Biological Interpretable Machine Learning Model for Predicting Pathological Grading in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Based on CT Urography Peritumoral Radiomics Features
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
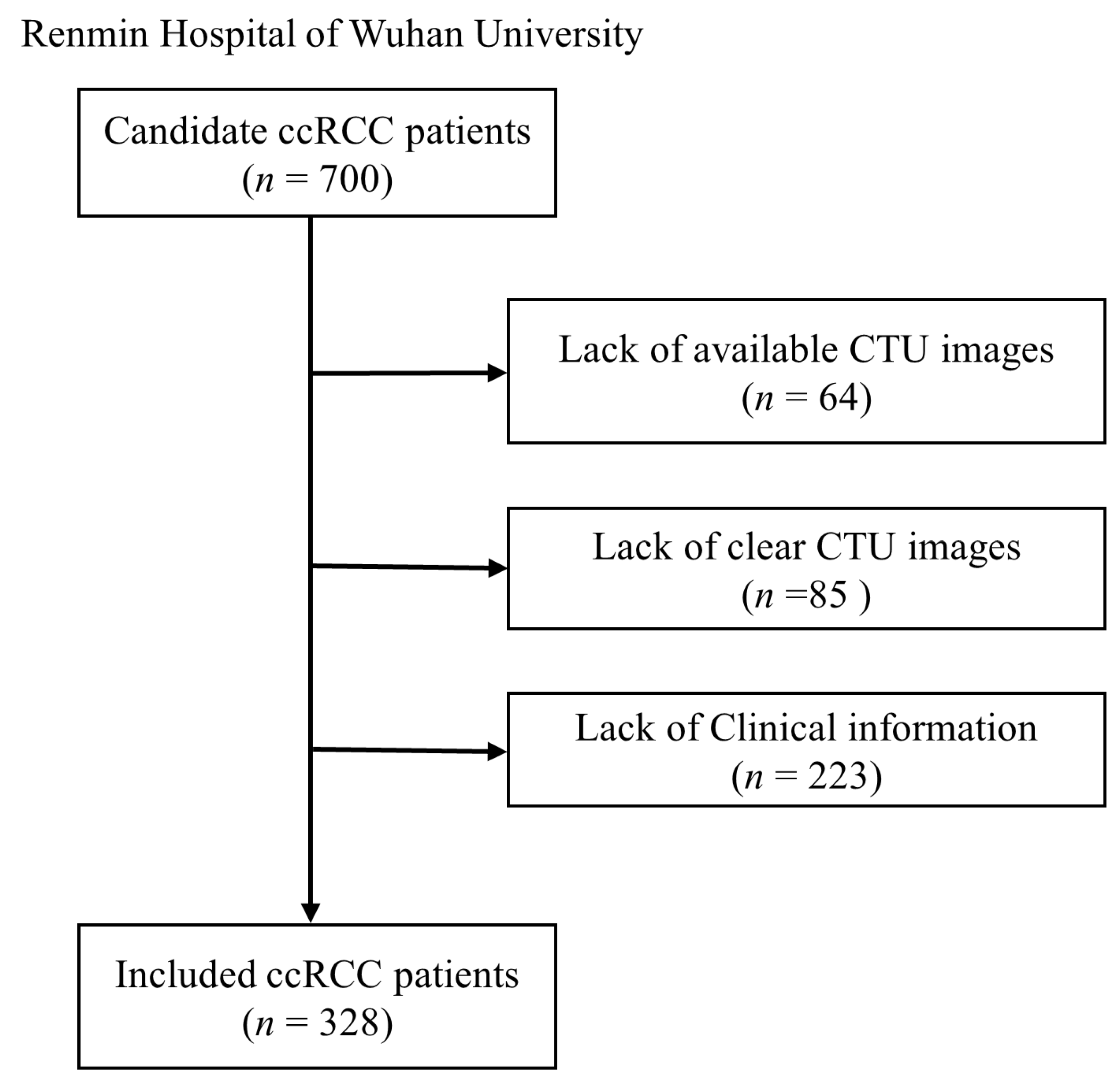
2.1. Study Population
2.2. CTU Images Collection
2.3. ISUP Evaluation
2.4. PAT Annotation
2.5. Radiomics Feature Extraction
2.6. Feature Dimension Reduction
2.7. Machine Learning Models Development
2.8. Biological Interpretability Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. PAT Radiomics Feature Extraction
3.3. PAT Feature Selection
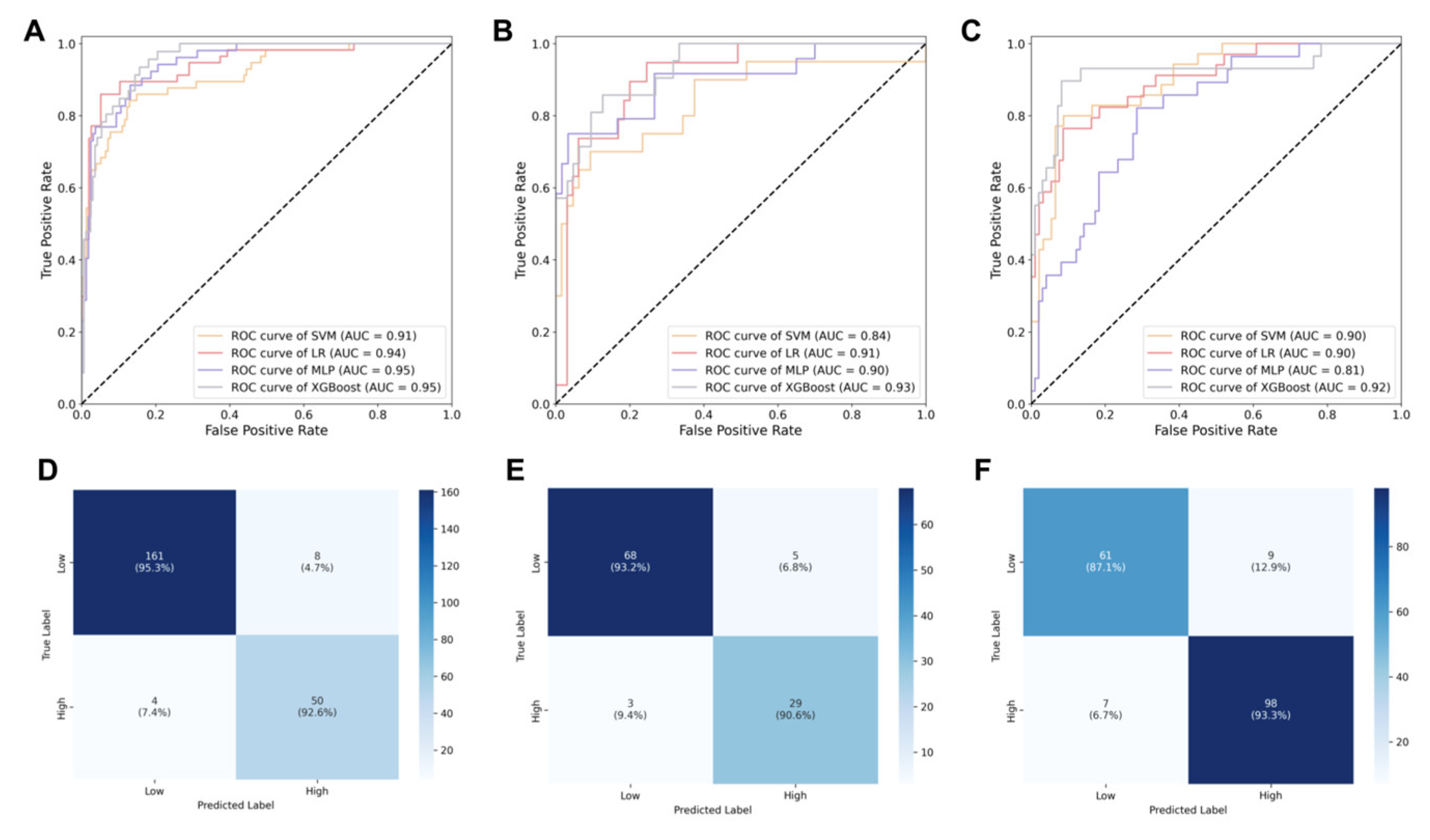
3.4. Performance of Machine Learning Models
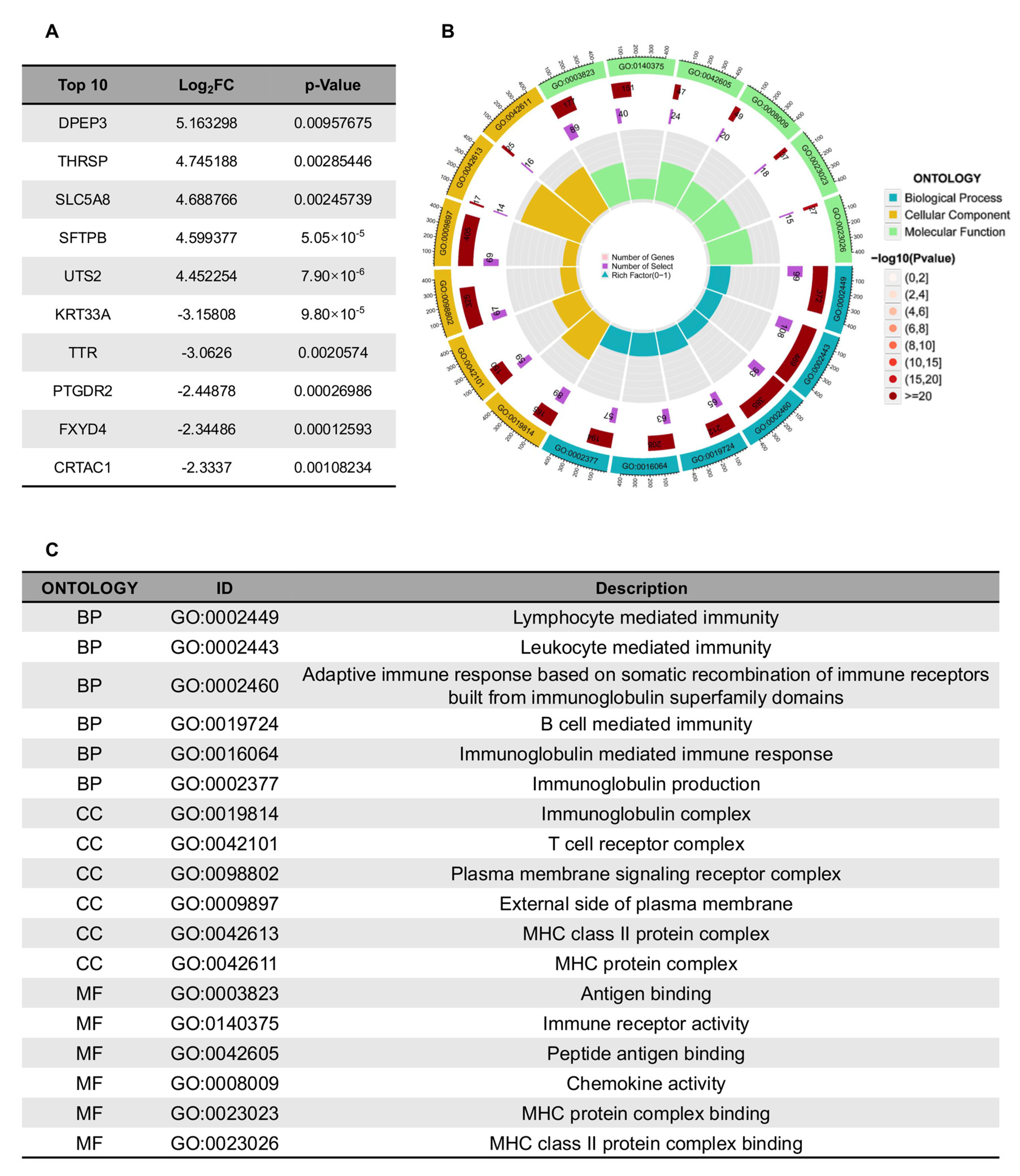
3.5. The Biological Interpretability of the Model
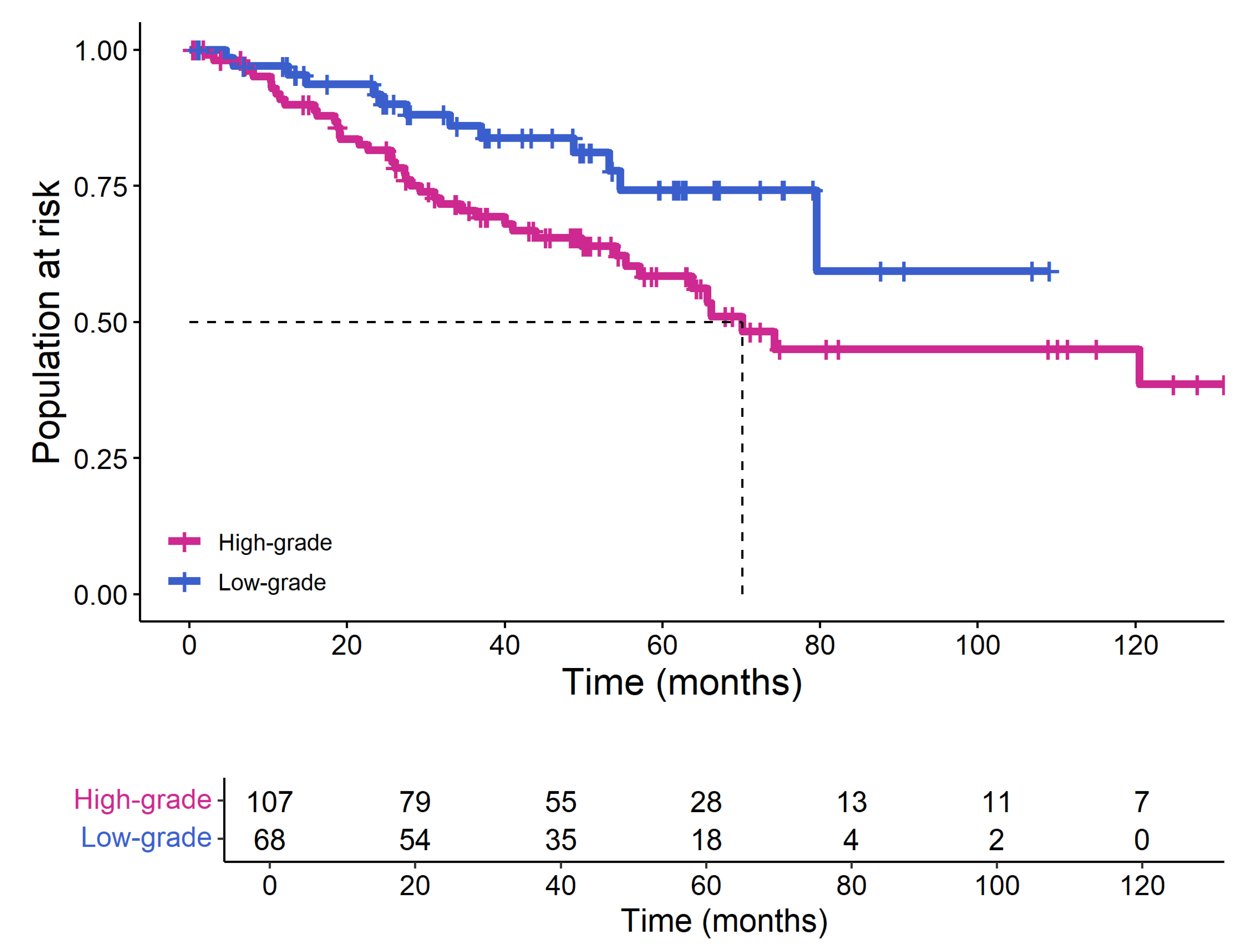
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RCC | Renal Cell Carcinoma |
| ccRCC | Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma |
| ISUP | International Society of Urological Pathology |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| PAT | Peritumoral Area |
| CTU | Computed Tomography Urography |
| DICOM | Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine |
| ROI | Region of Interest |
| GLCM | Gray-Level Co-occurrence Matrix |
| GLSZM | Gray-Level Size Zone Matrix |
| GLRLM | Gray-Level Run Length Matrix |
| GLDM | Gray-Level Dependence Matrix |
| ICC | Intraclass Correlation Coefficient |
| LASSO | Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator |
| LR | Logistic Regression |
| MLP | Multilayer Perceptron |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| XGBoost | Extreme Gradient Boosting |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| RHWU | Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University |
| CMP | Corticomedullary Phase |
References
- Capitanio, U.; Montorsi, F. Renal cancer. Lancet 2016, 387, 894–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moch, H.; Amin, M.B.; Berney, D.M.; Compérat, E.M.; Gill, A.J.; Hartmann, A.; Menon, S.; Raspollini, M.R.; Rubin, M.A.; Srigley, J.R.; et al. The 2022 World Health Organization Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs-Part A: Renal, Penile, and Testicular Tumours. Eur. Urol. 2022, 82, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moch, H.; Cubilla, A.L.; Humphrey, P.A.; Reuter, V.E.; Ulbright, T.M. The 2016 WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs-Part A: Renal, Penile, and Testicular Tumours. Eur. Urol. 2016, 70, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galtung, K.F.; Lauritzen, P.M.; Baco, E.; Berg, R.E.; Naas, A.M.; Rud, E. Predictive Performance of Prospectively Applied ISUP and Fuhrman Grade in Nonmetastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2022, 42, 2967–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconi, L.; Dabestani, S.; Lam, T.B.; Hofmann, F.; Stewart, F.; Norrie, J.; Bex, A.; Bensalah, K.; Canfield, S.E.; Hora, M.; et al. Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Diagnostic Accuracy of Percutaneous Renal Tumour Biopsy. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 660–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poggio, E.D.; McClelland, R.L.; Blank, K.N.; Hansen, S.; Bansal, S.; Bomback, A.S.; Canetta, P.A.; Khairallah, P.; Kiryluk, K.; Lecker, S.H.; et al. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Native Kidney Biopsy Complications. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 15, 1595–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.D.; Johnson, M.H.; Pierorazio, P.M.; Sozio, S.M.; Sharma, R.; Iyoha, E.; Bass, E.B.; Allaf, M.E. Diagnostic Accuracy and Risks of Biopsy in the Diagnosis of a Renal Mass Suspicious for Localized Renal Cell Carcinoma: Systematic Review of the Literature. J. Urol. 2016, 195, 1340–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.-J.; Su, G.-H.; You, C.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Jiang, Y.-Z.; Shao, Z.-M. Radiomics in breast cancer: Current advances and future directions. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronot, M.; Soyer, P. Can radiomics outperform pathology for tumor grading? Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2024, 105, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Zhao, B.; Li, B.; Lei, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tang, T.; Ju, S. MRI-Based Radiomics and Deep Learning in Biological Characteristics and Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Opportunities and Challenges. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2024, 59, 767–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, G.; Singh, A.; Bae, J.; Manjila, S.; Spektor, V.; Prasanna, P.; Lignelli, A. New frontiers in domain-inspired radiomics and radiogenomics: Increasing role of molecular diagnostics in CNS tumor classification and grading following WHO CNS-5 updates. Cancer Imaging 2024, 24, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Voort, S.R.; Incekara, F.; Wijnenga, M.M.J.; Kapsas, G.; Gahrmann, R.; Schouten, J.W.; Tewarie, R.N.; Lycklama, G.J.; Hamer, P.C.D.W.; Eijgelaar, R.S.; et al. Combined molecular subtyping, grading, and segmentation of glioma using multi-task deep learning. Neuro Oncol. 2023, 25, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeken, J.C.; Spraker, M.B.; Knebel, C.; Dapper, H.; Pfeiffer, D.; Devecka, M.; Thamer, A.; Shouman, M.A.; Ott, A.; von Eisenhart-Rothe, R.; et al. Tumor grading of soft tissue sarcomas using MRI-based radiomics. EBioMedicine 2019, 48, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, P.; Wang, B.; Ni, X.; Lu, Y.; Yang, R.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Mei, H.; Liu, X.; Weng, X.; et al. CT Urography-Based Radiomics to Predict ISUP Grading of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Cancer 2025, 16, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, E.; Li, Z.; Ma, C.; Li, Q.; Lei, Y.; Lan, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Li, R.; Long, W.; et al. Predicting the ISUP grade of clear cell renal cell carcinoma with multiparametric MR and multiphase CT radiomics. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 2912–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Xie, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Xie, W. Development and validation of a CT-based nomogram for preoperative prediction of clear cell renal cell carcinoma grades. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 6078–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lin, J.; Qi, H.; Dai, C.; Guo, Y.; Lin, D.; Zhou, J. Radiomics predict the WHO/ISUP nuclear grade and survival in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Insights Imaging 2024, 15, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liu, L.; Ji, Y.; Yan, T.; Shi, Z.; Pan, H.; Wang, S.; Yu, K.; Qin, C.; Zhang, T. Enhanced CT-Based Intratumoral and Peritumoral Radiomics Nomograms Predict High-Grade Patterns of Invasive Lung Adenocarcinoma. Acad. Radiol. 2025, 32, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Liu, Y.F.; Shu, X.; Qiao, X.F.; Ai, G.Y.; He, X.J. Peritumoral Radiomics Strategy Based on Ensemble Learning for the Prediction of Gleason Grade Group of Prostate Cancer. Acad. Radiol. 2023, 30 (Suppl. S1), S1–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, T.; Chen, X.; Tang, M.; Deng, J.; Cai, Z.; Cui, W. Intratumoral and peritumoral MRI-based radiomics prediction of histopathological grade in soft tissue sarcomas: A two-center study. Cancer Imaging 2023, 23, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Dong, D.; Bai, X.; Huang, Q.; Guo, A.; Ye, H.; Tian, J.; Wang, H. Multiparametric MRI Radiomic Model for Preoperative Predicting WHO/ISUP Nuclear Grade of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 52, 1557–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yushkevich, P.A.; Piven, J.; Hazlett, H.C.; Smith, R.G.; Ho, S.; Gee, J.C.; Gerig, G. User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: Significantly improved efficiency and reliability. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Griethuysen, J.J.M.; Fedorov, A.; Parmar, C.; Hosny, A.; Aucoin, N.; Narayan, V.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Fillion-Robin, J.-C.; Pieper, S.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Computational Radiomics System to Decode the Radiographic Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e104–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, M.; Abualrous, E.T.; Sticht, J.; Álvaro-Benito, M.; Stolzenberg, S.; Noé, F.; Freund, C. Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) Class I and MHC Class II Proteins: Conformational Plasticity in Antigen Presentation. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Xie, A.X.; Liu, E.M.; Kuo, F.; Kim, M.; DiNatale, R.G.; Golkaram, M.; Chen, Y.-B.; Gupta, S.; Motzer, R.J.; et al. Immunometabolic coevolution defines unique microenvironmental niches in ccRCC. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 1424–1440.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Narayanan, S.P.; Mannan, R.; Raskind, G.; Wang, X.; Vats, P.; Su, F.; Hosseini, N.; Cao, X.; Kumar-Sinha, C.; et al. Single-cell analyses of renal cell cancers reveal insights into tumor microenvironment, cell of origin, and therapy response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2103240118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, D.J.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Petralia, F.; Pan, J.; Song, X.; Hu, Y.; da Veiga Leprevost, F.; Reva, B.; Lih, T.S.M.; Chang, H.Y.; et al. Integrated Proteogenomic Characterization of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cell 2019, 179, 964–983.e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qi, L.; Ye, B.; Wang, A.; Lu, J.; Qu, L.; Luo, P.; Wang, L.; Jiang, A. MOICS, a novel classier deciphering immune heterogeneity and aid precise management of clear cell renal cell carcinoma at multiomics level. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2024, 25, 2345977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonasch, E.; Walker, C.L.; Rathmell, W.K. Clear cell renal cell carcinoma ontogeny and mechanisms of lethality. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021, 17, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.; Sui, C.; Wang, C.; Zhu, T. MRI-based intratumoral and peritumoral radiomics for preoperative prediction of glioma grade: A multicenter study. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1401977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Cheng, J.; Qiu, A.; Zhao, D.; Wang, J.; Liu, J. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-based intratumoral and peritumoral radiomics for prognosis prediction in glioma patients. Clin. Radiol. 2024, 79, e1383–e1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, N.; Fan, X.; Chen, D.; Chen, J.; Yu, H.; He, M.; Liu, H.; Yin, X.; Li, B.; Wang, H. Peritumoral and Intratumoral Texture Features Based on Multiparametric MRI and Multiple Machine Learning Methods to Preoperatively Evaluate the Pathological Outcomes of Pancreatic Cancer. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2023, 58, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Characteristics | RHWU (N = 328) | TCGA (N = 175) |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 59 (25, 84) | 59 (26, 88) |
| Gender | ||
| Female | 124 (37.8%) | 64 (36.5%) |
| Male | 204 (62.2%) | 111 (63.5%) |
| pT stage | ||
| pT1 | 224 (68.3%) | 92 (52.5%) |
| pT2 | 40 (12.1%) | 19 (10.9%) |
| pT3 | 51 (15.6%) | 61 (34.9%) |
| pT4 | 13 (4.0%) | 3 (1.7%) |
| pN stage | ||
| pN0 | 326 (99.4%) | 74 (42.3%) |
| pN1 | 2 (0.6%) | 3 (1.7%) |
| pNx | 0 (0%) | 98 (56.0%) |
| pM stage | ||
| pM0 | 326 (99.4%) | 144 (82.3%) |
| pM1 | 2 (0.6%) | 25 (14.3%) |
| pMx | 0 (0%) | 6 (3.4%) |
| pTNM stage | ||
| Stage I | 225 (68.6%) | 89 (50.9%) |
| Stage II | 39 (11.9%) | 15 (8.6%) |
| Stage III | 51 (15.5%) | 44 (25.1%) |
| Stage IV | 13 (4.0%) | 27 (15.4%) |
| ISUP | ||
| Low | 242 (73.8%) | 71 (40.1%) |
| High | 86 (26.2%) | 104 (59.9%) |
| Signature | Coefficients |
|---|---|
| original_shape_LeastAxisLength | 0.000658846 |
| original_shape_Maximum2DDiameterslice | 0.009503959 |
| original_shape_MinorAxisLength | 0.038404090 |
| original_shape_surfaceArea | 0.021442057 |
| original_gldm_LargeDependenceEmphasis | 0.016409816 |
| original_glrlm_shortRunEmphasis | −0.004333667 |
| original_ngtdm_Busyness | 0.010288175 |
| Variable | Overall, N = 328 1 | Training Set, N = 223 1 | Internal Set, N = 105 1 | p-Value 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.079 | |||
| Female | 124 (38%) | 84 (38%) | 40 (38%) | |
| Male | 204 (62%) | 139 (62%) | 65 (52%) | |
| Age | 59 (52, 66) | 57 (51, 66) | 61 (55, 66) | 0.059 |
| pTNM stage | 0.096 | |||
| I | 225 (69%) | 169 (76%) | 56 (53%) | |
| II | 39 (12%) | 24 (11%) | 15 (7%) | |
| III | 51 (16%) | 22 (10%) | 29 (28%) | |
| IV | 13 (4.0%) | 8 (3%) | 5 (12%) | |
| ISUP Grade | 0.19 | |||
| Low-grade | 242 (74%) | 169 (76%) | 73 (70%) | |
| High-grade | 86 (26%) | 54 (24%) | 32 (30%) |
| Dataset | Model | AUC (95%CI) | Sensitivity (95%CI) | Accuracy (95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | LR | 0.94 (0.90, 0.97) | 0.92 (0.88, 0.94) | 0.91 (0.88, 0.94) |
| MLP | 0.95 (0.91, 0.97) | 0.93 (0.88, 0.95) | 0.93 (0.89, 0.96) | |
| SVM | 0.91 (0.88, 0.94) | 0.90 (0.86, 0.94) | 0.91 (0.88, 0.94) | |
| XGBoost | 0.95 (0.92, 0.98) | 0.95 (0.92, 0.97) | 0.95 (0.88, 0.94) | |
| Testing | LR | 0.91 (0.88, 0.94) | 0.90 (0.87, 0.93) | 0.89 (0.86, 0.93) |
| MLP | 0.90 (0.87, 0.92) | 0.88 (0.85, 0.91) | 0.87 (0.85, 0.89) | |
| SVM | 0.84 (0.81, 0.87) | 0.83 (0.81, 0.87) | 0.83 (0.81, 0.87) | |
| XGBoost | 0.93 (0.89, 0.96) | 0.93 (0.90, 0.95) | 0.92 (0.89, 0.96) | |
| Validation | LR | 0.90 (0.86, 0.93) | 0.85 (0.88, 0.94) | 0.88 (0.86, 0.90) |
| MLP | 0.81 (0.79, 0.84) | 0.80 (0.78, 0.84) | 0.81 (0.78, 0.86) | |
| SVM | 0.90 (0.88, 0.93) | 0.86 (0.83, 0.89) | 0.85 (0.82, 0.88) | |
| XGBoost | 0.92 (0.87, 0.95) | 0.87 (0.85, 0.90) | 0.91 (0.87, 0.94) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, D.; Mei, H.; Jiao, P.; Zheng, Q. Biological Interpretable Machine Learning Model for Predicting Pathological Grading in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Based on CT Urography Peritumoral Radiomics Features. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101125
Yang D, Mei H, Jiao P, Zheng Q. Biological Interpretable Machine Learning Model for Predicting Pathological Grading in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Based on CT Urography Peritumoral Radiomics Features. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(10):1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101125
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Dingzhong, Haonan Mei, Panpan Jiao, and Qingyuan Zheng. 2025. "Biological Interpretable Machine Learning Model for Predicting Pathological Grading in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Based on CT Urography Peritumoral Radiomics Features" Bioengineering 12, no. 10: 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101125
APA StyleYang, D., Mei, H., Jiao, P., & Zheng, Q. (2025). Biological Interpretable Machine Learning Model for Predicting Pathological Grading in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Based on CT Urography Peritumoral Radiomics Features. Bioengineering, 12(10), 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101125






