Bone Remodeling and Marginal Bone Loss of Simplified Versus Conventional Drilling: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Trial Design, Participants, and Settings
2.2. Interventions
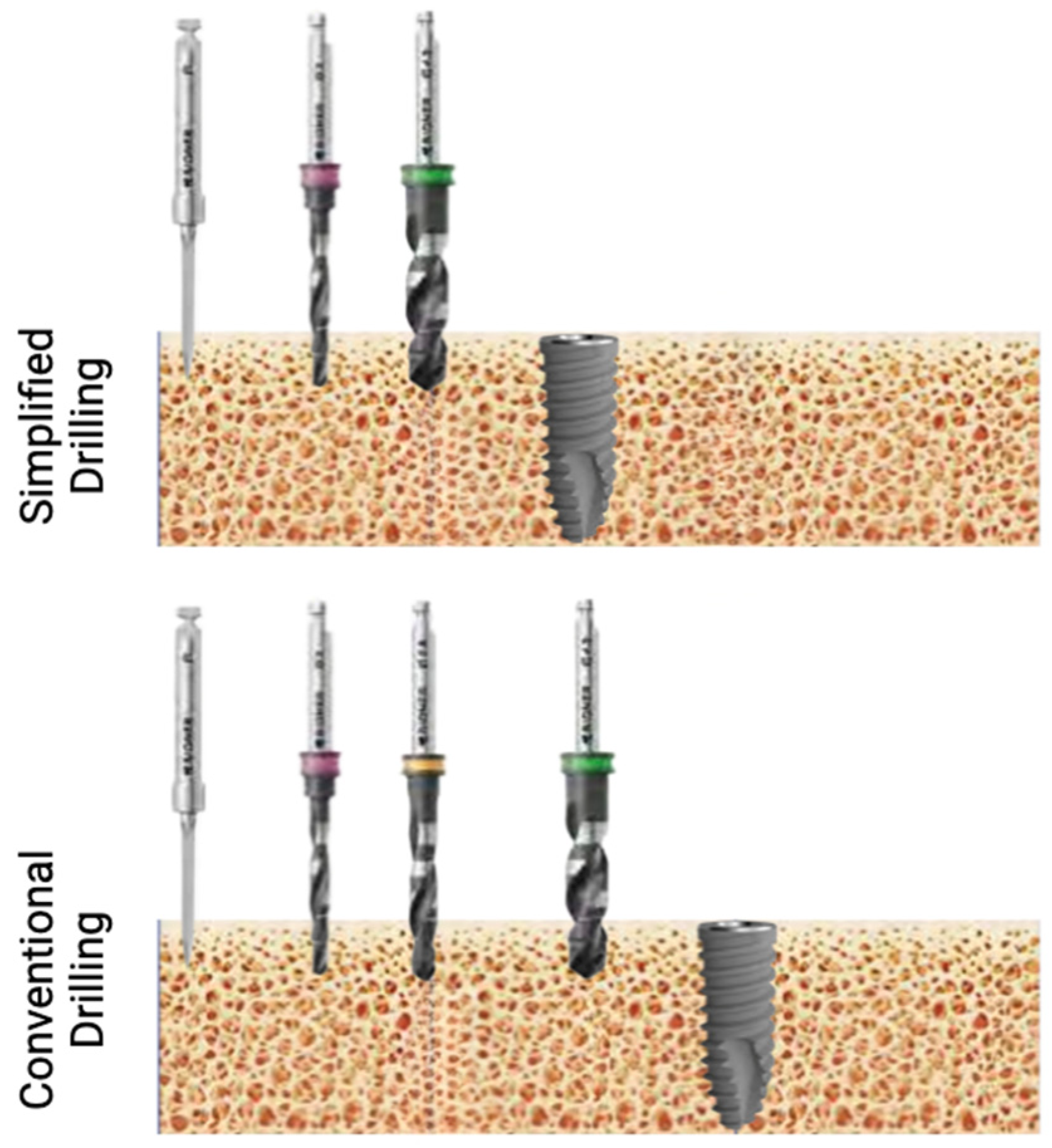
2.2.1. Study Products
2.2.2. Surgical Procedures
2.2.3. Healing Abutment Insertion
2.2.4. Definitive Prosthesis
2.3. Measurements and Primary and Secondary Outcomes
2.4. Sample Size
2.5. Randomization (Random Number Generation, Allocation Concealment, and Implementation)
2.6. Blinding
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sample Description
3.2. Bone Levels at Implant Placment and Restoration Delivery
3.3. Bone Remodeling Following Osteointegration Period
3.4. Marginal Bone Loss (MBL) at 12 and 24 Months After Restorative Period
3.5. Primary Stability
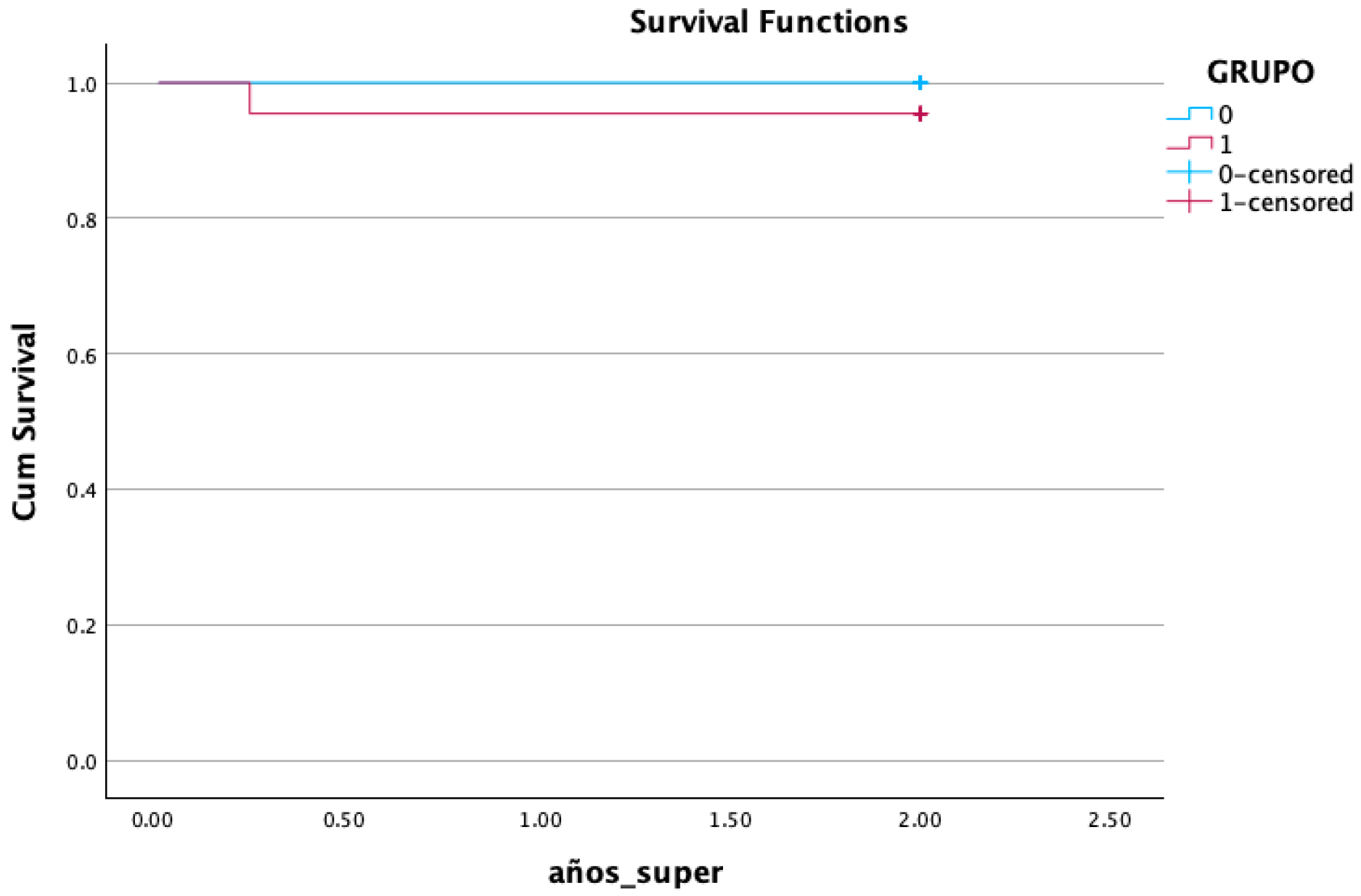
3.6. Survival Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lombardi, T.; Berton, F.; Salgarello, S.; Barbalonga, E.; Rapani, A.; Piovesana, F.; Gregorio, C.; Barbati, G.; Di Lenarda, R.; Stacchi, C. Factors Influencing Early Marginal Bone Loss around Dental Implants Positioned Subcrestally: A Multicenter Prospective Clinical Study. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo-Moreno, P.; Catena, A.; Perez-Sayans, M.; Fernandez-Barbero, J.E.; O’Valle, F.; Padial-Molina, M. Early marginal bone loss around dental implants to define success in implant dentistry: A retrospective study. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2022, 24, 630–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragucci, G.M.; Giralt-Hernando, M.; Mendez-Manjon, I.; Canto-Naves, O.; Hernandez-Alfaro, F. Factors Affecting Implant Failure and Marginal Bone Loss of Implants Placed by Post-Graduate Students: A 1-Year Prospective Cohort Study. Materials 2020, 13, 4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peker Tekdal, G.; Bostanci, N.; Belibasakis, G.N.; Gurkan, A. The effect of piezoelectric surgery implant osteotomy on radiological and molecular parameters of peri-implant crestal bone loss: A randomized, controlled, split-mouth trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2016, 27, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicer-Chover, H.; Penarrocha-Oltra, D.; Aloy-Prosper, A.; Sanchis-Gonzalez, J.C.; Penarrocha-Diago, M.A.; Penarrocha-Diago, M. Comparison of peri-implant bone loss between conventional drilling with irrigation versus low-speed drilling without irrigation. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2017, 22, e730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lin, X.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y. The Stability and Survival Rate of Dental Implants After Preparation of the Site by Piezosurgery vs Conventional Drilling: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2020, 30, e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocchero, M.; Toia, M.; Cecchinato, D.; Becktor, J.P.; Coelho, P.G.; Jimbo, R. Biomechanical, Biologic, and Clinical Outcomes of Undersized Implant Surgical Preparation: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2016, 31, 1247–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canullo, L.; Penarrocha, D.; Penarrocha, M.; Rocio, A.G.; Penarrocha-Diago, M. Piezoelectric vs. conventional drilling in implant site preparation: Pilot controlled randomized clinical trial with crossover design. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2014, 25, 1336–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Rebolledo, A.; Tariba-Forero, D.; Rios-Calvo, M.D.; Gay-Escoda, C. Effect of undersized drilling on the stability of immediate tapered implants in the anterior maxillary sector. A randomized clinical trial. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2021, 26, e187–e194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugam, M.; Valiathan, M.; Balaji, A.; Jeyaraj Samuel, A.F.; Kannan, R.; Varthan, V. Conventional Versus Osseodensification Drilling in the Narrow Alveolar Ridge: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial. Cureus 2024, 16, e56963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratu, E.; Mihali, S.; Shapira, L.; Bratu, D.C.; Wang, H.L. Crestal bone remodeling around implants placed using a short drilling protocol. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2015, 30, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, L.F.; Sarendranath, A.; Neiva, R.; Marao, H.F.; Tovar, N.; Bonfante, E.A.; Janal, M.N.; Castellano, A.; Coelho, P.G. Bone Healing Around Dental Implants: Simplified vs Conventional Drilling Protocols at Speed of 400 rpm. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2017, 32, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giro, G.; Tovar, N.; Marin, C.; Bonfante, E.A.; Jimbo, R.; Suzuki, M.; Janal, M.N.; Coelho, P.G. The effect of simplifying dental implant drilling sequence on osseointegration: An experimental study in dogs. Int. J. Biomater. 2013, 2013, 230310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Amri, M.D.; Al-Johany, S.S.; Al Baker, A.M.; Al Rifaiy, M.Q.; Abduljabbar, T.S.; Al-Kheraif, A.A. Soft tissue changes and crestal bone loss around platform-switched implants placed at crestal and subcrestal levels: 36-month results from a prospective split-mouth clinical trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2017, 28, 1342–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, T.J.; Yoon, J.; Misch, C.E.; Wang, H.L. The causes of early implant bone loss: Myth or science? J. Periodontol. 2002, 73, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guazzi, P.; Grandi, T.; Grandi, G. Implant site preparation using a single bur versus multiple drilling steps: 4-month post-loading results of a multicenter randomised controlled trial. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2015, 8, 283–290. [Google Scholar]
- Stacchi, C.; Troiano, G.; Montaruli, G.; Mozzati, M.; Lamazza, L.; Antonelli, A.; Giudice, A.; Lombardi, T. Changes in implant stability using different site preparation techniques: Osseodensification drills versus piezoelectric surgery. A multi-center prospective randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2023, 25, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford, C.M.; Barwacz, C.; Raes, S.; De Bruyn, H.; Cecchinato, D.; Bittner, N.; Brandt, J. Multicenter Clinical Randomized Controlled Trial Evaluation of an Implant System Designed for Enhanced Primary Stability. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2016, 31, 906–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakha, T.; Kheur, M.; Hammerle, C.; Kheur, S.; Qamri, B. Comparative Evaluation of Marginal Bone Levels, ISQ Trends, and Implant Survival Rates Between Conventional Drilling and Osteotome Technique Using Implants of Varied Lengths: A Split-Mouth Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2023, 36, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Gil, L.F.; Castellano, A.; Freitas, G.; Navarro, D.; Peredo, A.P.; Tovar, N.; Coelho, P. Effect of Simplified One-Step Drilling Protocol on Osseointegration. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2016, 36, e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ercoli, C.; Funkenbusch, P.D.; Lee, H.J.; Moss, M.E.; Graser, G.N. The influence of drill wear on cutting efficiency and heat production during osteotomy preparation for dental implants: A study of drill durability. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2004, 19, 335–349. [Google Scholar]
- Yacker, M.J.; Klein, M. The effect of irrigation on osteotomy depth and bur diameter. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1996, 11, 634–638. [Google Scholar]
- Benington, I.C.; Biagioni, P.A.; Briggs, J.; Sheridan, S.; Lamey, P.J. Thermal changes observed at implant sites during internal and external irrigation. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2002, 13, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musskopf, M.L.; Finger Stadler, A.; Fiorini, T.; Ramos, U.D.; de Sousa Rabelo, M.; de Castro Pinto, R.N.; Susin, C. Performance of a new implant system and drilling protocol-A minipig intraoral dental implant model study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2024, 35, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Variable | Conventional (%) | Simplified (%) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.361 Pearson’s chi-square | ||
| Male | 11 (50%) | 14 (63.6%) | |
| Female | 11 (50%) | 8 (36.4%) | |
| Substituted tooth | 1.00 Pearson’s chi-square | ||
| Premolar | 7 (31.8%) | 9 (31.8%) | |
| Molar | 15 (68.2%) | 13 (68.2%) | |
| Arch | 0.540 Pearson’s chi-square | ||
| Maxilla | 8 (36.3%) | 10(45.4%) | |
| Mandible | 14 (63.7%) | 12 (54.6%) | |
| Implant insertion torque | 0.487 (likelihood ratio) | ||
| <15 N | 0 (0%) | 1 (4.5%) | |
| 15–40 N | 10 (45.5%) | 9 (40.9%) | |
| >40 N | 12 (54.5) | 12 (54.5%) | |
| Implant diameter | 0.652 (likelihood ratio) | ||
| 3.5 | 5 (22.7%) | 6 (27.3%) | |
| 4.0 | 14 (63.6%) | 12 (54.5%) | |
| 4.2 | 0 (0%) | 1 (4.5%) | |
| 5.0 | 3 (13.6%) | 3 (13.6%) | |
| Implant length | 0.106 (likelihood ratio) | ||
| 7 | 0 (0%) | 1 (4.5%) | |
| 8.5 | 8 (36.4%) | 2 (9.1%) | |
| 10 | 8 (36.4%) | 12 (54.5%) | |
| 11.5 | 6 (27.3%) | 7 (31.8%) |
| Variable | Conventional Mean (±SD) | Simplified Mean (±SD) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 56.35 (12.22) | 50.11 (14.16) | 0.125 |
| Insertion torque (primary stability) (Ncm) | 47.68 (16.50) | 45.95 (13.41) | 0.705 |
| Bone level at implant placment | |||
| Mesial | 1.60 (0.19) | 1.56 (0.15) | 0.904 |
| Distal | 1.74 (0.23) | 1.58 (0.15) | 0.579 |
| Avarage | 1.67 (0.18) | 1.57 (0.14) | 0.688 |
| Bone level at restoration delivery | |||
| Mesial | 0.30 (0.33) | 0.42 (0.50) | 0.372 |
| Distal | 0.58 (0.60) | 0.20 (0.26) | 0.027 |
| Average | 0.42 (0.38) | 0.31 (0.34) | 0.171 |
| Outcome Variable | Control, N = 22 (Conventional Drilling) | Test, N = 22 (Simplified Drilling) | Mean Difference (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔBone levels post-osteintegration | ||||
| Mesial | 1.29 (1.04) | 1.14 (0.83) | 0.28 (−0.73; 0.43) | 0.608 |
| Distal | 1.20 (1.14) | 1.36 (0.71) | 0.29 (−0.43; 0.75) | 0.595 |
| Avarage | 1.24 (1.01) | 1.25 (0.68) | 0.26 (−0.53; 0.54) | 0.98 |
| ΔMBL 12 months post-restorative | ||||
| Mesial | 0.01 (0.29) | 0.16 (0.48) | 0.14 (−0.10; 0.39) | 0.257 |
| Distal | 0.11 (0.38) | 0.44 (0.51) | 0.32 (0.04; 0.60) | 0.022 |
| Average | 0.06 (0.25) | 0.30 (0.40) | 0.23 (0.03; 0.44) | 0.026 |
| ΔMBL 24 months post-restorative | ||||
| Mesial | 0.12 (0.68) | 0.22 (0.85) | 0.10 (−0.30; 0.58) | 0.662 |
| Distal | 0.15 (0.63) | 0.34 (0.72) | 0.19 (−0.22; 0.60) | 0.363 |
| Average | 0.13 (0.41) | 0.28 (0.71) | 0.14 (−0.21; 0.51) | 0.413 |
| Variable | Conventional (%) | Simplified (%) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| survival | 22 (100%) | 21 (95.5%) | 0.371 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruiz García, A.; Lijnev, A.; Soleymani, F.; Elango, J.; Maté Sánchez de Val, J.E.; Pérez-Albacete Martínez, C. Bone Remodeling and Marginal Bone Loss of Simplified Versus Conventional Drilling: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12020178
Ruiz García A, Lijnev A, Soleymani F, Elango J, Maté Sánchez de Val JE, Pérez-Albacete Martínez C. Bone Remodeling and Marginal Bone Loss of Simplified Versus Conventional Drilling: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(2):178. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12020178
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuiz García, Alberto, Artiom Lijnev, Fatemeh Soleymani, Jeevithan Elango, José Eduardo Maté Sánchez de Val, and Carlos Pérez-Albacete Martínez. 2025. "Bone Remodeling and Marginal Bone Loss of Simplified Versus Conventional Drilling: A Randomized Clinical Trial" Bioengineering 12, no. 2: 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12020178
APA StyleRuiz García, A., Lijnev, A., Soleymani, F., Elango, J., Maté Sánchez de Val, J. E., & Pérez-Albacete Martínez, C. (2025). Bone Remodeling and Marginal Bone Loss of Simplified Versus Conventional Drilling: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Bioengineering, 12(2), 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12020178







