Integrative Bioinformatics-Guided Analysis of Glomerular Transcriptome Implicates Potential Therapeutic Targets and Pathogenesis Mechanisms in IgA Nephropathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Data and Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes
2.2. Enrichment Analysis
2.3. Construction of the Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis
2.4. Screening of Hub Genes by LASSO Regression and Random Forest Model
2.5. Validation of Hub Genes in IgAN Using ROCs
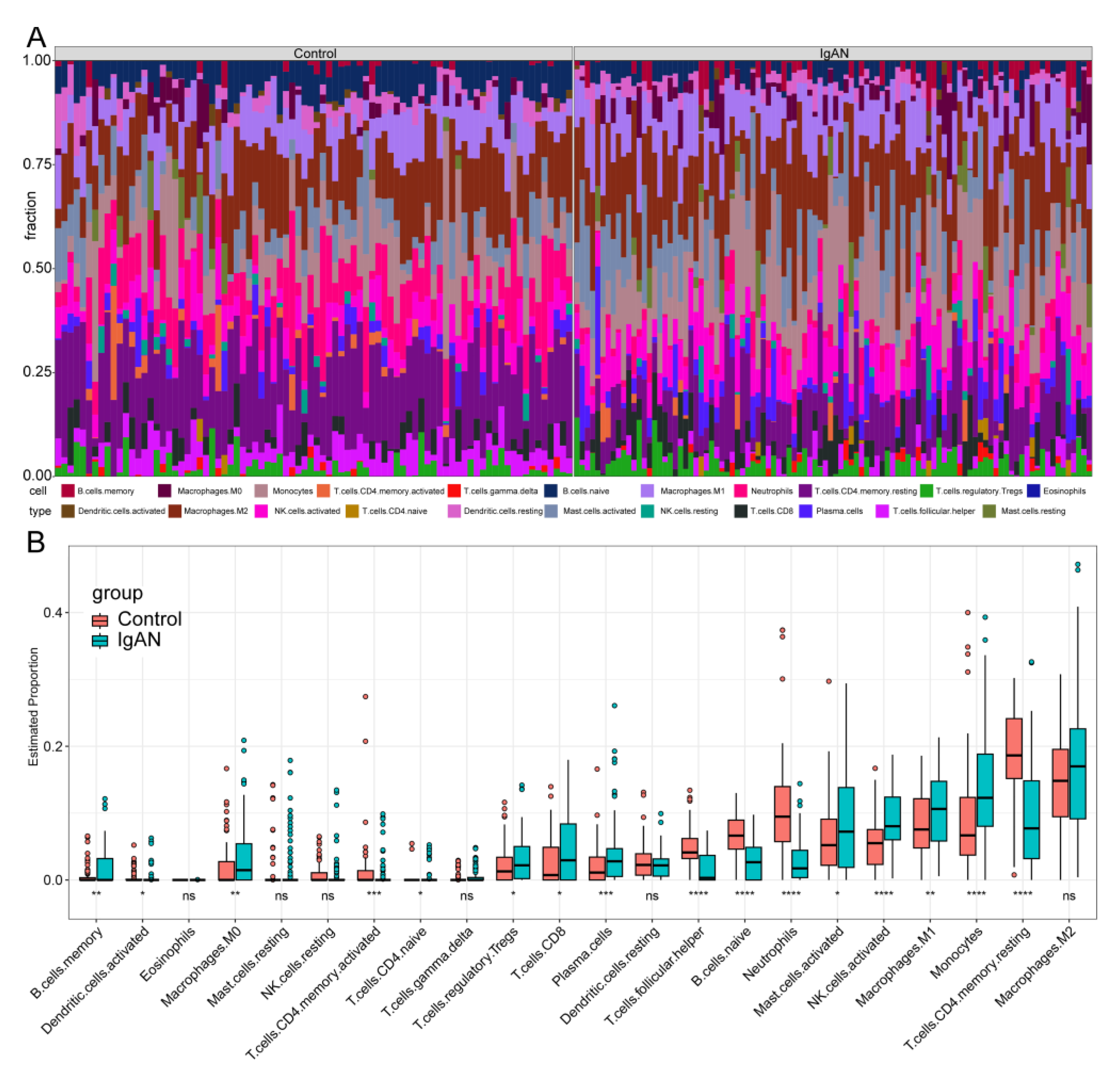
2.6. In Silico Estimation of Immune Infiltration Patterns from Transcriptomic Profiles
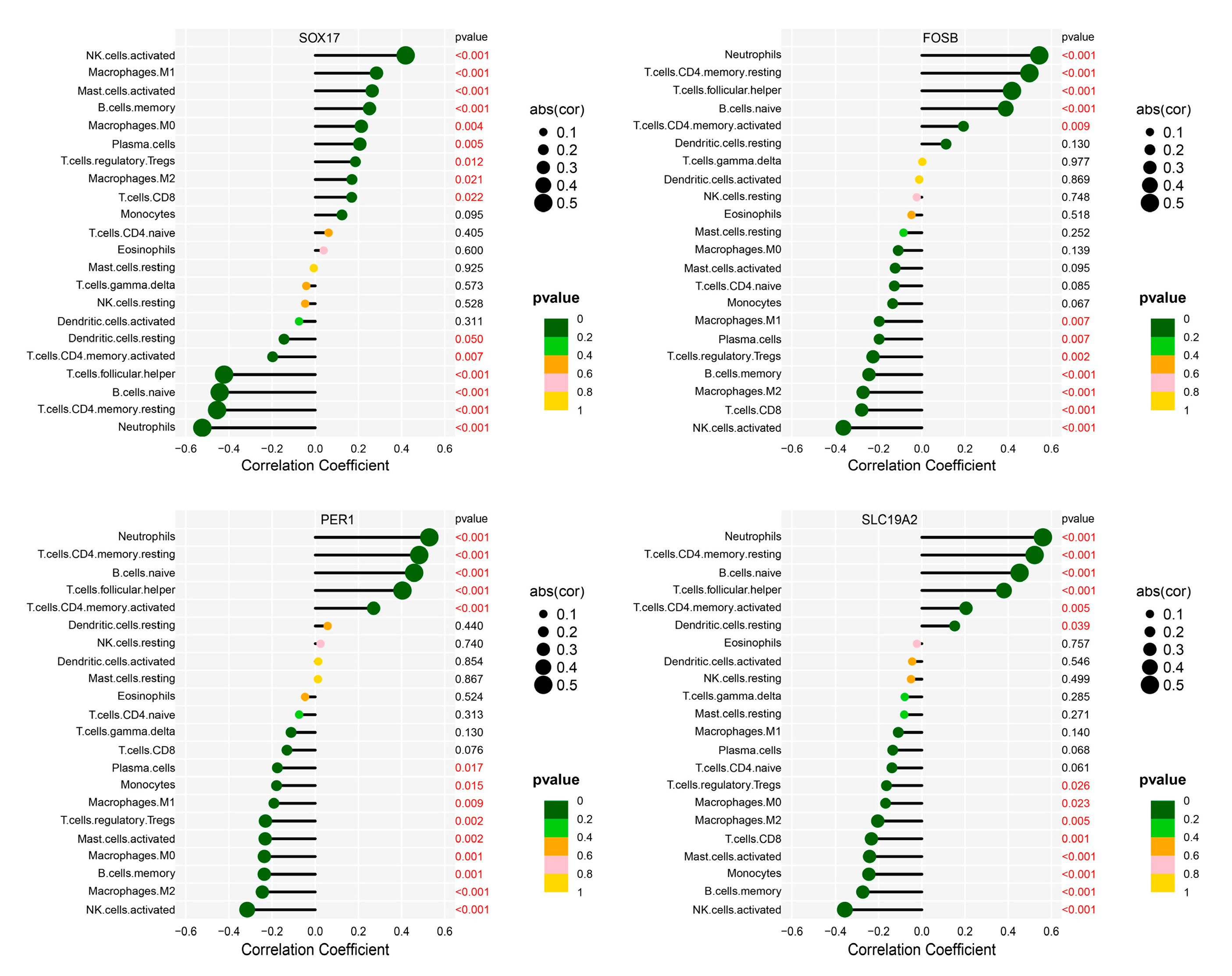
2.7. Correlation Analysis Between Hub Genes and Infiltrating Immune Cells
3. Results
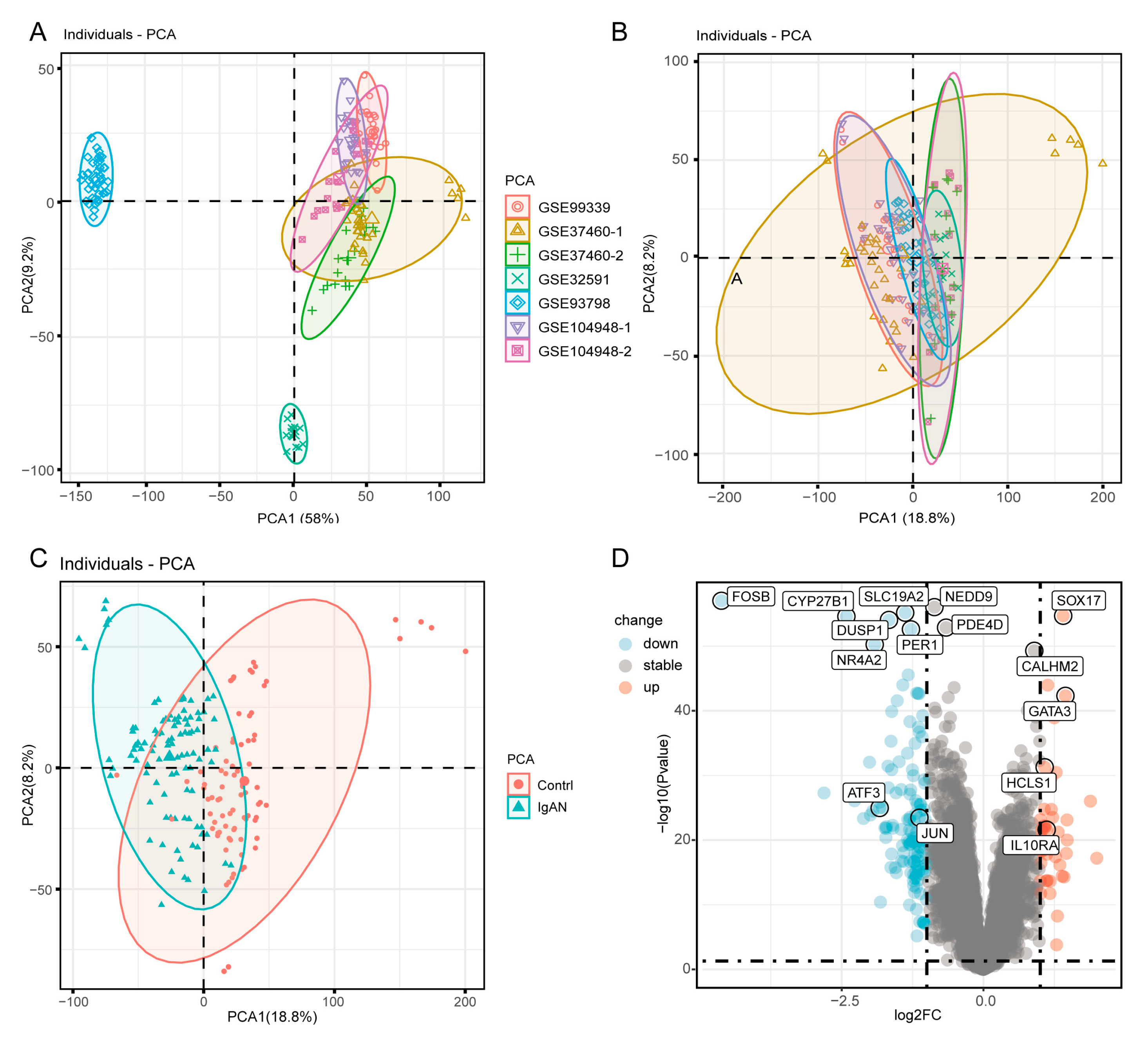
3.1. Identification of DEGs Between IgAN and Healthy Controls
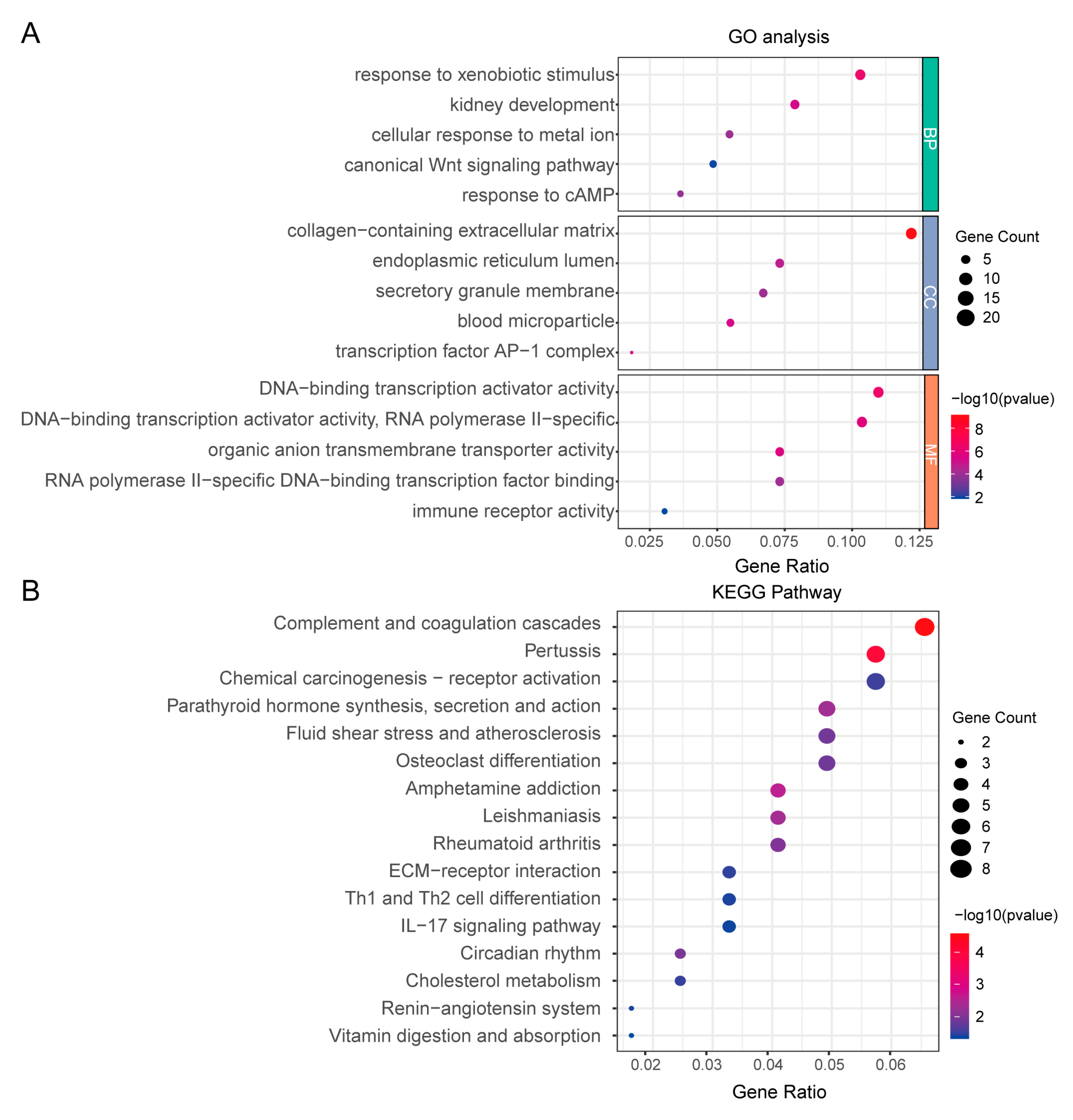
3.2. Function Enrichment Analysis
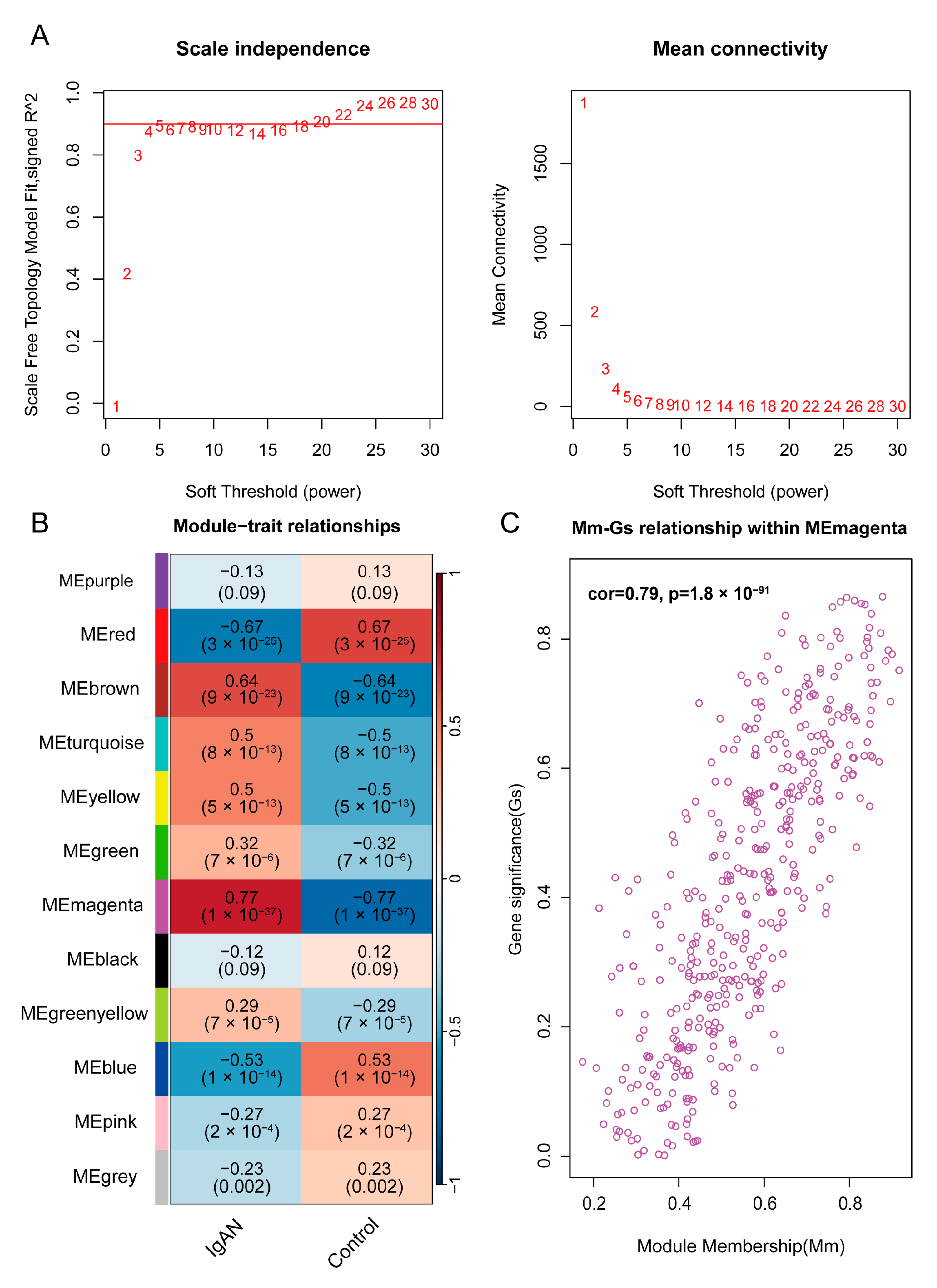
3.3. Construction of WGCNA Network of IgAN
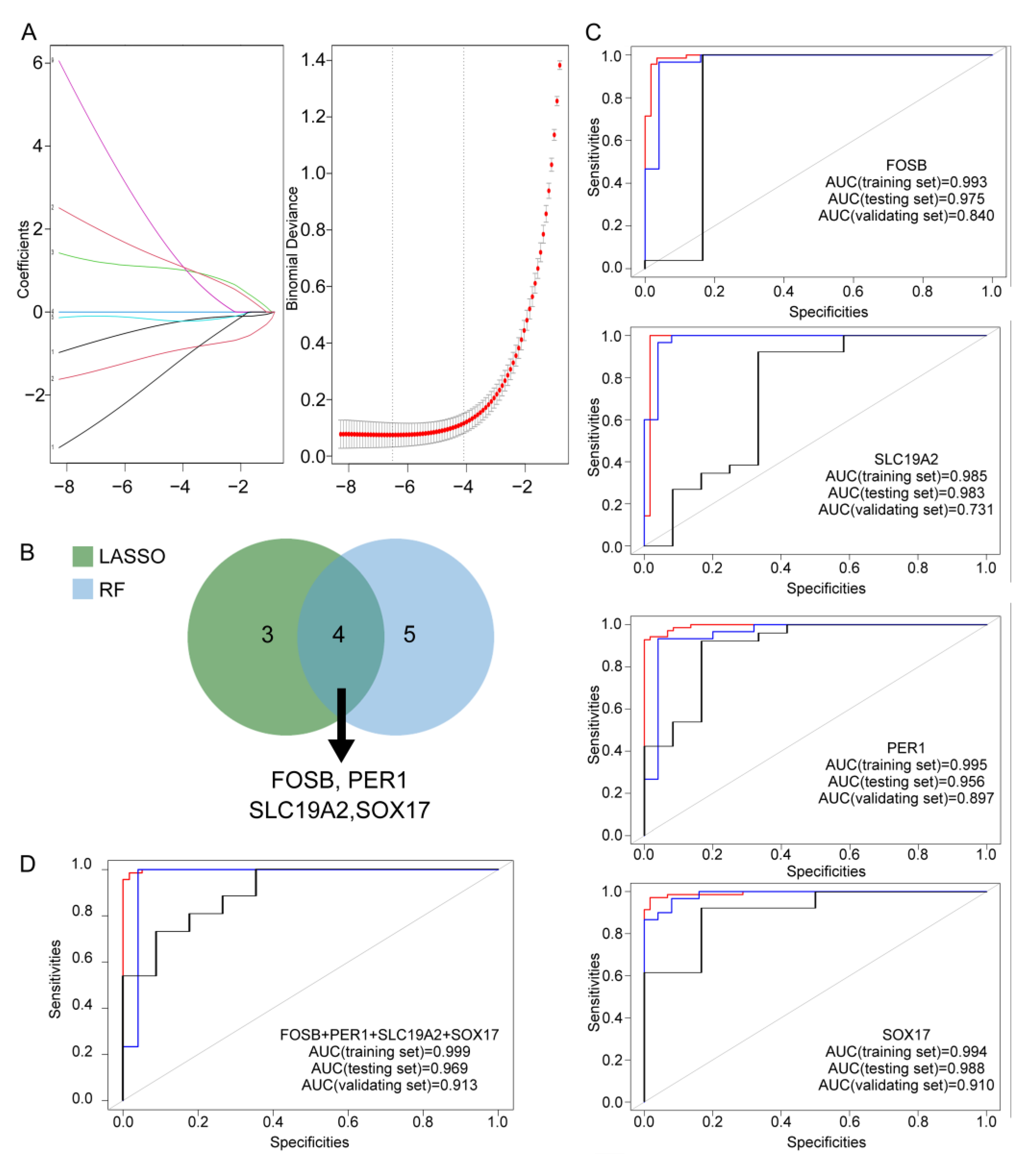
3.4. Identification and Validation of Hub Genes in IgAN
3.5. In Silico Analysis of Immune Infiltration in IgAN
3.6. Correlation of Hub Genes with Infiltrating Immune Cells in IgAN
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IgAN | IgA nephropathy |
| DEGs | differentially expressed genes |
| GEO | Gene Expression Omnibus |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| WGCNA | weighted gene co-expression network analysis |
| AUC | area under the receiver operating characteristic curve |
| GS | gene significance |
| MM | module membership |
| LASSO | Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator |
| RF | random forest |
| PCA | principal component analysis |
| BP | biological process |
| CC | cell composition |
| MF | molecular function |
References
- Floege, J.; Rauen, T.; Tang, S.C.W. Current treatment of IgA nephropathy. Semin. Immunopathol. 2021, 43, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, A.; Julian, B.A.; Rizk, D.V. IgA Nephropathy: An Interesting Autoimmune Kidney Disease. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 361, 176–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J. Intercapillary deposits of IgA-IgG, French. J. Urol. Nephrol. 1968, 74, 694–695. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, H.; Kiryluk, K.; Novak, J.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Herr, A.B.; Renfrow, M.B.; Wyatt, R.J.; Scolari, F.; Mestecky, J.; Gharavi, A.G.; et al. The pathophysiology of IgA nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1795–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serino, G.; Sallustio, F.; Curci, C.; Cox, S.N.; Pesce, F.; De Palma, G.; Schena, F.P. Role of let-7b in the regulation of N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 2 in IgA nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serino, G.; Sallustio, F.; Cox, S.N.; Pesce, F.; Schena, F.P. Abnormal miR-148b expression promotes aberrant glycosylation of IgA1 in IgA nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Kwan, B.C.; Lai, F.M.; Chow, K.M.; Li, P.K.; Szeto, C.C. Urinary miR-21, miR-29, and miR-93: Novel biomarkers of fibrosis. Am. J. Nephrol. 2012, 36, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhang, P.; Ding, X.; Yu, G.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Fang, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; et al. Integrating bioinformatics and metabolomics to identify potential biomarkers of hypertensive nephropathy. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Li, P.; Shan, W.; Gu, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Bao, K. Prediction of biomarkers associated with membranous nephropathy: Bioinformatic analysis and experimental validation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 126, 111266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Feng, J.; Zhong, J.; Lu, M.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y. Screening of the Key Genes and Signalling Pathways for Diabetic Nephropathy Using Bioinformatics Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 864407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Wang, L.; Fu, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, X.; Cao, M. Bioinformatics analysis identifies immune-related gene signatures and subtypes in diabetic nephropathy. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1048139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.R.; Abbas, Z.; Zahir, A.; Lee, S.W. Advancing genome-based precision medicine: A review on machine learning applications for rare genetic disorders. Brief. Bioinform. 2025, 26, bbaf329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, F.; Vakanski, A. Machine Learning Methods for Cancer Classification Using Gene Expression Data: A Review. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shved, N.; Warsow, G.; Eichinger, F.; Hoogewijs, D.; Brandt, S.; Wild, P.; Kretzler, M.; Cohen, C.D.; Lindenmeyer, M.T. Transcriptome-based network analysis reveals renal cell type-specific dysregulation of hypoxia-associated transcripts. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthier, C.C.; Bethunaickan, R.; Gonzalez-Rivera, T.; Nair, V.; Ramanujam, M.; Zhang, W.; Bottinger, E.P.; Segerer, S.; Lindenmeyer, M.; Cohen, C.D.; et al. Cross-species transcriptional network analysis defines shared inflammatory responses in murine and human lupus nephritis. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 988–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Zhang, W.; Su, J.; Xu, H.; Yang, H. Prediction of Drug Positioning for Quan-Du-Zhong Capsules Against Hypertensive Nephropathy Based on the Robustness of Disease Network. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Lassén, E.; Nair, V.; Berthier, C.C.; Suguro, M.; Sihlbom, C.; Kretzler, M.; Betsholtz, C.; Haraldsson, B.; Ju, W.; et al. Transcriptomic and Proteomic Profiling Provides Insight into Mesangial Cell Function in IgA Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 2961–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayson, P.C.; Eddy, S.; Taroni, J.N.; Lightfoot, Y.L.; Mariani, L.; Parikh, H.; Lindenmeyer, M.T.; Ju, W.; Greene, C.S.; Godfrey, B.; et al. Metabolic pathways and immunometabolism in rare kidney diseases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Green, M.R.; Gentles, A.J.; Feng, W.; Xu, Y.; Hoang, C.D.; Diehn, M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianping, W.; Wei, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, R.; Han, Q.; Yang, Q. Identifying DUSP-1 and FOSB as hub genes in immunoglobulin A nephropathy by WGCNA and DEG screening and validation. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Song, L.; Tan, J.; Yang, F. Identification of key genes for IgA nephropathy based on machine learning algorithm and correlation analysis of immune cells. Transpl. Immunol. 2023, 78, 101824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Xiaoyi, W.; Zi, Y. Screening and Bioinformatics Analysis of IgA Nephropathy Gene Based on GEO Databases. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 8794013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorieva, I.V.; Oszwald, A.; Grigorieva, E.F.; Schachner, H.; Neudert, B.; Ostendorf, T.; Floege, J.; Lindenmeyer, M.T.; Cohen, C.D.; Panzer, U.; et al. A Novel Role for GATA3 in Mesangial Cells in Glomerular Development and Injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 30, 1641–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H. Identification and Validation of Prognostic Biomarkers Specifically Expressed in Macrophage in IgA Nephropathy Patients Based on Integrated Bioinformatics Analyses. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 884588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, K.; Kanmatsuse, K. Interleukin-17 stimulates the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines by blood monocytes in patients with IgA nephropathy. Scand. J. Urol. Nephrol. 2003, 37, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aikawa, Y.; Morimoto, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Chaki, H.; Hashiramoto, A.; Narita, H.; Hirono, S.; Shiozawa, S. Treatment of arthritis with a selective inhibitor of c-Fos/activator protein-1. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruszkowski, J.; Lisowska, K.A.; Pindel, M.; Heleniak, Z.; Dębska-Ślizień, A.; Witkowski, J.M. T cells in IgA nephropathy: Role in pathogenesis, clinical significance and potential therapeutic target. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2019, 23, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Crew, R.; Zhang, N.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Y. Serum Levels of Soluble ST2 and IL-10 Are Associated with Disease Severity in Patients with IgA Nephropathy. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 6540937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.R.; Seol, H.; Abbas, Z.; Lee, S.W. Exploring the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Smart Healthcare: A Capability and Function-Oriented Review. Healthcare 2025, 13, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chweidan, H.; Rudyuk, N.; Tzur, D.; Goldstein, C.; Almoznino, G. Statistical Methods and Machine Learning Algorithms for Investigating Metabolic Syndrome in Temporomandibular Disorders: A Nationwide Study. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mehedi Hasan, M.; Maniruzzaman, M.; Shin, J. Identification of key candidate genes for IgA nephropathy using machine learning and statistics based bioinformatics models. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Sun, M. Identification of key genes, pathways and potential therapeutic agents for IgA nephropathy using an integrated bioinformatics analysis. J. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2020, 21, 1470320320919635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, F.; Saleem, M.H.; Aslam, M.F.; Ahmad, A.; Aslam, S. Construction of miRNA-mRNA network for the identification of key biological markers and their associated pathways in IgA nephropathy by employing the integrated bioinformatics analysis. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 4938–4945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, P. Expression of CCL2, FOS, and JUN May Help to Distinguish Patients With IgA Nephropathy From Healthy Controls. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 840890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.L.; Wang, D.; Yuan, F.L.; Lei, Q.F.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J.Z. Identification of key genes and pathways in IgA nephropathy using bioinformatics analysis. Medicine 2020, 99, e21372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.; Xue, M.; Li, Y.; Jia, Y.-J.; Zheng, Z.-J.; Yang, Y.-L.; Guan, M.-P.; Sun, L.; Xue, Y.-M. Early Growth Response 1 (Egr1) Is a Transcriptional Activator of NOX4 in Oxidative Stress of Diabetic Kidney Disease. J. Diabetes Res. 2018, 2018, 3405695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenz, R.; Eferl, R.; Scheinecker, C.; Redlich, K.; Smolen, J.; Schonthaler, H.B.; Kenner, L.; Tschachler, E.; Wagner, E.F. Activator protein 1 (Fos/Jun) functions in inflammatory bone and skin disease. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008, 10, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Lin, Y.; Ye, Z.; Zeng, X.; Wei, F. MicroRNA-27a-3p directly targets FosB to regulate cell proliferation, apoptosis, and inflammation responses in immunoglobulin a nephropathy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 529, 1124–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Kim, J.W.; Cho, B.S.; Chung, J.H. Association of FOS-like antigen 1 promoter polymorphism with podocyte foot process effacement in immunoglobulin A nephropathy patients. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2014, 28, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eferl, R.; Wagner, E.F. AP-1: A double-edged sword in tumorigenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Liang, L.; Qin, J.; Lu, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Lin, C.; Zhou, Q.; Feng, S.; Yip, S.H.; et al. Functional networks of aging markers in the glomeruli of IgA nephropathy: A new therapeutic opportunity. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 33616–33626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzano, S.A.; Barría, M.; Droguett, M.A.; Burgos, M.E.; Ardiles, L.G.; Flores, C.; Egido, J. Tubular NF-kappaB and AP-1 activation in human proteinuric renal disease. Kidney Int. 2001, 60, 1366–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zietara, A.; Spires, D.R.; Juffre, A.; Costello, H.M.; Crislip, G.R.; Douma, L.G.; Levchenko, V.; Dissanayake, L.V.; Klemens, C.A.; Nikolaienko, O.; et al. Knockout of the Circadian Clock Protein PER1 (Period1) Exacerbates Hypertension and Increases Kidney Injury in Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rats. Hypertension 2022, 79, 2519–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Yang, Z.; He, Y.; Wang, T.; Hua, P.; Yao, Q.; Gu, H. Circadian rhythm disruption promotes M1 macrophages polarization exacerbating the inflammatory response in rosacea. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2025, 317, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Chen, G.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, M.; Li, Z.; Shi, Y.; Luo, X.; Li, Z.; Huang, H.; Chen, X.; et al. Circadian Rhythm Disruption Exacerbates Autoimmune Uveitis: The Essential Role of PER1 in Treg Cell Metabolic Support for Stability and Function. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2400004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karachalias, N.; Babaei-Jadidi, R.; Rabbani, N.; Thornalley, P.J. Increased protein damage in renal glomeruli, retina, nerve, plasma and urine and its prevention by thiamine and benfotiamine therapy in a rat model of diabetes. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 1506–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliskan, Y.; Demir, E.; Karatay, E.; Ozluk, Y.; Mirioglu, S.; Dirim, A.B.; Artan, A.S.; Akgul, S.U.; Oto, O.A.; Oguz, F.S.; et al. Oxidative stress and macrophage infiltration in IgA nephropathy. J. Nephrol. 2022, 35, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Hong, T.; Ye, J.; Chu, C.; Zuo, L.; Zhang, J.; Cui, X. Targeting a positive regulatory loop in the tumor-macrophage interaction impairs the progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 932–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Tan, S.; Chen, X.; Yang, X. SOX17 Antagonizes the WNT Signaling Pathway and is Epigenetically Inactivated in Clear-Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2021, 14, 3383–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, H.; Hanamatsu, Y.; Saigo, C.; Takeuchi, T.; Iwata, H. SOX17 expression in tumor-penetrating vessels in relation to CD8(+) T-cell infiltration in cancer stroma niches. Thorac. Cancer 2024, 15, 2319–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeilschifter, J. Cross-talk between transmembrane signalling systems: A prerequisite for the delicate regulation of glomerular haemodynamics by mesangial cells. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1989, 19, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlöndorff, D.; Banas, B. The mesangial cell revisited: No cell is an island. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tataranni, T.; Agriesti, F.; Mazzoccoli, C.; Ruggieri, V.; Scrima, R.; Laurenzana, I.; D’AUria, F.; Falzetti, F.; Di Ianni, M.; Musto, P.; et al. The iron chelator deferasirox affects redox signalling in haematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 170, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.; Yang, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Adams, R.H.; Wells, J.M.; Morrison, S.J.; Koh, G.Y.; et al. Sox17 promotes tumor angiogenesis and destabilizes tumor vessels in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 418–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Kobayashi, N.; Ikeda, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Tsuge, T.; Horikoshi, S.; Emancipator, S.N.; Tomino, Y. Down-regulation of core 1 beta1,3-galactosyltransferase and Cosmc by Th2 cytokine alters O-glycosylation of IgA1. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant 2010, 25, 3890–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, T.; Dai, M.; Zhang, F.; Wen, W. Integrative Bioinformatics-Guided Analysis of Glomerular Transcriptome Implicates Potential Therapeutic Targets and Pathogenesis Mechanisms in IgA Nephropathy. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101040
Yang T, Dai M, Zhang F, Wen W. Integrative Bioinformatics-Guided Analysis of Glomerular Transcriptome Implicates Potential Therapeutic Targets and Pathogenesis Mechanisms in IgA Nephropathy. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(10):1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101040
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Tiange, Mengde Dai, Fen Zhang, and Weijie Wen. 2025. "Integrative Bioinformatics-Guided Analysis of Glomerular Transcriptome Implicates Potential Therapeutic Targets and Pathogenesis Mechanisms in IgA Nephropathy" Bioengineering 12, no. 10: 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101040
APA StyleYang, T., Dai, M., Zhang, F., & Wen, W. (2025). Integrative Bioinformatics-Guided Analysis of Glomerular Transcriptome Implicates Potential Therapeutic Targets and Pathogenesis Mechanisms in IgA Nephropathy. Bioengineering, 12(10), 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101040





