A Capillary-Force-Driven, Single-Cell Transfer Method for Studying Rare Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Tumor Cell Micromanipulation
3.2. Tapered Capillary Optimization
3.3. Determination of Equivalent Pressure Change
3.4. Analysis of Critical Membrane Tension Caused by Capillary Aspiration
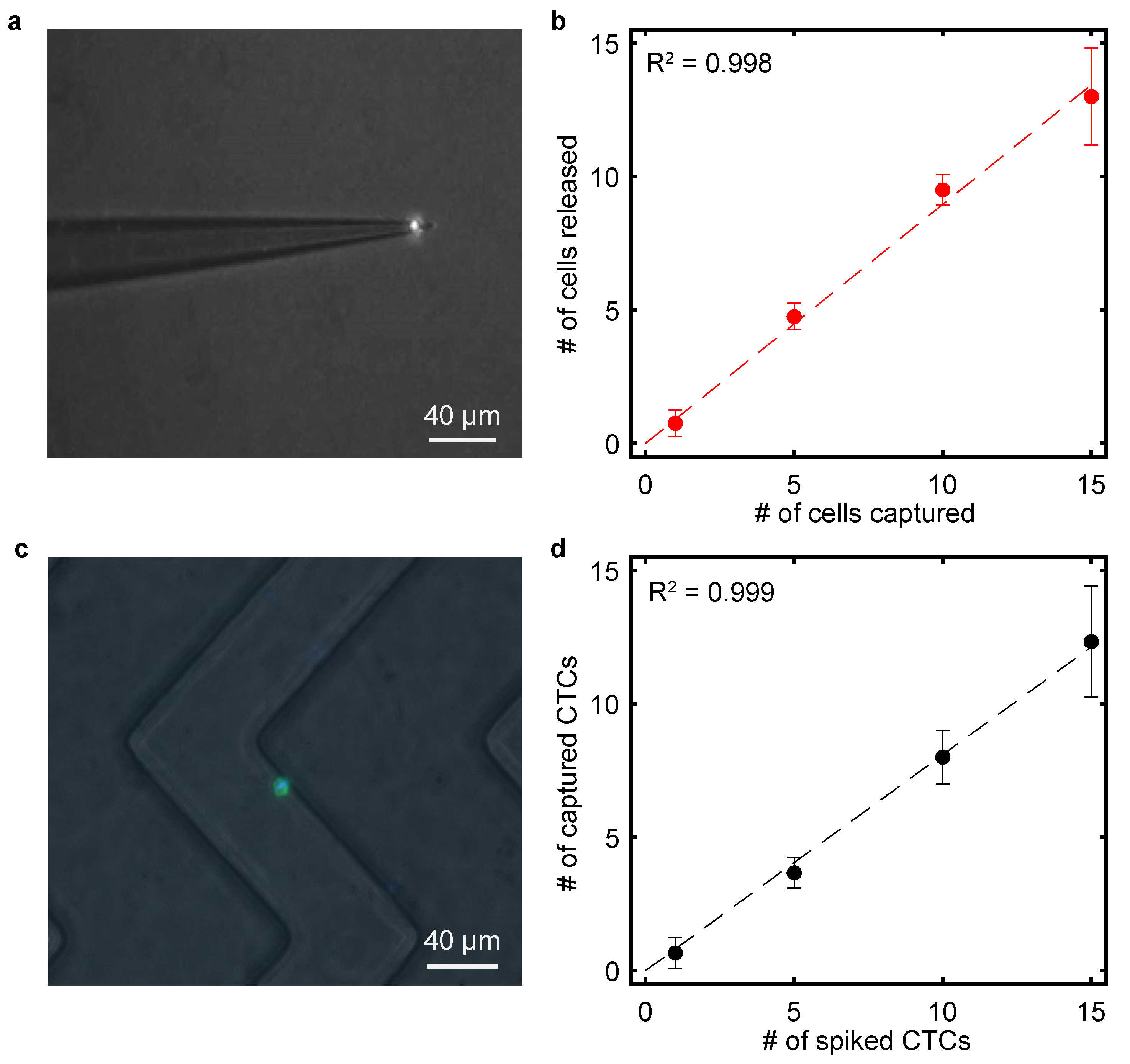
3.5. Calibration of Single-Cell Transfer
3.6. Capture of Spiked Tumor Cells in Microfluidic Devices
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heumos, L.; Schaar, A.C.; Lance, C.; Litinetskaya, A.; Drost, F.; Zappia, L.; Lücken, M.D.; Strobl, D.C.; Henao, J.; Curion, F. Best practices for single-cell analysis across modalities. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2023, 24, 550–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, E.; Carr, A.J.; Plitas, G.; Cornish, A.E.; Konopacki, C.; Prabhakaran, S.; Nainys, J.; Wu, K.; Kiseliovas, V.; Setty, M.; et al. Single-Cell Map of Diverse Immune Phenotypes in the Breast Tumor Microenvironment. Cell 2018, 174, 1293–1308.e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.L.; Mahalingam, D.; Osmulski, P.; Jadhav, R.R.; Wang, C.M.; Leach, R.J.; Chang, T.C.; Weitman, S.D.; Kumar, A.P.; Sun, L.; et al. Single-cell analysis of circulating tumor cells identifies cumulative expression patterns of EMT-related genes in metastatic prostate cancer. Prostate 2013, 73, 813–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, G.; Krishnakumar, S.; Powell, A.A.; Zhang, H.; Mindrinos, M.N.; Telli, M.L.; Davis, R.W.; Jeffrey, S.S. Single cell mutational analysis of PIK3CA in circulating tumor cells and metastases in breast cancer reveals heterogeneity, discordance, and mutation persistence in cultured disseminated tumor cells from bone marrow. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitzer, E.; Auer, M.; Gasch, C.; Pichler, M.; Ulz, P.; Hoffmann, E.M.; Lax, S.; Waldispuehl-Geigl, J.; Mauermann, O.; Lackner, C.; et al. Complex tumor genomes inferred from single circulating tumor cells by array-CGH and next-generation sequencing. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 2965–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Packer, J.S.; Ramani, V.; Cusanovich, D.A.; Huynh, C.; Daza, R.; Qiu, X.; Lee, C.; Furlan, S.N.; Steemers, F.J.; et al. Comprehensive single-cell transcriptional profiling of a multicellular organism. Science 2017, 357, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benham-Pyle, B.W.; Brewster, C.E.; Kent, A.M.; Mann, F.G., Jr.; Chen, S.; Scott, A.R.; Box, A.C.; Sánchez Alvarado, A. Identification of rare, transient post-mitotic cell states that are induced by injury and required for whole-body regeneration in Schmidtea mediterranea. Nat. Cell Biol. 2021, 23, 939–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Chen, K.; Xia, F.; Atwal, R.; Wang, H.; Ahmed, S.U.; Cardarelli, L.; Lui, I.; Duong, B.; Wang, Z.; et al. Phage-Based Profiling of Rare Single Cells Using Nanoparticle-Directed Capture. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 19202–19210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broersen, L.H.A.; van Pelt, G.W.; Tollenaar, R.A.E.M.; Mesker, W.E. Clinical application of circulating tumor cells in breast cancer. Cell. Oncol. 2014, 37, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xun, Z.; Ma, K.; Liang, S.; Li, X.; Zhou, S.; Sun, L.; Liu, Y.; Du, Y.; Guo, X.; et al. Identification of a tumour immune barrier in the HCC microenvironment that determines the efficacy of immunotherapy. J. Hepatol. 2023, 78, 770–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Wang, C.; Xie, M.; Zhu, C.; Shu, Y.; Tang, J.; Guan, X. Heterogeneity of CTC contributes to the organotropism of breast cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, W.; Chen, T.; Tan, W.; Fan, Z.H. Multivalent DNA nanospheres for enhanced capture of cancer cells in microfluidic devices. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 7067–7076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, J.M.; Casavant, B.P.; Beebe, D.J. Circulating Tumor Cells: Getting More from Less. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 141ps13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stott, S.L.; Hsu, C.-H.; Tsukrov, D.I.; Yu, M.; Miyamoto, D.T.; Waltman, B.A.; Rothenberg, S.M.; Shah, A.M.; Smas, M.E.; Korir, G.K.; et al. Isolation of circulating tumor cells using a microvortex-generating herringbone-chip. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18392–18397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagrath, S.; Sequist, L.V.; Maheswaran, S.; Bell, D.W.; Irimia, D.; Ulkus, L.; Smith, M.R.; Kwak, E.L.; Digumarthy, S.; Muzikansky, A.; et al. Isolation of rare circulating tumour cells in cancer patients by microchip technology. Nature 2007, 450, 1235–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Dopico, P.; Varillas, J.; Zhang, J.; George, T.J.; Fan, Z.H. Integration of Lateral Filter Arrays with Immunoaffinity for Circulating-Tumor-Cell Isolation. Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 7688–7692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa, V.A.; Chen, K.; George, T.J.; Fan, Z.H. Gold Nanoparticle-Based Microfluidic Chips for Capture and Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells. Biosensors 2023, 13, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Carlo, D. Inertial microfluidics. Lab. A Chip 2009, 9, 3038–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, S.C.; Henderson-MacLennan, N.K.; McCabe, E.R.; Di Carlo, D. Deformability-based cell classification and enrichment using inertial microfluidics. Lab. A Chip 2011, 11, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Mao, Z.; Peng, Z.; Zhou, L.; Chen, Y.; Huang, P.-H.; Truica, C.I.; Drabick, J.J.; El-Deiry, W.S.; Dao, M.; et al. Acoustic separation of circulating tumor cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 4970–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkumur, E.; Shah, A.M.; Ciciliano, J.C.; Emmink, B.L.; Miyamoto, D.T.; Brachtel, E.; Yu, M.; Chen, P.-i.; Morgan, B.; Trautwein, J. Inertial focusing for tumor antigen–dependent and–independent sorting of rare circulating tumor cells. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, ra147–ra179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudineh, M.; Aldridge, P.M.; Ahmed, S.; Green, B.J.; Kermanshah, L.; Nguyen, V.; Tu, C.; Mohamadi, R.M.; Nam, R.K.; Hansen, A. Tracking the dynamics of circulating tumour cell phenotypes using nanoparticle-mediated magnetic ranking. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labib, M.; Wang, Z.; Ahmed, S.U.; Mohamadi, R.M.; Duong, B.; Green, B.; Sargent, E.H.; Kelley, S.O. Tracking the expression of therapeutic protein targets in rare cells by antibody-mediated nanoparticle labelling and magnetic sorting. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Gagliardi, M.; Mohamadi, R.M.; Ahmed, S.U.; Labib, M.; Zhang, L.; Popescu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Sargent, E.H.; Keller, G.M. Ultrasensitive and rapid quantification of rare tumorigenic stem cells in hPSC-derived cardiomyocyte populations. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay7629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ahmed, S.; Labib, M.; Wang, H.; Hu, X.; Wei, J.; Yao, Y.; Moffat, J.; Sargent, E.H.; Kelley, S.O. Efficient recovery of potent tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes through quantitative immunomagnetic cell sorting. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 6, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Ahmed, S.; Labib, M.; Wang, H.; Wu, L.; Bavaghar-Zaeimi, F.; Shokri, N.; Blanco, S.; Karim, S.; Czarnecka-Kujawa, K.; et al. Isolation of tumour-reactive lymphocytes from peripheral blood via microfluidic immunomagnetic cell sorting. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 7, 1188–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Wang, Z.; Flynn, C.D.; Mahmud, A.; Labib, M.; Wang, H.; Geraili, A.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Sargent, E.H.; et al. A high-dimensional microfluidic approach for selection of aptamers with programmable binding affinities. Nat. Chem. 2023, 15, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Xu, S.; Wang, J.; Paguirigan, A.L.; Radich, J.P.; Qin, Y.; Chiu, D.T. Capillary-Mediated Single-Cell Dispenser. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 10750–10755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krylov, S.N.; Starke, D.A.; Arriaga, E.A.; Zhang, Z.; Chan, N.W.; Palcic, M.M.; Dovichi, N.J. Instrumentation for chemical cytometry. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumann, R.; Stobrawa, S.; Eppendorf, A. Precise and Oil-Free Transfer of ES Cells into Early Embryos with CellTram® 4r Air. Application note No. 394, Eppendorf AG, Hamburg, Germany.
- Hannart, H.; Berger, A.; Aeberli, L.; Forchelet, D.; Uffer, N.; Muller, G.; Barrandon, Y.; Renaud, P.; Bonzon, D. Traceable impedance-based single-cell pipetting, from a research set-up to a robust and fast automated robot: DispenCell-S1. SLAS Technol. 2022, 27, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallone, V.F.; Ludwik, K.; Stachelscheid, H.; Izaguirre, F.; Beurton, F.; Jo, M. cellenONE® as automated single cell seeding platform for hiPSC subcloning. Application note, Cellenion a BICO Company, Lyon, France.
- Kind, D.; Baskaran, P.; Ramirez, F.; Giner, M.; Hayes, M.; Santacruz, D.; Koss, C.K.; El Kasmi, K.C.; Wijayawardena, B.; Viollet, C. Automation enables high-throughput and reproducible single-cell transcriptomics library preparation. SLAS Technol. 2022, 27, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallejo, D.; Nikoomanzar, A.; Paegel, B.M.; Chaput, J.C. Fluorescence-Activated Droplet Sorting for Single-Cell Directed Evolution. ACS Synth. Biol. 2019, 8, 1430–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Yu, Z.B.; Wu, M.; Lan, Y.W.; Jia, C.P.; Zhao, J.L. Single-cell sorting using integrated pneumatic valve droplet microfluidic chip. Talanta 2023, 253, 124044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xue, J.; Luo, N.; Chen, F.; Chen, B.; Zhao, Y. Microwell array chip-based single-cell analysis. Lab. A Chip 2023, 23, 1066–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Shao, N.; Bessa de Castro, R.; Zhang, P.; Ma, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, F.; Wang, R.F.; Qin, L. Evaluation of Single-Cell Cytokine Secretion and Cell-Cell Interactions with a Hierarchical Loading Microwell Chip. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustamante, C.J.; Chemla, Y.R.; Liu, S.X.; Wang, M.D. Optical tweezers in single-molecule biophysics. Nat. Rev. Method. Prime 2021, 1, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R.; Avsievich, T.; Popov, A.; Meglinski, I. Optical Tweezers in Studies of Red Blood Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, L.; Ellett, F.; Edd, J.; Wong, K.H.K.; Uygun, K.; Irimia, D.; Stott, S.L.; Toner, M. A highly-occupied, single-cell trapping microarray for determination of cell membrane permeability. Lab. A Chip 2017, 17, 4077–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, W.; Chen, T.; Kamath, R.; Xiong, X.; Tan, W.; Fan, Z.H. Aptamer-Enabled Efficient Isolation of Cancer Cells from Whole Blood Using a Microfluidic Device. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 4199–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkins, W.D.; Brown, F. The determination of surface tension (free surface energy), and the weight of falling drops: The surface tension of water and benzene by the capillary height method. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1919, 41, 499–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, L.; Schmid-Schonbein, G.W. Biomechanical interactions of cancer cells with the microvasculature during metastasis. Cell Biophys. 1989, 14, 187–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbore, C.; Perego, L.; Sergides, M.; Capitanio, M. Probing force in living cells with optical tweezers: From single-molecule mechanics to cell mechanotransduction. Biophys. Rev. 2019, 11, 765–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Project Components | Eppendorf | Olympus | Our Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manipulator accuracy | <20 nm | 40 nm | 150 nm |
| Assembly components | 17 | 19 | 7 |
| Price estimate | USD 18,700 | USD 18,920 | USD 865 |
| Consumables (i.e., capillaries) | USD 595 | USD 400 | USD 40 |
| Total price (USD) | USD 19,265 | USD 19,320 | USD 905 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amontree, J.; Chen, K.; Varillas, J.; Fan, Z.H. A Capillary-Force-Driven, Single-Cell Transfer Method for Studying Rare Cells. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060542
Amontree J, Chen K, Varillas J, Fan ZH. A Capillary-Force-Driven, Single-Cell Transfer Method for Studying Rare Cells. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(6):542. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060542
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmontree, Jacob, Kangfu Chen, Jose Varillas, and Z. Hugh Fan. 2024. "A Capillary-Force-Driven, Single-Cell Transfer Method for Studying Rare Cells" Bioengineering 11, no. 6: 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060542
APA StyleAmontree, J., Chen, K., Varillas, J., & Fan, Z. H. (2024). A Capillary-Force-Driven, Single-Cell Transfer Method for Studying Rare Cells. Bioengineering, 11(6), 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060542








