Artificial Intelligence-Based Methods and Omics for Mental Illness Diagnosis: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
- Studies involving human participants or clinically relevant human-derived samples (blood, urine, CSF, neuroimaging data, etc.).
- Research explicitly addressing biomarker discovery, validation, or application for diagnosis or prognosis of depression, bipolar disorder, or anxiety disorders.
- Studies applying artificial intelligence, machine learning, deep learning, or computational modelling in the analysis of psychiatric biomarkers, particularly within an omics framework.
- Studies involving only animal models without translational validation.
- Articles not directly addressing diagnosis or biomarker discovery in psychiatric disorders.
- Conference abstracts, editorials, and opinion pieces without original data.
3. Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning
4. Computational Modelling
5. Making the Invisible Visible: The Role of Explainable AI in Mental Health Diagnostics
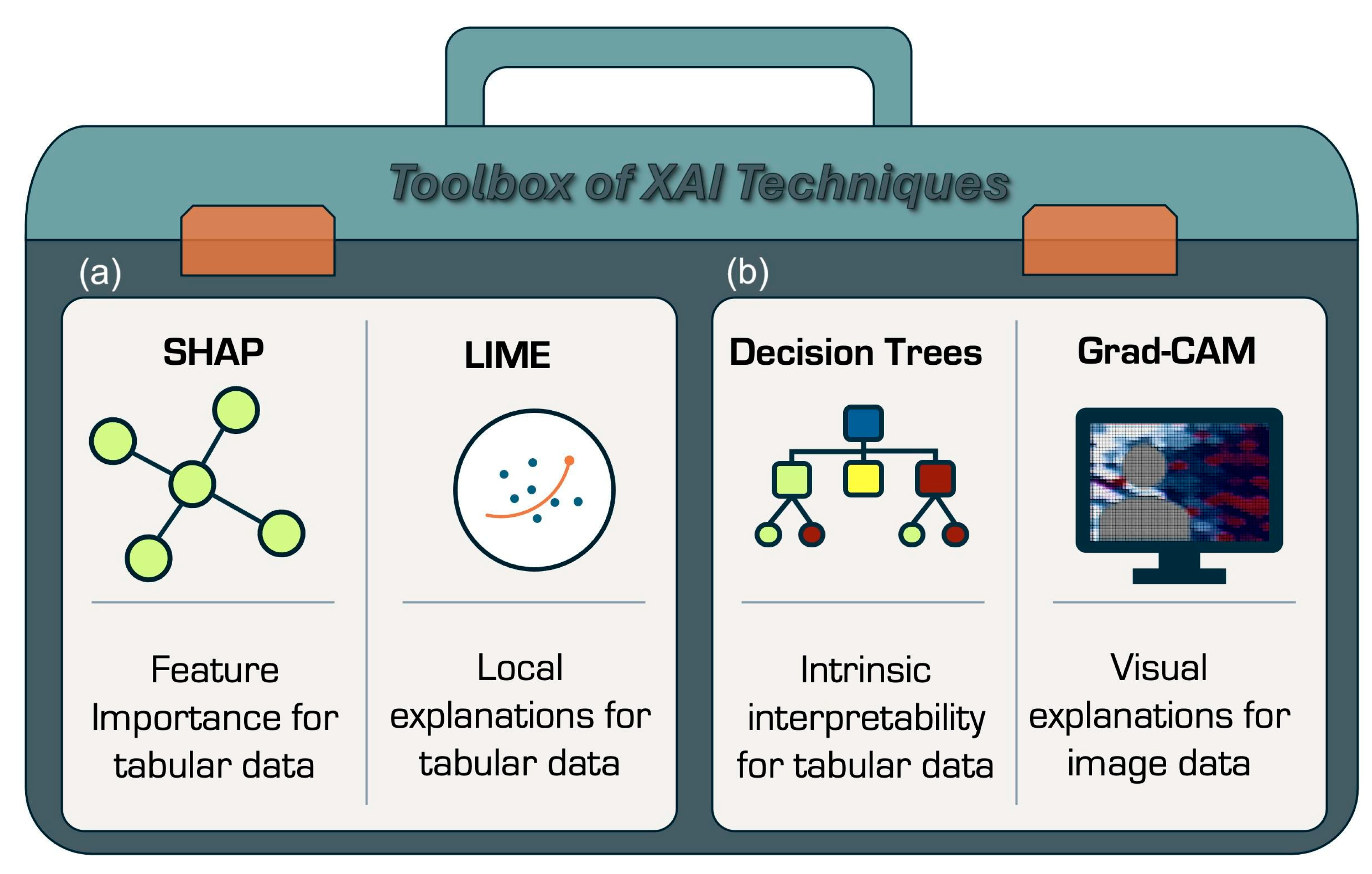
5.1. What Is Explainability and Why It Matters
5.2. Explainability in Practice: What Techniques Are Used
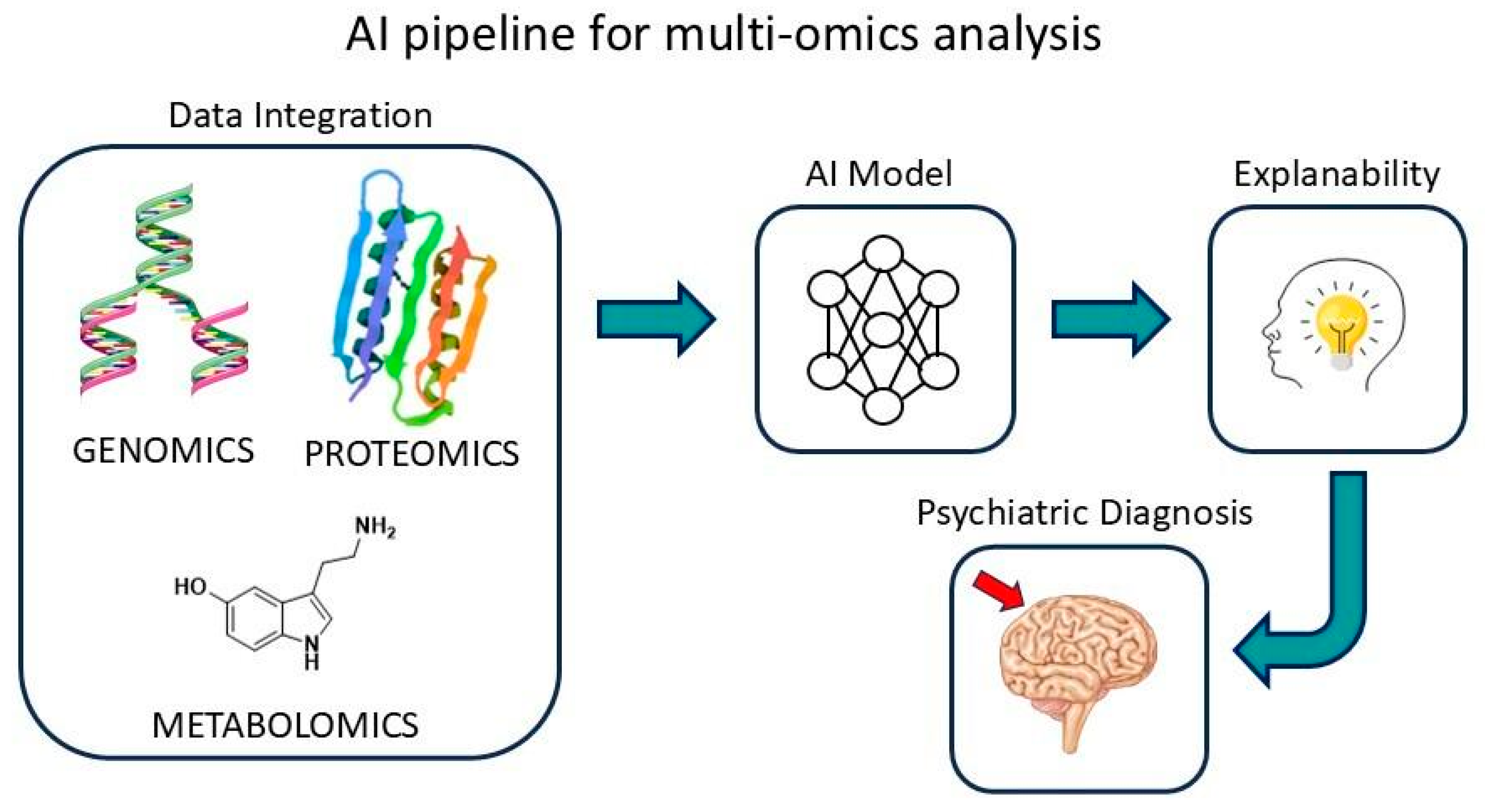
6. Multi-Omics and AI in Psychiatry
7. From Multi-Omics to Machine Learning: Advances in Psychiatric Diagnostics
7.1. Bipolar Disorder
7.2. Anxiety Disorders
7.3. Depression
| Disorder | Potential Biomarkers | Sample Type | Measurement | Sampling * | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolomics/Lipidomics | |||||
| Anxiety | N-methyl nicotinamide, amino malonic acid, azelaic acid, and hippuric acid | Urine | NMR and GC-MS | AD with or without depression (N = 48) and HC (N = 48) | Chen et al., 2018 [111] |
| Anxiety | Glycoprotein acetyls, docosahexaenoic acid, serum total triglycerides, omega-3 fatty acids, apolipoprotein B, VLDL cholesterol, and glucose, among others (13 metabolites) | Plasma | NMR | AD + depression (N = 531), depression (N = 304), AD (N = 548), remitted depression and/or AD (N = 897), and HC (N = 634) | Kluiver et al., 2021 [112] |
| Anxiety | Increased histidine, 2-phenylacetamide, cytosine, and 4-hydroxy hippuric acid; decreased glutamine, threonic acid, L-methionine, malic acid, L-valine, citric acid, tyrosine, and propionyl carnitine, among others (22 metabolites) | Serum | LC-MS | AD (N = 18) and HC (N = 31) | Vismara et al., 2020 [51] |
| Anxiety | Uridine, 3-methoxy tyrosine, L-methionine, L-leucine, and xanthine, among others (43 metabolites) | Serum | UPLC-MS/MS | PD (N = 55) and HC (N = 55) | Shan et al., 2023 [113] |
| Depression | 57 male-related and 53 female-related differential metabolites, where biliverdin was a male-specific biomarker and phosphatidylcholine (10:0/14:1) was a female-specific biomarker | Plasma | UPLC-Q-TOF/MS | MDD (N = 84—42 male and 42 female) and HC (N = 49—27 male and 22 female) | Jiang et al., 2022 [106] |
| Depression and Bipolar | MDD: succinic acid, γ-aminobutyric acid, glutamine, α-ketoglutaric acid, L-tyrosine, tyramine, dopamine, tryptophan, and kynurenine | Plasma neurotransmitters | LC-MS/MS and GC-MS | MDD (N = 49), BD (N = 30), and HC (N = 40) | Pan et al., 2018 [107] |
| Bipolar | Nervonic acid, 4-phenylbutyric acid, and 1-methyluric acid | Plasma | UPLC-MS/MS-/Orbitrap | BD (N = 91 and HC (N = 92) | Wei et al., 2021 [114] |
| Bipolar | Betaine, glycerol, hippuric acid, indole sulphate, trimethylamine oxide (upregulated), and inositol (downregulated) | Urine | NMR | BD (N = 37) and HC (N = 48) | Ren et al., 2021 [115] |
| Bipolar and Depression | DD: 2-hydroxyhippuric acid, tyramine-O-sulfate, and isobutyryl-L-carnitine (upregulated); 4-hydroxyphenylacetylglycine, vanilloylglycine, and L-cysteinylglycine disulfide (downregulated) BD: 2-aminoisobutyric acid, dopamine, pyridoxal, hexanoylglycine, citric acid, 3-hydroxysebacic acid, leucylproline, N-undecanoylglycine, norepinephrine sulfate, and hexanoylcarnitine (Upregulated) Shared: urobilin, hypoxanthine, guanine, serotonin, tyrosine, 4-pyridoxic acid, N-acetyl-L-glutamic acid, and dihydroxyindole, (upregulated) | Urine | UHPLC-MS | DD (N = 50), BD (N = 12), and HC (N = 50) | Wang et al., 2024 [116] |
| Bipolar | BH, BE, and BM: 3-hydroxyacetic acid, N-acetyl-glycoprotein, and mannose (upregulated) BH and BE: glucose (upregulated); lactate and acetoacetate (downregulated) BM: alanine and dimethylglycine (upregulated); acetate and ascorbate (downregulated) | Serum | NMR | BD and depressive episodes (BE, N = 59), BD and mania/hypomania episodes (BH, N = 16), BD and mixed episodes BM (N = 10), and HC (N = 10) | Guo et al., 2024 [76] |
| Bipolar | Threonine, aspartate, gamma-aminobutyric acid, 2-hydroxybutyric acid, serine, mannose, 3-hydroxybutyric acid, arginine, lysine, tyrosine, phenylalanine, glycerol, lactate, alanine, valine, leucine, isoleucine, glutamine, glutamate, glucose, and choline | Serum | NMR | BD (N = 33) and HC (N = 39) | Simić et al., 2023 [75] |
| Bipolar | Kynurenic acid, kynurenine, tryptophan, and picolinic acid (upregulated) | CSF | UPLC-MS/MS | BD (N = 101) and HC (N = 80) | Trepci et al., 2021 [79] |
| Proteomics | |||||
| Anxiety | Receptor tyrosine kinase (AXL), vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1, a membrane protein), and 3 other proteins of patients with comorbidities | Serum | Multi-analyte profiling immunoassay platform | SAD or depression (N = 2329) and HC (N = 652) | Gottschalk et al., 2015 [117] |
| Anxiety | Brain-derived neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) protein | Serum | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits | PD (N = 90) and HC (N = 99) | Li, J. et al., 2023 [118] |
| Anxiety | Proteins related to the immune response and GAD: A1BG, C4-A, TF, V3-3, and DEFA1 | Serum | Tandem mass tags (TMT) combined with HPLC-MS/MS | drug-naïve GAD (N = 21) and HC (N = 22) | Li, X et al., 2024 [119] |
| Depression | Pancreatic polypeptide, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), prostatin, angiogenin, apolipoprotein D, luteinising hormone, α-1-antitrypsin, α-1-antichymotrypsin, macrophage migration inhibitory factor, growth-regulated α-protein, insulin growth factor-binding protein-5, etc. | Serum | Multiplexed microbead immunoassays | current MDD (N = 687), remitted MDD (N = 482), and HC (N = 420) | Bot et al., 2015 [108] |
| Bipolar | Platelet-Derived Growth factor BB (PDGF-BB) and thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1) | Blood | Multiplex immunoassay | BD (N = 70), MDD (N = 42), and HC (N = 18) | Kittel-Schneider et al., 2020 [120] |
| Bipolar | BD and MDD: C3 (upregulated). BD and MDD: C4BPα and CFI (downregulated) | Plasma | Two-dimensional electrophoresis (2-DE and MALDI-TOF/TOF MS | BD (N = 20), MDD (N = 30), and HC (N = 30) | Chen et al., 2015 [121] |
| Bipolar | BD: serotransferrin, vanin, apolipoprotein A-I; endoglin, suprabasin; sulfhydryl oxidase (upregulated); alpha-1-acid glycoprotein, C-type mannose receptor 2, antileukoproteinase (downregulated) | Serum | LC-MS/MS | BD (N = 30) and HC (N = 30) | Ren et al., 2017 [122] |
| Bipolar | CLEC1B, TNFRSF21, tenascin-R, disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 23, cell adhesion molecule 3, RGM domain family member B, plexin-B1, brorin, CACNG4, and PLIN5 | CSF | LC-MS/MS | Two independent case-control cohorts (total N = 351) | Göteson et al., 2021 [123] |
| Bipolar | IL6, MCP-1, TGF-α, IL8, β-NGF, and IL10-RB (upregulated) | Plasma | ELISA/Olink proteomics | BD (N = 32) and HC (N = 16) | Xu et al., 2024 [124] |
| Genomics/Transcriptomics | |||||
| Anxiety | STK32B gene | Blood | Microarray technique (methylation) | Low-risk of GAD (N = 164) and high-risk of GAD (N = 55) | Ciuculete et al., 2018 [94] |
| Anxiety | Genes MUTYH, TOE1, MIR3146, DIP2C, SEC23IP, INPP5A, ESRRA, and ZNF689, among others (17 methylation biomarkers) | Blood | Bootstrapping techniques | AD (N = 94) and HC (N = 296) | Kwon et al., 2024 [95] |
| Depression | ABCA13 rs4917029, BNIP3 rs9419139, CACNA1E rs704329, EXOC4 rs6978272, GRIN2B rs7954376, LHFPL3 rs4352778, NELL1 rs2139423, NUAK1 rs2956406, PREX1 rs4810894, and SLIT3 rs139863958 | Analysis of genetic and clinical factors | Deep learning technique—multilayer feedforward neural networks (MFNNs). | MDD (N = 455) | Lin et al., 2018 [125] |
| Bipolar | FADS1/2 gene | Brain | LC-MS/MS | Fads1/2 knockout mice | Yamamoto et al., 2023 [78] |
| Bipolar | Found 64 associated genomic loci, including CACNB2, KCNB1, BTN2A1, HTR6, MCHR1, DCLK3, and FURIN | Brain | GWAS | BD (N = 41,917) and HC (N = 371,549) | Mullins et al., 2021 [66] |
| Bipolar | ANK3, CACNA1C, CACNA1B, HOMER1, KCNB1, MCHR1, NCAN, and SHANK2 | Brain | GWAS | - | Li et al., 2021 [126] |
| Bipolar | TRANK1 | Brain | GWAS and eQTL | BD (N = 1784) and HC (N = 2474) | Li et al., 2021 [127] |
| Bipolar | 298 genome significant loci, including FURIN, MED24, THRA, ALDH2, ANKK1, ARHGAP15, CACNA1B, ERBB4, ESR1, FES, GPR139, HTT, MLEC, MSH6, PSMD14, TOMM2 ALDH2, ESR1, HTT, ERBB4, CACNA1B, SHANK2, OLFM1, SHISA9, SORCS3, and LR5NF | Brain | GWAS | BD (N = 158,036) and HC (N = 2.8 million) | O’Connell et al., 2025 [128] |
| Bipolar and Depression | SYT14 | Brain | GWAS | BD (N = 1822) and HC (N = 4650); MDD (N = 5303) and HC (N = 5337); | Zhang et al., 2025 [129] |
| Bipolar | CRMP1, SYT4, UCHL1, ADCY1, and ZBTB18 | Brain | Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) and GWAS | RNA-seq (N = 8, 1266 cells and B GWAS data (N = 413,466) | Wei et al., 2024 [130] |
8. Perspectives, Challenges, and Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ICD-11 2022 Release. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/11-02-2022-icd-11-2022-release (accessed on 7 June 2025).
- Cloninger, C.R.; Svrakic, D.M.; Lester, N.C.; Lecic-Tosevski, D.; Koldobsky, N.; Botbol, M. Personality Disorders. In Person Centered Psychiatry; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 427–444. ISBN 9783319397221. [Google Scholar]
- American Psychiatric Association Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5-TR; American Psychiatric Association Publishing: Washington, DC, USA, 2022; ISBN 9780890425756.
- Hopwood, C.J.; Thomas, K.M.; Markon, K.E.; Wright, A.G.C.; Krueger, R.F. DSM-5 Personality Traits and DSM-IV Personality Disorders. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2012, 121, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skodol, A.E.; Morey, L.C.; Bender, D.S.; Oldham, J.M. The Alternative DSM-5 Model for Personality Disorders: A Clinical Application. Am. J. Psychiatry 2015, 172, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, A.W.; Gunderson, J.; Mulder, R. Treatment of Personality Disorder. Lancet 2015, 385, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herpertz, S.C.; Huprich, S.K.; Bohus, M.; Chanen, A.; Goodman, M.; Mehlum, L.; Moran, P.; Newton-Howes, G.; Scott, L.; Sharp, C. The Challenge of Transforming the Diagnostic System of Personality Disorders. J. Pers. Disord. 2017, 31, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.B.; Wei, W.-Q.; Weeraratne, D.; Frisse, M.E.; Misulis, K.; Rhee, K.; Zhao, J.; Snowdon, J.L. Precision Medicine, AI, and the Future of Personalized Health Care. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2021, 14, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Shen, L. Advances and Trends in Omics Technology Development. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 911861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, H. Artificial Intelligence in Multi-Omics Data Integration: Advancing Precision Medicine, Biomarker Discovery and Genomic-Driven Disease Interventions. Int. J. Sci. Res. Arch. 2023, 8, 1012–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Prelaj, A.; Miskovic, V.; Zanitti, M.; Trovo, F.; Genova, C.; Viscardi, G.; Rebuzzi, S.E.; Mazzeo, L.; Provenzano, L.; Kosta, S.; et al. Artificial Intelligence for Predictive Biomarker Discovery in Immuno-Oncology: A Systematic Review. Ann. Oncol. 2024, 35, 29–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, C.; Langendoerfer, P.; Zarrin, P.S.; Díaz, M.; Rubio, B. Kafka-ML: Connecting the Data Stream with ML/AI Frameworks. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2022, 126, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houhou, R.; Bocklitz, T. Trends in Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Chemometrics Applied to Chemical Data. Anal. Sci. Adv. 2021, 2, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, J.; Shu, J.; Li, M.; Mudappathi, R.; Jin, Y.; Lewis, F.; Boon, A.; Qin, X.; Liu, L.; Gu, H. Artificial Intelligence in Metabolomics: A Current Review. Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 178, 117852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudai, C.; Galizia, A.; Geraci, F.; Le Pera, L.; Morea, V.; Salerno, E.; Via, A.; Colombo, T. AI Applications in Functional Genomics. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 5762–5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.B. Navigating with Chemometrics and Machine Learning in Chemistry. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 9089–9114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, K.M.; Broadhurst, D.I.; Reinke, S.N. The Application of Artificial Neural Networks in Metabolomics: A Historical Perspective. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lac, L.; Leung, C.K.; Hu, P. Computational Frameworks Integrating Deep Learning and Statistical Models in Mining Multimodal Omics Data. J. Biomed. Inform. 2024, 152, 104629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Chu, L.; Zhang, J.; Luo, X.; Zhang, Y. Serum BDNF Levels Are Involved in the Diagnosis and Treatment Response in Patients with PD. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 327, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, J.E.; Claborne, D.M.; Weller, Z.D.; Webb-Robertson, B.-J.M.; Waters, K.M.; Bramer, L.M. Missing Data in Multi-Omics Integration: Recent Advances through Artificial Intelligence. Front. Artif. Intell. 2023, 6, 1098308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stransky, S.; Sun, Y.; Shi, X.; Sidoli, S. Ten Questions to AI Regarding the Present and Future of Proteomics. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1295721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Li, L.; Xu, Y.; Yang, J. Machine Learning Meets Omics: Applications and Perspectives. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbab460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dräger, A.; Helikar, T.; Barberis, M.; Birtwistle, M.; Calzone, L.; Chaouiya, C.; Hasenauer, J.; Karr, J.R.; Niarakis, A.; Rodríguez Martínez, M.; et al. SysMod: The ISCB Community for Data-Driven Computational Modelling and Multi-Scale Analysis of Biological Systems. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 3702–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanijou, J.K.; Kulyk, H.; Bergès, C.; Khoo, L.W.; Ng, P.; Yeo, H.C.; Helmy, M.; Bellvert, F.; Chew, W.; Selvarajoo, K. Metabolomics and Modelling Approaches for Systems Metabolic Engineering. Metab. Eng. Commun. 2022, 15, e00209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Falco, B.; Giannino, F.; Carteni, F.; Mazzoleni, S.; Kim, D.-H. Metabolic Flux Analysis: A Comprehensive Review on Sample Preparation, Analytical Techniques, Data Analysis, Computational Modelling, and Main Application Areas. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 25528–25548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejc, Ž.; Magdevska, L.; Tršelič, T.; Osolin, T.; Vodopivec, R.; Mraz, J.; Pavliha, E.; Zimic, N.; Cvitanović, T.; Rozman, D.; et al. Computational Modelling of Genome-Scale Metabolic Networks and Its Application to CHO Cell Cultures. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 88, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourato, A.; Valente, R.; Xavier, J.; Brito, M.; Avril, S.; de Sá, J.C.; Tomás, A.; Fragata, J. Computational Modelling and Simulation of Fluid Structure Interaction in Aortic Aneurysms: A Systematic Review and Discussion of the Clinical Potential. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadkin, L.E.; Makarenko, I.; Parker, N.G.; Shukurov, A.; Figueiredo, F.C.; Lako, M. Human Stem Cells for Ophthalmology: Recent Advances in Diagnostic Image Analysis and Computational Modelling. Curr. Stem Cell Rep. 2023, 9, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yevtushenko, P.; Goubergrits, L.; Franke, B.; Kuehne, T.; Schafstedde, M. Modelling Blood Flow in Patients with Heart Valve Disease Using Deep Learning: A Computationally Efficient Method to Expand Diagnostic Capabilities in Clinical Routine. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1136935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, T.U.; Will, G.-J.; Dubois, M.; Dolan, R.J. Annual Research Review: Developmental Computational Psychiatry. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatry 2019, 60, 412–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs-Dean, T.; Katthagen, T.; Tsenkova, I.; Ali, R.; Liang, X.; Spencer, T.; Diederen, K. Belief Updating in Psychosis, Depression and Anxiety Disorders: A Systematic Review across Computational Modelling Approaches. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 147, 105087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamori, Y.; Robinson, O.J. Computational Perspectives on Human Fear and Anxiety. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 144, 104959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowislo, J.F.; Orth, U. Does Low Self-Esteem Predict Depression and Anxiety? A Meta-Analysis of Longitudinal Studies. Psychol. Bull. 2013, 139, 213–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linardatos, P.; Papastefanopoulos, V.; Kotsiantis, S. Explainable AI: A Review of Machine Learning Interpretability Methods. Entropy 2020, 23, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassija, V.; Chamola, V.; Mahapatra, A.; Singal, A.; Goel, D.; Huang, K.; Scardapane, S.; Spinelli, I.; Mahmud, M.; Hussain, A. Interpreting Black-Box Models: A Review on Explainable Artificial Intelligence. Cognit. Comput. 2024, 16, 45–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulsen, T. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): Concepts and Challenges in Healthcare. AI 2023, 4, 652–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, D.; Kakinuma, T.; Fujita, S.; Kamagata, K.; Fushimi, Y.; Ito, R.; Matsui, Y.; Nozaki, T.; Nakaura, T.; Fujima, N.; et al. Fairness of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: Review and Recommendations. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2024, 42, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamparia, A.; Gupta, D. (Eds.) Explainable Artificial Intelligence for Biomedical and Healthcare Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; ISBN 9781003220107. [Google Scholar]
- Voigt, P.; von dem Bussche, A. The EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): A Practical Guide; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; ISBN 9783031623288. [Google Scholar]
- Ponce-Bobadilla, A.V.; Schmitt, V.; Maier, C.S.; Mensing, S.; Stodtmann, S. Practical Guide to SHAP Analysis: Explaining Supervised Machine Learning Model Predictions in Drug Development. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2024, 17, e70056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr Kumarakulasinghe, N.; Blomberg, T.; Liu, J.; Saraiva Leao, A.; Papapetrou, P. Evaluating Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations on Clinical Machine Learning Classification Models. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 33rd International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), Rochester, MN, USA, 28–30 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Podgorelec, V.; Kokol, P.; Stiglic, B.; Rozman, I. Decision Trees: An Overview and Their Use in Medicine. J. Med. Syst. 2002, 26, 445–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brima, Y.; Atemkeng, M. Saliency-Driven Explainable Deep Learning in Medical Imaging: Bridging Visual Explainability and Statistical Quantitative Analysis. BioData Min. 2024, 17, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ogasawara, K. Grad-CAM-Based Explainable Artificial Intelligence Related to Medical Text Processing. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, M.; Scott-Boyer, M.-P.; Bodein, A.; Périn, O.; Droit, A. Integration Strategies of Multi-Omics Data for Machine Learning Analysis. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 3735–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, J.L.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Shen, L.; Long, Q. Deep Learning-Based Approaches for Multi-Omics Data Integration and Analysis. BioData Min. 2024, 17, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, L.; Lapuschkin, S.; Binder, A.; Samek, W. Beyond Explaining: Opportunities and Challenges of XAI-Based Model Improvement. Inf. Fusion. 2023, 92, 154–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.E.; Torous, J.; De Choudhury, M.; Depp, C.A.; Graham, S.A.; Kim, H.-C.; Paulus, M.P.; Krystal, J.H.; Jeste, D.V. Artificial Intelligence for Mental Health Care: Clinical Applications, Barriers, Facilitators, and Artificial Wisdom. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2021, 6, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Abuhmed, T.; El-Sappagh, S.; Muhammad, K.; Alonso-Moral, J.M.; Confalonieri, R.; Guidotti, R.; Del Ser, J.; Díaz-Rodríguez, N.; Herrera, F. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): What We Know and What Is Left to Attain Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence. Inf. Fusion. 2023, 99, 101805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roseberry, K.; Le-Niculescu, H.; Levey, D.F.; Bhagar, R.; Soe, K.; Rogers, J.; Palkowitz, S.; Pina, N.; Anastasiadis, W.A.; Gill, S.S.; et al. Towards Precision Medicine for Anxiety Disorders: Objective Assessment, Risk Prediction, Pharmacogenomics, and Repurposed Drugs. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 2894–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vismara, M.; Girone, N.; Cirnigliaro, G.; Fasciana, F.; Vanzetto, S.; Ferrara, L.; Priori, A.; D’Addario, C.; Viganò, C.; Dell’Osso, B. Peripheral Biomarkers in DSM-5 Anxiety Disorders: An Updated Overview. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Abraham, S.; Singh, A.; Balaji, S.; Mukunthan, K.S. From Data to Cure: A Comprehensive Exploration of Multi-Omics Data Analysis for Targeted Therapies. Mol. Biotechnol. 2025, 67, 1269–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Dwivedi, Y. Recent Developments in Omics Studies and Artificial Intelligence in Depression and Suicide. Transl. Psychiatry 2025, 15, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagenberg, J.; BeCOME Study Group; OPTIMA Study Group; Brückl, T.M.; Erhart, M.; Kopf-Beck, J.; Ködel, M.; Rehawi, G.; Röh-Karamihalev, S.; Sauer, S.; et al. Dissecting Depression Symptoms: Multi-Omics Clustering Uncovers Immune-Related Subgroups and Cell-Type Specific Dysregulation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2025, 123, 353–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos-Moreno, M.P.; Pinto, J.V.; Hasse-Sousa, M.; de Souza Melo, I.M.; Saviatto, N.G.; Lucas, P.K.; Baldez, D.P.; Passos, I.C.; Kapczinski, F. Diagnosis, Clinical Features, Differential Diagnosis, and Psychiatric Comorbidities. In Bipolar Disorder; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 105–146. ISBN 9783031855184. [Google Scholar]
- Buch, A.M.; Liston, C. Dissecting Diagnostic Heterogeneity in Depression by Integrating Neuroimaging and Genetics. Neuropsychopharmacology 2021, 46, 156–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bipolar Disorder. Available online: https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/bipolar-disorder (accessed on 9 June 2025).
- GBD 2019 Mental Disorders Collaborators. Global, Regional, and National Burden of 12 Mental Disorders in 204 Countries and Territories, 1990-2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Psychiatry 2022, 9, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bipolar Disorder. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/bipolar-disorder (accessed on 9 June 2025).
- Siegel-Ramsay, J.E.; Bertocci, M.A.; Wu, B.; Phillips, M.L.; Strakowski, S.M.; Almeida, J.R.C. Distinguishing between Depression in Bipolar Disorder and Unipolar Depression Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Systematic Review. Bipolar Disord. 2022, 24, 474–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadr, S.S.; Samimi-Ardestani, S.M.; Semnani, Y.; Adel, N.; Tajari, F.; Samani, N. Neurological Soft Signs in Type I Bipolar Disorder and Bipolar Spectrum Patients and Their Unaffected First-Degree Relatives: A Cross-Sectional Study. Health Sci. Rep. 2025, 8, e70341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva, V.; Fico, G.; De Prisco, M.; Gonda, X.; Rosa, A.R.; Vieta, E. Bipolar Disorders: An Update on Critical Aspects. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2025, 48, 101135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaini, G.; Valvassori, S.S.; Diaz, A.P.; Lima, C.N.; Benevenuto, D.; Fries, G.R.; Quevedo, J. Neurobiology of Bipolar Disorders: A Review of Genetic Components, Signaling Pathways, Biochemical Changes, and Neuroimaging Findings. Braz. J. Psychiatry 2020, 42, 536–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nierenberg, A.A.; Agustini, B.; Köhler-Forsberg, O.; Cusin, C.; Katz, D.; Sylvia, L.G.; Peters, A.; Berk, M. Diagnosis and Treatment of Bipolar Disorder: A Review. JAMA 2023, 330, 1370–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uffelmann, E.; Huang, Q.Q.; Munung, N.S.; de Vries, J.; Okada, Y.; Martin, A.R.; Martin, H.C.; Lappalainen, T.; Posthuma, D. Genome-Wide Association Studies. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2021, 1, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, N.; Forstner, A.J.; O’Connell, K.S.; Coombes, B.; Coleman, J.R.I.; Qiao, Z.; Als, T.D.; Bigdeli, T.B.; Børte, S.; Bryois, J.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study of More than 40,000 Bipolar Disorder Cases Provides New Insights into the Underlying Biology. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, L.N.; McGuire, A.B.; Manzardo, A.M.; Butler, M.G. High-Resolution Chromosome Ideogram Representation of Recognized Genes for Bipolar Disorder. Gene 2016, 586, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Long, F.; Cai, B.; Chen, X.; Chen, G. A Novel Relationship for Schizophrenia, Bipolar and Major Depressive Disorder Part 5: A Hint from Chromosome 5 High Density Association Screen. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 2473–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oraki Kohshour, M.; Papiol, S.; Ching, C.R.K.; Schulze, T.G. Genomic and Neuroimaging Approaches to Bipolar Disorder. BJPsych Open 2022, 8, e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Bergen, S.E.; Akula, N.; Song, J.; Hultman, C.M.; Landén, M.; Adli, M.; Alda, M.; Ardau, R.; Arias, B.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study of 40,000 Individuals Identifies Two Novel Loci Associated with Bipolar Disorder. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 3383–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, M.; Carvalho, A.F. The Compensatory Immune-Regulatory Reflex System (CIRS) in Depression and Bipolar Disorder. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 8885–8903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, D.R.; Rapaport, M.H.; Miller, B.J. A Meta-Analysis of Blood Cytokine Network Alterations in Psychiatric Patients: Comparisons between Schizophrenia, Bipolar Disorder and Depression. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 1696–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madireddy, S.; Madireddy, S. Therapeutic Interventions to Mitigate Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress-Induced Damage in Patients with Bipolar Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordovez, F.J.A.; McMahon, F.J. The Genetics of Bipolar Disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 544–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simić, K.; Miladinović, Z.; Todorović, N.; Trifunović, S.; Avramović, N.; Gavrilović, A.; Jovanović, S.; Gođevac, D.; Vujisić, L.; Tešević, V.; et al. Metabolomic Profiling of Bipolar Disorder by H-NMR in Serbian Patients. Metabolites 2023, 13, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Jia, J.; Sun, X.L.; Yang, H.; Ren, Y. Comparing the Metabolic Pathways of Different Clinical Phases of Bipolar Disorder through Metabolomics Studies. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1319870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellendorf, F.T.; Gostner, J.M.; Lenger, M.; Platzer, M.; Birner, A.; Maget, A.; Queissner, R.; Tmava-Berisha, A.; Pater, C.A.; Ratzenhofer, M.; et al. Tryptophan Metabolism in Bipolar Disorder in a Longitudinal Setting. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Lee-Okada, H.-C.; Ikeda, M.; Nakamura, T.; Saito, T.; Takata, A.; Yokomizo, T.; Iwata, N.; Kato, T.; Kasahara, T. GWAS-Identified Bipolar Disorder Risk Allele in the FADS1/2 Gene Region Links Mood Episodes and Unsaturated Fatty Acid Metabolism in Mutant Mice. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 2848–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trepci, A.; Sellgren, C.M.; Pålsson, E.; Brundin, L.; Khanlarkhani, N.; Schwieler, L.; Landén, M.; Erhardt, S. Central Levels of Tryptophan Metabolites in Subjects with Bipolar Disorder. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021, 43, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlis, R.H.; Goldberg, J.F.; Ostacher, M.J.; Schneck, C.D. Clinical Decision Support for Bipolar Depression Using Large Language Models. Neuropsychopharmacology 2024, 49, 1412–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, P.; Xue, B.; Liu, Y.; Shen, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, X. Machine Learning for the Diagnosis Accuracy of Bipolar Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Psychiatry 2024, 15, 1515549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Ugaz, W.A.; Palacios Garay, J.P.; Rivera-Lozada, O.; Alarcón Diaz, M.A.; Fuster-Guillén, D.; Tejada Arana, A.A. An Overview of Bipolar Disorder Diagnosis Using Machine Learning Approaches: Clinical Opportunities and Challenges. Iran. J. Psychiatry 2023, 18, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, L.; Bhat, R.R.; Viswanath, V.; Li, X. DeepBipolar: Identifying Genomic Mutations for Bipolar Disorder via Deep Learning. Hum. Mutat. 2017, 38, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Xiao, C.; Qiao, X.; Zhu, Q.; Yan, H.; Pan, J.; Feng, Y. A Diagnostic Model Based on Bioinformatics and Machine Learning to Differentiate Bipolar Disorder from Schizophrenia and Major Depressive Disorder. Schizophrenia 2024, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.W.; Wee, P.H.; Low, L.L.; Koong, Y.L.A.; Htay, H.; Fan, Q.; Foo, W.Y.M.; Seng, J.J.B. Prevalence and Risk Factors for Elevated Anxiety Symptoms and Anxiety Disorders in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2021, 69, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szuhany, K.L.; Simon, N.M. Anxiety Disorders: A Review. JAMA 2022, 328, 2431–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penninx, B.W.; Pine, D.S.; Holmes, E.A.; Reif, A. Anxiety Disorders. Lancet 2021, 397, 914–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Verbeke, W.J.M.I. Understanding Importance of Clinical Biomarkers for Diagnosis of Anxiety Disorders Using Machine Learning Models. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandelow, B.; Michaelis, S.; Wedekind, D. Treatment of Anxiety Disorders. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 19, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anxiety Disorders. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/anxiety-disorders (accessed on 9 June 2025).
- Javaid, S.F.; Hashim, I.J.; Hashim, M.J.; Stip, E.; Samad, M.A.; Ahbabi, A.A. Epidemiology of Anxiety Disorders: Global Burden and Sociodemographic Associations. Middle East. Curr. Psychiatr. 2023, 30, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarino, A.; Harper, S.; Malcolm, R.; Stainthorpe, A.; Warren, G.; Margoum, M.; Hooper, J.; Blackwell, A.D.; Welchman, A.E. Economic Evaluation of 27,540 Patients with Mood and Anxiety Disorders and the Importance of Waiting Time and Clinical Effectiveness in Mental Healthcare. Nat. Ment. Health 2023, 1, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chodavadia, P.; Teo, I.; Poremski, D.; Fung, D.S.S.; Finkelstein, E.A. Prevalence and Economic Burden of Depression and Anxiety Symptoms among Singaporean Adults: Results from a 2022 Web Panel. BMC Psychiatry 2023, 23, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciuculete, D.M.; Boström, A.E.; Tuunainen, A.-K.; Sohrabi, F.; Kular, L.; Jagodic, M.; Voisin, S.; Mwinyi, J.; Schiöth, H.B. Changes in Methylation within the STK32B Promoter Are Associated with an Increased Risk for Generalized Anxiety Disorder in Adolescents. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2018, 102, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.; Blazyte, A.; Jeon, Y.; Kim, Y.J.; An, K.; Jeon, S.; Ryu, H.; Shin, D.-H.; Ahn, J.; Um, H.; et al. Identification of 17 Novel Epigenetic Biomarkers Associated with Anxiety Disorders Using Differential Methylation Analysis Followed by Machine Learning-Based Validation. Clin. Epigenetics 2025, 17, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Min, W.; Xiang, M.; Zhou, B.; Li, T. Integrated Genome-Wide Methylation and Expression Analyses Provide Predictors of Diagnosis and Early Response to Antidepressant in Panic Disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 322, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, P.H.A.; Gonçalves, C.A.; Nunes, F.A.d.S.F.; Becho, R.C. AI-Based Anxiety Monitoring: Development and Clinical Applications. Delos 2025, 18, e4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manole, A.; Cârciumaru, R.; Brînzaș, R.; Manole, F. Harnessing AI in Anxiety Management: A Chatbot-Based Intervention for Personalized Mental Health Support. Information 2024, 15, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qu, H.Q.; Chang, X.; Mentch, F.D.; Qiu, H.; Torkamandi, S.; Nguyen, K.; Ostberg, K.; Wang, T.; Glessner, J.; et al. Deep Learning Algorithms Reveal Genomic Markers for Anxiety Disorder in a Large Cohort of Children with down Syndrome. Mol. Psychiatry 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, R.; Singh, S.; Moudgil, A. A Deep Learning-Based Technique for Detection of Generalized Anxiety Disorder Using CNN and ResNet-like Approach. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depressive Disorder (Depression). Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/depression (accessed on 9 June 2025).
- Xu, Y.; Li, R.; Hu, C.; He, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jin, L. Global, Regional, and National Incidence Trends of Depressive Disorder, 1990-2019: An Age-Period-Cohort Analysis Based on the Global Burden of Disease 2019 Study. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2024, 88, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.-L.; Qian, Y.; Jin, X.-H.; Yu, H.-R.; Wu, H.; Du, L.; Chen, H.-L.; Shi, Y.-Q. Suicide Rates among People with Serious Mental Illness: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Psychol. Med. 2023, 53, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semkovska, M.; Quinlivan, L.; O’Grady, T.; Johnson, R.; Collins, A.; O’Connor, J.; Knittle, H.; Ahern, E.; Gload, T. Cognitive Function Following a Major Depressive Episode: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 2019, 6, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLachlan, C.; Shelton, R.; Li, L. Obesity, Inflammation, and Depression in Adolescents. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1221709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Qin, M.; Teng, T.; Li, X.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; He, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xie, P. Identification of Sex-Specific Plasma Biomarkers Using Metabolomics for Major Depressive Disorder in Children and Adolescents. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 929207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.-X.; Xia, J.-J.; Deng, F.-L.; Liang, W.-W.; Wu, J.; Yin, B.-M.; Dong, M.-X.; Chen, J.-J.; Ye, F.; Wang, H.-Y.; et al. Diagnosis of Major Depressive Disorder Based on Changes in Multiple Plasma Neurotransmitters: A Targeted Metabolomics Study. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bot, M.; Chan, M.K.; Jansen, R.; Lamers, F.; Vogelzangs, N.; Steiner, J.; Leweke, F.M.; Rothermundt, M.; Cooper, J.; Bahn, S.; et al. Serum Proteomic Profiling of Major Depressive Disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2015, 5, e599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouzid, A.; Almidani, A.; Zubrikhina, M.; Kamzanova, A.; Ilce, B.Y.; Zholdassova, M.; Yusuf, A.M.; Bhamidimarri, P.M.; AlHaj, H.A.; Kustubayeva, A.; et al. Integrative Bioinformatics and Artificial Intelligence Analyses of Transcriptomics Data Identified Genes Associated with Major Depressive Disorders Including. Neurobiol. Stress. 2023, 26, 100555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squarcina, L.; Villa, F.M.; Nobile, M.; Grisan, E.; Brambilla, P. Deep Learning for the Prediction of Treatment Response in Depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 281, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-J.; Bai, S.-J.; Li, W.-W.; Zhou, C.-J.; Zheng, P.; Fang, L.; Wang, H.-Y.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Xie, P. Urinary Biomarker Panel for Diagnosing Patients with Depression and Anxiety Disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kluiver, H.; Jansen, R.; Milaneschi, Y.; Bot, M.; Giltay, E.J.; Schoevers, R.; Penninx, B.W.J.H. Metabolomic Profiles Discriminating Anxiety from Depression. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2021, 144, 178–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, D.; You, L.; Wan, X.; Yang, H.; Zhao, M.; Chen, S.; Jiang, W.; Xu, Q.; Yuan, Y. Serum Metabolomic Profiling Revealed Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers in Patients with Panic Disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 323, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Zhao, L.; Du, Y.; Tian, Y.; Ni, P.; Ni, R.; Wang, Y.; Ma, X.; Hu, X.; Li, T. A Plasma Metabolomics Study Suggests Alteration of Multiple Metabolic Pathways in Patients with Bipolar Disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2021, 299, 113880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Chen, Z.-Z.; Sun, X.-L.; Duan, H.-J.; Tian, J.-S.; Wang, J.-Y.; Yang, H. Metabolomic Analysis to Detect Urinary Molecular Changes Associated with Bipolar Depression. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 742, 135515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Niu, N.; Ding, B.; Wang, P.; Zhao, H.; Li, N.; Chao, Y.; Gao, S.; et al. Evaluation of Metabolomics-Based Urinary Biomarker Models for Recognizing Major Depression Disorder and Bipolar Disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2024, 356, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, M.G.; Cooper, J.D.; Chan, M.K.; Bot, M.; Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Bahn, S. Discovery of Serum Biomarkers Predicting Development of a Subsequent Depressive Episode in Social Anxiety Disorder. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 48, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, R.; Li, D.; Zhang, J.; Luo, X.; Zhang, Y. Serum BDNF Levels and State Anxiety Are Associated with Somatic Symptoms in Patients with Panic Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1168771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zheng, S.; Feng, Z.; Liu, X.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, G.; Liu, M.; Zhu, H.; Jia, H. Serum Proteomics Analysis of Drug-Naïve Patients with Generalised Anxiety Disorder: Tandem Mass Tags and Multiple Reaction Monitoring. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2024, 25, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittel-Schneider, S.; Hahn, T.; Haenisch, F.; McNeill, R.; Reif, A.; Bahn, S. Proteomic Profiling as a Diagnostic Biomarker for Discriminating Between Bipolar and Unipolar Depression. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, C.; Song, Y.; Shi, H.; Wu, D.; Yang, Y.; Rao, C.; Liao, L.; Wu, Y.; Tang, J.; et al. Comparative Proteomic Analysis of Plasma from Bipolar Depression and Depressive Disorder: Identification of Proteins Associated with Immune Regulatory. Protein Cell 2015, 6, 908–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Zhao, G.; Sun, X.; Liu, H.; Jiang, P.; Chen, J.; Wu, Z.; Peng, D.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, C. Identification of Plasma Biomarkers for Distinguishing Bipolar Depression from Major Depressive Disorder by iTRAQ-Coupled LC-MS/MS and Bioinformatics Analysis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2017, 86, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göteson, A.; Isgren, A.; Jonsson, L.; Sparding, T.; Smedler, E.; Pelanis, A.; Zetterberg, H.; Jakobsson, J.; Pålsson, E.; Holmén-Larsson, J.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Proteomics Targeted for Central Nervous System Processes in Bipolar Disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 7446–7453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Su, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T.; Xie, T.; Wang, Y. Olink Proteomics Analysis Uncovers Inflammatory Proteins in Patients with Different States of Bipolar Disorder. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 131, 111816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, E.; Kuo, P.-H.; Liu, Y.-L.; Yu, Y.W.-Y.; Yang, A.C.; Tsai, S.-J. A Deep Learning Approach for Predicting Antidepressant Response in Major Depression Using Clinical and Genetic Biomarkers. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, T.; Xiao, X.; Chen, J.; Hu, Z.; Fang, Y. Phenotypes, Mechanisms and Therapeutics: Insights from Bipolar Disorder GWAS Findings. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 2927–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Cai, X.; Li, H.-J.; Song, M.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, L.; et al. Independent Replications and Integrative Analyses Confirm TRANK1 as a Susceptibility Gene for Bipolar Disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 2021, 46, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, K.S.; Koromina, M.; van der Veen, T.; Boltz, T.; David, F.S.; Yang, J.M.K.; Lin, K.-H.; Wang, X.; Coleman, J.R.I.; Mitchell, B.L.; et al. Genomics Yields Biological and Phenotypic Insights into Bipolar Disorder. Nature 2025, 639, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Yuan, J.; Jiang, H.; Sun, P.; Hui, L.; Xu, L.; Yu, L.; Guo, Z.; Wang, L.; et al. Human Mood Disorder Risk Gene Synaptotagmin-14 Contributes to Mania-like Behaviors in Mice. Mol. Psychiatry 2025, 30, 3466–3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Cheng, B.; Yang, X.; Chu, X.; He, D.; Qin, X.; Zhang, N.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, S.; Cai, Q.; et al. Single-Cell Multiomics Analysis Reveals Cell/tissue-Specific Associations in Bipolar Disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2024, 14, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, K.-K.; Pichika, M.R. Artificial Intelligence in Drug Development: Present Status and Future Prospects. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barberis, E.; Khoso, S.; Sica, A.; Falasca, M.; Gennari, A.; Dondero, F.; Afantitis, A.; Manfredi, M. Precision Medicine Approaches with Metabolomics and Artificial Intelligence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, M.; Alizadeh, S.; Jamalabadi, H.; Lueken, U.; Dannlowski, U.; Walter, H.; Olbrich, S.; Colic, L.; Kambeitz, J.; Koutsouleris, N.; et al. Translational Machine Learning for Psychiatric Neuroimaging. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 91, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudroff, T. Artificial Intelligence as a Replacement for Animal Experiments in Neurology: Potential, Progress, and Challenges. Neurol. Int. 2024, 16, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, A.J.; Gaudet, V.C.; Black, S.E.; Vasdev, N.; Rosa-Neto, P.; Zukotynski, K.A. Artificial Intelligence for Molecular Neuroimaging. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maron, E.; Nutt, D. Biological Markers of Generalized Anxiety Disorder. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 19, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; Ashjan, B.; Ghufran, M.; Taghreed, S.; Nada, A.; Nada, A.; Maryam, A. Classification of Anxiety Disorders Using Machine Learning Methods: A Literature Review. Insights Biomed. Res. 2020, 4, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; He, L. Recent Advances in Explainable Artificial Intelligence for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Chen, K.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Hu, M.; Chu, Y.-H.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Hu, J.; Yue, Q.; Liu, M. Exploring the Feasibility of Integrating Ultra-high Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging Neuroimaging with Multimodal Artificial Intelligence for Clinical Diagnostics. iRadiology 2024, 2, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, A.; Nawab, S.; Jin, Y.; Hassan, H.; Kaushik, A.C.; Wei, D.-Q. Ranking Breast Cancer Drugs and Biomarkers Identification Using Machine Learning and Pharmacogenomics. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2023, 6, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Oliveira, G.S.; Rodrigues, F.H.d.S.; Pontes, J.G.d.M.; Tasic, L. Artificial Intelligence-Based Methods and Omics for Mental Illness Diagnosis: A Review. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101039
de Oliveira GS, Rodrigues FHdS, Pontes JGdM, Tasic L. Artificial Intelligence-Based Methods and Omics for Mental Illness Diagnosis: A Review. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(10):1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101039
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Oliveira, Glenda Santos, Fábio Henrique dos Santos Rodrigues, João Guilherme de Moraes Pontes, and Ljubica Tasic. 2025. "Artificial Intelligence-Based Methods and Omics for Mental Illness Diagnosis: A Review" Bioengineering 12, no. 10: 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101039
APA Stylede Oliveira, G. S., Rodrigues, F. H. d. S., Pontes, J. G. d. M., & Tasic, L. (2025). Artificial Intelligence-Based Methods and Omics for Mental Illness Diagnosis: A Review. Bioengineering, 12(10), 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101039








