Applications of Fibronectin in Biomedicine and Cosmetics: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
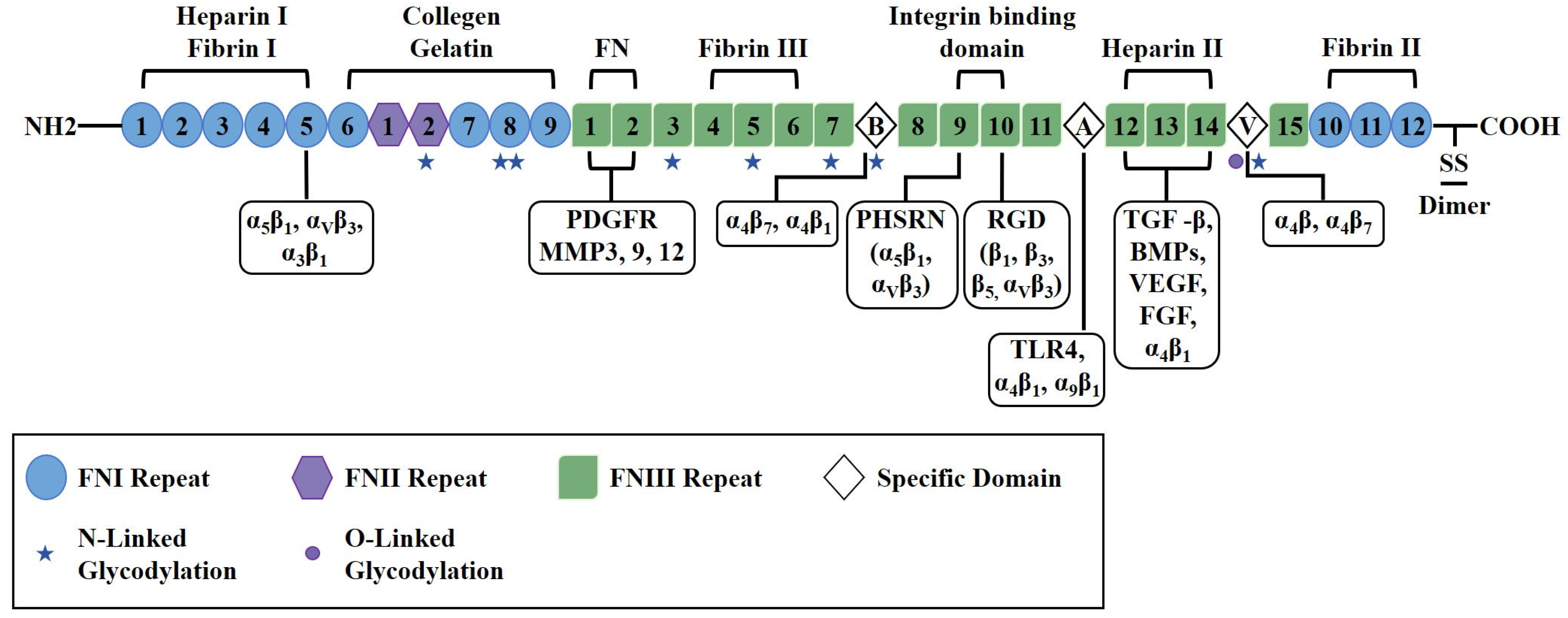
2. Molecular Structure
2.1. Domain Organization and Functional Motifs
2.2. Isoform Diversity Through Alternative Splicing
3. Physiological Forms and Pathological Expressions: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Implications
3.1. Plasma and Cellular FN: Distinct Characteristics
3.2. Altered Expression in Pathological Conditions
3.3. The Context-Dependent Dual Faces of Fibronectin
4. Function Dictates Application Scenarios: Regenerative Medicine and Cosmetic Science
4.1. Foundations and Applications in Regenerative Medicine
4.1.1. Wound Healing Applications
4.1.2. Role as a Biomedical Material Matrix
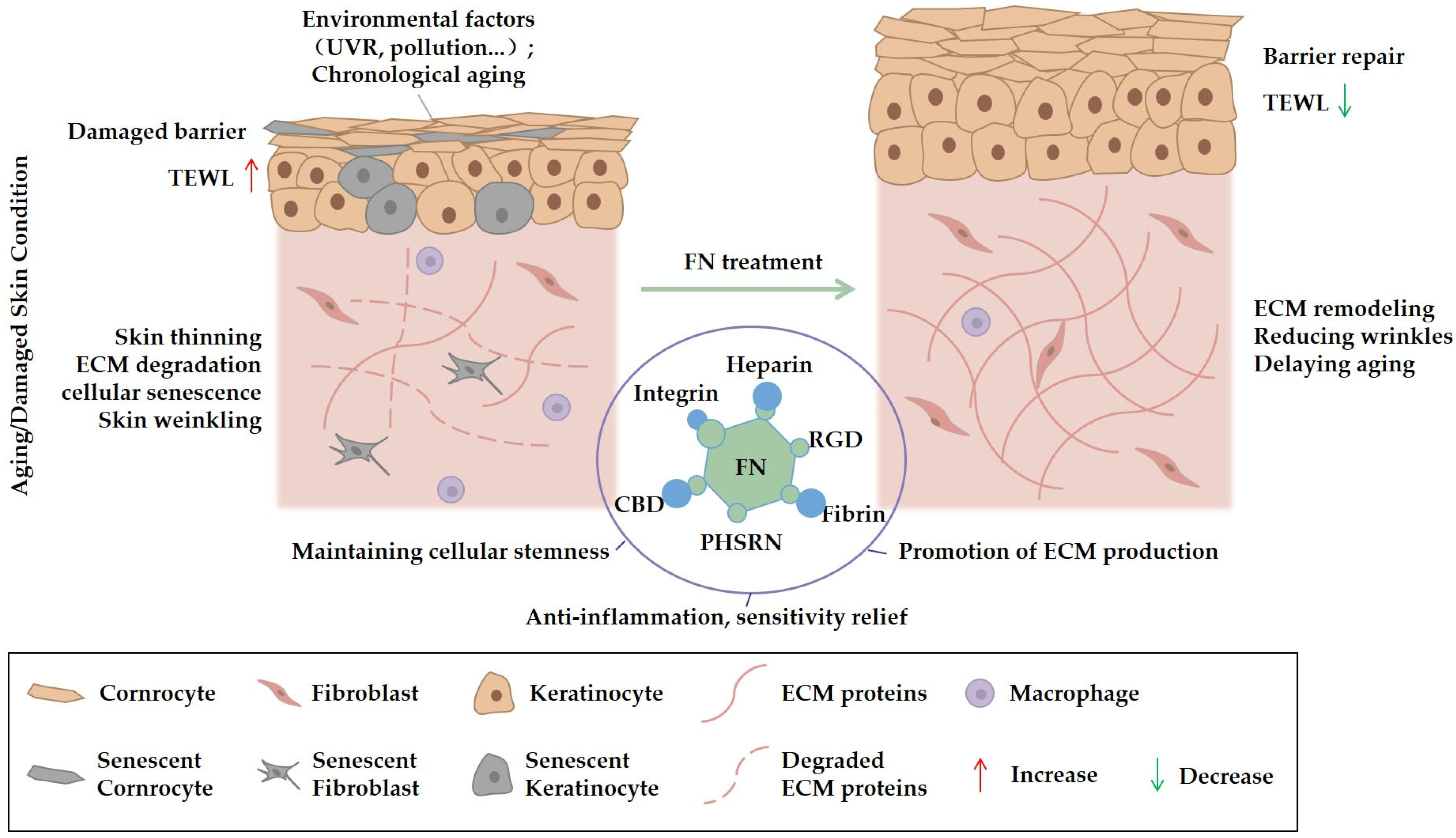
4.2. Cosmetic Applications: Skin Repair and Anti-Aging
4.2.1. Barrier Repair and Anti-Sensitivity
4.2.2. Anti-Aging Applications of FN
5. Recombinant Production Approaches: Addressing Manufacturing Challenges
5.1. Production Advantages and Technical Optimization
5.2. Methods for Detecting Recombinant Fibronectin in Cosmetics
5.3. Expanding Applications and Innovations of Recombinant Fibronectin in Skin Repair
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FN | Fibronectin |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| EDA+ | Extra Domain A-Containing Isoform |
| EDB+ | Extra Domain B-Containing Isoform |
| RGD | Arg-Gly-Asp |
| GAGs | Glycosaminoglycans |
| TGF-β | Transforming Growth Factor-Beta |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
| MMPs | Matrix Metalloproteinases |
| pFN | Plasma Fibronectin |
| cFN | Cellular Fibronectin |
| PHSRN | Pro-His-Ser-Arg-Asn |
| IIICS | Type III Connecting Segment |
| LOX | Lysyl Oxidase |
| FA | Focal Adhesion |
| LINC | Linker of Nucleoskeleton and Cytoskeleton |
| YAP | Yes-Associated Protein |
| MRTF | Myocardin-Related Transcription Factor |
| TLR4 | Toll-Like Receptor 4 |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor Kappa B |
| PRF | Platelet-rich Fibrin |
| FLG | Filaggrin |
| LOR | Loricrin |
| TEWL | Transepidermal Water Loss |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| AGEs | Advanced Glycation End Products |
| SASP | Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype |
| HepII | Heparin-Binding Domain II |
| CBD | Collagen-Binding Domain |
| rhFNP | Recombinant Human Fibronectin Peptide |
| hMSCs | Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells |
| ADSCs | Adipose-Derived Stem Cells |
| AD-MSCs | Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells |
| PDGF-BB | Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB |
| FACSs | FN-Attached Cell Sheets |
| Fn-rLys-Col/SF-S | Fibronectin-Recombinant Lysostaphin-Collagen/Silk Fibroin-Sericin |
| rFN | Recombinant Fibronectin |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis |
| WB | Western blot |
| IR | Infrared Spectroscopy |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry |
| BCA | Bicinchoninic Acid Assay |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| HPLC | High-Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| EGF | Epidermal Growth Factor |
| PEG-FN | Polyethylene Glycol-Fibronectin |
| BMP-2 | Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 |
| DAMPs | Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns |
| IL-8 | Interleukin-8 |
| SLE | Systemic Lupus Erythematosus |
| shRNA | Short Hairpin RNA |
| PDE4D5 | Phosphodiesterase 4D5 |
| cAMP | Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate |
| FAK | Focal Adhesion Kinase |
| Src | Proto-oncogene Tyrosine-Protein Kinase Src |
| RhoA | Ras Homolog Family Member A |
| TAZ | Transcriptional Co-activator with PDZ-Binding Motif |
| QC | Quality Control |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
References
- da Silva, P.H.R.; Borges, B.C.; Uehara, I.A.; Soldi, L.R.; de Araújo, R.A.; Silva, M.J.B. Chemokines and the extracellular matrix: Set of targets for tumor development and treatment. Cytokine 2021, 144, 155548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Heng, S.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Xia, T.; Ji, C.; Zhang, L.J. Dermal extracellular matrix molecules in skin development, homeostasis, wound regeneration and diseases. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 128, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Moretti, L.; Su, X.; Yeh, C.R.; Torres, M.P.; Barker, T.H. Strain-dependent glutathionylation of fibronectin fibers impacts mechano-chemical behavior and primes an integrin switch. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, C.J.; Lemmon, C.A. Fibronectin: Molecular Structure, Fibrillar Structure and Mechanochemical Signaling. Cells 2021, 10, 2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Hamlin, A.J.; Schwarzbauer, J.E. Fibronectin matrix assembly at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2025, 138, jcs263834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, L.; Stalfort, J.; Barker, T.H.; Abebayehu, D. The interplay of fibroblasts, the extracellular matrix, and inflammation in scar formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resovi, A.; Persichitti, P.; Brunelli, L.; Minoli, L.; Borsotti, P.; Garattini, G.; Tironi, M.; Dugnani, E.; Redegalli, M.; De Simone, G.; et al. Fibronectin fragments generated by pancreatic trypsin act as endogenous inhibitors of pancreatic tumor growth. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Hu, R.; Cavinato, C.; Zhuang, Z.W.; Zhang, J.; Yun, S.; Fernandez Tussy, P.; Singh, A.; Murtada, S.I.; Tanaka, K.; et al. Fibronectin–Integrin α5 Signaling in Vascular Complications of Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes 2022, 71, 2020–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, C.J.; Dhakal, S.; Lemmon, C.A. Measuring the biomechanical properties of cell-derived fibronectin fibrils. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2025, 24, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Ma, X.; Xie, X.; Wu, H.; Wang, L.; Feng, Y.; Yu, Z.; Liu, C.; Qi, J.; Zhu, Q. FN-EDA mediates angiogenesis of hepatic fibrosis via integrin-VEGFR2 in a CD63 synergetic manner. Cell Death Discov. 2020, 6, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzobo, K.; Dandara, C. The Extracellular Matrix: Its Composition, Function, Remodeling, and Role in Tumorigenesis. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javid, H.; Oryani, M.A.; Rezagholinejad, N.; Esparham, A.; Tajaldini, M.; Karimi-Shahri, M. RGD peptide in cancer targeting: Benefits, challenges, solutions, and possible integrin-RGD interactions. Cancer Med. 2024, 13, e6800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbalaei, M.; Rezaee, S.A.; Farsiani, H. Pichia pastoris: A highly successful expression system for optimal synthesis of heterologous proteins. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 5867–5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; Yuan, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, M.; Chen, B.; Yu, H. Strategies to overcome the challenges of low or no expression of heterologous proteins in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Adv. 2024, 75, 108417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariotti, M.; Rogowska-Wrzesinska, A.; Hägglund, P.; Davies, M.J. Cross-linking and modification of fibronectin by peroxynitrous acid: Mapping and quantification of damage provides a new model for domain interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Abla, A.; Boeuf, G.; Elmarjou, A.; Dridi, C.; Poirier, F.; Changotade, S.; Lutomski, D.; Elm’selmi, A. Engineering of Bio-Adhesive Ligand Containing Recombinant RGD and PHSRN Fibronectin Cell-Binding Domains in Fusion with a Colored Multi Affinity Tag: Simple Approach for Fragment Study from Expression to Adsorption. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, J.M.D.; Martino, M.M. Growth Factor and Cytokine Delivery Systems for Wound Healing. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2022, 14, a041234. [Google Scholar]
- Patten, J.; Wang, K. Fibronectin in development and wound healing. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 170, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missirlis, D.; Heckmann, L.; Haraszti, T.; Spatz, J.P. Fibronectin anchoring to viscoelastic poly(dimethylsiloxane) elastomers controls fibroblast mechanosensing and directional motility. Biomaterials 2022, 287, 121646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeown-Longo, P.J.; Higgins, P.J. Hyaluronan, Transforming Growth Factor β, and Extra Domain A-Fibronectin: A Fibrotic Triad. Adv. Wound Care 2021, 10, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonadio, J.D.; Bashiri, G.; Halligan, P.; Kegel, M.; Ahmed, F.; Wang, K. Delivery technologies for therapeutic targeting of fibronectin in autoimmunity and fibrosis applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2024, 209, 115303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, T.; Pan, Y.; Liu, J. Research trends on the extracellular domain A/B of fibronectin in tumor microenvironment: Scientometric and visual analysis. Discov. Med. 2025, 2, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chen, P.; Wei, B.; Tan, H.L.; Zhao, Y.X.; Ai, L.; Li, N.; Jiang, Y.K.; Lin, J.; Li, S.J.; et al. FN1 shapes the behavior of papillary thyroid carcinoma through alternative splicing of EDB region. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, R.; Li, M.; Wang, C. Fibronectin and colorectal cancer: Signaling pathways and clinical implications. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 2021, 41, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemańska-Perek, A.; Adamik, B. Fibronectin and its soluble EDA-FN isoform as biomarkers for inflammation and sepsis. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2019, 28, 1561–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, T.; Pan, Y.; Liu, J. Exploring the mechanism of fibronectin extra domain B in the tumor microenvironment and implications for targeted immunotherapy and diagnostics (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2025, 31, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longstreth, J.H.; Wang, K. The role of fibronectin in mediating cell migration. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2024, 326, C1212–C1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Kashina, A. Post-translational Modifications of the Protein Termini. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 719590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Jian, W. Different roles of endothelial cell-derived fibronectin and plasma fibronectin in endothelial dysfunction. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 53, 1667–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowski, M.T.; Zook, H.N.; Chigumba, D.N.; Johnstone, C.P.; Caldera, L.F.; Shih, H.P.; Tirrell, D.A.; Ku, H.T. A matrigel-free method for culture of pancreatic endocrine-like cells in defined protein-based hydrogels. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1144209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idborg, H.; Oke, V. Cytokines as Biomarkers in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Value for Diagnosis and Drug Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.R.; Wang, M.Y.; Zhang, C.L.; Wang, Y. Endothelial dysfunction in vascular complications of diabetes: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and implications. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1359255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeyama, H.; Manome, Y. Serum Sialyl Fibronectin Is an Indicator of Good Prognosis in Thyroid Cancer. Cancer Diagn. Progn. 2023, 3, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Waquar, S.; Idrees, N.; Malik, A. Impending role of inflammatory markers and their specificity and sensitivity in breast cancer patients. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 15117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R.C.; Vaidya, A.M.; Schiemann, W.P.; Pan, Q.; Lu, Z.R. RNA-Seq Analysis of Extradomain A and Extradomain B Fibronectin as Extracellular Matrix Markers for Cancer. Cells 2023, 12, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Nitto, C.; Ravazza, D.; Gilardoni, E.; Look, T.; Sun, M.; Prodi, E.; Moisoiu, V.; Pellegrino, C.; Manz, M.G.; Puca, E.; et al. An IL-7 fusion protein targeting EDA fibronectin upregulates TCF1 on CD8+ T-cells, preferentially accumulates to neoplastic lesions, and boosts PD-1 blockade. J. Immunother. Cancer 2024, 12, e008504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtari, R.B.; Ashayeri, N.; Baghaie, L.; Sambi, M.; Satari, K.; Baluch, N.; Bosykh, D.A.; Szewczuk, M.R.; Chakraborty, S. The Hippo Pathway Effectors YAP/TAZ-TEAD Oncoproteins as Emerging Therapeutic Targets in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers 2023, 15, 3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudelova, E.; Smolar, M.; Holubekova, V.; Hornakova, A.; Dvorska, D.; Lucansky, V.; Koklesova, L.; Kudela, E.; Kubatka, P. Genetic Heterogeneity, Tumor Microenvironment and Immunotherapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wan, W.; Lu, J.; Liu, P. Inhalable FN-binding liposomes or liposome-exosome hybrid bionic vesicles encapsulated microparticles for enhanced pulmonary fibrosis therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 656, 124096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.H.; Chen, S.C.; Chen, H.Y.; Wu, C.B.; Huang, W.T.; Chiang, H.Y. Astrocyte-associated fibronectin promotes the proinflammatory phenotype of astrocytes through β1 integrin activation. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2023, 125, 103848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; He, M.; Lu, Q. Fibronectin Connecting Cell Sheet Based on Click Chemistry for Wound Repair. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2306746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.T.; Huang, L.D.; Liu, K.; Pang, K.F.; Tang, H.; Li, T.; Huang, Y.P.; Zhang, W.Q.; Wang, J.J.; Yin, G.L.; et al. Nano-Biomimetic Fibronectin/Lysostaphin-Co-Loaded Silk Fibroin Dressing Accelerates Full-Thickness Wound Healing via ECM-Mimicking Microarchitecture and Dual-Function Modulation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2025, 20, 7469–7487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno-LLuch, I.; Benito-Jardón, M.; Guerrero-Barberà, G.; Burday, N.; Costell, M. The Role of the Fibronectin Synergy Site for Skin Wound Healing. Cells 2022, 11, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Shi, H.; Ma, X.; Xia, T.; Wu, Y.; Chen, L.; Ren, Z.; Lei, L.; Jiang, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Highly stable fibronectin-mimetic-peptide-based supramolecular hydrogel to accelerate corneal wound healing. Acta. Biomater. 2023, 159, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawati, A.; Jang, D.; Cho, D.; Cho, S.; Jeong, H.; Park, S.; Gwak, J.; Ryu, S.R.; Jung, W.H.; Ju, B.G.; et al. An Accelerated Wound-Healing Surgical Suture Engineered with an Extracellular Matrix. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, e2001686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Chen, X. A Bioactive Fibronectin-Functionalized Surgical Mesh with Dual-Antimicrobial and Pro-Healing Properties for Abdominal Wall Reconstruction. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2024, 10, 4567–4581. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Akhtar, N.; Zhao, J.; Spandau, D.F.; Kaplan, M.H. Fibronectin Promotes Wound Healing in an Atopic Human Skin Xenografting Model. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 144, 1415–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Smith, J.; Johnson, A.B.; Davis, R.; Brown, K.L.; Wilson, M.P. Development of a Fibronectin-Enriched Collagen Sponge for Chronic Wound Treatment: Efficacy in a Diabetic Mouse Model. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2023, 17, 2345–2359. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, M.; Li, F.; Wu, S.; Xu, J.; Thompson, C.; Williams, R. Enhancing Diabetic Wound Healing with a Fibronectin-Mimetic Peptide Hydrogel: Synergistic Effects of Angiogenesis and ECM Remodeling. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 102. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Mao, X.; Cong, J.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, W.; Yan, K.; Huang, Y.; Su, D.; Xiang, Q. Recombinantly expressed rhFEB remodeled the skin defect of db/db mice. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Zhu, J.; Luo, X.; Jin, G.; Huang, Y.; Li, L. A Thermally Stable Recombinant Human Fibronectin Peptide-Fused Protein (rhFN3C) for Faster Aphthous Ulcer (AU) Healing. Bioengineering 2023, 11, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, J.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, T.; Cai, X.; Xu, J.; Guo, R.; He, R.; Xiang, Q. Recombinant human fibronectin segment (rhFN1024) hydrogel carried hPDLSCs to repair diabetic trauma by activated NF-κB signaling pathway. Regen. Biomater. 2025, 12, rbaf027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.P.; Liu, C.L.; Xie, J.; Li, T.H.; Li, H.; Bai, X.J.; Li, Z.F.; W, W. Clinical application of platelet-rich fibrin in chronic refractory wounds. J. Clin. Surg. 2021, 29, 580. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.Y.; Cui, Z.J.; Zhao, H. The research on clinical use of platelet-rich fibrin in treatment of chronic wounds. J. Clin. Surg. 2023, 31, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Nica, C.; Sculean, A.; Asparuhova, M.B. Positive Effects of Three-Dimensional Collagen-Based Matrices on the Behavior of Osteoprogenitors. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 708830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, M.R.; Reis, R.L.; Martins, A.; Neves, N.M. Fibronectin Bound to a Fibrous Substrate Has Chondrogenic Induction Properties. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 1368–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fan, Y.; Dong, Y.; Yu, X.; Gao, J.; Ma, X. Therapeutic Effect of a Recombinant Human Fibronectin Construct in Skeletal Muscle Repair and Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Xin, J.; Wang, P.; Song, Y.; Fan, X.; Yang, L.; Guo, G.; Fu, D.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, F.; et al. Enhancing the biocompatibility of phakic intraocular lens via selective fibronectin trapping. Acta. Biomater. 2025, 197, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Bratlie, K.M. Macrophage Phenotypic Changes on FN-Coated Physical Gradient Hydrogels. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2021, 4, 6758–6768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacker, M.; Riedel, J.; Walles, H.; Groll, J.; Lübberstedt, M.; Zimmermann, S.; Rottmar, M.; Kania, G.; Rieger, M.A. Comparative Evaluation on Impacts of Fibronectin, Heparin-Chitosan, and Albumin Coating of Bacterial Nanocellulose Small-Diameter Vascular Grafts on Endothelialization In Vitro. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Chen, L.C.; Wu, Y.Q.; Ye, Z.H. Research Progress of Fibronectin and Its Application in Cosmetics. Deterg. Cosmet. 2021, 11, 44. [Google Scholar]
- Farage, M.A. The Prevalence of Sensitive Skin. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lim, K.M. Skin barrier dysfunction and filaggrin. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2021, 44, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liao, H.; Lu, X.; Cong, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Deng, C.; Cheng, Y.; Shu, P.; et al. Anti photoaging mechanism of a novel recombinant human fibronectin peptide (rhFNP) derived from the extracellular matrix. Heliyon 2025, 11, e42730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.H.; Liu, T.Z.; Zhao, W.B. Fibronectin-based Scalp Repair Products and Their Applications. Flavour Fragr. Cosmet. 2025, 1, 151–155. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Wang, X.; Ren, X.; Ge, X. MMP12 disrupts epithelial barrier integrity in oral lichen planus by degrading fibronectin. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhu, W.; Lei, X.; Luo, X.; Xiang, Q.; Zhu, X.; Pan, Q.; Jin, P.; Cheng, B. Treatment of Acute Wounds with Recombinant Human-Like Collagen and Recombinant Human-Like Fibronectin in C57BL/6 Mice Individually or in Combination. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 908585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaccio, F.; D Arino, A.; Caputo, S.; Bellei, B. Focus on the Contribution of Oxidative Stress in Skin Aging. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, N.; Papismadov, N.; Solomonov, I.; Sagi, I.; Krizhanovsky, V. The ECM path of senescence in aging: Components and modifiers. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 2636–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmulevich, R.; Krizhanovsky, V. Cell Senescence, DNA Damage, and Metabolism. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2021, 34, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaccio, G.; Park, B.H.; Jeong, E.S.; Lee, S.; Jang, J.H. Bio-functionalization and in-vitro evaluation of titanium surface with recombinant fibronectin and elastin fragment in human mesenchymal stem cell. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260760. [Google Scholar]
- Guillem-Marti, J.; Gelabert, M.; Heras-Parets, A.; Pegueroles, M.; Ginebra, M.P.; Manero, J.M. RGD Mutation of the Heparin Binding II Fragment of Fibronectin for Guiding Mesenchymal Stem Cell Behavior on Titanium Surfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 3666–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tragoonlugkana, P.; Pruksapong, C.; Ontong, P.; Kamprom, W.; Supokawej, A. Fibronectin and vitronectin alleviate adipose-derived stem cells senescence during long-term culture through the AKT/MDM2/P53 pathway. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Carlton, M.; Chen, X.; Kaur, N.; Ryan, H.; Parker, T.J.; Lin, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, Y. Effect of fibronectin, FGF-2, and BMP4 in the stemness maintenance of BMSCs and the metabolic and proteomic cues involved. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Filppula, A.M.; Zhao, Y.; Shang, L.; Zhang, H. Mechanically regulated microcarriers with stem cell loading for skin photoaging therapy. Bioact. Mater. 2025, 46, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyakov, I.N.; Mavletova, D.A.; Chernyshova, I.N.; Snegireva, N.A.; Gavrilova, M.V.; Bushkova, K.K.; Dyachkova, M.S.; Alekseeva, M.G.; Danilenko, V.N. FN3 protein fragment containing two type III fibronectin domains from B. longum GT15 binds to human tumor necrosis factor alpha in vitro. Anaerobe 2020, 65, 102247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, J.T.; Schwarzbauer, J.E.; Ginsberg, M.H. Fibronectin matrix as a scaffold for procollagen proteinase binding and collagen processing. Mol. Biol. Cell 2019, 30, 2218–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Geng, D.; Zhang, Q.; Ye, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Xiang, Q. Recombinant expression a novel fibronectin—Collage fusion peptide modulating stem cell stemness via integrin β3. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 3765–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielkopf, C.L.; Bauer, W.; Urbatsch, I.L. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis of Proteins. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2021, 12, 102228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.L.; Wang, L.; Zonderman, J.; Rouse, J.C.; Kim, H.Y. Automated, High-Throughput Infrared Spectroscopy for Secondary Structure Analysis of Protein Biopharmaceuticals. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 109, 3223–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alley, W.R., Jr.; Mann, B.F.; Novotny, M.V. High-sensitivity analytical approaches for the structural characterization of glycoproteins. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 2668–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Højrup, P. Analysis of Polypeptides by Amino Acid Analysis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2024, 2821, 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, L.; Walt, D.R. Highly Sensitive and Multiplexed Protein Measurements. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 293–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, G.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Chatel, J.-M.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, C. Recombinant invasive Lactobacillus plantarum expressing fibronectin binding protein A induce specific humoral immune response by stimulating differentiation of dendritic cells. Benef. Microbes 2019, 10, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, J.; Liu, L.; Kang, J.; Luo, X.; Kong, Y.; Zhang, G. Identification and Characterization of Fibronectin-Binding Peptides in Gelatin. Polymers 2022, 14, 3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.A.; Rawlings, T.M.; Muter, J.; Walker, M.; Brosens, J.J.; Cameron, N.R.; Eissa, A.M. Covalent Attachment of Fibronectin onto Emulsion-Templated Porous Polymer Scaffolds Enhances Human Endometrial Stromal Cell Adhesion, Infiltration, and Function. Macromol. Biosci. 2018, 19, e1800351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Purpose | Method | Primary Use/Characteristics | Advantages | Disadvantages/Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qualitative/ Structural Detection | Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) | Molecular weight and purity | Simple, provides basic information | Lacks specificity, not quantitative | [79] |
| Western blot (WB) | Identity using specific antibodies | High specificity, confirms target protein | Semi-quantitative, multi-step procedure | [66] | |
| Infrared Spectroscopy (IR) | Provides secondary structure information | Useful for structural analysis | Susceptible to interference, hard to quantify | [80] | |
| Peptide Mapping (e.g., LC-MS/MS) | High-precision identification via characteristic peptides after enzymatic digestion | High accuracy and specificity | Expensive instrumentation, complex workflow | [81] | |
| Amino Acid Analysis | Indirect absolute quantification via acid hydrolysis | Absolute quantification, high accuracy | Time-consuming, requires expertise | [82] | |
| Content Detection | Total Protein Assays (e.g., BCA) | Estimation of total protein content | Fast, economical, high-throughput | Lacks specificity, prone to interference | [83] |
| Immunoassays (ELISA) | Highly sensitive and specific quantification using antibodies | High sensitivity, specific, widely used | Dependent on antibody quality, relatively costly | [84] | |
| Chromatography (HPLC) | Separation and quantification based on hydrophobicity/size, provides purity information | Simultaneous separation, quantification, and purity check | Lower sensitivity, complex sample preparation | [85] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Yang, D.; Xiao, L.; Xie, W.; Zheng, H.; Ye, S.; Deng, C.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Applications of Fibronectin in Biomedicine and Cosmetics: A Review. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111249
Wang Y, Zhang Q, Zhou X, Yang D, Xiao L, Xie W, Zheng H, Ye S, Deng C, Cheng Y, et al. Applications of Fibronectin in Biomedicine and Cosmetics: A Review. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(11):1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111249
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yuan, Qirong Zhang, Xiandong Zhou, Dingshan Yang, Lin Xiao, Wenlan Xie, Huaping Zheng, Shuiwei Ye, Chaoqing Deng, Yong Cheng, and et al. 2025. "Applications of Fibronectin in Biomedicine and Cosmetics: A Review" Bioengineering 12, no. 11: 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111249
APA StyleWang, Y., Zhang, Q., Zhou, X., Yang, D., Xiao, L., Xie, W., Zheng, H., Ye, S., Deng, C., Cheng, Y., Shu, P., & Xiang, Q. (2025). Applications of Fibronectin in Biomedicine and Cosmetics: A Review. Bioengineering, 12(11), 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12111249






