A Coarse-to-Fine Framework with Curvature Feature Learning for Robust Point Cloud Registration in Spinal Surgical Navigation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A novel and robust coarse-to-fine registration framework has been proposed to address significant initial pose differences, low overlapping ratio, and noise interference issues.
- A novel Curvature Feature Learning-based Point Matching (CFL-PM) algorithm based on a curvature feature coder and graph attention network is proposed. The algorithm effectively generates more reliable correspondences for coarse registration and shows strong anti-interference ability against noise.
- A challenging dataset consisting of cross-source, low-overlapping pre- and intra-operative point cloud pairs to simulate real surgical environments. The noise-free conditions simulate an ideal surgical scenario, while noisy conditions simulate various noises present in the surgical field, such as soft tissues and blood. The results verified the feasibility and robustness of the proposed algorithm in the surgical navigation system.
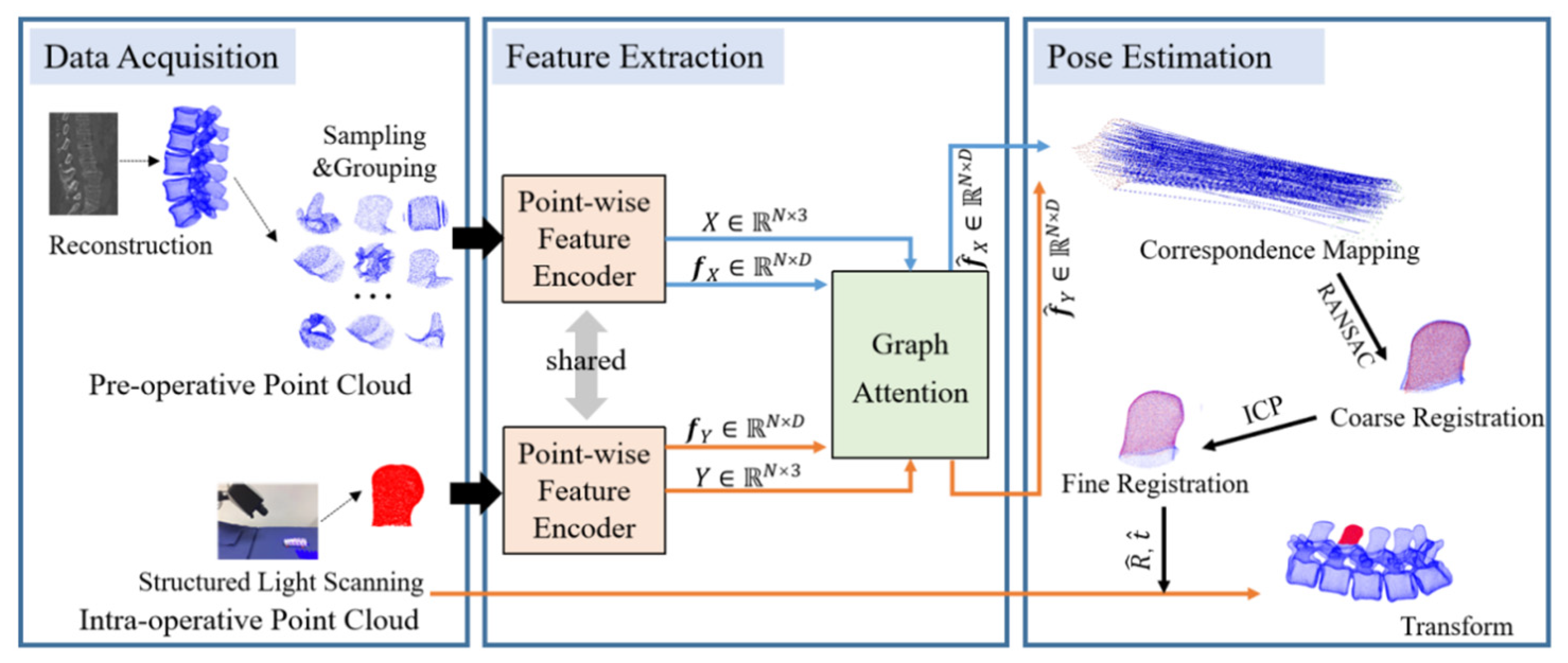
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Curvature Feature Encoder
2.2. Correspondence Identification and Transformation Matrix Estimation
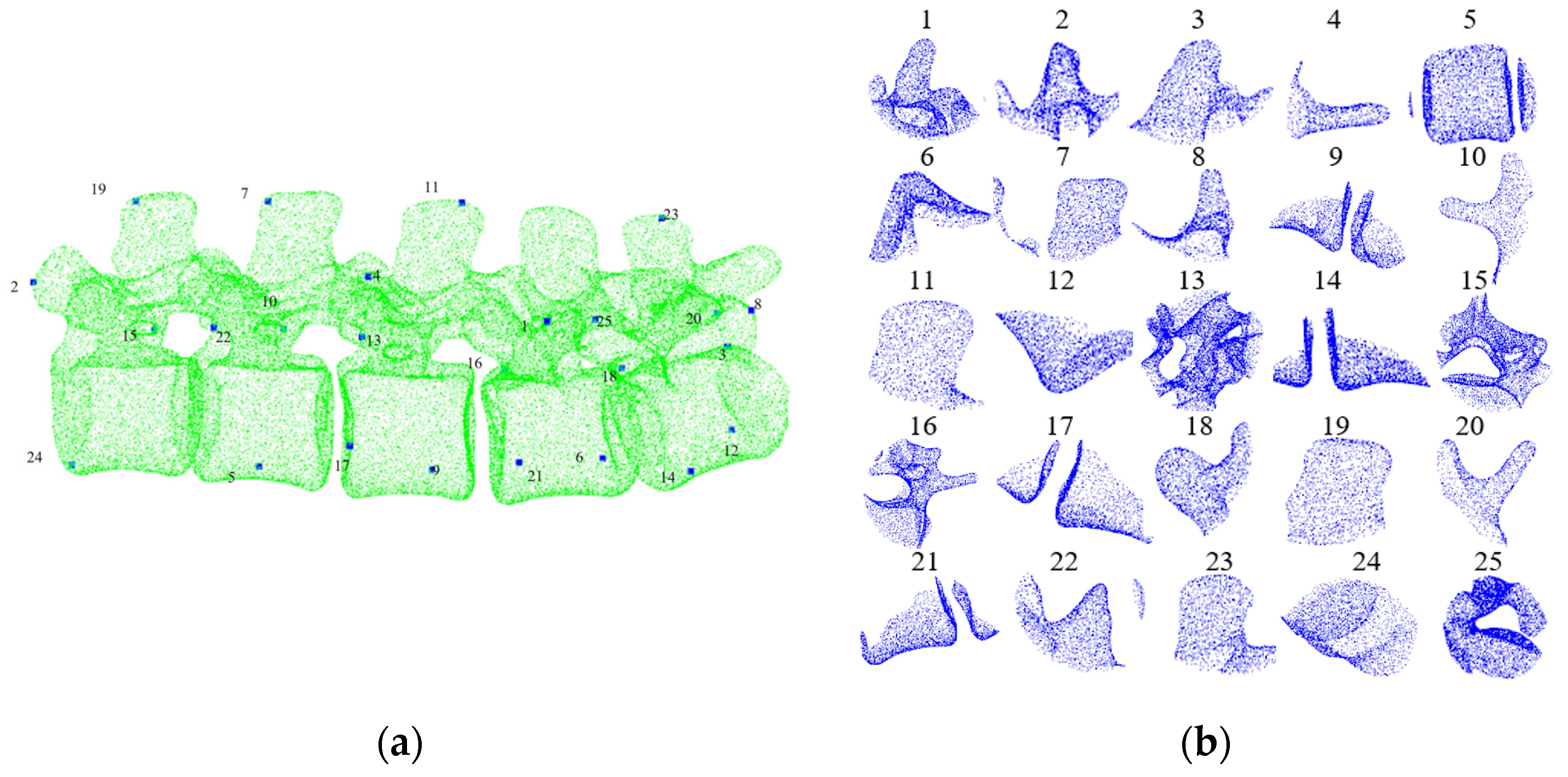
2.3. Pre- and Intra-Operative Registration of Cross-Source and Low Overlapping Ratio Point Clouds
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation Metrics
3.2. Model Training and Testing
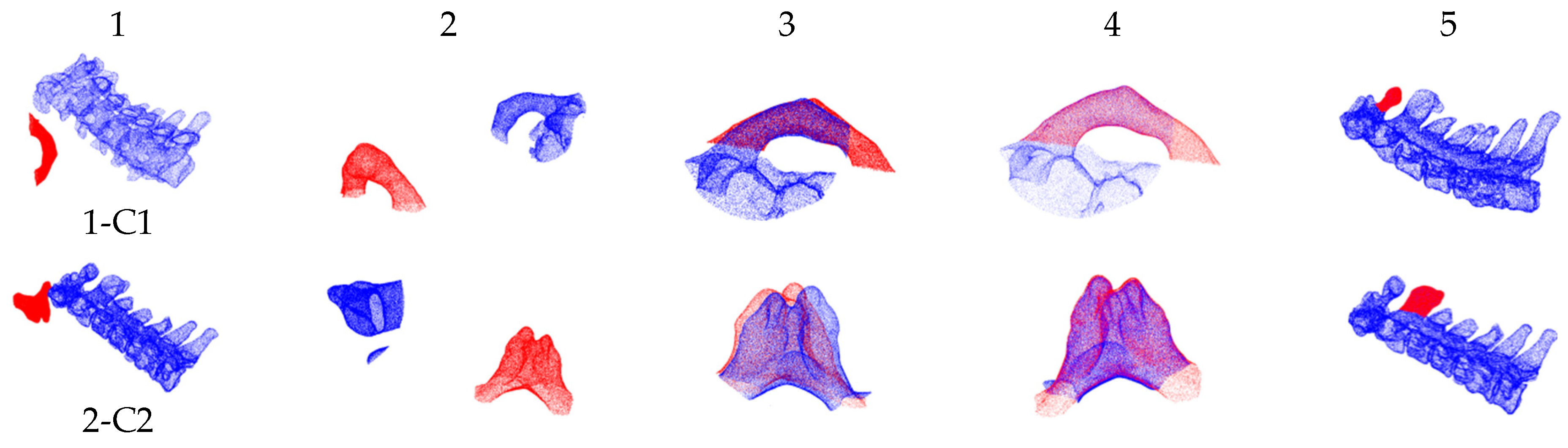
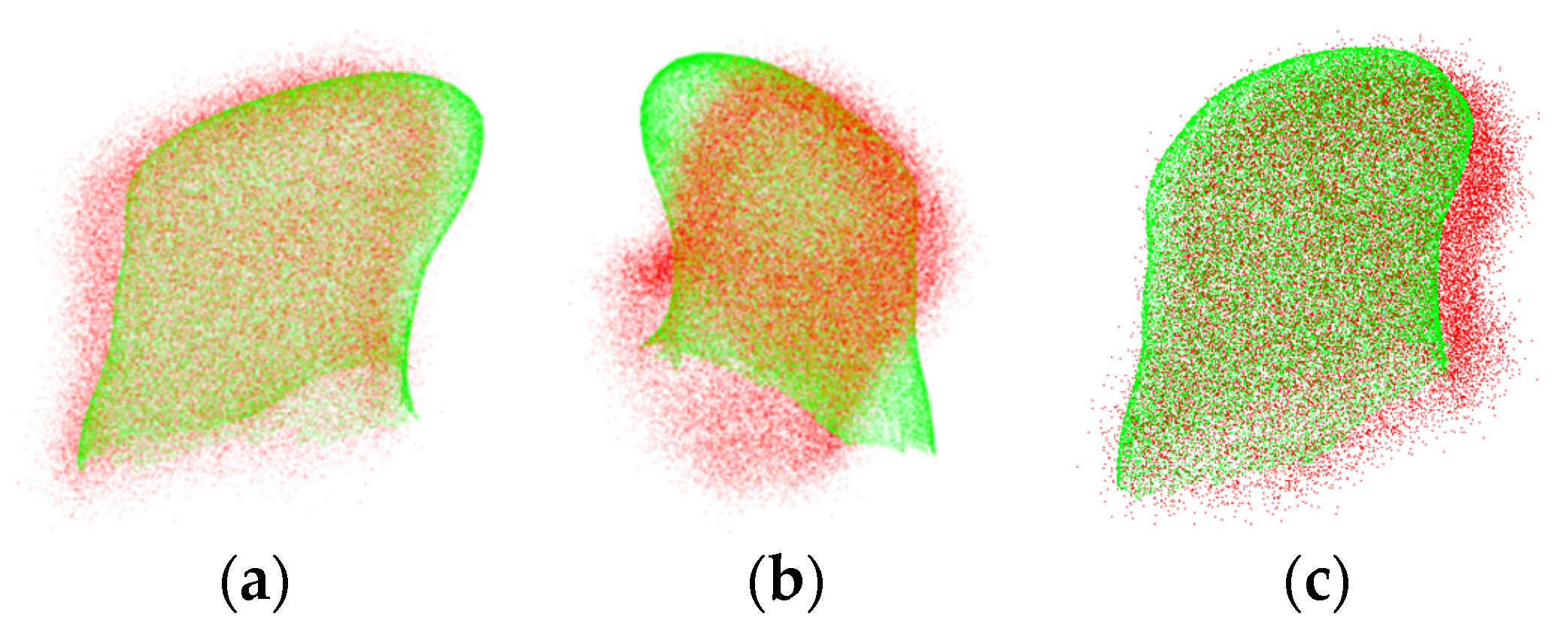
3.3. Experiment on Pre- and Intra-Operative Registration of Cross-Source and Low Overlapping Ratio Point Clouds
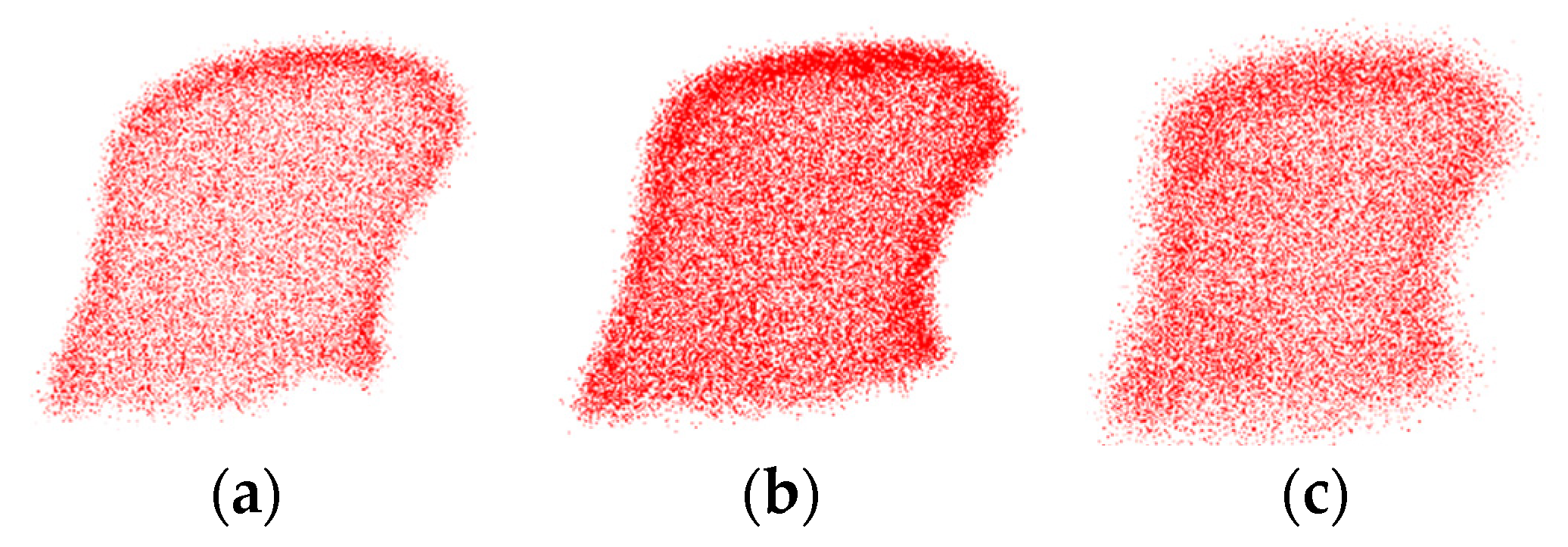
3.4. Robustness Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, K.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, B.; He, D.; Liu, Y.J.; Tian, W. The Clinical Application of Tianji II Robot-assisted Pedicle Screw Internal Fixation for Thoracolumbar Spine. Beijing Biomed. Eng. 2022, 41, 297–301. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A.D.; Teague, A.J.; Naik, A.; Janbahan, M.; Smith, E.J.; Krist, D.T.; Parupalli, S.; Teal, K.; Hassaneen, W. Robotic External Ventricular Drain Placement for Acute Neurosurgical Care in Low-Resource Settings: Feasibility Considerations and a Prototype Design. Neurosurg. Focus 2022, 52, E14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Liu, P.; Xiong, C.; Li, C.; Zhang, F.; Shen, S.; Shao, P.; Yao, P.; Niu, C.; Xu, R. Stereotactic Co-Axial Projection Imaging for Augmented Reality Neuro-navigation: A Proof-Of-Concept Study. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2022, 12, 3792–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Jiang, S.; Yang, Z.Y.; Yang, S.; Zhou, Z.Y. Microscopic augmented reality calibration with contactless line-structured light registration for surgical navigation. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2025, 63, 1463–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, P.X.; Qin, C.X.; Guo, Y.; Li, D.Y.; Lungu, A.J.; Wang, H.X. Ultrasound Image Guided and Mixed Reality-Based Surgical System with Real-Time Soft Tissue Deformation Computing for Robotic Cervical Pedicle Screw Placement. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 69, 2593–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hsieh, C.; Hsu, W.; Tseng, C.; Chang, C. Two-Dimensional C-arm Robotic Navigation System (i-Navi) in Spine Surgery: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2022, 17, 2281–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Wang, M. A 3D Image Registration Method for Laparoscopic Liver Surgery Navigation. Electronics 2022, 11, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Otoo, E.M.; Fan, Y.B.; Tao, C.J.; Wang, T.M.; Rhode, K. Autostereoscopic 3D Augmented Reality Navigation for Laparoscopic Surgery: A Preliminary Assessment. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 70, 1413–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharjan, N.; Alsadoon, A.; Prasad, P.; Abdullah, S.; Rashid, T.A. A Novel Visualization System of Using Augmented Reality in Knee Replacement Surgery: Enhanced Bidirectional Maximum Correntropy Algorithm. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2021, 17, e2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadat, S.; Perriman, D.; Scarvell, L.M.; Smith, P.N.; Galvin, C.R.; Lynch, J.; Pickering, M.R. An Efficient Hybrid Method for 3D to 2D Medical Image Registration. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2022, 17, 1313–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Shao, L.J.; Wu, J.Y.; Xu, X.F.; Chen, X.R.; Zhang, S.L. LL-MAROCO: A Large Language Model-Assisted Robotic System for Oral and Craniomaxillofacial Osteotomy. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aukema, L.M.N.; Geer, A.F.D.; Alphen, M.J.A.; Schreuder, W.H.; Veen, R.L.P.; Ruers, T.J.M.; Siepel, F.J.; Karakullukcu, M.B. Hybrid registration of the fibula for electromagnetically navigated osteotomies in mandibular reconstructive surgery: A phantom study. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2025, 20, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.S.; Wu, B.; Ye, C.; Wang, Y.; Duan, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, N. Multiple Instruments Motion Trajectory Tracking in Optical Surgical Navigation. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 15827–15845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Kowal, J.; González Ballester, M.A.; Caversaccio, M.; Nolte, L. Registration Techniques for Computer Navigation. Curr. Orthop. 2007, 21, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.; Sim, T. Automated Machine Learning (AutoML)-Based Surface Registration Methodology for Image-Guided Surgical Navigation System. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 4845–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.K.; Fu, Z.Y.; Zhang, D.B.; Wang, G.Q.; Zhang, C.; Xie, X. A Registration Method for Total Knee Arthroplasty Surgical Robot. In Proceedings of the IEEE 6th Information Technology and Mechatronics Engineering Conference (ITOEC), Chongqing, China, 4–6 March 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.; Choi, A.; Mun, J.H. Deep Learning-Based Fine-Tuning Approach of Coarse Registration for Ear-Nose-Throat (ENT) Surgical Navigation Systems. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Sun, W.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y. Coarse Registration of Point Clouds with Low Overlap Rate On Feature Regions. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2021, 98, 116428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, B.; Kang, J. Registration of 3D Point Clouds Using a Local Descriptor Based On Grid Point Normal. Appl. Opt. 2021, 60, 8818–8828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.R.; Xu, J.B.; Zou, Y.N.; Liu, P.X. A Point Cloud Registration Method Based on Segmenting Sphere Region Feature Descriptor and Overlapping Region Matching Strategy. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 38387–38401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.Q.; Zhang, L.J.; Wang, W.; Wu, B. Preoperative and Intra-operative Point Cloud Registration Algorithm Based on SHOT and Symmetric ICP with Objective Function for Low Overlap Rates. Beijing Biomed. Eng. 2023, 42, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.J.; Wang, B.B.; Wang, W.; Wu, B.; Zhang, N. Point Cloud Registration Algorithm with Cross-Source and Low Overlapping Ratio for Pedicle Screw Fixation. Chin. J. Lasers 2023, 50, 0907108. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.; Yang, X.; Hao, J.; Luo, H.L.; Mei, G.H.; Jia, F.C. Preoperative and Intraoperative Laparoscopic Liver Surface Registration Using Deep Graph Matching of Representative Overlapping Points. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2025, 20, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Sun, J.D.; Dai, Y.C.; Fan, B.; He, M.Y. VRNet: Learning the Rectified Virtual Corresponding Points for 3D Point Cloud Registration. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 4997–5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.X.; Cai, Y.Y.; Davoodi, A.; Borghesan, G.; Vander Poorten, E. 3D Ultrasound Shape Completion and Anatomical Feature Detection for Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.P.; Yang, B.; Ye, H.L.; Cao, F.L. Two-view Point Cloud Registration Network: Feature and Geometry. Appl. Intell. 2024, 54, 3135–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Gojcic, Z.; Usvyatsov, M.; Wieser, A.; Schindler, K. PREDATOR: Registration of 3D Point Clouds with Low Overlap. In Proceedings of the 2021 Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, G.; Wang, X.; Wu, H. Sparse and Low-Overlapping Point Cloud Registration Network for Indoor Building Environments. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2021, 35, 402006901–402006913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Li, X.; Jiang, W. SCANet: A Spatial and Channel Attention based Network for Partial-to-Partial Point Cloud Registration. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2021, 151, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. A Two-Stage Correspondence-Free Algorithm for Partially Overlapping Point Cloud Registration. Sensors 2022, 22, 5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, E.; Mozaffari, S.; Dianati, M. Fast and Robust Registration of Partially Overlapping Point Clouds. IEEE Robtics Autom. Lett. 2021, 7, 1502–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.R.; Yi, L.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet++: Deep Hierarchical Feature Learning on Point Sets in a Metric Space. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Y.W.; Xiao, C.X.; Zhou, M.H.; Peng, Q.S. Estimation of Principal Curvatures and Principal Normals in Point Sampled Surfaces. In Proceedings of the Second National Conference on Geometric Design and Computing, Huangshan, China, 15–18 April 2005. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Yang, J.; Hou, X.; Pang, S.Y.; Chen, J. ICP Registration with DCA Descriptor for 3D Point Clouds. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 20423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Grossman, J.C. Crystal Graph Convolutional Neural Networks for an Accurate and Interpretable Prediction of Material Properties. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 145301.1–145301.6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, F.; Ebadi, H.; Pfeifer, N.; Sedaghat, A. Uniform and Competency-Based 3D Keypoint Detection for Coarse Registration of Point Clouds with Homogeneous Structure. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, R.B.; Blodow, N.; Beetz, M. Fast Point Feature Histograms (FPFH) for 3D Registration. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Kobe, Japan, 12–17 May 2009; pp. 3212–3217. [Google Scholar]
- Salti, S.; Tombari, F.; Stefano, L.D. SHOT: Unique Signatures of Histograms for Surface and Texture Description. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2014, 125, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, M.S.; Ali, A.; Rara, H.; Arnold, B.; Farag, A.A.; Fahmi, R.; Xiang, P. A Novel 3D Segmentation of Vertebral Bones from Volumetric CT Images Using Graph Cuts. In Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Advances in Visual Computing (ISVC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 30 November–2 December 2009; pp. 519–528. [Google Scholar]
- Aslan, M.S.; Shalaby, A.; Farag, A.A. Clinically Desired Segmentation Method for Vertebral Bodies. In Proceedings of the IEEE 10th International Symposlum on Biomedical Imaging, San Francisco, CA, USA, 7–11 April 2013; pp. 840–843. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.; Yang, B.; Liang, F.; Huang, R.; Scherer, S. Hierarchical Registration of Unordered TLS Point Clouds Based on Binary Shape Context Descriptor. J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 144, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, C.; Marconi, E.; Riva, M.; Ekanayake, J.; Elson, D.S.; Rodriguez y Baena, F. Towards Markerless Intraoperative Tracking of Deformable Spine Tissue. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI, Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 23–27 September 2025; Volume 15968, pp. 627–637. [Google Scholar]




| Data | Exposed Site | Overlapping Ratio (%) | Rotation Angles (°) | Relative Distances (mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y | Z | X | Y | Z | |||
| 1 | C1 | 2.04 | −93.94 | −83.85 | 150.77 | 3.63 | 21.99 | −31.57 |
| 2 | C2 | 1.98 | 78.07 | −51.48 | 10.12 | −48.17 | 60.95 | 37.35 |
| 3 | C2–C3 | 4.27 | −169.52 | −55.43 | −136.57 | 5.81 | 6.19 | 33.71 |
| 4 | L1 | 1.35 | −76.59 | 68.13 | −88.32 | −98.28 | −59.36 | 26.07 |
| 5 | L1 | 1.66 | 89.39 | 58.15 | 82.35 | −57.78 | −42.73 | 38.71 |
| 6 | L1 | 1.67 | 96.94 | 22.41 | 82.55 | −89.11 | 45.34 | 42.65 |
| 7 | L1 | 1.79 | 80.76 | −62.50 | −48.06 | −52.53 | 110.76 | −86.79 |
| 8 | L2 | 1.53 | 89.98 | −73.34 | −78.47 | 6.99 | 102.23 | 0.95 |
| 9 | L2 | 1.69 | 148.53 | 48.47 | 138.47 | 114.08 | −64.99 | −103.52 |
| 10 | L3 | 1.85 | 161.82 | −83.28 | −116.87 | −4.17 | −83.28 | −91.19 |
| 11 | L3 | 2.29 | 109.48 | 28.19 | 79.30 | −55.67 | 7.23 | 40.84 |
| Data | Exposed Site | Algorithm | Coarse Registration | Fine Registration | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (°) | (mm) | Time (s) | (°) | (mm) | Time (s) | |||
| 1 | C1 | [37] + ICP | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| [38] + ICP | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| [22] | 23.75 | 29.42 | 102.95 | / | / | / | ||
| Proposed | 10.11 | 19.04 | 8.11 | 0.43 | 0.37 | 0.33 | ||
| 2 | C2 | [37] + ICP | 36.64 | 44.52 | 27.56 | 0.43 | 0.23 | 0.40 |
| [38] + ICP | 29.37 | 15.03 | 37.56 | 0.32 | 0.31 | 0.34 | ||
| [22] | 7.43 | 8.97 | 115.30 | 0.21 | 0.37 | 0.20 | ||
| Proposed | 6.32 | 7.28 | 7.89 | 0.30 | 0.24 | 0.25 | ||
| 3 | C2–C3 | [37] + ICP | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| [38] + ICP | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| [22] | 18.89 | 23.73 | 124.56 | 1.07 | 0.83 | 0.47 | ||
| Proposed | 2.30 | 0.70 | 9.85 | 0.43 | 0.36 | 0.30 | ||
| 4 | L1 | [37] + ICP | 19.82 | 40.49 | 47.01 | 0.99 | 0.41 | 0.35 |
| [38] + ICP | 20.62 | 35.22 | 64.90 | / | / | / | ||
| [22] | 8.43 | 4.84 | 115.18 | 0.25 | 0.85 | 0.08 | ||
| Proposed | 4.03 | 3.91 | 10.18 | 0.38 | 66 | 0.09 | ||
| 5 | L1 | [37] + ICP | 2.71 | 1.16 | 43.25 | 0.28 | 0.27 | 0.29 |
| [38] + ICP | 3.02 | 1.81 | 57.61 | 0.41 | 0.58 | 0.31 | ||
| [22] | 2.79 | 3.00 | 108.35 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.05 | ||
| Proposed | 5.36 | 7.38 | 10.68 | 0.37 | 0.10 | 0.04 | ||
| 6 | L1 | [37] + ICP | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| [38] + ICP | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| [22] | 4.12 | 8.51 | 113.54 | 0.59 | 0.60 | 0.06 | ||
| Proposed | 4.52 | 5.54 | 9.84 | 0.38 | 0.41 | 0.04 | ||
| 7 | L1 | [37] + ICP | 10.28 | 26.16 | 26.96 | 0.33 | 3.50 | 0.45 |
| [38] + ICP | 12.84 | 14.71 | 46.39 | 0.39 | 1.52 | 0.57 | ||
| [22] | 1.60 | 1.26 | 129.48 | 0.88 | 0.51 | 0.15 | ||
| Proposed | 6.83 | 11.45 | 9.88 | 0.30 | 0.25 | 0.18 | ||
| 8 | L2 | [37] + ICP | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| [38] + ICP | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| [22] | 4.84 | 3.11 | 115.44 | 0.31 | 0.47 | 0.31 | ||
| Proposed | 5.93 | 5.86 | 9.96 | 0.49 | 0.11 | 0.21 | ||
| 9 | L2 | [37] + ICP | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| [38] + ICP | 36.45 | 43.43 | 58.97 | 0.60 | 0.78 | 0.69 | ||
| [22] | 14.81 | 9.81 | 92.30 | 0.45 | 0.32 | 0.07 | ||
| Proposed | 6.89 | 7.99 | 11.10 | 0.31 | 0.16 | 0.06 | ||
| 10 | L3 | [37] + ICP | 35.13 | 26.52 | 47.65 | 0.33 | 0.38 | 0.44 |
| [38] + ICP | 19.97 | 21.54 | 55.70 | 0.71 | 0.66 | 0.40 | ||
| [22] | 9.27 | 9.80 | 117.78 | 0.35 | 0.32 | 0.26 | ||
| Proposed | 2.76 | 4.21 | 9.75 | 0.26 | 0.14 | 0.26 | ||
| 11 | L3 | [37] + ICP | 8.78 | 9.86 | 44.42 | 1.00 | 0.41 | 0.35 |
| [38] + ICP | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| [22] | 8.21 | 3.54 | 89.544 | 0.25 | 0.85 | 0.08 | ||
| Proposed | 7.43 | 8.94 | 9.486 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.07 | ||
| Data | Exposed Site | Algorithm | δ = 0.25 mm | δ = 0.5 mm | δ = 0.75 mm | δ = 1.0 mm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (°) | (mm) | (°) | (mm) | (°) | (mm) | (°) | ||||
| 1 | C1 | [37] | 27.32 | 22.97 | 28.89 | 23.18 | / | / | / | / |
| [38] | 35.42 | 25.16 | 27.83 | 14.04 | 52.35 | 20.30 | 40.86 | 21.12 | ||
| CFL-PM | 4.21 | 7.81 | 8.76 | 15.70 | 12.28 | 20.57 | 17.26 | 20.20 | ||
| 2 | C2 | [37] | 32.64 | 17.49 | 33.99 | 14.58 | / | / | / | / |
| [38] | 36.85 | 20.71 | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| CFL-PM | 6.36 | 5.99 | 16.32 | 5.85 | 20.18 | 10.03 | 25.24 | 8.51 | ||
| 3 | C2–C3 | [37] | 11.25 | 3.81 | 20.66 | 6.28 | / | / | / | / |
| [38] | 23.61 | 5.45 | 23.38 | 8.43 | 18.48 | 6.20 | 23.01 | 9.20 | ||
| CFL-PM | 7.61 | 5.03 | 11.68 | 5.96 | 7.52 | 1.72 | 20.49 | 9.01 | ||
| 4 | L1 | [37] | 33.32 | 12.02 | 20.08 | 25.96 | 41.76 | 23.17 | 31.08 | 46.65 |
| [38] | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| CFL-PM | 3.22 | 3.08 | 2.32 | 2.20 | 3.93 | 4.07 | 7.55 | 10.19 | ||
| 5 | L1 | [37] | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| [38] | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | ||
| CFL-PM | 4.73 | 6.61 | 2.24 | 2.58 | 3.52 | 1.64 | 9.58 | 16.90 | ||
| 6 | L1 | [37] | 5.78 | 1.44 | 15.12 | 4.23 | 36.62 | 7.30 | / | / |
| [38] | 3.97 | 0.98 | 52.64 | 6.93 | 15.50 | 1.73 | 21.63 | 7.08 | ||
| CFL-PM | 3.24 | 0.30 | 3.99 | 1.21 | 3.10 | 5.04 | 6.26 | 2.84 | ||
| 7 | L1 | [37] | 20.28 | 24.90 | 46.56 | 27.81 | 19.68 | 24.23 | / | / |
| [38] | 13.91 | 16.95 | 35.54 | 24.44 | 6.40 | 14.67 | / | / | ||
| CFL-PM | 8.48 | 14.73 | 2.49 | 11.77 | 5.88 | 11.11 | 7.60 | 24.5 | ||
| 8 | L2 | [37] | 10.77 | 4.11 | 21.12 | 14.54 | 21.09 | 14.35 | / | / |
| [38] | 7.42 | 6.34 | 12.54 | 5.52 | 9.02 | 7.93 | 20.51 | 15.04 | ||
| CFL-PM | 2.52 | 2.10 | 4.56 | 3.46 | 5.54 | 6.99 | 5.66 | 9.31 | ||
| 9 | L2 | [37] | 26.79 | 13.78 | 22.16 | 16.58 | 33.39 | 15.64 | 21.18 | 16.43 |
| [38] | 14.41 | 5.40 | 13.98 | 6.80 | 35.32 | 19.01 | 23.75 | 14.79 | ||
| CFL-PM | 1.79 | 1.40 | 3.57 | 1.06 | 5.18 | 9.19 | 6.28 | 9.09 | ||
| 10 | L3 | [37] | 48.27 | 47.20 | 47.43 | 43.02 | 19.8 | 33.28 | 52.49 | 46.78 |
| [38] | 22.96 | 31.99 | 15.56 | 36.17 | 55.52 | 54.19 | 34.00 | 44.69 | ||
| CFL-PM | 8.98 | 28.11 | 2.37 | 24.78 | 6.63 | 31.85 | 5.26 | 29.11 | ||
| 11 | L3 | [37] | 10.78 | 7.30 | 16.41 | 2.27 | 26.03 | 7.52 | 52.79 | 10.39 |
| [38] | 9.67 | 5.71 | 5.49 | 0.77 | 6.45 | 1.20 | 16.98 | 3.18 | ||
| CFL-PM | 4.27 | 0.48 | 9.43 | 1.45 | 3.41 | 1.57 | 8.98 | 4.67 | ||
| Mean coarse registration error | [37] | 22.72 | 15.50 | 27.24 | 17.85 | 28.34 | 17.93 | 39.38 | 30.06 | |
| [38] | 18.69 | 13.19 | 23.37 | 12.89 | 24.88 | 15.65 | 25.82 | 16.44 | ||
| CFL-PM | 5.04 | 6.88 | 6.16 | 6.91 | 7.02 | 9.43 | 10.92 | 13.12 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Liu, T.; Guo, J.; Wu, B.; Zhang, N. A Coarse-to-Fine Framework with Curvature Feature Learning for Robust Point Cloud Registration in Spinal Surgical Navigation. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101096
Zhang L, Wang W, Liu T, Guo J, Wu B, Zhang N. A Coarse-to-Fine Framework with Curvature Feature Learning for Robust Point Cloud Registration in Spinal Surgical Navigation. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(10):1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101096
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lijing, Wei Wang, Tianbao Liu, Jiahui Guo, Bo Wu, and Nan Zhang. 2025. "A Coarse-to-Fine Framework with Curvature Feature Learning for Robust Point Cloud Registration in Spinal Surgical Navigation" Bioengineering 12, no. 10: 1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101096
APA StyleZhang, L., Wang, W., Liu, T., Guo, J., Wu, B., & Zhang, N. (2025). A Coarse-to-Fine Framework with Curvature Feature Learning for Robust Point Cloud Registration in Spinal Surgical Navigation. Bioengineering, 12(10), 1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101096







