Explore the Value of Multi-Parameter MRI in Non-Invasive Assessment of Prognostic Risk and Oxford Classification in Children with IgAN or IgAVN
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Clinical and Pathological Information
2.3. The International IgA Nephropathy Prediction Tool in Children
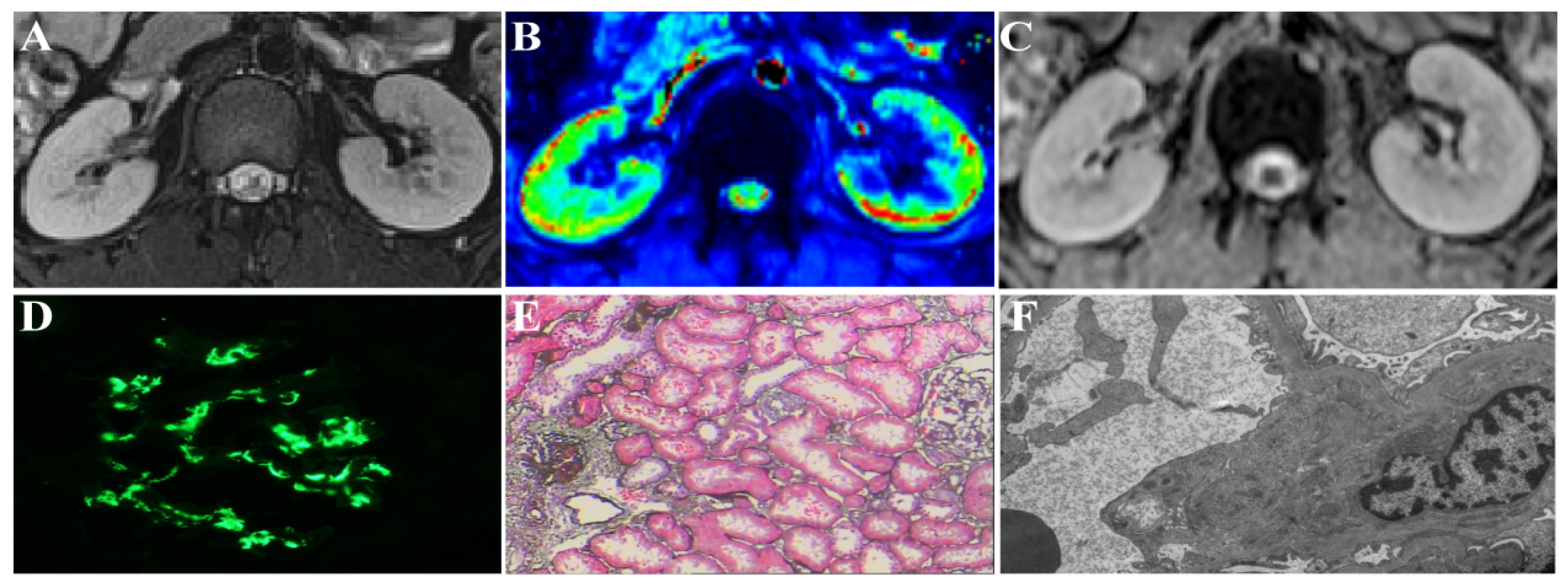
2.4. MRI Techniques
2.5. Image Analysis and Data Measurement
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical and Pathological Characteristics
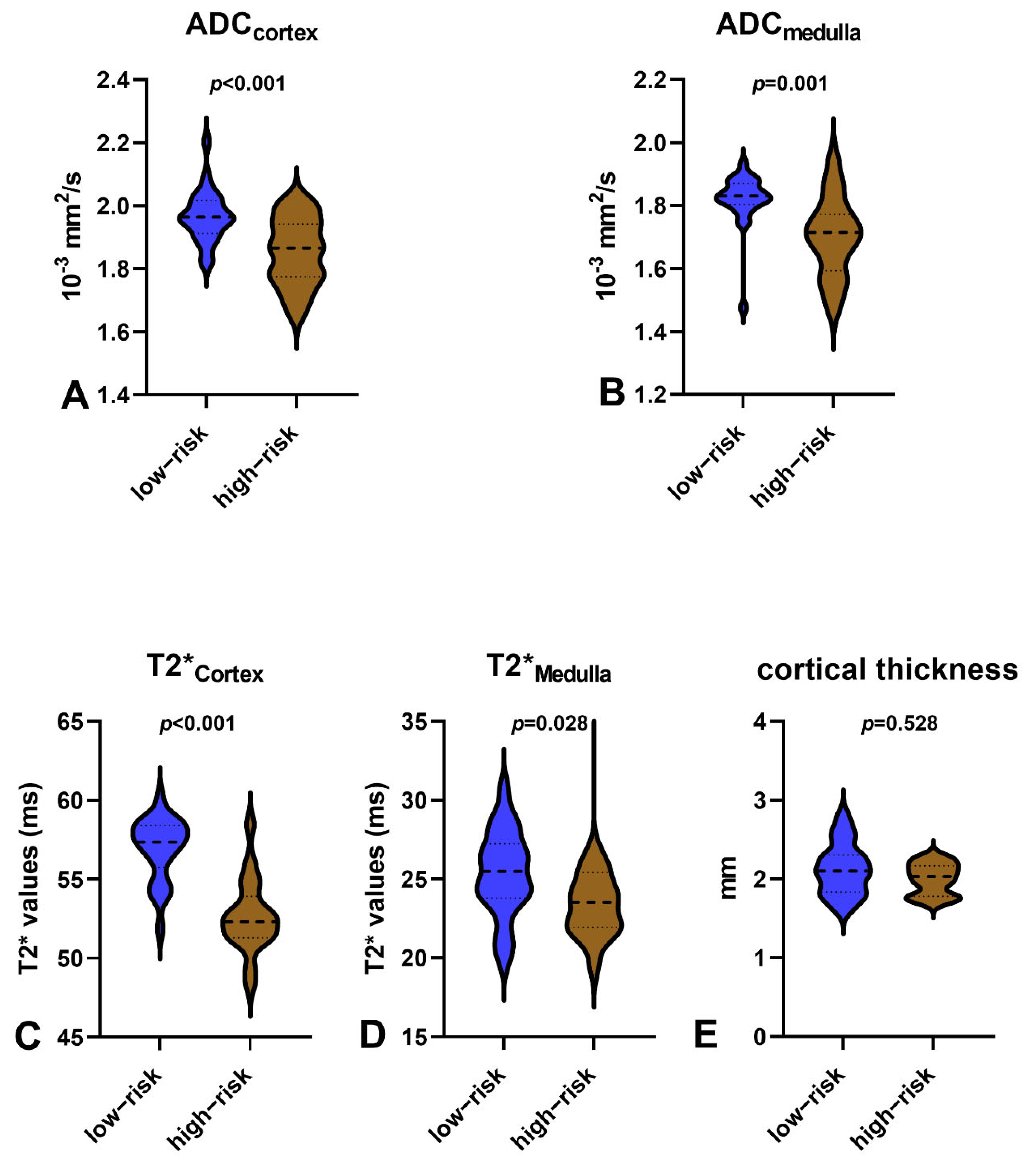
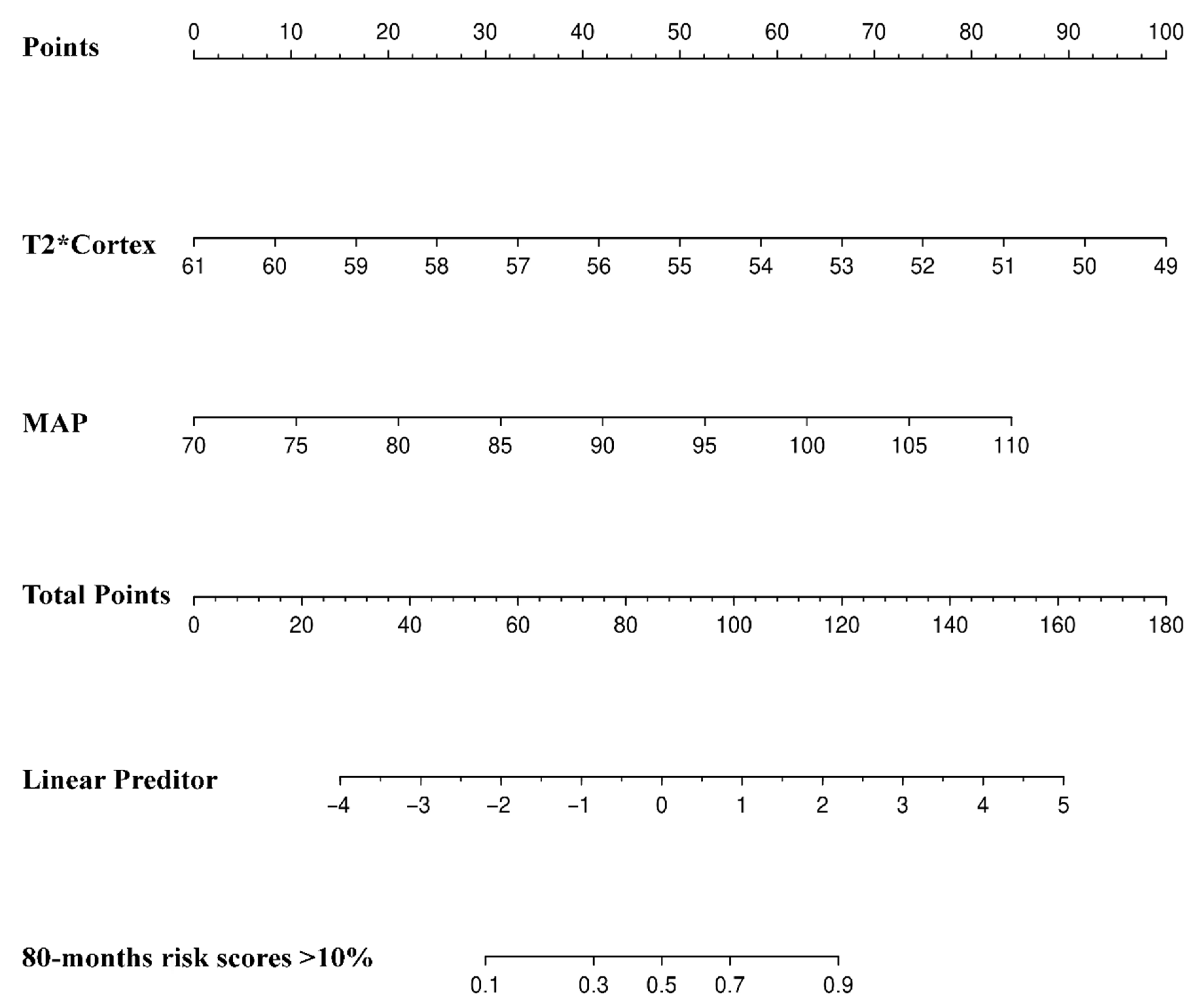
3.2. Comparisons between 80-Month Risk Scores ≤10% and 80-Month Risk Scores >10%
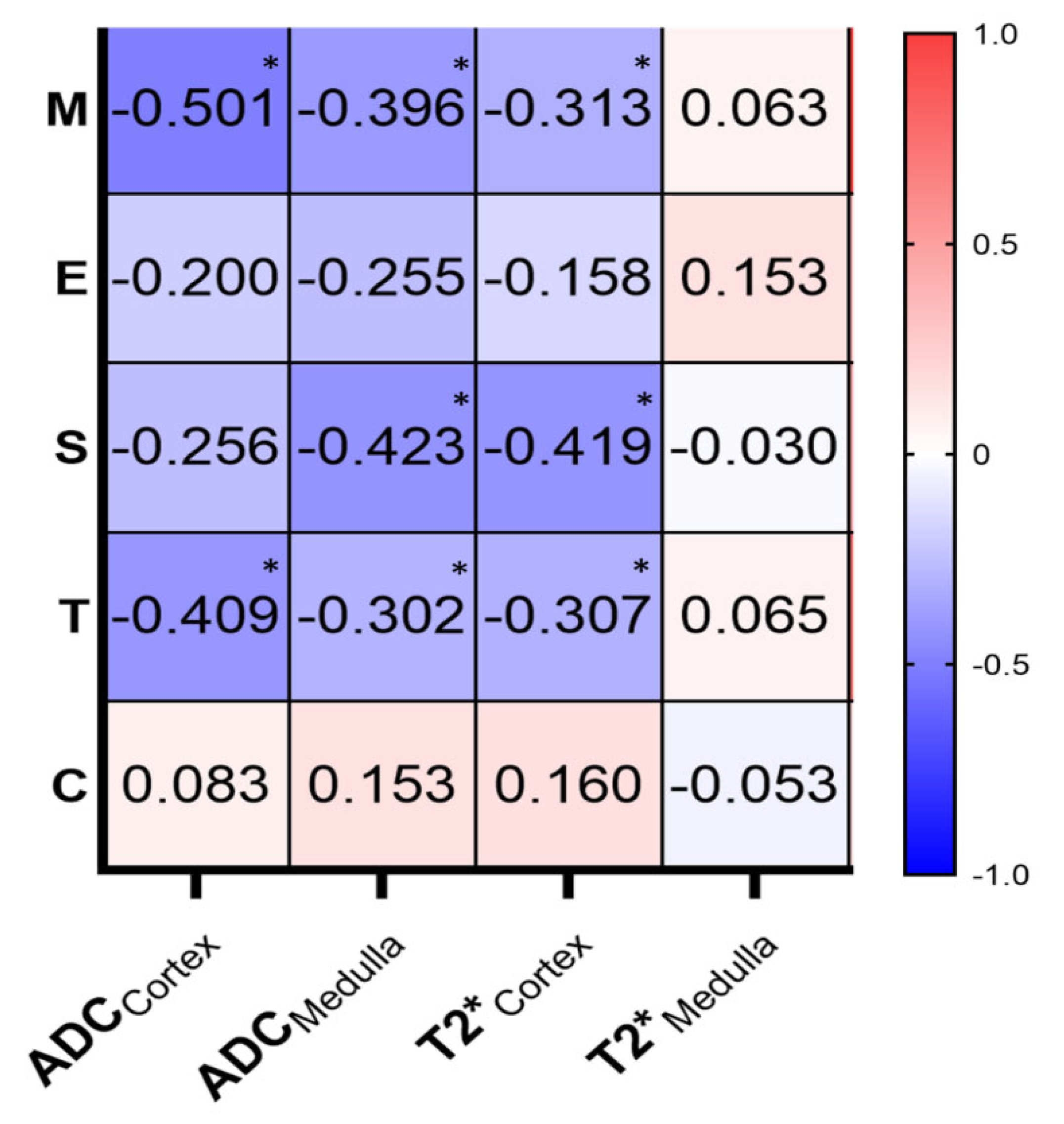
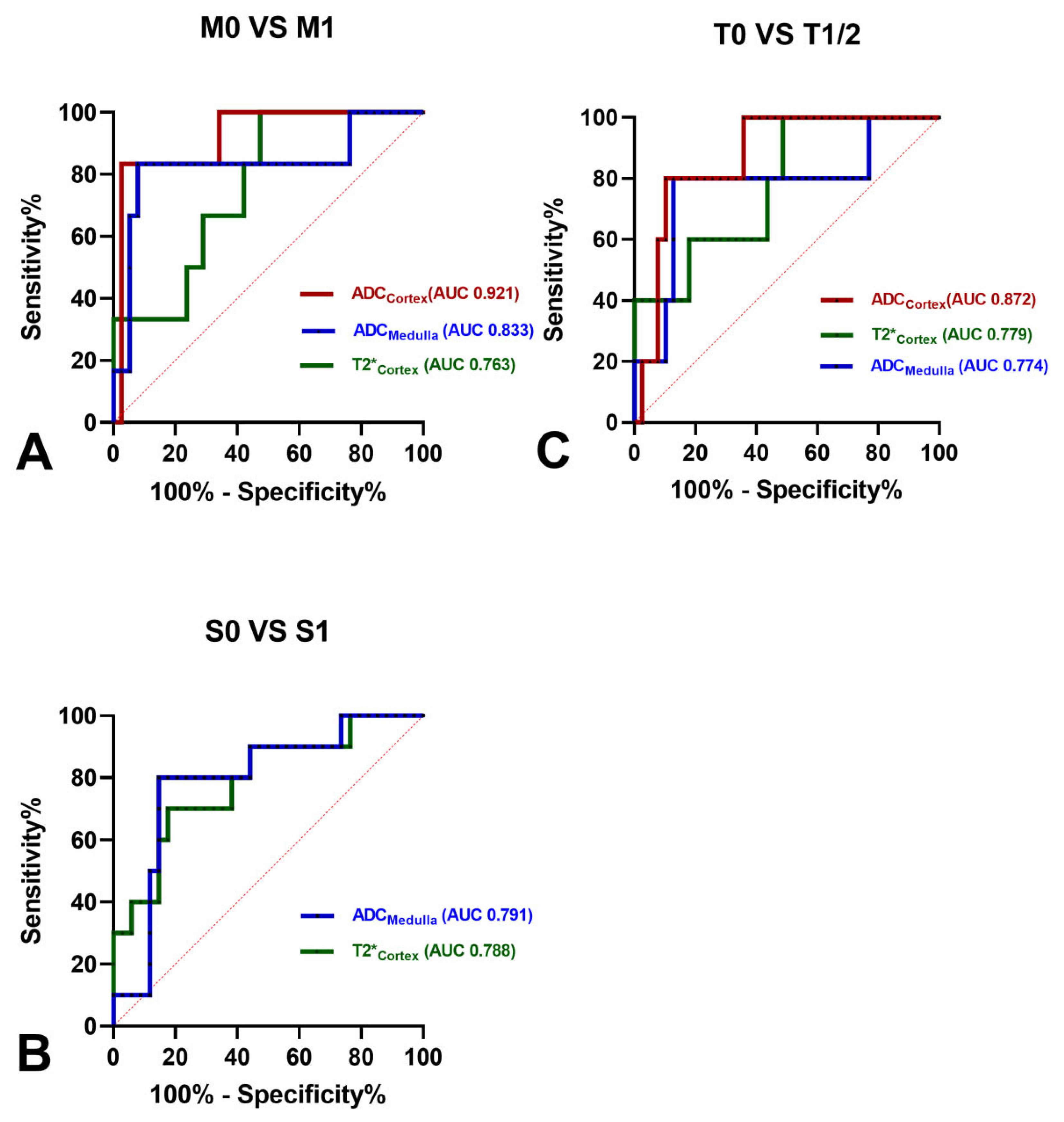
3.3. Correlations of MRI Parameters and MEST-C Scores
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, R.; Quan, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhou, X.J.; Xing, G. Spectrum of Biopsy Proven Renal Diseases in Central China: A 10-Year Retrospective Study Based on 34,630 Cases. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Tao, L.; Li, C.; Zhong, X.; Wang, H.; Ding, J. The Spectrum and Changes of Biopsy-Proven Kidney Diseases in Chinese Children. J. Nephrol. 2023, 36, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davin, J.C.; Ten Berge, I.J.; Weening, J.J. What Is the Difference between IgA Nephropathy and Henoch-Schönlein Purpura Nephritis? Kidney Int. 2001, 59, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppo, R. Pediatric IgA Nephropathy: Clinical and Therapeutic Perspectives. Semin. Nephrol. 2008, 28, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, A.R.; White, R.H.; Akuse, R.; Chantler, C. Long-Term Follow-up of Childhood Henoch-Schönlein Nephritis. Lancet 1992, 339, 280–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozen, S.; Marks, S.D.; Brogan, P.; Groot, N.; De Graeff, N.; Avcin, T.; Bader-Meunier, B.; Dolezalova, P.; Feldman, B.M.; Kone-Paut, I.; et al. European Consensus-Based Recommendations for Diagnosis and Treatment of Immunoglobulin A Vasculitis-the SHARE Initiative. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 1607–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trimarchi, H.; Barratt, J.; Cattran, D.C.; Cook, H.T.; Coppo, R.; Haas, M.; Liu, Z.-H.; Roberts, I.S.D.; Yuzawa, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Oxford Classification of IgA Nephropathy 2016: An Update from the IgA Nephropathy Classification Working Group. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.H.; Lim, B.J.; Bae, Y.S.; Kwon, Y.E.; Kim, Y.L.; Nam, K.H.; Park, K.S.; An, S.Y.; Koo, H.M.; Doh, F.M.; et al. Using the Oxford Classification of IgA Nephropathy to Predict Long-Term Outcomes of Henoch-Schönlein Purpura Nephritis in Adults. Mod. Pathol. 2014, 27, 972–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittier, W.L.; Korbet, S.M. Timing of Complications in Percutaneous Renal Biopsy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatir, D.S.; Pedersen, M.; Jespersen, B.; Buus, N.H. Reproducibility of MRI Renal Artery Blood Flow and BOLD Measurements in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Healthy Controls. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 40, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, W.; Ding, X.; Ding, Y.; Cao, B.; Fu, C.; Kuehn, B.; Benkert, T.; Grimm, R.; Nickel, D.; Zhou, J.; et al. Evaluation of Interstitial Fibrosis in Chronic Kidney Disease by Multiparametric Functional MRI and Histopathologic Analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 4138–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, W.; Zhou, J.; Zeng, M.; Ding, Y.; Qu, L.; Chen, C.; Ding, X.; Wang, Y.; Fu, C. Chronic Kidney Disease: Pathological and Functional Evaluation with Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion-Weighted Imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 47, 1251–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Yuan, G.; Li, S.; Peng, Y.; Xu, C.; Benkert, T.; Hu, D.; Han, M.; Li, Z. Noninvasive Assessment of the Renal Function, Oxford Classification and Prognostic Risk Stratification of IgAN by Using Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Blood Oxygenation Level-Dependent MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 58, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, P.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Xu, C.; Yuan, G.; Hu, D.; Kamel, I.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. Noninvasive Assessment of Kidney Dysfunction in Children by Using Blood Oxygenation Level-Dependent MRI and Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion-Weighted Imaging. Insights Imaging 2021, 12, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillman, J.R.; Benoit, S.W.; Gandhi, D.B.; Trout, A.T.; Tkach, J.A.; VandenHeuvel, K.; Devarajan, P. Multiparametric Quantitative Renal MRI in Children and Young Adults: Comparison between Healthy Individuals and Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Abdom. Radiol. 2022, 47, 1840–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, F.; Liao, Y.; Cui, K.; Tao, Y. Noninvasive Evaluation of Renal Oxygenation in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease Using Blood-Oxygen-Level-Dependent Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Pediatr. Radiol. 2020, 50, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, G.J.; Muñoz, A.; Schneider, M.F.; Mak, R.H.; Kaskel, F.; Warady, B.A.; Furth, S.L. New Equations to Estimate GFR in Children with CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbour, S.J.; Coppo, R.; Er, L.; Russo, M.L.; Liu, Z.-H.; Ding, J.; Katafuchi, R.; Yoshikawa, N.; Xu, H.; Kagami, S.; et al. Updating the International IgA Nephropathy Prediction Tool for Use in Children. Kidney Int. 2021, 99, 1439–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; He, K.; Yuan, G.; Yong, X.; Meng, X.; Feng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Kamel, I.R.; Li, Z. WHO/ISUP Grade and Pathological T Stage of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: Value of ZOOMit Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging and Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer Imaging. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 4429–4439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, H.; Xie, S.; Masokano, I.B.; Bai, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhong, L.; Wu, Y.; Nie, J.; Zhou, G.; et al. Comparing the Clinical Utility of Single-Shot, Readout-Segmented and ZOOMit Echo-Planar Imaging in Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of the Kidney at 3 T. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evidence Reviews for the Diagnostic Accuracy of eGFR Calculations in Adults, Children, and Young People from Black, Asian and Other Minority Ethnic Groups with CKD: Chronic Kidney Disease: Evidence Review A; NICE Evidence Reviews Collection; National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE): London, UK, 2021; ISBN 978-1-4731-4233-6.
- Torun Bayram, M.; Heybeli, C.; Yıldız, G.; Soylu, A.; Celik, A.; Sarioglu, S.; Kavukçu, S. Comparison of Clinical, Pathological and Long-Term Renal Outcomes of Children with Henoch-Schonlein Purpura Nephritis and IgA Nephropathy. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2022, 54, 1925–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davin, J.-C.; Coppo, R. Henoch-Schönlein Purpura Nephritis in Children. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014, 10, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yue, S.; Mei, X.; Bi, L.; Zhai, W.; Ren, X.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, S.; et al. Correlation of Urine Protein/Creatinine Ratios to 24-h Urinary Protein for Quantitating Proteinuria in Children. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2020, 35, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canney, M.; Barbour, S.J.; Zheng, Y.; Coppo, R.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.-H.; Matsuzaki, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Katafuchi, R.; Reich, H.N.; et al. Quantifying Duration of Proteinuria Remission and Association with Clinical Outcome in IgA Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, W.; Liang, S.; Hu, Y.; Deng, K.; Bao, H.; Zeng, C.; Liu, Z. Long-Term Renal Survival and Related Risk Factors in Patients with IgA Nephropathy: Results from a Cohort of 1155 Cases in a Chinese Adult Population. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 1479–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Q.; Shang, S.-Q.; Liu, A.-M.; Zhang, T.; Shen, H.-Q.; Chen, X.-J.; Mao, J.-H. 24 h Urinary Protein Levels and Urine Protein/Creatinine Ratios Could Probably Forecast the Pathological Classification of HSPN. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-T.; Lam, K.-K.; Lee, W.-C.; Hsu, K.-T.; Wu, C.-H.; Cheng, B.-C.; Ng, H.-Y.; Chi, P.-J.; Lee, Y.-T.; Lee, C.-T. Albuminuria, Proteinuria, and Urinary Albumin to Protein Ratio in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2012, 26, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiyama, K.; Inoue, T.; Kozawa, E.; Ishikawa, M.; Shimada, A.; Kobayashi, N.; Tanaka, J.; Okada, H. Reduced Oxygenation but Not Fibrosis Defined by Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Predicts the Long-Term Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35, 964–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, T.; Kozawa, E.; Ishikawa, M.; Fukaya, D.; Amano, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Tomori, K.; Kobayashi, N.; Niitsu, M.; Okada, H. Comparison of Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging Sequences with Laboratory Parameters for Prognosticating Renal Function in Chronic Kidney Disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, A.; Cai, X.; Lee, J.; Li, W.; Larive, B.; Kendrick, C.; Gassman, J.J.; Middleton, J.P.; Carr, J.; Raphael, K.L.; et al. Kidney Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Change in eGFR in Individuals with CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 15, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dionne, J.M.; Jiang, S.; Ng, D.K.; Flynn, J.T.; Mitsnefes, M.M.; Furth, S.L.; Warady, B.A.; Samuels, J.A.; CKiD Study Group. Mean Arterial Pressure and Chronic Kidney Disease Progression in the CKiD Cohort. Hypertension 2021, 78, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsnefes, M.M.; Wühl, E. Role of Hypertension in Progression of Pediatric CKD. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2023, 38, 3519–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnier, M.; Damianaki, A. Hypertension as Cardiovascular Risk Factor in Chronic Kidney Disease. Circ. Res. 2023, 132, 1050–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackensen-Haen, S.; Bader, R.; Grund, K.E.; Bohle, A. Correlations between Renal Cortical Interstitial Fibrosis, Atrophy of the Proximal Tubules and Impairment of the Glomerular Filtration Rate. Clin. Nephrol. 1981, 15, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruggenenti, P.; Perna, A.; Gherardi, G.; Garini, G.; Zoccali, C.; Salvadori, M.; Scolari, F.; Schena, F.P.; Remuzzi, G. Renoprotective Properties of ACE-Inhibition in Non-Diabetic Nephropathies with Non-Nephrotic Proteinuria. Lancet 1999, 354, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, M.; Jiang, Z.; Ding, J.; Di, J.; Cui, L. Renal Hypoxia: An Important Prognostic Marker in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Nephrol. 2018, 48, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerber, E.L.; Padberg, C.; Koll, N.; Schuetzhold, V.; Fandrey, J.; Winning, S. The Importance of Hypoxia-Inducible Factors (HIF-1 and HIF-2) for the Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Li, Z.-L.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Wen, Y.; Gao, Y.-M.; Liu, B.-C. Hypoxia and Chronic Kidney Disease. EBioMedicine 2022, 77, 103942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variables | All | Low-Risk | High-Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| n = 44 | n = 25 | n = 19 | |
| sex | |||
| Male | 34 (77.27) | 19 (76.00) | 15 (78.95) |
| Female | 10 (22.73) | 6 (3.00) | 4 (21.05) |
| age (y) | 9.84 ± 2.74 | 9.28 ± 2.46 | 10.58 ± 2.97 |
| Height (cm) | 144.27 ± 16.26 | 140.60 ± 15.52 | 149.11 ± 16.35 |
| Weight (kg) | 38.62 ± 15.40 | 35.83 ± 11.25 | 42.28 ± 13.17 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 18.15 ± 3.37 | 17.76 ± 3.09 | 18.67 ± 3.73 |
| eGFR (ml(min × 1.73 m2)) | 118.49 ± 29.16 | 126.55 ± 30.83 | 107.89 ± 23.56 |
| Urea (mmol/L) | 5.37 ± 2.45 | 5.35 ± 3.04 | 5.40 ± 1.41 |
| Scr (μmol/L) | 48.16 ± 17.27 | 44.2 ± 17.74 | 53.37 ± 15.57 |
| Uric acid (μmol/L) | 287.44 ± 91.38 | 292.24 ± 90.71 | 281.26 ± 94.37 |
| HCO3− (mmol/L) | 22.73 ± 2.38 | 22.29 ± 2.36 | 23.30 ± 2.36 |
| NLR | 2.40 ± 2.01 | 1.92 ± 1.33 | 3.01 ± 2.57 |
| β2-MG (mg/L) | 0.55 ± 0.76 | 0.33 ± 0.33 | 0.84 ± 1.04 |
| cystantin C (mg/L) | 0.96 ± 0.27 | 0.91 ± 0.22 | 1.02 ± 0.32 |
| 24 h-Upro (g) | 1.15 ± 1.56 | 0.64 ± 0.98 | 1.83 ± 1.91 |
| 24 h-PCR (mg/mmol) | 219.00 ± 367.00 | 128.70 ± 184.78 | 337.80 ± 500.00 |
| Urinary occult blood | |||
| 1+ | 5 (11.36) | 3 (12.00) | 2 (10.53) |
| 2+ | 10 (22.73) | 9 (36.00) | 1 (5.26) |
| 3+ | 29 (65.91) | 13 (52.00) | 16 (84.21) |
| SBP (mmHg) | 107.25 ± 14.21 | 99.76 ± 9.75 | 117.11 ± 13.24 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 74.98 ± 10.48 | 70.16 ± 7.73 | 81.32 ± 10.40 |
| MAP (mmHg) | 85.73 ± 11.00 | 80.03 ± 7.72 | 93.25 ± 10.21 |
| The SHARE initiative | |||
| Mild | 34 (77.27) | 23 (92.00) | 11 (57.89) |
| Moderate/Severe | 10 (22.73) | 2 (8.00) | 8 (42.11) |
| Variable | All | Low-Risk | High-Risk | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 44 | n = 25 | n = 19 | ||||
| M | M0 | Absent to ≤50% of glomeruli | 38 | 25 | 13 | 0.002 * |
| M1 | >50% of glomeruli | 6 | 0 | 6 | ||
| E | E0 | Absent | 36 | 21 | 15 | 0.667 |
| E1 | Present | 8 | 4 | 4 | ||
| S | S0 | Absent | 34 | 24 | 10 | 0.001 * |
| S1 | Present | 10 | 1 | 9 | ||
| T | T0 | Absent to ≤25% of the cortex | 39 | 25 | 14 | 0.006 * |
| T1/2 | 25–50% of the cortex or>50% of the cortex | 5 | 0 | 5 | ||
| C | C0 | Absent | 17 | 9 | 8 | 0.68 |
| C1/2 | 1%–24% of the glomeruli or≥25% of the glomeruli | 27 | 16 | 11 | ||
| Variable | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95%CI | p-Value | OR | 95%CI | p-Value | |
| sex | ||||||
| male | 0.844 | 0.201–3.546 | 0.817 | |||
| female | ||||||
| Age (y) | 1.203 | 0.95–1.525 | 0.126 | |||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 1.806 | 0.906–1.302 | 0.373 | |||
| eGFR(ml(min × 1.73 m2)) | 0.975 | 0.951–0.999 | 0.044 * | 0.965 | ||
| Urea (mmol/L) | 1.009 | 0.789–1.289 | 0.946 | |||
| Scr (μmol/L) | 1.035 | 0.994–1.077 | 0.096 | |||
| Uric acid (μmol/L) | 0.999 | 0.992–1.005 | 0.687 | |||
| HCO3− (mmol/L) | 1.212 | 0.919–1.598 | 0.173 | |||
| NLR | 1.354 | 0.951–1.929 | 0.093 | |||
| β2-MG (mg/L) | 6.039 | 0.891–40.929 | 0.066 | |||
| cystantin C (mg/L) | 5.364 | 0.747–60.646 | 0.175 | |||
| 24 h-Upro (g) | 1.001 | 1–1.001 | 0.04 * | 0.675 | ||
| 24 h-PCR (mg/mmol) | 1.003 | 0.999–1.006 | 0.116 | |||
| Urinary occult blood | 2.123 | 0.809–6.052 | 0.122 | |||
| MAP (mmHg) | 1.239 | 1.089–1.409 | 0.001 * | 1.190 | 1.304–1.370 | 0.016 * |
| The SHARE initiative | ||||||
| Mild | 8.364 | 1.516–46.148 | 0.015 * | 0.367 | ||
| Moderate/Severe | ||||||
| MRI parameters | ||||||
| ADCCortex | 0.986 | 0.977–0.995 | 0.003 * | 0.503 | ||
| ADCMedulla | 0.989 | 0.981–0.997 | 0.005 * | 0.969 | ||
| T2*Cortex | 0.457 | 0.302–0.693 | <0.001* | 0.512 | 0.327–0.801 | 0.003* |
| T2*Medulla | 1.007 | 0.987–1.028 | 0.479 | |||
| cortical thickness (mm) | 3.598 | 0.397–32.627 | 0.255 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, Z.; Yuan, G.; He, K.; Li, S.; Gao, M.; Liang, P.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. Explore the Value of Multi-Parameter MRI in Non-Invasive Assessment of Prognostic Risk and Oxford Classification in Children with IgAN or IgAVN. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 750. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080750
Liao Z, Yuan G, He K, Li S, Gao M, Liang P, Xu C, Zhang Y, Li Z. Explore the Value of Multi-Parameter MRI in Non-Invasive Assessment of Prognostic Risk and Oxford Classification in Children with IgAN or IgAVN. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(8):750. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080750
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Zhouyan, Guanjie Yuan, Kangwen He, Shichao Li, Mengmeng Gao, Ping Liang, Chuou Xu, Yu Zhang, and Zhen Li. 2024. "Explore the Value of Multi-Parameter MRI in Non-Invasive Assessment of Prognostic Risk and Oxford Classification in Children with IgAN or IgAVN" Bioengineering 11, no. 8: 750. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080750
APA StyleLiao, Z., Yuan, G., He, K., Li, S., Gao, M., Liang, P., Xu, C., Zhang, Y., & Li, Z. (2024). Explore the Value of Multi-Parameter MRI in Non-Invasive Assessment of Prognostic Risk and Oxford Classification in Children with IgAN or IgAVN. Bioengineering, 11(8), 750. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080750






