Application of Explainable Artificial Intelligence Based on Visual Explanation in Digestive Endoscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
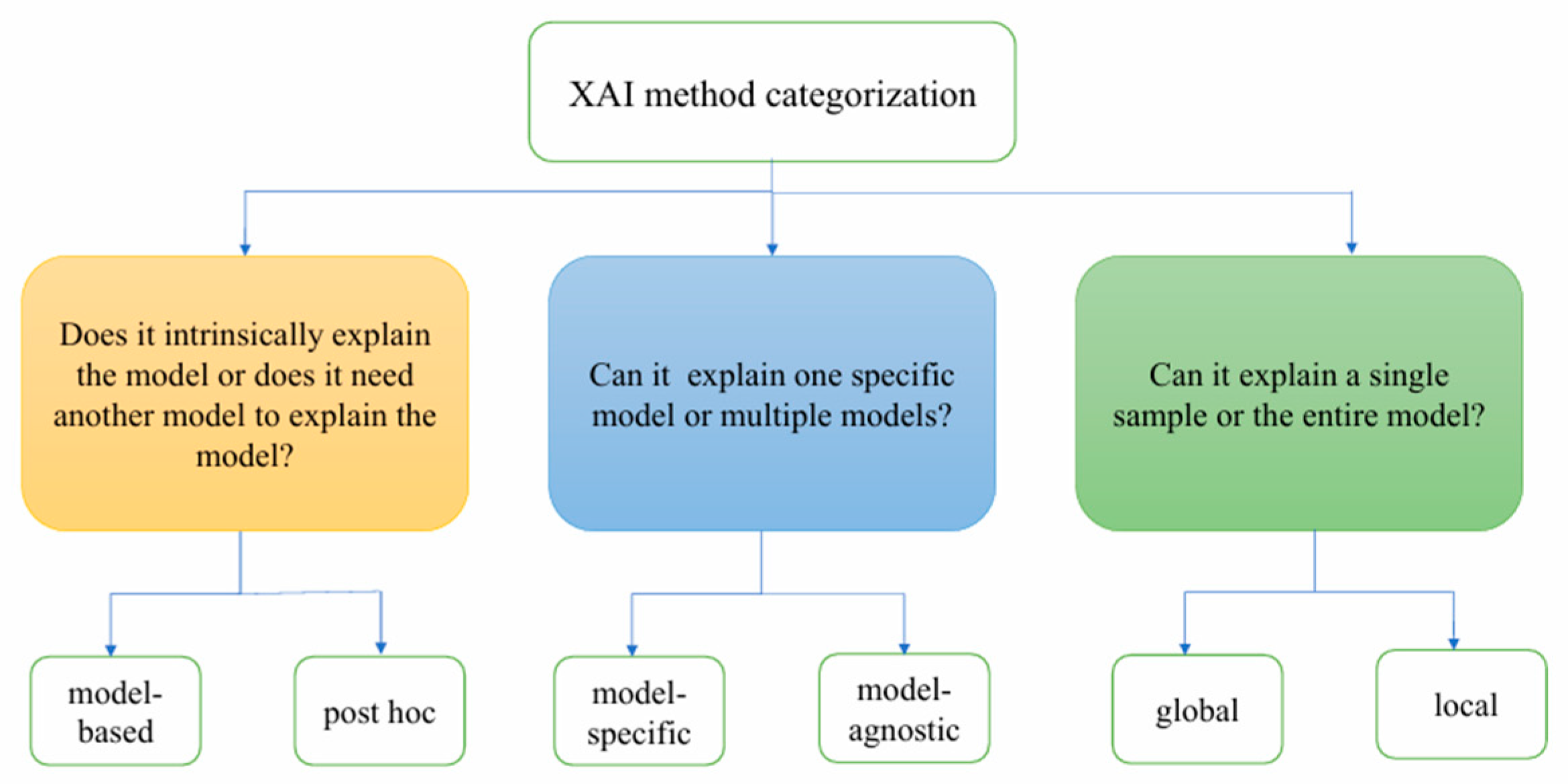
2. Definition and Classification of XAI
2.1. Definition of XAI
2.2. Classification of XAI
2.2.1. Model-Based Explanation vs. Post Hoc Explanation
2.2.2. Model-Specific Explanation vs. Model-Agnostic Explanation
2.2.3. Global Explanation vs. Local Explanation
3. XAI Methods Based on Visual Explanation
3.1. Backpropagation-Based Methods
3.1.1. Saliency Map Visualization
3.1.2. Deconvolution Networks (DeconvNets) and Guided BackPropagation (GBP)
3.1.3. Class Activation Mapping (CAM)
3.1.4. Gradient-Weighted Class Activation Mapping (Grad-CAM)
3.1.5. Layer-Wise Relevance Propagation (LRP)
3.2. Perturbation-Based Methods
3.2.1. Occlusion
3.2.2. Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations (LIME)
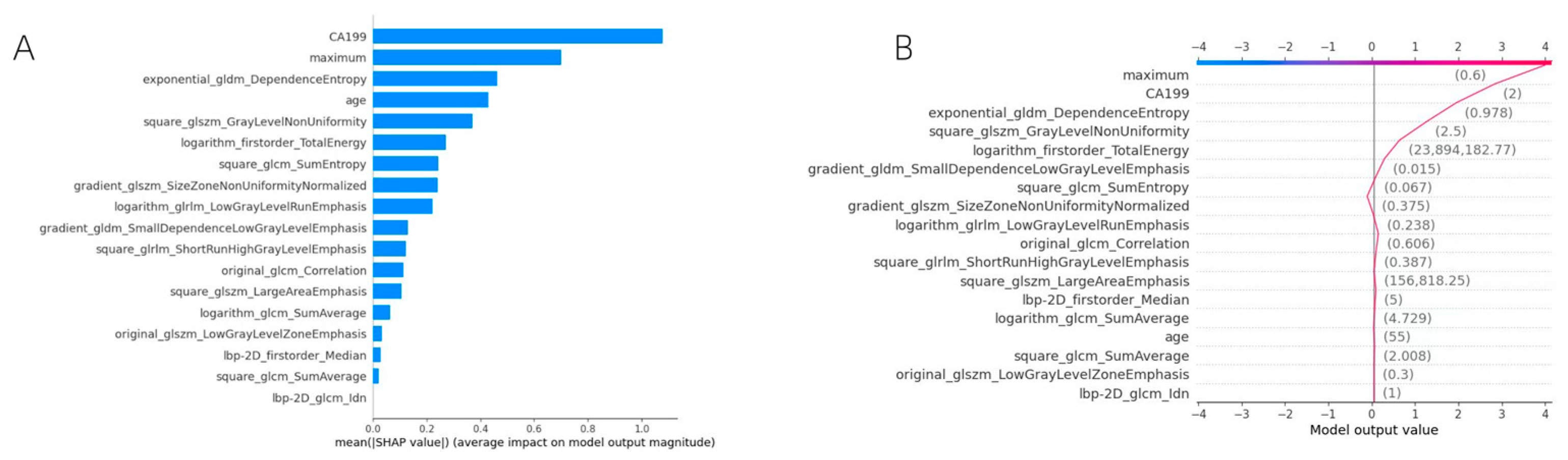
3.2.3. SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP)
4. Applications of XAI Methods Based on Visual Explanation in Digestive Endoscopy
4.1. Applications in Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
4.2. Applications in Colonoscopy
4.3. Applications in Endoscopic Ultrasonography
4.4. Applications in Wireless Capsule Endoscopy
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenbacke, R.; Melhus, Å.; McKee, M.; Stuckler, D. How Explainable Artificial Intelligence Can Increase or Decrease Clinicians’ Trust in AI Applications in Health Care: Systematic Review. JMIR AI 2024, 3, e53207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröner, P.T.; Engels, M.M.; Glicksberg, B.S.; Johnson, K.W.; Mzaik, O.; van Hooft, J.E.; Wallace, M.B.; El-Serag, H.B.; Krittanawong, C. Artificial intelligence in gastroenterology: A state-of-the-art review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 6794–6824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.J.; Bang, C.S. Application of artificial intelligence in gastroenterology. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 1666–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borys, K.; Schmitt, Y.A.; Nauta, M.; Seifert, C.; Krämer, N.; Friedrich, C.M.; Nensa, F. Explainable AI in medical imaging: An overview for clinical practitioners-Saliency-based XAI approaches. Eur. J. Radiol. 2023, 162, 110787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, J.C.L. Quantum Computing and Machine Learning in Medical Decision-Making: A Comprehensive Review. Algorithms 2025, 18, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinonquel, P.; Eelbode, T.; Bossuyt, P.; Maes, F.; Bisschops, R. Artificial intelligence and its impact on quality improvement in upper and lower gastrointestinal endoscopy. Dig. Endosc. 2021, 33, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, S.E.; Mori, Y.; Misawa, M.; Takeda, K.; Kudo, T.; Itoh, H.; Oda, M.; Mori, K. Artificial intelligence and colonoscopy: Current status and future perspectives. Dig. Endosc. 2019, 31, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekadir, K.; Osuala, R.; Gallin, C.; Lazrak, N.; Kushibar, K.; Tsakou, G.; Aussó, S.; Alberich, L.C.; Marias, K.; Tsiknakis, M.; et al. FUTURE-AI: Guiding Principles and Consensus Recommendations for Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging. arXiv 2019, arXiv:2109.09658. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Sengupta, S.; Lakshminarayanan, V. Explainable Deep Learning Models in Medical Image Analysis. J. Imaging 2020, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adadi, A.; Berrada, M. Peeking Inside the Black-Box: A Survey on Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI). IEEE Access 2018, 6, 52138–52160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Velden, B.H.M.; Kuijf, H.J.; Gilhuijs, K.G.A.; Viergever, M.A. Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) in deep learning-based medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 79, 102470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, A.; Galazzo, I.B.; Gkontra, P.; Lee, A.M.; Lekadir, K.; Raisi-Estabragh, Z.; Petersen, S.E. Explainable Artificial Intelligence and Cardiac Imaging: Toward More Interpretable Models. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2023, 16, e014519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; He, L. Recent Advances in Explainable Artificial Intelligence for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Tseng, H.-H.; Cui, S.; Wei, L.; Ten Haken, R.K.; El Naqa, I. Balancing accuracy and interpretability of machine learning approaches for radiation treatment outcomes modeling. BJR Open 2019, 1, 20190021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C. Stop Explaining Black Box Machine Learning Models for High Stakes Decisions and Use Interpretable Models Instead. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2019, 1, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, R.A.; Yadav, M.; Yadava, U.; Rai, N.; Negi, S.; Yadav, H.S. Active site determination of novel plant versatile peroxidase extracted from Citrus sinensis and bioconversion of β-naphthol. 3 Biotech 2023, 13, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barredo Arrieta, A.; Díaz-Rodríguez, N.; Del Ser, J.; Bennetot, A.; Tabik, S.; Barbado, A.; Garcia, S.; Gil-Lopez, S.; Molina, D.; Benjamins, R.; et al. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): Concepts, taxonomies, opportunities and challenges toward responsible AI. Inf. Fusion. 2020, 58, 82–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdoch, W.J.; Singh, C.; Kumbier, K.; Abbasi-Asl, R.; Yu, B. Definitions, methods, and applications in interpretable machine learning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 22071–22080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, R.; Bourgeois, D.; You, J.; Zitnik, M.; Leskovec, J. GNNExplainer: Generating Explanations for Graph Neural Networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process Syst. 2019, 32, 9240–9251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salahuddin, Z.; Woodruff, H.C.; Chatterjee, A.; Lambin, P. Transparency of deep neural networks for medical image analysis: A review of interpretability methods. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 140, 105111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Luo, C.; Chen, X.; Feng, Y.; Feng, J.; Zhang, R.; Ouyang, F.; Li, X.; Tan, Z.; Deng, L.; et al. Noninvasive prediction of perineural invasion in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma by clinicoradiological features and computed tomography radiomics based on interpretable machine learning: A multicenter cohort study. Int. J. Surg. 2024, 110, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancona, M.; Ceolini, E.; Öztireli, C.; Gross, M. Towards Better Understanding of Gradient-Based Attribution Methods for Deep Neural Networks. 2018. Available online: https://openreview.net/forum?id=Sy21R9JAW (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- Borys, K.; Schmitt, Y.A.; Nauta, M.; Seifert, C.; Krämer, N.; Friedrich, C.M.; Nensa, F. Explainable AI in medical imaging: An overview for clinical practitioners–Beyond saliency-based XAI approaches. Eur. J. Radiol. 2023, 162, 110786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Wattenberg, M.; Gilmer, J.; Cai, C.; Wexler, J.; Viegas, F.; Sayres, R. Interpretability Beyond Feature Attribution: Quantitative Testing with Concept Activation Vectors (TCAV). In Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018. PMLR 80. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.; Rad, P. Opportunities and Challenges in Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): A Survey. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.11371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Vedaldi, A.; Zisserman, A. Deep Inside Convolutional Networks: Visualising Image Classification Models and Saliency Maps. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1312.6034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiler, M.D.; Fergus, R. Visualizing and Understanding Convolutional Networks. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2014; Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 818–833. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-Based Localization. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Khosla, A.; Lapedriza, A.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Learning Deep Features for Discriminative Localization. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 2921–2929. [Google Scholar]
- Bach, S.; Binder, A.; Montavon, G.; Klauschen, F.; Müller, K.-R.; Samek, W. On Pixel-Wise Explanations for Non-Linear Classifier Decisions by Layer-Wise Relevance Propagation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadimi, E.S.; Braun, J.-M.; Schelde-Olesen, B.; Khare, S.; Gogineni, V.C.; Blanes-Vidal, V.; Baatrup, G. Towards full integration of explainable artificial intelligence in colon capsule endoscopy’s pathway. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Li, X.; Fatehi, M.; Hamarneh, G. Generating post-hoc explanation from deep neural networks for multi-modal medical image analysis tasks. MethodsX 2023, 10, 102009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huff, D.T.; Weisman, A.J.; Jeraj, R. Interpretation and visualization techniques for deep learning models in medical imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2021, 66, 04TR01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, M.T.; Singh, S.; Guestrin, C. ‘Why Should I Trust You?’: Explaining the Predictions of Any Classifier. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1135–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2017/hash/8a20a8621978632d76c43dfd28b67767-Abstract.html (accessed on 13 July 2025).
- Ali, S.; Akhlaq, F.; Imran, A.S.; Kastrati, Z.; Daudpota, S.M.; Moosa, M. The enlightening role of explainable artificial intelligence in medical & healthcare domains: A systematic literature review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 166, 107555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.T.; Zhu, S.L. Overview of the Types and Applications of Digestive Endoscopy. World Latest Med. Inf. 2019, 19, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.S.; Lu, Z.Y.; Chen, M.Y.; Zhang, B.; Juengpanich, S.; Hu, J.H.; Li, S.J.; Topatana, W.; Zhou, X.Y.; Feng, X.; et al. Artificial intelligence in gastroenterology and hepatology: Status and challenges. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 1664–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Wang, B.; Chang, J.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, J.; Duan, Z. Using deep learning and explainable artificial intelligence to assess the severity of gastroesophageal reflux disease according to the Los Angeles Classification System. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 58, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, L.A.; Mendel, R.; Strasser, S.; Ebigbo, A.; Probst, A.; Messmann, H.; Papa, J.P.; Palm, C. Convolutional Neural Networks for the evaluation of cancer in Barrett’s esophagus: Explainable AI to lighten up the black-box. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 135, 104578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Peraza-Herrera, L.C.; Everson, M.; Lovat, L.; Wang, H.-P.; Wang, W.L.; Haidry, R.; Stoyanov, D.; Ourselin, S.; Vercauteren, T. Intrapapillary capillary loop classification in magnification endoscopy: Open dataset and baseline methodology. Int. J. CARS 2020, 15, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everson, M.A.; Garcia-Peraza-Herrera, L.; Wang, H.-P.; Lee, C.-T.; Chung, C.-S.; Hsieh, P.-H.; Chen, C.-C.; Tseng, C.-H.; Hsu, M.-H.; Vercauteren, T.; et al. A clinically interpretable convolutional neural network for the real-time prediction of early squamous cell cancer of the esophagus: Comparing diagnostic performance with a panel of expert European and Asian endoscopists. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 94, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueyama, H.; Kato, Y.; Akazawa, Y.; Yatagai, N.; Komori, H.; Takeda, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Ueda, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Hojo, M.; et al. Application of artificial intelligence using a convolutional neural network for diagnosis of early gastric cancer based on magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 36, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Gong, L.; Dong, D.; Zhu, L.; Wang, M.; He, J.; Shu, L.; Cai, Y.; Cai, S.; Su, W.; et al. Identifying early gastric cancer under magnifying narrow-band images with deep learning: A multicenter study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 93, 1333–1341.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.-J.; Bang, C.S.; Lee, J.J.; Seo, C.W.; Kim, J.H. Prediction of Submucosal Invasion for Gastric Neoplasms in Endoscopic Images Using Deep-Learning. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, P.O.; Dunbar, K.; Schnoll-Sussman, F.H.; Greer, K.B.; Yadlapati, R.; Spechler, S.J. ACG Clinical Guideline: Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 117, 27–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatta, W.; Koike, T.; Ogata, Y.; Kondo, Y.; Ara, N.; Uno, K.; Asano, N.; Imatani, A.; Masamune, A. Comparison of Magnifying Endoscopy with Blue Light Imaging and Narrow Band Imaging for Determining the Invasion Depth of Superficial Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma by the Japanese Esophageal Society’s Intrapapillary Capillary Loop Classification. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, E.; Tanis, P.J.; Vleugels, J.L.A.; Kasi, P.M.; Wallace, M.B. Colorectal cancer. Lancet 2019, 394, 1467–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Wagle, N.S.; Cercek, A.; Smith, R.A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, A.; Carey, F.A.; Pratt, N.R.; Steele, R.J.C. The colorectal adenoma–carcinoma sequence. Br. J. Surg. 2002, 89, 845–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, S.; Pan, P.; Xia, T.; Chang, X.; Yang, X.; Guo, L.; Meng, Q.; Yang, F.; Qian, W.; et al. Magnitude, Risk Factors, and Factors Associated With Adenoma Miss Rate of Tandem Colonoscopy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1661–1674.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, M.H.J.; Neumann, H.; Shirin, H.; Katz, L.H.; Benson, A.A.; Kahloon, A.; Soons, E.; Hazzan, R.; Landsman, M.J.; Lebwohl, B.; et al. A computer-aided polyp detection system in screening and surveillance colonoscopy: An international, multicentre, randomised, tandem trial. Lancet Digit. Health 2024, 6, e157–e165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corley, D.A.; Jensen, C.D.; Marks, A.R.; Zhao, W.K.; Lee, J.K.; Doubeni, C.A.; Zauber, A.G.; de Boer, J.; Fireman, B.H.; Schottinger, J.E.; et al. Adenoma detection rate and risk of colorectal cancer and death. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1298–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, G.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Xia, K.; Xu, X. AI support for colonoscopy quality control using CNN and transformer architectures. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024, 24, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickstrøm, K.; Kampffmeyer, M.; Jenssen, R. Uncertainty and interpretability in convolutional neural networks for semantic segmentation of colorectal polyps. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 60, 101619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, E.H.; Lee, D.; Bae, J.H.; Kang, H.Y.; Kwak, M.-S.; Seo, J.Y.; Yang, J.I.; Yang, S.Y.; Lim, S.H.; Yim, J.Y.; et al. Improved Accuracy in Optical Diagnosis of Colorectal Polyps Using Convolutional Neural Networks with Visual Explanations. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 2169–2179.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.-W.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; Dai, Z.-H.; Zhao, R.; Huang, J.; Qiu, H.; Tang, Z.-R.; Niu, B.; Zhang, X.-B.; et al. Multi-step validation of a deep learning-based system with visual explanations for optical diagnosis of polyps with advanced features. iScience 2024, 27, 109461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.; Choi, S.J.; Kim, E.S. Computer-Aided Diagonosis for Colorectal Cancer using Deep Learning with Visual Explanations. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2020, 2020, 1156–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chierici, M.; Puica, N.; Pozzi, M.; Capistrano, A.; Donzella, M.D.; Colangelo, A.; Osmani, V.; Jurman, G. Automatically detecting Crohn’s disease and Ulcerative Colitis from endoscopic imaging. BMC Med. Inf. Decis. Mak. 2022, 22, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, R.T.; Zai Ane, O.R.; Goebel, R.; Baumgart, D.C. Artificial intelligence enabled automated diagnosis and grading of ulcerative colitis endoscopy images. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, F.; Meng, Y.; Lu, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Xu, L.; Cheng, D.; Zhu, J. Differentiation of intestinal tuberculosis and Crohn’s disease through an explainable machine learning method. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabralla, L.A.; Hussien, A.M.; AlMohimeed, A.; Saleh, H.; Alsekait, D.M.; El-Sappagh, S.; Ali, A.A.; Refaat Hassan, M. Automated Diagnosis for Colon Cancer Diseases Using Stacking Transformer Models and Explainable Artificial Intelligence. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binzagr, F. Explainable AI-driven model for gastrointestinal cancer classification. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1349373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auzine, M.M.; Heenaye-Mamode Khan, M.; Baichoo, S.; Gooda Sahib, N.; Bissoonauth-Daiboo, P.; Gao, X.; Heetun, Z. Development of an ensemble CNN model with explainable AI for the classification of gastrointestinal cancer. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0305628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahan, F.; Shah, J.H.; Saleem, R.; Hasnain, M.; Afzal, M.; Alfakih, T.M. A hybrid XAI-driven deep learning framework for robust GI tract disease diagnosis. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 21139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gideon, S.G.; Princess, P.J.B. Explainable AI for Gastrointestinal Disease Detection using Ensemble Deep Learning Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2025 International Conference on Visual Analytics and Data Visualization (ICVADV), Tirunelveli, India, 4–6 March 2025; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2025; pp. 1113–1119. [Google Scholar]
- Vleugels, J.L.A.; Hazewinkel, Y.; Dijkgraaf, M.G.W.; Koens, L.; Fockens, P.; Dekker, E.; DISCOUNT study group. Optical diagnosis expanded to small polyps: Post-hoc analysis of diagnostic performance in a prospective multicenter study. Endoscopy 2019, 51, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Fan, X.; Liu, W. Applications and Prospects of Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Endoscopic Ultrasound in Digestive System Diseases. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Yamashita, Y.; Kitano, M. Endoscopic Ultrasound for Early Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sooklal, S.; Chahal, P. Endoscopic Ultrasound. Surg. Clin. North. Am. 2020, 100, 1133–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Huang, J.; Cai, X.; Maihemuti, A.; Li, S.; Fang, W.; Wang, B.; Liu, W. Clinical value of the nomogram model based on endoscopic ultrasonography radiomics and clinical indicators in identifying benign and malignant lesions of the pancreas. Front. Oncol. 2025, 15, 1504593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Pan, J.; Hu, J.; Dai, L.; Zhang, K.; Wang, B.; He, M.; Zhao, Q.; Jiang, T. Prospective assessment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma diagnosis from endoscopic ultrasonography images with the assistance of deep learning. Cancer 2023, 129, 2214–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, N.; Mo, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Huang, C.; Qin, S.; Jiang, H. An endoscopic ultrasound-based interpretable deep learning model and nomogram for distinguishing pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors from pancreatic cancer. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marya, N.B.; Powers, P.D.; Chari, S.T.; Gleeson, F.C.; Leggett, C.L.; Abu Dayyeh, B.K.; Chandrasekhara, V.; Iyer, P.G.; Majumder, S.; Pearson, R.K.; et al. Utilisation of artificial intelligence for the development of an EUS-convolutional neural network model trained to enhance the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut 2021, 70, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, S.; Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Qin, S. Endoscopic ultrasonography-based intratumoral and peritumoral machine learning ultrasomics model for predicting the pathological grading of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. BMC Med. Imaging 2025, 25, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.H.; Fan, X.F.; Li, S.; Fang, W.L.; Wang, B.M.; Wang, Y.F.; Feng, Y.; Mu, J.B.; Liu, W.T. Construction of a multimodal interpretable machine learning model based on radiomics and clinical features for distinguishing benign and malignant pancreatic lesions. World Chin. J. Dig. 2025, 33, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Zhao, Y.; Xiong, S.; Feng, Y.; Li, P.; Lv, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wang, R.; Xie, P.; Luo, Z.; et al. Diagnosing Solid Lesions in the Pancreas With Multimodal Artificial Intelligence. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2422454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.Q.; Cui, Y.T.; Hu, G.B.; Guo, H.Y.; Chen, X.R.; Zuo, J.; Qi, Z.R.; Wang, X.F. Development and validation of a machine-learning model for preoperative risk of gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumors. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2025, 29, 101864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.S.; Huang, P.Y.; Wen, M.L.; Zhuang, S.S.; Hua, J.; He, X.P. Application of endoscopic ultrasonography for detecting esophageal lesions based on convolutional neural network. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 2457–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uema, R.; Hayashi, Y.; Kizu, T.; Igura, T.; Ogiyama, H.; Yamada, T.; Takeda, R.; Nagai, K.; Inoue, T.; Yamamoto, M.; et al. A novel artificial intelligence-based endoscopic ultrasonography diagnostic system for diagnosing the invasion depth of early gastric cancer. J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 59, 543–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Hou, X.; Lin-Hu, E.-Q.; Sheng, J.-Q.; Ge, Z.-Z.; Jiang, B.; Hou, X.-H.; Liu, J.-Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, Q.-Y.; et al. Accuracy of Magnetically Controlled Capsule Endoscopy, Compared With Conventional Gastroscopy, in Detection of Gastric Diseases. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 1266–1273.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhi, A.; Kampik, T.; Pannu, H.; Madhikermi, M.; Framling, K. Explaining Machine Learning-Based Classifications of In-Vivo Gastral Images. In 2019 Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA); IEEE: Perth, Australia, 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, H.; Zhang, H. Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Ulcer Recognition in Wireless Capsule Endoscopy: Experimental Feasibility and Optimization. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2019, 2019, 7546215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtorov, D.; Rakhmonova, M.; Muksimova, S.; Cho, Y.-I. Endoscopic Image Classification Based on Explainable Deep Learning. Sensors 2023, 23, 3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascarenhas, M.; Afonso, J.; Ribeiro, T.; Cardoso, H.; Andrade, P.; Ferreira, J.P.S.; Saraiva, M.M.; Macedo, G. Performance of a Deep Learning System for Automatic Diagnosis of Protruding Lesions in Colon Capsule Endoscopy. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadimi, E.S.; Buijs, M.M.; Herp, J.; Kroijer, R.; Kobaek-Larsen, M.; Nielsen, E.; Pedersen, C.D.; Blanes-Vidal, V.; Baatrup, G. Application of deep learning for autonomous detection and localization of colorectal polyps in wireless colon capsule endoscopy. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2020, 81, 106531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakogeorgiou, I.; Karantzalos, K. Evaluating explainable artificial intelligence methods for multi-label deep learning classification tasks in remote sensing. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 103, 102520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, M.; Maurer, M.H.; Thomas, R.P. Explainable Artificial Intelligence in Radiological Cardiovascular Imaging—A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budhkar, A.; Song, Q.; Su, J.; Zhang, X. Demystifying the black box: A survey on explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) in bioinformatics. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2025, 27, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, A.F.; Kors, J.A.; Rijnbeek, P.R. The role of explainability in creating trustworthy artificial intelligence for health care: A comprehensive survey of the terminology, design choices, and evaluation strategies. J. Biomed. Inform. 2021, 113, 103655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doshi-Velez, F.; Kim, B. Towards a rigorous science of interpretable machine learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1702.08608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zeng, X.; Gong, D.; Liu, J.; Pan, J.; Shang, R.; et al. Explainable artificial intelligence incorporated with domain knowledge diagnosing early gastric neoplasms under white light endoscopy. NPJ Digit. Med. 2023, 6, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Types of Digestive Endoscopy | Author | Year | Aim | Main Visual XAI Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Esophagogastroduodenoscopy | Ge et al. [39] | 2023 | Diagnosis of Los Angeles classification of GERD | Grad-CAM |
| De Souza et al. [40] | 2021 | Identification of BE and esophageal adenocarcinoma | Saliency map, GBP, etc. | |
| García-Peraza-Herrera et al. [41] | 2020 | Classification of IPCLs | CAM | |
| Everson et al. [42] | 2021 | Classification of IPCLs | CAM | |
| Ueyama et al. [43] | 2021 | Diagnosis of EGC | Grad-CAM | |
| Hu et al. [44] | 2021 | Diagnosis of EGC | Grad-CAM | |
| Cho et al. [45] | 2020 | Prediction of submucosal invasion for gastric neoplasms | CAM |
| Types of Digestive Endoscopy | Author | Year | Aim | Main Visual XAI Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colonoscopy | Chen et al. [54] | 2024 | Evaluation of key quality indicators for colonoscopy | Grad-CAM, Guided Grad-CAM, SHAP |
| Wickstrom et al. [55] | 2020 | Polyp recognition | GBP | |
| Jin et al. [56] | 2020 | Polyp classification | Grad-CAM | |
| Zhang et al. [57] | 2024 | Polyp classification | Grad-CAM | |
| Choi et al. [58] | 2020 | Polyp classification | CAM | |
| Chierici et al. [59] | 2022 | Identification of CD and UC | GBP | |
| Sutton et al. [60] | 2022 | Diagnosis and grading of UC | Grad-CAM | |
| Weng et al. [61] | 2022 | Differentiation of CD and ITB | SHAP | |
| Gabralla et al. [62] | 2023 | Identification of colon cancer | Grad-CAM | |
| Binzagr F et al. [63] | 2024 | Classification of gastrointestinal cancer | SHAP | |
| Auzine MM et al. [64] | 2024 | Classification of gastrointestinal cancer | SHAP, LIME | |
| Dahan et al. [65] | 2025 | Detection of gastrointestinal disease | Grad-CAM | |
| Gideon et al. [66] | 2025 | Detection of gastrointestinal disease | Grad-CAM, SHAP |
| Types of Digestive Endoscopy | Author | Year | Aim | Main Visual XAI Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Endoscopic Ultrasonography | Gu et al. [72] | 2023 | Diagnosis of PDAC | Grad-CAM |
| Yi et al. [73] | 2025 | Identification of PDAC and PNETs | Grad-CAM, SHAP | |
| Marya et al. [74] | 2021 | Diagnosis of pancreatic diseases | Occlusion | |
| Mo et al. [75] | 2025 | Prediction of PNETs pathological grading | SHAP | |
| Cai et al. [76] | 2025 | Diagnosis of pancreatic diseases | SHAP | |
| Cui et al. [77] | 2024 | Diagnosis of pancreatic diseases | Grad-CAM, SHAP | |
| Liang et al. [78] | 2025 | Preoperative risk prediction of GISTs | SHAP | |
| Liu et al. [79] | 2022 | Identification of the lesion invasion depth and lesion source of esophageal submucosal tumors | CAM | |
| Uema et al. [80] | 2024 | Identification of the invasion depth of EGC | CAM |
| Types of Digestive Endoscopy | Author | Year | Aim | Main Visual XAI Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wireless Capsule Endoscopy | Malhi et al. [82] | 2019 | Detection of gastrointestinal bleeding | LIME |
| Wang et al. [83] | 2019 | Recognition of peptic ulcer | CAM | |
| Mukhtorov et al. [84] | 2023 | Detection of gastrointestinal disease | Grad-CAM | |
| Mascarenhas et al. [85] | 2022 | Diagnosis of colonic protruding lesions | Grad-CAM | |
| Nadimi et al. [86] | 2020 | Detection of colorectal polyps | Saliency map |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Liu, W.; Fan, X. Application of Explainable Artificial Intelligence Based on Visual Explanation in Digestive Endoscopy. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101058
Cai X, Zhang Z, Zhao S, Liu W, Fan X. Application of Explainable Artificial Intelligence Based on Visual Explanation in Digestive Endoscopy. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(10):1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101058
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Xiaohan, Zexin Zhang, Siqi Zhao, Wentian Liu, and Xiaofei Fan. 2025. "Application of Explainable Artificial Intelligence Based on Visual Explanation in Digestive Endoscopy" Bioengineering 12, no. 10: 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101058
APA StyleCai, X., Zhang, Z., Zhao, S., Liu, W., & Fan, X. (2025). Application of Explainable Artificial Intelligence Based on Visual Explanation in Digestive Endoscopy. Bioengineering, 12(10), 1058. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101058






