Retrospective Study of Maxillary Sinus Augmentation Using Demineralized Tooth Block Bone for Dental Implant
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
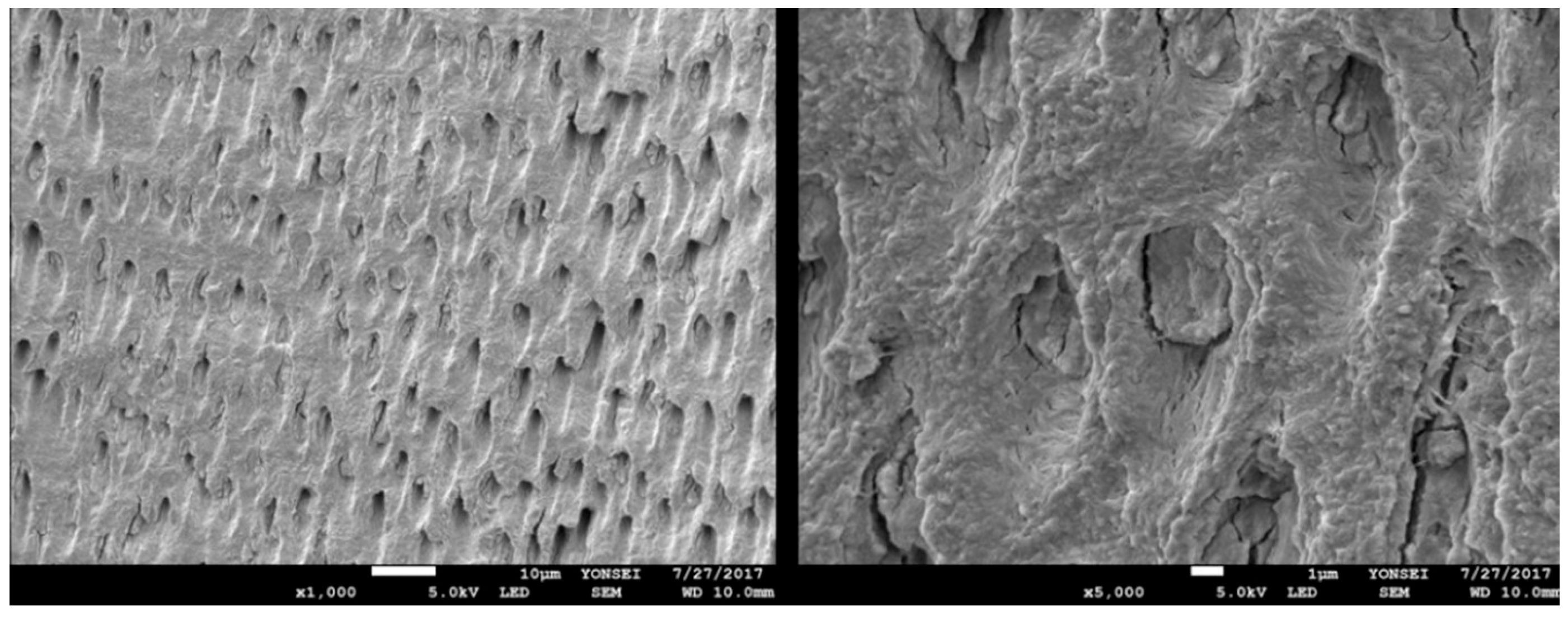
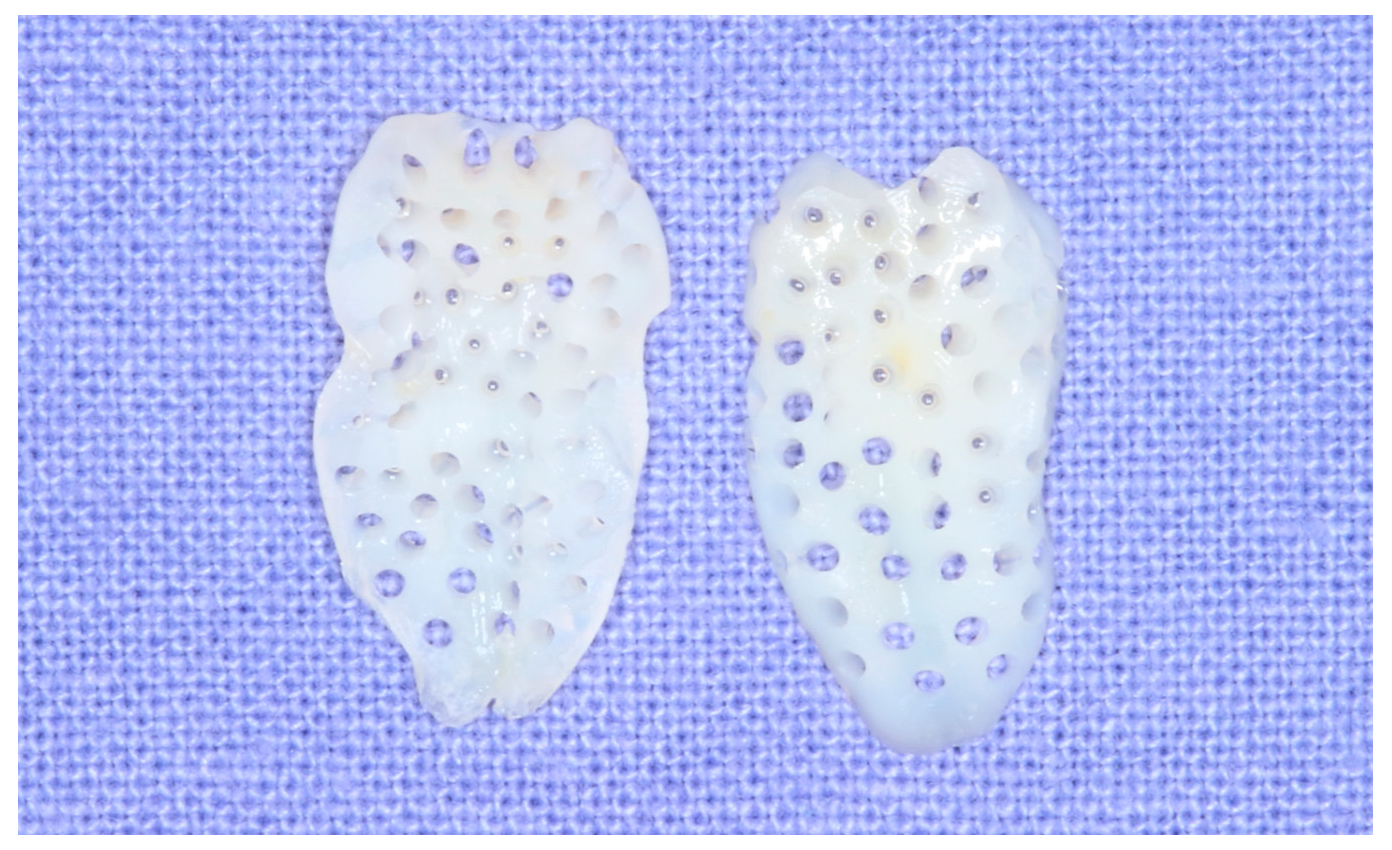
2.2. Preparation of Osteoinductive Tooth Block Bone
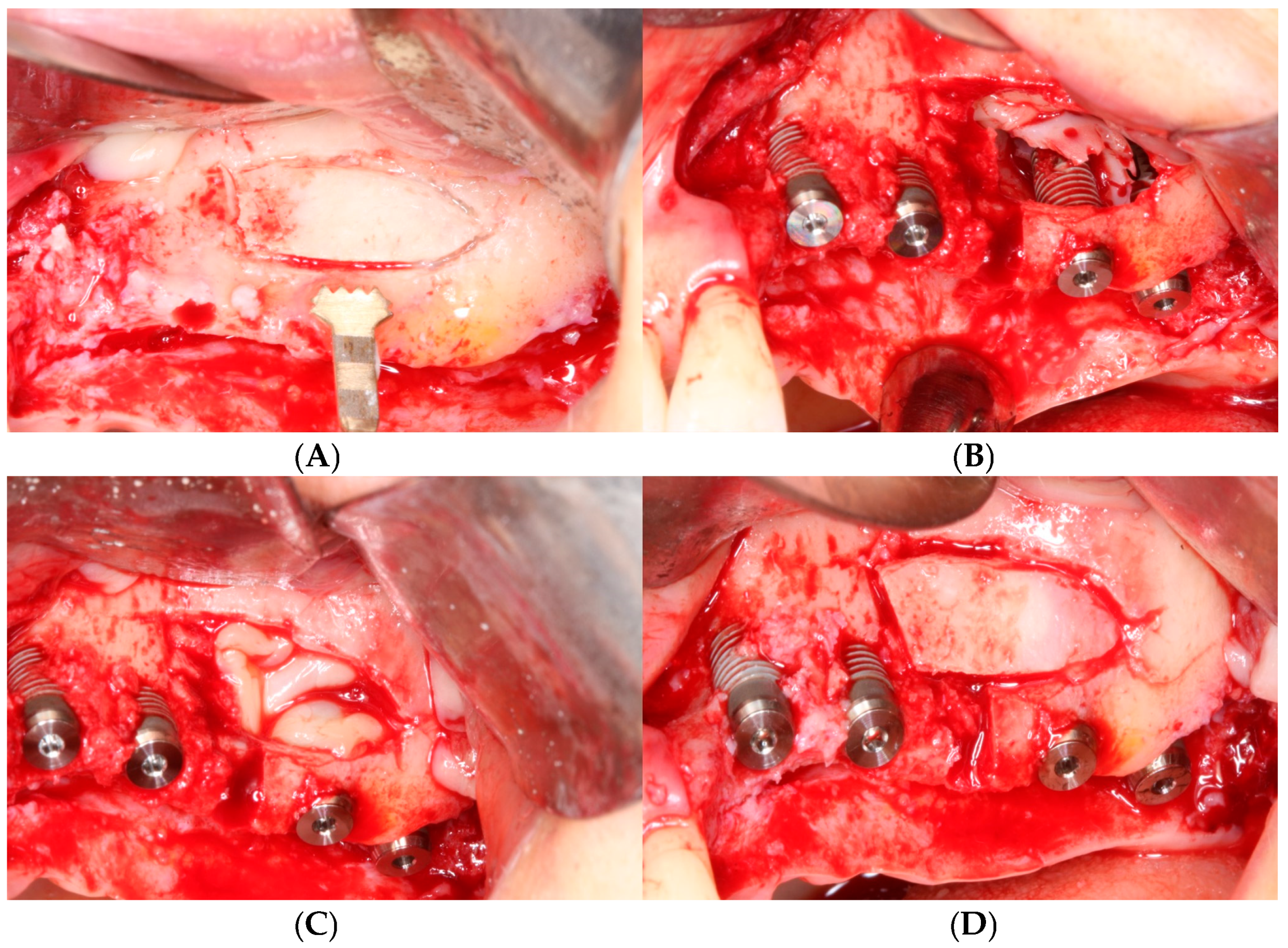
2.3. Surgical Protocol
3. Results
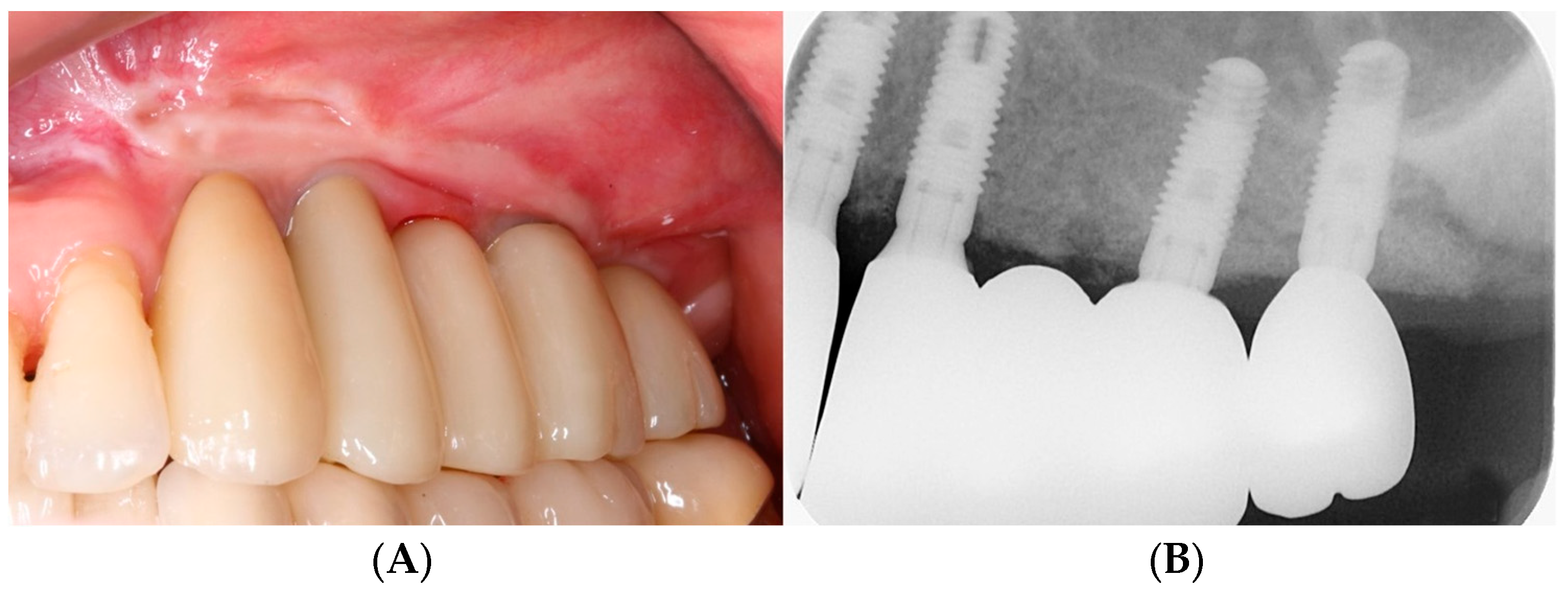
3.1. Clinical Results
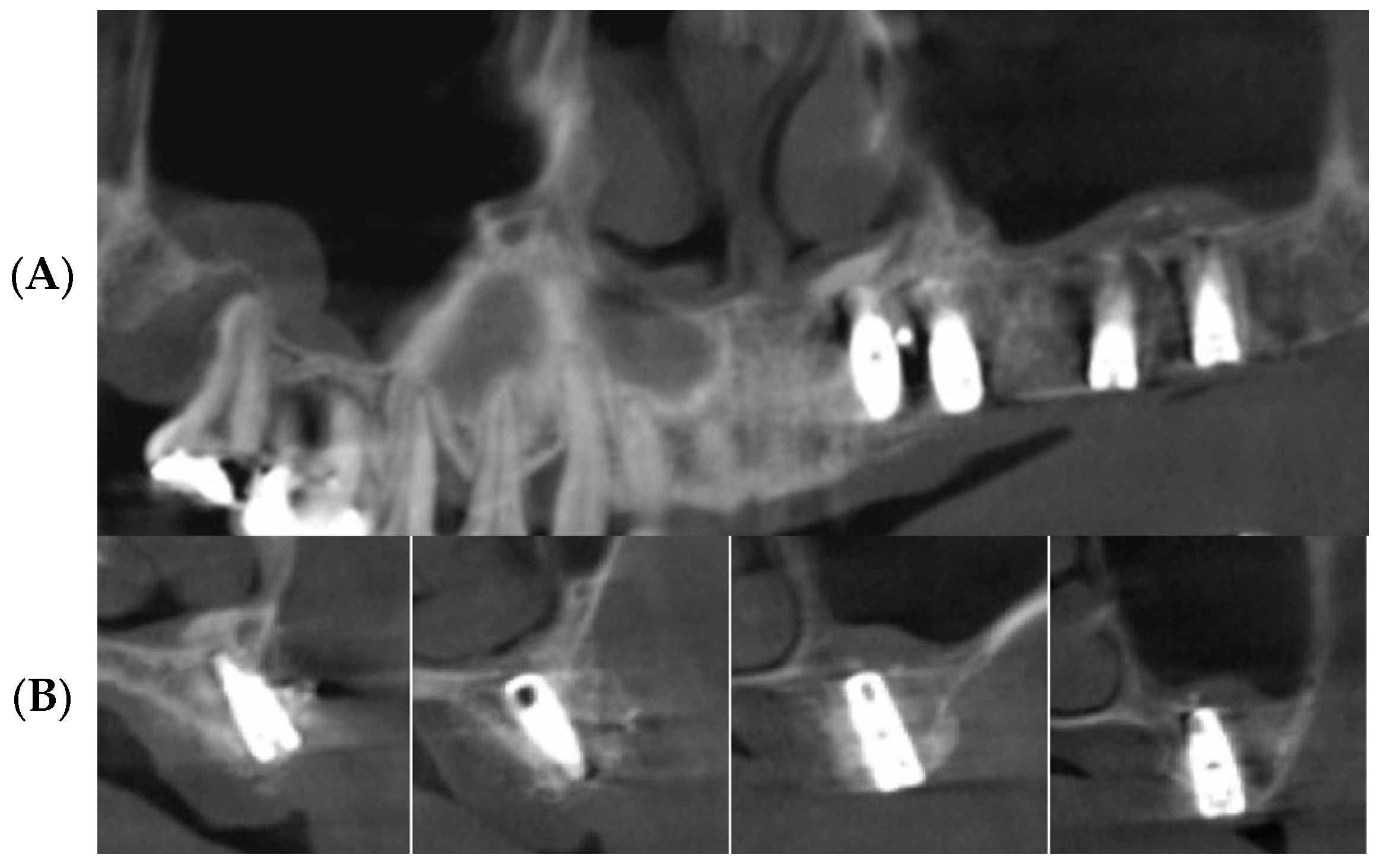
3.2. Radiographic Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Le Guéhennec, L.; Soueidan, A.; Layrolle, P.; Amouriq, Y. Surface treatments of titanium dental implants for rapid osseointegration. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misch, C.E. Maxillary sinus augmentation for endosteal implants: Organized alternative treatment plans. Int. J. Oral Implantol. 1987, 4, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smiler, D.G.; Johnson, P.W.; Lozada, J.L.; Misch, C.; Rosenlicht, J.L.; Tatum, O.H.; Wagner, J.R. Sinus lift grafts and endosseous implants: Treatment of the atrophic posterior maxilla. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 1992, 36, 151–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanavaz, M. Maxillary sinus: Anatomy, physiology, surgery, and bone grafting related to implantology—Eleven years of surgical experience (1979–1990). J. Oral Implantol. 1990, 16, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bernardi, S.; Bianchi, S.; Gerardi, D.; Petrelli, P.; Rinaldi, F.; Piattelli, M.; Macchiarelli, G.; Varvara, G. Anatomy of maxillary sinus: Focus on vascularization and underwood septa via 3D imaging. Tomography 2024, 10, 444–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomason, J.M.; Heydecke, G.; Feine, J.S.; Ellis, J.S. How do patients perceive the benefit of reconstructive dentistry with regard to oral health-related quality of life and patient satisfaction? A systemic review. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2007, 18, 168–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, D.S.; Heo, J.U.; Kwak, D.H.; Kim, D.E.; Kim, J.M.; Moon, J.W.; Lee, J.H.; Park, I.S. Bone regeneration in the maxillary sinus using an autologous fibrin-rich block with concentrated growth factors alone. Implant. Dent. 2011, 20, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffin, R.A.; Berman, C.L. The excessive loss of Branemark fixtures in type IV bone: A 5-year analysis. J. Periodontol. 1991, 62, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyne, P.J. Grafting of the maxillary sinus floor with autogenous marrow and bone. J. Oral Surg. 1980, 38, 613–616. [Google Scholar]
- Tatum, H., Jr. Maxillary and sinus implant reconstructions. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 1986, 30, 207–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaloo, T.L.; Moy, P.K. Which hard tissue augmentation techniques are the most successful in furnishing bony support for implant placement? Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2007, 22, 49–70. [Google Scholar]
- Adell, R.; Lekholm, U.; Gröndahl, K.; Brånemark, P.-I.; Lindström, J.; Jacobsson, M. Reconstruction of severely resorbed edentulous maxillae using osseointegrated fixtures in immediate autogenous bone grafts. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1990, 5, 233–246. [Google Scholar]
- Klijn, R.J.; Meijer, G.J.; Bronkhorst, E.M.; Jansen, J.A. A meta-analysis of histomorphometric results and graft healing time of various biomaterials compared to autologous bone used as sinus floor augmentation material in humans. Tissue Eng. Part. B Rev. 2010, 16, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlegel, K.A.; Fichtner, G.; Schultze-Mosgau, S.; Wiltfang, J. Histologic findings in sinus augmentation with autogenous bone chips versus a bovine bone substitute. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2003, 18, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.Y.; Kim, K.W. A double layers technique for maxillary sinus augmentation with demineralized and mineralized bone graft materials. Maxillofac. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 31, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Hatano, N.; Shimizu, Y.; Ooya, K. A clinical long-term radiographic evaluation of graft height changes after maxillary sinus floor augmentation with a 2:1 autogenous bone/xenograft mixture and simultaneous placement of dental implants. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2004, 15, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.K.; Lee, J.; Yun, J.Y.; Yun, P.Y.; Um, I.W. Comparison of autogenous tooth bone graft and synthetic bone graft materials used for bone resorption around implants after crestal approach sinus lifting: A retrospective study. J. Periodontal Implant. Sci. 2014, 44, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iezzi, G.; Degidi, M.; Piattelli, A.; Mangano, C.; Scarano, A.; Shibli, J.A.; Perrotti, V. Comparative histological results of different biomaterials used in sinus augmentation procedures: A human study at 6 months. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2012, 23, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.W.; Chang, H.S.; Leung, K.W.; Lai, Y.L.; Kao, S.Y. Implant placement immediately after the lateral approach of the trap door window procedure to create a maxillary sinus lift without bone grafting: A 2-year retrospective evaluation of 47 implants in 33 patients. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2007, 65, 2324–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazor, Z.; Peleg, M.; Garg, A.K.; Luboshitz, J. Platelet-rich plasma for bone graft enhancement in sinus floor augmentation with simultaneous implant placement: Patient series study. Implant. Dent. 2004, 13, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.W.; Shin, H.I.; Jung, J.K. New bone formation in the maxillary sinus using peripheral venous blood alone. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 69, 2357–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urist, M.R.; Huo, Y.K.; Brownell, A.G.; Hohl, W.M.; Buyske, J.; Lietze, A.; Tempst, P.; Hunkapiller, M.; DeLange, R.J. Purification of bovine bone morphogenetic protein by hydroxyapatite chromatography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeomans, J.D.; Urist, M.R. Bone induction by decalcified dentine implanted into oral, osseous and muscle tissues. Arch. Oral Biol. 1967, 12, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.S.; Kang, J.Y.; Kim, J.J.; Kim, K.W.; Lee, E.Y. Space maintenance in autogenous fresh demineralized tooth blocks with platelet-rich plasma for maxillary sinus bone formation: A prospective study. Springerplus 2016, 5, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peleg, M.; Garg, A.K.; Misch, C.M.; Mazor, Z. Maxillary sinus and ridge augmentations using a surface-derived autogenous bone graft. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2004, 62, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinchasov, G.; Juodzbalys, G. Graft-free sinus augmentation procedure: A literature review. J. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2014, 5, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerardi, D.; Santostasi, N.; Torge, D.; Rinaldi, F.; Bernardi, S.; Bianchi, S.; Piattelli, M.; Varvara, G. Regenerative Potential of Platelet—Rich Fibrin in Maxillary Sinus Floor Lift Techniques: A Systematic Review. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2023, 37, 2357–2369. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Shimizu, Y.; Ooya, K. Histomorphometric study of the stability of newly formed bone after elevation of the floor of the maxillary sinus. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2005, 43, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlegel, A.K.; Donath, K. BIO-OSS—A resorbable bone substitute? J. Long-Term Eff. Med. Implant. 1998, 8, 201–209. [Google Scholar]
- Hallman, M.; Cederlund, A.; Lindskog, S.; Lundgren, S.; Sennerby, L. A clinical histologic study of bovine hydroxyapatite in combination with autogenous bone and fibrin glue for maxillary sinus floor augmentation: Results after 6 to 8 months of healing. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2001, 12, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.K.; Lee, J.; Um, I.W.; Kim, K.W.; Murata, M.; Akazawa, T.; Mitsugi, M. Tooth-derived bone graft material. J. Korean Assoc. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 39, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Cho, W.J.; Um, I.W.; Murata, M.; Mitsugi, M. Autogenous tooth bone graft block for sinus augmentation with simultaneous implant installation: A technical note. J. Korean Assoc. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 41, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, F.; Golubovic, V.; Becker, K.; Mihatovic, I. Extracted tooth roots used for lateral alveolar ridge augmentation: A proof-of-concept study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2016, 43, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K.; Drescher, D.; Hönscheid, R.; Golubovic, V.; Mihatovic, I.; Schwarz, F. Biomechanical, micro-computed tomographic and immunohistochemical analysis of early osseous integration at titanium implants placed following lateral ridge augmentation using extracted tooth roots. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2017, 28, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfour, A.; Farzad, P.; Andersson, L.; Joseph, B.; Dahlin, C. Host tissue reactions of non-demineralized autogenic and xenogenic dentin blocks implanted in a non-osteogenic environment. An experimental study in rabbits. Dent. Traumatol. 2014, 30, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.M.; Kim, D.H.; Pang, E.K. Bone formation of demineralized human dentin block graft with different demineralization time: In vitro and in vivo study. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 45, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urist, M.R. Bone histogenesis and morphogenesis in implants of demineralized enamel and dentin. J. Oral Surg. 1971, 29, 88–102. [Google Scholar]
- Bang, G. Induction of heterotopic bone formation by demineralized dentin in guinea pigs: Antigenicity of the dentin matrix. J. Oral Pathol. 1972, 1, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, G. Induction of heterotopic bone formation by demineralized dentin: An experimental model in guinea pigs. Scand. J. Dent. Res. 1973, 81, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.A.; Murata, M.; Akazawa, T.; Kusano, K.; Yamada, K.; Ito, M. Evaluation of perforated demineralized dentin scaffold on bone regeneration in critical-size sheep iliac defects. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2017, 28, e227–e235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y.S.; Sohn, D.S.; Kim, G.; Park, I.S. Comparative histomorphometric evaluation of bone regeneration with different preparations of xenogeneic tooth block bone. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2019, 34, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.K.; Pang, K.M.; Yun, P.Y.; Leem, D.H.; Um, I.W. Long-term follow-up of autogenous tooth bone graft blocks with dental implants. Clin. Case Rep. 2017, 5, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.Y.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, K.W. Scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy studies on processed tooth graft material by vacuum-ultrasonic acceleration. Maxillofac. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 36, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, M.F.; Abreu PP de Morosolli, A.R.C.; Araújo, M.M.; Goulart, M.d.G.V. Densitometric analysis of the autogenous demineralized dentin matrix on the dental socket wound healing process in humans. Braz. Oral Res. 2006, 20, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, D.S.; Lui, A.; Choi, H. Utilization of Tenting Pole Abutments for the Reconstruction of Severely Resorbed Alveolar Bone: Technical Considerations and Case Series Reports. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, D.S.; Moon, J.W.; Lee, H.W.; Choi, B.J.; Shin, I.H. Comparison of two piezoelectric cutting inserts for lateral bony window osteotomy: A retrospective study of 127 consecutive sites. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2010, 25, 571–576. [Google Scholar]






| Subject | Sex/Age | Region | Failed Site | Sinus Membrane Perforation | Months to Second-Stage Surgery | Months in Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M/50 | #16 | - | No | 4 | 58 |
| 2 | M/46 | #26 | - | No | 6 | 42 |
| 3 | F/50 | #27 | - | Yes | 4.5 | 60 |
| 4 | M/46 | #14,15,16,17 | - | No | 7 | 51 |
| 5 | M/59 | #26,27 | - | No | 5 | 50 |
| 6 | F/57 | #26 | - | No | 5 | 48 |
| 7 | F/52 | #17 | - | Yes | 10 | 50 |
| 8 | F/52 | #27 | - | No | 5.5 | 55 |
| 9 | M/65 | #16 | - | Yes | 6.5 | 54 |
| 10 | M/50 | #16,26 | - | No | 7.5 | 59 |
| 11 | F/58 | #26,27 | - | No | 7.5 | 52 |
| 12 | F/47 | #27 | - | No | 4 | 58 |
| 13 | M/64 | #16 | - | No | 3 | 50 |
| 14 | M/75 | #26 | - | No | 6 | 60 |
| 15 | F/54 | #16 | - | No | 10 | 46 |
| 16 | M/45 | #17 | - | No | 3.5 | 49 |
| 17 | M/52 | #26,27 | - | No | 5 | 53 |
| 18 | M/45 | #27 | - | No | 10.5 | 54 |
| 19 | F/57 | #26,27 | - | No | 5 | 61 |
| Subject | Region | Preoperative Bone Height (mm) | Maxillary Sinus Width (mm) | Amount of Sinus Membrane Elevation (mm) | Bone Height at the End of the Study (mm) | Increment in Bone Height (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | #16 | 5 | 12 | 18 | 14 | 9 |
| 2 | #26 | 3 | 18 | 17 | 13 | 10 |
| 3 | #27 | 5 | 16 | 16 | 14 | 9 |
| 4 | #14,15,16,17 | 5,3,5,5 | 22 | 15,18,14,16 | 15,16,14,14 | 10,13,9,8 |
| 5 | #26,27 | 4,4 | 16 | 16,16 | 15,12 | 11,8 |
| 6 | #26 | 6 | 16 | 18 | 20 | 14 |
| 7 | #17 | 2 | 24 | 16 | 15 | 13 |
| 8 | #27 | 2 | 22 | 19 | 18 | 16 |
| 9 | #16 | 2 | 22 | 16 | 14 | 12 |
| 10 | #16,26 | 3,3 | 23 | 23,20 | 20,22 | 17,19 |
| 11 | #26,27 | 3,2 | 24 | 19,18 | 20,16 | 17,14 |
| 12 | #27 | 4 | 22 | 16 | 15 | 11 |
| 13 | #16 | 5 | 12 | 14 | 14 | 9 |
| 14 | #26 | 4 | 16 | 12 | 12 | 8 |
| 15 | #16 | 1 | 20 | 22 | 18 | 17 |
| 16 | #17 | 5 | 13 | 17 | 20 | 15 |
| 17 | #26,27 | 6,6 | 15 | 10,11 | 15,16 | 9,10 |
| 18 | #27 | 3 | 25 | 12 | 14 | 11 |
| 19 | #26,27 | 1,2 | 20 | 21 | 14,14 | 13,12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, H.; Sohn, D.-S. Retrospective Study of Maxillary Sinus Augmentation Using Demineralized Tooth Block Bone for Dental Implant. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 633. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060633
Choi H, Sohn D-S. Retrospective Study of Maxillary Sinus Augmentation Using Demineralized Tooth Block Bone for Dental Implant. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(6):633. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060633
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Hyunsuk, and Dong-Seok Sohn. 2024. "Retrospective Study of Maxillary Sinus Augmentation Using Demineralized Tooth Block Bone for Dental Implant" Bioengineering 11, no. 6: 633. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060633
APA StyleChoi, H., & Sohn, D.-S. (2024). Retrospective Study of Maxillary Sinus Augmentation Using Demineralized Tooth Block Bone for Dental Implant. Bioengineering, 11(6), 633. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060633






