Advancement in Anaerobic Ammonia Oxidation Technologies for Industrial Wastewater Treatment and Resource Recovery: A Comprehensive Review and Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
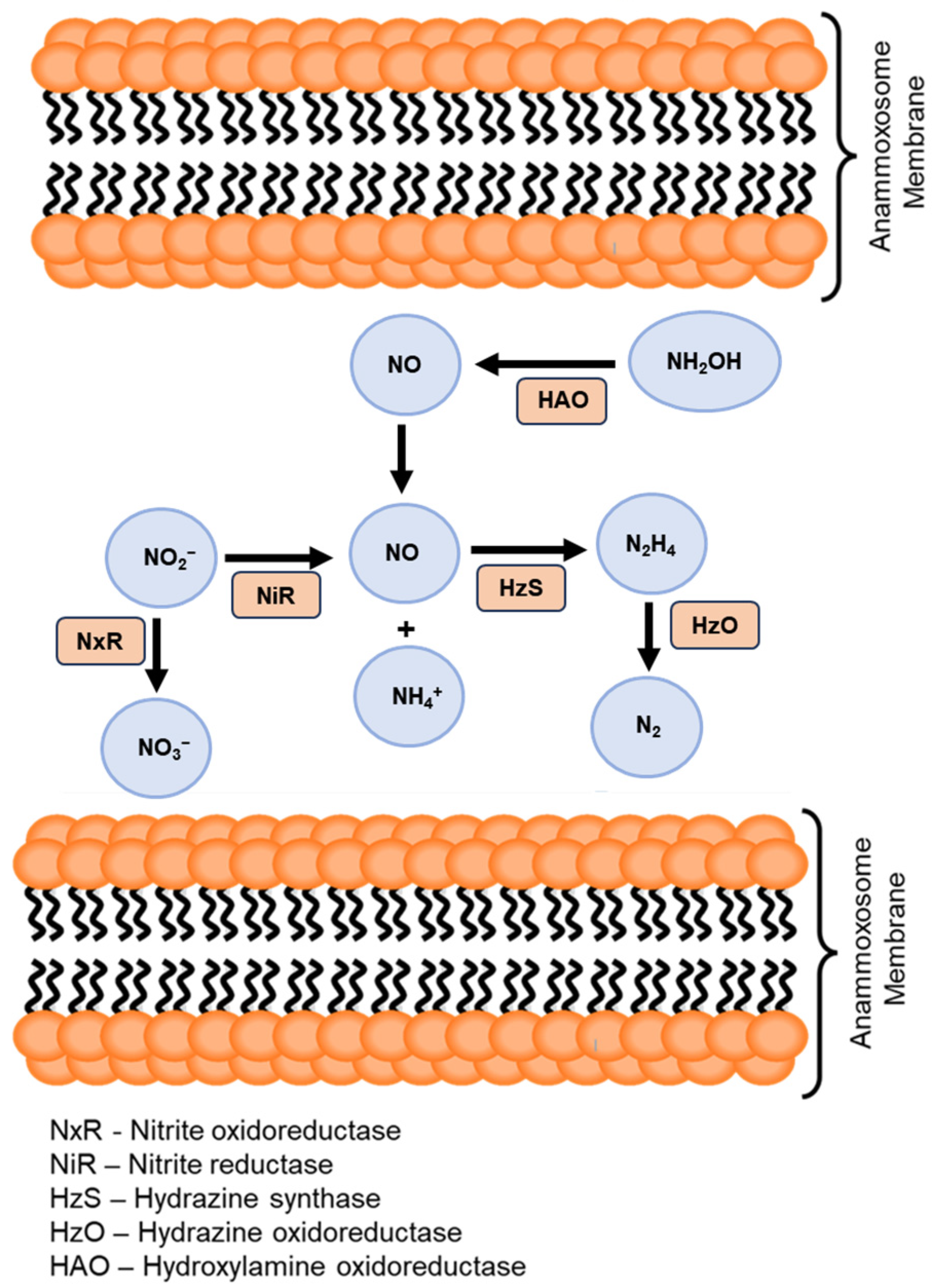
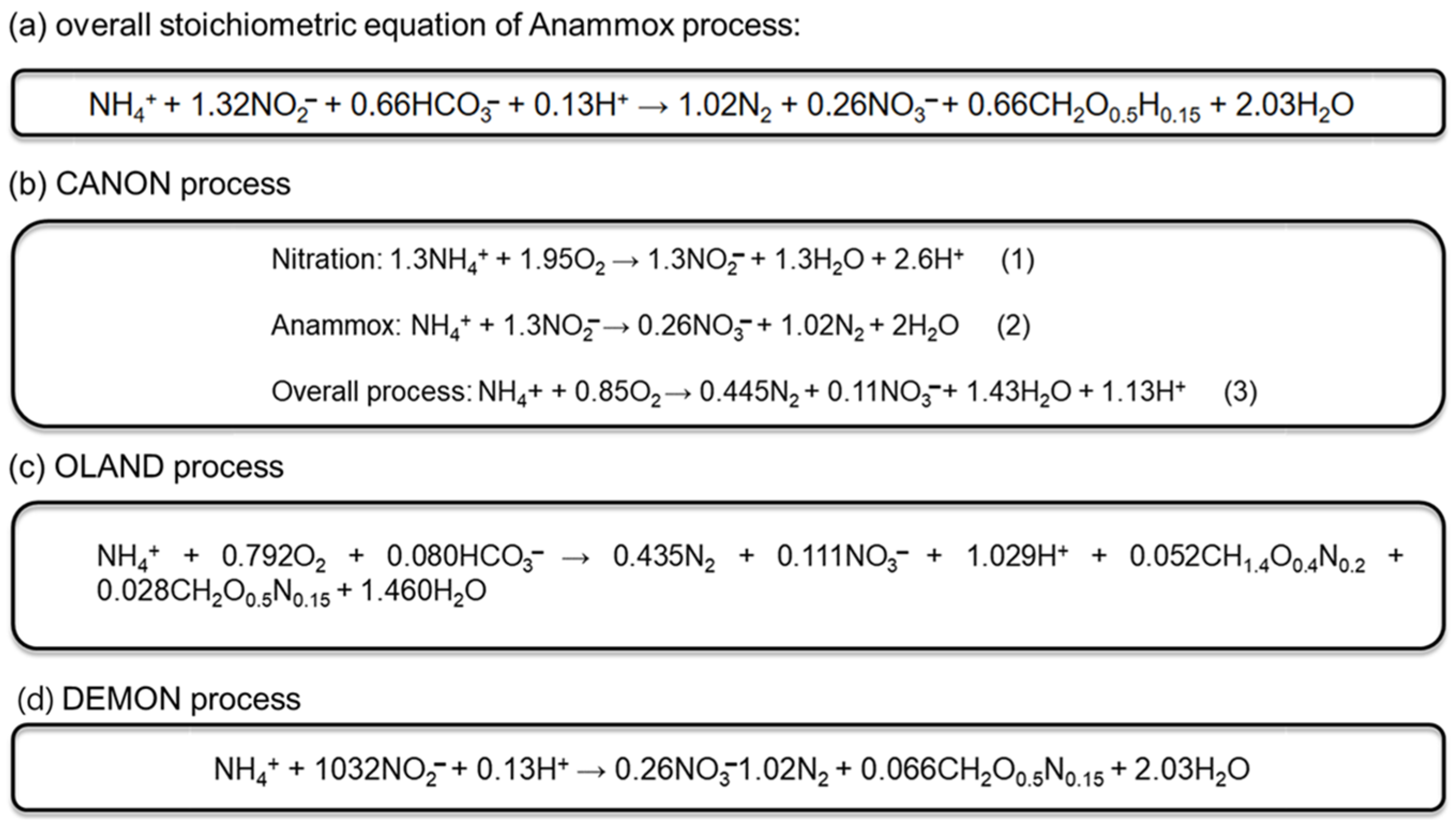
2. Anammox
3. Importance of Anammox Processes
3.1. SHARON
3.2. CANON

3.3. OLAND
3.4. DEMON
3.5. DEAMOX
3.6. SNAD
3.7. Partial Single-Reactor System for High-Activity Ammonium Removal over Nitrite
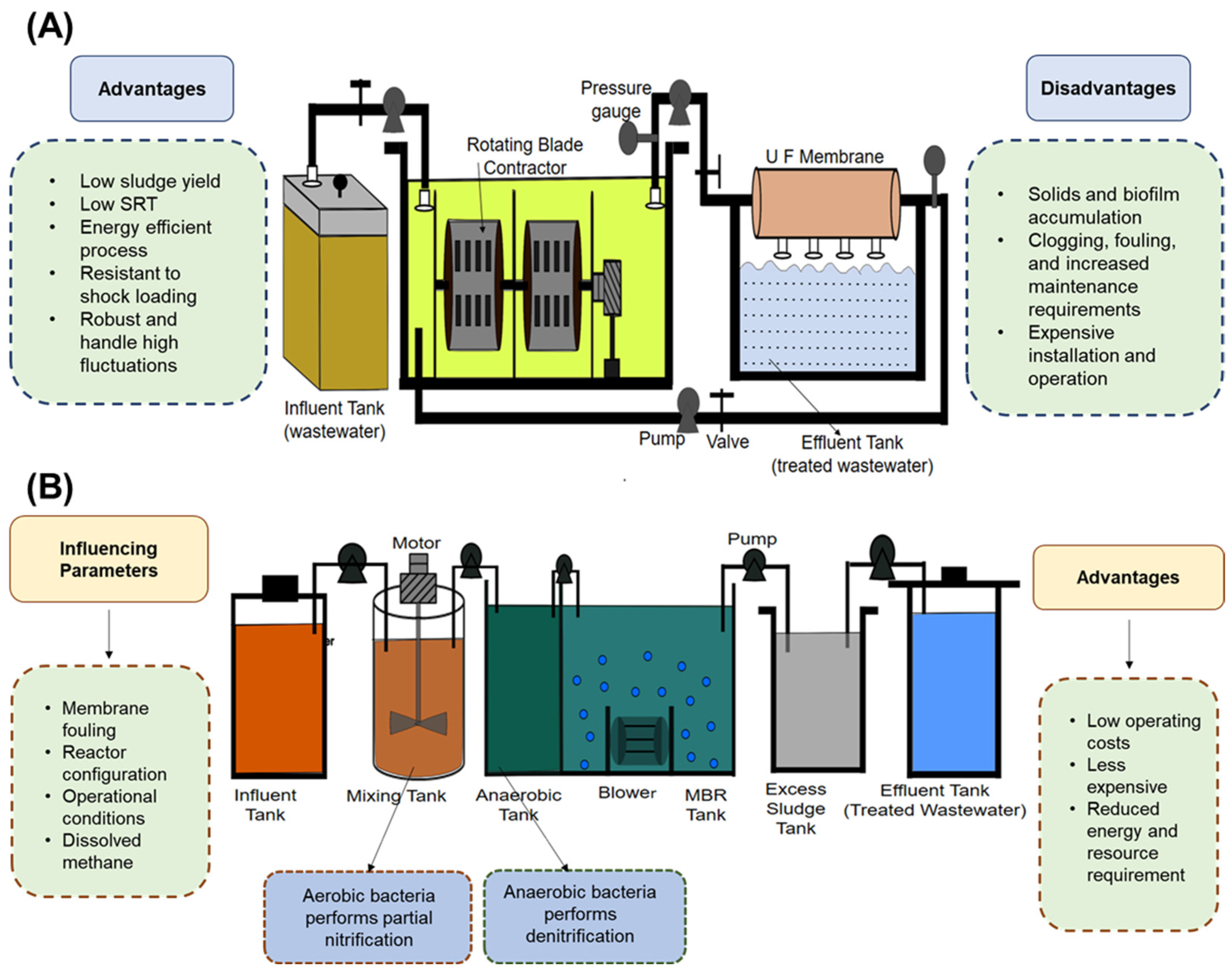
3.8. Integrated Fixed-Film Activated Sludge
3.9. Simultaneous Nitrogen and Phosphorus Removal
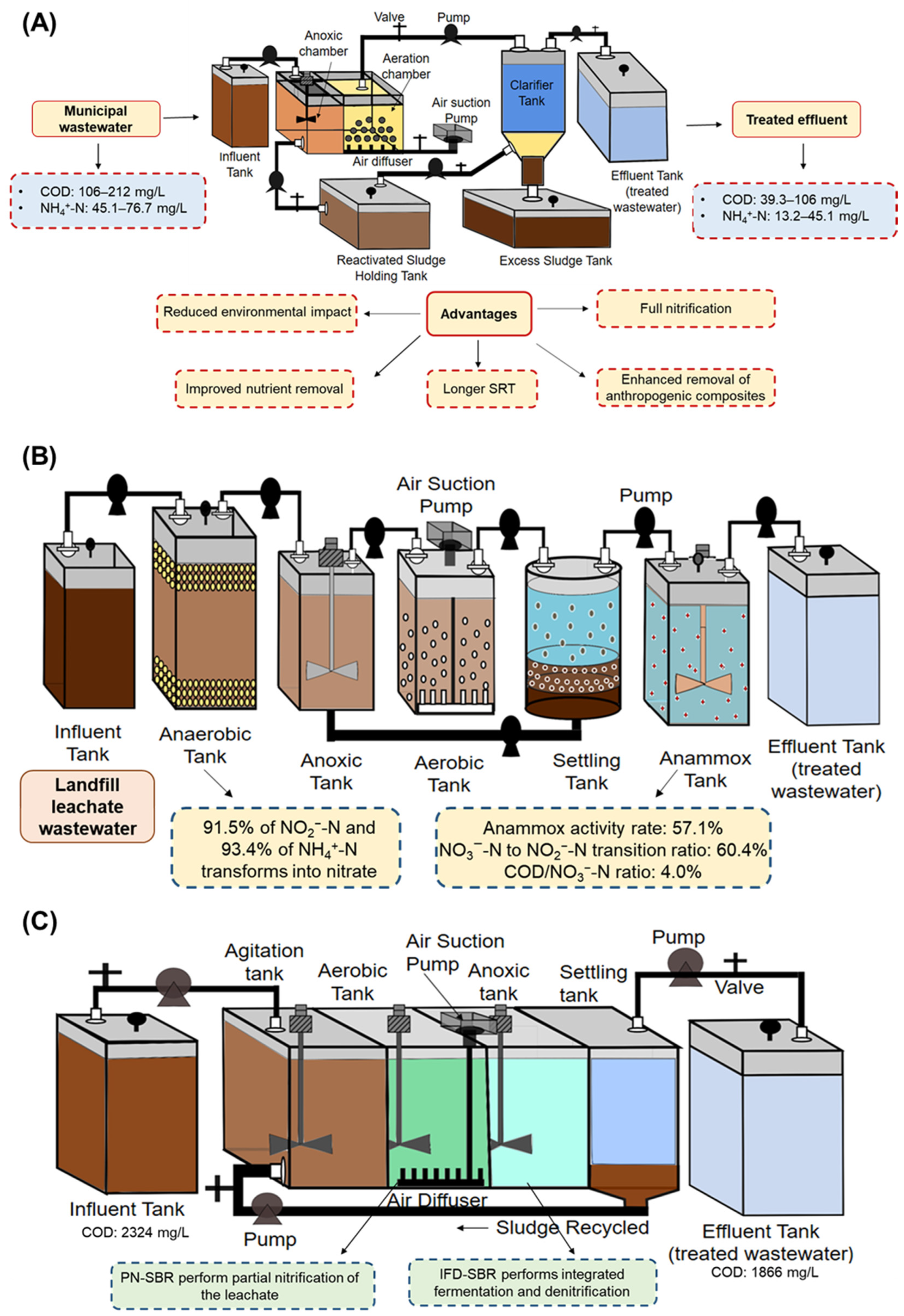
3.10. PN/A and Partial Denitrification-Anammox (Three Stage System-Based Processes)
3.11. Simultaneous Ammonium Oxidation Denitrification
3.12. Partial Nitrification and Integrated Fermentation Denitritation
4. Factors Affecting Anammox Process
4.1. Instability in Interaction Between Functional Microbial Communities Involved in Anammox
4.2. Sustainability of Maintaining Anammox Biomass (Granular/Biofilm)
4.3. Physiochemical Parameters
4.3.1. Temperature
4.3.2. pH
4.3.3. DO
4.3.4. Nitrogen Loading
4.3.5. Carbon Sources
4.3.6. Substrate
4.4. Other Environmental Factors
4.4.1. Nitrite
4.4.2. Sulfide
4.4.3. Toxic Metals
4.4.4. Toxic Organic Compounds
4.4.5. Antibiotics
5. Anammox Bacterial Diversity and Processes Efficiency
6. Prospects of Anammox Process
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weralupitiya, C.; Wanigatunge, R.; Joseph, S.; Athapattu, B.C.L.; Lee, T.H.; Biswas, J.K.; Ginige, M.P.; Lam, S.S.; Kumar, P.S.; Vithanage, M. Anammox bacteria in treating ammonium rich wastewater: Recent perspective and appraisal. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 334, 125240. [Google Scholar]
- Karri, R.R.; Sahu, J.N.; Chimmiri, V. Critical review of abatement of ammonia from wastewater. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 261, 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Ranjit, P.; Jhansi, V.; Reddy, K.V. Conventional Wastewater Treatment Processes. In Advances in the Domain of Environmental Biotechnology: Environmental and Microbial Biotechnology; Maddela, N.R., Cruzatty, L.C.C., Chakraborty, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 455–479. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Q.; Domingo-Felez, C.; Zhi, M.; Jensen, M.M.; Xu, B.; Ng, H.Y.; Smets, B.F. Formation and fate of reactive nitrogen during biological nitrogen removal from water: Important yet often ignored chemical aspects of the nitrogen cycle. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 22480–22501. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Y.; Zhang, K.; Peng, X.; Zhou, Q.; Pan, Z.; Xing, B.; Liu, X. Research progress on biological denitrification process in wastewater treatment. Water 2025, 17, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Fan, G.; Xu, Z.; Wu, S.; Xie, J.; Qiang, W.; Xu, K.-Q. A comprehensive review of antibiotics stress on anammox systems: Mechanisms, applications, and challenges. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 418, 131950. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Peng, Y. Establishing a two-stage system to efficiently treat real domestic sewage by partial nitrification-SBR and air-lift anammox-UASB: Reactivating and enhancing anammox bacteria to optimize the nitrogen removal performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 506, 160333. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.; Kang, H.; Oh, H.C.; Ahn, J.; Park, S.; Yun, S.L.; Kim, K. Long-term examination of water chemistry changes following treatment of cyanobacterial bloom with coagulants and minerals. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seruga, P.; Krzywonos, M.; Pyzanowska, J.; Urbanowska, A.; Pawlak-Kruczek, H.; Niedźwiecki, Ł. Removal of ammonia from the municipal waste treatment effuents using natural minerals. Molecules 2019, 24, 3633. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, I.N.; Zulkarnaini, Z.; Umar, Z.; Ismail, S.B. Development of an anaerobic ammonium oxidation (ANAMMOX) process reactor for aquaculture wastewater treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2024, 90, 1886–1896. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Gao, D.; Xu, A.; Gong, X.; Cao, J.; Gong, F.; Liu, Z.; Yang, T.; Liang, H. Rapid enrichment of AnAOB with a novel vermiculite/tourmaline modification technology for enhanced DEAMOX process. Chemosphere 2024, 361, 142526. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.; Liang, Z.; Yu, N.; Song, W.; Wang, Z.; Hu, M.; Yuan, T.; Shaw, D.R.; Saikaly, P.E.; Zhang, W. Enhanced nitrogen and phosphorus removal in gravity driven membrane bioreactor: Performance and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 362, 131688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Bruggen, B. Microfiltration, Ultrafiltration, Nanofiltration, Reverse Osmosis, and forward Osmosis. In Fundamental Modeling of Membrane Systems; Luis, P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 25–70. [Google Scholar]
- Kinidi, L.; Tan, I.A.W.; Wahab, N.B.A.; Tamrin, K.F.B.; Hipolito, C.N.; Salleh, S.F. Recent development in ammonia stripping process for industrial wastewater treatment. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 2018, 3181087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochs, P.; Martin, B.; Germain-Cripps, E.; Stephenson, T.; van Loosdrecht, M.; Soares, A. Techno-economic analysis of sidestream ammonia removal technologies: Biological options versus thermal stripping. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2023, 13, 100220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.-J.; Duan, C.-S.; Yu, C.; Song, Y.-X.; Chai, L.-Y.; Xiao, R.; Xiao, R.; Wei, Z.; Min, X.-B. Removal of nitrogen from wastewaters by anaerobic ammonium oxidation (ANAMMOX) using granules in upflow reactors. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2017, 15, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E. Advantages and disadvantages of techniques used for wastewater treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, I.S.; Medhi, K. Nitrification and denitrification processes for mitigation of nitrous oxide from waste water treatment plants for biovalorization: Challenges and opportunities. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 282, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, N.; Ren, H.; Geng, J.; Ding, L.; Xu, K. Engineering application of anaerobic ammonium oxidation process in wastewater treatment. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 33, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Q.; Yang, P. The effect of electricity generation on the performance of microbial fuel cells for anammox. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, C.; Song, Y.; Yan, W.; Zhang, T.; Li, Y.-Y. Anaerobic membrane bioreactor and Anammox in municipal wastewater treatment: Mainstream versus side-stream, challenges, and prospects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Review. 2025, 210, 115154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Peng, Y.; Ji, J.; Shi, L.; Gao, R.; Li, X. Partial denitrification providing nitrite: Opportunities of extending application for anammox. Environ. Int. 2019, 131, 105001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, C.L.; de Araújo, J.C. Inhibition of anammox activity by municipal and industrial wastewater pollutants: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Zhou, Y. New direction in biological nitrogen removal from industrial nitrate wastewater via anammox. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 7459–7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Du, R.; Zhou, Y. Integrated thermal hydrolysis pretreated anaerobic digestion centrate and municipal wastewater treatment via partial nitritation/anammox process: A promising approach to alleviate inhibitory effects and enhance nitrogen removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 356, 127310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, H.; He, X.; Lu, Y.; Gao, H.; Song, H.; Cheng, S. Enhancing the nitrogen removal of anammox sludge by setting up novel redox mediators-mediated anammox process. Chemosphere 2025, 365, 143360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsenga Kumwimba, M.; Lotti, T.; Şenel, E.; Li, X.; Suanon, F. Anammox-based processes: How far have we come and what work remains? A review by bibliometric analysis. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Dai, H.; Jiang, D.; Cao, X.; Wang, R.; Dai, Z.; Zhang, W.; Abbasi, H.N.; Li, B.; Zhu, G.; et al. Screening, identification, and application of anaerobic ammonia oxidizing bacteria in activated sludge systems: A comprehensive review. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 375, 124272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, R.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, W. Application of the anammox in China—A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, N.-S.; Bai, Y.-H.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, J.-J.; Zhou, W.-L.; Huang, B.-C.; Jin, R.-C. A two-stage anammox process for the advanced treatment of high-strength ammonium wastewater: Microbial community and nitrogen transformation. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 121148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y. The roads taken and not taken: Trends of anammox-based wastewater treatment in China. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2023, 13, 100221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broda, E. Two kinds of lithotrophs missing in nature. J. Basic Microbiol. 1977, 17, 491–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Kambey, C.; Nguyen, V.K. Performance of anammox processes for wastewater treatment: A critical review on effects of operational conditions and environmental stresses. Water 2020, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, A.S.; Nawaz, A.; Qyyum, M.A.; Ismail, S.; Aslam, M.; Tawfik, A.; Yun, C.M.; Lee, M. Energy saving anammox technology-based nitrogen removal and bioenergy recovery from wastewater: Inhibition mechanisms, state-of-the-art control strategies, and prospects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, X.; Zhou, M.; Wang, T.; Wang, W.; Kumari, S.; Wang, Y. Multidisciplinary characterization of nitrogen-removal granular sludge: A review of advances and technologies. Water Res. 2022, 214, 118214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulder, A.; van de Graaf, A.A.; Robertson, L.A.; Kuenen, J.G. Anaerobic ammonium oxidation discovered in a denitrifying fluidized bed reactor. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1995, 16, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, J.; Gao, R.; Wang, M.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Peng, Y. A critical review of one-stage anammox processes for treating industrial wastewater: Optimization strategies based on key functional microorganisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Sun, K.; Wei, Q.; Urata, K.; Yamashita, Y.; Hong, N.; Hama, T.; Kawagoshi, Y. One-stage partial nitritation and anammox in membrane bioreactor. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 11149–11162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.Q.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.G.; Du, X.N.; Huang, B.C.; Jin, R.C. A review of anammox-based nitrogen removal technology: From microbial diversity to engineering applications. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 363, 127896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, D.; Kusmayadi, A.; Yen, H.-W.; Dong, C.-D.; Lee, D.-J.; Chang, J.-S. Current advances in biological swine wastewater treatment using microalgae-based processes. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 289, 121718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Du, W.-L.; Miao, L.-L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.-P. Microbial community dynamics in an ANAMMOX reactor for piggery wastewater treatment with startup, raising nitrogen load, and stable performance. AMB Expr. 2018, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tabassum, S.; Li, J. Effects of fulvic acid on the denitrification performance of completely autotrophic nitrogen removal over nitrite (CANON) process for the treatment of landfill leachate. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2021, 4, 100173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Jia, F.; Liu, T.; Guo, J.; Yao, H. Evaluation of the joint effects of Cu(2+), Zn(2+) and Mn(2+) on completely autotrophic nitrogen-removal over nitrite (CANON) process. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, T.V.; Nguyen, P.D.; Phan, T.N.; Luong, D.H.; Truong, T.T.V.; Huynh, K.A.; Furukawa, K. Application of CANON process for nitrogen removal from anaerobically pretreated husbandry wastewater. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2019, 136, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Third, K.A.; Olav Sliekers, A.; Kuenen, J.G.; Jetten, M.S.M. The CANON system (Completely autotrophic nitrogen-removal over nitrite) under ammonium Limitation: Interaction and competition between three groups of bacteria. System. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 24, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Yuan, L.; Xing, F. One-step start-up and subsequent operation of CANON process in a fixed-bed reactor by inoculating mixture of partial nitrification and Anammox sludge. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 130075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.; Banerjee, A. Technologies for biological and bioelectrochemical removal of inorganic nitrogen from wastewater: A review. Nitrogen 2022, 3, 298–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaubroeck, T.; Bagchi, S.; De Clippeleir, H.; Carballa, M.; Verstraete, W.; Vlaeminck, S.E. Successful hydraulic strategies to start up OLAND sequencing batch reactors at lab scale. Microb. Biotechnol. 2012, 5, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wett, B. Solved upscaling problems for implementing deammonification of rejection water. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 53, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardin, N.; Hennerkes, J. Full-scale experience with the deammonification process to treat high strength sludge water—A case study. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 65, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamp, A.; Ottosen, L.D.M.; Thøgersen, N.B.; Revsbech, N.; Thamdrup, B.; Andersen, M.H. Anammox and partial nitritation in the mainstream of a wastewater treatment plant in a temperate region (Denmark). Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 79, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podmirseg, S.M.; Gomez-Brandon, M.; Muik, M.; Stres, B.; Hell, M.; Pumpel, T.; Murthy, S.; Chandran, K.; Park, H.; Insam, H.; et al. Microbial response on the first full-scale DEMON ® biomass transfer for mainstream deammonification. Water Res. 2022, 218, 118517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, S.; Trego, A.C.; Prevedello, M.; Vrieze, J.D.; O’Flaherty, V.; Lens, P.N.L.; Collins, G. Unifying concepts in methanogenic, aerobic, and anammox sludge granulation. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2024, 17, 100310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyuzhnyi, S.; Gladchenko, M. DEAMOX—New microbiological process of nitrogen removal from strong nitrogenous wastewater. Desalination 2009, 248, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Du, R.; Cao, S.; Wang, S.; Peng, Y. Mechanisms and characteristics of biofilm formation via novel DEAMOX system based on sequencing biofilm batch reactor. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2019, 127, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.; Bao, P.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, Y. Long-term stable simultaneous partial nitrification, anammox and denitrification (SNAD) process treating real domestic sewage using suspended activated sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 339, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, J. Nitrogen removal in recirculating aquaculture water with high dissolved oxygen conditions using the simultaneous partial nitrification, anammox and denitrification system. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 305, 123037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Xia, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Ma, X. Pathway governing nitrogen removal in artificially aerated constructed wetlands: Impact of aeration mode and influent chemical oxygen demand to nitrogen ratios. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 257, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Dong, F.; He, C.; Hu, Z.; Yuan, S.; Wang, W. Enhancement of performance robustness and nitrogen removal by coupling anammox with denitrification in a corncob-dosed reactor. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2019, 36, 1482–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetten, M.S.M.; Wagner, M.; Fuerst, J.; Van Loosdrecht, M.; Kuenen, G.; Strous, M. Microbiology and application of the anaerobic ammonium oxidation (’anammox’) process. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2001, 12, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqas, S.; Bilad, M.R.; Man, Z.; Wibisono, Y.; Jaafar, J.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Khan, A.L.; Aslam, M. Recent progress in integrated fixed-film activated sludge process for wastewater treatment: A review. J. Environ. Manage. 2020, 268, 110718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Yu, D.; Wang, X.; Zhen, J.; Bi, C.; Gong, X.; Zhao, J. Achieving simultaneous nitritation, anammox and denitrification (SNAD) in an integrated fixed-biofilm activated sludge (IFAS) reactor: Quickly culturing self-generated anammox bacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, A. Wastewater treatment in 2050: Challenges ahead and future vision in a European context. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2020, 2, 100030. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Peng, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q. A novel SNPR process for advanced nitrogen and phosphorus removal from mainstream wastewater based on anammox, endogenous partial-denitrification and denitrifying dephosphatation. Water Res. 2020, 170, 115363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, H.; Ren, S.; Wang, W.; Peng, Y. A continuous-flow combined process based on partial nitrification-Anammox and partial denitrification-Anammox (PN/A + PD/A) for enhanced nitrogen removal from mature landfill leachate. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122483. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Peng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, H. High-efficient nitrogen removal from mature landfill leachate and waste activated sludge (WAS)reduction via partial nitrification and integrated fermentation-denitritation process (PNIFD). Water Res. 2019, 160, 394–404. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Ren, S.; Peng, Y. Simultaneous Ammonium oxidation denitrifying (SAD) in an innovative three-stage process for energy-efficient mature landfill leachate treatment with external sludge reduction. Water Res. 2020, 169, 115156. [Google Scholar]
- Straka, L.L.; Meinhardt, K.A.; Bollmann, A.; Stahl, D.A.; Winkler, M.K.H. Affinity informs environmental cooperation between ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) and anaerobic ammonia-oxidizing (Anammox) bacteria. ISME J. 2019, 13, 1997–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler-Jofra, A.; Pérez, J.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Hydroxylamine and the nitrogen cycle: A review. Water Res. 2021, 190, 116723. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kosgey, K.; Chandran, K.; Gokal, J.; Kiambi, S.L.; Bux, F.; Kumari, S. Critical analysis of biomass retention strategies in mainstream and sidestream ANAMMOX-mediated nitrogen removal systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Guo, Y.; Shen, J.; Qin, Y.; Li, Y.-Y. Biofilm growth characterization and treatment performance in a single stage partial nitritation/anammox process with a biofilm carrier. Water Res. 2022, 217, 118437. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, M.; Xie, J.; Xie, J.; Chang, Y.; Gao, M.; Chen, C.; Zhang, T.C. The effect of carrier addition on Anammox start-up and microbial community: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 19, 355–368. [Google Scholar]
- Liébana, R.; Modin, O.; Persson, F.; Wilén, B.-M. Integration of aerobic granular sludge and membrane bioreactors for wastewater treatment. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2018, 38, 801–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, L.; Wang, S.; Cao, T.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z. Advanced nitrogen removal from landfill leachate via anammox system based on sequencing biofilm batch reactor (SBBR): Effective protection of biofilm. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 220, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Peng, Y.; Han, X.; Gan, Y. Nitrogen removal performance and microbial distribution in pilot- and full-scale integrated fixed-biofilm activated sludge reactors based on nitritation-anammox process. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 196, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Guo, G.; Li, Y.-Y. A review on upgrading of the anammox-based nitrogen removal processes: Performance, stability, and control strategies. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 364, 127992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, O.I.M.; Araujo, J.M.; Silva, P.M.J.; Magnus, B.S.; Gavazza, S.; Florencio, L.; Kato, M.T. Formation and stability of aerobic granular sludge in a sequential batch reactor for the simultaneous removal of organic matter and nutrients from low-strength domestic wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 156988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. Development of specific granular growth anaerobic membrane bioreactors for domestic wastewater treatment. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Technology, Sydney, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.; Wang, Y.; Tang, X.; Li, L.; Feng, F.; Mahmood, Q.; Wu, D.; Tang, C.-J. Quantitative determination of cavitation formation and sludge flotation in Anammox granules by using a new diffusion-reaction integrated mathematical model. Water Res. 2020, 174, 115632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Bai, L.; Qiang, Z.; Dong, H.; Wang, D. Nitrogen removal through ‘Candidatus Brocadia sinica’ treating high-salinity and low-temperature wastewater with glycine addition: Enhanced performance and kinetics. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 270, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yan, Y.; Song, C.; Pan, M.; Wang, Y. The microbial community structure change of an anaerobic ammonia oxidation reactor in response to decreasing temperatures. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 35330–35341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Chen, Y.; Qin, M.; Mao, Z.; Yuan, L.; Niu, Q.; Tan, X. Effects of temperature on anammox performance and community structure. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 260, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talan, A.; Tyagi, R.D.; Drogui, P. Critical review on insight into the impacts of different inhibitors and performance inhibition of anammox process with control strategies. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hong, Y.; Gu, J.D.; Wu, J.; Yan, J.; Lin, J.G. Influence of critical factors on nitrogen removal contribution by anammox and denitrification in an anammox-inoculated wastewater treatment system. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Kwok, B.H.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Daigger, G.; Png, H.Y.; Long, W.Y.; Eng, O.K. The influence of dissolved oxygen on partial nitritation/anammox performance and microbial community of the 200,000 m(3)/d activated sludge process at the Changi water reclamation plant (2011 to 2016). Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Wang, X.; Liang, H.; Wei, Q.; Dou, Y.; Li, L. Anaerobic ammonia oxidizing bacteria: Ecological distribution, metabolism, and microbial interactions. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2018, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Li, Y.Y. A new process for simultaneous nitrogen removal and phosphorus recovery using an anammox expanded bed reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 267, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.C.; Yang, G.F.; Yu, J.J.; Zheng, P. The inhibition of the Anammox process: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 197, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhou, Y. Mainstream nitrogen removal in membrane aerated biofilm reactor at minimal lumen pressure. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ruiz, M.J.; Maza-Márquez, P.; González-López, J.; Osorio, F. Nitrogen removal capacity and bacterial community dynamics of a Canon biofilter system at different organic matter concentrations. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, W.; He, S.; Han, M.; Wang, B.; Niu, Q.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H. Nitrogen removal performance and microbial community structure in the start-up and substrate inhibition stages of an anammox reactor. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2018, 126, 88–95. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.-B.; Liu, X.-L.; Bu, C.-N.; Ni, S.-Q.; Sung, S. Microbial diversity reveals the partial denitrification-anammox process serves as a new pathway in the first mainstream anammox plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 142917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pous, N.; Bañeras, L.; Corvini, F.X.; Liu, S.J.; Puig, S. Direct ammonium oxidation to nitrogen gas (Dirammox) in Alcaligenes strain HO-1: The electrode role. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2023, 15, 100253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudkivi, M.; Zekker, I.; Rikmann, E.; Vabamäe, P.; Kroon, K.; Tenno, T. Nitrite inhibition and limitation—The effect of nitrite spiking on anammox biofilm, suspended and granular biomass. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Val del Río, Á.; da Silva, T.; Martins, T.H.; Foresti, E.; Campos, J.L.; Mendez, R.; Mosquera-Corral, A. Partial nitritation-anammox granules: Short-term inhibitory effects of seven metals on anammox activity. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.M.; Thamdrup, B.; Dalsgaard, T. Effects of specific inhibitors on anammox and denitrification in marine sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 3151–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ude, E.O.; Haas, J.; Kaiyoum, M.K.; Ding, C.; Adrian, L. Effects of reducing, stabilizing, and antibiotic agents on ‘Candidatus Kuenenia stuttgartiensis’. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 1829–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; You, J.; Yin, S.; Yang, H.; He, S.; Feng, L.; Li, J.; Zhao, Q.; Wei, L. Extracellular polymeric substances—Antibiotics interaction in activated sludge: A review. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2023, 13, 100212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Rogers, M.J.; Ng, S.S.; He, J. Fixed nitrogen removal mechanisms associated with sulfur cycling in tropical wetlands. Water Res. 2021, 189, 116619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodha, T.; Narvekar, S.; Karodi, P. Classification of uncultivated anammox bacteria and Candidatus Uabimicrobium into new classes and provisional nomenclature as Candidatus Brocadiia classis nov. and Candidatus Uabimicrobiia classis nov. of the phylum Planctomycetes and novel family Candidatus Scalinduaceae fam. nov to accommodate the genus Candidatus Scalindua. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 44, 126272. [Google Scholar]
- Nejidat, A.; Diaz-Reck, D.; Massalha, N.; Arbiv, A.; Dawas, A.; Dosoretz, C.; Sabbah, I. Abundance and diversity of anammox bacteria in a mainstream municipal wastewater treatment plant. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 6713–6723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal, B.; Rattray, J.; van Niftrik, L.A.; van de Vossenberg, J.; Schmid, M.C.; Webb, R.I.; Schouten, S.; Fuerst, J.A.; Damste, J.S.; Jetten, M.S.M.; et al. Candidatus ‘Anammoxoglobus propionicus’ a new propionate oxidizing species of anaerobic ammonium oxidizing bacteria. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 30, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.T.; Chen, S.S.; Jetten, M.S.M.; Lin, J.G. Nanoarchitectured structure and population dynamics of anaerobic ammonium oxidizing (anammox) bacteria in a wastewater treatment plant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 396, 122714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimoto, C.; Waki, M.; Soda, S. Adaptation of anammox granules in swine wastewater treatment to low temperatures at a full-scale simultaneous partial nitrification, anammox, and denitrification plant. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 131027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Speth, D.R.; Francoijs, K.-J.; Quan, Z.-X.; Jetten, M.S.M. Metagenome analysis of a complex community reveals the metabolic blueprint of anammox bacterium ‘Candidatus Jettenia asiatica. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Faustin, F.; Liu, W. Characterization of the start-up of single and two-stage Anammox processes with real low-strength wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Star, W.R.L.; Dijkema, C.; De Waard, P.; Picioreanu, C.; Strous, M.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. An intracellular pH gradient in the anammox bacterium Kuenenia stuttgartiensis as evaluated by 31P NMR. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 86, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Li, J.; Dong, H.; Qiang, Z. Insights into microbial community variability and functional genes of various Candidatus Scalindua-based anammox processes treating nitrogen-rich saline wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 142544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, T.; Yoshinaga, I.; Okada, K.; Yamagishi, T.; Ueda, S.; Obuchi, A.; Sako, Y.; Suwa, Y. Detection of anammox activity and diversity of anammox bacteria-related 16S rRNA genes in coastal marine sediment in Japan. Microbes Environ. 2007, 22, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Du, R. Highly efficient and synchronous nitrogen removal from ammonia-rich wastewater and domestic wastewater via a novel anammox coupled with double-nitrite-shunt process at low temperature. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 131449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Cao, S.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S. Combined Partial Denitrification (PD)-Anammox: A method for high nitrate wastewater treatment. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, L. Advanced nitrogen removal from municipal wastewater via two-stage partial nitrification-simultaneous anammox and denitrification (PN-SAD) process. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 304, 122955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalini, S.S.; Joseph, K. Combined SHARON and ANAMMOX processes for ammoniacal nitrogen stabilisation in landfill bioreactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 250, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q. Simultaneous partial nitritation and denitritation coupled with polished anammox for advanced nitrogen removal from low C/N domestic wastewater at low dissolved oxygen conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 305, 123045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laureni, M.; Weissbrodt, D.G.; Villez, K.; Robin, O.; de Jonge, N.; Rosenthal, A.; Wells, G.; Nielsen, J.L.; Morgenroth, E.; Joss, A. Biomass segregation between biofilm and flocs improves the control of nitrite-oxidizing bacteria in mainstream partial nitritation and anammox processes. Water Res. 2019, 154, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xu, D.; Shan, X.; Zheng, P. Potential of anammox process towards high-efficient nitrogen removal in wastewater treatment: Theoretical analysis and practical case with a SBR. Chemosphere 2021, 281, 130729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Li, D.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, H. Fast start-up of anammox process with mixed activated sludge and settling option. Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 3088–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Liu, G.-H.; Ma, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, H. A pilot-scale study on start-up and stable operation of mainstream partial nitrification-anammox biofilter process based on online pH-DO linkage control. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 350, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, B.; Li, X.; Wu, L.; Wang, S. Partial nitrification-anammox (PNA) treating sewage with intermittent aeration mode: Effect of influent C/N ratios. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekker, I.; Artemchuk, O.; Rikmann, E.; Ohimai, K.; Bhowmick, G.D.; Ghangrekar, M.M.; Burlakovs, J.; Tenno, T. Start-up of anammox SBR from non-specific inoculum and process acceleration methods by hydrazine. Water 2021, 13, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Peng, Y. Advanced nitrogen removal from low C/N municipal wastewater by combining partial nitrification-anammox and endogenous partial denitrification-anammox (PN/A-EPD/A) process in a single-stage reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 339, 125501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekyavas, G.; Yangin-Gomec, C. Response of Anammox bacteria to elevated nitrogen and organic matter in pre-digested chicken waste at a long-term operated UASB reactor initially seeded by methanogenic granules. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2019, 7, 100222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.-X.; Ali, M.; Feng, F.; Chai, X.-L.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Tang, C.-J. Performance of a high-rate anammox reactor under high hydraulic loadings: Physicochemical properties, microbial structure and process kinetics. J. Cent. S. Univ. 2020, 27, 1197–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nancharaiah, Y.V.; Venkata Mohan, S.; Lens, P.N.L. Recent advances in nutrient removal and recovery in biological and bioelectrochemical systems. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2016, 215, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gualtieri, M.; Goglio, A.; Clagnan, E.; Adani, F. The importance of the electron acceptor: Comparison between flooded and tidal bioelectrochemical systems for wastewater treatment and nutrients enriched solution production. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2023, 24, 101617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Microorganism | Source | Form of Nutrition | Physiological Conditions | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | pH | ||||
| Anammoximicrobium moscowii | Wetland/wastewater sludge | Chemolithoautotrophic | 19–22 | 7.8–8.3 | [99,100] |
| Anammoxoglobus propionicus | Municipal synthetic wastewater | Chemolithoautotrophic/propionate oxidizing | 33 | 7.0–7.3 | [63,101,102] |
| Brocadia anammoxidans | Landfill leachate wastewater | Chemolithoautotrophic | 20–43 | 6.7–8.3 | [19,103] |
| Jettenia asiatica | Swine wastewater | Chemolithoautotrophic | 30–35 | 8.0–8.5 | [104,105] |
| Kuenenia stuttgartiensis | Municipal wastewater/freshwater | Chemolithoautotrophic | 25–37 | 6.5–9.0 | [106,107] |
| Scalindua wagneri | Saline wastewater/marine | Chemolithoautotrophic | 22–25 | 7.0–8.0 | [108,109] |
| Stages | Process | Treated Object | Bioreactor (Working Volume) | Seed Sludge | Influent Parameters (Feed) | Effluent Parameters (Treated Object) | NRE (%) [AC] (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| One | DEAMOX | Synthetic wastewater | SBBR (10 L) | DEAMOX suspended sludge | NH4+-N: 151–157 mg N/L NO3−-N: 166–201 mg N/L HRT: 5–10 h Temp: 30 ± 5 °C | NH4+-N: 0.68 mg N/L NO3−-N: 1.92 mg N/L HRT: 5–10 h Temp: 30 °C | >90 | [55] |
| CANON | Synthetic wastewater | FBR (2.6 L) | - a | NH4+-N: 50 mg N/L Temp: 32 °C DO: <0.3 mg/L HRT: 1 d pH: 7.8–8.0 | Temp: 32 °C DO: <0.3 mg/L HRT: 1 d pH: 7.8–8.0 | 91.8 | [46] | |
| SNAD | Municipal wastewater | IFAS (8 L) | Lab-scale SBR | NH4+-N: 45.1 mg N/L NO2−-N: <0.3 mg N/L COD: 106–212 mg/L Temp: 18.5–30 ± 1 °C C/N ratio: < 3 | TN: 13.2 mg N/L COD: 39.3 mg/L ORE: 78.8% | 92.8 | [62] | |
| Two | SHARON/A | Ammonium-rich wastewater | Control LFBR (43 L) | - | - | TN removal efficiency: 84% | 71.0 | [113] |
| SHARON/A LFBR | ||||||||
| SPND/A | Domestic wastewater | SPND-SBBR (10 L) | Nitrification sludge | NH4+-N: 71.4 mg N/L NO2−-N: 0.2 mg N/L NO3−-N: 0.3 mg N/L COD: 239 mg/L C/N ratio: 3.4 pH: 7.1–7.5 HRT: 2 h DO: 0.1 mg/L | NH4+-N: 0.6 mg N/L NO2−-N: 0.2 mg N/L NO3−-N: 7.6 mg N/L COD: 33.2 mg/L | 88.2 [75.0] | [114,116] | |
| A-UASB (2 L) | Anaerobic digestive sludge | |||||||
| PD/A | Municipal sewage | PD-SBR (5 L) | - | NH4+-N: 58.3 mg N/L NO3−-N: 107 mg N/L COD: 194 mg/L HRT: 3.1–3.6 h Temp: 14.8–28.2 °C | TN: 11.0 mg N/L C/N ratio: 1.7 | 92.8 [78.9] | [110,111] | |
| A-UASB (3.2 L) | ||||||||
| SNPR | Synthetic sewage wastewater | SNPR-SBR (10 L) | PD sludge from EPD reactor | HRT: 6.7 h pH: 8.0–8.4 Temp: 27 ± 2 °C NH4+-N: 60 mg N/L COD: 180 mg/L | NH4+-N: 2.1 mg N/L TN: 3.6 mg N/L PO43−-P: 0.3 mg P/L | 93.9 PRE: 94.2 [82.9] | [15,64] | |
| N-SBR (10 L) | Suspended sludge | DO: <5 mg/L HRT: 5 h pH: 7.3–8.1 | ||||||
| PN-SAD | Municipal wastewater | PN-SBR (10 L) | PN reactor | NH4+-N: 52.1 mg N/L NO2−-N: 0.10 mg N/L COD: 164 mg/L HRT: 6 h Temp: 18.5–28.2 °C DO: <1 mg/L | NH4+-N: 0.4 mg N/L NO2−-N: 1.6 mg N/L COD: 38.4 mg/L HRT: 6 h Temp: 18.5–28.2 °C DO: < 1mg/L | 97.1 [80.0] | [112] | |
| SAD-UASB (4 L) | PN reactor | |||||||
| DNS/A | Domestic wastewater | PNA-SBR (10 L) | Synthetic ammonia-rich wastewater | NH4+-N: 300 mg N/L HRT: 20–26 h DO: 0.2–0.8 mg/L Temp: 26.8–13.0 °C | TN: 1.2 mg N/L HRT: 4.5–7.5 h DO: 0.0–0.1 mg/L | 99.6 [94.4] | [110] | |
| PDA-SBR (6 L) | ||||||||
| Three | PN/A+ PD/A | Landfill leachate | A/O-CFR (10.5 L) | PN-sludge domestic wastewater | - | ATR: 93.4% NAR: 91.5% FA: 43.5 mg/L FNA: 0.18 mg/L | 7.0 | [65,93] |
| PD/A-UASB (3.5 L) | PD/A SBR reactor | - | TN: 15.7 mg N/L | 18.0 | ||||
| A/UASB (10 L) | Synthetic wastewater | - | NH4+-N: 19.6 mg N/L NO2−-N: 11.5 mg N/L | 73.0 | ||||
| PNIFD | Mature landfill leachate | PN-SBR | - | COD: 2324 mg/L | NRR: 0.63 kg/m3.d COD: 1866 mg/L SRR: 5.9 kg/m3.d | 95.0 ORE: 19.7 | [15,66] | |
| SAD | Mature landfill leachate | PN-SBR (10 L) | PN-SBR sewage wastewater | NH4+-N: 1760 mg N/L NO2−-N: 3 mg N/L NO3−-N: 4 mg N/L COD: 217 mg/L pH: 7.8 | TN: 16.7 mg/L SRR: 2.5 kg/m3.d | 98.3 [83] | [53,67] | |
| IFD-SBR (6 L) | PN-SBR sewage wastewater | |||||||
| SAD-UASB (2 L) | Granular anammox-PD reactor |
| Types | Feed | IAC (mg N/L) | ICOD (mg N/L) | C/N Ratio | HRT (H) | SRT (D) | pH | Temp. (°C) | DO (mg N/L) | EAC (mg N/L) | NRR (mg N/L.d) | NRE (%) | MO | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MBBR | Municipal wastewater | 23.0 | 54.0 | - | 11.0 | 6.80–24.5 | 7.40 | 15.0 | 1.20–0.17 | 1.90 | 80.0 | - | Thauera, anammox bacteria | [115] |
| SBR | Reject water | 220 | <180 | 10/1 | 2.00–3.00 | NA | NA | 30.0 | - | 40–70 | 80.0 kgN/L.d | 80.0 | NA | [120] |
| Sewage wastewater | 33.0–76.9 | 39.1–184 | 1.20–2.50 | 218 | - | 7.49–7.74 | 30.0 | 1.5–3.0 | - | 94.7 | 84.0–95.0 | Thauera, anammox bacteria | [119] | |
| Low-nitrogen-containing wastewater | 6.20 | - a | - | 5.42 | - | - | 30.0 | - | 1.90 | 0.54 kg N/L.d | 86.5 | Thauera, anammox bacteria | [116] | |
| Municipal wastewater | 65.0 | 300 | - | - | 4.60 | 7.50 | 25.0 | 2.50 | <5.00 | - | 90.0 | Candidatus brocadi | [118] | |
| Mixed activated sludge | 64.0 | - | - | - | - | - | 28.0 | 2.00–3.00 | 2.70 | 214 g N/L.d | 93.0–99.0 | Candidatus kuenenia | [117] | |
| SBR-IFAS | Municipal wastewater | 120 | - | <3.20 | 8.00 | 25.0 | - | 30.0 | 0.40 | - | 105 | 90.1 | Candidatus brocadia, Candidatus competibacter | [121] |
| UASB | Chicken digestate wastewater | 330 | 2868 | - | - | - | 8.0–8.2 | - | - | - | - | 57.0 | - | [122] |
| Synthetic wastewater | 100–180 | - | - | 4.76–1.06 | ~40.0 | 6.90–7.20 | 30.0 | - | - | 1577 kgN/L.d | 93.7 | Candidatus kuenenia, Candidatus brocadia | [123] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, P.; Bisen, M.; Kulshreshtha, S.; Kumar, L.; Choudhury, S.R.; Nath, M.J.; Mandal, M.; Kumar, A.; Patel, S.K.S. Advancement in Anaerobic Ammonia Oxidation Technologies for Industrial Wastewater Treatment and Resource Recovery: A Comprehensive Review and Perspectives. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040330
Singh P, Bisen M, Kulshreshtha S, Kumar L, Choudhury SR, Nath MJ, Mandal M, Kumar A, Patel SKS. Advancement in Anaerobic Ammonia Oxidation Technologies for Industrial Wastewater Treatment and Resource Recovery: A Comprehensive Review and Perspectives. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(4):330. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040330
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Pradeep, Monish Bisen, Sourabh Kulshreshtha, Lokender Kumar, Shubham R. Choudhury, Mayur J. Nath, Manabendra Mandal, Aman Kumar, and Sanjay K. S. Patel. 2025. "Advancement in Anaerobic Ammonia Oxidation Technologies for Industrial Wastewater Treatment and Resource Recovery: A Comprehensive Review and Perspectives" Bioengineering 12, no. 4: 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040330
APA StyleSingh, P., Bisen, M., Kulshreshtha, S., Kumar, L., Choudhury, S. R., Nath, M. J., Mandal, M., Kumar, A., & Patel, S. K. S. (2025). Advancement in Anaerobic Ammonia Oxidation Technologies for Industrial Wastewater Treatment and Resource Recovery: A Comprehensive Review and Perspectives. Bioengineering, 12(4), 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040330








