Effect of 10 kV/m Electric Field Therapy in a Pressure Injury Model in Rats: An Innovative Preliminary Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
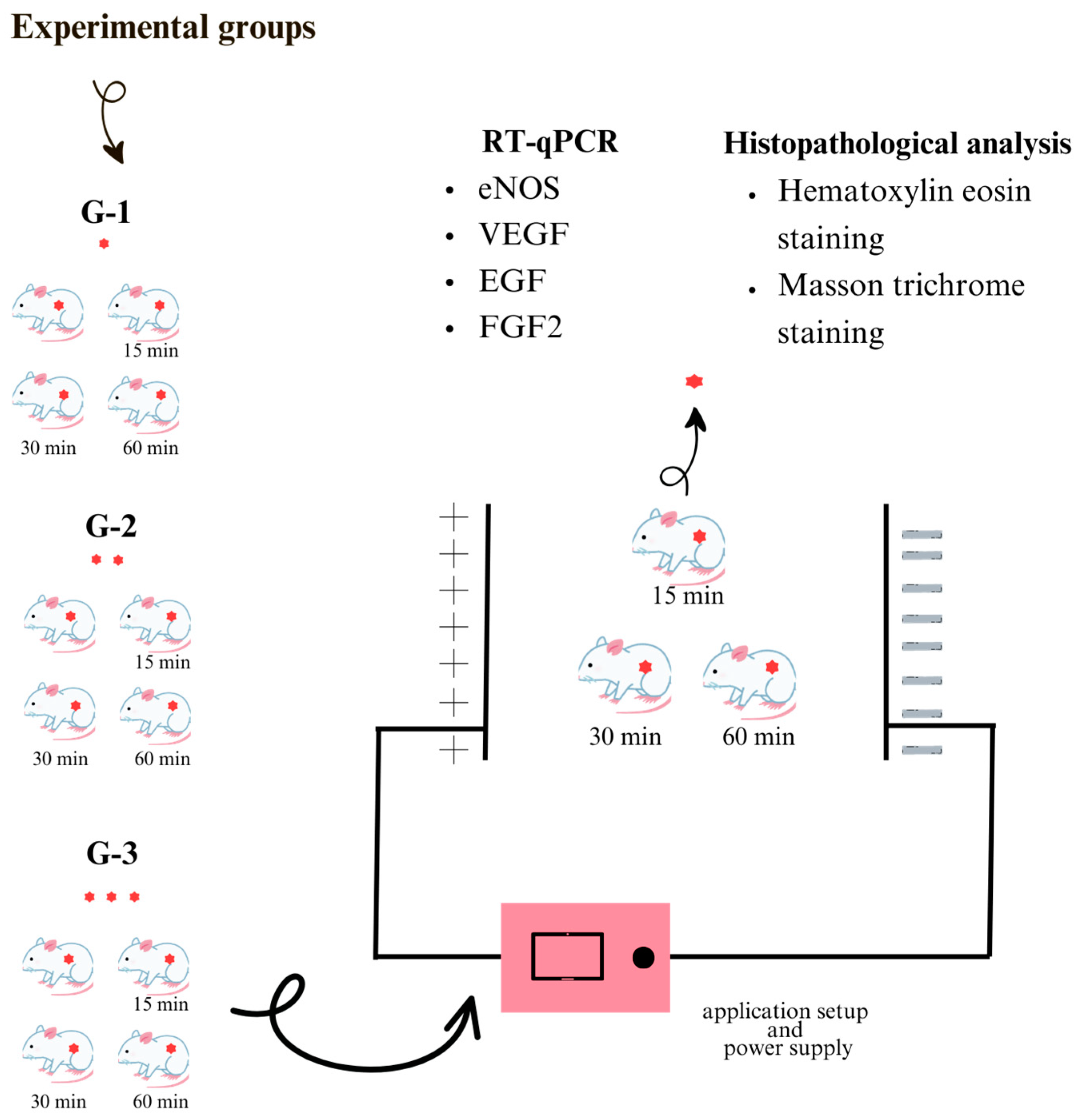
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Electric Field Application Setup
2.2. Experimental Groups and Animals
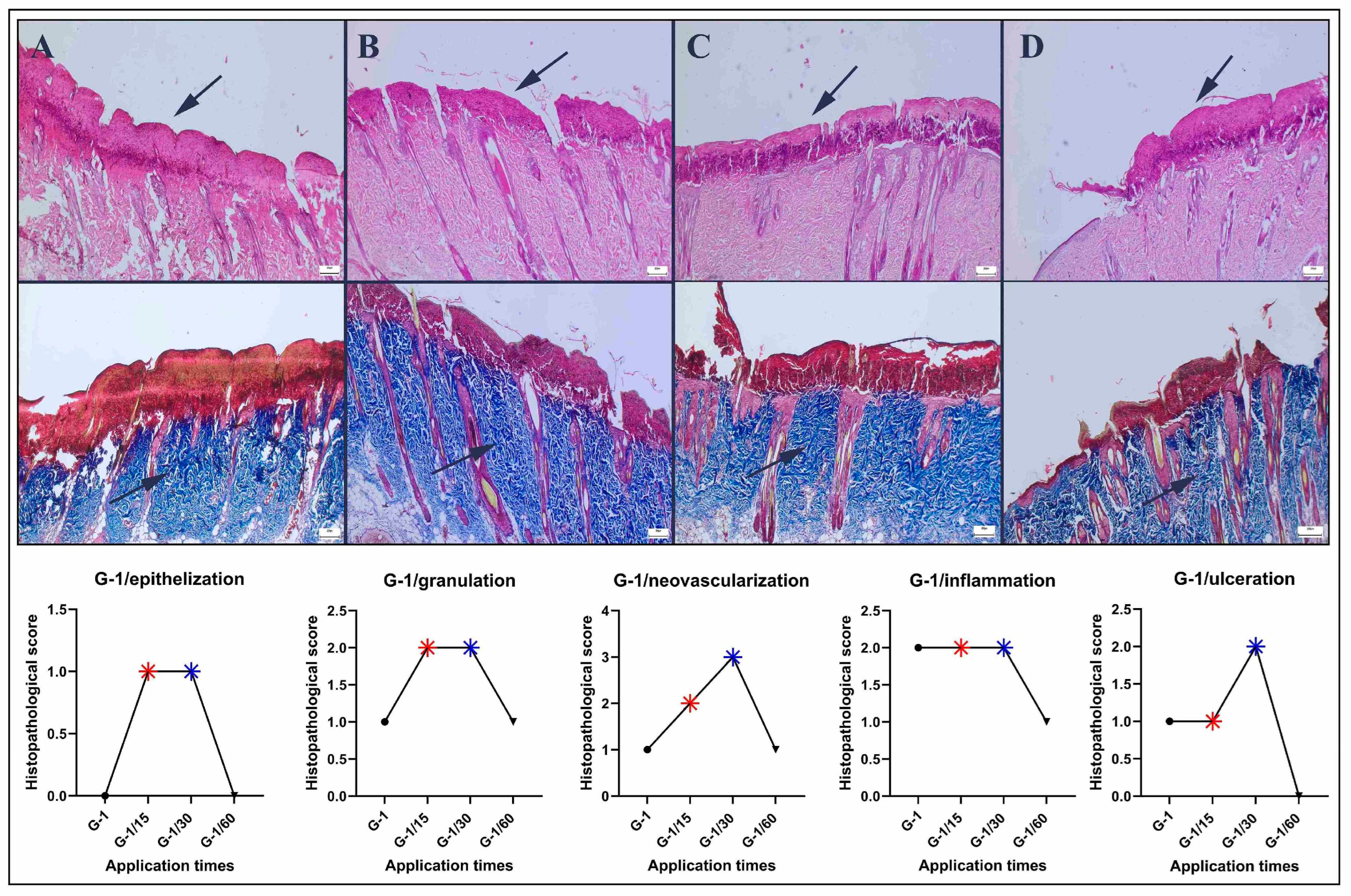
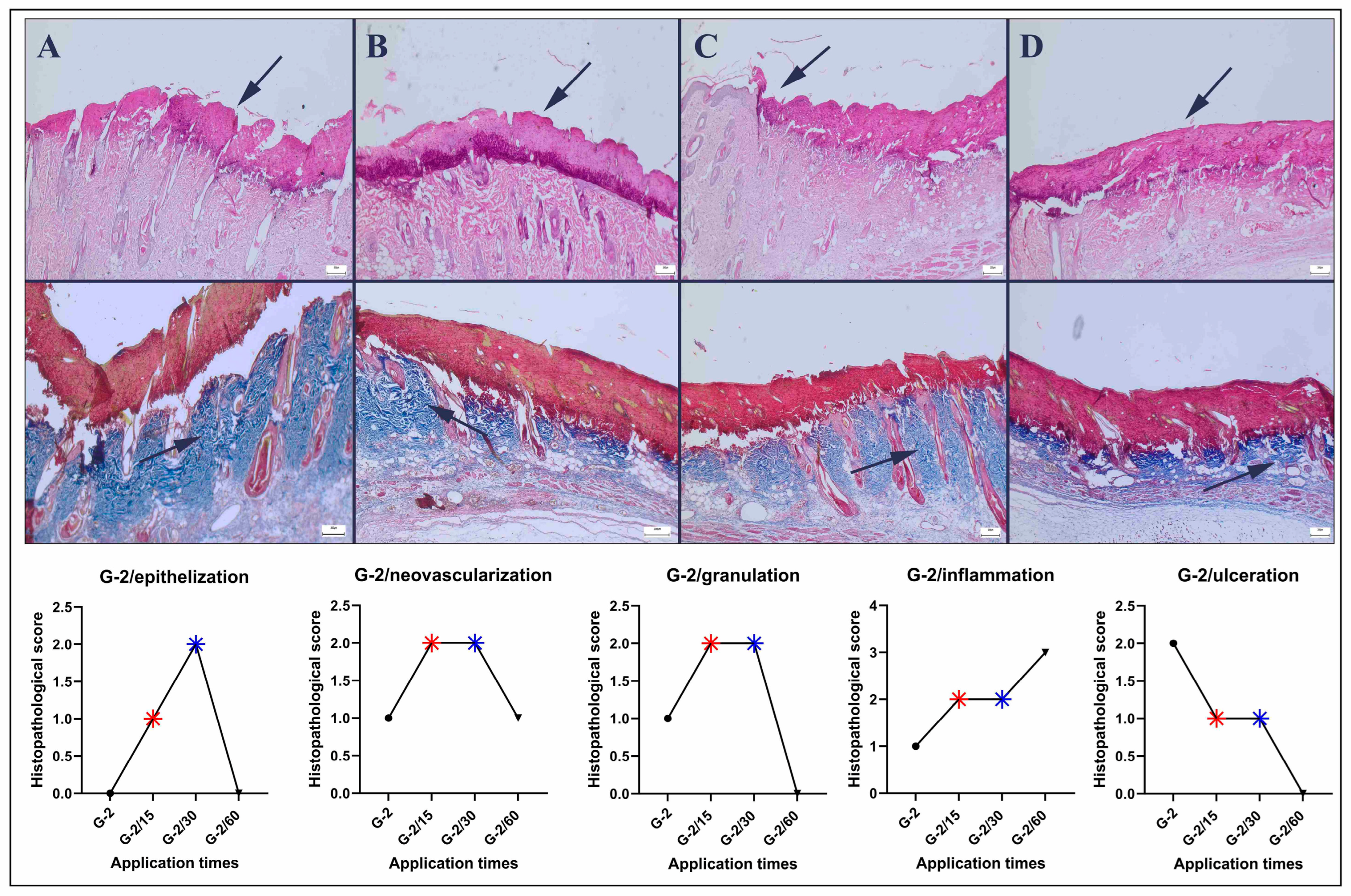
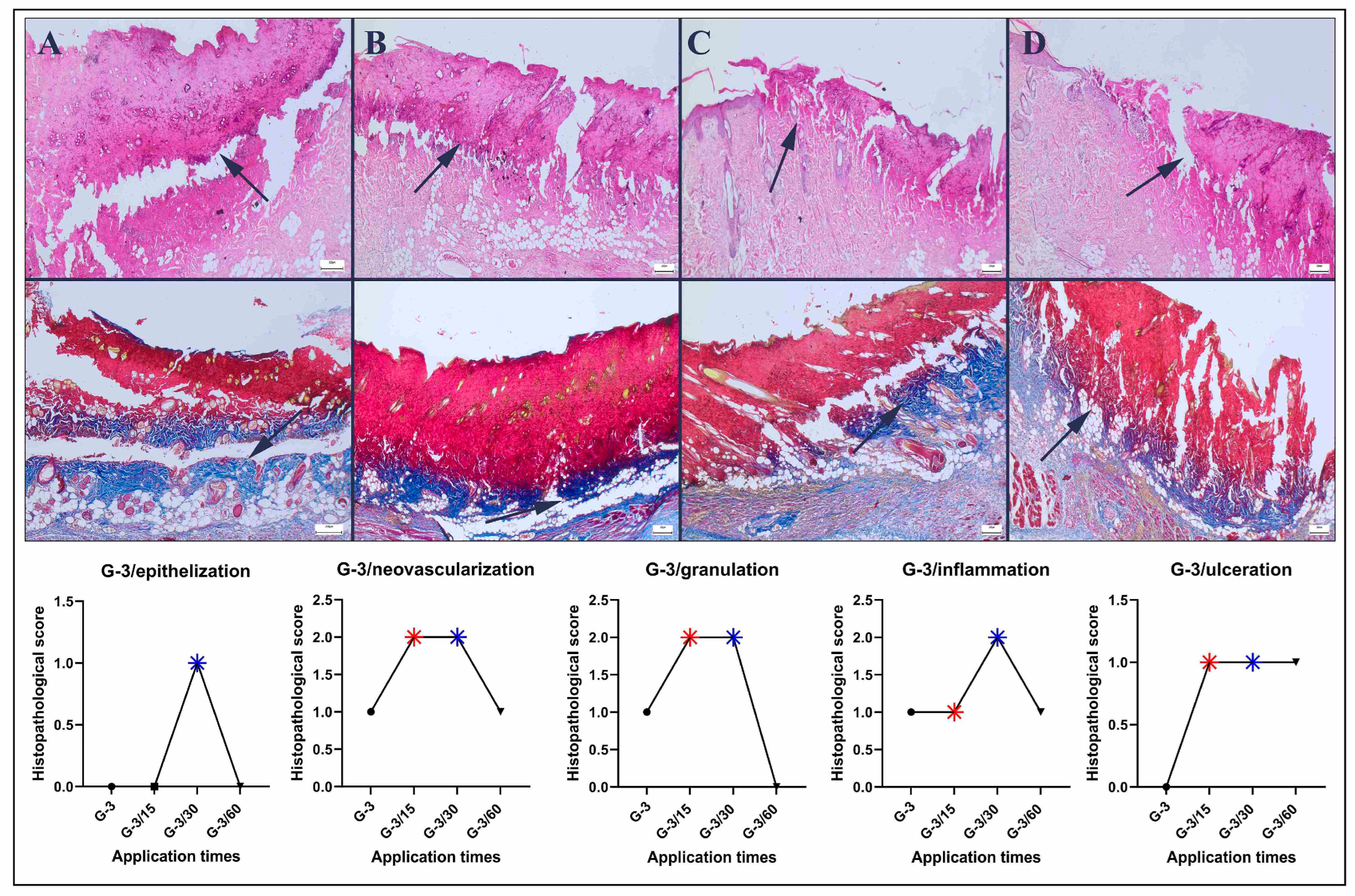
2.3. Histopathological Analysis
2.4. Reverse Transcription–Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT–qPCR)
3. Results
3.1. Histopathological Findings
3.2. RT–qPCR Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hajhosseini, B.; Longaker, M.T.; Gurtner, G.C. Pressure Injury. Ann. Surg. 2020, 271, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottner, J.; Cuddigan, J.; Carville, K.; Balzer, K.; Berlowitz, D.; Law, S.; Litchford, M.; Mitchell, P.; Moore, Z.; Pittman, J.; et al. Pressure ulcer/injury classification today: An international perspective. J. Tissue Viability 2020, 29, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Y.; Pan, J.; Wu, Y.; Huang, L.; Li, H. Advance in topical biomaterials and mechanisms for the intervention of pressure injury. iScience 2023, 26, 106956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, C.; de Abreu, M.G.; Mascha, E.J.; Rowbottom, J.; Harvester, E.; Khanna, A.; Sura, T.; Sessler, D.I.; Patarroyo, F.R.; Gulluoglu, A.; et al. Pressure injury treatment by intermittent electrical stimulation (PROTECT-2): Protocol for a multicenter randomized clinical trial. Trials 2024, 25, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haesler, E.; Cuddigan, J.; Carville, K.; Moore, Z.; Kottner, J.; Ayello, E.A.; Berlowitz, D.; Carruth, A.; Yee, C.Y.; Cox, J.; et al. Protocol for the Development of the Fourth Edition of the Prevention and Treatment of Pressure Ulcers/Injuries: Clinical Practice Guideline Using GRADE Methods. Adv. Skin. Wound Care 2024, 37, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, L.J.; Alderden, J.; Aslam, R.; Barbul, A.; Bogie, K.M. WHS guidelines for the treatment of pressure ulcers-2023 update. Wound Repair Regen. 2024, 32, 6–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.W.; Lee, S.; Park, J.H. Closed-incision negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) in elderly patients following sacral pressure sore reconstruction. BMC Geriatr. 2024, 24, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Gao, Y.; Tian, J.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Mei, F.; Li, Z. Negative pressure wound therapy for treating pressure ulcers. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 5, Cd011334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, G.K.; Martinez-Rodriguez, S.; Md Fadilah, N.I.; Looi Qi Hao, D.; Markey, G.; Shukla, P. Progress in Wound-Healing Products Based on Natural Compounds, Stem Cells, and MicroRNA-Based Biopolymers in the European, USA, and Asian Markets: Opportunities, Barriers, and Regulatory Issues. Polymers 2024, 16, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westby, M.J.; Dumville, J.C.; Soares, M.O.; Stubbs, N.; Norman, G. Dressings and topical agents for treating pressure ulcers. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 6, Cd011947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, H.N.; Hardman, M.J. Wound healing: Cellular mechanisms and pathological outcomes. Open Biol. 2020, 10, 200223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, S.; Grose, R. Regulation of wound healing by growth factors and cytokines. Physiol. Rev. 2003, 83, 835–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Tian, H.; Liu, J.; Lv, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y. Application of stable continuous external electric field promotes wound healing in pig wound model. Bioelectrochemistry 2020, 135, 107578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, C.; Jiang, X.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, J. Bioelectric fields coordinate wound contraction and re-epithelialization process to accelerate wound healing via promoting myofibroblast transformation. Bioelectrochemistry 2022, 148, 108247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.; Teng, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, X. Electric field down-regulates CD9 to promote keratinocytes migration through AMPK pathway. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 17, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Huang, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ji, R.; Wu, C.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, X. Electric field promotes dermal fibroblast transdifferentiation through activation of RhoA/ROCK1 pathway. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 20, 1326–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, S.B.; Challen, K.; Wright, K.L.; Hardy, J.G. Electrical Stimulation to Enhance Wound Healing. J. Funct. Biomater. 2021, 12, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Shen, H.; Chen, R.; Ye, R.; Hu, C. Reliability of evidence supporting the role of electrical stimulation in the treatment of pressure ulcers. Int. Wound J. 2024, 21, e14620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szołtys-Brzezowska, B.; Bańkowska, A.; Piejko, L.; Zarzeczny, R.; Nawrat-Szołtysik, A.; Kloth, L.C.; Polak, A. Electrical Stimulation in the Treatment of Pressure Injuries: A Systematic Review of Clinical Trials. Adv. Skin. Wound Care 2023, 36, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Guan, L.; Fan, P.; Liu, X.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Bai, H. Direct Current Electric Field Stimulates Nitric Oxide Production and Promotes NO-Dependent Angiogenesis: Involvement of the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. J. Vasc. Res. 2020, 57, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ye, L.; Guan, L.; Fan, P.; Liu, R.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Physiological electric field works via the VEGF receptor to stimulate neovessel formation of vascular endothelial cells in a 3D environment. Biol. Open 2018, 7, bio035204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Dai, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z. Accelerated Skin Wound Healing by Electrical Stimulation. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, e2100557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, I.; Zhang, R.Y.; Oskoui, P.; Whittaker, M.S.; Lanzafame, R.J. Development of a simple, noninvasive, clinically relevant model of pressure ulcers in the mouse. J. Investig. Surg. 2004, 17, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudhantoro, L.; Hidajat, N.N.; Ismiarto, Y.D.; Ismono, D. Histopathological Effects of Ageratum Leaf Extract (Ageratum conyzoides) on Wound Healing Acceleration After Acute Excisional Wound on Epidermis in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Model of Sprague Dawley Rats (Rattus norvegicus). Maj. Kedokt. Bdg. 2019, 51, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K. Effects of Electrical Stimulation of the Cell: Wound Healing, Cell Proliferation, Apoptosis, and Signal Transduction. Med. Sci. 2023, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farber, P.L.; Isoldi, F.C.; Ferreira, L.M. Electric Factors in Wound Healing. Adv. Wound Care 2021, 10, 461–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, Y.; Sutrisna, E. The effect of short duration of electrical stimulation on wound healing in acute wound in a rat model. Wound Med. 2019, 24, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raziyeva, K.; Kim, Y.; Zharkinbekov, Z.; Kassymbek, K.; Jimi, S.; Saparov, A. Immunology of Acute and Chronic Wound Healing. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.H.; Koh, Y.G.; Lee, W.G.; Seok, J.; Park, K.Y. The use of epidermal growth factor in dermatological practice. Int. Wound J. 2023, 20, 2414–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, D.G.; Fukumura, D.; Jain, R.K. Role of eNOS in neovascularization: NO for endothelial progenitor cells. Trends Mol. Med. 2004, 10, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Haus, J.M.; Chen, L.; Wu, S.C.; Urao, N.; Koh, T.J.; Minshall, R.D. CCL28-induced CCR10/eNOS interaction in angiogenesis and skin wound healing. Faseb J 2020, 34, 5838–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, M.; Harvey, L.A.; Glinsky, J.V.; Nier, L.; Lavrencic, L.; Kifley, A.; Cameron, I.D. Electrical stimulation for treating pressure ulcers. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 1, Cd012196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Scoring Criteria | Score | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Re-epithelialization | None | Partial | Complete, but thin | Complete and mature |
| Neovascularization | None | Up to 5 vessels/ HMF | 6–10 vessels/ HMF | >10 vessels/HMF |
| Maturation of granulation tissue | Immature | Mild maturation | Moderate maturation | Fully matured |
| Inflammation | None | Scant | Moderate | Abundant |
| Ulcer | Wide and deep ulcers, abscesses | Wide ulcers | None or very small | None |
| Genes | Primary Sequence | Product Size | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACTB (HouseKeeping) | F: CCCGCGAGTACAACCTTCTT | 481 bp | NM_031144.3 |
| R: AACACAGCCTGGATGGCTAC | |||
| eNOS | F: GGTTGACCAAGGCAAACCAC | 247 bp | NM_021838.2 |
| R: CCTAATACCACAGCCGGAGG | |||
| VEGF | F: TTCGTCCAACTTCTGGGCTC | 482 bp | NM_001287111.1 |
| R: GCTTTCTGCTCCCCTTCTGT | |||
| EGF | F: CCCATTGGCAAAACCAGGTG | 397 bp | XM_063281339.1 |
| R: TCCATCGCCAGCAAATCCTT | |||
| FGF2 | F: AAAACCTGACCCGATCCCTC | 121 BP | NM_019305.2 |
| R: CGTGACGCAGCTCCTAAAGT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Özcan, M.S.; Aşcı, H.; Karabacak, P.; Özden, E.S.; Taner, R.; Özmen, Ö.; Tepebaşı, M.Y.; Çömlekçi, S. Effect of 10 kV/m Electric Field Therapy in a Pressure Injury Model in Rats: An Innovative Preliminary Report. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12020183
Özcan MS, Aşcı H, Karabacak P, Özden ES, Taner R, Özmen Ö, Tepebaşı MY, Çömlekçi S. Effect of 10 kV/m Electric Field Therapy in a Pressure Injury Model in Rats: An Innovative Preliminary Report. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(2):183. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12020183
Chicago/Turabian StyleÖzcan, Mustafa Soner, Halil Aşcı, Pınar Karabacak, Eyyüp Sabri Özden, Rümeysa Taner, Özlem Özmen, Muhammet Yusuf Tepebaşı, and Selçuk Çömlekçi. 2025. "Effect of 10 kV/m Electric Field Therapy in a Pressure Injury Model in Rats: An Innovative Preliminary Report" Bioengineering 12, no. 2: 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12020183
APA StyleÖzcan, M. S., Aşcı, H., Karabacak, P., Özden, E. S., Taner, R., Özmen, Ö., Tepebaşı, M. Y., & Çömlekçi, S. (2025). Effect of 10 kV/m Electric Field Therapy in a Pressure Injury Model in Rats: An Innovative Preliminary Report. Bioengineering, 12(2), 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12020183







