Synergistic Antibacterial Properties of Silver Nanoparticles and Its Reducing Agent from Cinnamon Bark Extract
Abstract
1. Introduction
 + 2 Ag+ +2 OH−- →
+ 2 Ag+ +2 OH−- → 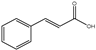 + 2 Ag0 + 2 H2O
+ 2 Ag0 + 2 H2O
2. Materials and Methods
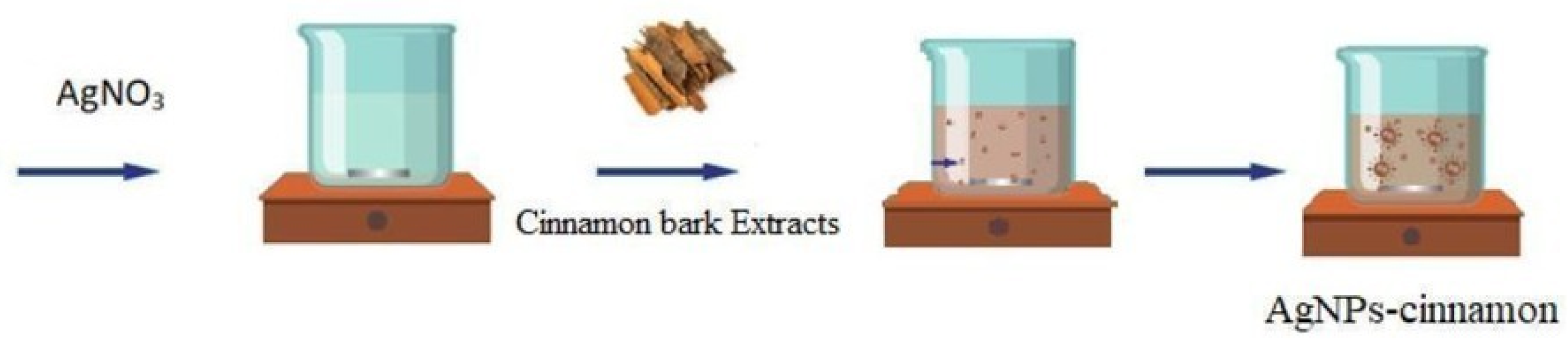
2.1. Preparation of Silver Nanoparticles from Cinnamon Bark Extract (AgNPs-Cinnamon)
2.2. Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs-Cinnamon)
2.3. Bactericidal Activity Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phytochemical Tests of Cinnamon Extract Cinnamon
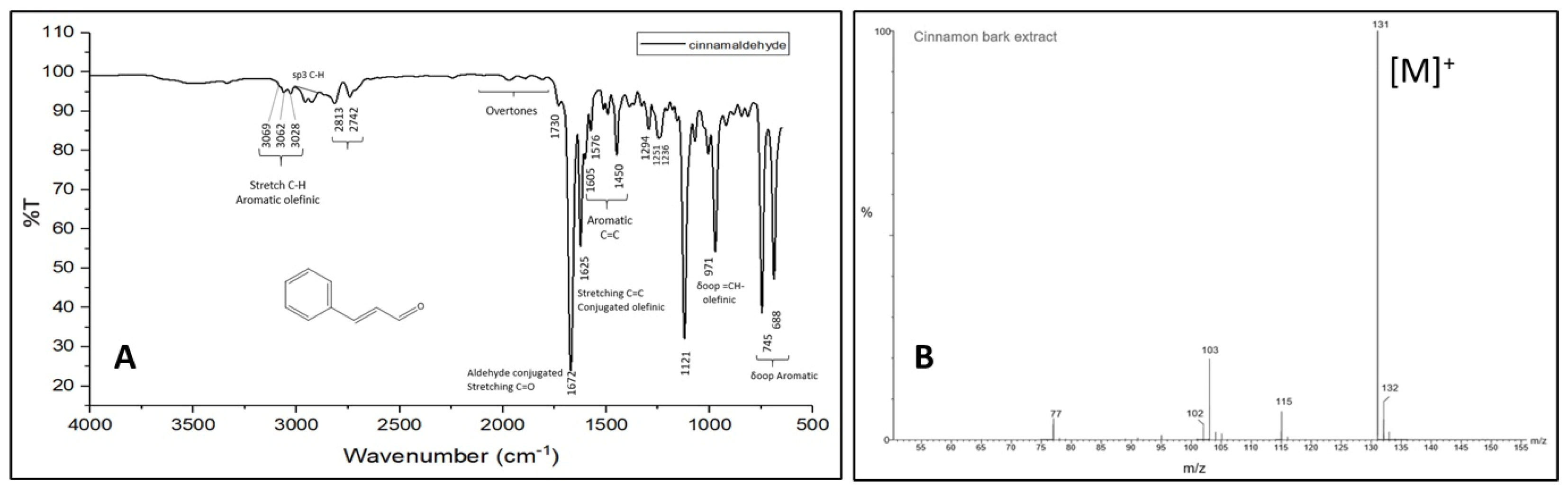
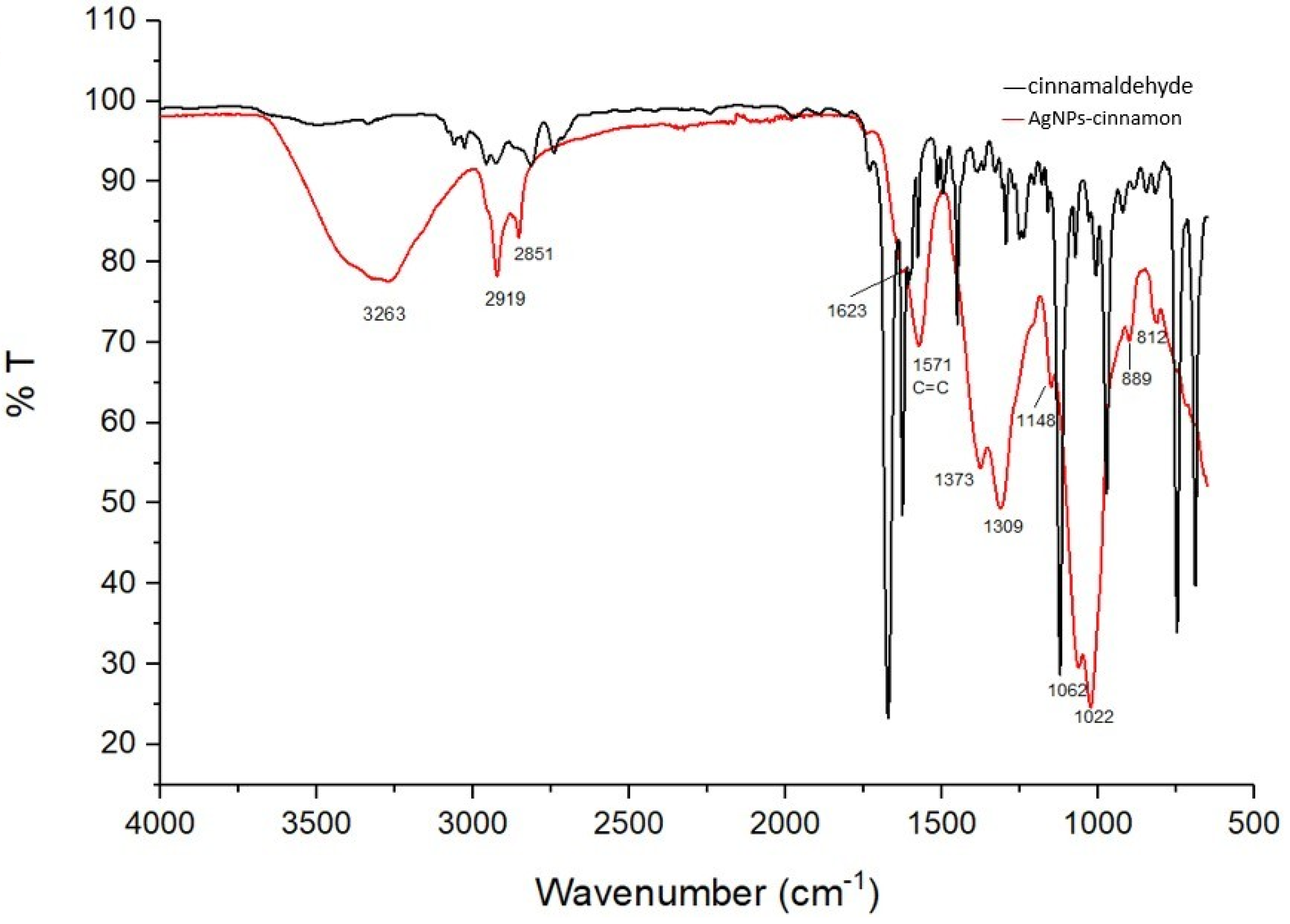
3.2. FTIR and GC-MS Characterization of Cinnamon Extract and AgNPs-Cinnamon
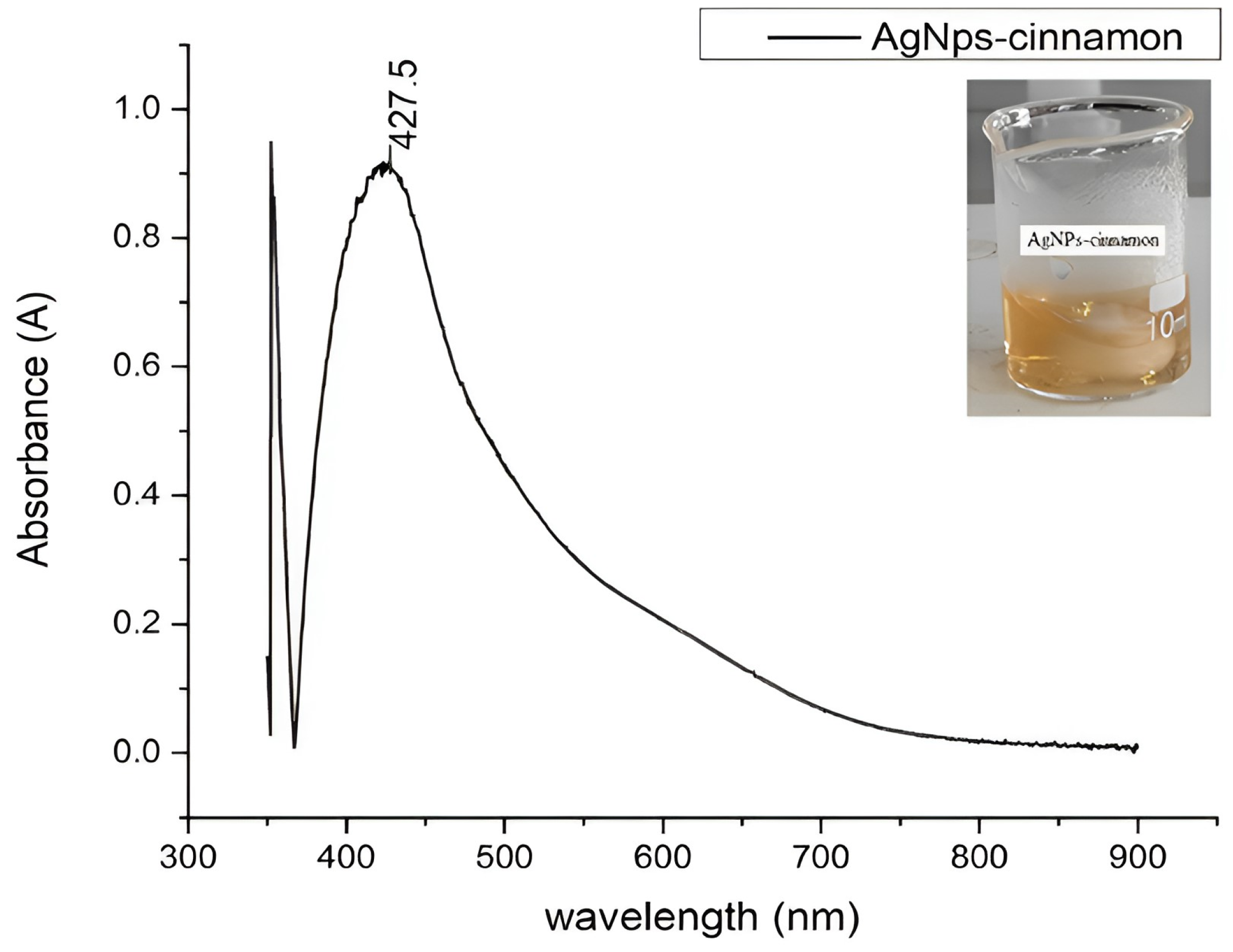
3.3. Surface Plasmon Resonance Analysis by UV-Vis Spectroscopy
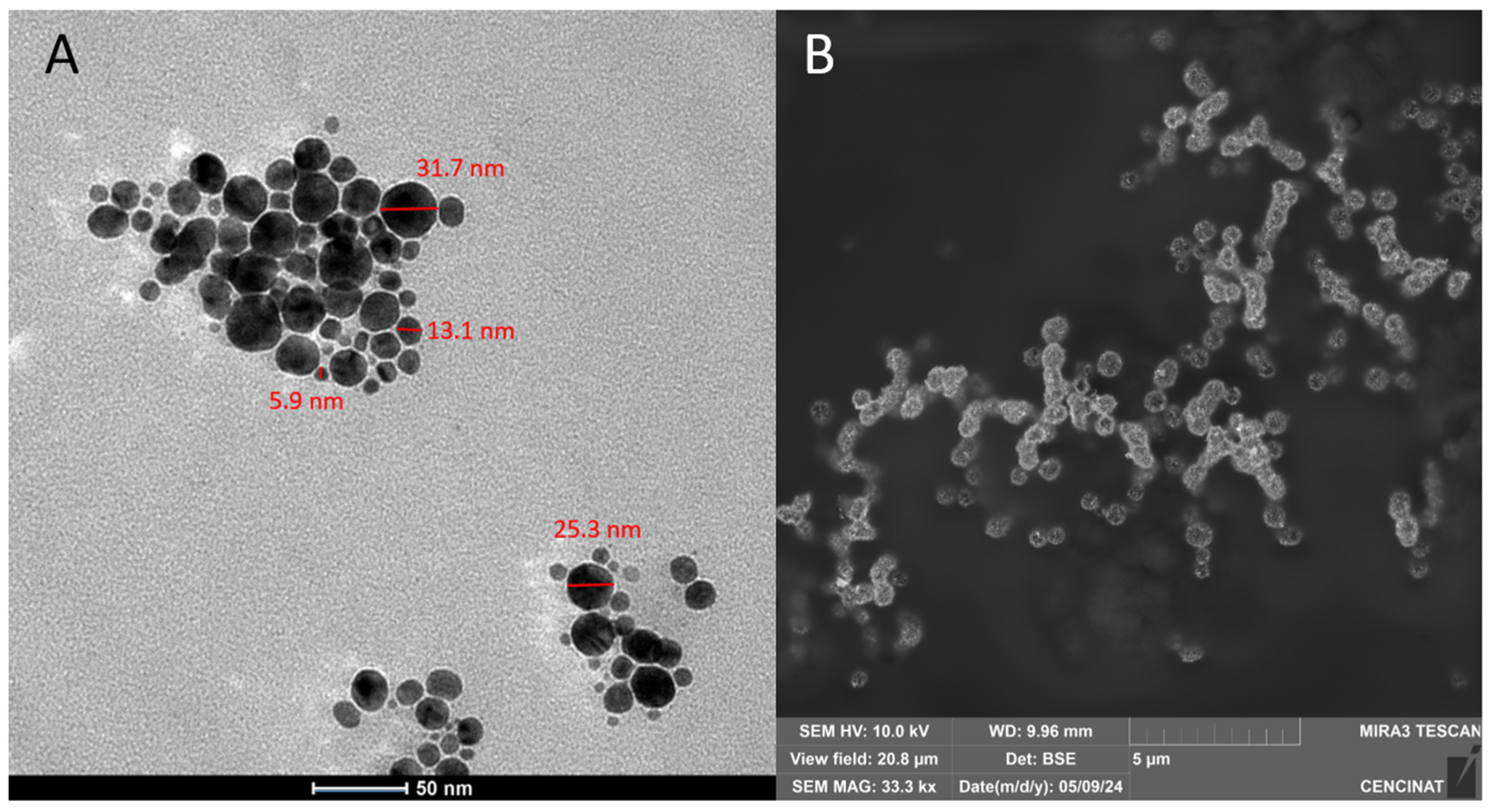
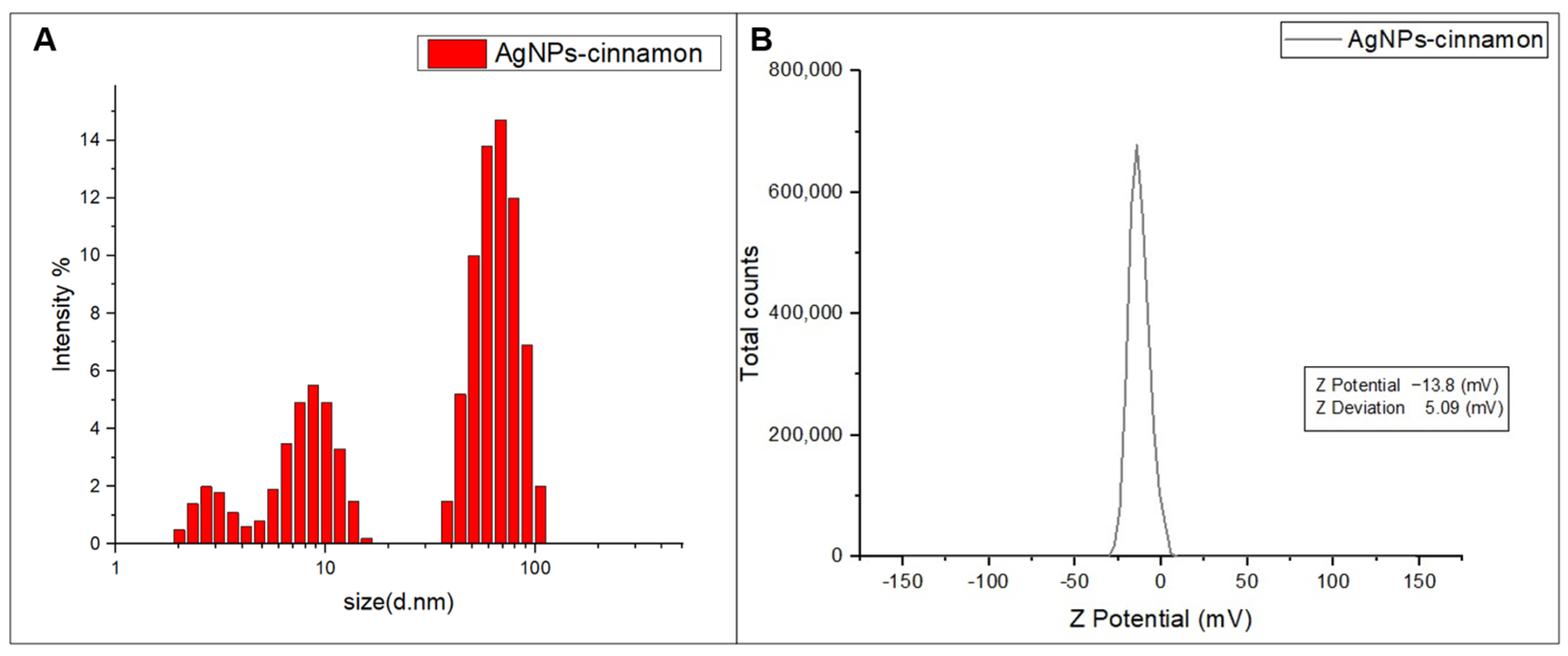
3.4. Morphological Analysis
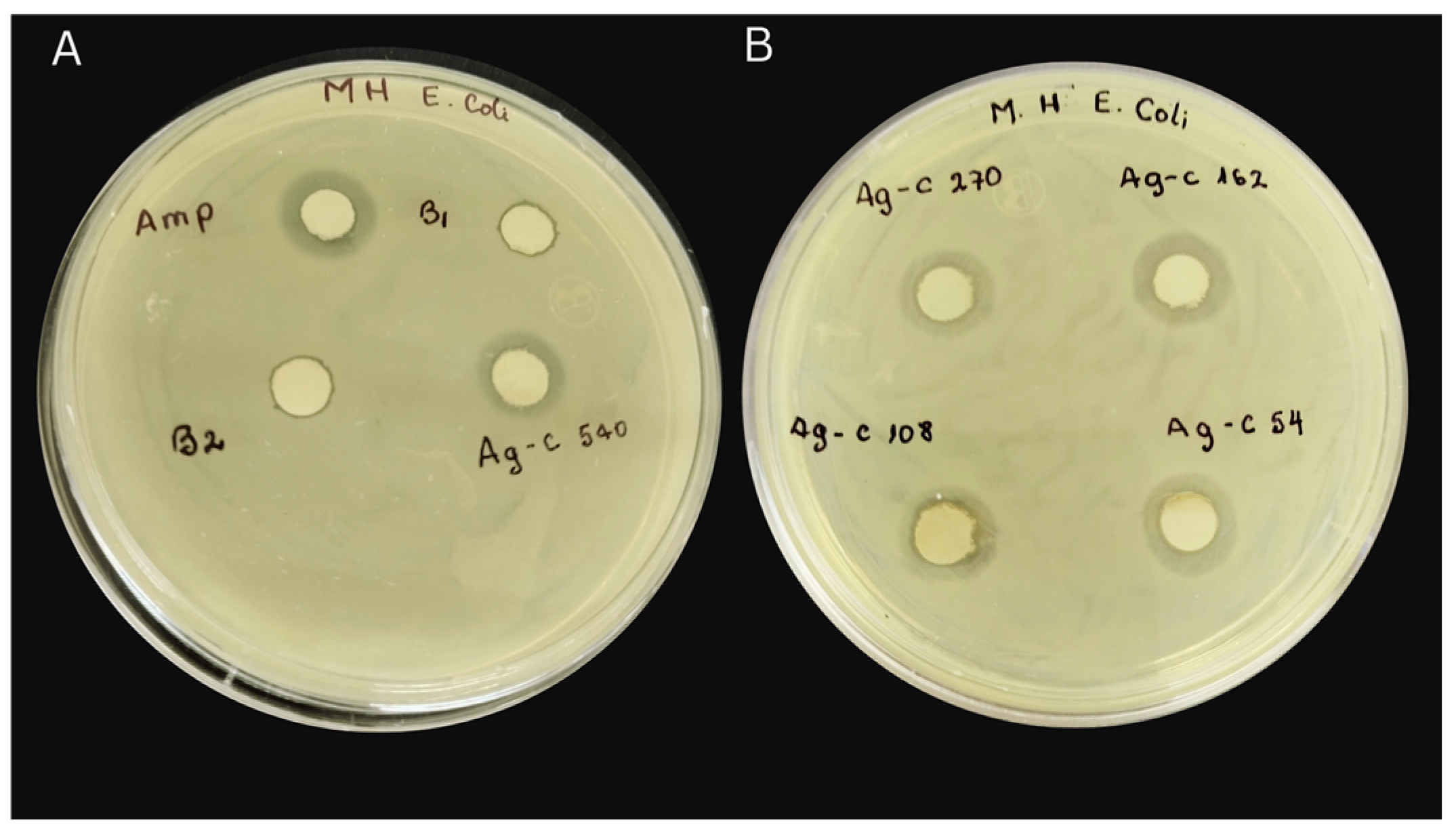
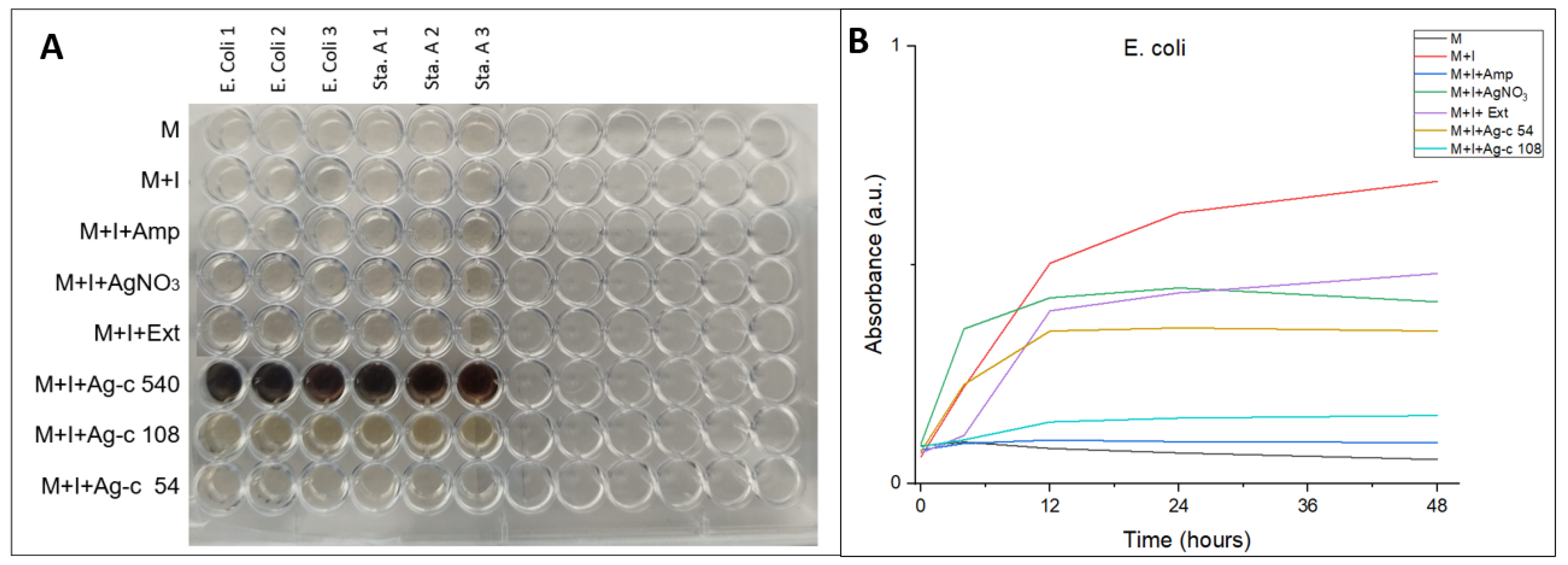
3.5. Evaluation of Antibacterial Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mansoori, G.A.; Brandenburg, K.S. A Comparative Study of Two Folate-Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles for Cancer Nanotechnology Applications. Cancers 2010, 2, 1911–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, R.O. Silver ions in the treatment of local infections. Met. Based Drugs 1999, 6, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- More, P.R.; Pandt, S.; Filippis, A.; Franci, G.; Mijakovic, I.; Galdiero, M. Silver Nanoparticles: Bactericidal and Mechanistic Approach against Drug Resistant Pathogens. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, A.K.; Jena, B.; Biswal, B.; Pradhan, A.K.; Arakha, M.; Acharya, S.; Acharya, L. Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Eugenia roxburghii DC. extract and activity against biofilm-producing bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8383. [Google Scholar]
- Yaqoob, A.A.; Umar, K.; Ibrahim, M.N.M. Silver nanoparticles: Various methods of synthesis, size affecting factors and their potential applications—A review. Appl. Nanosci. 2020, 10, 1369–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putta, S.; Sharma, R.K.; Khandelwal, P. Metal Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Biomedical Applications. In Nanomaterials Advanced and Applications; Singh, D., Singh, S., Singh, P., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2013; pp. 85–102. [Google Scholar]
- Tavker, N.; Gaur, U.; Sharma, M. Agro-waste extracted cellulose supported silver phosphate nanostructures as a green photocatalyst for improved photodegradation of RhB dye and industrial fertilizer effluents. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 2870–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granja, L.A.; Pineda-Aguilar, N.; Saucedo-Vázquez, J.P.; Suppan, G.; Lárez-Velázquez, C.; Galeas, S.; González, G.; López, F. Polyvinyl Alcohol Films Loaded with Silver Nanostructures with Different Sizes and Shapes with Tunable Plasmonic and Electric Properties. A Spectroscopic Study. Mater. Res. 2022, 25, e20210574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornyak, G.L.; Tibbals, H.F.; Dutta, J.; Moore, J.J. Introduction to Nanoscience Nanotechnology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Beyene, H.D.; Werkneh, A.A.; Bezabh, H.K.; Ambaye, T.G. Synthesis paradigm and applications of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), a review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2017, 13, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarman, F.; Shiddiq, M.; Armynah, B.; Tahir, D. Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) synthesis methods as heavy-metal sensors: A review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 9351–9368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menichetti, A.; Mavridi-Printezi, A.; Mordini, D.; Montalti, M. Effect of Size, Shape and Surface Functionalization on the Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.P.; Silveira, A.P.; Bonatto, C.C.; Reis, I.G.; Milreu, P.V. Silver Nanoparticles as Antimicrobial Agents: Past, Present, and Future. In Nanostructures for Antimicrobial Therapy: Nanostructures in Therapeutic Medicine Series; Ficai, A., Grumezescu, A.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 577–596. [Google Scholar]
- Bruna, T.; Maldonado-Bravo, F.; Jara, P.; Caro, N. Silver Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betts, J.W.; Hornsey, M.; La Ragione, R.M. Novel Antibacterials: Alternatives to Traditional Antibiotics. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2018, 73, 123–169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Natan, M.; Banin, E. From Nano to Micro: Using nanotechnology to combat microorganisms and their multidrug resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 302–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.Y.; Ko, W.C.; Hsueh, P.R. Nanoparticles in the treatment of infections caused by multidrug-resistant organisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasastha, R.V.; Yasur, J.; Abishad, P.; Unni, V.; Purushottam, D.; Nishanth, M.A.D.; Niyeditha, P.; Vergis, J.; Singh, S.V.; Kullaiah, B.; et al. Antimicrobial Efficacy of Green Synthesized Nanosilver with Entrapped Cinnamaldehyde against Multi-Drug Resistant Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli in Galleria mellonella. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, P.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, H. Synthesis, applications, toxicity and toxicity mechanisms of silver nanoparticles: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 253, 114636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Z.; Asanithi, P.; Chaiyakun, S.; Limsuwan, P. Growth of Silver Nanoparticles by DC Magnetron Sputtering. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 963909. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, P.; Morrisey, C.P.; Tuley, S.M.V.; Bingham, C.I. Synthesis and Stabilization of Colloidal Gold Nanoparticle Suspensions for SERS. In Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Stabilization, Passivation, and Functionalization; Nagarajan, R., Alan Hatton, T., Eds.; ACS Symposium Series; ACS Division of Colloid and Surface Chemistry: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, A.; Sinsermsuksakul, P.; Yang, P. Polyhedral Silver Nanocrystals with Distinct Scattering Signatures. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 4597–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiley, B.; Sun, Y.; Mayers, B.; Xia, Y. Shape-Controlled Synthesis of Metal Nanostructures: The Case of Silver. Chem. Eur. J. 2005, 11, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, L.; Arunachalam, J. Sunlight based irradiation strategy for rapid green synthesis of highly stable silver nanoparticles using aqueous garlic (Allium sativum) extract and their antibacterial potential. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 129, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, H.; Liu, X.; Zhou, S.; Horváth, P.G.; Bak, M.; Bejó, L.; Sipos, G.; Alpár, T. Functional silver nanoparticles synthesis from sustainable point of review: 2000 to 2023-A review on game changing materials. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, H.; Kumari, P.; Bontempi, E.; Yadav, S. Medicinal plants: Treasure trove for green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 24, 101518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Ahmad, M.; Swami, B.L.; Ikram, S. A Review on Plants Extract Mediated Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles for Antimicrobial Applications: A Green Expertise. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 7, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandran, S.; Chaudhary, M.; Pasricha, R.; Ahmad, A.; Satry, M. Synthesis of Gold Nanotriangles and Silver Nanoparticles Using Aloe Vera Plant Extract. Biotechnol. Prog. 2008, 22, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnaraj, C.; Jagan, E.G.; Rajasekar, S.; Selvakumar, P.; Kalaichelvan, P.T.; Mohan, N. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Acalypha indica leaf extracts and its antibacterial activity against water borne pathogens. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 76, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Kim, B.S. Rapid biological synthesis of silver nanoparticles using plant leaf extracts. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2009, 32, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Shen, Y.; Xie, A.; Yu, X.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Capsicum annuum L. extract. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MubarakAli, D.; Thajuddin, N.; Jeganathan, K.; Gunasekaran, M. Plant extract mediated synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles and its antibacterial activity against clinically isolated pathogens. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 85, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaviya, S.; Santhanalakshmi, J.; Viswanathan, B.; Muthumary, J.; Srinivasan, K. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using citrus sinensis peel extract and its antibacterial activity. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2011, 79, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, S.; Dabirian, S.; Kariminejad, F.; Koohi, D.E.; Nemattalab, M.; Majidimoghadam, S.; Zamani, E.; Yousefbeyk, F. Process optimization for green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Rubus discolor leaves extract and its biological activities against multi-drug resistant bacteria and cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alburae, N.; Alshamrani, R.; Mohammed, A.E. Bioactive silver nanoparticles fabricated using Lasiurus scindicus and Panicum turgidum seed extracts: Anticancer and antibacterial efficiency. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thirumoorthy, G.; Balasubramanian, B.; George, J.A.; Nizam, A.; Nagella, P.; Srinatha, N.; Pappuswamy, M.; Alanazi, A.M.; Meyyazhagan, A.; Rengasamy, K.R.R.; et al. Phytofabricated bimetallic synthesis of silver-copper nanoparticles using Aerva lanata extract to evaluate their potential cytotoxic and antimicrobial activities. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaji, D.S.; Basavaraja, S.; Deshpande, R.; Mahesh, D.B.; Prabhakar, B.K.; Venkataraman, A. Extracellular biosynthesis of functionalized silver nanoparticles by strains of Cladosporium cladosporioides fungus. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2009, 68, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustapha, T.; Misni, N.; Ithnin, N.R.; Daskum, A.M.; Unyah, N.Z. A Review on Plants and Microorganisms Mediated Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles, Role of Plants Metabolites and Applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 19, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Mushtaq, Z.; Saeed, F.; Afzaal, M.; Al Jbawi, E. Ultrasonic-assisted green synthesis of silver nanoparticles through cinnamon extract: Biochemical, structural, and antimicrobial properties. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 26, 1984–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, W.L.; Boriollo, M.F.G.; Tonon, C.C.; da Silva, J.J.; Cruz, F.M.; Martins, A.L.; Höfling, J.F.; Spolidorio, D.M.P. Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles and extracts of Syzygium cumini flowers and seeds: Periodontal, cariogenic and opportunistic pathogens. Arch. Oral Biol. 2021, 125, 105101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.R.; Shi, Q.S.; Ouyang, Y.S.; Chen, Y.B.; Duan, S.S. Antifungal effects of citronella oil against Aspergillus niger ATCC 16404. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 7483–7492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtado, G.; Medeiros, A. Single-Disk Diffusion Testing (Kirby-Bauer) of Susceptibility of Proteus mirabilis to Chloramphenicol: Significance of the Intermediate Category. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1980, 12, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, C.Y.; Wang, Z.X.; Xie, H. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, medical applications and biosafety. Theranostics 2020, 10, 8996–9031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabikhan, A.; Kandasamy, K.; Raj, A.; Alikunhi, N. Synthesis of antimicrobial silver nanoparticles by callus and leaf extracts forms saltmarsh plant, Sesuvium portulacastrum L. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 79, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambe, E.; Gotmare, S. Mass Spectra Interpretation of Cinnamaldehyde Present in Whole and Powdered Cinnamon Oil. Int. J. Recent Sci. Res. 2022, 13, 1127–1129. [Google Scholar]
- Mariselvan, R.; Ranjitsingh, A.L.; Usha, R.N.A.; Kalirajan, K.; Padmalatha, C.; Mosae, S.P. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from the extract of the inflorescence of Cocos nucifera (Family: Arecaceae) for enhanced antibacterial activity. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 6, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elavazhagan, T.; Arunachalam, K.D. Memecylon edule leaf extract mediated green synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 1265–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, Y.Y.; Rukayadi, Y.; Nor-Khaizura, M.A.; Kuan, C.H.; Chieng, B.W.; Nishibuchi, M.; Radu, S. In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity of Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles Against Selected Gram-Negative Foodborne Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Yin, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, T.H.; Liu, H.M.; Rao, S.S.; Tan, Y.J.; Qian, Y.X.; Liu, Y.W.; Hu, X.K.; et al. Ångstrom-scale silver particle–embedded carbomer gel promotes wound healing by inhibiting bacterial colonization and inflammation. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba0942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.X.; Chen, C.Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.X.; Huang, J.; Luo, Z.W.; Rao, S.S.; Tan, Y.J.; Liu, Y.W.; Yin, X.; et al. Ångstrom-Scale Silver Particles as a Promising Agent for Low-Toxicity Broad-Spectrum Potent Anticancer Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1808556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Zahoor, M.; Khan, R.S.; Ikram, M.; Islam, N. The impact of silver nanoparticles on the growth of plants: The agriculture applications. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petronella, F.; Madeleine, T.; De Mei, V.; Zaccagnini, F.; Striccoli, M.; D’Alessandro, G. Thermoplasmonic Controlled Optical Absorber Based on a Liquid Crystal Metasurface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 49468–49477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, I.X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, I.S.; Mei, M.L.; Li, Q.; Chu, C.H. The Antibacterial Mechanism of Silver Nanoparticles and Its Application in Dentistry. IJN 2020, 15, 2555–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalwar, K.; Shan, D. Antimicrobial Effect of Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) and Their Mechanism—A Mini Review. Micro Amp. Nano Lett. 2018, 13, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, A.D.; Hugo, W.B. Antimicrobial Activity and Action of Silver. In Progress in Medicinal Chemistry; Ellis, G.P., Luscombe, D.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; Volume 31, pp. 351–370. [Google Scholar]
- Adeyemi, O.S.; Shittu, E.O.; Akpor, O.B.; Rotimi, D.; Batiha, G. Silver Nanoparticles Restrict Microbial Growth by Promoting Oxidative Stress and DNA Damage. EXCLI J. 2020, 19, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ravichandiran, P.; Sheet, S.; Premnath, D.; Kim, A.R.; Yoo, D. 1,4-Naphthoquinone Analogues: Potent Antibacterial Agents and Mode of Action Evaluation. Molecules 2019, 24, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandiran, P.; Masłyk, M.; Sheet, S.; Janeczko, M.; Premnath, D.; Kim, A.R.; Park, B.H.; Han, M.H.; Yoo, D. Synthesis and Antimicrobial Evaluation of 1,4-Naphthoquinone Derivatives as Potential Antibacterial Agents. Chem. Open 2019, 8, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmuganathan, R.; MubarakAli, D.; Prabakar, D.; Muthukumar, H.; Thajuddin, N.; Kumar, S.S.; Pugazhendhi, A. An Enhancement of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Biogenic and Ceftriaxone-Conjugated Silver Nanoparticles: Green Approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 10362–10370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosh, I.N.; Patil, S.D.; Sharma, T.K.; Srivastava, S.K.; Pathania, R.; Navani, N.K. Synergistic action of cinnamaldehyde with silver nanoparticles against spore-forming bacteria: A case for judicious use of silver nanoparticles for antibacterial applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 4721–4731. [Google Scholar]
- Murugaiyan, J.; Kumar, P.A.; Rao, G.S.; Iskandar, K.; Hawser, S.; Hays, J.P.; Mohsen, Y.; Adukkadukkam, S.; Awuah, W.A.; Jose, R.A.M.; et al. Progress in Alternative Strategies to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance: Focus on Antibiotics. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weldick, P.J.; Wang, A.; Halbus, A.F.; Paunov, V.N. Emerging nanotechnologies for targeting antimicrobial resistance. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 4018–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R.; Srivastava, S.; Ghosh, S.; Khare, S.K. Phytochemical delivery through nanocarriers: A review. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 14, 111389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweet, M.J.; Chessher, A.; Singleton, I. Metal-Based Nanoparticles; Size, Function, and Areas for Advancement in Applied Microbiology. In Advances in Applied Microbiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Majeed, M.; Hakeem, K.R.; Rehman, R.U. Synergistic effects of plant extract coupled silver nanoparticles in various therapeutic applications- present insights and bottlenecks. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhathlan, A.H.; Al-Abdulkarim, H.A.; Khan, M.; Khan, M.; Alkholief, M.; Alshamsan, A.; Almomen, A.; Albekairi, N.; Alkhathlan, H.Z.; Siddiqui, M.R.H. Evaluation of the Anticancer Activity of Phytomolecules Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles Synthesized by Aqueous Extracts of Zingiber officinale (Ginger) and Nigella sativa L. Seeds (Black Cumin). Materials 2021, 14, 3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Liefferinge, E.; Forte, C.; Degroote, J.; Ovyn, A.; van Noten, N.; Mangelinckx, S.; Michiels, J. In vitro and in vivo antimicrobial activity of cinnamaldehyde and derivatives towards the intestinal bacteria of the weaned piglet. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 21, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bayati, F.A.; Muthanna, J.M. Isolation, identification, and purification of cinnamaldehyde from Cinnamomum zeylanicum bark oil. An antibacterial study. Pharm. Biol. 2009, 47, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, M.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J. Direct one-pot synthesis of cinnamaldehyde immobilized on gold nanoparticles and their antibiofilm properties. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 160, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattei, A.S.; Alves, S.H.; Severo, C.B.; Guazzelli Lda, S.; Oliveira Fde, M.; Severo, L.C. Use of Mueller-Hinton Broth and Agar in The Germ Tube Test. Ins. Med. Trop. 2014, 56, 483–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Premkumar, J.; Sudhakar, T.; Dhakal, A.; Shrestha, J.B.; Krishnakumar, S.; Balashanmugam, P. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) from cinnamon against bacterial pathogens. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 15, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, D.A.; Rodriguez, M. Nanoparticulas metalicas y plasmones de superficie: Una relacion profund. Av. En Cienc. E Ing. 2012, 3, 67–78. [Google Scholar]
- Amendola, V.; Pilot, R.; Frasconi, M.; Marago, O.M.; Iatì, M.A. Surface plasmon resonance in gold nanoparticles: A review. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2017, 29, 203002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anker, J.N.; Hall, W.P.; Lyandres, O.; Shah, N.C.; Zhao, J.; van Duyne, R. Biosensing with plasmonic nanosensors. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakal, T.C.; Kumar, A.; Majumdar, R.S.; Yadav, V. Mechanistic Basis of Antimicrobial Actions of Silver Nanoparticles. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.A.; Kanwal, Z.; Rauf, A.; Sabri, A.N.; Riaz, S.; Naseem, S. Size- and Shape-Dependent Antibacterial Studies of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Wet Chemical Routes. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, D.; Singha, K.M.; Pandey, P.; Mohanta, B.; Rajkumari, J.; Singha, L.P. Shape Dependent Physical Mutilation and Lethal Effects of Silver Nanoparticles on Bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.; Tak, Y.K.; Song, J.M. Does the Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Depend on the Shape of the Nanoparticle. A Study of the Gram-Negative Bacterium Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1712–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshareef, A.; Laird, K.; Cross, R.B.M. Shape-dependent antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles on Escherichia coli and Enterococcus faecium bacterium. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 424, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, J.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Rhee, Y.H.; Kwon, O.H.; Park, W.H. Shape-dependent antimicrobial activities of silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 2773–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Westerhoff, P.; Hristovski, K.; Crittenden, J.C. Stability of commercial metal oxide nanoparticles in water. Water Res. 2008, 42, 2204–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.R.; Sun, T.L.; Zhou, S.L.; Ma, Y.K.; Shi, Q.S.; Xie, Z.B.; Huang, X.M. A comparative analysis of antibacterial activity, dynamics, and effects of silver ions and silver nanoparticles against four bacterial strains. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 123, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouda, M. Some Nanoparticles Effects on Proteus sp. and KLebsiella sp. Isolated from Water. AJIDM 2014, 2, 4–10. [Google Scholar]
- Lara, H.H.; Ayala-Núñez, N.V.; Ixtepan, L.D.C.; Rodríguez, C. Bactericidal Effect of Silver Nanoparticles against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kora, A.J.; Arunachalam, J. Assessment of Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles on Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Its Mechanism of Action. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 27, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouhan, S.; Guleria, S. Green synthesis of AgNPs using Cannabis sativa leaf extract: Characterization, antibacterial, anti-yeast and a-amylase inhibitory activity. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2020, 3, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Zone of Inhibition (mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | C7230 | PE52 | AN54 | 29213 |
| Blank 1: AgNO3 | 5.2 | 5.1 | 5.1 | 5.2 |
| Blank 2: Cinnamon bark extract | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| AgNPs-cinnamon 54 µg/mL | 7 | 9 | 6 | 6 |
| AgNPs-cinnamon 108 µg/mL | 15 | 10 | 7 | 6 |
| AgNPs-cinnamon 162 µg/mL | 13 | 10 | 7 | 7 |
| AgNPs-cinnamon 270 µg/mL | 16 | 14 | 14 | 10 |
| AgNPs-cinnamon 540 µg/mL | 15 | 15 | 14 | 10 |
| Sample | KpE52 | KpLC1 | C7230 | DH5α | PAO1 | PE52 | AN2 | AN54 | 29213 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium and Inoculum | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| Cinnamon bark extract | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | |
| AgNPs-cinnamon | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Granja Alvear, A.; Pineda-Aguilar, N.; Lozano, P.; Lárez-Velázquez, C.; Suppan, G.; Galeas, S.; Debut, A.; Vizuete, K.; De Lima, L.; Saucedo-Vázquez, J.P.; et al. Synergistic Antibacterial Properties of Silver Nanoparticles and Its Reducing Agent from Cinnamon Bark Extract. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11050517
Granja Alvear A, Pineda-Aguilar N, Lozano P, Lárez-Velázquez C, Suppan G, Galeas S, Debut A, Vizuete K, De Lima L, Saucedo-Vázquez JP, et al. Synergistic Antibacterial Properties of Silver Nanoparticles and Its Reducing Agent from Cinnamon Bark Extract. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(5):517. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11050517
Chicago/Turabian StyleGranja Alvear, Araceli, Nayely Pineda-Aguilar, Patricia Lozano, Cristóbal Lárez-Velázquez, Gottfried Suppan, Salomé Galeas, Alexis Debut, Karla Vizuete, Lola De Lima, Juan Pablo Saucedo-Vázquez, and et al. 2024. "Synergistic Antibacterial Properties of Silver Nanoparticles and Its Reducing Agent from Cinnamon Bark Extract" Bioengineering 11, no. 5: 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11050517
APA StyleGranja Alvear, A., Pineda-Aguilar, N., Lozano, P., Lárez-Velázquez, C., Suppan, G., Galeas, S., Debut, A., Vizuete, K., De Lima, L., Saucedo-Vázquez, J. P., Alexis, F., & López, F. (2024). Synergistic Antibacterial Properties of Silver Nanoparticles and Its Reducing Agent from Cinnamon Bark Extract. Bioengineering, 11(5), 517. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11050517











