Breaking the Limit of Cardiovascular Regenerative Medicine: Successful 6-Month Goat Implant in World’s First Ascending Aortic Replacement Using Biotube Blood Vessels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
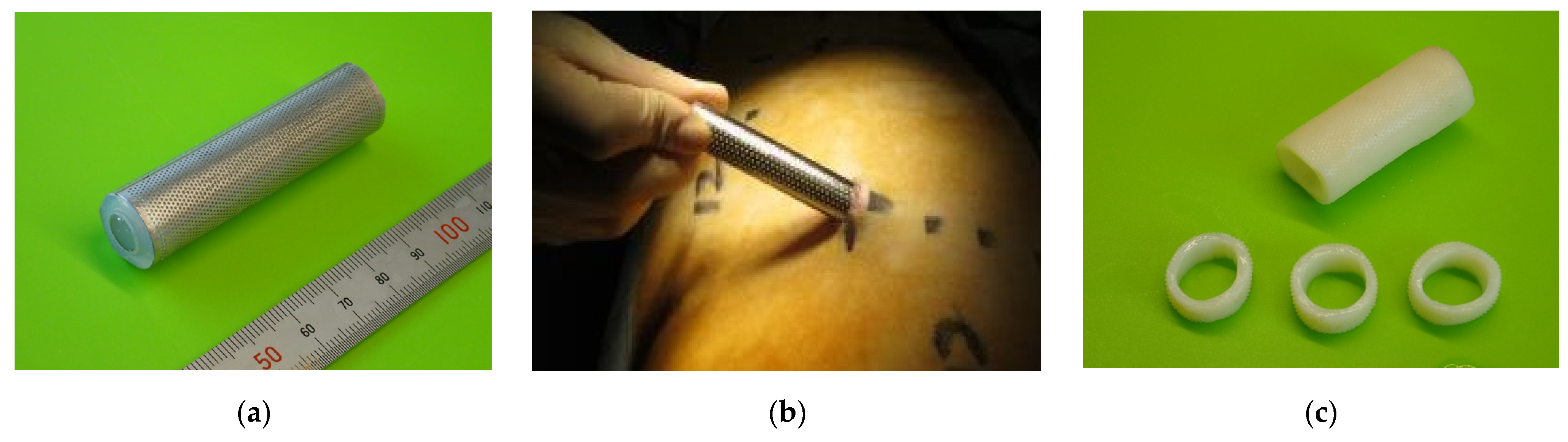
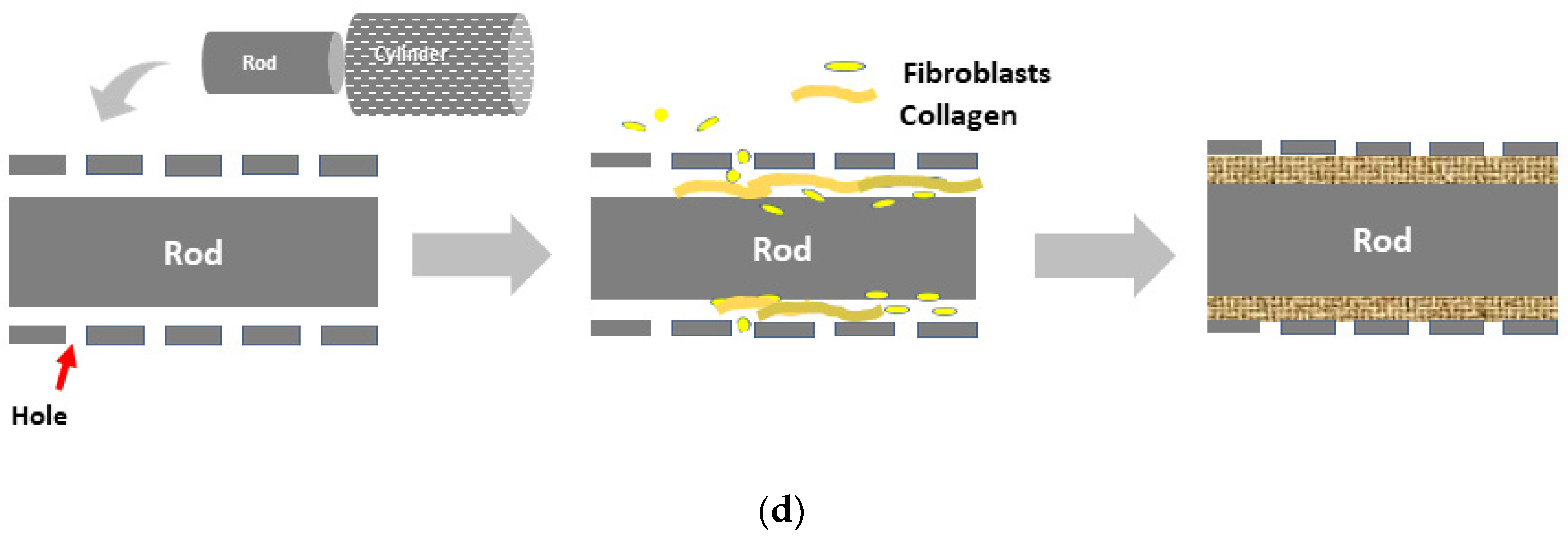
2.1. Biotube Production
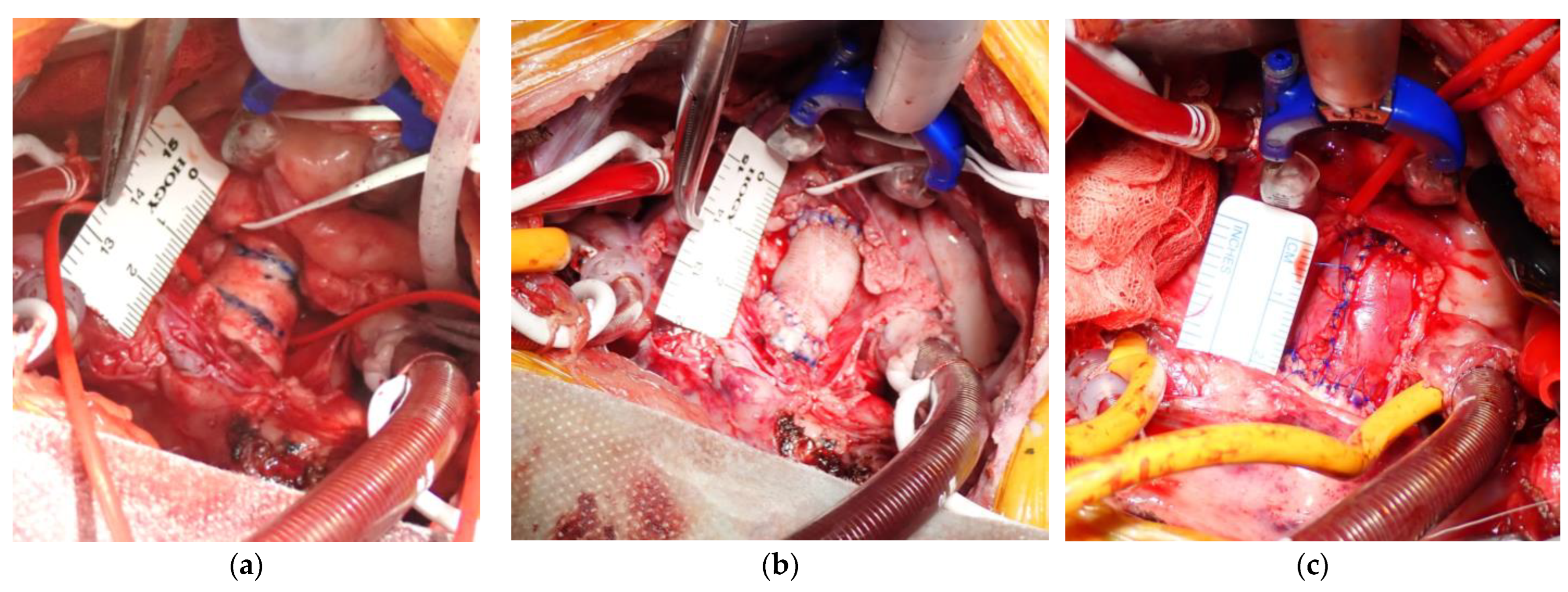
2.2. Aortic Replacement Procedure
2.3. Imaging and Histologic Tests
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethical Approval
3. Results
3.1. Procedural Results
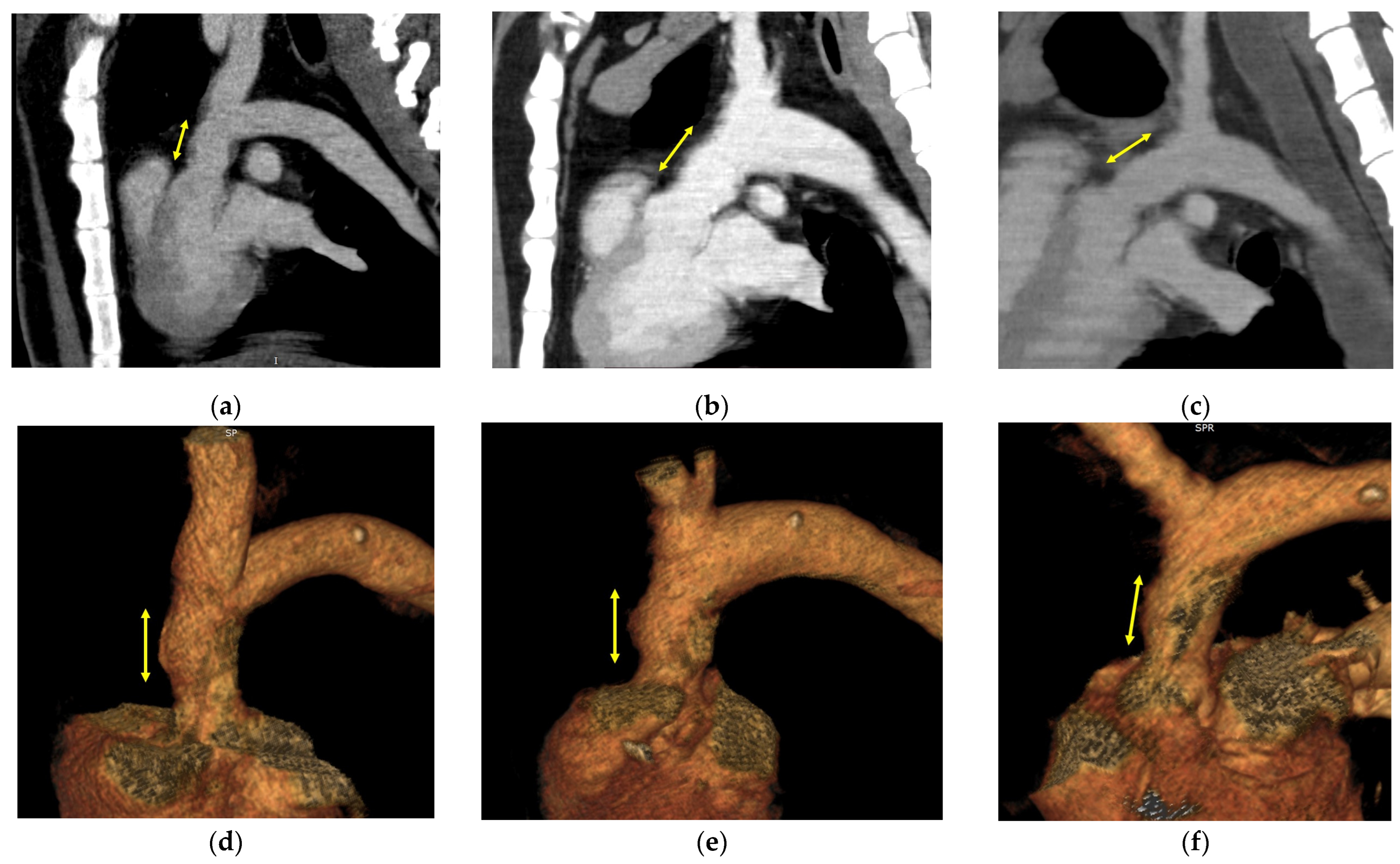
3.2. Image Evaluation
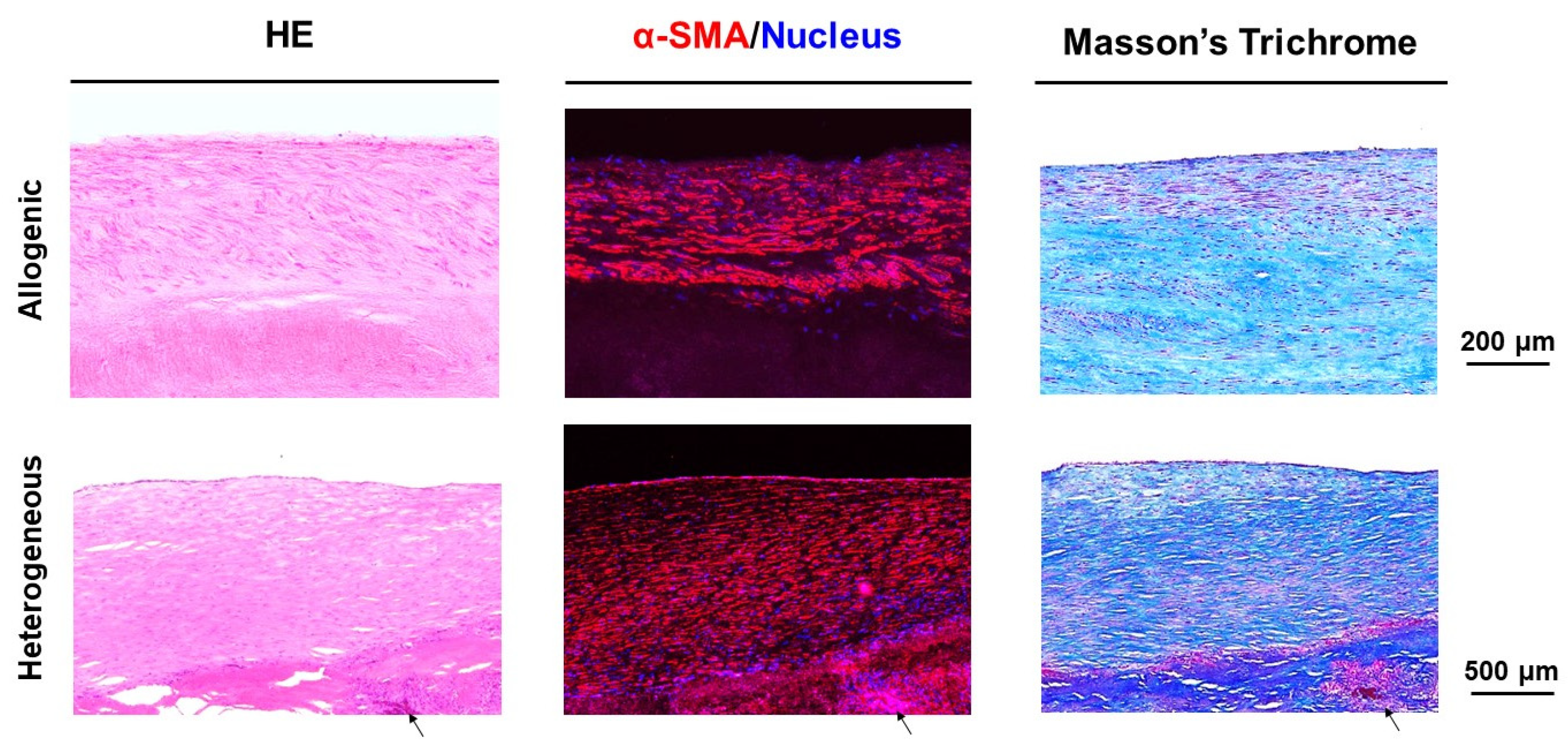
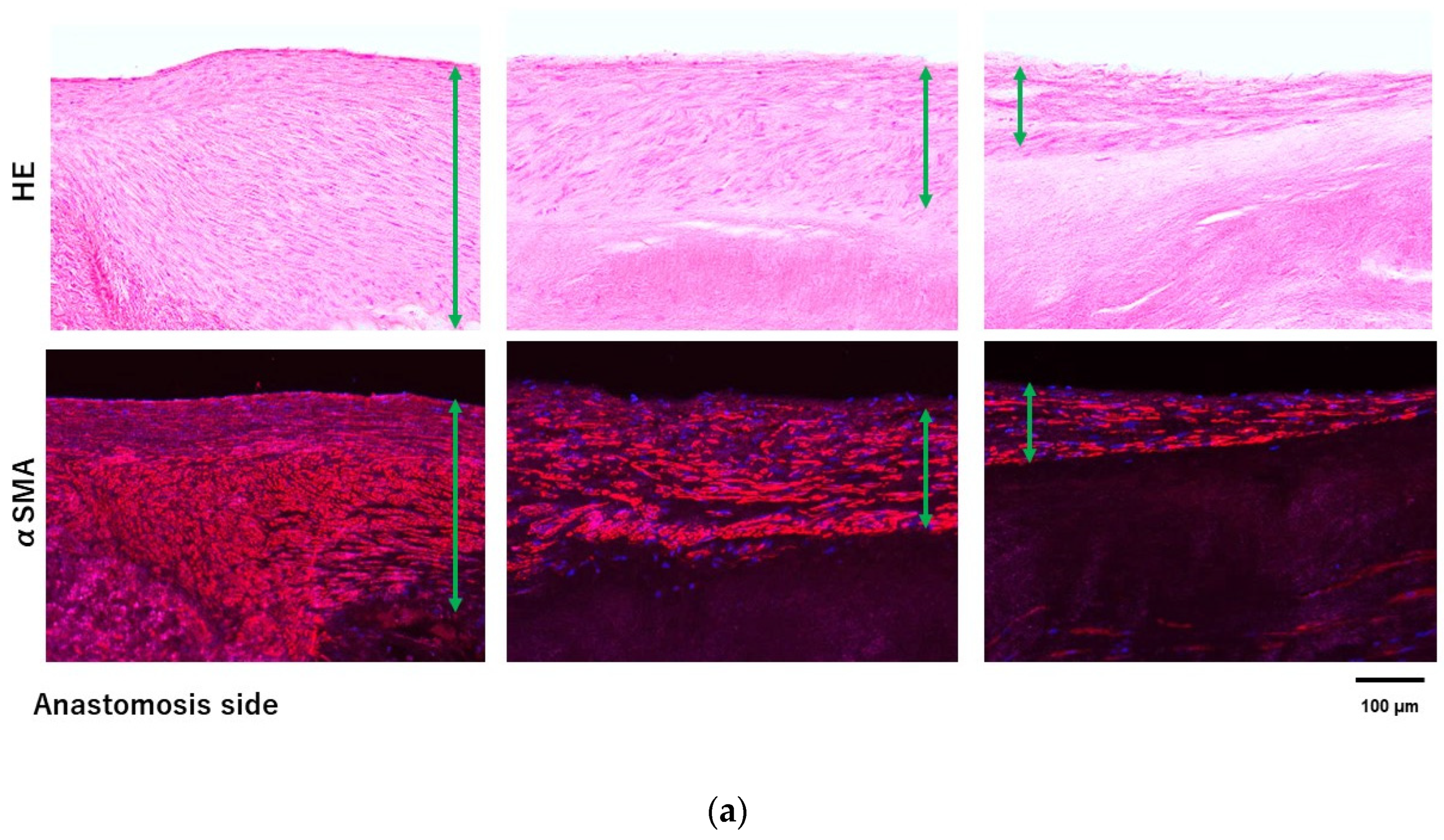
3.3. Histologic Evaluation
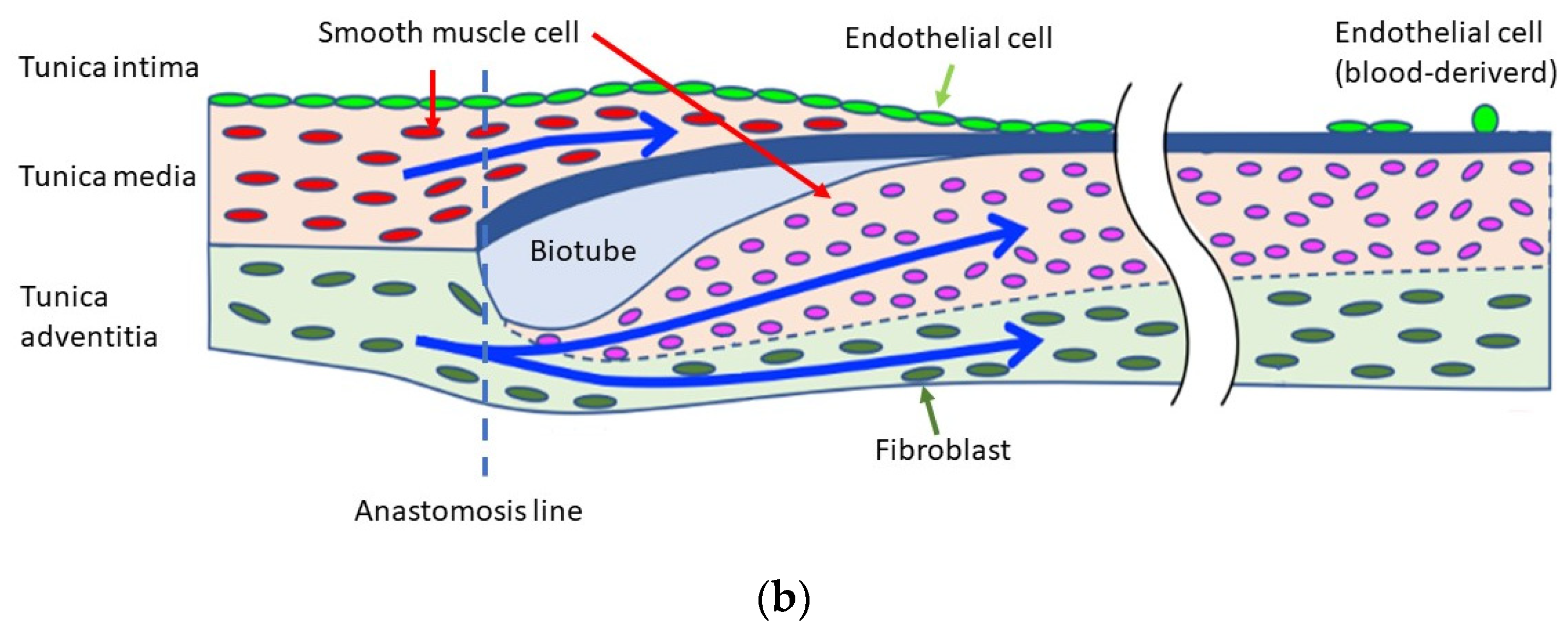
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oda, T.; Minatoya, K.; Kobayashi, J.; Okita, Y.; Akashi, H.; Tanaka, H.; Kawaharada, N.; Saiki, Y.; Kuniyoshi, Y.; Nishimura, K. Prosthetic vascular graft infection through a median sternotomy: A multicentre review. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2015, 20, 701–706; discussion 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sörelius, K.; Budtz-Lilly, J.; Mani, K.; Wanhainen, A. Systematic review of the management of mycotic aortic aneurysms. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2019, 58, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durán-Rey, D.; Crisóstomo, V.; Sánchez-Margallo, J.A.; Sánchez-Margallo, F.M. Systematic review of tissue-engineered vascular grafts. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 771400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawashima, T.; Umeno, T.; Terazawa, T.; Wada, T.; Shuto, T.; Nishida, H.; Anai, H.; Nakayama, Y.; Miyamoto, S. Aortic valve neocuspidization with in-body tissue-engineered autologous membranes: Preliminary results in a long-term goat model. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2021, 32, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, Y.; Furukoshi, M.; Terazawa, T.; Iwai, R. Development of long in vivo tissue-engineered “Biotube” vascular grafts. Biomaterials 2018, 185, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashita, R.; Nakayama, Y.; Shiraishi, Y.; Iwai, R.; Inoue, Y.; Yamada, A.; Terazawa, T.; Tajikawa, M.; Ohara, M.; Umeno, T.; et al. Acute phase pilot evaluation of small diameter long iBTA induced vascular graft “Biotube” in a goat model. EJVES Vasc. Forum 2022, 54, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, Y.; Iwai, R.; Terazawa, T.; Tajikawa, T.; Umeno, T.; Kawashima, T.; Nakashima, Y.; Shiraishi, Y.; Yamada, A.; Higashita, R.; et al. Pre-implantation evaluation of a small-diameter, long vascular graft (Biotube®) for below-knee bypass surgery in goats. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2022, 110, 2387–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umminger, J.; Krueger, H.; Beckmann, E.; Kaufeld, T.; Fleissner, F.; Haverich, A.; Shrestha, M.; Martens, A. Management of early graft infections in the ascending aorta and aortic arch: A comparison between graft replacement and graft preservation techniques. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2016, 50, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touma, J.; Cochennec, F.; Parisot, J.; Fialaire Legendre, A.; Becquemin, J.P.; Desgranges, P. In situ reconstruction in native and prosthetic aortic infections using cryopreserved arterial allografts. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2014, 48, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golemovic, M.; Skific, M.; Haluzan, D.; Pavic, P.; Golubic Cepulic, B. Ten-year experience with cryopreserved vascular allografts in the Croatian Cardiovascular Tissue Bank. Cell Tissue Bank. 2022, 23, 807–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, F.; Schenke-Layland, K.; Cohnert, T.U.; Starcher, B.; Halbhuber, K.J.; Martin, D.P.; Stock, U.A. Tissue engineering of aortic tissue: Dire consequence of suboptimal elastic fiber synthesis in vivo. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004, 63, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oropeza, B.P.; Adams, J.R.; Furth, M.E.; Chessa, J.; Boland, T. Bioprinting of decellularized porcine cardiac tissue for large-scale aortic models. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 855186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terazawa, T.; Lai, Y.P.; Nakayama, Y. Comparison of ethanol concentration as stock solution on mechanical properties of iBTA-induced collagenous tubular tissue “Biotube”. J. Biorheol. 2018, 32, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccafoschi, F.; Habermehl, J.; Vesentini, S.; Mantovani, D. Biological performances of collagen-based scaffolds for vascular tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 7410–7417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.J., Jr.; Yi, T.; Nasiri, B.; Breuer, C.K.; Andreadis, S.T. Implantation of VEGF-functionalized cell-free vascular grafts: Regenerative and immunological response. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 5089–5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copes, F.; Pien, N.; Van Vlierberghe, S.; Boccafoschi, F.; Mantovani, D. Collagen-based tissue engineering strategies for vascular medicine. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Dong, Y. Collagen-based biomaterials for tissue engineering. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 1132–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, H.; Endo, H.; Noma, M.; Ishii, H.; Tsuchiya, H.; Yoshimoto, A.; Takahashi, Y.; Inaba, Y.; Nishino, Y.; Nunokawa, M.; et al. Xenopericardial roll graft replacement for infectious pseudoaneurysms and graft infections of the aorta. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2015, 10, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, H.; Yamamoto, F.; Ishibashi, K.; Motokawa, M. In situ replacement with equine pericardial roll grafts for ruptured infected aneurysms of the abdominal aorta. J. Vasc. Surg. 2009, 49, 1041–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Itoh, M.; Mukae, Y.; Kitsuka, T.; Arai, K.; Nakamura, A.; Uchihashi, K.; Toda, S.; Matsubayashi, K.; Oyama, J.I.; Node, K.; et al. Development of an immunodeficient pig model allowing long-term accommodation of artificial human vascular tubes. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, D.; Fan, Y.; Xiao, W.; Liu, R.; Pivetti, C.; Walimbe, T.; Guo, F.; Zhang, X.; Farmer, D.L.; Wang, F.; et al. Rapid endothelialization of small diameter vascular grafts by a bioactive integrin-binding ligand specifically targeting endothelial progenitor cells and endothelial cells. Acta Biomater. 2020, 108, 178–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.M.; Herrera, G.A.; Battarbee, H.D. Role of glutaraldehyde in calcification of porcine aortic valve fibroblasts. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 154, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoen, F.J.; Levy, R.J. Calcification of tissue heart valve substitutes: Progress toward understanding and prevention. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2005, 79, 1072–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poppenborg, F.; Martens, S.; Martens, S. The influence of glutaraldehyde on the microscopic structure of human pericardium. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2022, 61, 107457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Pei, J.; Qin, Y.; Du, H.; Qu, X.; Li, W.; Huang, B.; Tan, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, G.; et al. Construction of tissue-engineered vascular grafts with enhanced patency by integrating heparin, cell-adhesive peptide, and carbon monoxide nanogenerators into acellular blood vessels. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 34, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radke, D.; Jia, W.; Sharma, D.; Fena, K.; Wang, G.; Goldman, J.; Zhao, F. Tissue engineering at the blood-contacting surface: A review of challenges and strategies in vascular graft development. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, e1701461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovanniello, F.; Asgari, M.; Breslavsky, I.D.; Franchini, G.; Holzapfel, G.A.; Tabrizian, M.; Amabili, M. Development and mechanical characterization of decellularized scaffolds for an active aortic graft. Acta Biomater. 2023, 160, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Kao, Y.C.; Lin, Y.H.; Ma, H.; Tsay, R.Y. A fiber-progressive-engagement model to evaluate the composition, microstructure, and nonlinear pseudoelastic behavior of porcine arteries and decellularized derivatives. Acta Biomater. 2016, 46, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mori, K.; Umeno, T.; Kawashima, T.; Wada, T.; Genda, T.; Arakura, M.; Oda, Y.; Mizoguchi, T.; Iwai, R.; Tajikawa, T.; et al. Breaking the Limit of Cardiovascular Regenerative Medicine: Successful 6-Month Goat Implant in World’s First Ascending Aortic Replacement Using Biotube Blood Vessels. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11040405
Mori K, Umeno T, Kawashima T, Wada T, Genda T, Arakura M, Oda Y, Mizoguchi T, Iwai R, Tajikawa T, et al. Breaking the Limit of Cardiovascular Regenerative Medicine: Successful 6-Month Goat Implant in World’s First Ascending Aortic Replacement Using Biotube Blood Vessels. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(4):405. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11040405
Chicago/Turabian StyleMori, Kazuki, Tadashi Umeno, Takayuki Kawashima, Tomoyuki Wada, Takuro Genda, Masanagi Arakura, Yoshifumi Oda, Takayuki Mizoguchi, Ryosuke Iwai, Tsutomu Tajikawa, and et al. 2024. "Breaking the Limit of Cardiovascular Regenerative Medicine: Successful 6-Month Goat Implant in World’s First Ascending Aortic Replacement Using Biotube Blood Vessels" Bioengineering 11, no. 4: 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11040405
APA StyleMori, K., Umeno, T., Kawashima, T., Wada, T., Genda, T., Arakura, M., Oda, Y., Mizoguchi, T., Iwai, R., Tajikawa, T., Nakayama, Y., & Miyamoto, S. (2024). Breaking the Limit of Cardiovascular Regenerative Medicine: Successful 6-Month Goat Implant in World’s First Ascending Aortic Replacement Using Biotube Blood Vessels. Bioengineering, 11(4), 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11040405






