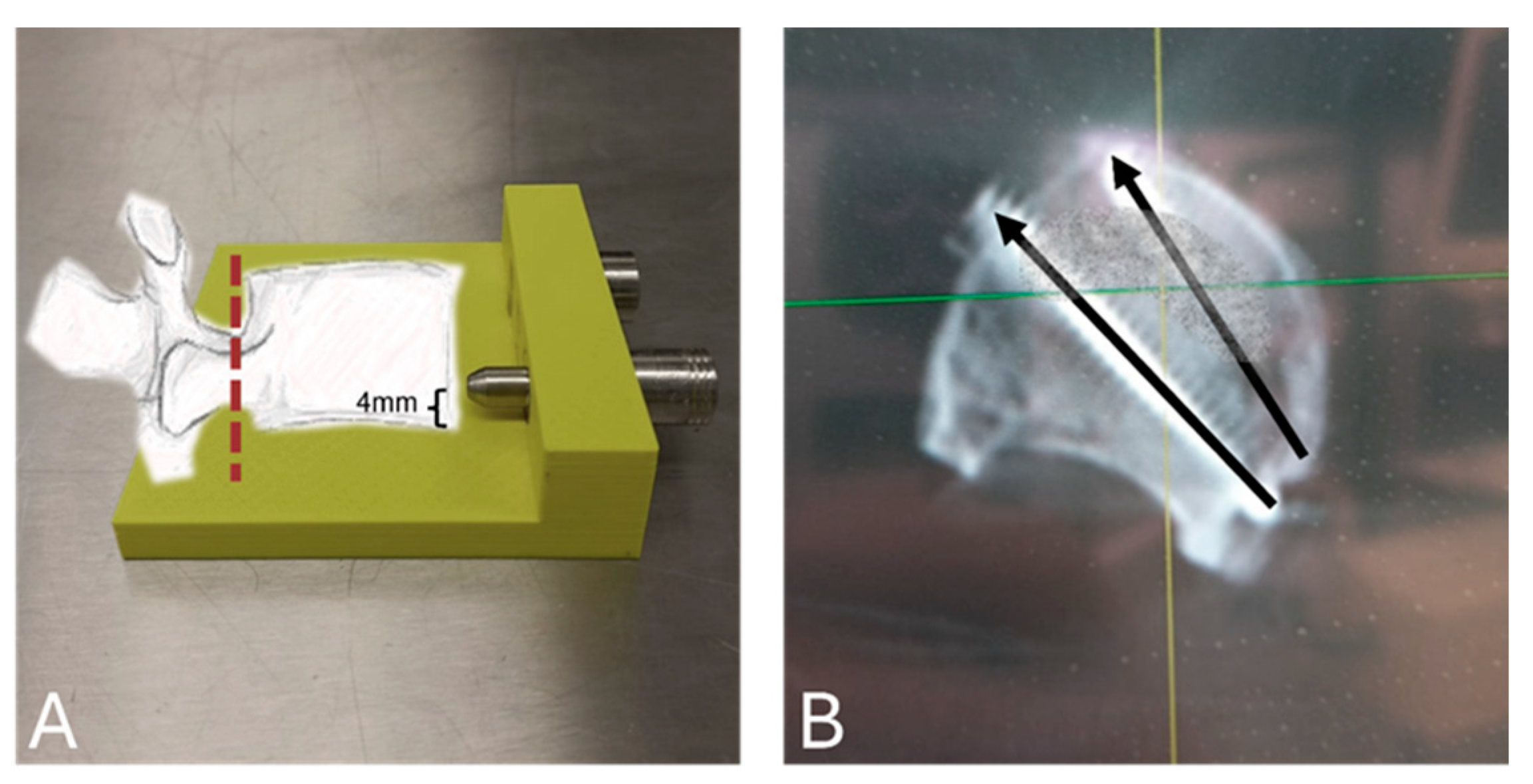
2.1. Specimens and Preparation
2.2. Surgical Technique
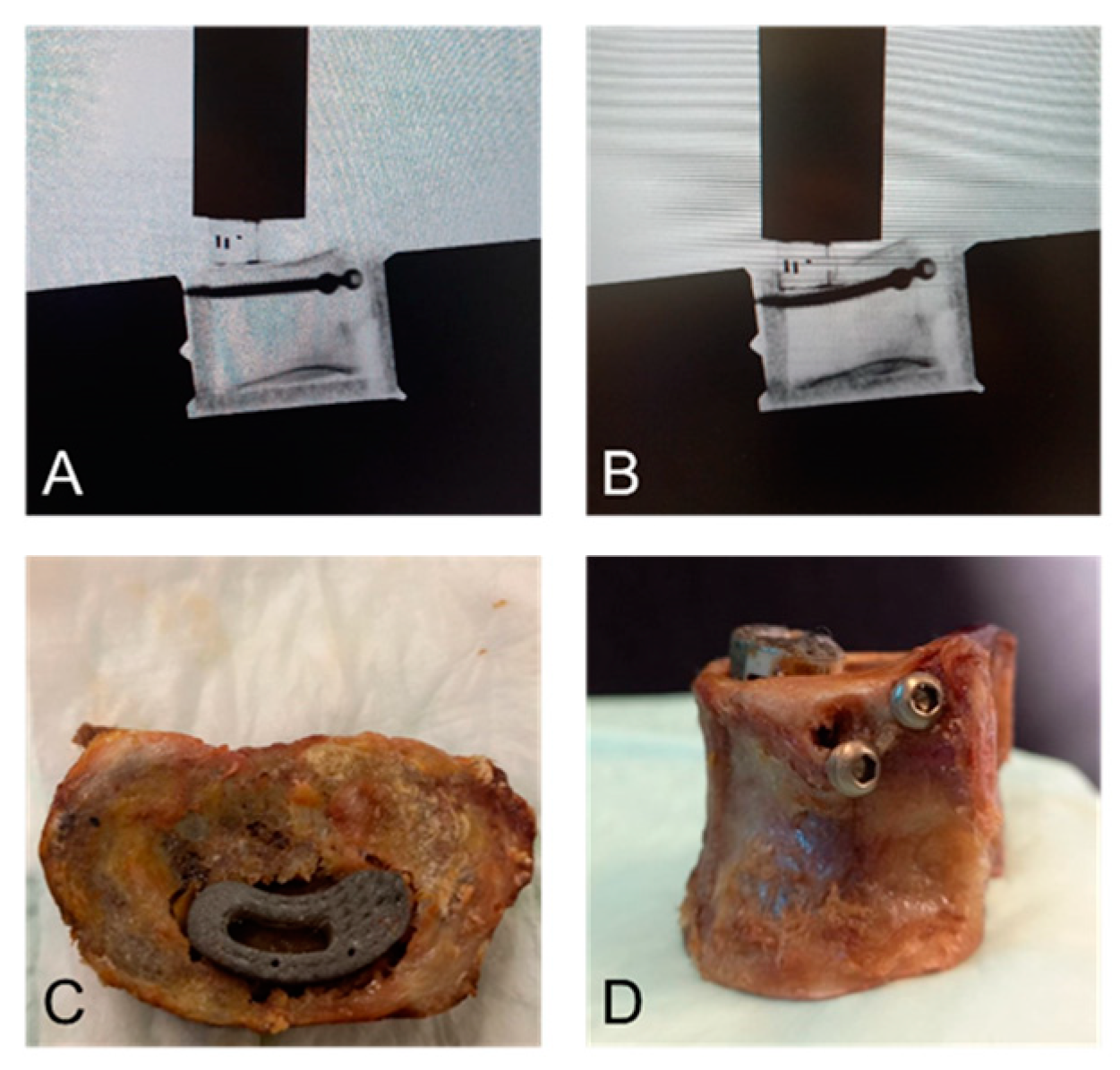
2.3. Biomechanical Testing
2.4. Data Acquisition and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Quasi-Static Testing
3.2. Cyclic Testing
3.3. Failure Modes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMD | Bone mineral density; |
| OLIF | Oblique lumbar interbody fusion; |
| PEEK | Polyether ether ketone; |
| TLIF | Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. |
References
- Vos, T.; Lim, S.S.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abbasi, M.; Abbasifard, M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; et al. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisener, M.-J.; Pumberger, M.; Shue, J.; Girardi, F.P.; Hughes, A.P. Trends in lumbar spinal fusion-a literature review. J. Spine Surg. 2020, 6, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindra, V.M.; Senglaub, S.S.; Rattani, A.; Dewan, M.C.; Härtl, R.; Bisson, E.; Park, K.B.; Shrime, M.G. Degenerative Lumbar Spine Disease: Estimating Global Incidence and Worldwide Volume. Glob. Spine J. 2018, 8, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Lynnger, T.M.; Zuckerman, S.L.; Morone, P.J.; Dewan, M.C.; Vasquez-Castellanos, R.A.; Cheng, J.S. Trends for Spine Surgery for the Elderly: Implications for Access to Healthcare in North America. Neurosurgery 2015, 77 (Suppl. 4), S136–S141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, B.I.; Mirza, S.K.; Spina, N.; Spiker, W.R.; Lawrence, B.; Brodke, D.S. Trends in Lumbar Fusion Procedure Rates and Associated Hospital Costs for Degenerative Spinal Diseases in the United States, 2004 to 2015. Spine 2019, 44, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAfee, P.C.; DeVine, J.G.; Chaput, C.D.; Prybis, B.G.; Fedder, I.L.; Cunningham, B.W.; Farrell, D.J.; Hess, S.J.; Vigna, F.E. The indications for interbody fusion cages in the treatment of spondylolisthesis: Analysis of 120 cases. Spine 2005, 30, S60–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumenthal, S.L.; Ohnmeiss, D.D. Intervertebral cages for degenerative spinal diseases. Spine J. 2003, 3, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, J.G.; Jeszenszky, D. Die posteriore, lumbale, interkorporelle Fusion in unilateraler transforaminaler Technik. Oper. Orthop. Traumatol. 1998, 10, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathbone, J.; Rackham, M.; Nielsen, D.; Lee, S.M.; Hing, W.; Riar, S.; Scott-Young, M. A systematic review of anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) versus posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF), transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF), posterolateral lumbar fusion (PLF). Eur. Spine J. 2023, 32, 1911–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisien, A.; Wai, E.K.; ElSayed, M.S.A.; Frei, H. Subsidence of Spinal Fusion Cages: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Spine Surg. 2022, 16, 1103–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, N.-H. Factors associated with intervertebral cage subsidence in posterior lumbar fusion. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2024, 19, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, H.A.; Pinter, Z.W.; Reed, R.; Harmer, J.R.; Raftery, K.; Nathani, K.R.; Katsos, K.; Bydon, M.; Fogelson, J.L.; Elder, B.D.; et al. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion subsidence: Computed tomography analysis of incidence, associated risk factors, and impact on outcomes. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2024, 1, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filley, A.; Baldwin, A.; Ben-Natan, A.R.; Hansen, K.; Arora, A.; Xiao, A.; Hammond, D.; Chen, C.; Tweedt, I.; Rohde, J.; et al. The influence of osteoporosis on mechanical complications in lumbar fusion surgery: A systematic review. N. Am. Spine Soc. J. 2024, 18, 100327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.S.; Kim, H.; Choung, Y.J.; Jeong, S.J.; Lee, C.H. Risk factors for new vertebral compression fracture after kyphoplasty and efficacy of osteoporosis treatment: A STROBE-compliant retrospective study. Medicine 2022, 101, e32018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okano, I.; Jones, C.; Salzmann, S.N.; Reisener, M.-J.; Sax, O.C.; Rentenberger, C.; Shue, J.; Carrino, J.A.; Sama, A.A.; Cammisa, F.P.; et al. Endplate volumetric bone mineral density measured by quantitative computed tomography as a novel predictive measure of severe cage subsidence after standalone lateral lumbar fusion. Eur. Spine J. 2020, 29, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calek, A.-K.; Cornaz, F.; Suter, M.; Fasser, M.-R.; Farshad, M.; Widmer, J. Endplate weakening during cage bed preparation significantly reduces endplate load capacity. Eur. Spine J. 2024, 33, 2621–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amorim-Barbosa, T.; Pereira, C.; Catelas, D.; Rodrigues, C.; Costa, P.; Rodrigues-Pinto, R.; Neves, P. Risk factors for cage subsidence and clinical outcomes after transforaminal and posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2022, 32, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Robinson, D.L.; Ackland, D.C.; Yang, Y.; Lee, P.V.S. Influence of the geometric and material properties of lumbar endplate on lumbar interbody fusion failure: A systematic review. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2022, 17, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Nüesch, C.; Mündermann, A.; Halbeisen, F.; Schären, S.; Netzer, C. Is Age a Risk Factor for Early Postoperative Cage Subsidence After Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion? A Retrospective Study in 170 Patients. Glob. Spine J. 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, T.; Hossain, M.; Jeong, J.H.; Im, S. Comparative Analysis of Radiologic Outcomes Between Polyetheretherketone and Three-Dimensional-Printed Titanium Cages After Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion. World Neurosurg. 2023, 179, e241–e255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbusera, F.; Schmidt, H.; Wilke, H.-J. Lumbar interbody fusion: A parametric investigation of a novel cage design with and without posterior instrumentation. Eur. Spine J. 2012, 21, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wilke, H.-J.; Volkheimer, D.; Robie, B.; Christensen, F.B. Two-piece ALIF cage optimizes the bone-implant interface in a 360° setting. Eur. Spine J. 2017, 26, 2747–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilke, H.J.; Kettler, A.; Claes, L. Primary stabilizing effect of interbody fusion devices for the cervical spine: An in vitro comparison between three different cage types and bone cement. Eur. Spine J. 2000, 9, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, T.G.; Hashim, S.; Wilson, L.A.; O’Brien, M.F.; Smith, D.A.B.; Diekmann, M.J.; Trommeter, J. A biomechanical study of regional endplate strength and cage morphology as it relates to structural interbody support. Spine 2004, 29, 2389–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, I.; Han, J.; Phan, K.; Mobbs, R. A meta-analysis comparing ALIF, PLIF, TLIF and LLIF. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 44, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilke, H.J.; Kettler, A.; Claes, L. Stabilizing effect and sintering tendency of 3 different cages and bone cement for fusion of cervical vertebrae segments. Orthopade 2002, 31, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- F04 Committee. Test Methods For Intervertebral Body Fusion Devices; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fushimi, K.; Miyagawa, T.; Iwai, C.; Nozawa, S.; Iinuma, N.; Tanaka, R.; Shirai, G.; Tanahashi, H.; Yokoi, T.; Akiyama, H. Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Double Banana Cages: Clinical Evaluations and Finite Element Model Analysis. Glob. Spine J. 2023, 14, 2031–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Liang, A.; Gao, W.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liang, G.; Huang, D. The relationship between concave angle of vertebral endplate and lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine 2012, 37, E1068–E1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; He, D.; Gao, J.; Zeng, Z.; Jiang, C.; Ni, W.; Yik, J.H.N.; Zhao, X.; Fan, S. The Influence of Endplate Morphology on Cage Subsidence in Patients With Stand-Alone Oblique Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion (OLIF). Glob. Spine J. 2023, 13, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Xie, T.; Wang, L.; Luo, C.; Huang, S.; Zeng, J. The Influence of Screw Positioning on Cage Subsidence in Patients with Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion Combined with Anterolateral Fixation. Orthop. Surg. 2023, 15, 3263–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Pu, L.; Zhao, L.; Lu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Song, Y.; Zeng, J. Influence of coronal-morphology of endplate and intervertebral space to cage subsidence and fusion following oblique lumbar interbody fusion. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minisola, S.; Cipriani, C.; Della Grotta, G.; Colangelo, L.; Occhiuto, M.; Biondi, P.; Sonato, C.; Vigna, E.; Cilli, M.; Pepe, J. Update on the safety and efficacy of teriparatide in the treatment of osteoporosis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2019, 11, 1759720X19877994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshtory, R.; Harris, J.A.; Patel, P.D.; Mirabile, B.A.; Bucklen, B.S. Lumbar Intervertebral Spacer With Cement Augmentation of Endplates and Integrated Screws as a Fixation Device in an Osteoporotic Model: An In Vitro Kinematic and Load-to-Failure Study. Int. J. Spine Surg. 2021, 15, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, S.-F.; Tsai, T.-T.; Wang, S.-F.; Hsieh, M.-K.; Kao, F.-C. Additional cement augmentation reduces cage subsidence and improves clinical outcomes in oblique lumbar interbody fusion combined with anterolateral screw fixation: A retrospective cohort study. Curr. Probl. Surg. 2024, 61, 101441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzantonis, C.; Czyz, M.; Pyzik, R.; Boszczyk, B.M. Intracardiac bone cement embolism as a complication of vertebroplasty: Management strategy. Eur. Spine J. 2017, 26, 3199–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.K.; Wroblewski, I.; Darki, A. Pulmonary Cement Embolism After Vertebroplasty. Cureus 2023, 15, e39194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothermich, M.A.; Buchowski, J.M.; Bumpass, D.B.; Patterson, G.A. Pulmonary cement embolization after vertebroplasty requiring pulmonary wedge resection. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2014, 472, 1652–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waler, A.R.; Sanchez, K.J.; Parikh, A.A.; Okorie, O.N. A Case of Pulmonary Cement Embolism Managed through Symptomatic Treatment. Case Rep. Crit. Care 2020, 2020, 2425973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, F.A.; Herrera, O.M.; Gaona, J.L.V.; Reyes, C.A.F.; Gutiérrez, M.L.C.; Saenz, L.C.M. Pulmonary cement embolism following transpedicular screws placement for thoracolumbar fractures. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2021, 12, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Huang, X.; Wu, L. Removal of intracardiac bone cement embolism after percutaneous kyphoplasty: A case report. Medicine 2020, 99, e19354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulme, P.A.; Krebs, J.; Ferguson, S.J.; Berlemann, U. Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: A systematic review of 69 clinical studies. Spine 2006, 31, 1983–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adida, S.; Taori, S.; Wong, V.R.; Tang, A.; Sefcik, R.K.; Zhang, X.; Gerszten, P.C. Analysis of injected cement volume and clinical outcomes following balloon-assisted kyphoplasty in a series of 368 patients. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2024, 243, 108367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Han, N.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, P.; Jiang, B. Comparison between headless cannulated screws and partially threaded screws in femoral neck fracture treatment: A retrospective cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Augmenting Screw Group (Mean ± SD) n = 10 | Control Group (Mean ± SD) n = 10 | p-Value | p-Value Variance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Failure load 3 mm subsidence | 887.5 ± 577.0 | 891.4 ± 441.2 | 0.956 | 0.392 |
| Failure load 5 mm subsidence | 1426.0 ± 863.6 | 682.2 ± 174.5 | <0.05 * | <0.001 *** |
| Variable | Augmenting Screw Group (Mean ± SD) n = 10 | Control Group (Mean ± SD) n = 10 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of cycles to 3 mm subsidence | 4960 ± 1369 | 4466 ± 1639 | 0.567 |
| Number of cycles to 5 mm subsidence | 7437 ± 2388 | 4812 ± 2035 | 0.068 |
| Number of cycles to 10 mm subsidence | 9645 ± 3050 | 5395 ± 2340 | <0.05 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jacob, A.; Feist, A.; Zderic, I.; Gueorguiev, B.; Caspar, J.; Wirtz, C.R.; Richards, G.; Loibl, M.; Haschtmann, D.; Fekete, T.F. Augmenting Screw Technique to Prevent TLIF Cage Subsidence: A Biomechanical In Vitro Study. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040337
Jacob A, Feist A, Zderic I, Gueorguiev B, Caspar J, Wirtz CR, Richards G, Loibl M, Haschtmann D, Fekete TF. Augmenting Screw Technique to Prevent TLIF Cage Subsidence: A Biomechanical In Vitro Study. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(4):337. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040337
Chicago/Turabian StyleJacob, Alina, Alicia Feist, Ivan Zderic, Boyko Gueorguiev, Jan Caspar, Christian R. Wirtz, Geoff Richards, Markus Loibl, Daniel Haschtmann, and Tamas F. Fekete. 2025. "Augmenting Screw Technique to Prevent TLIF Cage Subsidence: A Biomechanical In Vitro Study" Bioengineering 12, no. 4: 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040337
APA StyleJacob, A., Feist, A., Zderic, I., Gueorguiev, B., Caspar, J., Wirtz, C. R., Richards, G., Loibl, M., Haschtmann, D., & Fekete, T. F. (2025). Augmenting Screw Technique to Prevent TLIF Cage Subsidence: A Biomechanical In Vitro Study. Bioengineering, 12(4), 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040337







