Perlecan: An Islet Basement Membrane Protein with Protective Anti-Inflammatory Characteristics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Islet Isolation
2.2. Human Islet Culture
2.3. Islet Characterisation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
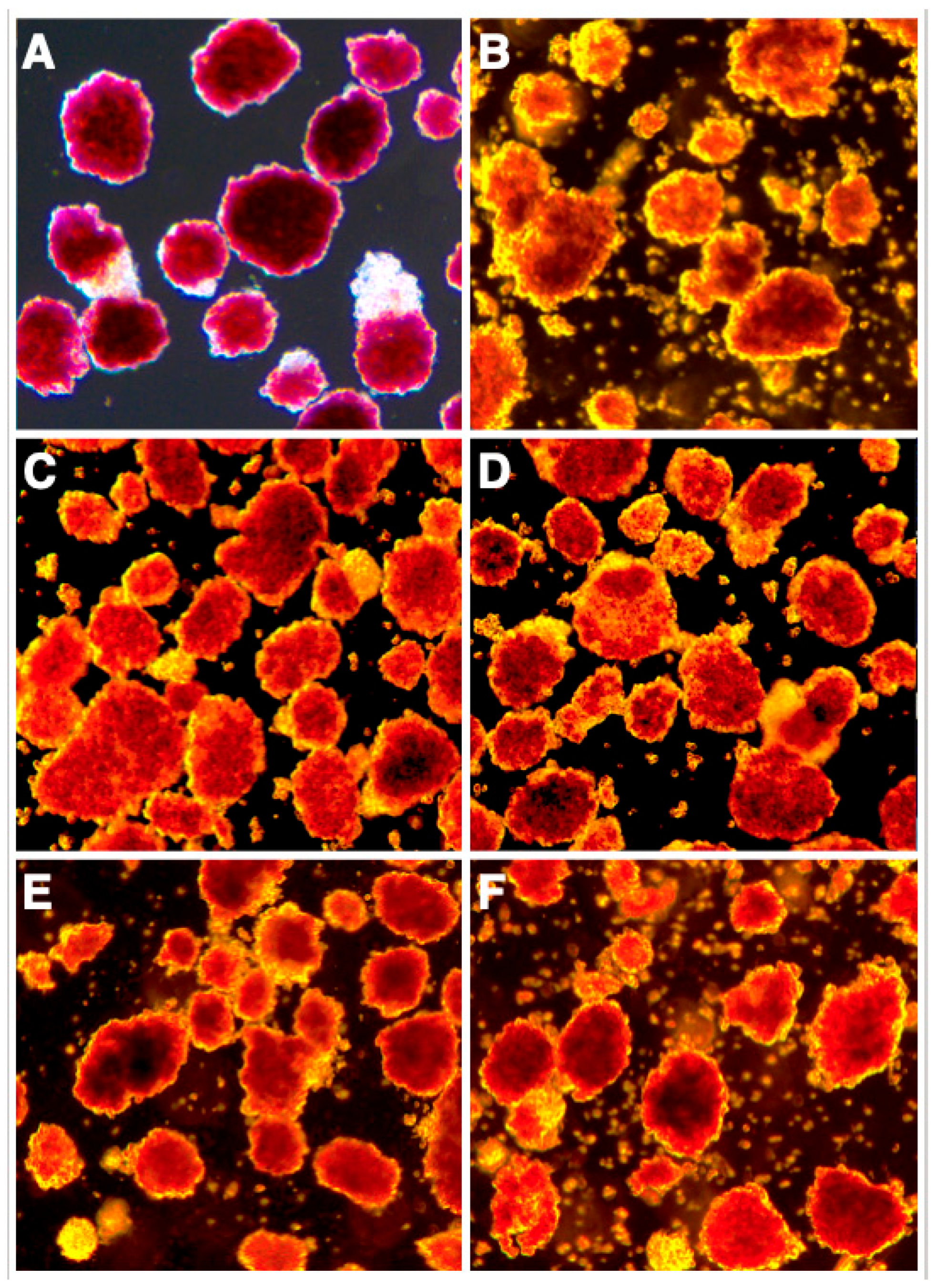
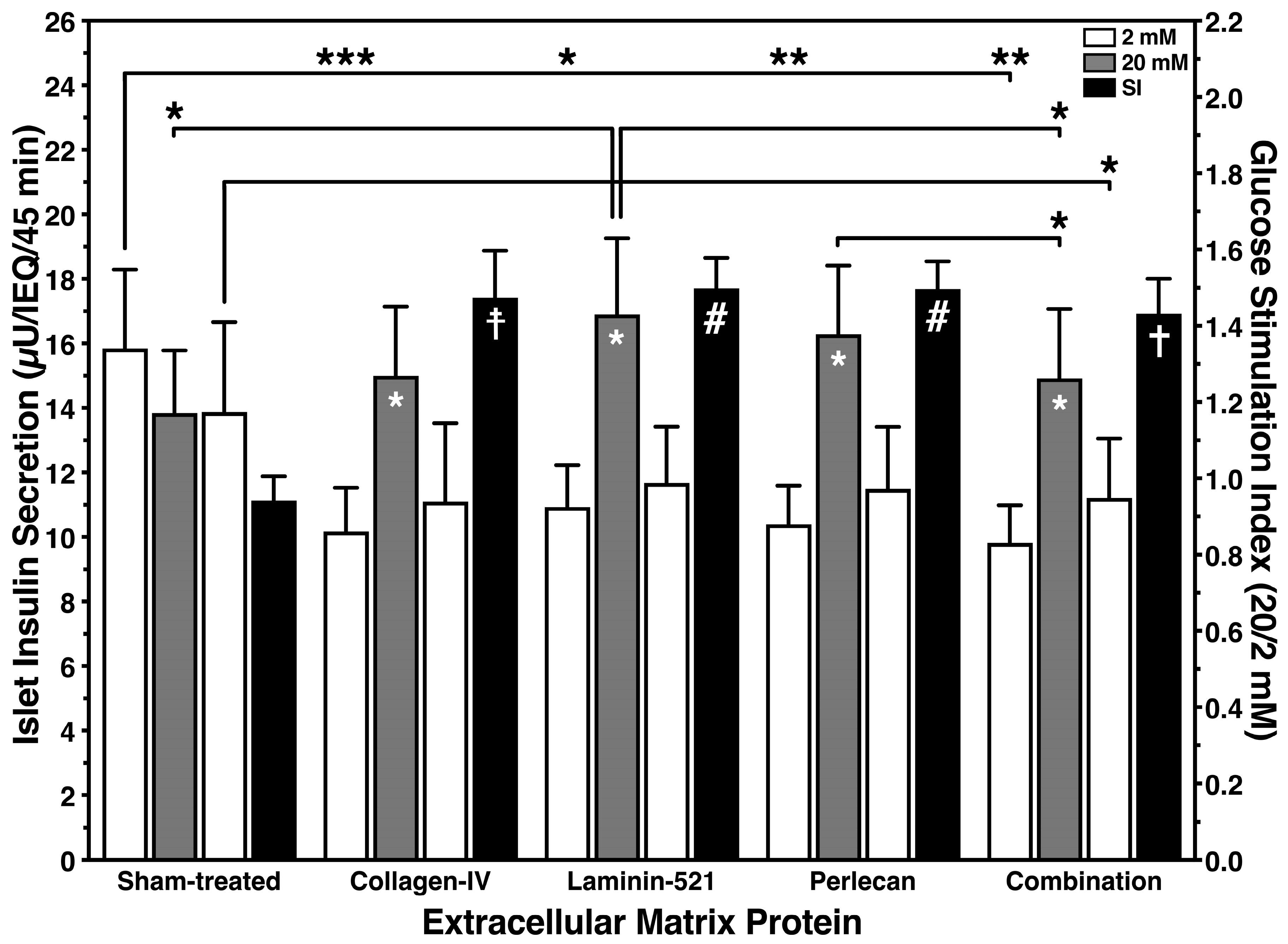
3.1. Protective Effect of Islet BMPs on Islet Survival and In Vitro Function
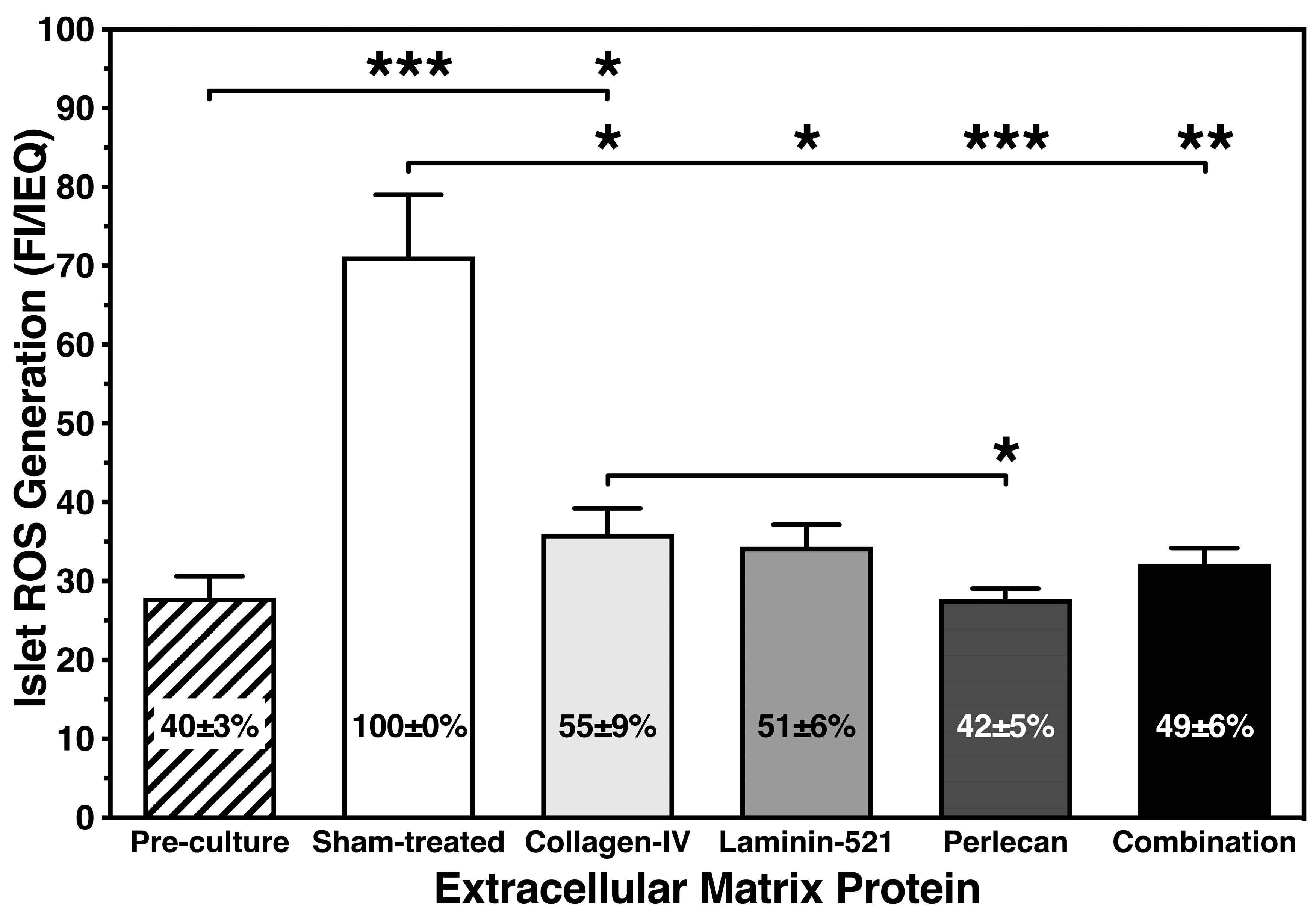
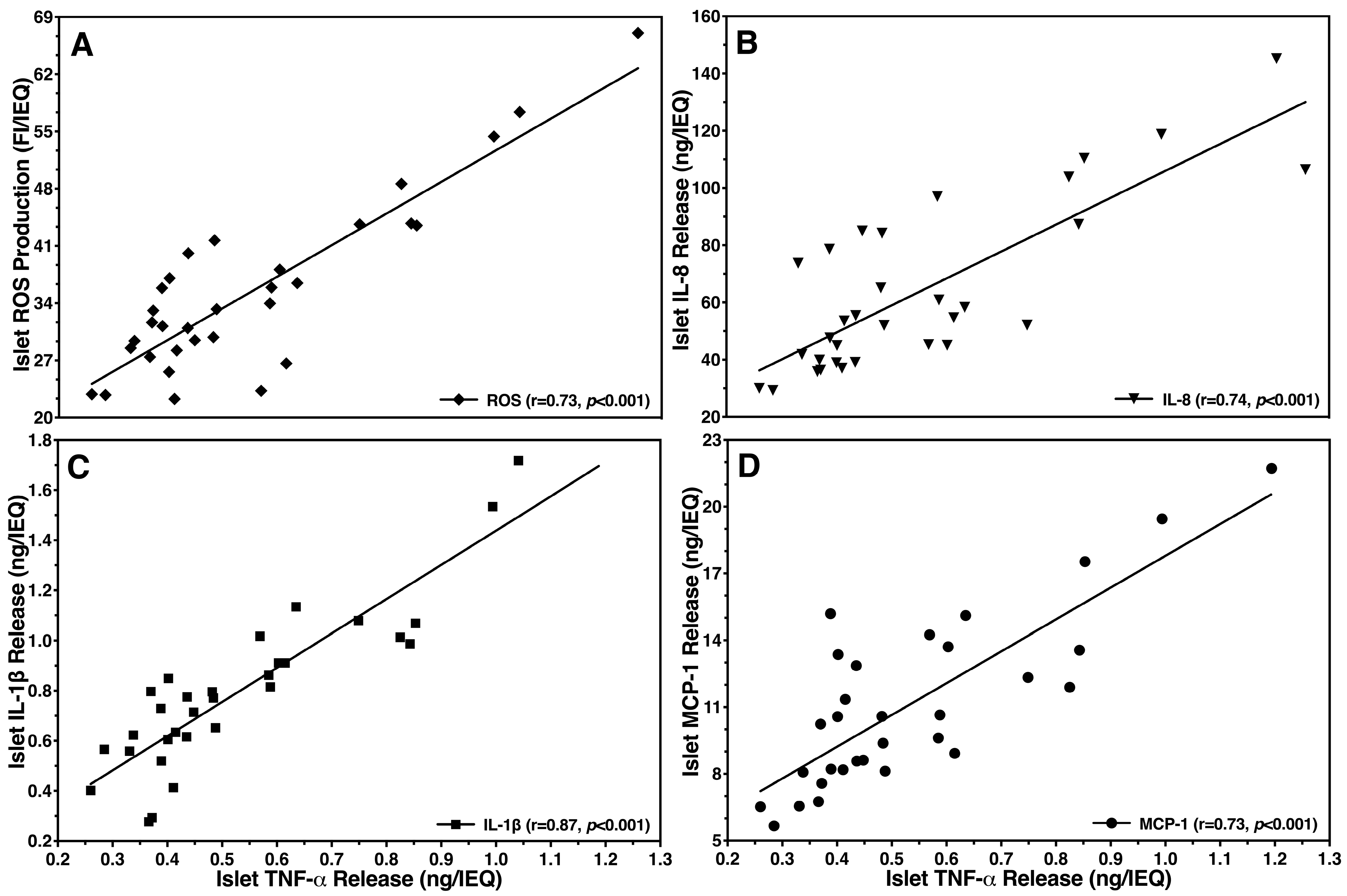
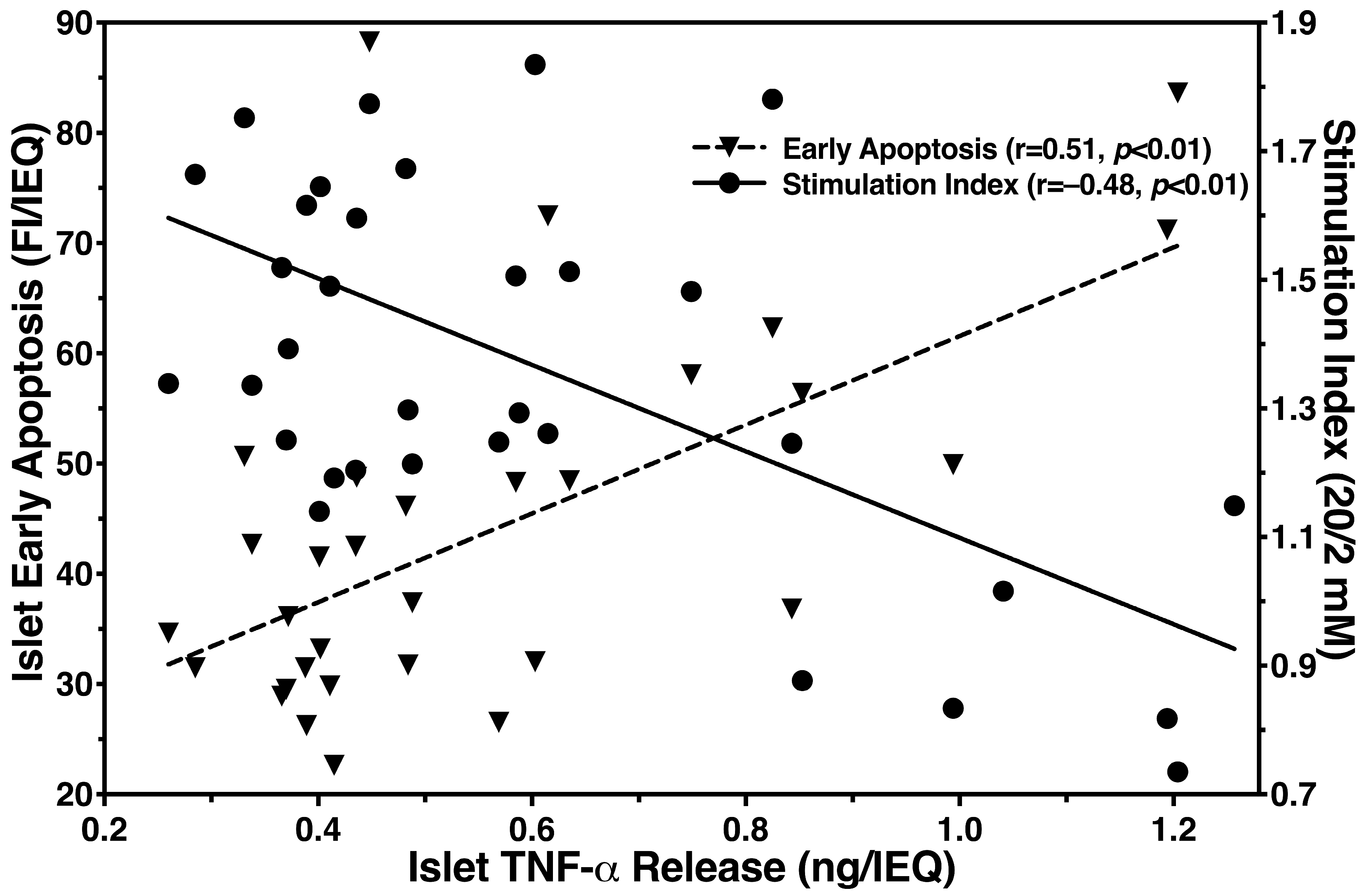
3.2. Inhibitory Effect of Islet BMPs on Islet-Related Inflammation and Apoptosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shapiro, A.M.J.; Verhoeff, K. A spectacular year for islet and stem cell transplantation. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 68–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bateman, P.A.; Devereuux-Cooke, K.J.; Johnson, J.D.; Brandhorst, H.; Brandhorst, D.; Gray, D.W.; Cross, S.E.; Hughes, S.J.; Johnson, P.R.V. Degradation of laminin and laminin-511 in the human peri-islet extracellular matrix is targeted by neutral protease and thermolysin, but not collagenase. Transplantation 2013, 96, S18. [Google Scholar]
- Cross, S.E.; Vaughan, R.H.; Willcox, A.J.; McBride, A.J.; Abraham, A.A.; Han, B.; Johnson, J.D.; Maillard, E.; Bateman, P.A.; Ramracheya, R.D.; et al. Key matrix proteins within the pancreatic islet basement membrane are differentially digested during human islet isolation. Am. J. Transplant. 2017, 17, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aumailley, M.; Battaglia, C.; Mayer, U.; Reinhardt, D.; Nischt, R.; Timpl, R.; Fox, J.W. Nidogen mediates the formation of ternary complexes of basement membrane components. Kidney Int. 1993, 43, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timpl, R.; Brown, J.C. Supramolecular assembly of basement membranes. Bioessays 1996, 18, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBleu, V.S.; Macdonald, B.; Kalluri, R. Structure and function of basement membranes. Exp. Biol. Med. 2007, 232, 1121–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruckner, P. Suprastructures of extracellular matrices: Paradigms of functions controlled by aggregates rather than molecules. Cell Tissue Res. 2010, 339, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virtanen, I.; Banerjee, M.; Palgi, J.; Korsgren, O.; Lukinius, A.; Thornell, L.E.; Kikkawa, Y.; Sekiguchi, K.; Hukkanen, M.; Konttinen, Y.T.; et al. Blood vessels of human islets of Langerhans are surrounded by a double basement membrane. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Chen, S.; Pei, Y.A.; Pei, M. Nidogen: A matrix protein with potential roles in musculoskeletal tissue regeneration. Genes Dis. 2021, 9, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, M.A.; Schaller, M.D.; Ginsberg, M.H. Integrins: Emerging paradigms of signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1995, 11, 549–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.N.; Rosenberg, L. Maintenance of beta-cell function and survival following islet isolation requires re-establishment of the islet-matrix relationship. J. Endocrinol. 1999, 163, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.N.; Paraskevas, S.; Rosenberg, L. Characterization of integrin expression in islets isolated from hamster, canine, porcine, and human pancreas. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1999, 47, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ris, F.; Hammar, E.; Bosco, D.; Pilloud, C.; Maedler, K.; Donath, M.Y.; Oberholzer, J.; Zeender, E.; Morel, P.; Rouiller, D.; et al. Impact of integrin-matrix matching and inhibition of apoptosis on the survival of purified human beta-cells in vitro. Diabetologia 2002, 45, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kragl, M.; Lammert, E. Basement membrane in pancreatic islet function. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 654, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bottino, R.; Balamurugan, A.N.; Tse, H.; Thirunavukkarasu, C.; Ge, X.; Profozich, J.; Milton, M.; Ziegenfuss, A.; Trucco, M.; Piganelli, J.D. Response of human islets to isolation stress and the effect of antioxidant treatment. Diabetes 2004, 53, 2559–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.N.; Li, J.M.; Lyte, K.; Yashpal, N.K.; Fellows, F.; Goodyer, C.G. Role for beta 1 integrin and its associated alpha 3, alpha 5, and alpha 6 subunits in development of the human fetal pancreas. Diabetes 2005, 54, 2080–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parnaud, G.; Hammar, E.; Rouiller, D.G.; Armanet, M.; Halban, P.A.; Bosco, D. Blockade of beta1 integrin-laminin-5 interaction affects spreading and insulin secretion of rat beta-cells attached on extracellular matrix. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1413–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Krishnamurthy, M.; Li, J.; Fellows, G.F.; Rosenberg, L.; Goodyer, C.G.; Wang, R. Integrin {alpha}3, but not {beta}1, regulates islet cell survival and function via PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, P.D.; Weinberg, A.; Chee, J.; Mariana, L.; Ayala, R.; Hawthorne, W.J.; O’Connell, P.J.; Loudovaris, T.; Cowley, M.J.; Kay, T.W.; et al. Expression of pro- and antiapoptotic molecules of the bcl-2 family in human islets postisolation. Cell Transplant. 2012, 21, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, M.J.; Weinberg, A.; Zammit, N.W.; Walters, S.N.; Hawthorne, W.J.; Loudovaris, T.; Thomas, H.; Kay, T.; Gunton, J.E.; Alexander, S.I.; et al. Human islets express a marked proinflammatory molecular signature prior to transplantation. Cell Transplant. 2012, 21, 2063–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negi, S.; Jetha, A.; Aikin, R.; Hasilo, C.; Sladek, R.; Paraskevas, S. Analysis of beta-cell gene expression reveals inflammatory signaling and evidence of dedifferentiation following human islet isolation and culture. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, L.M.; Anseth, K.S. Hydrogel encapsulation environments functionalized with extracellular matrix interactions increase islet insulin secretion. Matrix Biol. 2008, 27, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llacua, A.; de Haan, B.J.; Smink, S.A.; de Vos, P. Extracellular matrix components supporting human islet function in alginate-based immunoprotective microcapsules for treatment of diabetes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2016, 104, 1788–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llacua, L.A.; de Haan, B.J.; de Vos, P. Laminin and collagen IV inclusion in immunoisolating microcapsules reduces cytokine-mediated cell death in human pancreatic islets. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 12, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurchenco, P.D.; Schittny, J.C. Molecular architecture of basement membranes. FASEB J. 1990, 4, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.Y.; Raghunath, M.; Whitelock, J.; Poole-Warren, L. Matrix components and scaffolds for sustained islet function. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2011, 17, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hynes, R.O.; Naba, A. Overview of the matrisome--an inventory of extracellular matrix constituents and functions. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a004903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayadev, R.; Sherwood, D.R. Basement membranes. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R207–R211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.N.; Mathews, C.E.; Chandler, R.; Stabler, C.L. The Foundation for Engineering a Pancreatic Islet Niche. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 881525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stendahl, J.C.; Kaufman, D.B.; Stupp, S.I. Extracellular matrix in pancreatic islets: Relevance to scaffold design and transplantation. Cell Transplant. 2009, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daoud, J.T.; Petropavlovskaia, M.; Rosenberg, L.; Tabrizian, M. The effect of extracellular matrix components on the preservation of human islet function in vitro. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 1676–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaido, T.; Yebra, M.; Cirulli, V.; Rhodes, C.; Diaferia, G.; Montgomery, A.M. Impact of defined matrix interactions on insulin production by cultured human beta-cells: Effect on insulin content, secretion, and gene transcription. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2723–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaido, T.J.; Yebra, M.; Kaneto, H.; Cirulli, V.; Hayek, A.; Montgomery, A.M. Impact of integrin-matrix interaction and signaling on insulin gene expression and the mesenchymal transition of human beta-cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 224, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinkse, G.G.; Bouwman, W.P.; Jiawan-Lalai, R.; Terpstra, O.T.; Bruijn, J.A.; de Heer, E. Integrin signaling via RGD peptides and anti-beta1 antibodies confers resistance to apoptosis in islets of Langerhans. Diabetes 2006, 55, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandhorst, D.; Brandhorst, H.; Lee Layland, S.; Acreman, S.; Schenke-Layland, K.; Johnson, P.R.V. Basement membrane proteins improve human islet survival in hypoxia: Implications for islet inflammation. Acta Biomater. 2022, 137, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubbiotti, M.A.; Neill, T.; Iozzo, R.V. A current view of perlecan in physiology and pathology: A mosaic of functions. Matrix Biol. 2017, 57–58, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.J.; Farrugia, B.L.; Biose, I.J.; Bix, G.J.; Melrose, J.; Perlecan, A. Multi-Functional, Cell-Instructive, Matrix-Stabilizing Proteoglycan With Roles in Tissue Development Has Relevance to Connective Tissue Repair and Regeneration. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 856261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otonkoski, T.; Banerjee, M.; Korsgren, O.; Thornell, L.E.; Virtanen, I. Unique basement membrane structure of human pancreatic islets: Implications for beta-cell growth and differentiation. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2008, 10 (Suppl. S4), 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricordi, C.; Gray, D.W.; Hering, B.J.; Kaufman, D.B.; Warnock, G.L.; Kneteman, N.M.; Lake, S.P.; London, N.J.; Socci, C.; Alejandro, R.; et al. Islet isolation assessment in man and large animals. Acta Diabetol. Lat. 1990, 27, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandhorst, H.; Raemsch-Guenther, N.; Raemsch, C.; Friedrich, O.; Huettler, S.; Kurfuerst, M.; Korsgren, O.; Brandhorst, D. The ratio between collagenase class I and class II influences the efficient islet release from the rat pancreas. Transplantation 2008, 85, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- London, N.J.; Contractor, H.; Lake, S.P.; Aucott, G.C.; Bell, P.R.; James, R.F. A fluorometric viability assay for single human and rat islets. Horm. Metab. Res. Suppl. 1990, 25, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brandhorst, D.; Brandhorst, H.; Mullooly, N.; Acreman, S.; Johnson, P.R. High seeding density induces local hypoxia and triggers a proinflammatory response in isolated human islets. Cell Transplant. 2016, 25, 1539–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandhorst, H.; Asif, S.; Andersson, K.; Theisinger, B.; Andersson, H.H.; Felldin, M.; Foss, A.; Salmela, K.; Tibell, A.; Tufveson, G.; et al. A new oxygen carrier for improved long-term storage of human pancreata before islet isolation. Transplantation 2010, 89, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meghana, K.; Sanjeev, G.; Ramesh, B. Curcumin prevents streptozotocin-induced islet damage by scavenging free radicals: A prophylactic and protective role. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 577, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConkey, D.J. Biochemical determinants of apoptosis and necrosis. Toxicol. Lett. 1998, 99, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Ichikawa, F.; Ishiyama-Shigemoto, S.; Yuan, X.; Nonaka, K. Essential role of caspase-3 in apoptosis of mouse beta-cells transfected with human Fas. Diabetes 1999, 48, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motulsky, H.J.; Brown, R.E. Detecting outliers when fitting data with nonlinear regression—A new method based on robust nonlinear regression and the false discovery rate. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandhorst, D.; Brandhorst, H.; Linn, T. Induction and amelioration of environmental stress in isolated islets until transplantation. Immunol. Endoc. Metab. Agents Med. Chem. 2006, 6, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishtul, S.; Baruch, L.; Machluf, M. Processed tissue-derived extracellular matrices: Tailored platforms empowering diverse therapeutic applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1900386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loneker, A.E.; Faulk, D.M.; Hussey, G.S.; D’Amore, A.; Badylak, S.F. Solubilized liver extracellular matrix maintains primary rat hepatocyte phenotype in-vitro. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2016, 104, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandhorst, H.; Krishtul, S.; Brandhorst, D.; Baruch, L.; Machluf, M.; Johnson, P.R.V. Solubilized Pancreatic Extracellular Matrix from Juvenile Pigs Protects Isolated Human Islets from Hypoxia-Induced Damage: A Viable Option for Clinical Islet Transplantation. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2023, 2023, 7452682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.A.; Sampaio, L.C.; Ferdous, Z.; Gobin, A.S.; Taite, L.J. Decellularized matrices in regenerative medicine. Acta Biomater. 2018, 74, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, M.P. How mitochondria produce reactive oxygen species. Biochem. J. 2009, 417, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrester, S.J.; Kikuchi, D.S.; Hernandes, M.S.; Xu, Q.; Griendling, K.K. Reactive oxygen species in metabolic and inflammatory signaling. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 877–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, S.E.; Richards, S.K.; Clark, A.; Benest, A.V.; Bates, D.O.; Mathieson, P.W.; Johnson, P.R.; Harper, S.J.; Smith, R.M. Vascular endothelial growth factor as a survival factor for human islets: Effect of immunosuppressive drugs. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Movahedi, B.; Gysemans, C.; Jacobs-Tulleneers-Thevissen, D.; Mathieu, C.; Pipeleers, D. Pancreatic duct cells in human islet cell preparations are a source of angiogenic cytokines interleukin-8 and vascular endothelial growth factor. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2128–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Melzi, R.; Mercalli, A.; Sordi, V.; Cantarelli, E.; Nano, R.; Maffi, P.; Sitia, G.; Guidotti, L.G.; Secchi, A.; Bonifacio, E.; et al. Role of CCL2/MCP-1 in islet transplantation. Cell Transplant. 2010, 19, 1031–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puren, A.J.; Fantuzzi, G.; Gu, Y.; Su, M.S.; Dinarello, C.A. Interleukin-18 (IFNgamma-inducing factor) induces IL-8 and IL-1beta via TNFalpha production from non-CD14+ human blood mononuclear cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paleolog, E.M.; Young, S.; Stark, A.C.; McCloskey, R.V.; Feldmann, M.; Maini, R.N. Modulation of angiogenic vascular endothelial growth factor by tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1 in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1998, 41, 1258–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Yoshida, A.; Ishibashi, T. Induction of IL-8, MCP-1, and bFGF by TNF-alpha in retinal glial cells: Implications for retinal neovascularization during post-ischemic inflammation. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2004, 242, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, A.K.; Aggarwal, B.B. Reactive oxygen intermediates in TNF signaling. Mol. Immunol. 2002, 39, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze-Osthoff, K.; Beyaert, R.; Vandevoorde, V.; Haegeman, G.; Fiers, W. Depletion of the mitochondrial electron transport abrogates the cytotoxic and gene-inductive effects of TNF. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 3095–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grankvist, K.; Marklund, S.L.; Taljedal, I.B. CuZn-superoxide dismutase, Mn-superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase in pancreatic islets and other tissues in the mouse. Biochem. J. 1981, 199, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malaisse, W.J.; Malaisse-Lagae, F.; Sener, A.; Pipeleers, D.G. Determinants of the selective toxicity of alloxan to the pancreatic B cell. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenzen, S.; Drinkgern, J.; Tiedge, M. Low antioxidant enzyme gene expression in pancreatic islets compared with various other mouse tissues. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1996, 20, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, E.; Dixit, V.M. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species drive proinflammatory cytokine production. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadtman, E.R.; Levine, R.L. Free radical-mediated oxidation of free amino acids and amino acid residues in proteins. Amino Acids 2003, 25, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinovitch, A.; Sumoski, W.; Rajotte, R.V.; Warnock, G.L. Cytotoxic effects of cytokines on human pancreatic islet cells in monolayer culture. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1990, 71, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, H.U.; Haj-Yehia, A.; Levi-Schaffer, F. Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in apoptosis induction. Apoptosis 2000, 5, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaney, C.A.; Pavlovic, D.; Hoorens, A.; Pipeleers, D.G.; Eizirik, D.L. Cytokines induce deoxyribonucleic acid strand breaks and apoptosis in human pancreatic islet cells. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 2610–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoorens, A.; Stange, G.; Pavlovic, D.; Pipeleers, D. Distinction between interleukin-1-induced necrosis and apoptosis of islet cells. Diabetes 2001, 50, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinovitch, A.; Suarez-Pinzon, W.L.; Strynadka, K.; Schulz, R.; Lakey, J.R.; Warnock, G.L.; Rajotte, R.V. Human pancreatic islet beta-cell destruction by cytokines is independent of nitric oxide production. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1994, 79, 1058–1062. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eizirik, D.L.; Sandler, S.; Welsh, N.; Cetkovic-Cvrlje, M.; Nieman, A.; Geller, D.A.; Pipeleers, D.G.; Bendtzen, K.; Hellerstrom, C. Cytokines suppress human islet function irrespective of their effects on nitric oxide generation. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 1968–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armann, B.; Hanson, M.S.; Hatch, E.; Steffen, A.; Fernandez, L.A. Quantification of basal and stimulated ROS levels as predictors of islet potency and function. Am. J. Transplant. 2007, 7, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Piemonti, L.; Leone, B.E.; Nano, R.; Saccani, A.; Monti, P.; Maffi, P.; Bianchi, G.; Sica, A.; Peri, G.; Melzi, R.; et al. Human pancreatic islets produce and secrete MCP-1/CCL2: Relevance in human islet transplantation. Diabetes 2002, 51, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hynes, R.O. Integrins: Bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell 2002, 110, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphries, J.D.; Byron, A.; Humphries, M.J. Integrin ligands at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119 Pt 19, 3901–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, L.; Wang, R.; Paraskevas, S.; Maysinger, D. Structural and functional changes resulting from islet isolation lead to islet cell death. Surgery 1999, 126, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolova, G.; Jabs, N.; Konstantinova, I.; Domogatskaya, A.; Tryggvason, K.; Sorokin, L.; Fassler, R.; Gu, G.; Gerber, H.P.; Ferrara, N.; et al. The vascular basement membrane: A niche for insulin gene expression and Beta cell proliferation. Dev. Cell 2006, 10, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plow, E.F.; Haas, T.A.; Zhang, L.; Loftus, J.; Smith, J.W. Ligand binding to integrins. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 21785–21788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, N.E.; Beenken-Rothkopf, L.N.; Mirsoian, A.; Kojic, N.; Kaplan, D.L.; Barron, A.E.; Fontaine, M.J. Enhanced function of pancreatic islets co-encapsulated with ECM proteins and mesenchymal stromal cells in a silk hydrogel. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6691–6697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smink, A.M.; de Vos, P. Therapeutic strategies for modulating the extracellular matrix to improve pancreatic islet function and survival after transplantation. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2018, 18, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zbinden, A.; Layland, S.L.; Urbanczyk, M.; Carvajal Berrio, D.A.; Marzi, J.; Zauner, M.; Hammerschmidt, A.; Brauchle, E.M.; Sudrow, K.; Fink, S.; et al. Nidogen-1 mitigates ischemia and promotes tissue survival and regeneration. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2002500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, L.M.; Hayda, K.N.; Anseth, K.S. Cell-matrix interactions improve beta-cell survival and insulin secretion in three-dimensional culture. Tissue Eng. Part A 2008, 14, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brandhorst, D.; Brandhorst, H.; Acreman, S.; Johnson, P.R.V. Perlecan: An Islet Basement Membrane Protein with Protective Anti-Inflammatory Characteristics. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080828
Brandhorst D, Brandhorst H, Acreman S, Johnson PRV. Perlecan: An Islet Basement Membrane Protein with Protective Anti-Inflammatory Characteristics. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(8):828. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080828
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrandhorst, Daniel, Heide Brandhorst, Samuel Acreman, and Paul R. V. Johnson. 2024. "Perlecan: An Islet Basement Membrane Protein with Protective Anti-Inflammatory Characteristics" Bioengineering 11, no. 8: 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080828
APA StyleBrandhorst, D., Brandhorst, H., Acreman, S., & Johnson, P. R. V. (2024). Perlecan: An Islet Basement Membrane Protein with Protective Anti-Inflammatory Characteristics. Bioengineering, 11(8), 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080828








