Beat-by-Beat Estimation of Hemodynamic Parameters in Left Ventricle Based on Phonocardiogram and Photoplethysmography Signals Using a Deep Learning Model: Preliminary Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
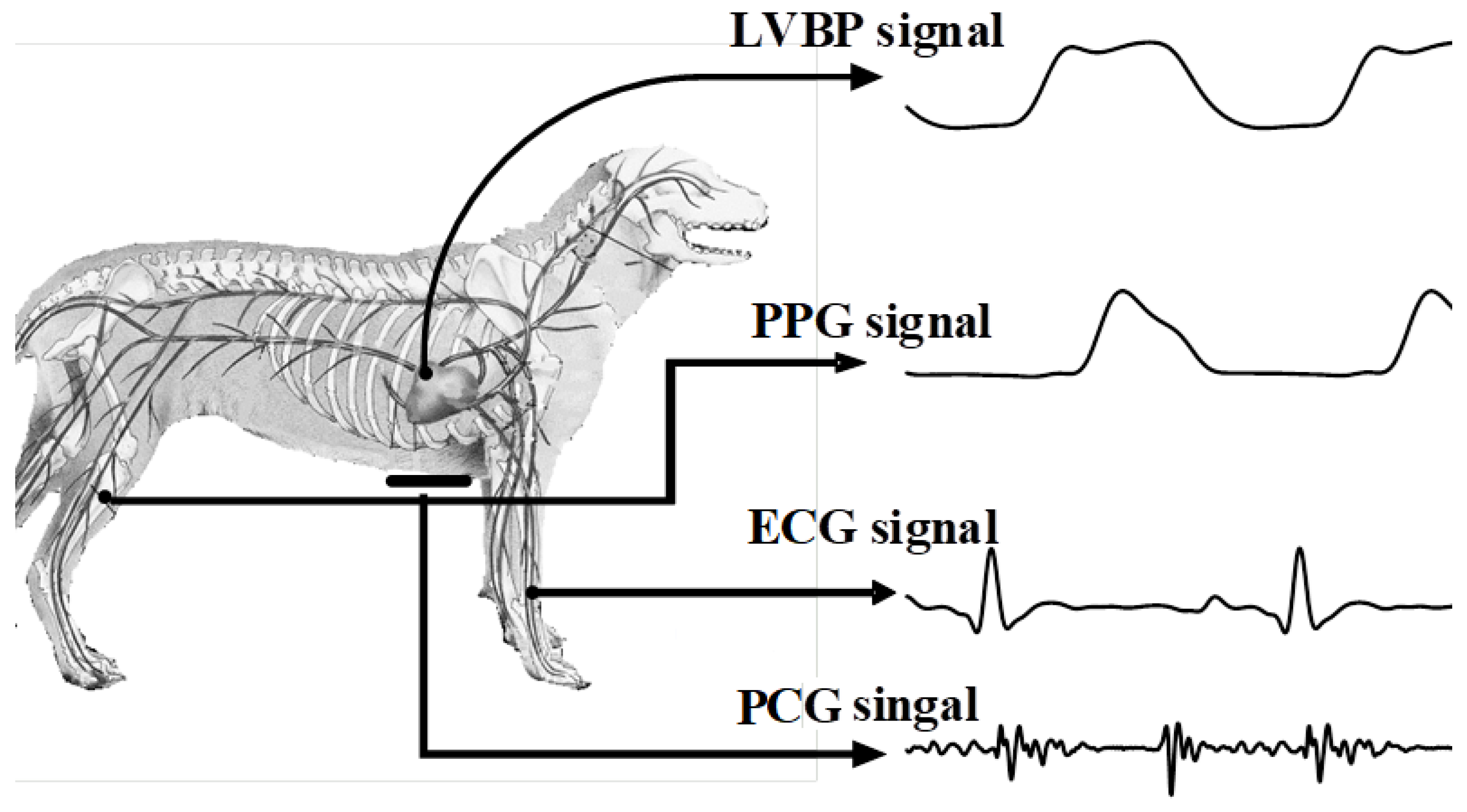
2.1. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
2.2. Hemodynamic Parameter Estimation Model
2.3. Hemodynamic Parameter Estimation Schemes
2.3.1. Scheme I: Five-Fold Cross-validation of Recordings within Subjects
2.3.2. Scheme II: Hemodynamic Parameter Estimation between Subjects
2.4. Performance Metrics
3. Results
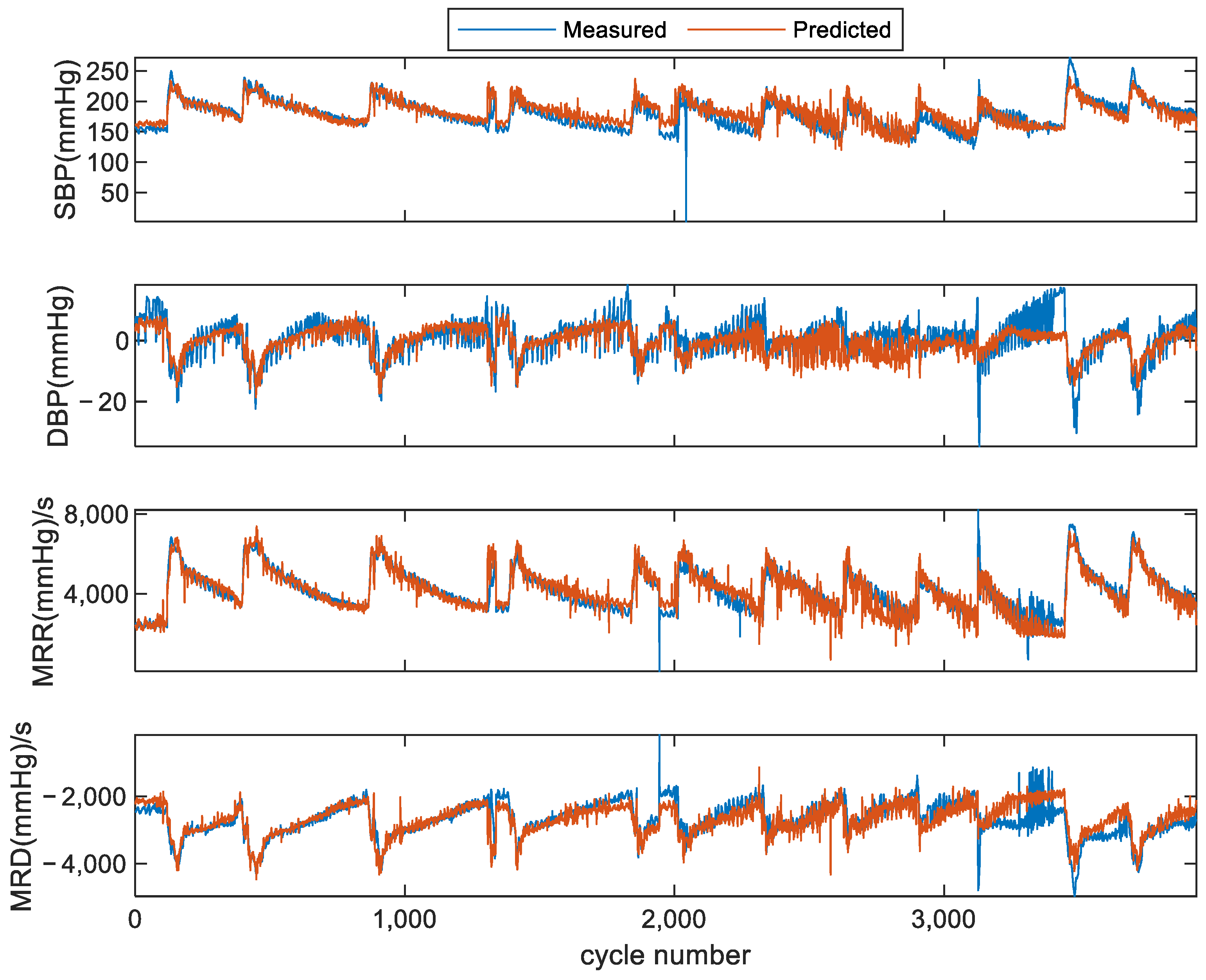
3.1. Results of Scheme I (within Subject)
3.2. Results of Scheme II (across Subjects)
3.3. Results with Calibration for Scheme II
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bastos, M.B.; Burkhoff, D.; Maly, J.; Daemen, J.; den Uil, C.A.; Ameloot, K.; Lenzen, M.; Mahfoud, F.; Zijlstra, F.; Schreuder, J.J.; et al. Invasive left ventricle pressure–volume analysis: Overview and practical clinical implications. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 1286–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlesinger, O.; Vigderhouse, N.; Moshe, Y.; Eytan, D. Estimation and Tracking of Blood Pressure Using Routinely Acquired Photoplethysmographic Signals and Deep Neural Networks. Crit. Care Explor. 2020, 2, e0095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamson, P.B.; Ginn, G.; Anker, S.D.; Bourge, R.C.; Abraham, W.T. Remote haemodynamic-guided care for patients with chronic heart failure: A meta-analysis of completed trials: Meta-analysis of haemodynamic monitoring. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017, 19, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonetti, I.; Trivella, M.G.; L’Abbate, A.; Neglia, D.; Macerata, A.; Marchesi, C.; Maseri, A.; Chierchia, S.; Lazzari, M.; Brunelli, C. Clinical application of monitoring techniques: Hemodynamic monitoring. Can. J. Cardiol. 1986, (Suppl. A), 163A–169A. [Google Scholar]
- Zile, M.R.; Bennett, T.D.; Sutton, M.S.J.; Cho, Y.K.; Adamson, P.B.; Aaron, M.F.; Aranda, J.J.M.; Abraham, W.T.; Smart, F.W.; Stevenson, L.W.; et al. Transition From Chronic Compensated to Acute Decompensated Heart Failure: Pathophysiological Insights Obtained From Continuous Monitoring of Intracardiac Pressures. Circulation 2008, 118, 1433–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondritzki, T.; Boehme, P.; White, J.; Park, J.W.; Hoffmann, J.; Vogel, J.; Kolkhof, P.; Walsh, S.; Sandner, P.; Bischoff, E.; et al. Remote Left Ventricular Hemodynamic Monitoring Using a Novel Intracardiac Sensor. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2018, 11, e006258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarazan, R.D.; Kroehle, J.P.; Main, B.W. Left ventricular pressure, contractility and dP/dtmax in nonclinical drug safety assessment studies. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2012, 66, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawes, C.M.M.; Hoorn, S.V.; Rodgers, A. Global burden of blood-pressure-related disease, 2001. Lancet 2008, 371, 1513–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.I.; Li, Y.; Adam, M.; Xie, M. Evaluation of Left Ventricular Systolic Function and Mass in Primary Hypertensive Patients by Echocardiography. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 38, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, L.; Marwick, T.H.; Popescu, B.A.; Donal, E.; Badano, L.P. Left Atrial Structure and Function, and Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 1961–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, H.; Seki, M.; Saiki, H.; Masutani, S.; Senzaki, H. Noninvasive assessment of left ventricular contractility in pediatric patients using the maximum rate of pressure rise in peripheral arteries. Heart Vessel. 2012, 27, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Liu, H.Q.; Lu, J. A new approach based on a 1D+2D convolutional neural network and evolving fuzzy system for the diagnosis of cardiovascular disease from heart sound signals. Appl. Acoust. 2024, 216, 109723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matamis, D.; Soilemezi, E.; Tsagourias, M.; Akoumianaki, E.; Dimassi, S.; Boroli, F.; Richard, J.-C.M.; Brochard, L. Sonographic evaluation of the diaphragm in critically ill patients. Technique and clinical applications. Intensive Care Med. 2013, 39, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, R.-C.; Yan, W.-R.; Zhang, N.-L.; Lin, W.-H.; Zhou, X.-L.; Zhang, Y.-T. Cuffless and Continuous Blood Pressure Estimation from the Heart Sound Signals. Sensors 2015, 15, 23653–23666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzorati, D.; Bovio, D.; Salito, C.; Mainardi, L.; Cerveri, P. Chest Wearable Apparatus for Cuffless Continuous Blood Pressure Measurements Based on PPG and PCG Signals. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 55424–55437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.M.; Mori, M.; Maccanon, D.M.; Luisada, A.A. Hemodynamic Correlates of the Various Components of the First Heart Sound. Circ. Res. 1963, 12, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.-S.; Kim, H.-S.; Lee, S.-A.; Hwang, G.-S.; Jung, W.; Moon, B.; Kang, K.-M.; Seo, W.-Y.; Song, J.-G.; Kim, S.-H. Correlations between heart sound components and hemodynamic variables. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Mondal, A.; Park, Y. A non-invasive approach to investigation of ventricular blood pressure using cardiac sound features. Physiol. Meas. 2017, 38, 289–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachuee, M.; Kiani, M.M.; Mohammadzade, H.; Shabany, M. Cuffless Blood Pressure Estimation Algorithms for Continuous Health-Care Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Sun, J.; Park, Y. Nonlinear relationship between systolic blood pressure and pulse transit time in anesthetized dogs. In Proceedings of the 2014 7th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Informatics, Dalian, China, 14–16 October 2014; pp. 363–367. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, C.; Li, Z.; Zhao, W.; Hu, J.; Jia, D.; Wang, H.; You, T. Novel Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Cuff-less Blood Pressure Measurement Using ECG and PPG Signals. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 1917–1920. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, S.G.; Zhang, J.; Chen, F.; Zheng, D. Blood Pressure Estimation Using Photoplethysmography Only: Comparison between Different Machine Learning Approaches. J. Healthc. Eng. 2018, 2018, 1548647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Yan, B.P.; Zhang, Y.-T.; Liu, J.; Zhao, N.; Tsang, H.K. Pulse Transit Time Based Continuous Cuffless Blood Pressure Estimation: A New Extension and A Comprehensive Evaluation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ainiwaer, A.; Hou, W.Q.; Qi, Q.; Kadier, K.; Qin, L.; Rehemuding, R.; Mei, M.; Wang, D.; Ma, X.; Dai, J.G.; et al. Deep learning of heart-sound signals for efficient prediction of obstructive coronary artery disease. Heliyon 2024, 10, e23354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannun, A.Y.; Rajpurkar, P.; Haghpanahi, M.; Tison, G.H.; Bourn, C.; Turakhia, M.P.; Ng, A.Y. Cardiologist-level arrhythmia detection and classification in ambulatory electrocardiograms using a deep neural network. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-M.; Huang, C.-H.; Shih, E.S.C.; Hu, Y.-F.; Hwang, M.-J. Detection and Classification of Cardiac Arrhythmias by a Challenge-Best Deep Learning Neural Network Model. iScience 2020, 23, 100886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Liu, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhao, N.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, H. Automatic Cardiac Arrhythmia Classification Using Combination of Deep Residual Network and Bidirectional LSTM. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 102119–102135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Tang, H.; Shang, S.; Mathiak, K.; Cong, F. Classification of Heart Sounds Using Convolutional Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Tian, C.; Cao, R.; Wang, B.; Niu, Y.; Hu, T.; Guo, H.; Xiang, J. Epileptic Seizure Detection Based on EEG Signals and CNN. Front. Neuroinform. 2018, 12, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiouris, Κ.Μ.; Pezoulas, V.C.; Zervakis, M.; Konitsiotis, S.; Koutsouris, D.D.; Fotiadis, D.I. A Long Short-Term Memory deep learning network for the prediction of epileptic seizures using EEG signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 99, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshimizu, H.; Kojima, R.; Kario, K.; Okuno, Y. Prediction of blood pressure variability using deep neural networks. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2020, 136, 104067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; He, P.; Chen, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Zheng, D. A novel deep learning based automatic auscultatory method to measure blood pressure. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2019, 128, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Tompkins, W.J. A Real-Time QRS Detection Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1985, 32, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Schuster, M.; Paliwal, K.K. Bidirectional recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1997, 45, 2673–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Gulcehre, C.; Cho, K.H.; Bengio, Y. Empirical Evaluation of Gated Recurrent Neural Networks on Sequence Modeling. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.3555. [Google Scholar]
- Kapur, G.; Chen, L.; Xu, Y.; Cashen, K.; Clark, J.; Feng, X.; Wu, S.F. Noninvasive Determination of Blood Pressure by Heart Sound Analysis Compared with Intra-Arterial Monitoring in Critically Ill Children—A Pilot Study of a Novel Approach. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 20, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaelpoor, J.; Moradi, M.H.; Kadkhodamohammadi, A. A multistage deep neural network model for blood pressure estimation using photoplethysmogram signals. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 120, 103719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






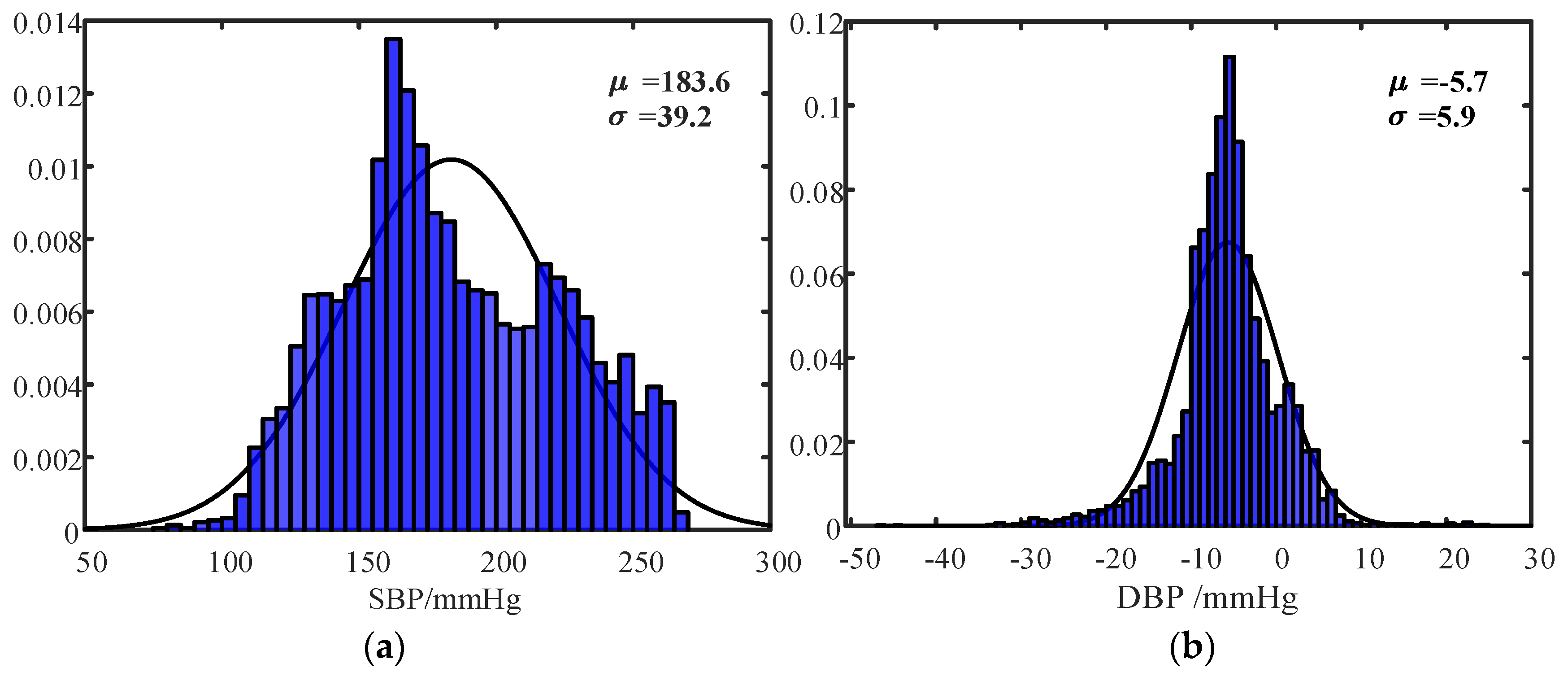

| Record Index | No. of Cardiac Cycles | SBP (mmHg) (Min–Max) | DBP (mmHg) (Min–Max) | MRR (mmHg/s) (Min–Max) | MRD (mmHg/s) (Min–Max) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subject 1 | 1 | 72 | [128, 158] | [2, 8] | [1812, 1981] | [−1998, −1900] |
| 2 | 567 | [115, 231] | [−22, −4] | [1452, 7595] | [−4795, −1450] | |
| 3 | 587 | [106, 268] | [−25, −3] | [1467, 9080] | [−5781, −1546] | |
| 4 | 563 | [112, 264] | [−22, −3] | [1430, 8946] | [−5756, −1437] | |
| 5 | 523 | [101, 252] | [−22, −3] | [481, 8564] | [−5431, −365] | |
| 6 | 419 | [102, 254] | [−26, −6] | [1329, 7910] | [−4501, −1524] | |
| 7 | 512 | [138, 258] | [−47, 9] | [1383, 6522] | [−4633, −1722] | |
| 8 | 574 | [152, 258] | [−30, 6] | [1749, 6496] | [−4715, −1699] | |
| 9 | 533 | [157, 250] | [−28, 5] | [1841, 6312] | [−5031, −1116] | |
| 10 | 502 | [153, 238] | [−29, 2] | [107, 5778] | [−4321, −70] | |
| 11 | 558 | [97, 234] | [−18, 7] | [1732, 7502] | [−5140, −855] | |
| 12 | 578 | [77, 268] | [−34, 10] | [1810, 9181] | [−5896, −859] | |
| 13 | 510 | [92, 264] | [−33, 2] | [1711, 8946] | [−5845, −1010] | |
| 14 | 503 | [122, 239] | [−26, 0] | [1535, 7942] | [−5041, −1539] | |
| 15 | 528 | [117, 241] | [−25, −3] | [1465, 7981] | [−5070, −1503] | |
| Subject 2 | 16 | 118 | [147, 160] | [−1, 14] | [2258, 273] | [−2552, −2166] |
| 17 | 142 | [144, 212] | [−14, 18] | [106, 6000] | [−3820, −175] | |
| 18 | 341 | [133, 218] | [−10, 12] | [1849, 6137] | [−3746, −1680] | |
| 19 | 315 | [137, 224] | [−8, 14] | [2664, 6097] | [−3654, −1676] | |
| 20 | 272 | [131, 213] | [−7, 11] | [2230, 5743] | [−3451, −1782] | |
| 21 | 247 | [122, 194] | [−7, 10] | [2594, 5624] | [−3390, −1384] | |
| 22 | 287 | [141, 235] | [−35, 17] | [699, 8198] | [−4793, −1143] | |
| 23 | 275 | [155, 272] | [−30, 17] | [2371, 7470] | [−4973, −2336] | |
| 24 | 254 | [164, 255] | [−24, 10] | [2753, 7091] | [−4257, −2287] | |
| 25 | 270 | [166, 250] | [−20, 9] | [3362, 6833] | [−4128, −2158] | |
| 26 | 439 | [162, 239] | [−22, 9] | [3293, 6731] | [−4290, −1974] | |
| 27 | 472 | [158, 231] | [−20, 9] | [3221, 6567] | [−4190, −1806] | |
| 28 | 38 | [149, 221] | [−17, 15] | [3094, 6137] | [−3847, −1799] | |
| 29 | 465 | [148, 218] | [−15, 14] | [3021, 6183] | [−3904, −1776] | |
| Subject 3 | 30 | 50 | [122, 138] | [4, 8] | [849, 1205] | [−1242, −1051] |
| 31 | 164 | [137, 255] | [−12, 11] | [6, 7896] | [−3838, −189] | |
| 32 | 107 | [140, 248] | [−12, 12] | [−53, 7258] | [−3693, −97] | |
| 33 | 85 | [137, 236] | [−11, 20] | [−48, 6828] | [−3496, −238] | |
| 34 | 42 | [142, 231] | [−11, 17] | [2, 6705] | [−3159, 4] | |
| 35 | 85 | [124, 200] | [−5, 7] | [−35, 5717] | [−3330, 0] | |
| 36 | 71 | [134, 217] | [−3, 15] | [100, 5035] | [−2784, −20] | |
| 37 | 49 | [137, 202] | [−1, 8] | [160, 4247] | [−1950, −32] | |
| 38 | 90 | [164, 272] | [−11, 12] | [136, 8019] | [−4104, −212] | |
| 39 | 118 | [159, 266] | [−11, 12] | [−442, 8319] | [−3674, −246] | |
| 40 | 3 | [235, 263] | [−12, −8] | [7237, 8089] | [−3673, −343] | |
| Total | 12,328 | [77, 272] | [−47, 20] | [106, 9181] | [−5896, −70] |
| Residual Blocks | No. of Conv | Kernel Length | Kernel Number | Stride of Conv | Pooling Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | #1 | 16 | 32 | 1 | 2 |
| #2 | 16 | 32 | 2 | ||
| 2nd | #1 | 16 | 32 | 1 | 1 |
| #2 | 16 | 32 | 1 | ||
| 3rd | #1 | 16 | 32 | 1 | 2 |
| #2 | 16 | 32 | 2 | ||
| 4th | #1 | 16 | 32 | 1 | 1 |
| #2 | 16 | 32 | 1 | ||
| 5th | #1 | 16 | 64 | 1 | 2 |
| #2 | 16 | 64 | 2 | ||
| 6th | #1 | 16 | 64 | 1 | 1 |
| #2 | 16 | 64 | 1 |
| Performance Metrics | Subject 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBP (mmHg) | DBP (mmHg) | MRR (mmHg/s) | MRD (mmHg/s) | |
| ME | −3.41 | −0.1 | −39 | 59 |
| MAE | 6.22 | 1.54 | 329 | 175 |
| SD | 6.69 | 2.42 | 428 | 226 |
| CC | 0.984 | 0.916 | 0.979 | 0.972 |
| p-value | <<0.001 | <<0.001 | <<0.001 | <<0.001 |
| 95% CI for CC | 0.982–0.985 | 0.908–0.924 | 0.977–0.981 | 0.969–0.975 |
| Performance metrics | Subject 2 | |||
| SBP (mmHg) | DBP (mmHg) | MRR (mmHg/s) | MRD (mmHg/s) | |
| ME | −0.12 | −0.4 | 37 | −0.9 |
| MAE | 8.23 | 2.77 | 267 | 169 |
| SD | 9.97 | 3.59 | 383 | 546 |
| CC | 0.897 | 0.812 | 0.922 | 0.873 |
| p-value | <<0.001 | <<0.001 | <<0.001 | <<0.001 |
| 95% CI for CC | 0.883–0.910 | 0.787–0.834 | 0.911–0.932 | 0.855–0.888 |
| Performance metrics | Subject 3 | |||
| SBP (mmHg) | DBP (mmHg) | MRR (mmHg/s) | MRD (mmHg/s) | |
| ME | 3.81 | 0.20 | 48.8 | −49.2 |
| MAE | 6.82 | 1.94 | 389 | 215 |
| SD | 6.99 | 2.92 | 468 | 446 |
| CC | 0.923 | 0.856 | 0.939 | 0.886 |
| p-value | <<0.001 | <<0.001 | <<0.001 | <<0.001 |
| 95% CI for CC | 0.921–0.942 | 0.848–0.864 | 0.927–0.941 | 0.869–0.895 |
| Performance Metrics | SBP (mmHg) | DBP (mmHg) | MRR (mmHg/s) | MRD (mmHg/s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subject 1 | ME | −0.675 | 2.365 | 147 | 226 |
| MAE | 13.14 | 5.04 | 776.5 | 414 | |
| SD | 17.47 | 5.595 | 975.5 | 561 | |
| CC | 0.908 | 0.715 | 0.937 | 0.919 | |
| p-value | <<0.001 | <<0.001 | <<0.001 | <<0.001 | |
| 95% CI for CC | 0.903–0.914 | 0.699–0.731 | 0.933–0.941 | 0.914–0.924 | |
| Subject 2 | ME | 7.895 | −4.905 | −419 | 73.5 |
| MAE | 12.52 | 5.74 | 541 | 314 | |
| SD | 14.71 | 4.605 | 549 | 378 | |
| CC | 0.759 | 0.556 | 0.848 | 0.657 | |
| p-value | <<0.001 | <<0.001 | <<0.001 | <<0.001 | |
| 95% CI for CC | 0.740–0.776 | 0.526–0.586 | 0.836–0.860 | 0.632–0.681 | |
| Subject 3 | ME | −0.386 | −2.895 | −234 | −236 |
| MAE | 13.90 | 5.09 | 792 | 412 | |
| SD | 18.41 | 5.260 | 950 | 526 | |
| CC | 0.885 | 0.693 | 0.903 | 0.862 | |
| p-value | <<0.001 | <<0.001 | <<0.001 | <<0.001 | |
| 95% CI for CC | 0.870–0.896 | 0.686–0.706 | 0.896–0.910 | 0.852–0.871 |
| Indicators | SBP (mmHg) | DBP (mmHg) | MRR (mmHg/s) | MRD (mmHg/s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subject 1 | ME | 9.06 | 0.32 | 153 | 150 |
| MAE | 14.180 | 3.970 | 773 | 379 | |
| SD | 14.34 | 5.00 | 904.00 | 541.50 | |
| CC | 0.94 | 0.72 | 0.95 | 0.94 | |
| p-value | <<0.001 | <<0.001 | <<0.001 | <<0.001 | |
| 95% CI for CC | 0.934–0.942 | 0.705–0.736 | 0.949–0.955 | 0.931–0.939 | |
| Subject 2 | ME | 6.93 | −0.98 | 54 | −37 |
| MAE | 10.67 | 3.06 | 335 | 222 | |
| SD | 12.595 | 3.995 | 446 | 294 | |
| CC | 0.824 | 0.674 | 0.904 | 0.792 | |
| p-value | <<0.001 | <<0.001 | <<0.001 | <<0.001 | |
| 95% CI for CC | 0.809–0.837 | 0.650–0.696 | 0.896–0.912 | 0.776–0.807 | |
| Subject 3 | ME | 8.43 | 0.68 | 83 | 67 |
| MAE | 12.87 | 4.46 | 547 | 306 | |
| SD | 13.45 | 4.85 | 679 | 436 | |
| CC | 0.854 | 0.71 | 0.913 | 0.832 | |
| p-value | <<0.001 | <<0.001 | <<0.001 | <<0.001 | |
| 95% CI for CC | 0.849–0.867 | 0.696–0.721 | 0.906–0.922 | 0.826–0.847 |
| References | Signal Sources | BP Type | Method | SBP Range (mmHg) | Performance | Performance Account for SBP Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tang et al. [18], 2017 | PCG | Left ventricular BP | Multi domain feature +SVM | same in this study | CC: 0.92 MAE: 6.86 mmHg SD: 8.96 mmHg | MAE: 3.5% SD: 4.6% |
| Peng et al. [14], 2015 | PCG | Finger cuff BP | Fourier spectrum of second heart sound +SVM | about 90–140 | CC: 0.707 MAE: 4.339 mmHg SD:6.121 mmHg | MAE: 8.6% SD: 12.2% |
| Kapur et al. [38], 2019 | PCG | Intra-arterial BP | Characteristics of S1 and S2 +ANN | 58–173 | 1. Without regularization: CC: 0.679 RMSE: 20.408 mmHg SD: 20 mmHg 2. Cuff BP regularization: CC: 0.964 RMSE: 7.305 mmHg SD: 7 mmHg | 1. RMSE: 17.7% SD: 17.4% 2. RMSE: 6.3% SD: 6.1% |
| Esmaelpoor et al. [39], 2020 | PPG | Invasive BP | Deep neural network | 80–180 | MAE: 3.97 mmHg SD: 5.55 mmHg | MAE: 4.0% SD: 5.6% |
| Yan et al. [21], 2019 | PPG + ECG | Arterial BP | Deep CNN | 80–180 | 1. Random split all subjects’ samples: MAE: 3.09 mmHg SD: 2.76 mmHg 2. Between subjects: MAE: 12.49 mmHg SD: 9.43 mmHg | 1. MAE: 3.1% SD: 2.8% 2. MAE: 12.5% SD: 9.4% |
| Current study | PCG + PPG | Left ventricular BP | Deep learning model | 77–272 | 1. Within subject: CC: 0.94 MAE: 7.23 mmHg SD: 8.33 mmHg 2. Between subjects: MAE: 12.8 mmHg SD: 16.1 mmHg | 1. MAE: 3.7% SD: 4.3% 2. MAE: 6.6% SD: 8.3% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mi, J.; Feng, T.; Wang, H.; Pei, Z.; Tang, H. Beat-by-Beat Estimation of Hemodynamic Parameters in Left Ventricle Based on Phonocardiogram and Photoplethysmography Signals Using a Deep Learning Model: Preliminary Study. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080842
Mi J, Feng T, Wang H, Pei Z, Tang H. Beat-by-Beat Estimation of Hemodynamic Parameters in Left Ventricle Based on Phonocardiogram and Photoplethysmography Signals Using a Deep Learning Model: Preliminary Study. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(8):842. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080842
Chicago/Turabian StyleMi, Jiachen, Tengfei Feng, Hongkai Wang, Zuowei Pei, and Hong Tang. 2024. "Beat-by-Beat Estimation of Hemodynamic Parameters in Left Ventricle Based on Phonocardiogram and Photoplethysmography Signals Using a Deep Learning Model: Preliminary Study" Bioengineering 11, no. 8: 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080842
APA StyleMi, J., Feng, T., Wang, H., Pei, Z., & Tang, H. (2024). Beat-by-Beat Estimation of Hemodynamic Parameters in Left Ventricle Based on Phonocardiogram and Photoplethysmography Signals Using a Deep Learning Model: Preliminary Study. Bioengineering, 11(8), 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080842







