Augmented Reality-Guided Extraction of Fully Impacted Lower Third Molars Based on Maxillofacial CBCT Scans
Abstract
1. Introduction
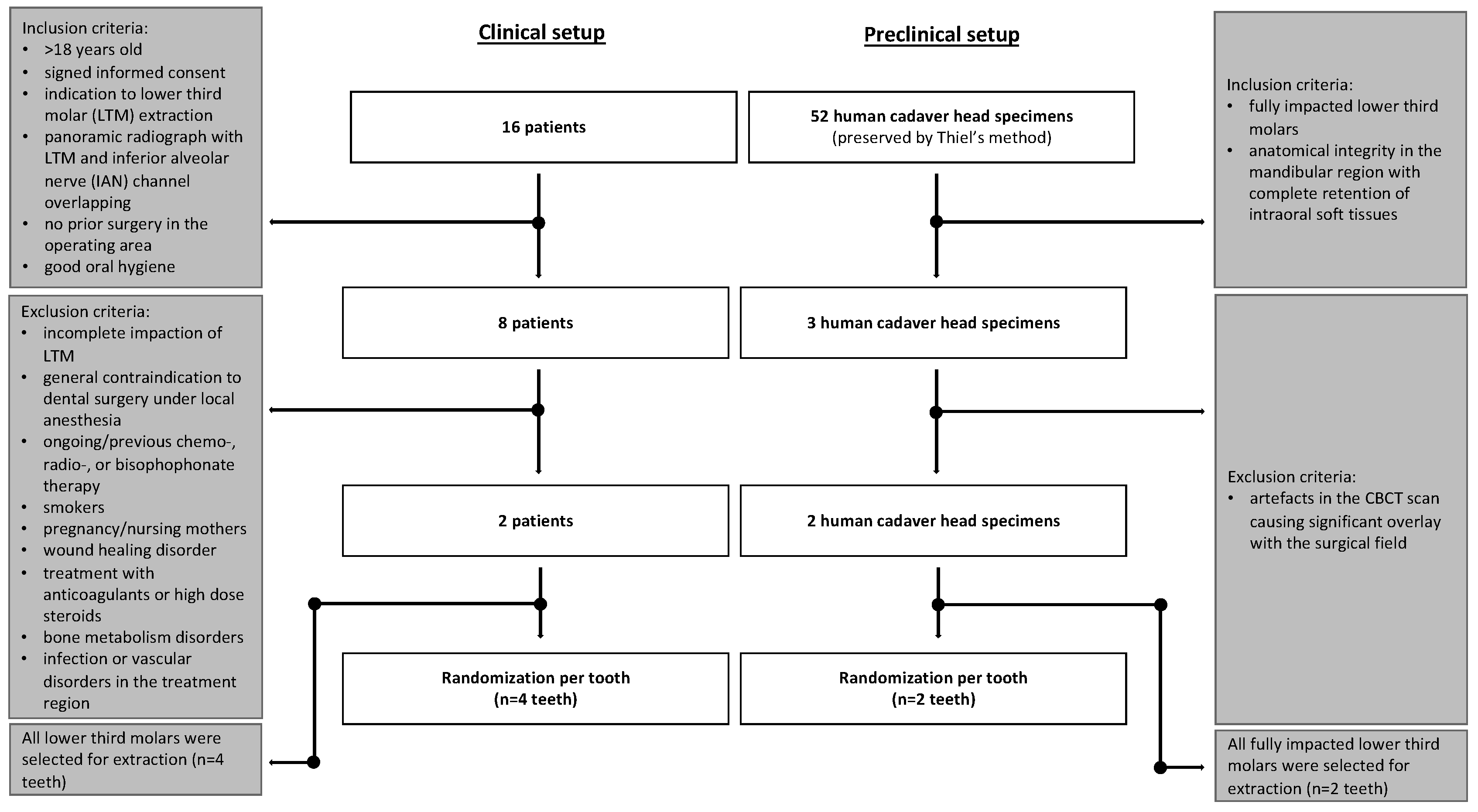
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Human Head Cadaver Specimens
2.3. Clinical Patients
2.3.1. Eligibility/Inclusion Criteria
2.3.2. Exclusion Criteria
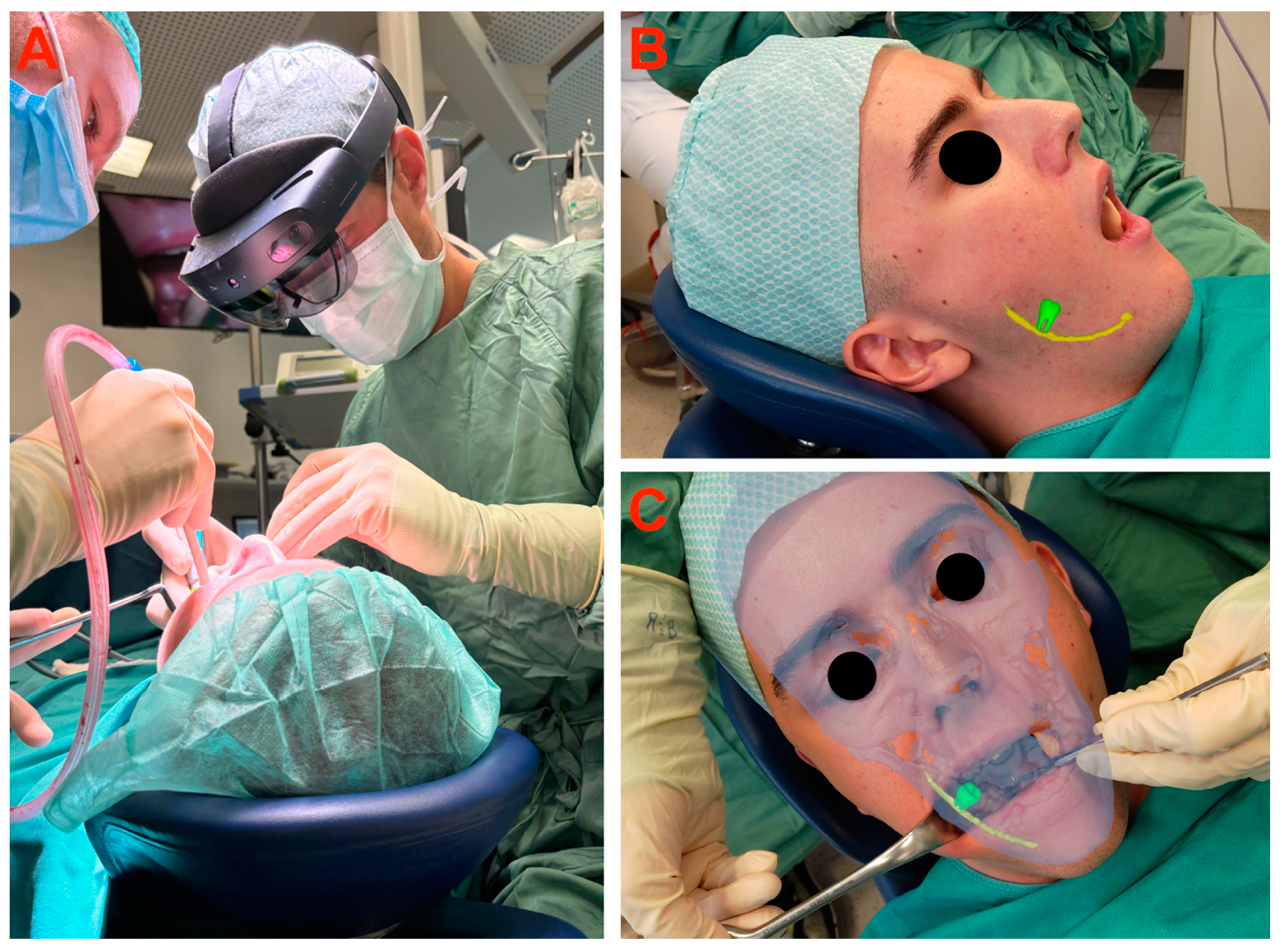
2.4. Augmented Reality System
2.5. Randomization and Training
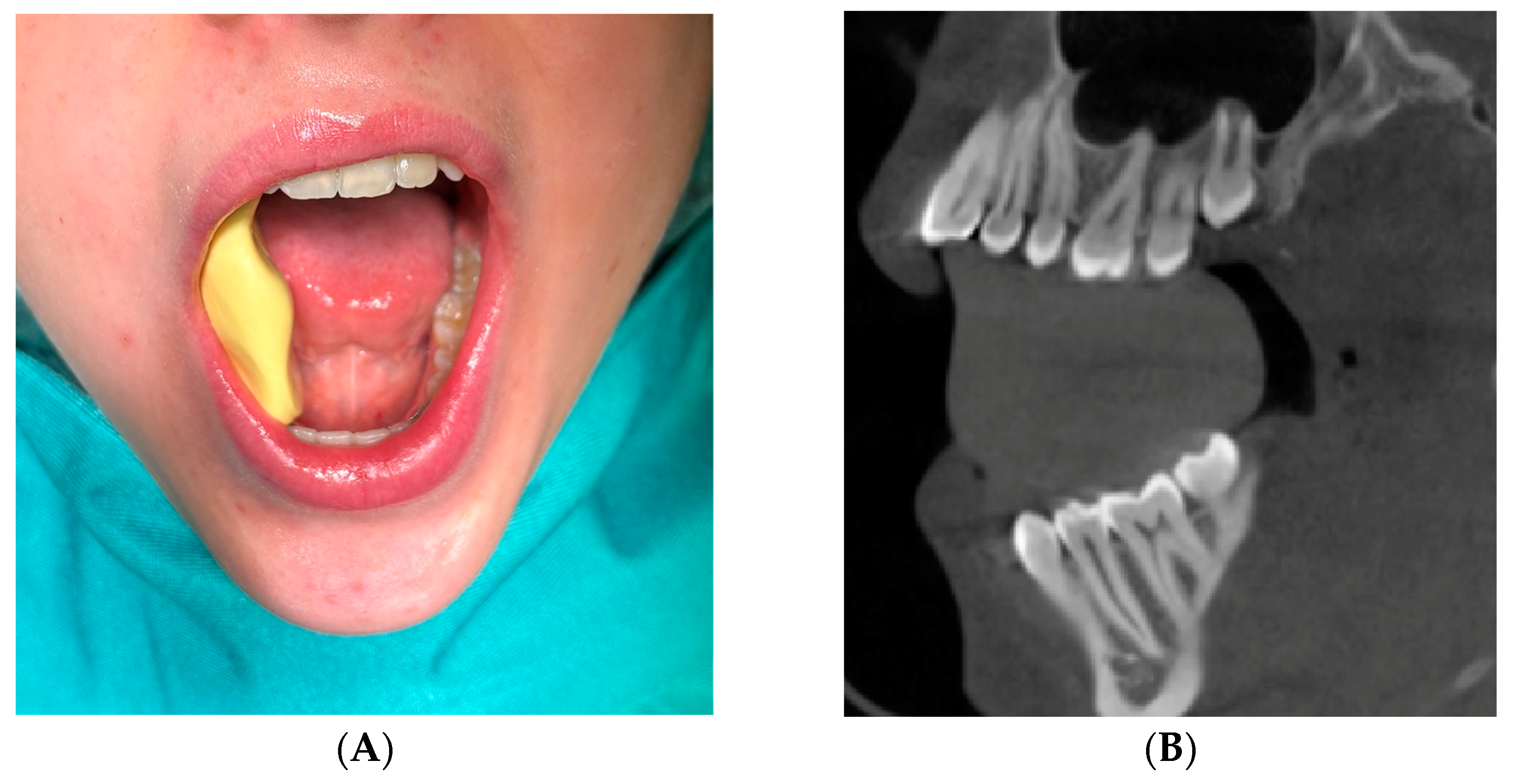
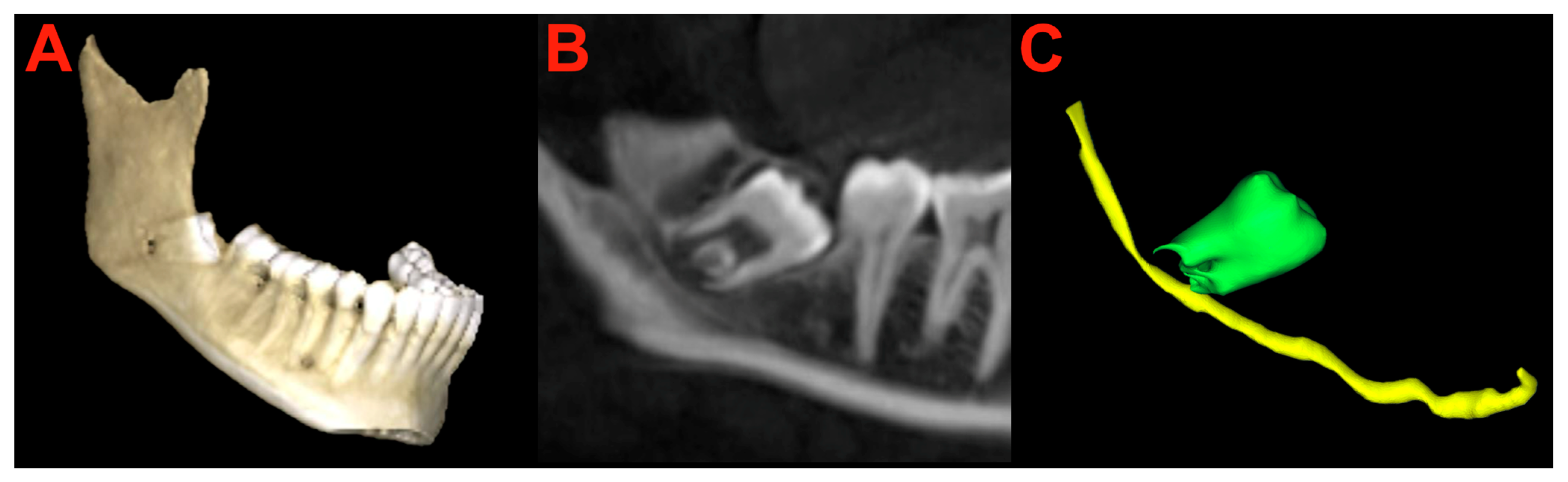
2.6. Segmentation and Preparation
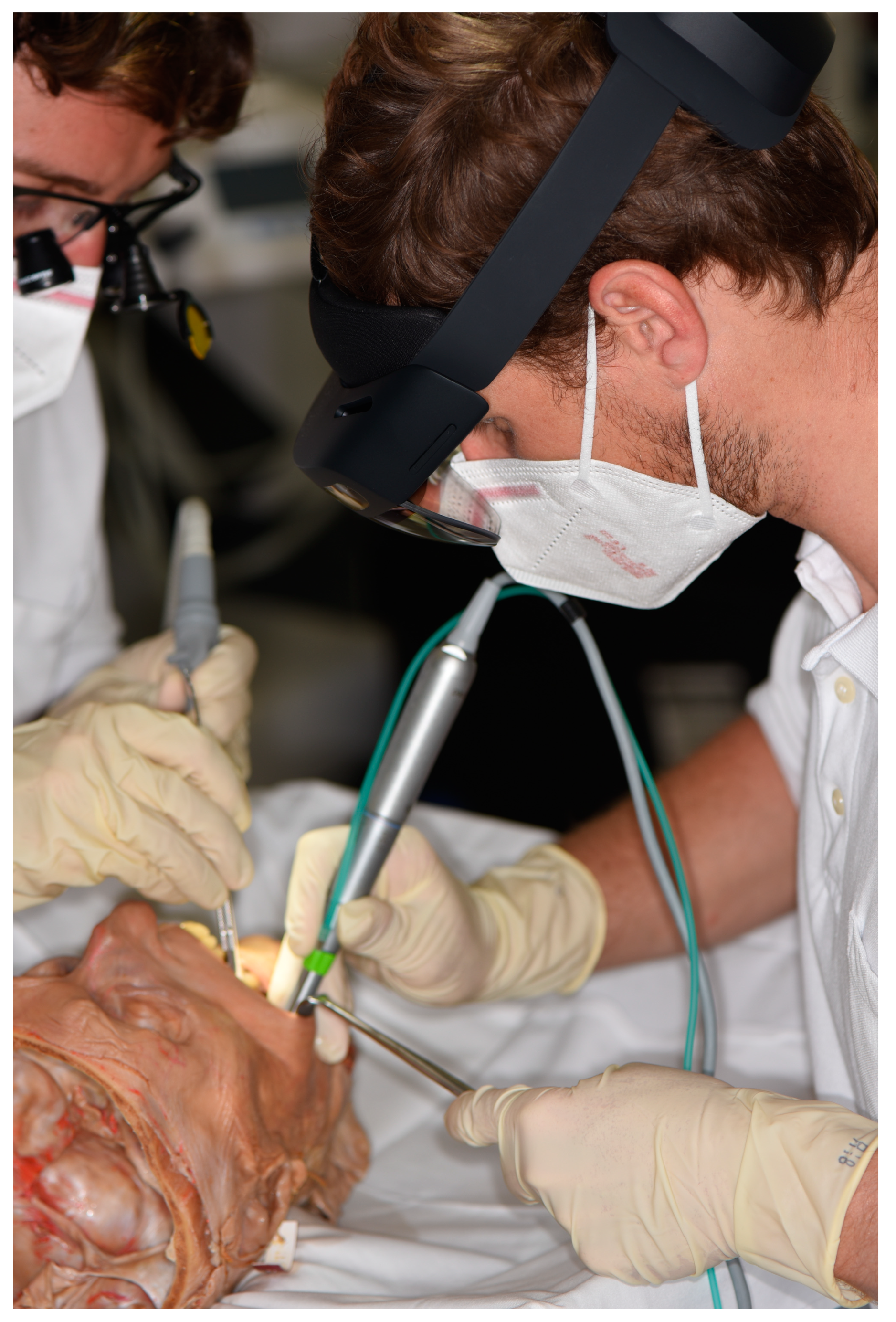
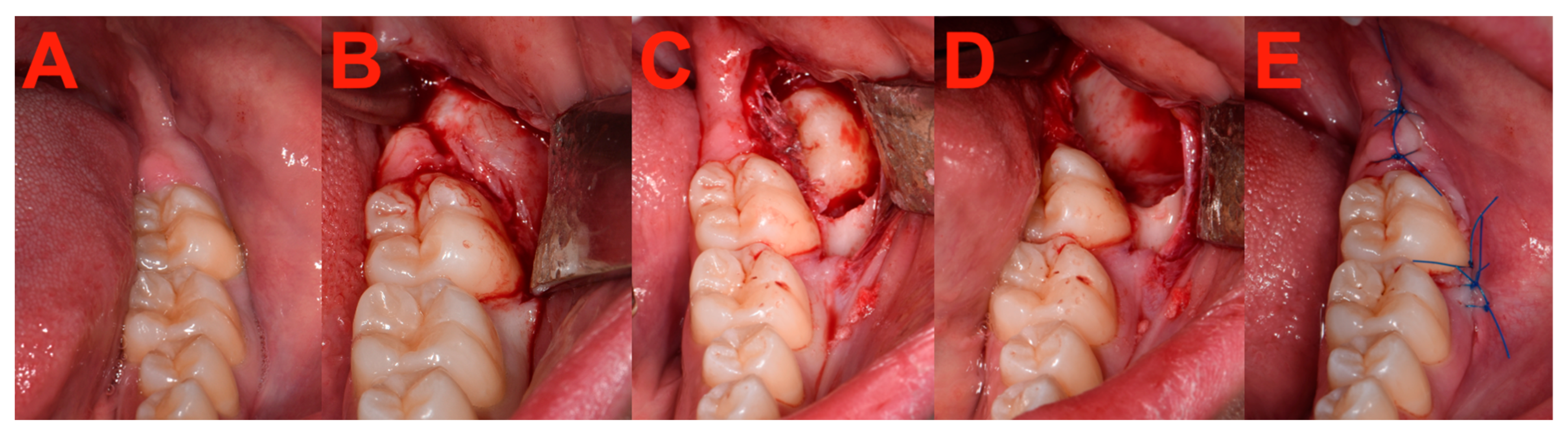
2.7. Surgery
2.8. Measurements
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Measurements
3.2. System Usability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AR | augmented reality |
| CBCT | cone beam computed tomography |
| CT | computed tomography |
| DN | dynamic navigation |
| FOV | field of view |
| HL | HoloLens 2 |
| IAN | inferior alveolar nerve |
| IGS | image-guided surgery |
| IQR | interquartile range |
| LN | lingual nerve |
| LTM | lower third molars |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| SD | standard deviation |
| SN | static navigation |
| SUS | system usability scale |
| UI | user interface |
References
- Synan, W.; Stein, K. Management of Impacted Third Molars. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 32, 519–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McArdle, L.W.; Patel, N.; Jones, J.; McDonald, F. The mesially impacted mandibular third molar: The incidence and consequences of distal cervical caries in the mandibular second molar. Surgeon 2018, 16, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfadil, L.; Almajed, E. Prevalence of impacted third molars and the reason for extraction in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Dent. J. 2020, 32, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopra, S.; Vranckx, M.; Ockerman, A.; Östgren, P.; Krüger-Weiner, C.; Benchimol, D.; Shujaat, S.; Jacobs, R. A retrospective longitudinal assessment of artificial intelligence-assisted radiographic prediction of lower third molar eruption. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiencało, A.; Jamka-Kasprzyk, M.; Panaś, M.; Wyszyńska-Pawelec, G. Analysis of complications after the removal of 339 third molars. Dent. Med. Probl. 2021, 58, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pourmand, P.P.; Sigron, G.R.; Mache, B.; Stadlinger, B.; Locher, M.C. The most common complications after wisdom-tooth removal: Part 2: A retrospective study of 1562 cases in the maxilla. Swiss Dent. J. 2014, 124, 1042–1056. [Google Scholar]
- Rieder, M.; Remschmidt, B.; Schrempf, V.; Schwaiger, M.; Jakse, N.; Kirnbauer, B. Neurosensory Deficits of the Mandibular Nerve Following Extraction of Impacted Lower Third Molars—A Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candotto, V.; Oberti, L.; Gabrione, F.; Scarano, A.; Rossi, D.; Romano, M. Complication in third molar extractions. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2019, 33, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Damsaz, M.; Castagnoli, C.Z.; Eshghpour, M.; Alamdari, D.H.; Alamdari, A.H.; Noujeim, Z.E.F.; Haidar, Z.S. Evidence-Based Clinical Efficacy of Leukocyte and Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Maxillary Sinus Floor Lift, Graft and Surgical Augmentation Procedures. Front. Surg 2020, 7, 537138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, E.U.; Bizelli, V.F.; Pereira Baggio, A.M.; Ferriolli, S.C.; Silva Prado, G.A.; Farnezi Bassi, A.P. Do the New Protocols of Platelet-Rich Fibrin Centrifugation Allow Better Control of Postoperative Complications and Healing After Surgery of Impacted Lower Third Molar? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 80, 1238–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataineh, A.B. Sensory nerve impairment following mandibular third molar surgery. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2001, 59, 1012–1017, discussion 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzey, D.; Röttger, S.; Bahner-Heyne, J.E.; Schulze-Kissing, D.; Dietz, A.; Meixensberger, J.; Strauss, G. Image-guided navigation: The surgeon’s perspective on performance consequences and human factors issues. Int. J. Med. Robot. 2009, 5, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novelli, G.; Moretti, M.; Meazzini, M.C.; Cassé, C.M.; Mazzoleni, F.; Sozzi, D. Introduction to Surgical Navigation in Oral Surgery: A Case-Series. Oral 2023, 3, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landaeta-Quinones, C.G.; Hernandez, N.; Zarroug, N.K. Computer-Assisted Surgery: Applications in Dentistry and Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 62, 403–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Day, T.; Tang, W.; John, N. Recent Developments and Future Challenges in Medical Mixed Reality. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR), Nantes, France, 9–13 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Eckert, M.; Volmerg, J.S.; Friedrich, C.M. Augmented Reality in Medicine: Systematic and Bibliographic Review. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2019, 7, e10967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrino, G.; Mangano, C.; Mangano, R.; Ferri, A.; Taraschi, V.; Marchetti, C. Augmented reality for dental implantology: A pilot clinical report of two cases. BMC Oral Health 2019, 19, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, H.N.; Dam, V.V.; Lee, D.H. Accuracy of Augmented Reality-Assisted Navigation in Dental Implant Surgery: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2023, 25, e42040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farronato, M.; Maspero, C.; Lanteri, V.; Fama, A.; Ferrati, F.; Pettenuzzo, A.; Farronato, D. Current state of the art in the use of augmented reality in dentistry: A systematic review of the literature. BMC Oral Health 2019, 19, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joda, T.; Gallucci, G.O.; Wismeijer, D.; Zitzmann, N.U. Augmented and virtual reality in dental medicine: A systematic review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 108, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, A.; Pulijala, Y. The application of virtual reality and augmented reality in Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery. BMC Oral Health 2019, 19, 238. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Parsons, M.; Stone-McLean, J.; Rogers, P.; Boyd, S.; Hoover, K.; Meruvia-Pastor, O.; Gong, M.; Smith, A. Augmented Reality as a Telemedicine Platform for Remote Procedural Training. Sensors 2017, 17, 2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Ma, L.; Zhang, B.; Fan, Y.; Qu, X.; Zhang, X.; Liao, H. Evaluation of the 3D Augmented Reality-Guided Intraoperative Positioning of Dental Implants in Edentulous Mandibular Models. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2018, 33, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, B.; Qu, X.; Ning, G.; Zhang, X.; Liao, H. Augmented reality surgical navigation with accurate CBCT-patient registration for dental implant placement. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2019, 57, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.K.; Yang, C.H.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Wang, J.C.; Hung, C.C. Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) applied in dentistry. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2018, 34, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uruthiralingam, U.; Rea, P.M. Augmented and Virtual Reality in Anatomical Education—A Systematic Review. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1235, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gsaxner, C.; Li, J.; Pepe, A.; Jin, Y.; Kleesiek, J.; Schmalstieg, D.; Egger, J. The HoloLens in medicine: A systematic review and taxonomy. Med. Image Anal. 2023, 85, 102757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gsaxner, C.; Li, J.; Pepe, A.; Schmalstieg, D.; Egger, J. Inside-Out Instrument Tracking for Surgical Navigation in Augmented Reality. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM Symposium on Virtual Reality Software and Technology, Osaka, Japan, 8–10 December 2021; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Gsaxner, C.; Pepe, A.; Li, J.; Ibrahimpasic, U.; Wallner, J.; Schmalstieg, D.; Egger, J. Augmented Reality for Head and Neck Carcinoma Imaging: Description and Feasibility of an Instant Calibration, Markerless Approach. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 200, 105854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gsaxner, C.; Pepe, A.; Wallner, J.; Schmalstieg, D.; Egger, J. Markerless Image-to-Face Registration for Untethered Augmented Reality in Head and Neck Surgery; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 236–244. [Google Scholar]
- Song, T.; Yang, C.; Dianat, O.; Azimi, E. Endodontic guided treatment using augmented reality on a head-mounted display system. Healthc. Technol. Lett. 2018, 5, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, W. The preservation of the whole corpse with natural color. Ann. Anat. 1992, 174, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.-Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2016; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.-Y.; Park, J.; Koltun, V. Fast Global Registration. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2016; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rusinkiewicz, S.; Levoy, M. Efficient variants of the ICP algorithm. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on 3-D Digital Imaging and Modeling, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 28 May–1 June 2001; pp. 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Fedorov, A.; Beichel, R.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Finet, J.; Fillion-Robin, J.C.; Pujol, S.; Bauer, C.; Jennings, D.; Fennessy, F.; Sonka, M.; et al. 3D Slicer as an image computing platform for the Quantitative Imaging Network. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 30, 1323–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirnbauer, B.; Jakse, N.; Truschnegg, A.; Dzidic, I.; Mukaddam, K.; Payer, M. Is perioperative antibiotic prophylaxis in the case of routine surgical removal of the third molar still justified? A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial with a split-mouth design. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 6409–6421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooke, J. SUS—a quick and dirty usability scale. Usability Eval. Ind. 1996, 198, 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Bangor, A.; Kortum, P.; Miller, J. Determining What Individual SUS Scores Mean: Adding an Adjective Rating Scale. J. Usability Stud. 2009, 4, 114–123. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, E.; Kashbour, W.; Shah, N.; Worthington, H.V.; Renton, T.F.; Coulthard, P. Surgical techniques for the removal of mandibular wisdom teeth. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 7, Cd004345. [Google Scholar]
- Gargallo-Albiol, J.; Buenechea-Imaz, R.; Gay-Escoda, C. Lingual nerve protection during surgical removal of lower third molars. a prospective randomised study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2000, 29, 268–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, L.K.; Leung, Y.Y.; Chow, L.K.; Wong, M.C.; Chan, E.K.; Fok, Y.H. Incidence of neurosensory deficits and recovery after lower third molar surgery: A prospective clinical study of 4338 cases. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 39, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remschmidt, B.; Rieder, M.; Gsaxner, C.; Gaessler, J.; Payer, M.; Wallner, J. Augmented Reality-Guided Apicoectomy Based on Maxillofacial CBCT Scans. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinho, F.C.; Qadir, S.J.; Griffin, I.L.; Melo, M.A.S.; Fay, G.G. Augmented Reality Head-Mounted Device and Dynamic Navigation System for Postremoval in Maxillary Molars. J. Endod. 2024, 50, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceccariglia, F.; Cercenelli, L.; Badiali, G.; Marcelli, E.; Tarsitano, A. Application of Augmented Reality to Maxillary Resections: A Three-Dimensional Approach to Maxillofacial Oncologic Surgery. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puladi, B.; Ooms, M.; Bellgardt, M.; Cesov, M.; Lipprandt, M.; Raith, S.; Peters, F.; Möhlhenrich, S.C.; Prescher, A.; Hölzle, F.; et al. Augmented Reality-Based Surgery on the Human Cadaver Using a New Generation of Optical Head-Mounted Displays: Development and Feasibility Study. JMIR Serious Games 2022, 10, e34781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesselius, T.S.; Meulstee, J.W.; Luijten, G.; Xi, T.; Maal, T.J.J.; Ulrich, D.J.O. Holographic Augmented Reality for DIEP Flap Harvest. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2021, 147, 25e–29e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.X.; Yan, Z.Y.; Cui, N.H.; Sun, F.; Wu, B.Z. Accuracy of computer-assisted dynamic navigation when performing coronectomy of the mandibular third molar: A pilot study. J. Dent. 2023, 139, 104762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pogrel, M.A.; Lee, J.S.; Muff, D.F. Coronectomy: A technique to protect the inferior alveolar nerve. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2004, 62, 1447–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emery, R.W.; Korj, O.; Agarwal, R. A Review of In-Office Dynamic Image Navigation for Extraction of Complex Mandibular Third Molars. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 75, 1591–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrino, G.; Lizio, G.; Ferri, A.; Marchetti, C. Flapless and bone-preserving extraction of partially impacted mandibular third molars with dynamic navigation technology. A report of three cases. Int. J. Comput. Dent. 2021, 24, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kato, T.; Watanabe, T.; Nakao, K. An experience of displaced third molar roots removed using computer-assisted navigation system. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 124, 101442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bensing, J.R.; McElroy, K.E.; Perez, L., Jr. Retrieval of Displaced Third Molar Into the Sublingual Space Using 3-Dimensional Navigation Assistance. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 79, 537.e1–537.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, A.; Costello, B.J. Retrieval of a displaced third molar using navigation and active image guidance. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 68, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Liu, Y.H.; Gao, X.; Yang, C.Y.; Li, Z. Computer-assisted navigation for removal of the foreign body in the lower jaw with a mandible reference frame: A case report. Medicine 2020, 99, e18875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badr, F.F.; Jadu, F.M. Performance of artificial intelligence using oral and maxillofacial CBCT images: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2022, 25, 1918–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, K.F.; Ai, Q.Y.H.; Wong, L.M.; Yeung, A.W.K.; Li, D.T.S.; Leung, Y.Y. Current Applications of Deep Learning and Radiomics on CT and CBCT for Maxillofacial Diseases. Diagnostics 2022, 13, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahoud, P.; Diels, S.; Niclaes, L.; Van Aelst, S.; Willems, H.; Van Gerven, A.; Quirynen, M.; Jacobs, R. Development and validation of a novel artificial intelligence driven tool for accurate mandibular canal segmentation on CBCT. J. Dent. 2022, 116, 103891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abesi, F.; Hozuri, M.; Zamani, M. Performance of artificial intelligence using cone-beam computed tomography for segmentation of oral and maxillofacial structures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2023, 15, e954–e962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Case ID | Tooth Region | Preparation Time (min:s) | Operation Time (min) | Suture Time (min:s) | SUS Score (System Usability Scale) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HHCST 1 | 48 | 04:00 | 14 | 02:55 | 87.5 |
| HHCST 2 | 48 | 03:00 | 15 | 03:15 | 92.5 |
| PT 1 | 38 | 02:00 | 28 | 05:35 | 70 |
| PT 2 | 48 | 02:50 | 25 | 04:31 | 70 |
| PT 3 | 48 | 01:58 | 20 | 04:22 | 75 |
| PT 4 | 38 | 02:50 | 26 | 03:55 | 80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rieder, M.; Remschmidt, B.; Gsaxner, C.; Gaessler, J.; Payer, M.; Zemann, W.; Wallner, J. Augmented Reality-Guided Extraction of Fully Impacted Lower Third Molars Based on Maxillofacial CBCT Scans. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060625
Rieder M, Remschmidt B, Gsaxner C, Gaessler J, Payer M, Zemann W, Wallner J. Augmented Reality-Guided Extraction of Fully Impacted Lower Third Molars Based on Maxillofacial CBCT Scans. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(6):625. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060625
Chicago/Turabian StyleRieder, Marcus, Bernhard Remschmidt, Christina Gsaxner, Jan Gaessler, Michael Payer, Wolfgang Zemann, and Juergen Wallner. 2024. "Augmented Reality-Guided Extraction of Fully Impacted Lower Third Molars Based on Maxillofacial CBCT Scans" Bioengineering 11, no. 6: 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060625
APA StyleRieder, M., Remschmidt, B., Gsaxner, C., Gaessler, J., Payer, M., Zemann, W., & Wallner, J. (2024). Augmented Reality-Guided Extraction of Fully Impacted Lower Third Molars Based on Maxillofacial CBCT Scans. Bioengineering, 11(6), 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060625







