Meibomian Gland Dysfunction and Dropout in Diabetic Patients with Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Craig, J.P.; Nichols, K.K.; Akpek, E.K.; Caffery, B.; Dua, H.S.; Joo, C.K.; Liu, Z.; Nelson, J.D.; Nichols, J.J.; Tsubota, K.; et al. TFOS DEWS II Definition and Classification Report. Ocul. Surf. 2017, 15, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsheer, R.P.; Arunachalam, C. A Clinical Study of Meibomian Gland Dysfunction in Patients with Diabetes. Middle East Afr. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 22, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bron, A.J.; de Paiva, C.S.; Chauhan, S.K.; Bonini, S.; Gabison, E.E.; Jain, S.; Knop, E.; Markoulli, M.; Ogawa, Y.; Perez, V.; et al. TFOS DEWS II Pathophysiology Report. Ocul. Surf. 2017, 15, 438–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomlinson, A.; Bron, A.J.; Korb, D.R.; Amano, S.; Paugh, J.R.; Ian Pearce, E.; Yee, R.; Yokoi, N.; Arita, R.; Dogru, M. The International Workshop on Meibomian Gland Dysfunction: Report of the Diagnosis Subcommittee. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 2006–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogurtsova, K.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Huang, Y.; Linnenkamp, U.; Guariguata, L.; Cho, N.H.; Cavan, D.; Shaw, J.E.; Makaroff, L.E. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global Estimates for the Prevalence of Diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 128, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Shi, W.-Y.; Song, A.-P.; Gao, Y.; Dang, G.-F.; Ding, G.; Yu, T.; Shi, W.-Y.; Song, A.-P.; Gao, Y.; et al. Changes of Meibomian Glands in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 9, 1740–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, L.; Deng, S.; Sun, X.; Wang, N. Dry Eye Syndrome in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: Prevalence, Etiology, and Clinical Characteristics. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 2016, 8201053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandra Johanna, G.P.; Antonio, L.A.; Andrés, G.S. Correlation between Type 2 Diabetes, Dry Eye and Meibomian Glands Dysfunction. J. Optom. 2019, 12, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pult, H.; Riede-Pult, B. Comparison of Subjective Grading and Objective Assessment in Meibography. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2013, 36, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, Y.W. Detection of Meibomian Glands and Classification of Meibography Images. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 086008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pult, H.; Nichols, J.J. A Review of Meibography. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2012, 89, E760–E769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Yan, H.; Cai, H.; Sheng, M.; Li, B. Evaluation of Meibomian Gland Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes with Dry Eye Disease: A Non-Randomized Controlled Trial. BMC Ophthalmol. 2023, 23, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Fang, X.; Luo, S.; Shang, X.; Xie, Z.; Dong, N.; Xiao, X.; Lin, Z.; Liu, Z. Meibomian Glands and Tear Film Findings in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 762493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Han, X.-G.; Gao, Y.; Song, A.-P.; Dang, G.-F.; Yu, T.; Han, X.-G.; Gao, Y.; Song, A.-P.; Dang, G.-F. Morphological and Cytological Changes of Meibomian Glands in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 12, 1415–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Xu, B.; Zheng, Y.; Coursey, T.G.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Fu, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.E. Meibomian Gland Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 2017, 3047867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association, A.D. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2018. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, S13–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, C.P.; Ferris, F.L.; Klein, R.E.; Lee, P.P.; Agardh, C.D.; Davis, M.; Dills, D.; Kampik, A.; Pararajasegaram, R.; Verdaguer, J.T.; et al. Proposed International Clinical Diabetic Retinopathy and Diabetic Macular Edema Disease Severity Scales. Ophthalmology 2003, 110, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed-Noriega, K.; Charles-Cantu, D.E.; Mohamed-Noriega, J.; Velasco-Sepúlveda, B.H.; Morales-Wong, F.; Villarreal-Méndez, G.; Mohamed-Hamsho, J. Face Mask and Tear Film Stability: A Pilot Study of the Objective Measurement of Tear Break-Up Time. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brissette, A.R.; Drinkwater, O.J.; Bohm, K.J.; Starr, C.E. The Utility of a Normal Tear Osmolarity Test in Patients Presenting with Dry Eye Disease like Symptoms: A Prospective Analysis. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2019, 42, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczesna-Iskander, D.H.; Muzyka-Wozniak, M.; Llorens Quintana, C. The Efficacy of Ocular Surface Assessment Approaches in Evaluating Dry Eye Treatment with Artificial Tears. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffman, R.M.; Christianson, M.D.; Jacobsen, G.; Hirsch, J.D.; Reis, B.L. Reliability and Validity of the Ocular Surface Disease Index. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2000, 118, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rueden, C.T.; Schindelin, J.; Hiner, M.C.; DeZonia, B.E.; Walter, A.E.; Arena, E.T.; Eliceiri, K.W. ImageJ2: ImageJ for the next Generation of Scientific Image Data. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arita, R.; Itoh, K.; Inoue, K.; Amano, S. Noncontact Infrared Meibography to Document Age-Related Changes of the Meibomian Glands in a Normal Population. Ophthalmology 2008, 115, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, R.; Itoh, K.; Maeda, S.; Maeda, K.; Furuta, A.; Fukuoka, S.; Tomidokoro, A.; Amano, S. Proposed Diagnostic Criteria for Obstructive Meibomian Gland Dysfunction. Ophthalmology 2009, 116, 2058–2063.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A Flexible Statistical Power Analysis Program for the Social, Behavioral, and Biomedical Sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, R.; Suehiro, J.; Haraguchi, T.; Shirakawa, R.; Tokoro, H.; Amano, S. Objective Image Analysis of the Meibomian Gland Area. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 98, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vehof, J.; Kozareva, D.; Hysi, P.G.; Hammond, C.J. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Dry Eye Disease in a British Female Cohort. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 98, 1712–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richdale, K.; Chao, C.; Hamilton, M. Eye Care Providers’ Emerging Roles in Early Detection of Diabetes and Management of Diabetic Changes to the Ocular Surface: A Review. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, e001094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapleton, F.; Alves, M.; Bunya, V.Y.; Jalbert, I.; Lekhanont, K.; Malet, F.; Na, K.S.; Schaumberg, D.; Uchino, M.; Vehof, J.; et al. TFOS DEWS II Epidemiology Report. Ocul. Surf. 2017, 15, 334–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manaviat, M.R.; Rashidi, M.; Afkhami-Ardekani, M.; Shoja, M.R. Prevalence of Dry Eye Syndrome and Diabetic Retinopathy in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. BMC Ophthalmol. 2008, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Chen, X.; Qin, G.; Xie, H.; Lv, P. Tear Film Function in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Retinopathy. Ophthalmologica 2008, 222, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neira-Zalentein, W.; Holopainen, J.M.; Tervo, T.M.T.; Borrás, F.; Carmen Acosta, M.; Belmonte, C.; Gallar, J. Corneal Sensitivity in Diabetic Patients Subjected to Retinal Laser Photocoagulation. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 6043–6049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lu, L.; Fu, Y. Assessment of Ocular Surface Damage during the Course of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 2018, 1206808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritchard, N.; Edwards, K.; Vagenas, D.; Shahidi, A.M.; Sampson, G.P.; Russell, A.W.; Malik, R.A.; Efron, N. Corneal Sensitivity as an Ophthalmic Marker of Diabetic Neuropathy. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2010, 87, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, J.S.; Mittal, S. Graded Corneal Sensitivity for Screening of Diabetic Retinopathy. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 1996, 44, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nitoda, E.; Kallinikos, P.; Pallikaris, A.; Moschandrea, J.; Amoiridis, G.; Ganotakis, E.S.; Tsilimbaris, M. Correlation of Diabetic Retinopathy and Corneal Neuropathy Using Confocal Microscopy. Curr. Eye Res. 2012, 37, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.L.; Patel, D.V.; McGhee, C.N.J.; Pradhan, M.; Kilfoyle, D.; Braatvedt, G.D.; Craig, J.P. Peripheral Neuropathy and Tear Film Dysfunction in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Diabetes Res. 2014, 2014, 848659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyei, S.; Dzasimatu, S.K.; Asiedu, K.; Ayerakwah, P.A. Association between Dry Eye Symptoms and Signs. J. Curr. Ophthalmol. 2018, 30, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onwubiko, S.N.; Eze, B.I.; Udeh, N.N.; Onwasigwe, E.N.; Umeh, R.E. Dry Eye Disease: Concordance between the Diagnostic Tests in African Eyes. Eye Contact Lens 2016, 42, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yeh, T.N.; Chakraborty, R.; Yu, S.X.; Lin, M.C. A Deep Learning Approach for Meibomian Gland Atrophy Evaluation in Meibography Images. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2019, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
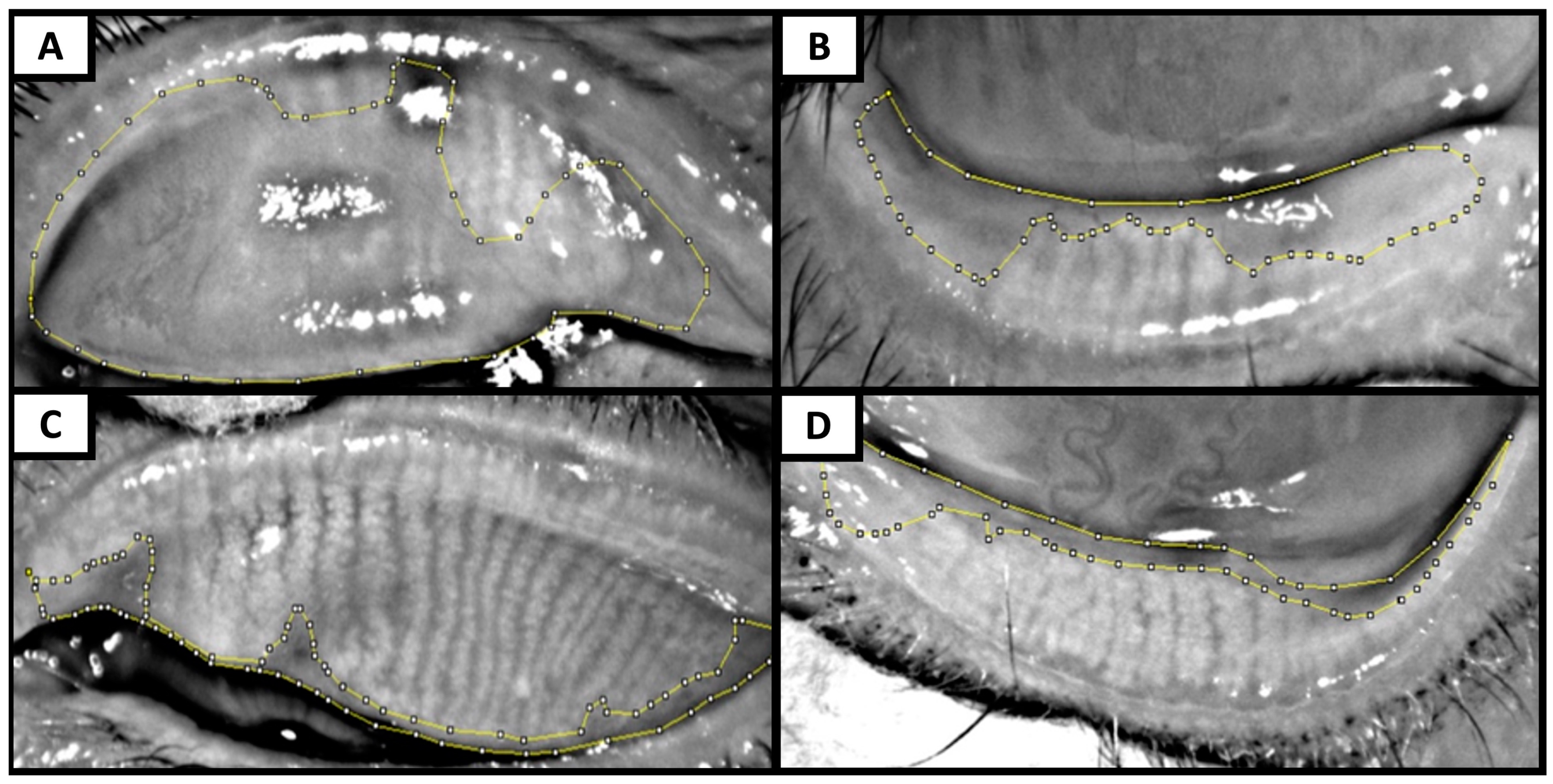
| Author/Country/Year | N= (Eyes) | MG Dropout Assessment on Meibography | Meiboscore DM vs. NDM | MG Dropout DM vs. NDM | Age and DM Duration (Years) | MG Dropout Correlation with Age and DM Duration | Other MGD Findings in DM vs. NDM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mohamed-Noriega et al. Mexico, 2024. (This study) | DM: 98 (all NPDR) NDM: 106 | Objective, with ImageJ and meiboscore | Higher in DM 3.8 ± 0.8 vs. 3.4 ± 1.0, p = 0.001 | Greater in DM 45 ± 11 vs. 39 ± 13, p = 0.016 | Age: 67 ± 10 Duration: 18 ± 9 | Correlation with age (r = 0.178, p = 0.014). No correlation with DM duration | Worse MG expressibility (3. 9 ± 1.6 vs. 4.4 ± 2.1, p = 0.017), meibum quality (1.9 ± 0.8 vs. 1.7 ± 0.5; p = 0.019), and Marx’s line (1.6 ± 0.8 vs. 1.8 ± 0.5, p < 0.001) |
| Yang Q et al. China, 2023 [12] | DM + DED: 30 NDM no DED: 16 | Objective, with ImageJ and meiboscore | Greater in DM 33.5 ± 8.2 vs. 16.5 ± 6.6, p = 0.001 | Age: 65 ± 9 Duration: 12 ± 8 | Correlation with DM duration (r = 0.509, p < 0.05) Age: not analyzed | Worse meibum score (2.2 ± 0.6 vs. 0.7 ± 0.6, p = 0.003) | |
| Wu, Huping, et al. China, 2022 [13] | DM: 99 NDM: 40 | Subjective, with meiboscore No ImageJ | Higher in DM 3.5 ± 1.0 vs. 2.3 ± 0.8, p < 0.001 | Age: 60 ± 6 Duration: 5 ± 3 | Correlation with age (β = 0.362, p = 0.001) and DM duration (p < 0.001) | Worse meibum score (25.0 ± 6.1 vs. 14.5 ± 4.1, p < 0.001) | |
| Yu T et al. China, 2019 [14] | DM: 132 NDM: 100 | Subjective, with meiboscore No ImageJ | Higher in DM (Z = −4.057, p < 0.001) | Age: 60 ± 8 Duration: 8 ± 5 | Correlation with DM duration (r = 0.509, p < 0.05) Age: not analyzed | ||
| Lin X et al. China, 2017 [15] | DM: 78 NDM: 108 | Subjective, with meiboscore No ImageJ | Higher in DM (4.3 ± 1.4 vs. 3.6 ± 1.4, p = 0.004) | Age: 67 ± 2 Duration: 9 ± 5 | Not analyzed | Worse MG expressibility (p = 0.039) and lid margin abnormality score (p = 0.04) | |
|
Yu T et al. China, 2016 [6] | DM: 118 NDM: 100 | Subjective, with meiboscore No ImageJ | More prevalence of MG dropout in DM: 57% vs. 33%, p ≤ 0.001 | Age: 60 ± 8 Duration: No data | Not analyzed |
| Variable | Patients with No Diabetes n = 106 Eyes | Patients with Diabetes with NPDR n = 98 Eyes | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Men | 26 (49.1%) | 24 (48.9%) | 0.896 |
| Women | 27 (50.9%) | 25 (51.1%) | |
| Age | 66.7 ± 9 | 67.1 ± 10 | 0.982 |
| Duration of diabetes | N/A | 18 ± 9 (3–31) | N/A |
| OSDI | 38.9 ± 20 | 45.98 ± 22 | 0.535 |
| TBUT | 7.0 ± 2.8 | 6.7 ± 2.8 | 0.969 |
| Osmolarity | 303 ± 19 | 298 ± 17 | 0.230 |
| MMP-9 positive | 5 (4.7%) | 3 (3.0%) | 0.725 |
| Oxford staining grade | 0.8 ± 1.1 | 1.4 ± 1.2 | 0.001 |
| NEI staining grade | 0.9 ± 1.1 | 1.7 ± 1.3 | 0.001 |
| Schirmer without anesthesia | 14.7 ± 8.0 | 17.0 ± 9.1 | 0.115 |
| Schirmer with anesthesia | 13.3 ± 6.2 | 14.4 ± 8.0 | 0.120 |
| Corneal esthesiometry | 5.9 ± 0.4 | 5.4 ± 1.1 | <0.001 |
| MG expressibility | 4.4 ± 2.1 | 3.9 ± 1.6 | 0.017 |
| Meibum quality | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 1.9 ± 0.8 | 0.019 |
| Marx’s line | 1.6 ± 0.8 | 1.8 ± 0.5 | <0.001 |
| Patients with No Diabetes Mean ± SD (min–max) | Patients with Diabetes with NPDR Mean ± SD (min–max) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Superior eyelid | |||
| Arita’s grade (0–3) | 1.4 ± 0.6 (1–3) | 1.8 ± 0.5 (1–3) | <0.001 |
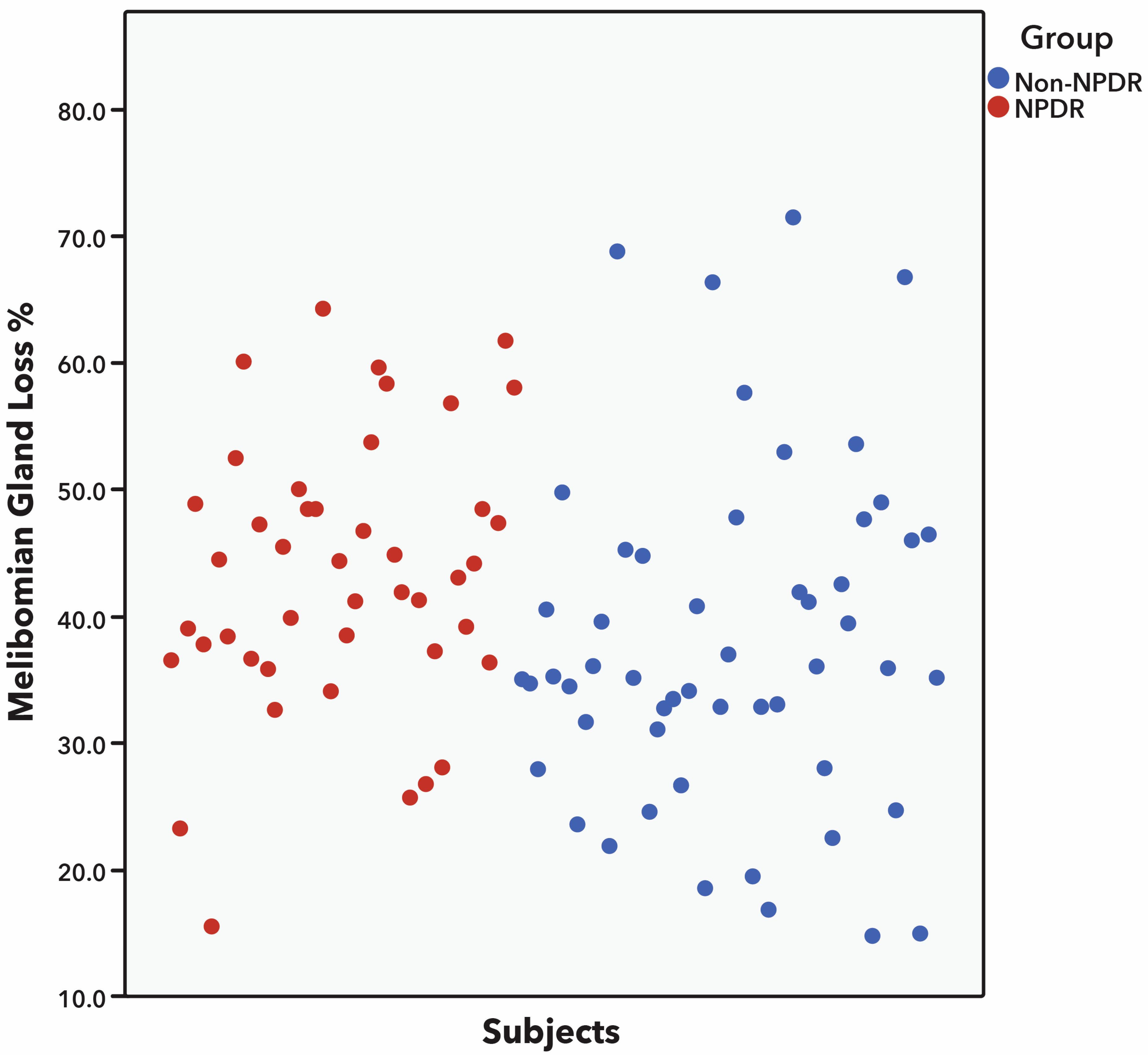
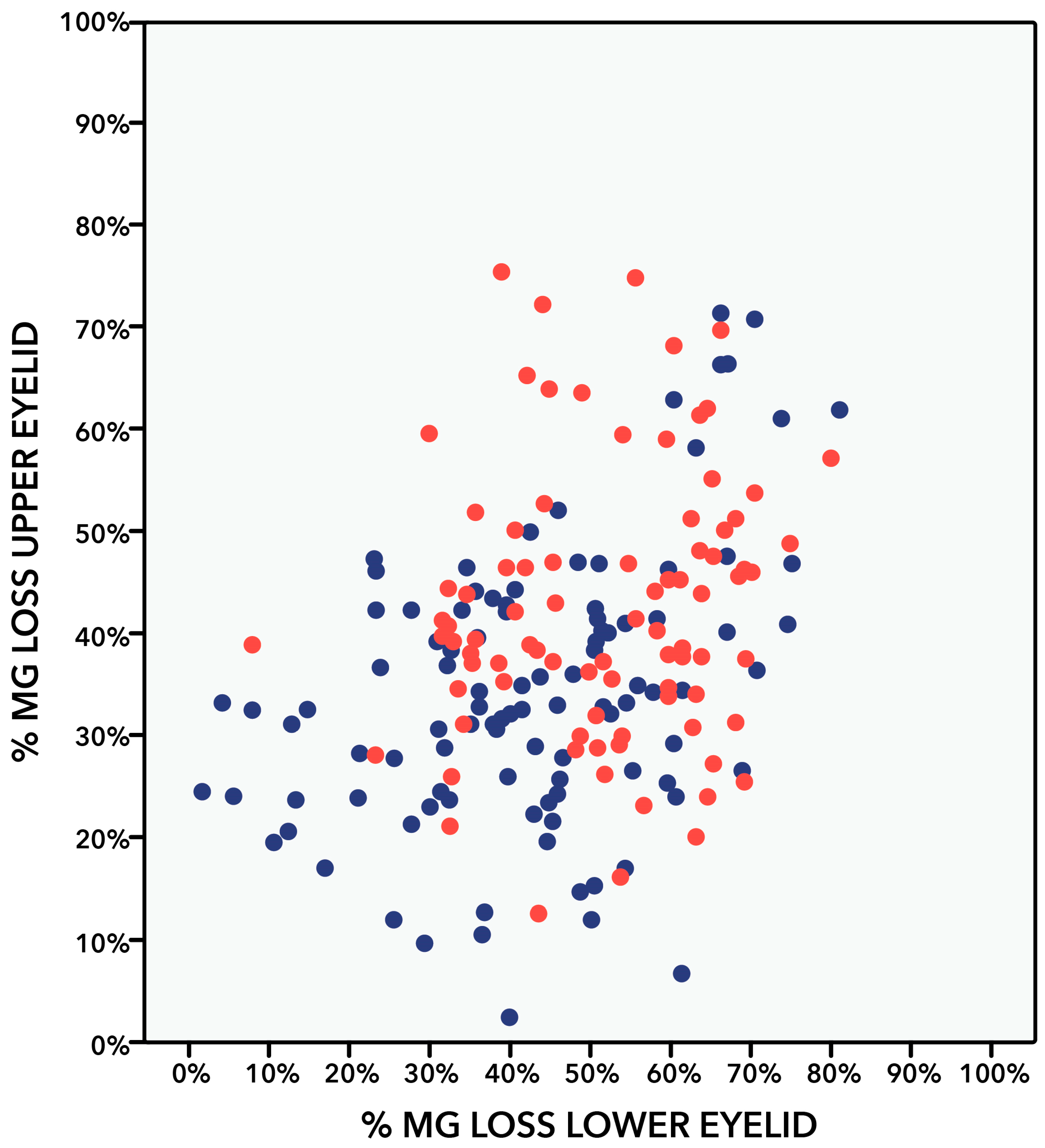
| MG dropout (%) | 34.6 ± 13.9 (7–71) | 42.3 ± 13.6 (13–72) | <0.001 |
| Inferior eyelid | |||
| Arita’s grade (0–3) | 1.7 ± 0.6 (1–3) | 2.0 ± 0.5 (1–3) | <0.001 |
| MG dropout (%) | 43.0 ± 17.3 (6–81) | 50.8 ± 14.4 (8–75) | 0.001 |
| Superior vs. inferior eyelid | |||
| p-Value Arita’s grade | <0.001 | 0.014 | N/A |
| p-value MG dropout | <0.001 | <0.001 | N/A |
| Both eyelids | |||
| Meiboscore grade * (0–6) | 3.4 ± 1.0 (2–6) | 3.8 ± 0.8 (2–5) | 0.002 |
| MG dropout (%) | 39.0 ± 13.2 (15–72) | 45.1 ± 10.5 (16–64) | <0.001 |
| Meiboscore Grade | Patients with No Diabetes | Patients with Diabetes with NPDR | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0.016 |
| 1 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| 2 | 20 (19) | 4 (4) | |
| 3 | 39 (37) | 22 (24) | |
| 4 | 34 (32) | 49 (55) | |
| 5 | 7 (6) | 13 (14) | |
| 6 | 5 (4) | 1 (1) |
| Variable | Patients with No Diabetes | Patients with Diabetics with NPDR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p | r | p | |
| OSDI | −0.013 | 0.895 | 0.063 | 0.560 |
| TBUT | 0.147 | 0.147 | −0.295 | 0.006 |
| Osmolarity | 0.110 | 0.281 | −0.095 | 0.385 |
| Oxford staining grade | −0.061 | 0.548 | 0.069 | 0.519 |
| NEI staining grade | 0.001 | 0.954 | −0.037 | 0.731 |
| Schirmer without anesthesia | 0.028 | 0.784 | −0.067 | 0.542 |
| Schirmer with anesthesia | 0.129 | 0.203 | −0.003 | 0.984 |
| Corneal esthesiometry | 0.046 | 0.650 | 0.130 | 0.563 |
| Marx’s line | −0.087 | 0.391 | 0.371 | 0.007 |
| MG expressibility | −0.105 | 0.300 | −0.428 | 0.002 |
| Meibum quality | 0.029 | 0.775 | 0.307 | 0.730 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohamed-Noriega, K.; González-Arocha, C.S.; Morales-Wong, F.; Velasco-Sepúlveda, B.H.; Rodríguez-Cuevas, J.O.; Cepeda-Ortegón, G.E.; Corral-Benavides, S.A.; Martínez-Delgado, J.F.; Mohamed-Noriega, J.; Fernández-De-Luna, M.L.; et al. Meibomian Gland Dysfunction and Dropout in Diabetic Patients with Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11090907
Mohamed-Noriega K, González-Arocha CS, Morales-Wong F, Velasco-Sepúlveda BH, Rodríguez-Cuevas JO, Cepeda-Ortegón GE, Corral-Benavides SA, Martínez-Delgado JF, Mohamed-Noriega J, Fernández-De-Luna ML, et al. Meibomian Gland Dysfunction and Dropout in Diabetic Patients with Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(9):907. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11090907
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohamed-Noriega, Karim, Carla Sofía González-Arocha, Fernando Morales-Wong, Braulio Hernán Velasco-Sepúlveda, Jonathan Octavio Rodríguez-Cuevas, Gerardo Esteban Cepeda-Ortegón, Sergio Antonio Corral-Benavides, José Francisco Martínez-Delgado, Jibran Mohamed-Noriega, Marissa L. Fernández-De-Luna, and et al. 2024. "Meibomian Gland Dysfunction and Dropout in Diabetic Patients with Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy" Bioengineering 11, no. 9: 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11090907
APA StyleMohamed-Noriega, K., González-Arocha, C. S., Morales-Wong, F., Velasco-Sepúlveda, B. H., Rodríguez-Cuevas, J. O., Cepeda-Ortegón, G. E., Corral-Benavides, S. A., Martínez-Delgado, J. F., Mohamed-Noriega, J., Fernández-De-Luna, M. L., & Mohamed-Hamsho, J. (2024). Meibomian Gland Dysfunction and Dropout in Diabetic Patients with Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. Bioengineering, 11(9), 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11090907






