Relationship Between Implant Connection and Implant Fracture: Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Articles published to date (01-11-25).
- Articles published in English.
- Studies based on finite elements.
- Articles relating to dental implant fractures and their connection characteristics.
- Only simulations or in vitro studies were included.
- Articles published in non-English languages.
- Studies unrelated to finite element tests.
- Studies that did not relate implant fracture to prosthetic connection.
- Reviews were discarded.
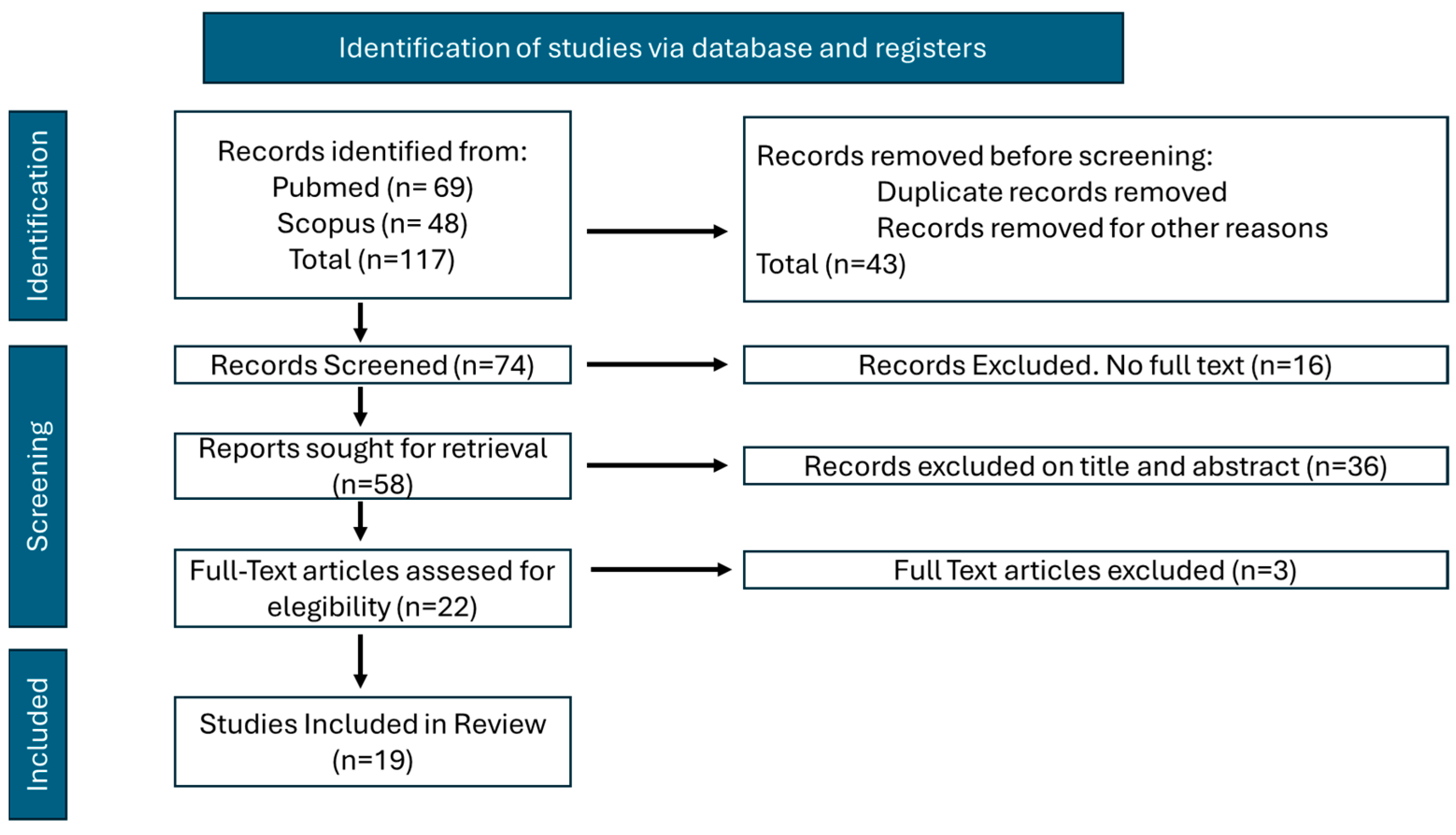
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The design of the connection seems to play an important role in the fatigue resistance of the implant under load, concentrating stress to a greater or lesser extent at a given point, depending on the design of the connection.
- The conical connection appears to be the one that performs best in the different biomechanical situations that may arise. However, no specific design appears to be superior to others.
- In compromised situations, such as short implants, it would be interesting to use a Tissue Level connection design. This type of connection seems to perform better under load.
- More tests must be carried out to establish a type of conical connection design that is more optimal for the different biomechanical situations. In addition, these studies must be carried out without other geometric or implant elements that could introduce bias.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raikar, S.; Talukdar, P.; Kumari, S.; Panda, S.K.; Oommen, V.M.; Prasad, A. Factors Affecting the Survival Rate of Dental Implants: A Retrospective Study. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2017, 7, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaumont, J.; McManus, G.; Darcey, J. Differentiating success from survival in modern implantology—Key considerations for case selection, predicting complications and obtaining consent. Br. Dent. J. 2016, 220, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, C.; Chen, Y.; Si, M.; Chen, X. The impact of biocorrosion and titanium ions release on peri-implantitis. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2025, 29, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaspyridakos, P.; Bordin, T.B.; Kim, Y.J.; El-Rafie, K.; Pagni, S.E.; Natto, Z.S.; Teixeira, E.R.; Chochlidakis, K.; Weber, H.P. Technical Complications and Prosthesis Survival Rates with Implant-Supported Fixed Complete Dental Prostheses: A Retrospective Study with 1- to 12-Year Follow-Up. J. Prosthodont. 2020, 29, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pjetursson, B.E.; Sailer, I.; Merino-Higuera, E.; Spies, B.C.; Burkhardt, F.; Karasan, D. Systematic review evaluating the influence of the prosthetic material and prosthetic design on the clinical outcomes of implant-supported multi-unit fixed dental prosthesis in the posterior area. Clin. Oral. Implant. Res. 2023, 34 (Suppl. S26), 86–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satpathy, M.; Loeb, M.; Jose, R.M.; Sinclair, M.J.; Duan, Y.; Salazar Marocho, S.M.; Roach, M.D.; Griggs, J.A. Screening dental implant design parameters for effect on the fatigue limit of reduced-diameter implants. Dent. Mater. 2025, 41, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goiato, M.C.; Pellizzer, E.P.; da Silva, E.V.; da Rcha Bonatto, L.; dos Santos, D.M. Is the internal connection more efficient than external connection in mechanical, biological, and esthetical point of views? A systematic review. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 19, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, C.A.A.; Verri, F.R.; Bonfante, E.A.; Santiago Júnior, J.F.; Pellizzer, E.P. Comparison of external and internal implant-abutment connections for implant supported prostheses. A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Dent. 2018, 70, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios-Garzón, N.; Mauri-Obradors, E.; Roselló-LLabrés, X.; Estrugo-Devesa, A.; Jané-Salas, E.; López-López, J. Comparison of Marginal Bone Loss Between Implants with Internal and External Connections: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implant. 2018, 33, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menini, M.; Pesce, P.; Bagnasco, F.; Carossa, M.; Mussano, F.; Pera, F. Evaluation of internal and external hexagon connections in immediately loaded full-arch rehabilitations: A within-person randomised split-mouth controlled trial. Int. J. Oral. Implantol. 2019, 12, 169–179. [Google Scholar]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; The PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, R.; Lipa, S.; Piechaczek, M.; Sowiński, J.; Kołkowska, A.; Simka, W. Finite Element Analysis and Fatigue Test of INTEGRA Dental Implant System. Materials 2024, 17, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poovarodom, P.; Rungsiyakull, C.; Suriyawanakul, J.; Li, Q.; Sasaki, K.; Yoda, N.; Rungsiyakull, P. Effect of gingival height of a titanium base on the biomechanical behavior of 2-piece custom implant abutments: A 3-dimensional nonlinear finite element study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2023, 130, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, A.; Corbella, S.; Francetti, L. Mechanical Resistance of a 2.9-mm-Diameter Dental Implant With a Morse-Taper Implant-Abutment Connection. J. Oral. Implantol. 2023, 49, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, S.H.; Seo, J.H.; Cho, R.Y.; Yi, S.M.; Kim, L.K.; Han, H.S.; On, S.W.; Kim, W.H.; An, H.W.; Yang, B.E. Finite Element Analysis of a New Non-Engaging Abutment System for Three-Unit Implant-Supported Fixed Dental Prostheses. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giner, S.; Bartolomé, J.F.; Gomez-Cogolludo, P.; Castellote, C.; Pradíes, G. Mechanical Performance of Chairside Ceramic CAD/CAM Restorations and Zirconia Abutments with Different Internal Implant Connections: In Vitro Study and Finite Element Analysis. Materials 2021, 14, 5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, C.A.A.; Verri, F.R.; Noritomi, P.Y.; de Souza Batista, V.E.; Cruz, R.S.; de Luna Gomes, J.M.; de Oliveira Limírio, J.P.J.; Pellizzer, E.P. Biomechanical Evaluation of Different Implant-Abutment Connections, Retention Systems, and Restorative Materials in the Implant-Supported Single Crowns Using 3D Finite Element Analysis. J. Oral. Implantol. 2022, 48, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, H.; Nakano, T.; Ono, S.; Yatani, H. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of extra short implants focusing on implant designs and materials. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2020, 6, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Park, S.; Noh, G. Biomechanical analysis of 4 types of short dental implants in a resorbed mandible. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 121, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prados-Privado, M.; Gehrke, S.A.; Rojo, R.; Prados-Frutos, J.C. Complete mechanical characterization of an external hexagonal implant connection: In vitro study, 3D FEM, and probabilistic fatigue. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2018, 56, 2233–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.T.; Chen, C.S.; Cheng, C.K.; Fang, H.W.; Huang, C.H.; Kao, H.C.; Hsu, M.L. Optimization of the Conical Angle Design in Conical Implant-Abutment Connections: A Pilot Study Based on the Finite Element Method. J. Oral. Implantol. 2018, 44, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordin, D.; Bergamo, E.T.P.; Fardin, V.P.; Coelho, P.G.; Bonfante, E.A. Fracture strength and probability of survival of narrow and extra-narrow dental implants after fatigue testing: In vitro and in silico analysis. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 71, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Geng, J.; Jones, D.; Xu, W. Comparison of the fracture resistance of dental implants with different abutment taper angles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 63, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flanagan, D.; Phillips, J.; Connor, M.; Dyer, T.; Kazerounian, K. Hoop stress and the conical connection. J. Oral. Implantol. 2015, 41, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balik, A.; Karatas, M.O.; Keskin, H. Effects of different abutment connection designs on the stress distribution around five different implants: A 3-dimensional finite element analysis. J. Oral. Implantol. 2012, 38, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tang, C.; Yu, J.; Dai, W.; Bao, Y.; Hu, D. The effect of platform switching on stress distribution in implants and periimplant bone studied by nonlinear finite element analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2014, 112, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas-Júnior, A.C.; Rocha, E.P.; Bonfante, E.A.; Almeida, E.O.; Anchieta, R.B.; Martini, A.P.; Assunção, W.G.; Silva, N.R.; Coelho, P.G. Biomechanical evaluation of internal and external hexagon platform switched implant-abutment connections: An in vitro laboratory and three-dimensional finite element analysis. Dent. Mater. 2012, 28, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Jo, M.; Noh, G. Biomechanical effects of dental implant diameter, connection type, and bone density on microgap formation and fatigue failure: A finite element analysis. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 200, 105863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paula, G.A.; Silva, G.C.; Vilaça, Ê.L.; Cornacchia, T.M.; de Magalhães, C.S.; Moreira, A.N. Biomechanical Behavior of Tooth-Implant Supported Prostheses With Different Implant Connections: A Nonlinear Finite Element Analysis. Implant. Dent. 2018, 27, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, D.; Gurav, P.; Rodrigues, S.; Khobragade, B.; Mahajan, A. Evaluation of stress distribution in and around dental implants using three different implant-abutment interfaces with platform-switched and non-platform-switched abutments: A three-dimensional finite element analysis. J. Dent. Res. Dent. Clin. Dent. Prospect. 2023, 17, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, L.; Tam, D.N.H.; Elshafay, A.; Dang, T.; Hirayama, K.; Huy, N.T. Quality assessment tools used in systematic reviews of in vitro studies: A systematic review. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2021, 21, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sailer, I.; Karasan, D.; Todorovic, A.; Ligoutsikou, M.; Pjetursson, B.E. Prosthetic failures in dental implant therapy. Periodontology 2000 2022, 88, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanauskaite, A.; Sader, R. Esthetic complications in implant dentistry. Periodontology 2000 2022, 88, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglundh, T.; Armitage, G.; Araujo, M.G.; Avila-Ortiz, G.; Blanco, J.; Camargo, P.M.; Chen, S.; Cochran, D.; Derks, J.; Figuero, E.; et al. Peri-implant diseases and conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 4 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. S1), 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreve, S.; Ferreira, I.; da Costa Valente, M.L.; Dos Reis, A.C. Relationship between dental implant macro-design and osseointegration: A systematic review. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2024, 28, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laleman, I.; Lambert, F. Implant connection and abutment selection as a predisposing and/or precipitating factor for peri-implant diseases: A review. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2023, 25, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Meda, R.; Esquivel, J.; Blatz, M.B. The esthetic biological contour concept for implant restoration emergence profile design. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2021, 33, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordin, D.; Witek, L.; Fardin, V.B.; Bonfante, E.A.; Coelho, P.G. Fatigue Failure of narrow implants with different implant-abutment connection designs. J. Prosthodont. 2018, 27, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, F.J.; Planell, J.A.; Padrós, A. Fracture and fatigue behaviour of shot blasted titanium dental implants. Implant. Dent. 2002, 11, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitaraf, T.; Keshtkar, A.; Rokn, A.R.; Monzavi, A.; Geramy, A.; Hashemi, K. Comparing short dental implant and standard dental implant in terms of marginal bone level changes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2019, 21, 796–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledano, M.; Fernández-Romero, E.; Vallecillo, C.; Toledano, R.; Osorio, M.T.; Vallecillo-Rivas, M. Short versus standard implants at sinus augmented sites: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2022, 26, 6681–6698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, R.A.; Gargallo, J.; Altuna, P.; Herrero-Climent, M.; Gil, F.J. Fatigue of Narrow Dental Implants: Influence of the Hardening Method. Materials 2020, 13, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro da Silva, J.; Castellano, A.; Malta Barbosa, J.P.; Gil, L.F.; Marin, C.; Granato, R.; Bonfante, E.A.; Tovar, N.; Janal, M.N.; Coelho, P.G. Histomorphological and Histomorphometric Analyses of Grade IV Commercially Pure Titanium and Grade V Ti-6Al-4V Titanium Alloy Implant Substrates: An In Vivo Study in Dogs. Implant. Dent. 2016, 25, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Authors | Journal | Type of Study | Type of Connection/s | Diseño estudio/ Conexión Analizada | Noteworthy Fact(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zieliński R et al. [12]. | Materials (Basel). | In vitro study | Hexagonal Internal | Biomechanical Analysis of a 3.35 Internal Hexagon Connection Implant (INTEGRA OPTIMA®) | The axial axis of the implant is related to the direction of forces, which is a key factor. Internal hexagon angle zones are critical zones. Fatigue resistance was determined at a F = 200–210 N level. |
| Poovarodom P et al. [13]. | J Prosthet Dent. | Simulations Study | Morse Cone | Implant with a Morse taper (Astratech®; Dentsply-Sirona®), with different gingival heights on the abutment | A TiBase abutment with a higher gingival height reduced stress magnitude. |
| Alberti A et al. [14]. | J Oral Implant. | In vitro study | Conical | Comparative study: Narrow 2.9 mm and 3.3 mm diameter implants with tapered connection (Conical) | The fatigue limit was recorded at 220 (2.9 mm) and 240 N (3.3 mm). No significant difference. |
| Byun SH et al. [15]. | Bioengineering (Basel). | Simulations Study | Conical | Comparative study: AnyOne® and BlueDiamond® Implants (MegaGen®) (conical connections) | Connection stability is a critical biomechanical factor. |
| Giner S et al. [16]. | Materials (Basel). | In vitro study | Tube-in-tube Conical | Comparative study: Implant with tube-in-tube connection and conical connection rehabilitated with monolithic crowns | The mechanical performance of the internal conical connection was superior to that of the tube-in-tube connection. (p < 0.05) |
| Lemos CAA et al. [17]. | J Oral Implant. | In vitro study | Hexagonal Internal Hexagonal Internal Morse Cone | Comparative study: External hexagonal connection vs. Morse Taper Cemented vs. bolted crowns Metal-ceramic vs. monolithic crowns | The Morse cone exhibited lower microstrain values (range: 1295–1432 με) compared to the external hexagonal connection (range: 1832–2715 µε). The retention system did not affect microstrain in cortical bone tissue under both loads. No differences between metal-ceramic and zirconia monolithic crowns were observed regarding microstrain and stress distribution. |
| Araki H et al. [18]. | Int J Implant Dent. | In vitro study | TL BL | Comparative study: Biomechanical analysis between standard and short implants with TL 1 and BL 2 connection of pure titanium and titanium-zirconia | When the implant body length must be shorter, TiZr 3 and a TL connection design may be a better mechanical choice than pure titanium and a BL 2 connection. |
| Lee H et al. [19]. | J Prosthetic Dent. | In vitro study | TL TL Wide BL Internal Bl External | Comparative study: Biomechanical analysis of short implants in 4 connection types (TL 1, TL 1 Wide, BL 2 Internal, BL 2 External) | The BL 2 internal connection abutment showed higher stresses in the implant components. TL 1 had better results. |
| Prados-Privado M et al. [20]. | Med Biol Eng Comput. | In vitro study | External Hexagon | Biomechanical analysis external connection implant 3.5 | Adequate biomechanical behavior over the reference values. |
| Yao KT et al. [21]. | J Oral Implant. | Simulations Study | Conical | Biomechanical simulation analysis of conical connection with different grades (Ankylos System) | The optimal design (based on the Ankylos system) was a 10.18° cone. |
| Bordin D et al. [22]. | J Mech Behav. Biomed Mater. | In vitro study | Conical | Comparative study: Biomechanical analysis of 2.9 mm vs. 3.3 mm conical connection implants. | Fatigue tests up to 180 N (both connections). No significant difference. Complications were reduced to abutment fracture. |
| Wang K et al. [23]. | Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. | In vitro study | Conical | Comparative study: Biomechanical analysis of conical connection with five types of taper degrees. | Significant differences in the degree of taper and implant strength. |
| Flanagan D et al. [24]. | J Oral Implant. | In vitro study | Conical | Biomechanical strength of the conical connection under load | Axial loading does not prove to be a problem. Oblique loading may compromise the implant’s resistance to fracture. |
| Balik A et al. [25] | J Oral Implant. | Simulations Study | Internal hexagonal External hexagonal Tube-in-tube Conical Conical with the internal hexagon. | Comparative study: Evaluation of 5 types of connection of different implant brands. Connections: Internal hexagonal, external hexagonal, tube-in-tube connection, conical, and conical are associated with the internal hexagon. | The conical connection associated with an internal hexagon presents the best results. |
| Liu S et al. [26] | J Prosthetic Dent. | Simulations Study | Internal Conical | Comparative study: Analysis between 2 types of connections. One with a change of platform and one without a change of platform. | The platform change seems to behave better under load than the regular platform. |
| Freitas-Júnior AC et al. [27] | Dent Mater. | In vitro study | Hexagon Interior External hexagon | Comparative study: Evaluation of internal vs. external hexagonal connection with and without platform change. | Changing the platform in the internal connection seems to improve fatigue resistance, but not in the external connection. |
| Lee H et al. [28] | Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. | Simulations Study | BL TL | Comparative study: BL vs. TL associated with different variables (load types, implant diameter, etc.) | Better loading behavior of the TL implant compared to BL. BL connection presented a more significant presence of microgaps than TL under load (p < 0.001). |
| De Paula GA et al. [29] | Implant Dent. | Simulations Study | External hexagon Conical | Comparative study: External connection vs. internal connection to the load. | Better performance and lower failure rate of the internal connection compared to the external connection. |
| Mitra D et al. [30] | J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. | Simulations Study | Hexagon Interior Three channels Conical | Comparative study: Load behavior of three types of connections with and without platform change: hexagonal internal, three-channel internal, and conical internal. | Better results in conical connection with platform change. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernández-Asián, I.; Torres-Lagares, D.; Serrera-Figallo, M.-Á.; Gutiérrez-Pérez, J.-L. Relationship Between Implant Connection and Implant Fracture: Systematic Review. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040333
Fernández-Asián I, Torres-Lagares D, Serrera-Figallo M-Á, Gutiérrez-Pérez J-L. Relationship Between Implant Connection and Implant Fracture: Systematic Review. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(4):333. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040333
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernández-Asián, Ignacio, Daniel Torres-Lagares, María-Ángeles Serrera-Figallo, and José-Luis Gutiérrez-Pérez. 2025. "Relationship Between Implant Connection and Implant Fracture: Systematic Review" Bioengineering 12, no. 4: 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040333
APA StyleFernández-Asián, I., Torres-Lagares, D., Serrera-Figallo, M.-Á., & Gutiérrez-Pérez, J.-L. (2025). Relationship Between Implant Connection and Implant Fracture: Systematic Review. Bioengineering, 12(4), 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040333









