Toe Box Shape of Running Shoes Affects In-Shoe Foot Displacement and Deformation: A Randomized Crossover Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
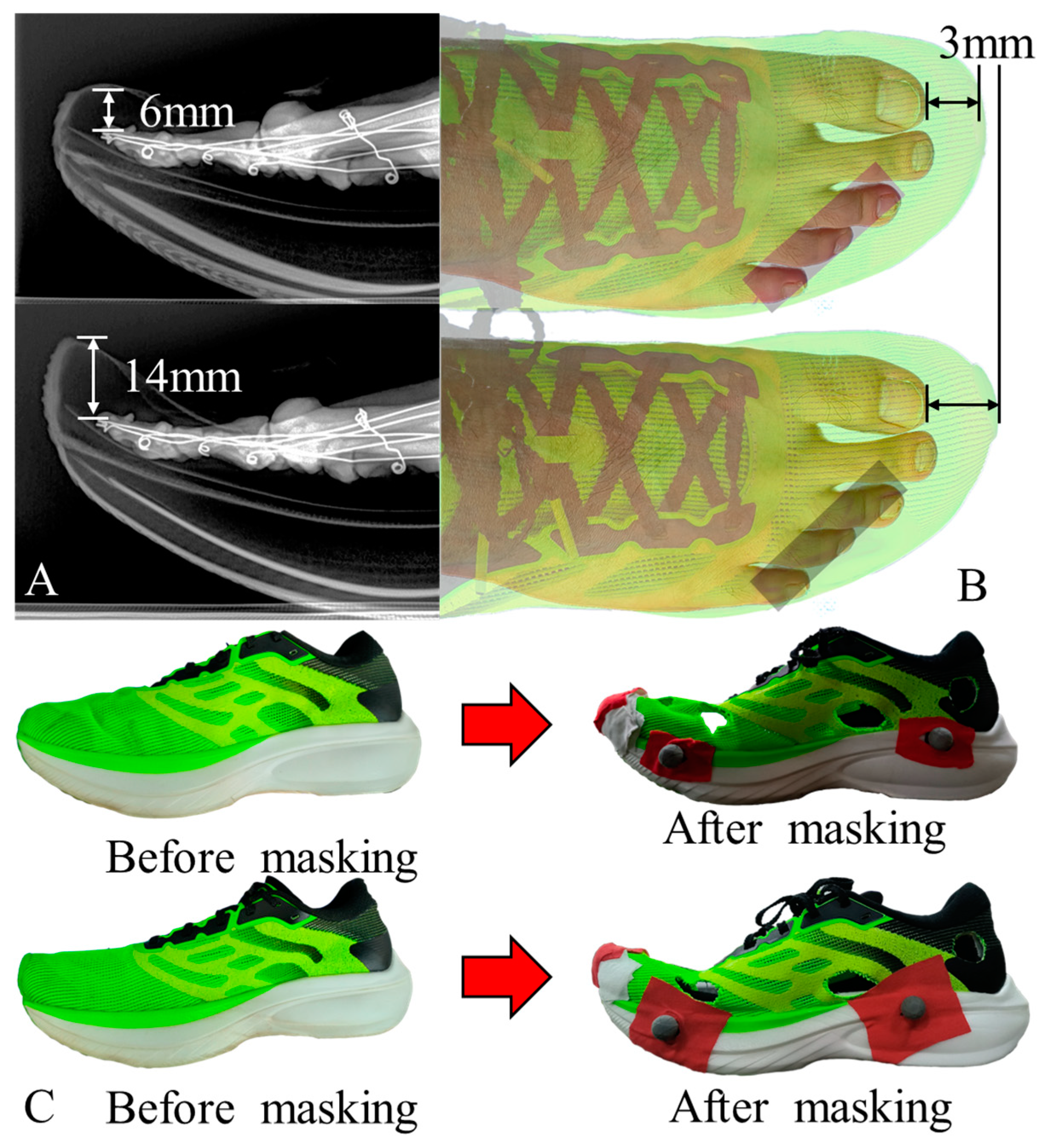
2.1. Footwear Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Experimental Procedure
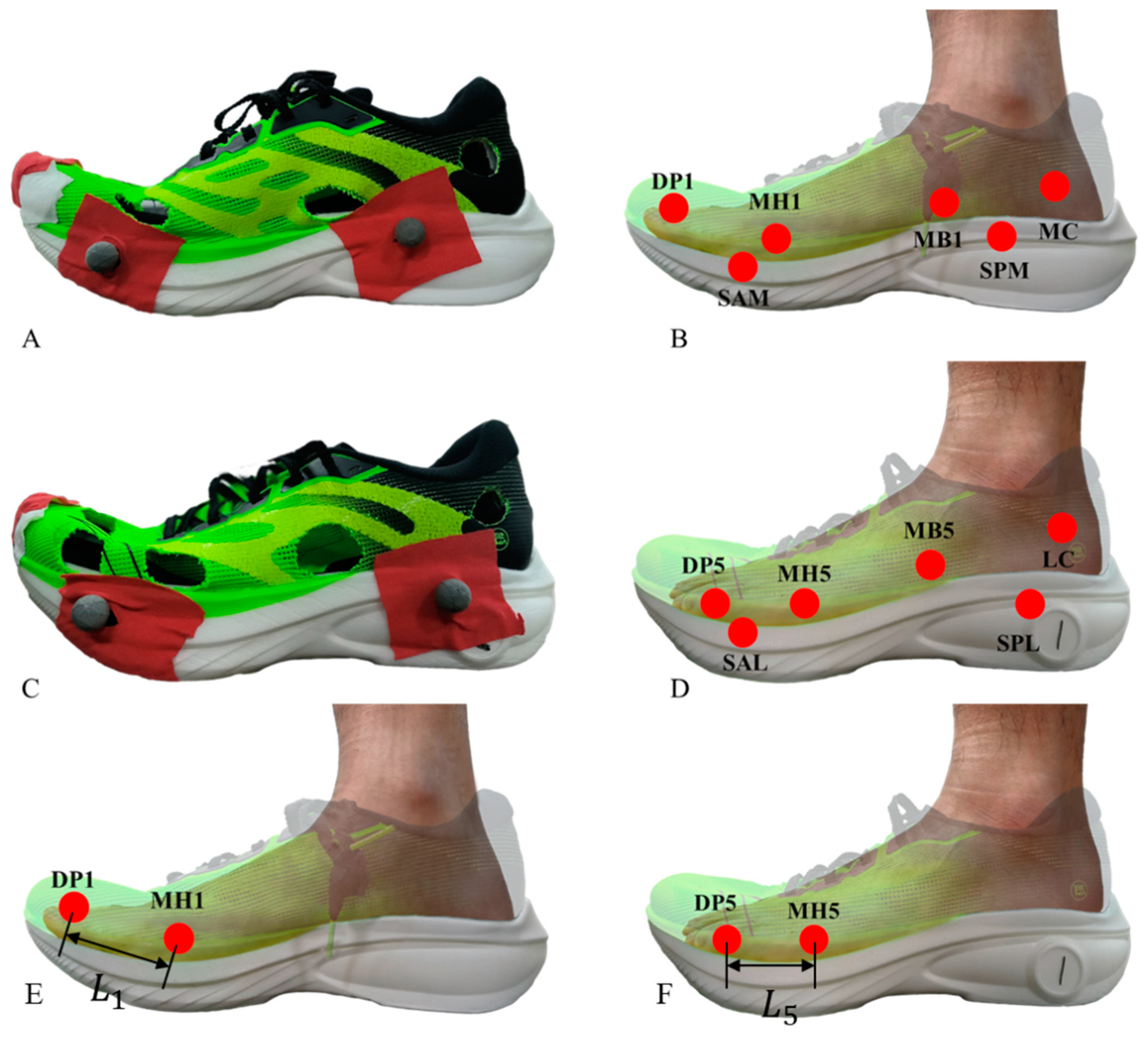
2.4. Data Collection
- (1)
- The changing range of the distance between MH1, MH5 and the midpoint of SAL and SAM. The changing range of the distance is used to reflect the range of movement of each part of the forefoot relative to the shoe.
- (2)
- The changing range of the distance between MB1 and the midpoints of SAM and SPM, and the changing range of the distance between MB5 and the midpoints of SAL and SPL, are used to reflect the range of movement of each part of the foot relative to the shoe.
- (3)
- The changing range of the distance between the midpoints of MC, LC, SPL, and SPM is used to reflect the range of movement of each part of the foot relative to the shoe.
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
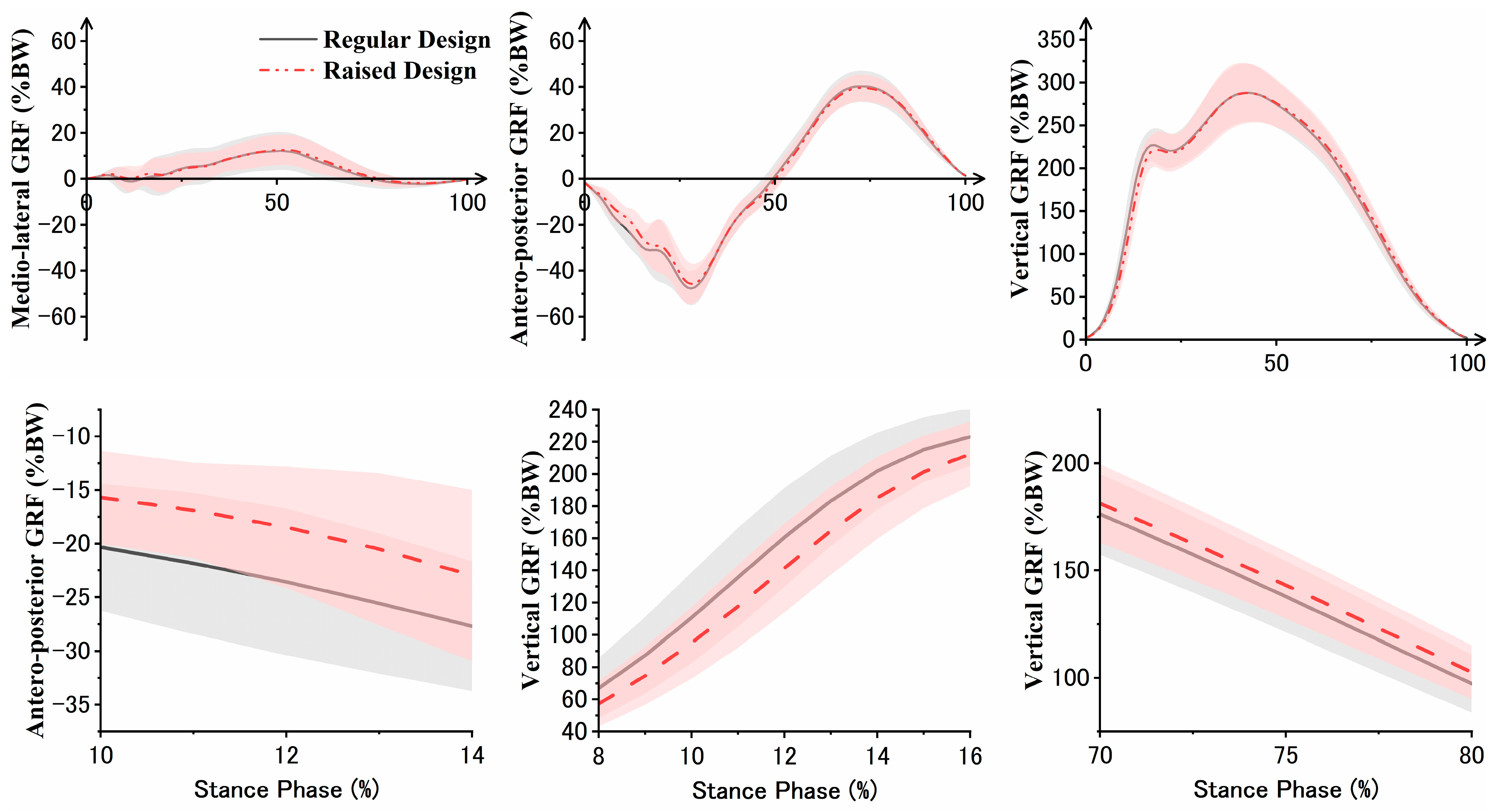
3.1. Ground Reaction Force
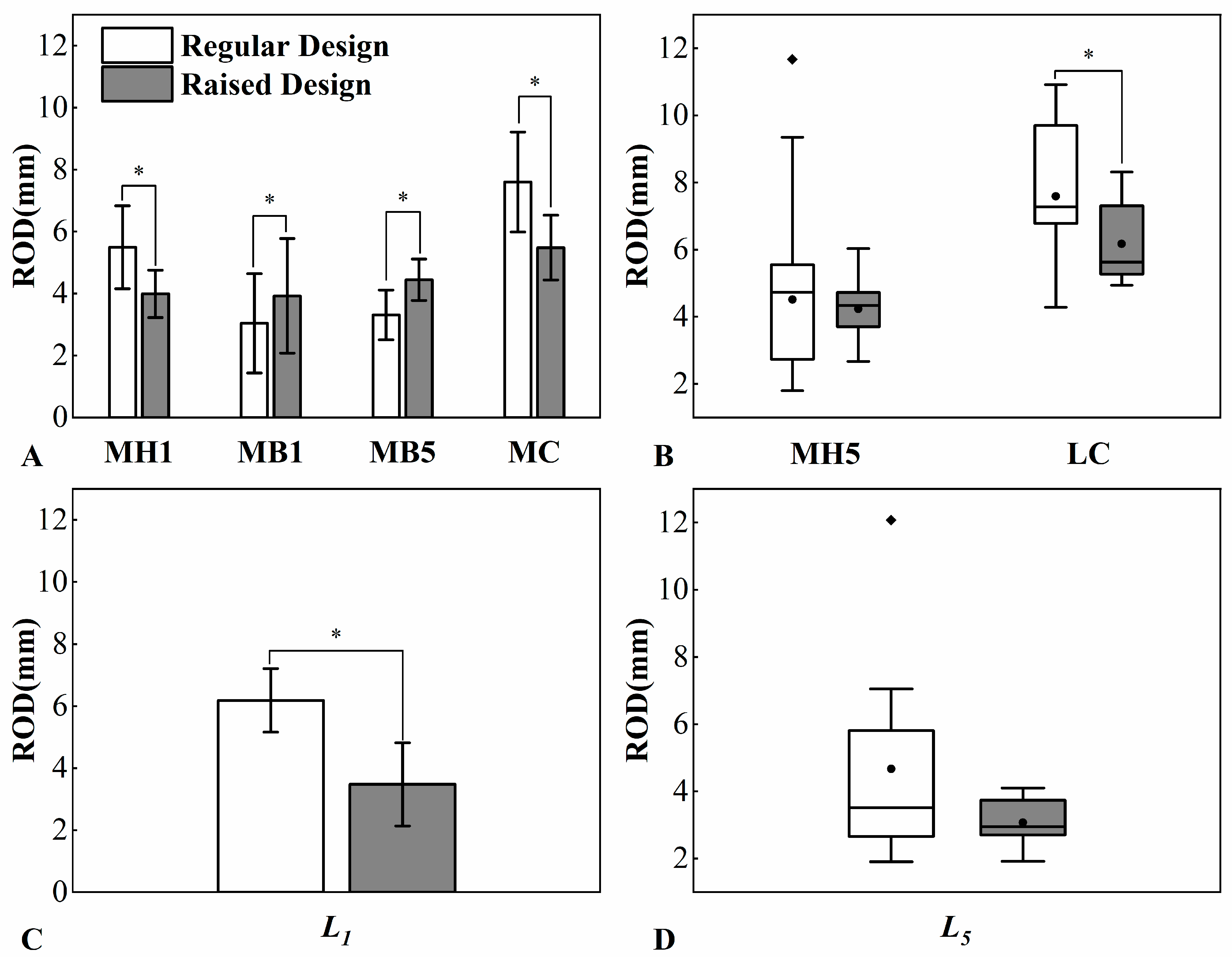
3.2. Foot–Shoe Interaction and Degree of Toe Deformation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burfoot, A. The History of the Marathon: 1976-Present. Sports Med. 2007, 37, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.W.; Ho, M.Y.M.; Loh, R.B.C.; Iskandar, M.N.S.; Kong, P.W. Foot Morphology and Running Gait Pattern between the Left and Right Limbs in Recreational Runners. Phys. Act. Health 2023, 7, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, E.; Xue, C.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, J. Unveiling Urban Marathon Development Characteristics and Urban Growth Strategies in China: Insights from Time Series Analysis of Baidu Search Index. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0287760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malchrowicz-Mośko, E.; Gravelle, F.; Dąbrowska, A.; León-Guereño, P. Do Years of Running Experience Influence the Motivations of Amateur Marathon Athletes? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malchrowicz-Mośko, E.; Poczta, J. Running as a Form of Therapy Socio-Psychological Functions of Mass Running Events for Men and Women. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulme, A.; Nielsen, R.O.; Timpka, T.; Verhagen, E.; Finch, C. Risk and Protective Factors for Middle- and Long-Distance Running-Related Injury. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 869–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Song, Y.; Xuan, R.; Sun, D.; Teo, E.C.; Bíró, I.; Gu, Y. Effect of long-distance running on inter-segment foot kinematics and ground reaction forces: A preliminary study. Front. Bioeng. Biotech. 2022, 10, 833774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gent, R.N.; Siem, D.; Van Middelkoop, M.; Van Os, A.G.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.M.A.; Koes, B.W.; Taunton, J.E. Incidence and Determinants of Lower Extremity Running Injuries in Long Distance Runners: A Systematic Review. Br. J. Sports Med. 2007, 41, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, W.O. A 12-Yr Profile of Medical Injury and Illness for the Twin Cities Marathon. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2000, 32, 1549–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krabak, B.J.; Waite, B.; Schiff, M.A. Study of Injury and Illness Rates in Multiday Ultramarathon Runners. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 2314–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailler, E.A.; Adams, B.B. The Wear and Tear of 26.2: Dermatological Injuries Reported on Marathon Day. Br. J. Sports Med. 2004, 38, 498–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mailler-Savage, E.A.; Adams, B.B. Skin Manifestations of Running. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2006, 55, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, B.B. Jogger’s Toenail. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2003, 48, S58–S59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, B.B. Dermatologic Disorders of the Athlete. Sports Med. 2002, 32, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Cen, X.; Sun, D.; Bíró, I.; Mao, Z.; Fang, Y.; Gu, Y. Influence of Changes in Foot Morphology and Temperature on Bruised Toenail Injury Risk during Running. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helm, M.F.; Helm, T.N.; Bergfeld, W.F. Skin Problems in the Long-distance Runner 2500 Years after the Battle of Marathon. Int. J. Dermatol. 2012, 51, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamston, J. Subungual Haematomas: JULIA GAMSTON Makes Practice Recommendations Based on a Literature Review of Treatment for Subungual Haematomas. Emerg. Nurse 2006, 14, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löser, C.R.; Nenoff, P.; Mainusch, O.; Dippel, E.; Balakirski, G. Common Diseases of the Nail: Diagnosis and Therapy. JDDG J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2021, 19, 1761–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Song, Y.; Cen, X.; Bálint, K.; Fekete, G.; Sun, D. The implications of sports biomechanics studies on the research and development of running shoes: A systematic review. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacoff, A.; Steger, J.; Stuessi, E.; Reinschmidt, C. Lateral Stability in Sideward Cutting Movements. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1996, 28, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apps, C.; Dawson, L.; Shering, B.; Siegkas, P. Grip Socks Improve Slalom Course Performance and Reduce In-Shoe Foot Displacement of the Forefoot in Male and Female Sports Players. J. Sports Sci. 2022, 40, 1351–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.Z.; Song, Y.; Fekete, G.; Gu, Y.D. The Variation of Plantar Temperature and Plantar Pressure during Shod Running with Socks or Not. J. Biomim. Biomater. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 35, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A Flexible Statistical Power Analysis Program for the Social, Behavioral, and Biomedical Sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, C.; Arnold, J.B.; Fraysse, F.; Thewlis, D. A Method to Investigate the Effect of Shoe-Hole Size on Surface Marker Movement When Describing in-Shoe Joint Kinematics Using a Multi-Segment Foot Model. Gait Posture 2015, 41, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pataky, T.C. Generalized N-Dimensional Biomechanical Field Analysis Using Statistical Parametric Mapping. J. Biomech. 2010, 43, 1976–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caravaggi, P.; Pataky, T.; Günther, M.; Savage, R.; Crompton, R. Dynamics of Longitudinal Arch Support in Relation to Walking Speed: Contribution of the Plantar Aponeurosis. J. Anat. 2010, 217, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hageman, E.R.; Hall, M.; Sterner, E.G.; Mirka, G.A. Medial Longitudinal Arch Deformation during Walking and Stair Navigation While Carrying Loads. Foot Ankle Int. 2011, 32, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeon, P.O.; Hertel, J.; Bramble, D.; Davis, I. The Foot Core System: A New Paradigm for Understanding Intrinsic Foot Muscle Function. Br. J. Sports Med. 2015, 49, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taddei, U.T.; Matias, A.B.; Ribeiro, F.I.A.; Bus, S.A.; Sacco, I.C.N. Effects of a Foot Strengthening Program on Foot Muscle Morphology and Running Mechanics: A Proof-of-Concept, Single-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Phys. Ther. Sport 2020, 42, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pinillos, F.; Lago-Fuentes, C.; Latorre-Román, P.A.; Pantoja-Vallejo, A.; Ramirez-Campillo, R. Jump-Rope Training: Improved 3-Km Time-Trial Performance in Endurance Runners via Enhanced Lower-Limb Reactivity and Foot-Arch Stiffness. Int. J. Sport. Physiol. 2020, 15, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Gu, Y.; Yu, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, Z. Do Arch Height and Arch Stiffness Relate to Physical Performance in Adult Men? J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2022, 61, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Xu, D.; Zhou, H.; Kovács, B.; Liang, M. The effect of heel height on the Achilles tendon and muscle activity in Latin dancers during a special-landing task. Int. J. Biomed. Eng. Technol. 2024, 44, 303–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydog, S.T.; Özçakar, L.; Tetik, O.; Demirel, H.A.; Hasçelik, Z.; Doral, M.N. Relation between Foot Arch Index and Ankle Strength in Elite Gymnasts: A Preliminary Study. Br. J. Sports Med. 2005, 39, e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, X.; Song, Y.; Yu, P.; Sun, D.; Simon, J.; Bíró, I.; Gu, Y. Effects of plantar fascia stiffness on the internal mechanics of idiopathic pes cavus by finite element analysis: Implications for metatarsalgia. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhou, H.; Quan, W.; Jiang, X.; Liang, M.; Li, S.; Ugbolue, U.C.; Baker, J.S.; Gusztav, F.; Ma, X. A New Method Proposed for Realizing Human Gait Pattern Recognition: Inspirations for the Application of Sports and Clinical Gait Analysis. Gait Posture 2024, 107, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmida, E.A.; Wille, C.M.; Stiffler-Joachim, M.R.; Kliethermes, S.A.; Heiderscheit, B.C. Vertical Loading Rate Is Not Associated with Running Injury, Regardless of Calculation Method. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2022, 54, 1382–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, T.; Kimura, M.; Morita, M. Application of Nine-Axis Accelerometer-Based Recognition of Daily Activities in Clinical Examination. Phys. Act. Health 2024, 8, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, L.M.; Martin, J.F.; Barton, C.J.; Bonanno, D.R. What Is the Effect of Changing Running Step Rate on Injury, Performance and Biomechanics? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. Open 2022, 8, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempster, J.; Dutheil, F.; Ugbolue, U.C. The Prevalence of Lower Extremity Injuries in Running and Associated Risk Factors: A Systematic Review. Phys. Act. Health 2021, 5, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Participants |
|---|---|
| Number | 25 |
| Age (years) | 22.7 ± 3.1 |
| Height (m) | 1.70 ± 0.02 |
| Weight (N) | 613.5 ± 44.1 |
| BMI | 21.7 ± 1.6 |
| Weekly running distance (km) | 52.3 ± 22.7 |
| Personal best (half marathon, h) 25 | 1.38 ± 0.07 |
| Personal best (full marathon, h) 5 | 3.07 ± 0.17 |
| Variable Category | Location | Toe Box Design | t | p | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regular | Raised | |||||
| Foot–shoe Relative Displacement | MH1 | 5.5 ± 1.4 | 4.0 ± 0.8 | 6.19 | <0.001 | 1.0~2.0 |
| MB1 | 3.0 ± 1.6 | 3.9 ± 1.9 | −3.57 | 0.002 | −1.4~−0.4 | |
| MB5 | 3.3 ± 0.8 | 4.4 ± 0.7 | −7.15 | <0.001 | −1.5~−0.8 | |
| MC | 7.6 ± 1.6 | 5.5 ± 1.1 | 6.67 | <0.001 | 1.5~2.8 | |
| Location | Regular | Raised | Z | p | ||
| MH5 | 4.7(2.7, 5.6) | 4.3(3.7, 4.8) | −0.12 | 0.916 | ||
| LC | 7.3(6.7, 9.8) | 5.6(5.3, 7.4) | −3.78 | <0.001 | ||
| Degree of Toe Deformation | Location | Regular | Raised | t | p | 95%CI |
| 6.2 ± 1.0 | 3.5 ± 1.4 | 8.04 | <0.001 | 2.0~3.4 | ||
| Location | Regular | Raised | Z | p | ||
| 3.5(2.7, 5.9) | 3.0(2.6, 3.7) | −1.84 | 0.067 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, C.; Song, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, A.; Baker, J.S.; Liu, W.; Gu, Y. Toe Box Shape of Running Shoes Affects In-Shoe Foot Displacement and Deformation: A Randomized Crossover Study. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11050457
Zhu C, Song Y, Xu Y, Zhu A, Baker JS, Liu W, Gu Y. Toe Box Shape of Running Shoes Affects In-Shoe Foot Displacement and Deformation: A Randomized Crossover Study. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(5):457. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11050457
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Chengyuan, Yang Song, Yufan Xu, Aojie Zhu, Julien S. Baker, Wei Liu, and Yaodong Gu. 2024. "Toe Box Shape of Running Shoes Affects In-Shoe Foot Displacement and Deformation: A Randomized Crossover Study" Bioengineering 11, no. 5: 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11050457
APA StyleZhu, C., Song, Y., Xu, Y., Zhu, A., Baker, J. S., Liu, W., & Gu, Y. (2024). Toe Box Shape of Running Shoes Affects In-Shoe Foot Displacement and Deformation: A Randomized Crossover Study. Bioengineering, 11(5), 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11050457








