MurSS: A Multi-Resolution Selective Segmentation Model for Breast Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We incorporate a large field of view as an explicit context within our model’s architecture, improving the cancer lesion segmentation performance.
- We address the challenge of ambiguity in segmentation tasks for pathological images through the strategic implementation of selective segmentation methods.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
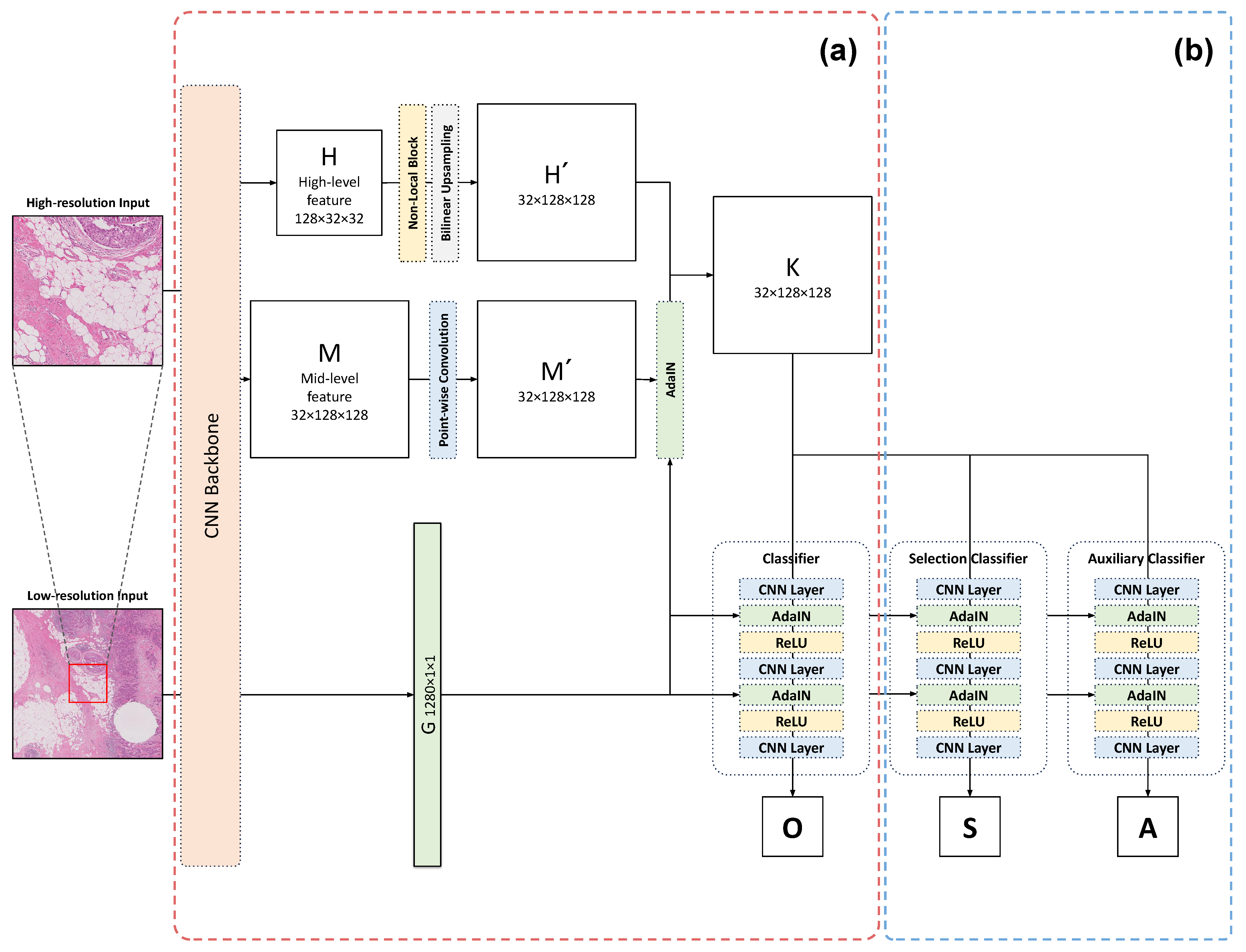
2.2.1. Multi-Resolution Adaptive Normalization
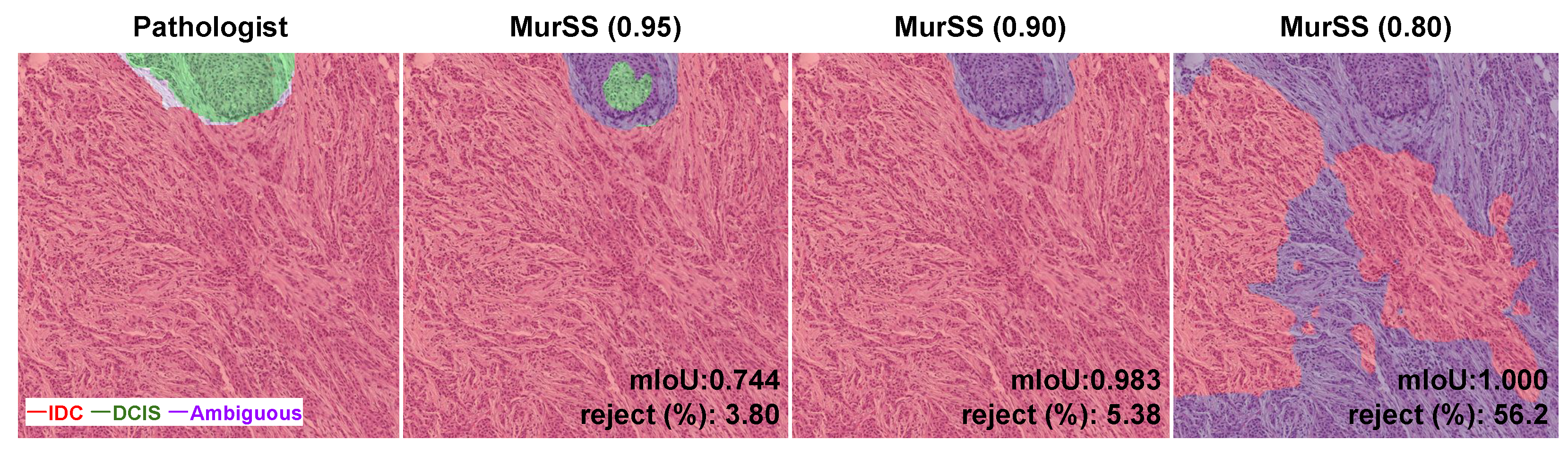
2.2.2. Selective Segmentation Method
2.2.3. Evaluation Metrics
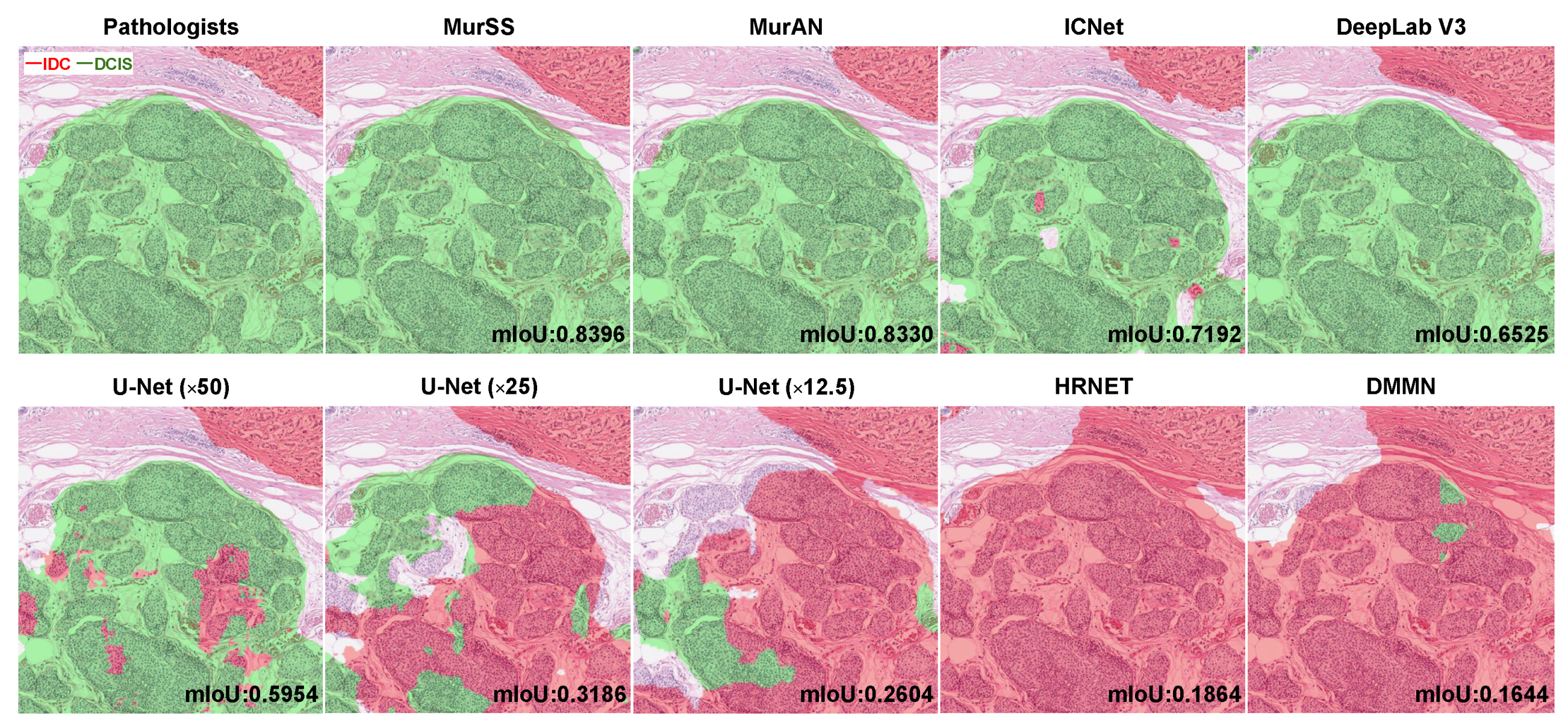
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Visualization Explanation
4.2. Limitations and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Accuracy | pixel-level accuracy (%) |
| AdaIN | adaptive instance normalization |
| BRCA | breast invasive carcinoma |
| CI | confidence interval |
| CNN | convolutional neural network |
| DCIS | ductal carcinoma in situ |
| H&E | hematoxylin and eosin |
| IDC | invasive ductal carcinoma |
| IoU | Intersection over Union |
| KUMC-Guro | Korea University Medical Center, Guro Hospital |
| mIoU | mean Intersection over Union |
| MurAN | multi-resolution adaptive normalization |
| MurSS | multi-resolution selective segmentation |
| SSM | selective segmentation method |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| WSI | whole-slide image |
References
- Chhikara, B.S.; Parang, K. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: The trends projection analysis. Chem. Biol. Lett. 2023, 10, 451. [Google Scholar]
- Hophan, S.L.; Odnokoz, O.; Liu, H.; Luo, Y.; Khan, S.; Gradishar, W.; Zhou, Z.; Badve, S.; Torres, M.A.; Wan, Y. Ductal carcinoma in situ of breast: From molecular etiology to therapeutic management. Endocrinology 2022, 163, bqac027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillon, D.; Guidi, A.; Schnitt, S. Pathology of invasive breast cancer. Dis. Breast 2010, 5, 381–410. [Google Scholar]
- Boyages, J.; Recht, A.; Connolly, J.L.; Schnitt, S.J.; Gelman, R.; Kooy, H.; Love, S.; Osteen, R.T.; Cady, B.; Silver, B.; et al. Early breast cancer: Predictors of breast recurrence for patients treated with conservative surgery and radiation therapy. Radiother. Oncol. 1990, 19, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsi, F.; Albasini, S.; Ciciriello, S.; Villani, L.; Truffi, M.; Sevieri, M.; Sorrentino, L. Extensive Intraductal Component in Breast Cancer: What Role in Disease-Free Survival? J. Surg. Res. 2023, 283, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elling, D.; Vesper, A.; Fiedler, B.; Martin, H.; Krocker, J. Intraductal component in invasive breast cancer: Analysis of 250 resected surgical specimens. Breast 2001, 10, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, K.; Czerwińska, P.; Wiznerowicz, M. Review The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA): An immeasurable source of knowledge. Contemp. Oncol. Onkol. 2015, 2015, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Li, Y.; Urtasun, R.; Zemel, R. Understanding the effective receptive field in deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2016, 29, 2–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III 18. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Xiao, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, J. Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 5693–5703. [Google Scholar]
- Miangoleh, S.M.H.; Dille, S.; Mai, L.; Paris, S.; Aksoy, Y. Boosting monocular depth estimation models to high-resolution via content-adaptive multi-resolution merging. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 9685–9694. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Qi, X.; Shen, X.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Icnet for real-time semantic segmentation on high-resolution images. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 405–420. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, D.J.; Yarlagadda, D.V.; D’Alfonso, T.M.; Hanna, M.G.; Grabenstetter, A.; Ntiamoah, P.; Brogi, E.; Tan, L.K.; Fuchs, T.J. Deep multi-magnification networks for multi-class breast cancer image segmentation. Comput. Med Imaging Graph. 2021, 88, 101866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsubaie, N.; Shaban, M.; Snead, D.; Khurram, A.; Rajpoot, N. A multi-resolution deep learning framework for lung adenocarcinoma growth pattern classification. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Understanding and Analysis: 22nd Conference, MIUA 2018, Southampton, UK, 9–11 July 2018; Proceedings 22. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Sirinukunwattana, K.; Alham, N.K.; Verrill, C.; Rittscher, J. Improving whole slide segmentation through visual context—A systematic study. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2018: 21st International Conference, Granada, Spain, 16–20 September 2018; Proceedings, Part II 11. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 192–200. [Google Scholar]
- Fumera, G.; Roli, F. Support vector machines with embedded reject option. In Proceedings of the Pattern Recognition with Support Vector Machines: First International Workshop, SVM 2002, Niagara Falls, ON, Canada, 10 August 2002; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 68–82. [Google Scholar]
- Hellman, M.E. The nearest neighbor classification rule with a reject option. IEEE Trans. Syst. Sci. Cybern. 1970, 6, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalitz, C. Reject options and confidence measures for knn classifiers. Schriftenreihe Fachbereichs Elektrotechnik Inform. Hochsch. Niederrh. 2009, 8, 16–38. [Google Scholar]
- De Stefano, C.; Sansone, C.; Vento, M. To reject or not to reject: That is the question-an answer in case of neural classifiers. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Part C Appl. Rev. 2000, 30, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Yaniv, R. On the Foundations of Noise-free Selective Classification. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2010, 11, 1605–1641. [Google Scholar]
- Geifman, Y.; El-Yaniv, R. Selectivenet: A deep neural network with an integrated reject option. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 2151–2159. [Google Scholar]
- Gal, Y.; Ghahramani, Z. Dropout as a bayesian approximation: Representing model uncertainty in deep learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, New York, NY, USA, 19–24 June 2016; pp. 1050–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Dodge, S.; Karam, L. Understanding how image quality affects deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 Eighth International Conference on Quality of Multimedia Experience (QoMEX), Lisbon, Portugal, 6–8 June 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Girshick, R.; Gupta, A.; He, K. Non-local neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7794–7803. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Xu, J.; Lin, S.; Wei, F.; Hu, H. Gcnet: Non-local networks meet squeeze-excitation networks and beyond. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Kalantidis, Y.; Li, J.; Yan, S.; Feng, J. A^ 2-nets: Double attention networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2018, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Xie, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, P. Global second-order pooling convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3024–3033. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Belongie, S. Arbitrary style transfer in real-time with adaptive instance normalization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1501–1510. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, J.M.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. Survey on deep learning with class imbalance. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madabhushi, A.; Lee, G. Image analysis and machine learning in digital pathology: Challenges and opportunities. Med. Image Anal. 2016, 33, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Confusion Matrix for IDC | Predicted Values | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benign | DCIS | IDC | ||
| Pathologists | Benign | TN | FN | FP |
| DCIS | FN | TN | FP | |
| IDC | FN | FN | TP | |
| Model | Coverage Ratio | Overall Measure (95% CI) | Intersection over Union (IoU) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy (%) | mIoU | Benign | DCIS | IDC | ||
| U-Net * | 1.0 | 94.77 (93.39, 95.89) | 0.6651 (0.6339, 0.6970) | 0.9470 | 0.3740 | 0.6743 |
| U-Net † | 1.0 | 94.97 (93.75, 95.96) | 0.6497 (0.6210, 0.6765) | 0.9504 | 0.3360 | 0.6626 |
| U-Net ‡ | 1.0 | 94.09 (92.48, 95.35) | 0.6375 (0.6040, 0.6688) | 0.9393 | 0.3463 | 0.6268 |
| HRNet * | 1.0 | 95.58 (94.57, 96.35) | 0.7005 (0.6593, 0.7312) | 0.9546 | 0.4361 | 0.7106 |
| DeepLabV3 * | 1.0 | 95.60 (94.71, 96.35) | 0.7013 (0.6631, 0.7341) | 0.9555 | 0.4360 | 0.7123 |
| ICNet *†‡ | 1.0 | 94.55 (93.49, 95.40) | 0.6714 (0.6349, 0.7016) | 0.9437 | 0.4008 | 0.6698 |
| DMMN *†‡ | 1.0 | 94.42 (93.23, 95.36) | 0.6424 (0.6170, 0.6699) | 0.9436 | 0.3287 | 0.6549 |
| MurAN *† | 1.0 | 95.88 (94.85, 96.71) | 0.7055 (0.6640, 0.7399) | 0.9577 | 0.4260 | 0.7328 |
| MurSS *† | 0.95 | 96.88 (95.97, 97.62) | 0.7283 (0.6865, 0.7640) | 0.9690 | 0.4324 | 0.7833 |
| MurSS *† | 0.90 | 97.09 (96.13, 97.85) | 0.7356 (0.6970, 0.7705) | 0.9707 | 0.4363 | 0.7999 |
| MurSS *† | 0.80 | 98.30 (97.53, 98.86) | 0.7603 (0.7067, 0.8061) | 0.9839 | 0.4485 | 0.8487 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.; Lee, G.; Kwak, T.-Y.; Kim, S.W.; Jin, M.-S.; Kim, C.; Chang, H. MurSS: A Multi-Resolution Selective Segmentation Model for Breast Cancer. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 463. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11050463
Lee J, Lee G, Kwak T-Y, Kim SW, Jin M-S, Kim C, Chang H. MurSS: A Multi-Resolution Selective Segmentation Model for Breast Cancer. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(5):463. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11050463
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Joonho, Geongyu Lee, Tae-Yeong Kwak, Sun Woo Kim, Min-Sun Jin, Chungyeul Kim, and Hyeyoon Chang. 2024. "MurSS: A Multi-Resolution Selective Segmentation Model for Breast Cancer" Bioengineering 11, no. 5: 463. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11050463
APA StyleLee, J., Lee, G., Kwak, T.-Y., Kim, S. W., Jin, M.-S., Kim, C., & Chang, H. (2024). MurSS: A Multi-Resolution Selective Segmentation Model for Breast Cancer. Bioengineering, 11(5), 463. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11050463






