A Novel Approach for the Detection and Severity Grading of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Based on Transformed Volumetric Capnography
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- A novel quantitative analysis method was proposed, transforming volumetric capnography into two-dimensional grayscale images using the Gramian Angular Field (GAF) transformation.
- (2)
- CapnoNet, a multi-scale convolutional neural network, was developed to classify and grade the severity of COPD from the transformed capnograms.
- (3)
- Data augmentation techniques, including the incorporation of Gaussian noise and elastic transformation, were employed to enhance the model’s robustness and generalizability across diverse clinical scenarios.
- (4)
- The proposed approach demonstrated a diagnostic accuracy of 95.83% in detecting COPD and an accuracy of 96.36% in grading the severity of the disease.
2. Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition
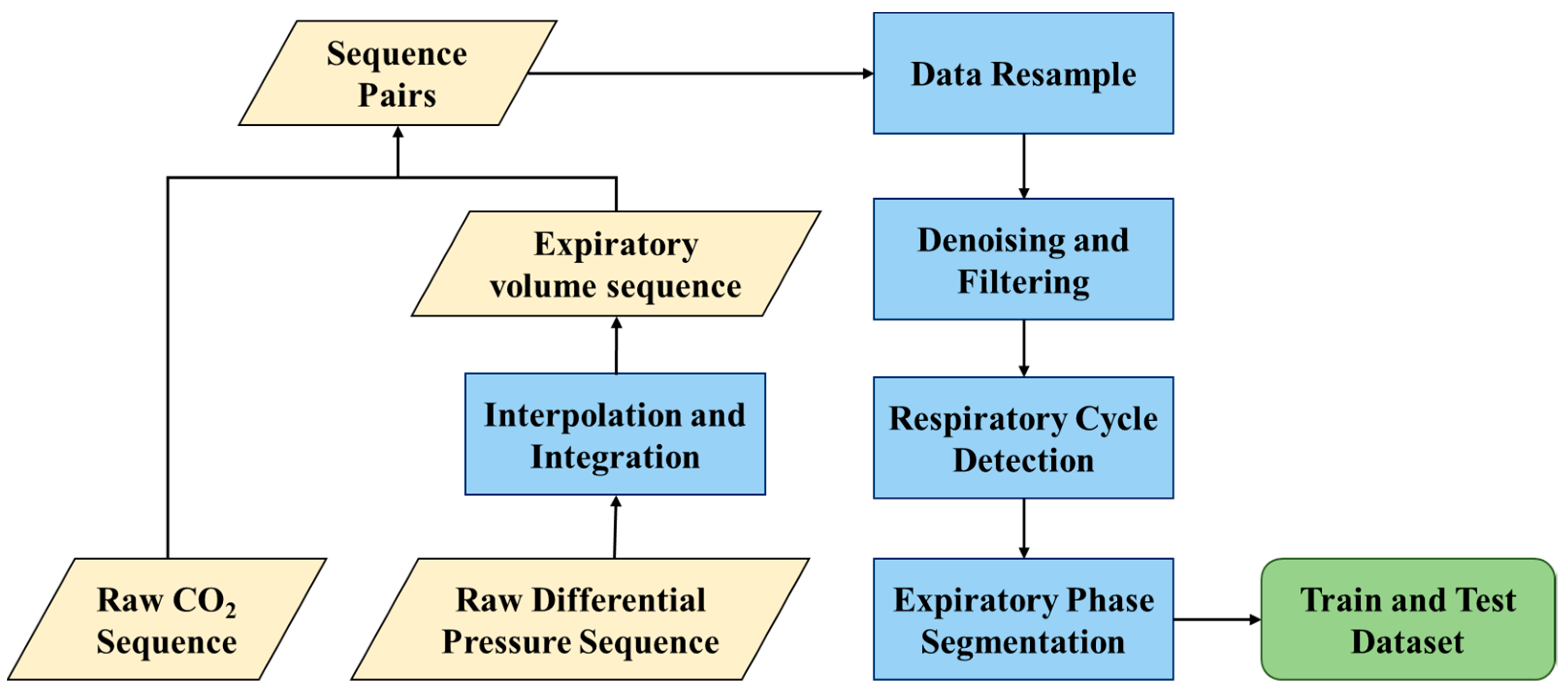
2.2. Data Preprocessing
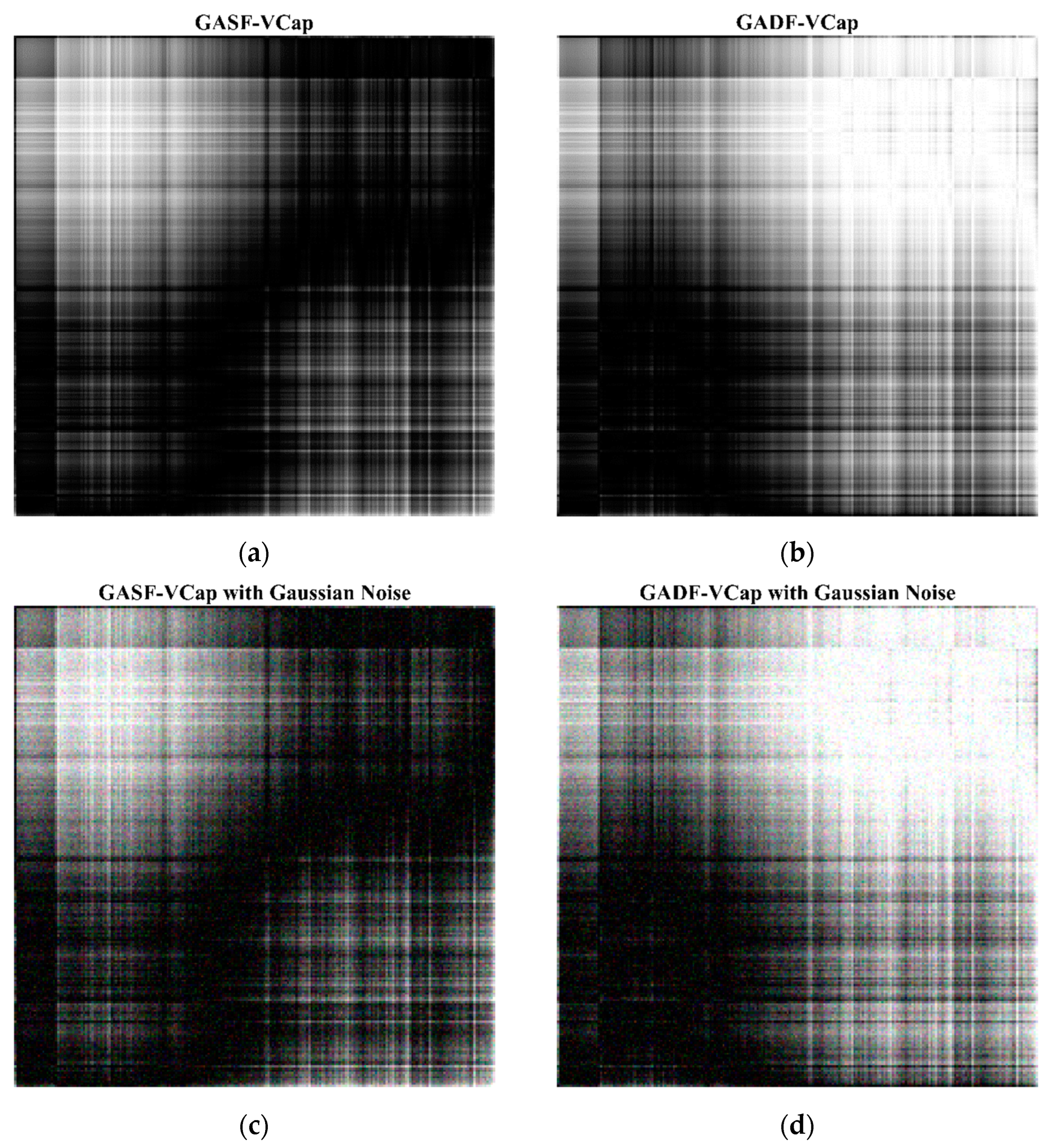
2.3. Gramian Angular Visualization of Volumetric Capnography
2.4. Data Augmentation Strategy
2.5. Neural Network Architecture
2.6. Evaluation Metric
3. Results
3.1. Subjects
3.2. Experimental Environment
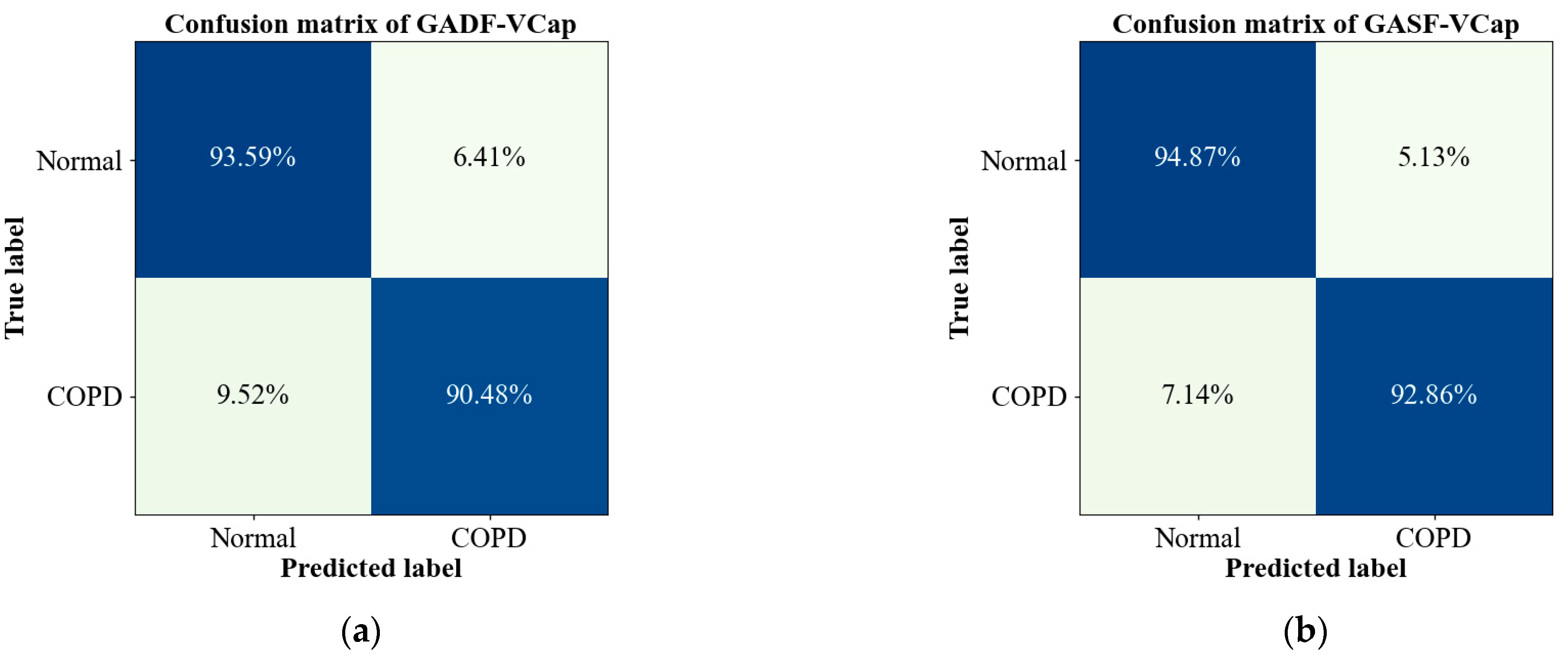
3.3. Evaluation of the Proposed Model on COPD Detection
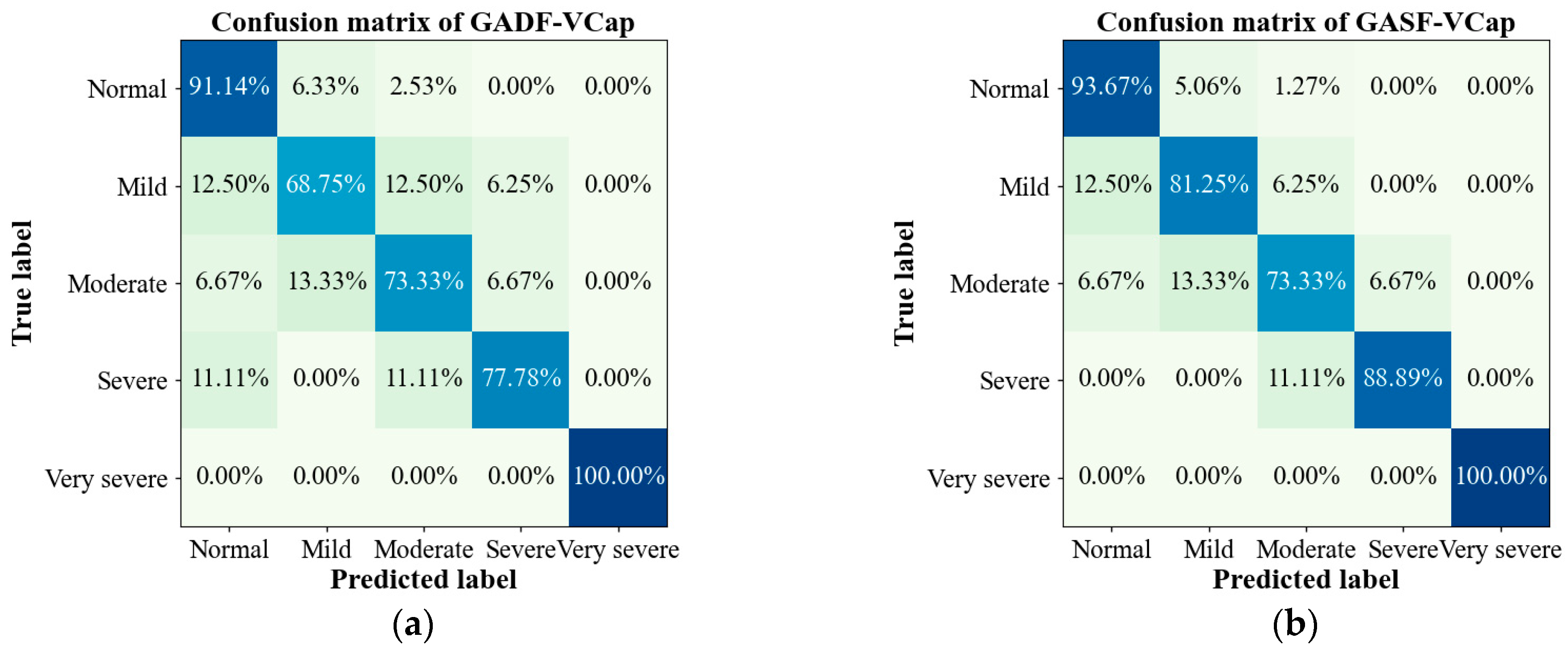
3.4. Evaluation of the Proposed Model on COPD Grading
3.5. Evaluation of Data Augmentation Strategies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robinson, T.; Scullion, J. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). In Oxford Handbook of Respiratory Nursing, 2nd ed.; Robinson, T., Scullion, J., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2021; pp. 235–284. [Google Scholar]
- Hillas, G.; Perlikos, F.; Tzanakis, N. Acute exacerbation of COPD: Is it the “stroke of the lungs”. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2016, 11, 1579–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safiri, S.; Carson-Chahhoud, K.; Noori, M.; Nejadghaderi, S.A.; Sullman, M.J.; Heris, J.A.; Ansarin, K.; Mansournia, M.A.; Collins, G.S.; Kolahi, A.A.; et al. Burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and its attributable risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. BMJ 2022, 378, e069679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirenga, B.J.; Alupo, P.; Van Gemert, F.; Jones, R. Implication of the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease 2023 report for resource-limited settings: Tracing the G in the GOLD. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 61, 2300484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desmond, K.J.; Allen, P.D.; Demizio, D.L.; Kovesi, T.; Coates, A.L. Redefining end of test (EOT) criteria for pulmonary function testing in children. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 156, 542–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremeier, P.; Böhm, S.H.; Tusman, G. Clinical use of volumetric capnography in mechanically ventilated patients. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2020, 34, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parazzi, P.; Marson, F.; Ribeiro, M.; Schivinski, C.; Ribeiro, J. Correlation between parameters of volumetric capnography and spirometry during a submaximal exercise protocol on a treadmill in patients with cystic fibrosis and healthy controls. Pulmonology 2019, 25, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellerer, C.; Schneider, A.; Klütsch, K.; Husemann, K.; Sorichter, S.; Jörres, R.A. Correspondence between capnovolumetric and conventional lung function parameters in the diagnosis of obstructive airway diseases. Respiration 2020, 99, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, Q.; Ji, Y.; Li, C. The relationship between volumetric capnography and the severity of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Chin. J. Geriatr. 2017, 36, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertzov, B.; Ronen, M.; Rosengarten, D.; Shitenberg, D.; Heching, M.; Shostak, Y.; Kramer, M.R. Use of capnography for prediction of obstruction severity in non-intubated COPD and asthma patients. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talker, L.; Neville, D.; Wiffen, L.; Selim, A.B.; Haines, M.; Carter, J.C.; Broomfield, H.; Lim, R.H.; Lambert, G.; Weiss, S.T.; et al. Machine diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease using a novel fast-response capnometer. Respir. Res. 2024, 24, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Ichikawa, T.; Wakabayashi, Y.; Abe, H. Technology Applications of Capnography Waveform Analytics for Evaluation of Heart Failure Severity. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2020, 13, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talker, L.; Dogan, C.; Neville, D.; Lim, R.H.; Broomfield, H.; Lambert, G.; Selim, A.; Brown, T.; Wiffen, L.; Carter, J.; et al. Diagnosis and Severity Assessment of COPD Using a Novel Fast-Response Capnometer and Interpretable Machine Learning. COPD J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2024, 21, 2321379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffe, M.B. Using the features of the time and volumetric capnogram for classification and prediction. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2017, 31, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mieloszyk, R.J.; Verghese, G.C.; Deitch, K.; Cooney, B.; Khalid, A.; Mirre-Gonzalez, M.A.; Heldt, T.; Krauss, B.S. Automated quantitative analysis of capnogram shape for COPD–normal and COPD–CHF classification. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 2882–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abubaker, M.B.; Babayiğit, B. Detection of cardiovascular diseases in ECG images using Machine learning and deep learning methods. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2022, 4, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee, K.; Khosravi, M.R.; Jabari, M.; Hesari, S.; Anari, M.S.; Aghaei, F. Graph convolutional network-based deep feature learning for cardiovascular disease recognition from heart sound signals. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2022, 37, 11250–11274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sushma, V.R.S.; Nikhil, K.; Reddy, K.A.; Sunitha, L. Diagnosis of cardiovascular disease using deep learning. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2023, 11, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagawati, M.; Paul, S.; Agarwal, S.; Protogeron, A.; Sfikakis, P.P.; Kitas, G.D.; Khanna, N.N.; Ruzsa, Z.; Sharma, A.M.; Tomazu, O.; et al. Cardiovascular disease/stroke risk stratification in deep learning framework: A review. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2023, 13, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, A.B.; Schlosser, C.; Grewal, J.; Coope, R.; Jones, S.J.; Yip, S. Rise of the machines: Advances in deep learning for cancer diagnosis. Trends Cancer 2019, 5, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Hu, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y. Deep learning for medical image-based cancer diagnosis. Cancers 2023, 15, 3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.U.; Shafique, A.; Ghadi, Y.Y.; Boulila, W.; Jan, S.U.; Gadekallu, T.R.; Driss, M.; Ahmad, J. A novel chaos-based privacy-preserving deep learning model for cancer diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Network Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 4322–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Mou, X.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, X.; Du, L.; Yang, T.; Zhan, Q.; Fang, Z. Prediction of pulmonary function parameters based on a combination algorithm. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Tim, O. Encoding time series as images for visual inspection and classification using tiled convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the Workshops at the Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Austin, TX, USA, 25–30 January 2015. [Google Scholar]




| Grade | Severity | Airflow Obstruction |
|---|---|---|
| GOLD1 | Mild | FEV1 ≥ 80% predicted |
| GOLD2 | Moderate | 50% ≤ FEV1 < 80% predicted |
| GOLD3 | Severe | 30% ≤ FEV1 < 50% predicted |
| GOLD4 | Very Severe | FEV1 < 30% predicted |
| Total (n = 1007) | Normal (n = 279) | COPD (n = 148) | GOLD 1 (n = 58) | GOLD 2 (n = 51) | GOLD 3 (n = 34) | GOLD 4 (n = 5) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male, n | 535 | 132 | 102 | 40 | 35 | 22 | 5 |
| Female, n | 472 | 147 | 46 | 18 | 16 | 12 | 0 |
| Age, mean ± SD | 48 ± 38 | 51 ± 13 | 58 ± 10 | 58 ± 11 | 61 ± 10 | 56 ± 11 | 61 ± 10 |
| Height, cm, mean ± SD | 165.45 ± 8.58 | 166.00 ± 8.12 | 166.27 ± 9.20 | 168.24 ± 10.73 | 166.10 ± 7.84 | 162.71 ± 7.86 | 168.50 ± 5.01 |
| Weight, kg, mean ± SD | 68.58 ± 14.00 | 70.92 ± 16.60 | 68.71 ± 12.32 | 73.05 ± 12.21 | 68.02 ± 10.76 | 64.29 ± 12.63 | 56.83 ± 7.36 |
| FEV1, L | 2.52 ± 0.86 | 3.11 ± 0.67 | 1.85 ± 0.87 | 2.61 ± 0.75 | 1.67 ± 0.41 | 1.00 ± 0.26 | 3.65 ± 0.17 |
| FVC, L | 3.48 ± 1.00 | 3.85 ± 0.85 | 3.33 ± 1.16 | 4.16 ± 1.17 | 3.02 ± 0.80 | 2.55 ± 0.68 | 2.35 ± 0.34 |
| FEV1/FVC, % | 71.91 ± 12.70 | 81.05 ± 4.40 | 53.98 ± 12.18 | 62.86 ± 5.37 | 56.00 ± 7.12 | 40.26 ± 8.27 | 27.36 ± 4.95 |
| Model Input | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GADF-VCap | 0.9333 | 0.9234 | 0.9322 | 0.9275 |
| GASF-VCap | 0.9583 | 0.9521 | 0.9570 | 0.9545 |
| Model Input | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GADF-VCap | 0.9471 | 0.8375 | 0.8567 | 0.8459 |
| GASF-VCap | 0.9636 | 0.8849 | 0.8999 | 0.8915 |
| Task | DA | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COPD Detection | no | 0.9417 | 0.9340 | 0.9386 | 0.9362 |
| yes | 0.9583 | 0.9521 | 0.9570 | 0.9545 | |
| COPD Grading | no | 0.9570 | 0.8640 | 0.8743 | 0.8678 |
| yes | 0.9636 | 0.8849 | 0.8999 | 0.8915 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mou, X.; Wang, P.; Sun, J.; Chen, X.; Du, L.; Zhan, Q.; Xia, J.; Yang, T.; Fang, Z. A Novel Approach for the Detection and Severity Grading of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Based on Transformed Volumetric Capnography. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060530
Mou X, Wang P, Sun J, Chen X, Du L, Zhan Q, Xia J, Yang T, Fang Z. A Novel Approach for the Detection and Severity Grading of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Based on Transformed Volumetric Capnography. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(6):530. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060530
Chicago/Turabian StyleMou, Xiuying, Peng Wang, Jie Sun, Xianxiang Chen, Lidong Du, Qingyuan Zhan, Jingen Xia, Ting Yang, and Zhen Fang. 2024. "A Novel Approach for the Detection and Severity Grading of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Based on Transformed Volumetric Capnography" Bioengineering 11, no. 6: 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060530
APA StyleMou, X., Wang, P., Sun, J., Chen, X., Du, L., Zhan, Q., Xia, J., Yang, T., & Fang, Z. (2024). A Novel Approach for the Detection and Severity Grading of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Based on Transformed Volumetric Capnography. Bioengineering, 11(6), 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11060530







