Precision Oncology for High-Grade Gliomas: A Tumor Organoid Model for Adjuvant Treatment Selection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
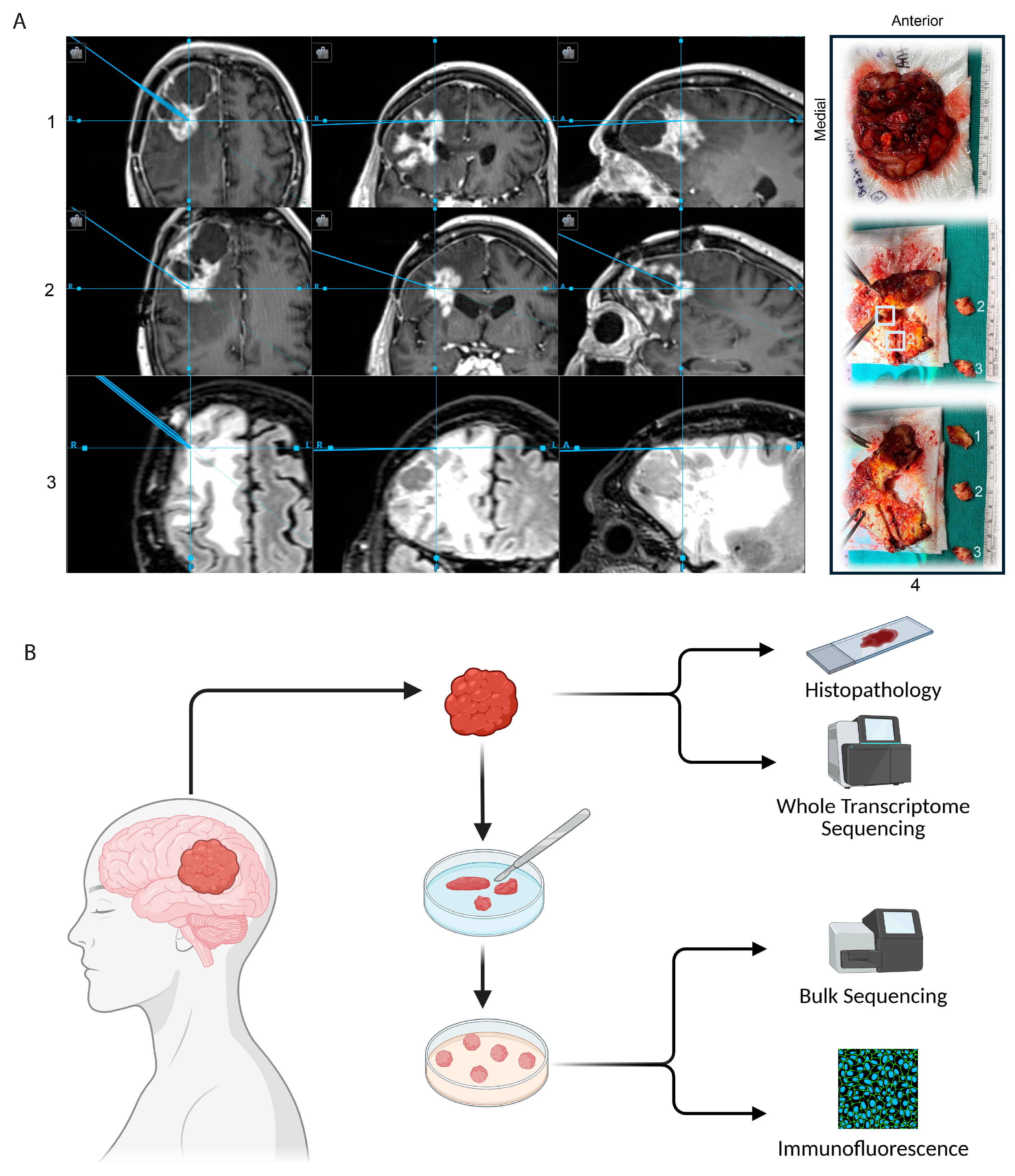
2.1. Collection of Glioma Tumor Specimens
2.2. Clinical Analysis and Transcriptomic Sequencing
2.3. Generation and Maintenance of Tumor Organoids
2.4. Organoid Fixation, Sectioning, and Slide Preparation
2.5. Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining
2.6. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.7. Organoid Bulk RNA Sequencing
2.8. Bulk RNA Sequencing Analysis
2.9. High-Throughput Drug Testing
3. Results
3.1. Generation of GTOs
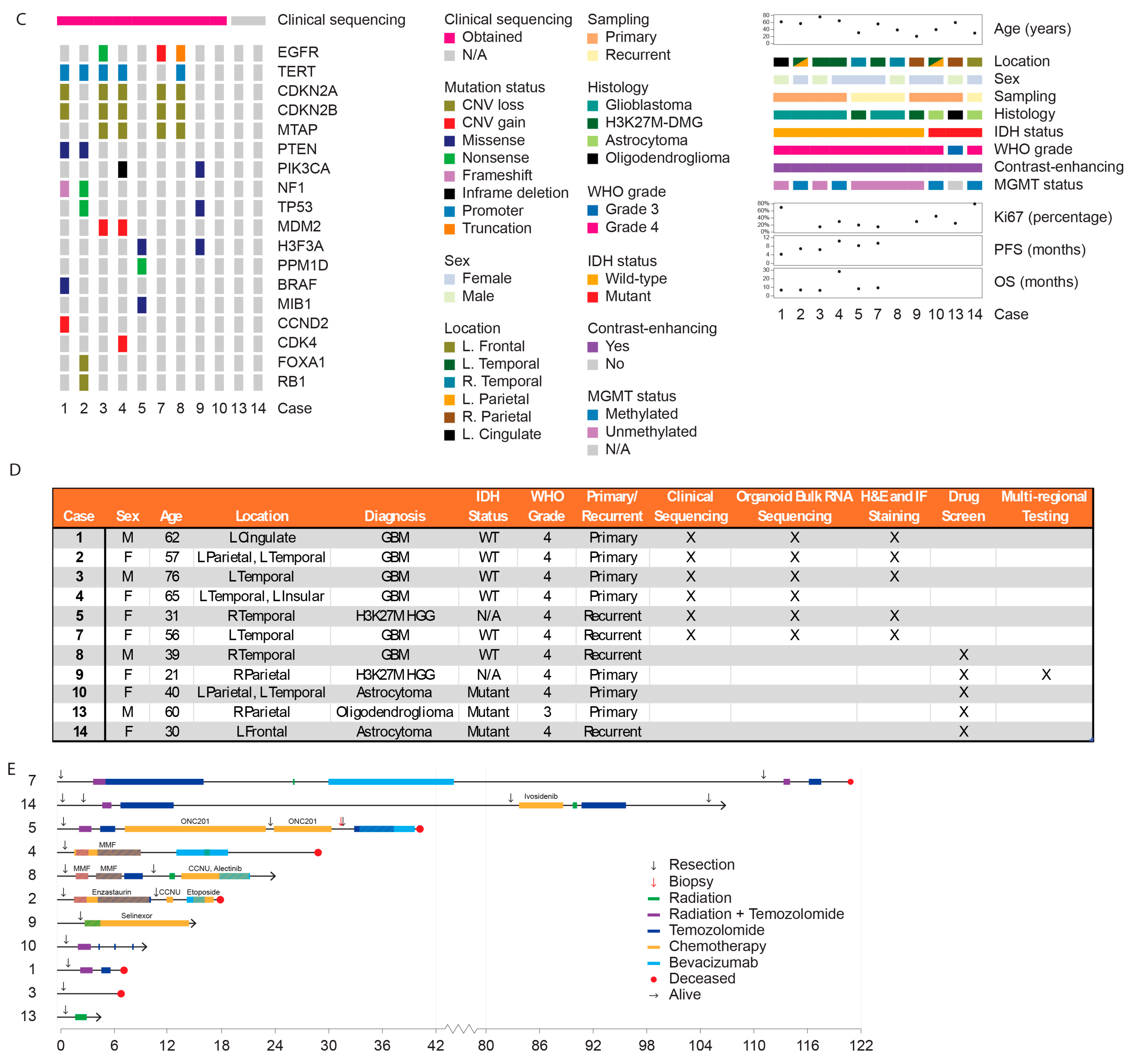
3.2. Cohort Clinical Characteristics
3.3. Characterizing Heterogeneity Between GTOs
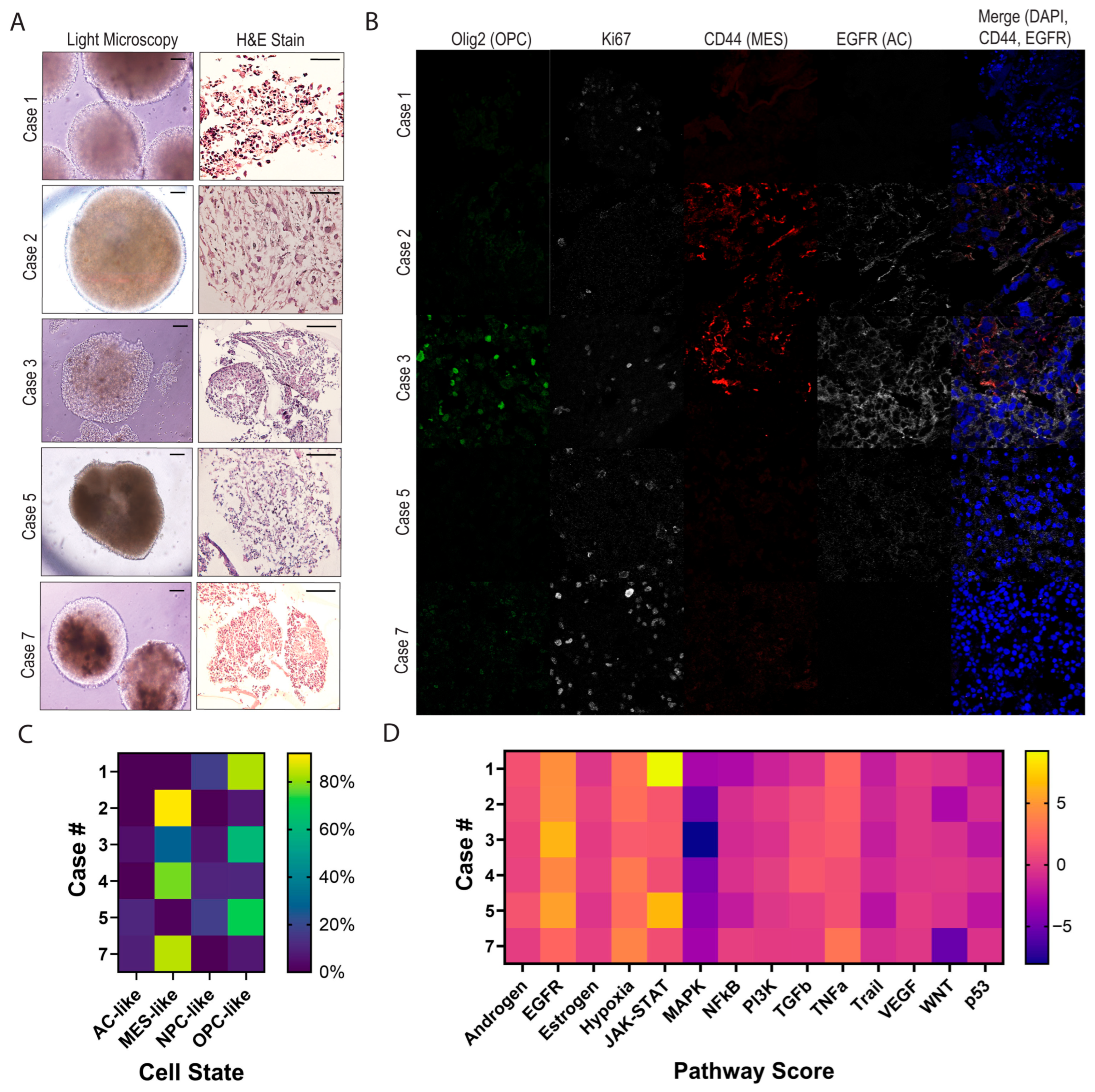
3.4. GTOs May Recapitulate Patient Tumor Characteristics
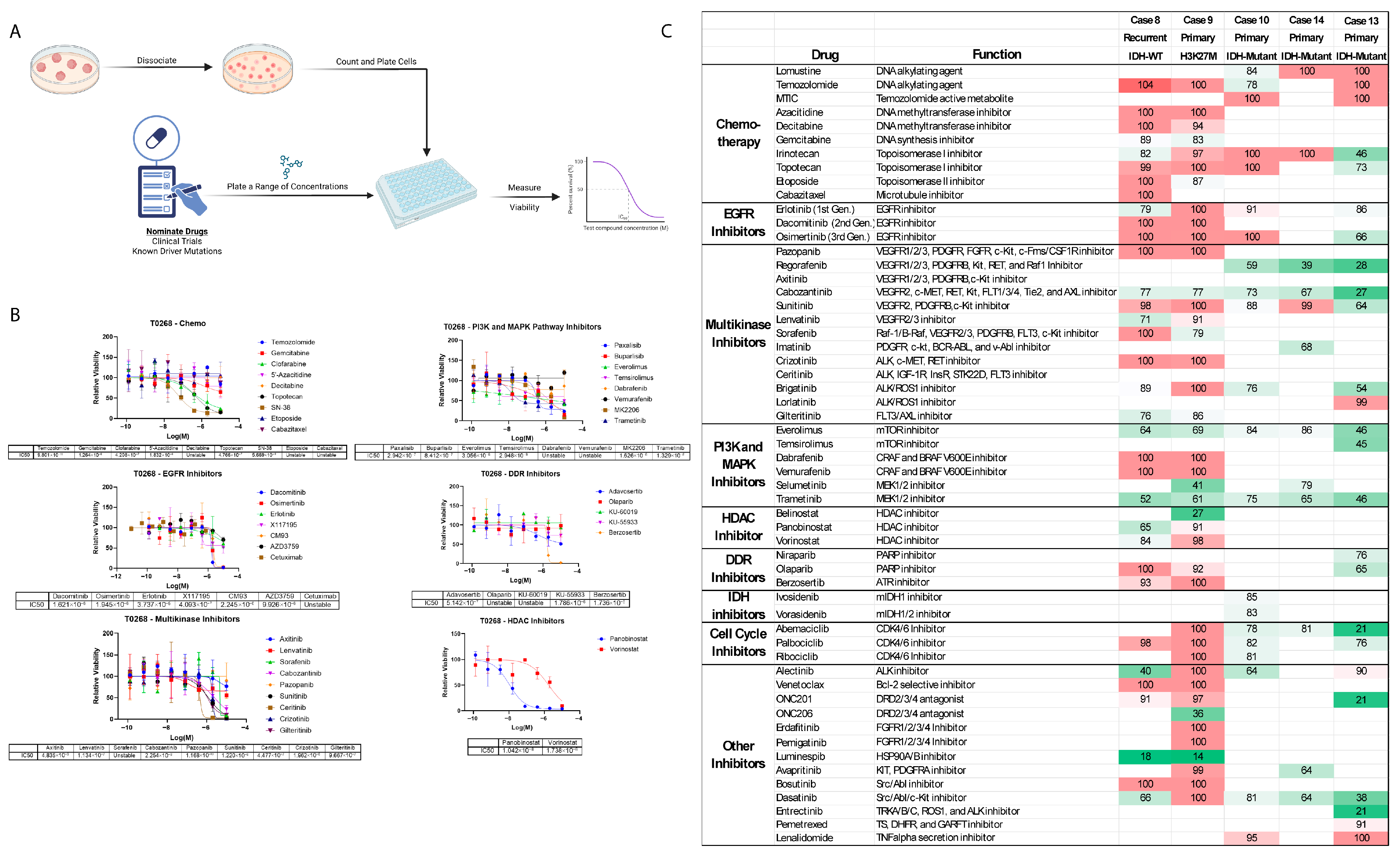
3.5. Heterogeneous Drug Reponses Between GTOs
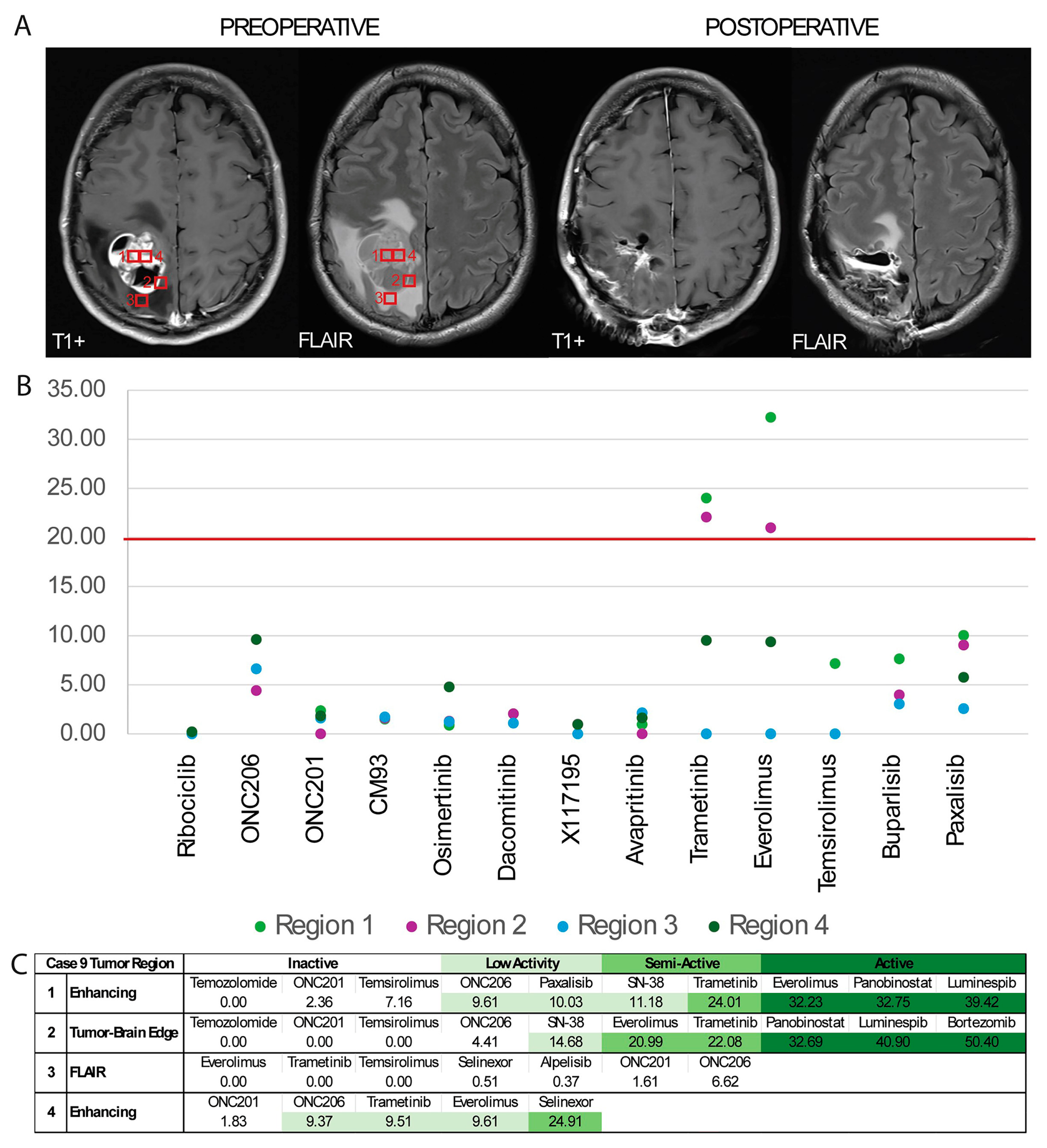
3.6. Multiregional GTO Drug Testing Demonstrates Heterogenous Response
4. Discussion
4.1. Production of IDH-Mutant GTOs
4.2. In Vitro GTO Drug Testing Results Match Clinical Response
4.3. Strategies for Utilizing Drug Testing Results
4.4. Multiregional Drug Testing Reveals Differential Results
4.5. Limitations for Application of GTO Drug Screening
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3D | Three-dimensional |
| BBB | Blood–Brain Barrier |
| Cave | Average Plasma Concentration |
| Cmax | Maximum Plasma Concentration |
| CAP | College of American Pathologists |
| CLIA | Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments |
| DMG | Diffuse Midline Glioma |
| DSS3 | Drug Sensitivity Score 3 |
| EGFR | Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor |
| FLAIR | Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery |
| GBM | Glioblastoma Multiforme |
| GTO | Glioma Tumor Organoid |
| HGG | High-Grade Glioma |
| HPLM | Human Plasma-Like Medium |
| IHC/IF | Immunochemistry/Immunofluorescence |
| PDX | Patient-Derived Xenografts |
| RIN | RNA integrity number |
| TMZ | Temozolomide |
| WT | Wild Type |
References
- Narang, K.; Kataria, T.; Bisht, S.S.; Gupta, D.; Banerjee, S.; Mayank, M.; Shishak, S.; Kaliyaperumal, V.; Tamilselvan, S.; Kamaraj, D.; et al. Contemporary Long-term Survival Outcomes and Prognostic Factors in Adult grade 4 Astrocytoma: An Institutional Analysis. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 40, 103788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Noorbakhsh, A.; Hirshman, B.R.; Zhou, T.; Tang, J.A.; Chang, D.C.; Carter, B.S.; Chen, C.C. Survival trends of grade I, II, and III astrocytoma patients and associated clinical practice patterns between 1999 and 2010: A SEER-based analysis. Neuro-Oncol. Pract. 2016, 3, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, N.F.; Ottaviani, D.; Tazare, J.; Gregson, J.; Kitchen, N.; Brandner, S.; Fersht, N.; Mulholland, P. Survival Outcomes and Prognostic Factors in Glioblastoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.P.; Tirosh, I.; Trombetta, J.J.; Shalek, A.K.; Gillespie, S.M.; Wakimoto, H.; Cahill, D.P.; Nahed, B.V.; Curry, W.T.; Martuza, R.L.; et al. Single-cell RNA-seq highlights intratumoral heterogeneity in primary glioblastoma. Science 2014, 344, 1396–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Carmona, E.; Narayanan, A.; Hernandez, I.; Nieto, J.C.; Elosua-Bayes, M.; Sun, X.; Schmidt, C.; Pamir, N.; Ozduman, K.; Herold-Mende, C.; et al. Tumor heterogeneity and tumor-microglia interactions in primary and recurrent IDH1-mutant gliomas. Cell Rep. Med. 2023, 4, 101249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, K.M.; Kim, J.; Jin, J.; Kim, M.; Seol, H.J.; Muradov, J.; Yang, H.; Choi, Y.L.; Park, W.Y.; Kong, D.S.; et al. Patient-specific orthotopic glioblastoma xenograft models recapitulate the histopathology and biology of human glioblastomas in situ. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 260–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, F.; Salinas, R.D.; Zhang, D.Y.; Nguyen, P.T.T.; Schnoll, J.G.; Wong, S.Z.H.; Thokala, R.; Sheikh, S.; Saxena, D.; Prokop, S.; et al. A Patient-Derived Glioblastoma Organoid Model and Biobank Recapitulates Inter- and Intra-tumoral Heterogeneity. Cell 2020, 180, 188–204.e122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Avera, A.D.; Kim, Y. Biomanufacturing of glioblastoma organoids exhibiting hierarchical and spatially organized tumor microenvironment via transdifferentiation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2022, 119, 3252–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, F.; Weygant, N.; Zhang, J.; Hu, P.; Qin, Z.; Yang, J.; Cheng, Q.; Fan, F.; Zeng, Y.; et al. A novel integrated system using patient-derived glioma cerebral organoids and xenografts for disease modeling and drug screening. Cancer Lett. 2021, 500, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loong, H.H.; Wong, A.M.; Chan, D.T.; Cheung, M.S.; Chow, C.; Ding, X.; Chan, A.K.; Johnston, P.A.; Lau, J.Y.; Poon, W.S.; et al. Patient-derived tumor organoid predicts drugs response in glioblastoma: A step forward in personalized cancer therapy? J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 78, 400–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, K.D.; Duffy, J.T.; Babak, M.V.; Balyasnikova, I.V. Modeling glioblastoma complexity with organoids for personalized treatments. Trends Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 282–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, J.; Pao, G.M.; Shokhirev, M.N.; Verma, I.M. Glioblastoma Model Using Human Cerebral Organoids. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 1220–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, B.; Mathew, R.K.; Polson, E.S.; Williams, J.; Wurdak, H. Spontaneous Glioblastoma Spheroid Infiltration of Early-Stage Cerebral Organoids Models Brain Tumor Invasion. SLAS Discov. 2018, 23, 862–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, M.; Yang, C.; Liu, L.; Gamboa, C.M.; Jara, K.; Lee, H.; Sabaawy, H.E. Rapid Processing and Drug Evaluation in Glioblastoma Patient-Derived Organoid Models with 4D Bioprinted Arrays. iScience 2020, 23, 101365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, E.; Clark, C.; Sivakumar, H.; Yoo, K.; Aleman, J.; Rajan, S.A.P.; Forsythe, S.; Mazzocchi, A.; Laxton, A.W.; Tatter, S.B.; et al. Immersion Bioprinting of Tumor Organoids in Multi-Well Plates for Increasing Chemotherapy Screening Throughput. Micromachines 2020, 11, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, C.G.; Rivera, M.; Spangler, L.C.; Wu, Q.; Mack, S.C.; Prager, B.C.; Couce, M.; McLendon, R.E.; Sloan, A.E.; Rich, J.N. A Three-Dimensional Organoid Culture System Derived from Human Glioblastomas Recapitulates the Hypoxic Gradients and Cancer Stem Cell Heterogeneity of Tumors Found In Vivo. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2465–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straehla, J.P.; Hajal, C.; Safford, H.C.; Offeddu, G.S.; Boehnke, N.; Dacoba, T.G.; Wyckoff, J.; Kamm, R.D.; Hammond, P.T. A predictive microfluidic model of human glioblastoma to assess trafficking of blood-brain barrier-penetrant nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2118697119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang-Schomer, M.D.; Bookland, M.J.; Sargent, J.E.; Jackvony, T.N. Human Patient-Derived Brain Tumor Models to Recapitulate Ependymoma Tumor Vasculature. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sood, D.; Tang-Schomer, M.; Pouli, D.; Mizzoni, C.; Raia, N.; Tai, A.; Arkun, K.; Wu, J.; Black, L.D., 3rd; Scheffler, B.; et al. 3D extracellular matrix microenvironment in bioengineered tissue models of primary pediatric and adult brain tumors. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang-Schomer, M.D.; Chandok, H.; Wu, W.B.; Lau, C.C.; Bookland, M.J.; George, J. 3D patient-derived tumor models to recapitulate pediatric brain tumors In Vitro. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 20, 101407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linkous, A.; Balamatsias, D.; Snuderl, M.; Edwards, L.; Miyaguchi, K.; Milner, T.; Reich, B.; Cohen-Gould, L.; Storaska, A.; Nakayama, Y.; et al. Modeling Patient-Derived Glioblastoma with Cerebral Organoids. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 3203–3211.e3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napoli, G.C.; Figg, W.D.; Chau, C.H. Functional Drug Screening in the Era of Precision Medicine. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 912641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golebiewska, A.; Hau, A.C.; Oudin, A.; Stieber, D.; Yabo, Y.A.; Baus, V.; Barthelemy, V.; Klein, E.; Bougnaud, S.; Keunen, O.; et al. Patient-derived organoids and orthotopic xenografts of primary and recurrent gliomas represent relevant patient avatars for precision oncology. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 140, 919–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Li, H.W.; Wang, Y.L.; Lee, C.C.; Shen, Y.C.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Lin, H.L.; Chen, X.X.; Cho, D.Y.; Hsieh, C.L.; et al. Patient-derived tumor organoids as a platform of precision treatment for malignant brain tumors. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachogiannis, G.; Hedayat, S.; Vatsiou, A.; Jamin, Y.; Fernandez-Mateos, J.; Khan, K.; Lampis, A.; Eason, K.; Huntingford, I.; Burke, R.; et al. Patient-derived organoids model treatment response of metastatic gastrointestinal cancers. Science 2018, 359, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrill, N.M.; Kaffenberger, S.D.; Bao, L.; Vandecan, N.; Goo, L.; Apfel, A.; Cheng, X.; Qin, Z.; Liu, C.J.; Bankhead, A.; et al. Integrative Drug Screening and Multiomic Characterization of Patient-derived Bladder Cancer Organoids Reveal Novel Molecular Correlates of Gemcitabine Response. Eur. Urol. 2024, 86, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morikawa, A.; Li, J.; Ulintz, P.; Cheng, X.; Apfel, A.; Robinson, D.; Hopkins, A.; Kumar-Sinha, C.; Wu, Y.M.; Serhan, H.; et al. Optimizing Precision Medicine for Breast Cancer Brain Metastases with Functional Drug Response Assessment. Cancer Res. Commun. 2023, 3, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morikawa, A.; Merrill, N.; Bao, L.; Cheng, X.; Freedman, R.; Verbal, K.; Heth, J.; Soellner, M.; Merajver, S. Real-time drug testing using patient-derived organoids from resected breast cancer brain metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, e14003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polley, M.Y.; Leung, S.C.; McShane, L.M.; Gao, D.; Hugh, J.C.; Mastropasqua, M.G.; Viale, G.; Zabaglo, L.A.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Bartlett, J.M.; et al. An international Ki67 reproducibility study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 1897–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempus Labs, I. Tempus xR Validation; Tempus.com: Chicago, IL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Shao, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; E, Q.; Wang, W.; Jiang, Z.; Gan, W.; Huang, Y. The generation of glioma organoids and the comparison of two culture methods. Cancer Med. 2024, 13, e7081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Fortune, K.A.; Randolph, M.L.; Wu, H.H.; Cramer, H.M. Improvements in cell block processing: The Cell-Gel method. Cancer Cytopathol. 2017, 125, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MasterTech Automotive. HistoGel™—Specimen Processing Gel Instructions Cancer Diagnostics; MasterTech Inc.: Golden, CO, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Norton, A.J. Microwave oven heating for antigen unmasking in routinely processed tissue sections. J. Pathol. 1993, 171, 79–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, T.; Wang, Z.; Pe’er, D.; Danko, C.G. Cell type and gene expression deconvolution with BayesPrism enables Bayesian integrative analysis across bulk and single-cell RNA sequencing in oncology. Nat. Cancer 2022, 3, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Moreno, C.; Salas, S.M.; Samuelsson, E.; Minaeva, M.; Ibarra, I.; Grillo, M.; Brandner, S.; Roy, A.; Forsberg-Nilsson, K.; Kranendonk, M.E.G.; et al. Charting the Single-Cell and Spatial Landscape of IDH-Wildtype Glioblastoma with GBmap. Neuro-Oncol. 2025, 27, 2281–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, I.; Jiang, L.; Samuelsson, E.R.; Marco Salas, S.; Beck, A.; Hack, O.A.; Jeong, D.; Shaw, M.L.; Englinger, B.; LaBelle, J.; et al. The landscape of tumor cell states and spatial organization in H3-K27M mutant diffuse midline glioma across age and location. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 1881–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, M.; Klinger, B.; Klunemann, M.; Sieber, A.; Uhlitz, F.; Sauer, S.; Garnett, M.J.; Bluthgen, N.; Saez-Rodriguez, J. Perturbation-response genes reveal signaling footprints in cancer gene expression. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.A.; Morgan, P.; Vogel, W.M.; Walker, D.K. The use of C(av) rather than AUC in safety assessment. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 57, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, B.; Pemovska, T.; Szwajda, A.; Kulesskiy, E.; Kontro, M.; Karjalainen, R.; Majumder, M.M.; Malani, D.; Murumagi, A.; Knowles, J.; et al. Quantitative scoring of differential drug sensitivity for individually optimized anticancer therapies. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neftel, C.; Laffy, J.; Filbin, M.G.; Hara, T.; Shore, M.E.; Rahme, G.J.; Richman, A.R.; Silverbush, D.; Shaw, M.L.; Hebert, C.M.; et al. An Integrative Model of Cellular States, Plasticity, and Genetics for Glioblastoma. Cell 2019, 178, 835–849.e821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filbin, M.G.; Tirosh, I.; Hovestadt, V.; Shaw, M.L.; Escalante, L.E.; Mathewson, N.D.; Neftel, C.; Frank, N.; Pelton, K.; Hebert, C.M.; et al. Developmental and oncogenic programs in H3K27M gliomas dissected by single-cell RNA-seq. Science 2018, 360, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, L.E.; Hilz, S.; Grimmer, M.R.; Mazor, T.; Najac, C.; Mukherjee, J.; McKinney, A.; Chow, T.; Pieper, R.O.; Ronen, S.M.; et al. Patient-derived cells from recurrent tumors that model the evolution of IDH-mutant glioma. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2020, 2, vdaa088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, O.; Sergi, Z.; Yu, G.; Yamamoto, K.; Quezado, M.; Abdullaev, Z.; Crooks, D.R.; Kishimoto, S.; Li, Q.; Lu, P.; et al. A patient-derived cell model for malignant transformation in IDH-mutant glioma. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2024, 12, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsalkini, M.; Cibulková, V.; Breun, M.; Kessler, A.F.; Schulz, T.; Cattaneo, A.; Wipplinger, C.; Hübner, J.; Ernestus, R.I.; Nerreter, T.; et al. Cultivating Ex Vivo Patient-Derived Glioma Organoids Using a Tissue Chopper. J. Vis. Exp. 2024, 203, e65952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermelo, I.; Haapala, I.; Makela, M.; Jacome Sanz, D.; Kontunen, A.; Karjalainen, M.; Muller, P.; Lehtimaki, K.; Nykter, M.; Frosen, J.; et al. Patient-derived glioma organoids real time identification of IDH mutation, 1p/19q-codeletion and CDKN2A/B homozygous deletion with differential ion mobility spectrometry. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2025, 171, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, M.; Stupp, R.; Reifenberger, G.; Brandes, A.A.; van den Bent, M.J.; Wick, W.; Hegi, M.E. MGMT promoter methylation in malignant gliomas: Ready for personalized medicine? Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellinghoff, I.K.; van den Bent, M.J.; Blumenthal, D.T.; Touat, M.; Peters, K.B.; Clarke, J.; Mendez, J.; Yust-Katz, S.; Welsh, L.; Mason, W.P.; et al. Vorasidenib in IDH1- or IDH2-Mutant Low-Grade Glioma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellinghoff, I.K.; Ellingson, B.M.; Touat, M.; Maher, E.; De La Fuente, M.I.; Holdhoff, M.; Cote, G.M.; Burris, H.; Janku, F.; Young, R.J.; et al. Ivosidenib in Isocitrate Dehydrogenase 1-Mutated Advanced Glioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3398–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janne, P.A.; Yang, J.C.; Kim, D.W.; Planchard, D.; Ohe, Y.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Ahn, M.J.; Kim, S.W.; Su, W.C.; Horn, L.; et al. AZD9291 in EGFR inhibitor-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, D.P. Extent of Resection of Glioblastoma: A Critical Evaluation in the Molecular Era. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 32, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Liang, H.; Cheng, P.; Yang, H.; Zhao, P. Gross Total vs. Subtotal Resection on Survival Outcomes in Elderly Patients With High-Grade Glioma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallotti, A.L.; Rossi, M.; Conti Nibali, M.; Sciortino, T.; Gay, L.G.; Puglisi, G.; Leonetti, A.; Bruno, F.; Ruda, R.; Soffietti, R.; et al. Neuro-oncological superiority of supratotal resection in lower-grade gliomas. Neuro-Oncol. 2025, 27, 1270–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Greco, M.C.; Milazzotto, R.; Liardo, R.L.E.; Acquaviva, G.; La Rocca, M.; Altieri, R.; Certo, F.; Barbagallo, G.M.; Basile, A.; Foti, P.V.; et al. Relapsing High-Grade Glioma from Peritumoral Zone: Critical Review of Radiotherapy Treatment Options. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalho, M.J.; Andrade, S.; Coelho, M.A.N.; Loureiro, J.A.; Pereira, M.C. Biophysical interaction of temozolomide and its active metabolite with biomembrane models: The relevance of drug-membrane interaction for Glioblastoma Multiforme therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 136, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrenko, D.; Chubarev, V.; Syzrantsev, N.; Ismail, N.; Merkulov, V.; Sologova, S.; Grigorevskikh, E.; Smolyarchuk, E.; Alyautdin, R. Temozolomide Efficacy and Metabolism: The Implicit Relevance of Nanoscale Delivery Systems. Molecules 2022, 27, 3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagley, S.J.; Kothari, S.; Rahman, R.; Lee, E.Q.; Dunn, G.P.; Galanis, E.; Chang, S.M.; Nabors, L.B.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Stupp, R.; et al. Glioblastoma Clinical Trials: Current Landscape and Opportunities for Improvement. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tripathy, A.; Ji, S.; Serhan, H.; Raghunathan, R.C.; Syed, S.; Ravijumar, V.; Shankar, S.; Huang, D.-L.; Alomary, Y.; Haydin, Y.; et al. Precision Oncology for High-Grade Gliomas: A Tumor Organoid Model for Adjuvant Treatment Selection. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101121
Tripathy A, Ji S, Serhan H, Raghunathan RC, Syed S, Ravijumar V, Shankar S, Huang D-L, Alomary Y, Haydin Y, et al. Precision Oncology for High-Grade Gliomas: A Tumor Organoid Model for Adjuvant Treatment Selection. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(10):1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101121
Chicago/Turabian StyleTripathy, Arushi, Sunjong Ji, Habib Serhan, Reka Chakravarthy Raghunathan, Safiulla Syed, Visweswaran Ravijumar, Sunita Shankar, Dah-Luen Huang, Yazen Alomary, Yacoub Haydin, and et al. 2025. "Precision Oncology for High-Grade Gliomas: A Tumor Organoid Model for Adjuvant Treatment Selection" Bioengineering 12, no. 10: 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101121
APA StyleTripathy, A., Ji, S., Serhan, H., Raghunathan, R. C., Syed, S., Ravijumar, V., Shankar, S., Huang, D.-L., Alomary, Y., Haydin, Y., Adam, T., Wink, K., Clarke, N., Koschmann, C., Merrill, N., Hara, T., Merajver, S. D., & Al-Holou, W. N. (2025). Precision Oncology for High-Grade Gliomas: A Tumor Organoid Model for Adjuvant Treatment Selection. Bioengineering, 12(10), 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101121







