Evaluation of Parkinson’s Disease Motor Symptoms via Wearable Inertial Measurements Units and Surface Electromyography Sensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Materials and Methods
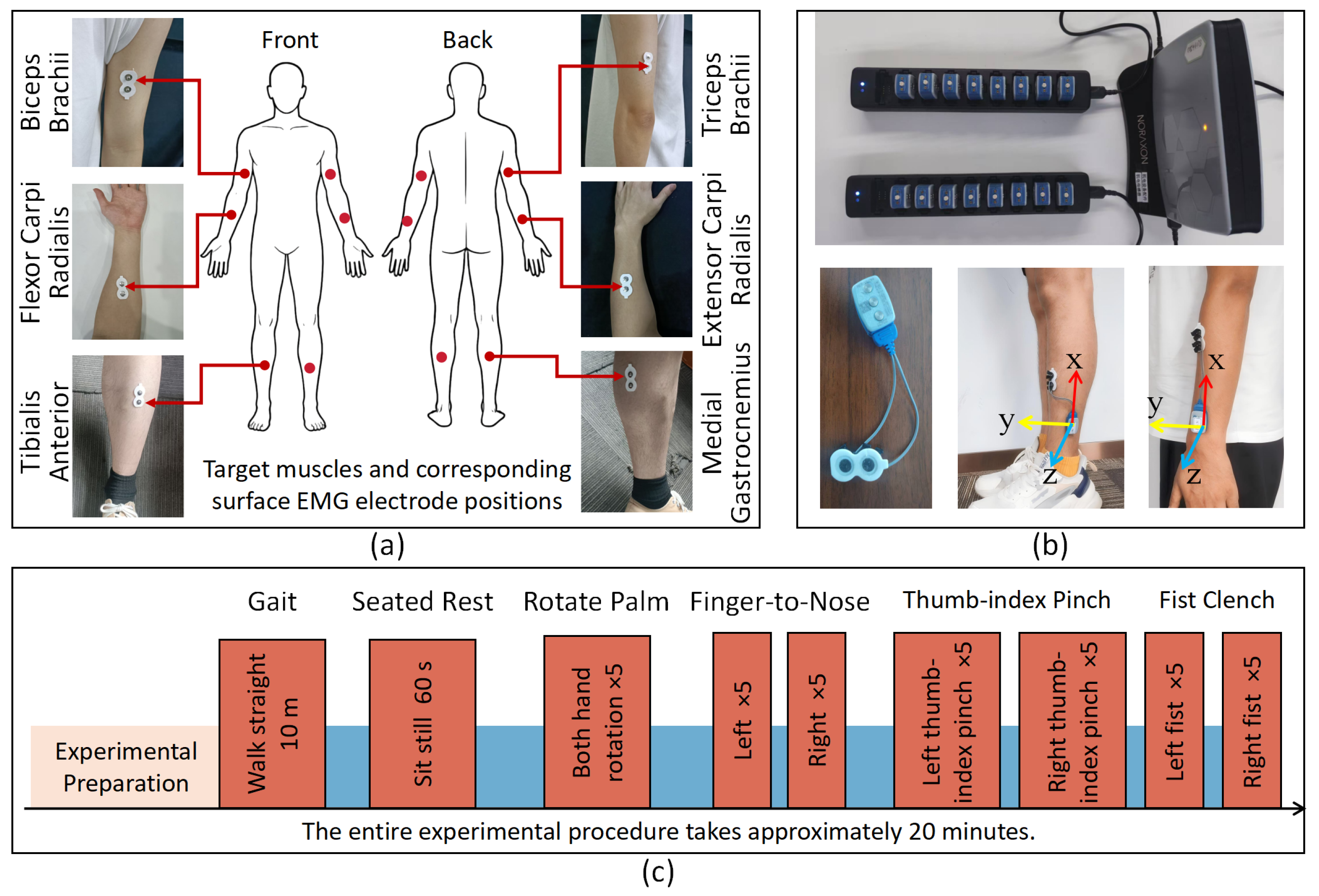
3.1. Participants and Protocols
3.2. Feature Extraction Methods for Multichannel Surface EMG Signals
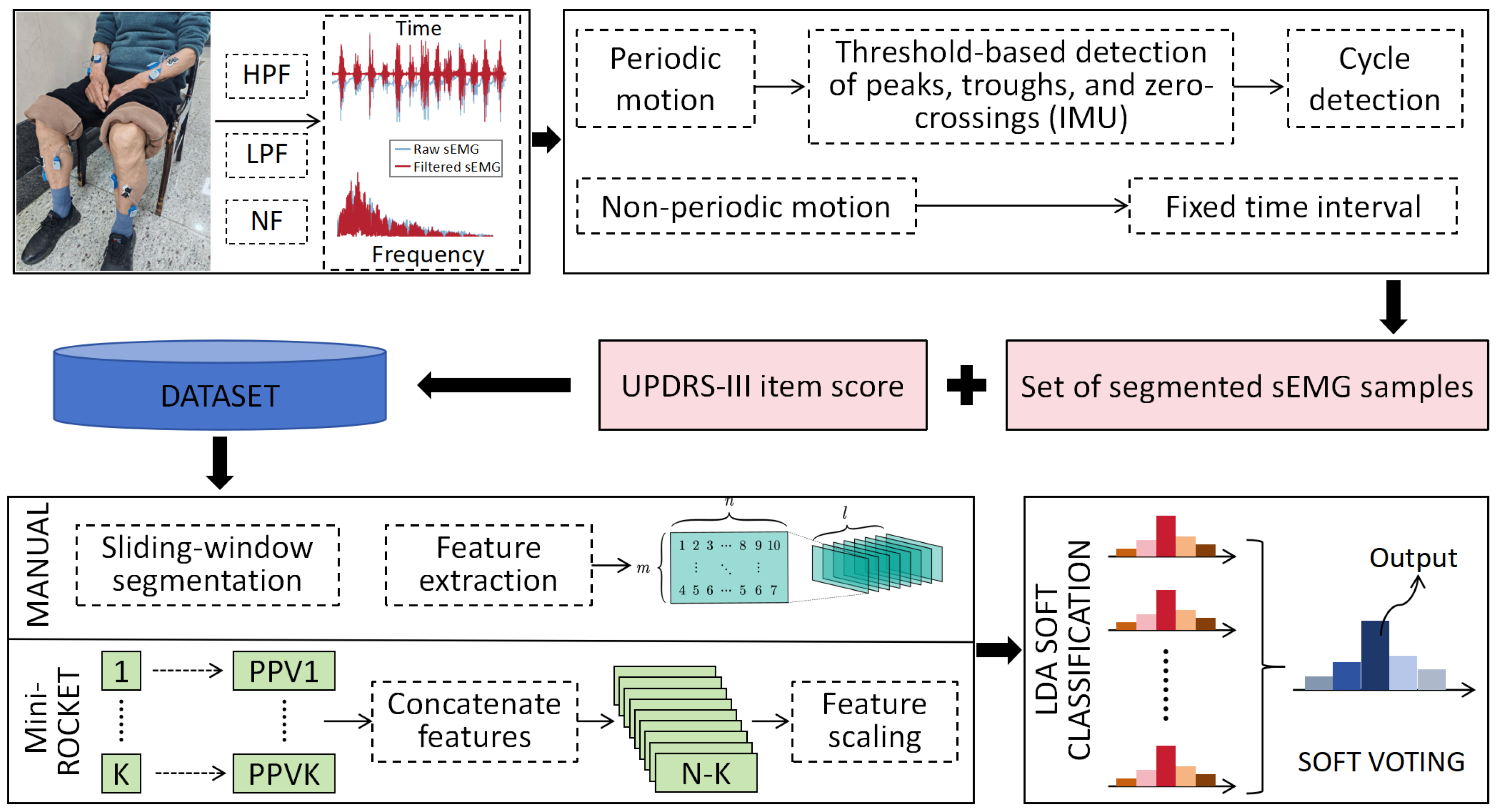
3.2.1. Data Preprocessing
3.2.2. Feature Extraction Methods
3.3. UPDRS Score Prediction Model Based on sEMG Features
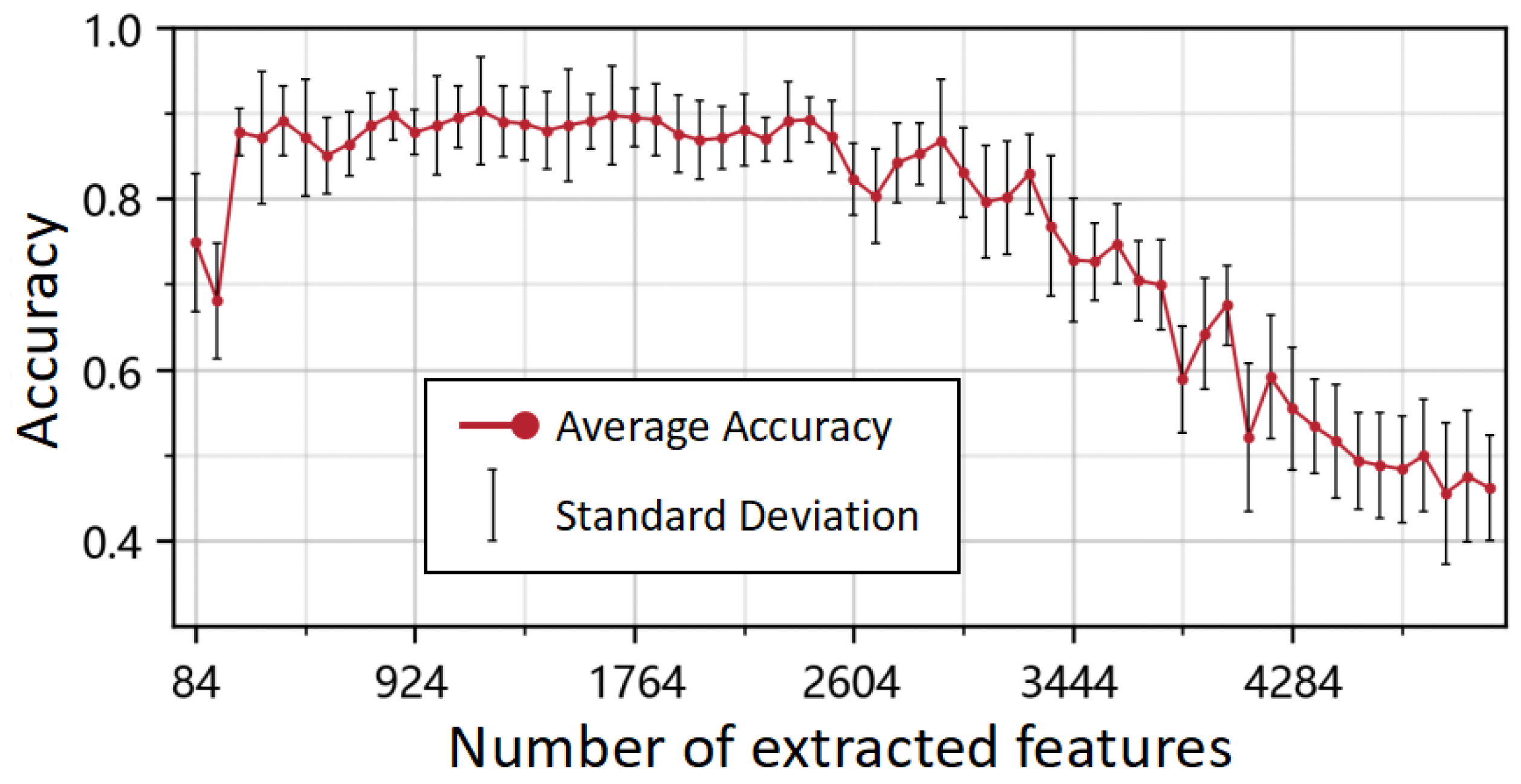
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, J.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yan, R.; Su, D.; Zhao, D.; Wang, A.; Feng, T. Temporal trends in the prevalence of Parkinson’s disease from 1980 to 2023: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2024, 5, e464–e479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Shi, Z.; Ji, Y. Prevalence of Parkinson’s disease in adults aged 65 years and older in China: A multicenter population-based survey. Neuroepidemiology 2022, 56, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloem, B.R.; Okun, M.S.; Klein, C. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 2284–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenganatt, M.A.; Jankovic, J. Parkinson disease subtypes. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, C.G.; Tilley, B.C.; Shaftman, S.R.; Stebbins, G.T.; Fahn, S.; Martinez-Martin, P.; Poewe, W.; Sampaio, C.; Stern, M.B.; Dodel, R.; et al. Movement Disorder Society-sponsored revision of the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS): Scale presentation and clinimetric testing results. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2008, 23, 2129–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Q.C.; Xiong, A.B.; Zhao, X.G.; Han, J.D. Research and Application Review of Motion Intention Recognition Methods Based on Surface Electromyography. Acta Autom. Sin. 2016, 42, 13–25. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xia, W.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, X.; He, K.; Liu, H. Toward portable hybrid surface electromyography/a-mode ultrasound sensing for human–machine interface. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 5219–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Luo, H.; Jia, J.; Yeow, J.T.; Jiang, N. Wrist and finger gesture recognition with single-element ultrasound signals: A comparison with single-channel surface electromyogram. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 66, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchantchane, R.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, S.; Alici, G. A review of hand gesture recognition systems based on noninvasive wearable sensors. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2023, 5, 2300207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, B.; He, Z.; Liu, T. An IMU-based ground reaction force estimation method and its application in walking balance assessment. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2023, 32, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, B.; Liu, T. A potential-real-time thigh orientation prediction method based on two shanks-mounted IMUs and its clinical application. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2022, 21, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Pan, W.; Sun, Y.; Lin, S.; Liu, T. Automated UPDRS Gait Scoring Using Wearable Sensor Fusion and Deep Learning. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Huang, F.; Liu, J.; Zhang, D. A novel posture for better differentiation between Parkinson’s tremor and essential tremor. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisticò, R.; Quattrone, A.; Crasà, M.; De Maria, M.; Vescio, B.; Quattrone, A. Evaluation of rest tremor in different positions in Parkinson’s disease and essential tremor plus. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 43, 3621–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinholdermann, U.; Wullstein, M.; Pedrosa, D. Prediction of motor Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale scores in patients with Parkinson’s disease using surface electromyography. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2021, 132, 1708–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adem, H.M.; Tessema, A.W.; Simegn, G.L. Classification of Parkinson’s disease using EMG signals from different upper limb movements based on multiclass support vector machine. Int. J. Bioautom. 2022, 26, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rissanen, S.M.; Koivu, M.; Hartikainen, P.; Pekkonen, E. Ambulatory surface electromyography with accelerometry for evaluating daily motor fluctuations in Parkinson’s disease. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2021, 132, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovini, E.; Maremmani, C.; Cavallo, F. How wearable sensors can support Parkinson’s disease diagnosis and treatment: A systematic review. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, C.; Alizadeh, J.; Zakhary, N.; Woost, T.B.; Bogdan, M.; Classen, J. Evaluation of three machine learning algorithms for the automatic classification of EMG patterns in gait disorders. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 666458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nardo, F.; Romanato, M.; Spolaor, F.; Volpe, D.; Fioretti, S.; Sawacha, Z. Simplified Muscle-Recruitment Strategy During Walking in Parkinson’s Disease People: A Time-Frequency Analysis of EMG Signal. IRBM 2023, 44, 100798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanato, M.; Piatkowska, W.; Spolaor, F.; To, D.K.; Volpe, D.; Sawacha, Z. Different perspectives in understanding muscle functions in Parkinson’s disease through surface electromyography: Exploring multiple activation patterns. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2022, 64, 102658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, Z.; Li, H.; Huang, D.; Wang, L.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ma, L.; Feng, H.; Pan, J.; et al. Multimodal data for the detection of freezing of gait in Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, A.; Li, J.; Contag, C.H.; Currano, L.J.; Pyles, C.O.; Hinkle, D.A.; Patil, V.S. Wearable surface electromyography system to predict freeze of gait in Parkinson’s disease patients. Sensors 2024, 24, 7853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.C.; Jiao, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, X.W. The role of surface electromyography in the assessment of myotonia in Parkinson’s disease. Chin. J. Contemp. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2024, 24, 158. [Google Scholar]
- Meigal, A.; Gerasimova-Meigal, L.; Kuzmina, A.; Antonen, E.; Peskova, A.; Burkin, M. Electromyographic characteristics of postactivation effect in dopamine-dependent spectrum models observed in Parkinson’s disease and schizophrenia. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sushkova, O.S.; Morozov, A.A.; Gabova, A.V.; Karabanov, A.V. Investigation of surface EMG and acceleration signals of limbs’ tremor in Parkinson’s disease patients using the method of electrical activity analysis based on wave trains. In Proceedings of the Ibero-American Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Trujillo, Peru, 13–16 November 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 253–264. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.M.; Tsai, C.H.; Lu, M.K.; Tseng, H.C.; Lu, G.; Liu, B.L.; Lin, H.C. The neuromuscular responses in patients with Parkinson’s disease under different conditions during whole-body vibration training. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2022, 22, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vescio, B.; Nisticò, R.; Augimeri, A.; Quattrone, A.; Crasà, M.; Quattrone, A. Development and validation of a new wearable mobile device for the automated detection of resting tremor in Parkinson’s disease and essential tremor. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee, K.; Savarkar, S.; Yu, X.; Zhang, J. A hybrid deep transfer learning-based approach for Parkinson’s disease classification in surface electromyography signals. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 71, 103161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Qiao, Z.; Han, L.; Zhang, X. EEG-based emotion recognition with autoencoder feature fusion and MSC-TimesNet model. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2025, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnall, A.; Davis, L.; Hills, J.; Lines, J. Transformation based ensembles for time series classification. In Proceedings of the 2012 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining, Anaheim, CA, USA, 26–28 April 2012; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012; pp. 307–318. [Google Scholar]
- Middlehurst, M.; Large, J.; Flynn, M.; Lines, J.; Bostrom, A.; Bagnall, A. HIVE-COTE 2.0: A new meta ensemble for time series classification. Mach. Learn. 2021, 110, 3211–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middlehurst, M.; Large, J.; Bagnall, A. The canonical interval forest (CIF) classifier for time series classification. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Atlanta, GA, USA, 10–13 December 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 188–195. [Google Scholar]
- Dempster, A.; Petitjean, F.; Webb, G.I. ROCKET: Exceptionally fast and accurate time series classification using random convolutional kernels. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2020, 34, 1454–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempster, A.; Schmidt, D.F.; Webb, G.I. Minirocket: A very fast (almost) deterministic transform for time series classification. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, Singapore, 14–18 August 2021; pp. 248–257. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail Fawaz, H.; Lucas, B.; Forestier, G.; Pelletier, C.; Schmidt, D.F.; Weber, J.; Webb, G.I.; Idoumghar, L.; Muller, P.A.; Petitjean, F. Inceptiontime: Finding alexnet for time series classification. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2020, 34, 1936–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dau, H.A.; Keogh, E.; Kamgar, K.; Yeh, C.M.; Zhu, Y.; Gharghabi, S.; Ratanamahatana, C.A.; Chen, Y.; Hu, B.; Begum, N.; et al. The UCR Time Series Classification Archive. 2018. Available online: https://www.cs.ucr.edu/~eamonn/time_series_data_2018/ (accessed on 23 August 2025).
- Bagnall, A.; Dau, H.A.; Lines, J.; Flynn, M.; Large, J.; Bostrom, A.; Southam, P.; Keogh, E. The UEA multivariate time series classification archive. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.00075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, H.R.; Kobravi, H.; Homam, M. Quantification of Parkinson tremor intensity based on EMG signal analysis using fast orthogonal search algorithm. Iran. J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2018, 14, 106–115. [Google Scholar]
- Stocchi, F.; Bravi, D.; Emmi, A.; Antonini, A. Parkinson disease therapy: Current strategies and future research priorities. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2024, 20, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.O.; Jog, M.; Lee, J.; Jabbari, B. Novel botulinum toxin injection protocols for parkinson tremor and essential tremor–the yale technique and sensor-based kinematics procedure for safe and effective treatment. Tremor Other Hyperkinetic Mov. 2020, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminian, K.; Najafi, B.; Büla, C.; Leyvraz, P.F.; Robert, P. Spatio-temporal parameters of gait measured by an ambulatory system using miniature gyroscopes. J. Biomech. 2002, 35, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Cai, G.; Lin, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ye, Q. Validation of inertial sensing-based wearable device for tremor and bradykinesia quantification. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 25, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanato, M.; Volpe, D.; Guiotto, A.; Spolaor, F.; Sartori, M.; Sawacha, Z. Electromyography-informed modeling for estimating muscle activation and force alterations in Parkinson’s disease. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 25, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Task | CNN (%) | LSTM (%) | InceptionTime (%) | OUR (%) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acc | Prec | Rec | F1 | Acc | Prec | Rec | F1 | Acc | Prec | Rec | F1 | Acc | Prec | Rec | F1 | |
| TR | 90.48 | 81.95 | 90.48 | 85.98 | 90.48 | 91.48 | 90.48 | 89.15 | 95.24 | 96.83 | 95.24 | 94.92 | 95.24 | 95.50 | 95.24 | 94.51 |
| AT | 76.92 | 77.89 | 76.92 | 76.92 | 80.77 | 77.88 | 80.77 | 79.26 | 88.46 | 88.63 | 88.46 | 88.40 | 96.15 | 92.58 | 96.15 | 94.30 |
| RG | 70.59 | 69.16 | 70.59 | 68.29 | 76.47 | 73.28 | 76.47 | 74.25 | 82.35 | 87.39 | 82.35 | 84.71 | 76.47 | 71.90 | 76.47 | 74.05 |
| FT | 84.21 | 83.68 | 84.21 | 82.38 | 89.47 | 91.39 | 89.47 | 89.25 | 84.21 | 86.09 | 84.21 | 84.56 | 94.74 | 90.06 | 94.74 | 92.26 |
| HM | 76.00 | 76.97 | 76.00 | 75.88 | 88.00 | 88.39 | 88.00 | 88.05 | 92.00 | 93.33 | 92.00 | 92.03 | 96.00 | 96.29 | 96.00 | 95.41 |
| RAM | 81.25 | 88.28 | 81.25 | 81.75 | 75.00 | 82.29 | 75.00 | 77.37 | 81.25 | 87.95 | 81.25 | 79.97 | 81.25 | 83.33 | 81.25 | 81.57 |
| LA | 81.63 | 85.48 | 81.63 | 77.84 | 89.80 | 90.49 | 89.80 | 89.67 | 95.92 | 97.96 | 95.92 | 96.43 | 97.96 | 98.02 | 97.96 | 97.93 |
| AC | 77.55 | 84.02 | 77.55 | 73.27 | 85.71 | 84.52 | 85.71 | 84.84 | 93.88 | 94.01 | 93.88 | 93.88 | 95.92 | 96.05 | 95.92 | 95.91 |
| PO | 70.59 | 70.38 | 70.59 | 70.03 | 70.59 | 72.55 | 70.59 | 70.87 | 76.47 | 76.76 | 76.47 | 76.09 | 76.47 | 79.46 | 76.47 | 74.73 |
| GA | 87.76 | 88.78 | 87.76 | 86.72 | 87.76 | 87.76 | 87.76 | 87.76 | 93.88 | 94.90 | 93.88 | 93.99 | 95.92 | 96.05 | 95.92 | 95.84 |
| PS | 89.47 | 91.58 | 89.47 | 89.47 | 84.21 | 84.80 | 84.21 | 84.26 | 94.74 | 90.06 | 94.74 | 92.26 | 94.74 | 95.32 | 94.74 | 94.75 |
| BBM | 81.25 | 81.99 | 81.25 | 81.25 | 75.00 | 77.19 | 75.00 | 74.70 | 81.25 | 81.56 | 81.25 | 81.02 | 81.25 | 83.82 | 81.25 | 79.05 |
| Compare | Task | ΔAcc | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔAcc | CI_Low | CI_High | |||||
| Our vs. CNN | TR | 4.76 | −4.52 | 4.76 | 1.0000 | 100.00 | 3.664 |
| AT | 19.23 | −4.24 | 26.73 | 0.1250 | 85.71 | 0.000 | |
| RG | 5.88 | −14.32 | 17.35 | 1.0000 | 66.67 | 2.373 | |
| FT | 10.53 | −12.88 | 20.79 | 0.6250 | 75.00 | 0.389 | |
| HM | 20.00 | −4.41 | 27.80 | 0.1250 | 85.71 | −0.053 | |
| RAM | 0.00 | −12.19 | 12.19 | 1.0000 | 50.00 | 2.631 | |
| LA | 16.33 | 4.26 | 16.33 | 0.0078 | 100.00 | 2.660 | |
| AC | 18.37 | 3.92 | 22.35 | 0.0117 | 90.91 | 1.273 | |
| PO | 5.88 | −26.02 | 33.02 | 1.0000 | 57.14 | −0.100 | |
| GA | 8.16 | −3.46 | 12.14 | 0.2188 | 83.33 | 2.045 | |
| PS | 5.26 | −5.00 | 5.26 | 1.0000 | 100.00 | 3.555 | |
| BBM | 0.00 | −28.64 | 28.64 | 1.0000 | 50.00 | −0.847 | |
| Our vs. LSTM | TR | 4.76 | −11.59 | 14.05 | 1.0000 | 66.67 | 0.903 |
| AT | 15.38 | −6.52 | 22.88 | 0.2188 | 83.33 | 0.217 | |
| RG | 0.00 | −11.47 | 11.47 | 1.0000 | 50.00 | 2.968 | |
| FT | 5.26 | −12.81 | 15.52 | 1.0000 | 66.67 | 0.788 | |
| HM | 8.00 | −9.79 | 15.80 | 0.6250 | 75.00 | 0.717 | |
| RAM | 6.25 | −27.65 | 35.09 | 1.0000 | 57.14 | −1.199 | |
| LA | 8.16 | −3.46 | 12.14 | 0.2188 | 83.33 | 0.969 | |
| AC | 10.20 | −2.25 | 14.18 | 0.1250 | 85.71 | 1.854 | |
| PO | 5.88 | −20.79 | 26.31 | 1.0000 | 60.00 | 1.099 | |
| GA | 8.16 | −3.46 | 12.14 | 0.2188 | 83.33 | 2.045 | |
| PS | 10.53 | −7.20 | 10.53 | 0.5000 | 100.00 | 2.986 | |
| BBM | 6.25 | −27.65 | 35.09 | 1.0000 | 57.14 | −1.199 | |
| Our vs. InceptionTime | TR | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.0000 | 50.00 | 4.812 |
| AT | 7.69 | −9.41 | 15.19 | 0.6250 | 75.00 | 0.762 | |
| RG | −5.88 | −17.35 | 14.32 | 1.0000 | 33.33 | 2.120 | |
| FT | 10.53 | −12.88 | 20.79 | 0.6250 | 75.00 | 0.389 | |
| HM | 4.00 | −9.74 | 11.80 | 1.0000 | 66.67 | 1.099 | |
| RAM | 0.00 | −28.64 | 28.64 | 1.0000 | 50.00 | −0.847 | |
| LA | 2.04 | −1.94 | 2.04 | 1.0000 | 100.00 | 4.554 | |
| AC | 2.04 | −7.21 | 9.13 | 1.0000 | 60.00 | 0.933 | |
| PO | 0.00 | −20.35 | 20.35 | 1.0000 | 50.00 | 1.526 | |
| GA | 2.04 | −7.21 | 9.13 | 1.0000 | 60.00 | 0.933 | |
| PS | 0.00 | −10.26 | 10.26 | 1.0000 | 50.00 | 1.358 | |
| BBM | 0.00 | −28.64 | 28.64 | 1.0000 | 50.00 | −0.847 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Pan, W.; Wu, Z.; Liu, X.; Sun, Y.; Fan, B.; Cai, M.; Li, T.; Liu, T. Evaluation of Parkinson’s Disease Motor Symptoms via Wearable Inertial Measurements Units and Surface Electromyography Sensors. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101116
Zhang X, Pan W, Wu Z, Liu X, Sun Y, Fan B, Cai M, Li T, Liu T. Evaluation of Parkinson’s Disease Motor Symptoms via Wearable Inertial Measurements Units and Surface Electromyography Sensors. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(10):1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101116
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiangliang, Wenhao Pan, Zhuoneng Wu, Xiangzhi Liu, Yiping Sun, Bingfei Fan, Miao Cai, Tong Li, and Tao Liu. 2025. "Evaluation of Parkinson’s Disease Motor Symptoms via Wearable Inertial Measurements Units and Surface Electromyography Sensors" Bioengineering 12, no. 10: 1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101116
APA StyleZhang, X., Pan, W., Wu, Z., Liu, X., Sun, Y., Fan, B., Cai, M., Li, T., & Liu, T. (2025). Evaluation of Parkinson’s Disease Motor Symptoms via Wearable Inertial Measurements Units and Surface Electromyography Sensors. Bioengineering, 12(10), 1116. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101116







