Evaluation of Deep Learning Model Architectures for Point-of-Care Ultrasound Diagnostics
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A 27-swine subject dataset was curated with positive and negative injury conditions for certain eFAST scan locations.
- A convolutional neural network (CNN) was optimized for each eFAST scan site using a two-step optimization process, which involved exhaustive and Bayesian optimization of a wide range of hyperparameters.
- Custom model architectures were compared against lighter models with fewer parameters and larger conventional models using a leave-one-subject-out cross-validation approach.
Overview of the eFAST Procedure
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Image Setup
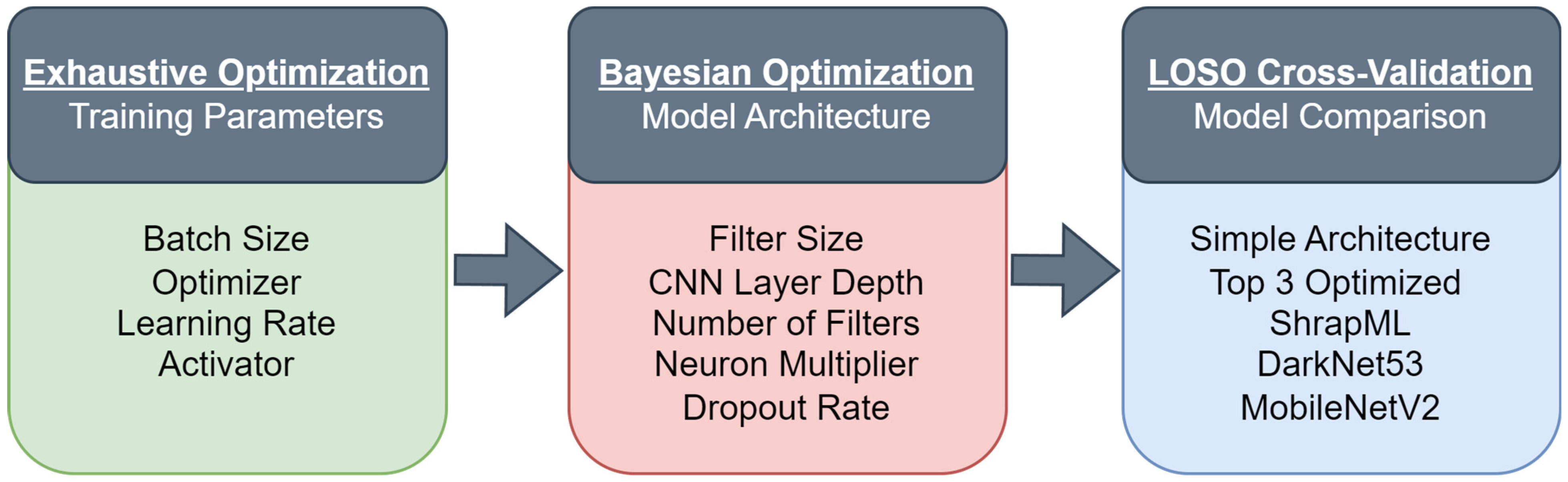
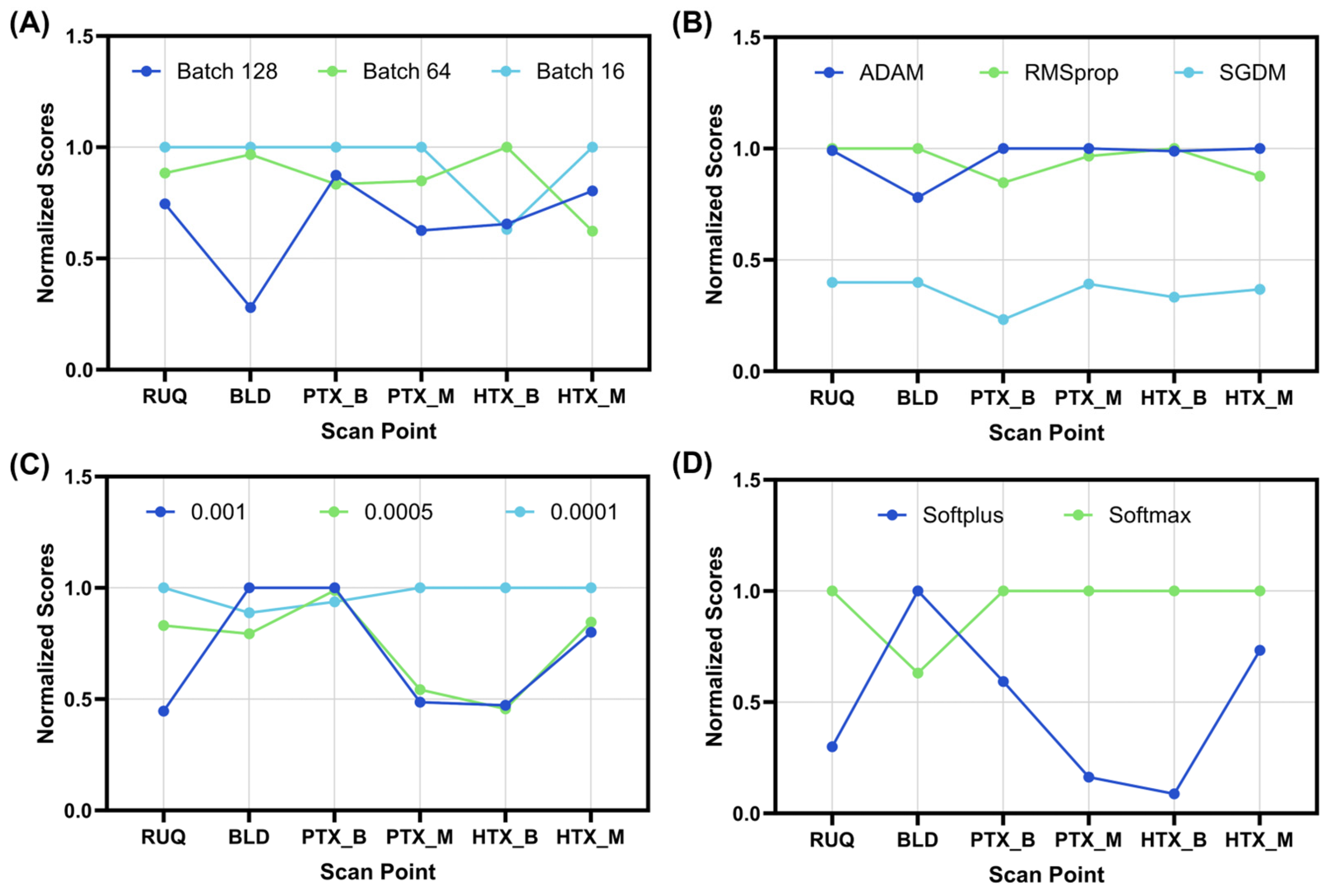
2.3. Exhaustive Optimization for Training Parameters
2.4. Bayesian Optimization for Algorithm Architecture
2.5. Overview of LOSO Training
2.6. LOSO Model Performance Evaluation and Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of a CNN Architecture for eFAST
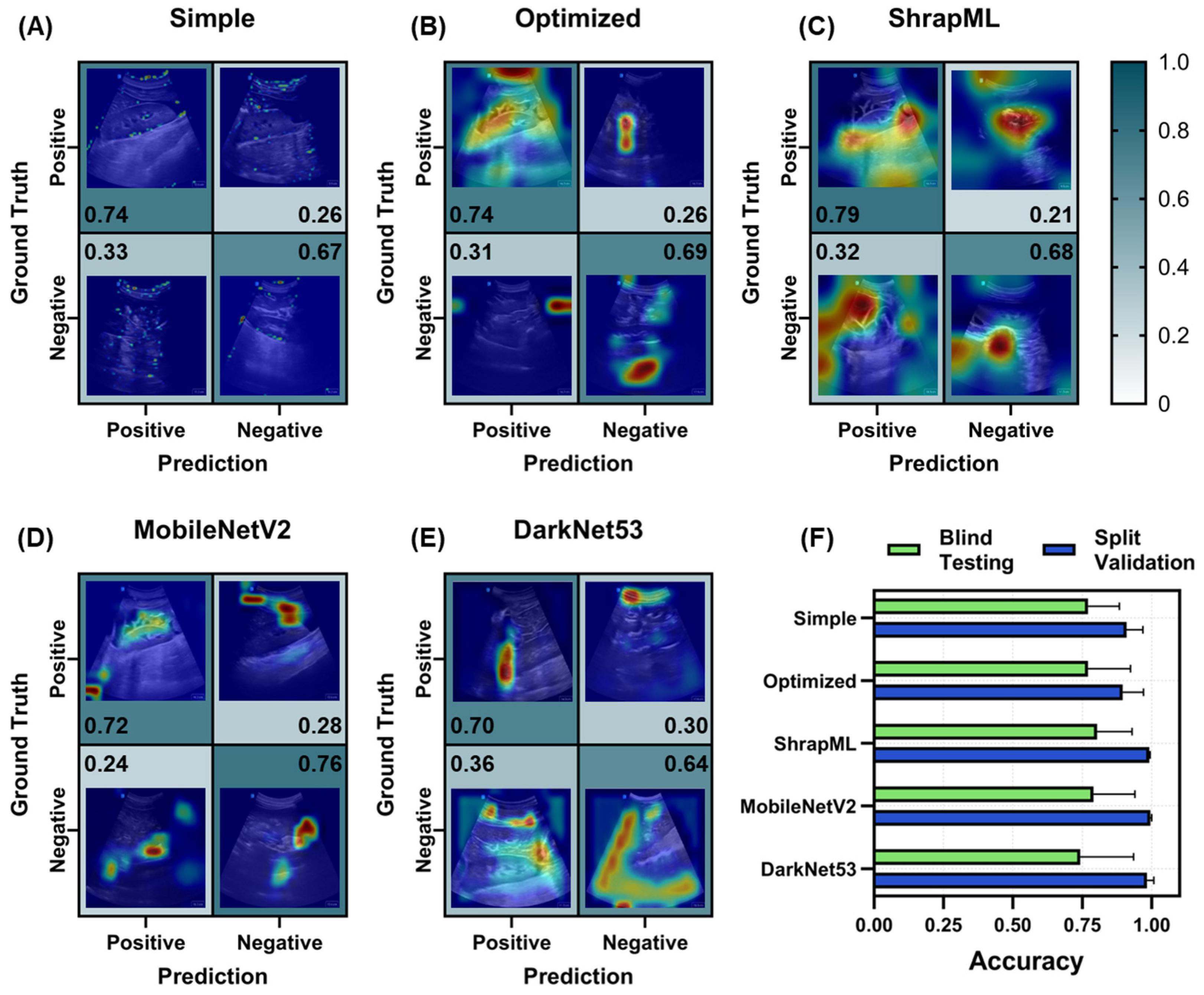
3.2. Evaluation of Different Model Architectures across eFAST Scan Points
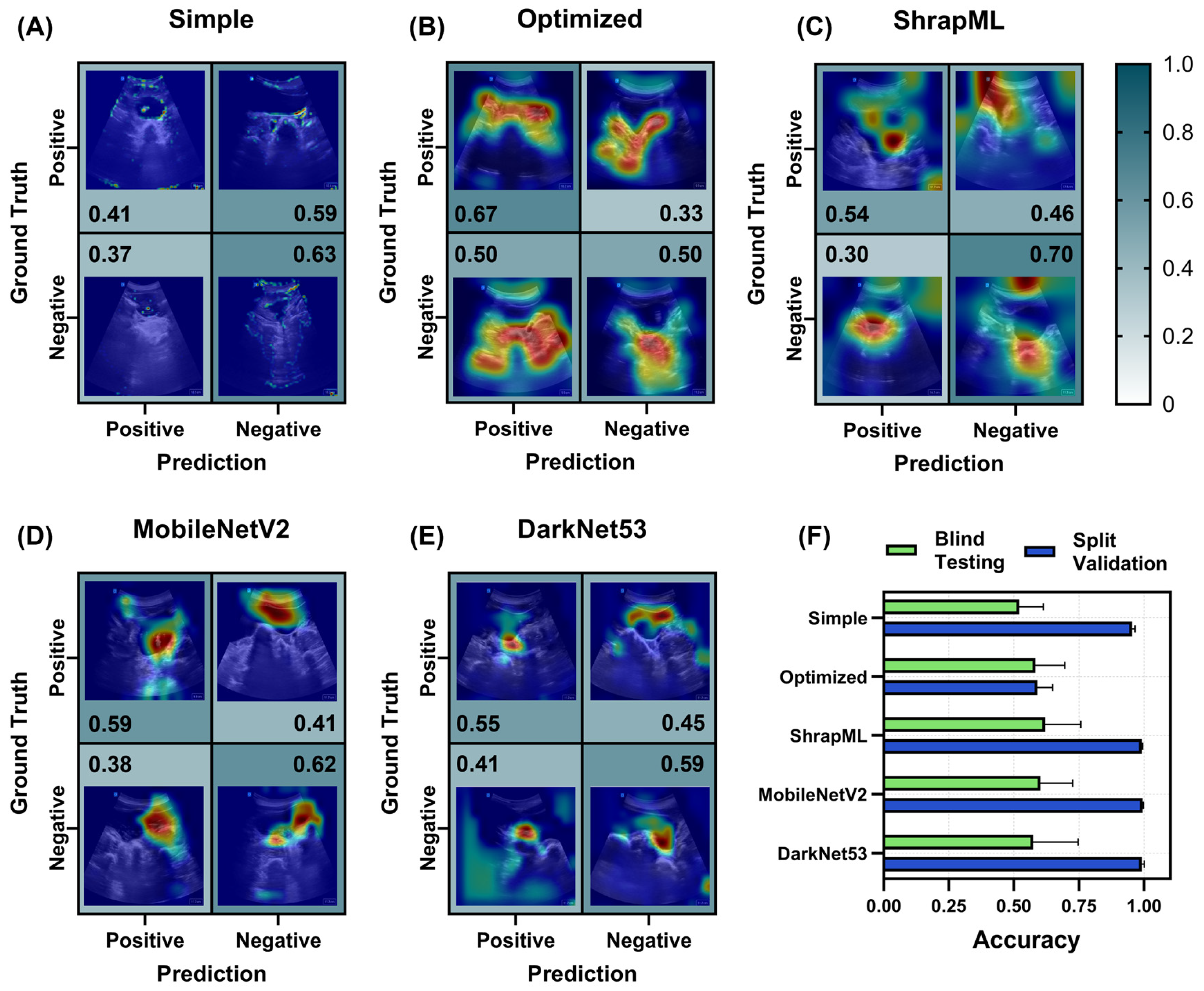
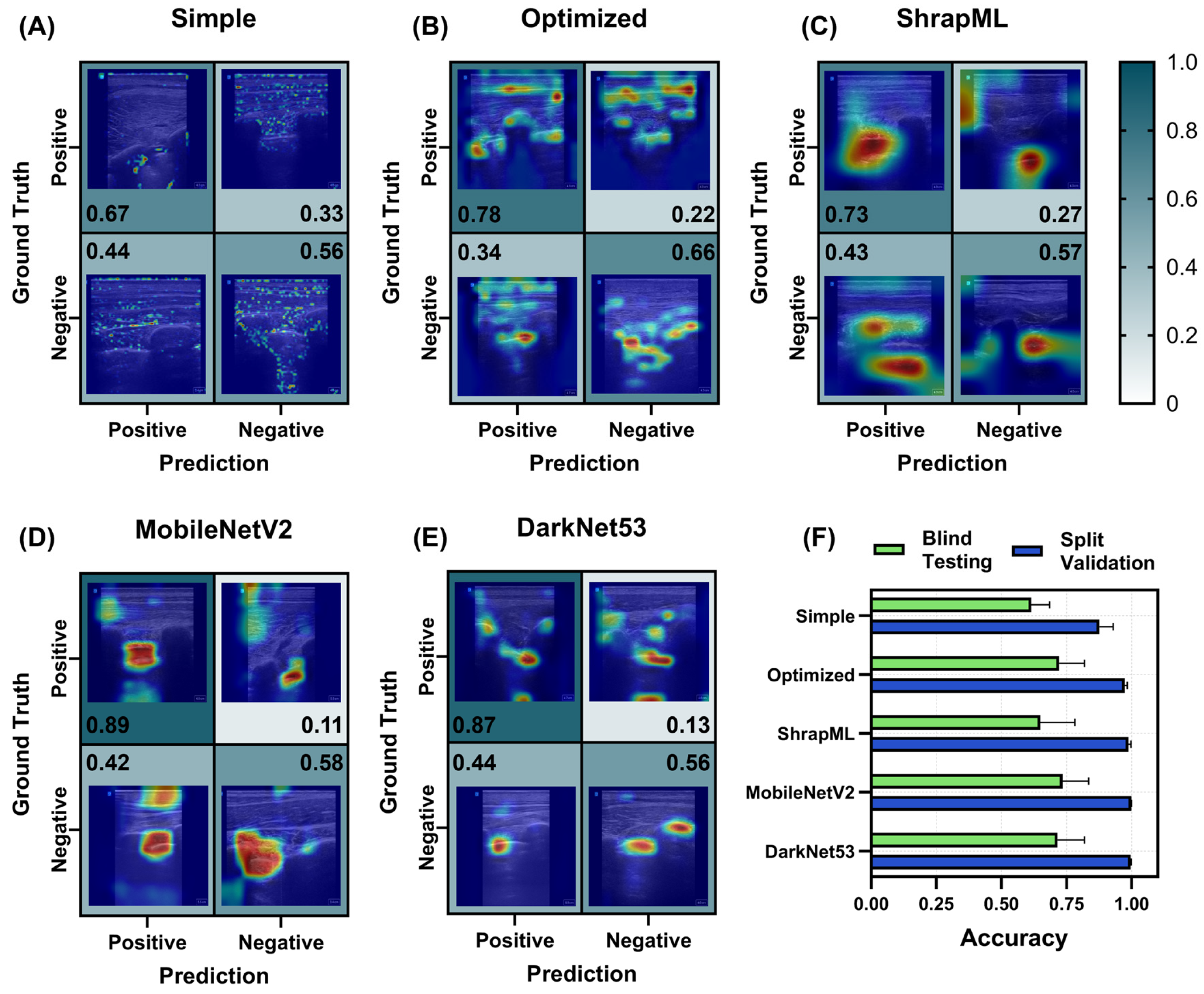
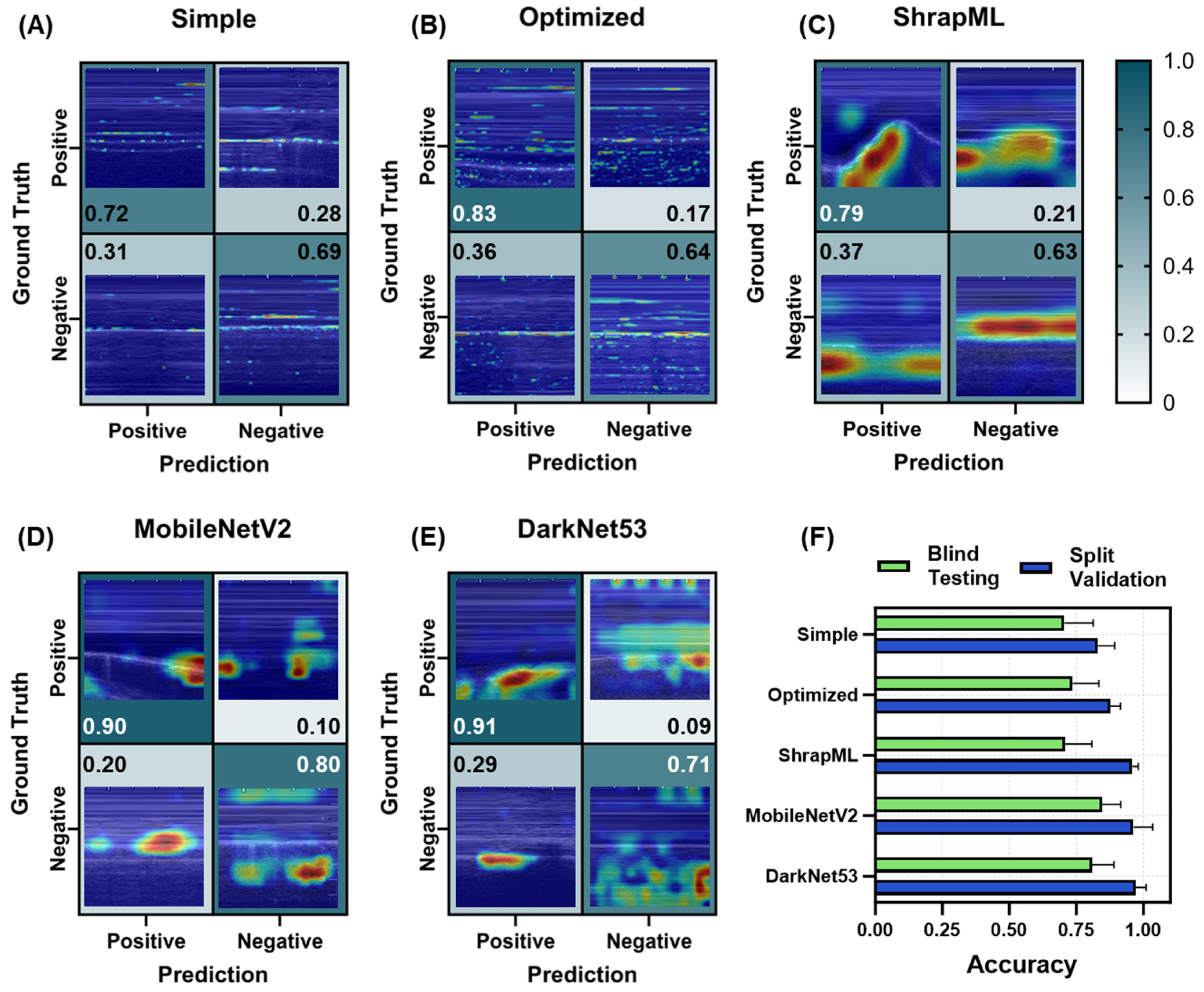
3.2.1. Right Upper Quadrant (RUQ) Models for Abdominal Hemorrhage Injury
3.2.2. Bladder (BLD) Models for Abdominal Hemorrhage Injury
3.2.3. Pneumothorax (PTX) Models for Thoracic Scan Site Injury
3.2.4. Hemothorax (HTX) Models for Thoracic Scan Site Injury
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Regulatory Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
DOD Disclaimer
References
- Iserson, K.V.; Moskop, J.C. Triage in Medicine, Part I: Concept, History, and Types. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2007, 49, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, S.; Lasher, W. The U.S. Army in Multi-Domain Operations 2028; U.S. Army: Arlington, VA, USA, 2018.
- Epstein, A.; Lim, R.; Johannigman, J.; Fox, C.J.; Inaba, K.; Vercruysse, G.A.; Thomas, R.W.; Martin, M.J.; Konstantyn, G.; Schwaitzberg, S.D.; et al. Putting Medical Boots on the Ground: Lessons from the War in Ukraine and Applications for Future Conflict with Near-Peer Adversaries. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2023, 237, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkpatrick, A.W.; Sirois, M.; Laupland, K.B.; Liu, D.; Rowan, K.; Ball, C.G.; Hameed, S.M.; Brown, R.; Simons, R.; Dulchavsky, S.A.; et al. Hand-Held Thoracic Sonography for Detecting Post-Traumatic Pneumothoraces: The Extended Focused Assessment With Sonography For Trauma (EFAST). J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2004, 57, 288–295. [Google Scholar]
- American College of Emergency Physicians Council Resolution on Ultrasound. ACEP News 1990, 9, 1–15.
- Basnet, S.; Shrestha, S.K.; Pradhan, A.; Shrestha, R.; Shrestha, A.P.; Sharma, G.; Bade, S.; Giri, L. Diagnostic Performance of the Extended Focused Assessment with Sonography for Trauma (EFAST) Patients in a Tertiary Care Hospital of Nepal. Trauma Surg. Acute Care Open 2020, 5, e000438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saposnik, G.; Redelmeier, D.; Ruff, C.C.; Tobler, P.N. Cognitive Biases Associated with Medical Decisions: A Systematic Review. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2016, 16, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alowais, S.A.; Alghamdi, S.S.; Alsuhebany, N.; Alqahtani, T.; Alshaya, A.I.; Almohareb, S.N.; Aldairem, A.; Alrashed, M.; Bin Saleh, K.; Badreldin, H.A.; et al. Revolutionizing Healthcare: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Practice. BMC Med. Educ. 2023, 23, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.; Fox, J.; Purohit, M.P. Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Healthcare Delivery. J. R. Soc. Med. 2019, 112, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajpurkar, P.; Chen, E.; Banerjee, O.; Topol, E.J. AI in Health and Medicine. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Jin, S.; Yan, Q.; Xu, H.; Luo, C.; Wei, L.; Zhao, W.; Hou, X.; Ma, W.; Xu, Z. AI-Assisted CT Imaging Analysis for COVID-19 Screening: Building and Deploying a Medical AI System. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 98, 106897. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Fu, F.; Zheng, B.; Bai, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wu, J.; Sun, L.; Liu, Q.; Liu, M.; Yang, Y. Development of an AI System for Accurately Diagnose Hepatocellular Carcinoma from Computed Tomography Imaging Data. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 125, 1111–1121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morales, M.A.; Manning, W.J.; Nezafat, R. Present and Future Innovations in AI and Cardiac MRI. Radiology 2024, 310, e231269. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zlochower, A.; Chow, D.S.; Chang, P.; Khatri, D.; Boockvar, J.A.; Filippi, C.G. Deep Learning AI Applications in the Imaging of Glioma. Top. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 29, 115-00. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barnett, M.; Wang, D.; Beadnall, H.; Bischof, A.; Brunacci, D.; Butzkueven, H.; Brown, J.W.L.; Cabezas, M.; Das, T.; Dugal, T. A Real-World Clinical Validation for AI-Based MRI Monitoring in Multiple Sclerosis. npj Digit. Med. 2023, 6, 196. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner, C.F.; Kamnitsas, K.; Matthew, J.; Fletcher, T.P.; Smith, S.; Koch, L.M.; Kainz, B.; Rueckert, D. SonoNet: Real-Time Detection and Localisation of Fetal Standard Scan Planes in Freehand Ultrasound. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 2204–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, S.; Li, F.; Funk, C.; Peethumangsin, E.; Morris, M.; Anderson, J.T.; Hersh, A.M.; Aylward, S. Detection of Pneumothorax on Ultrasound Using Artificial Intelligence. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2023, 94, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, M.; Sakai, A.; Dozen, A.; Shozu, K.; Yasutomi, S.; Machino, H.; Asada, K.; Kaneko, S.; Hamamoto, R. Towards Clinical Application of Artificial Intelligence in Ultrasound Imaging. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Extended Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma—PMC. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7807983/ (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Canelli, R.; Leo, M.; Mizelle, J.; Shrestha, G.S.; Patel, N.; Ortega, R. Use of eFAST in Patients with Injury to the Thorax or Abdomen. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximus, S.; Figueroa, C.; Whealon, M.; Pham, J.; Kuncir, E.; Barrios, C. eFAST for Pneumothorax: Real-Life Application in an Urban Level 1 Center by Trauma Team Members. Am. Surg. 2018, 84, 220–224. [Google Scholar]
- Boice, E.N.; Hernandez-Torres, S.I.; Knowlton, Z.J.; Berard, D.; Gonzalez, J.M.; Snider, E.J. Training Ultrasound Image Classification Deep-Learning Algorithms for Pneumothorax Detection Using a Synthetic Tissue Phantom. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Image Classification|TensorFlow Core. Available online: https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/images/classification (accessed on 4 March 2024).
- Kurbiel, T.; Khaleghian, S. Training of Deep Neural Networks Based on Distance Measures Using RMSProp. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1708.01911. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, K.P. Machine Learning: A Probabilistic Perspective; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-0-262-01802-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ramezani-Kebrya, A.; Khisti, A.; Liang, B. On the Generalization of Stochastic Gradient Descent with Momentum. arXiv 2021, arXiv:1809.04564. [Google Scholar]
- Postalcıoğlu, S. Performance Analysis of Different Optimizers for Deep Learning-Based Image Recognition. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 2051003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A Simple Way to Prevent Neural Networks from Overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Chen, X.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, L.-D.; Lei, H.; Deng, S.-H. Hyperparameter Optimization for Machine Learning Models Based on Bayesian Optimizationb. J. Electron. Sci. Technol. 2019, 17, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholamiangonabadi, D.; Kiselov, N.; Grolinger, K. Deep Neural Networks for Human Activity Recognition With Wearable Sensors: Leave-One-Subject-Out Cross-Validation for Model Selection. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 133982–133994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Torres, S.I.; Bedolla, C.; Berard, D.; Snider, E.J. An Extended Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma Ultrasound Tissue-Mimicking Phantom for Developing Automated Diagnostic Technologies. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1244616. [Google Scholar]
- Snider, E.J.; Hernandez-Torres, S.I.; Boice, E.N. An Image Classification Deep-Learning Algorithm for Shrapnel Detection from Ultrasound Images. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.-C. MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boice, E.N.; Hernandez-Torres, S.I.; Snider, E.J. Comparison of Ultrasound Image Classifier Deep Learning Algorithms for Shrapnel Detection. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-Cam: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-Based Localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Saul, T.; Siadecki, S.D.; Berkowitz, R.; Rose, G.; Matilsky, D.; Sauler, A. M-Mode Ultrasound Applications for the Emergency Medicine Physician. J. Emerg. Med. 2015, 49, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elboushaki, A.; Hannane, R.; Afdel, K.; Koutti, L. MultiD-CNN: A Multi-Dimensional Feature Learning Approach Based on Deep Convolutional Networks for Gesture Recognition in RGB-D Image Sequences. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 139, 112829. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, R.J.; Sharma, U.; Kaur, K.; Kadhim, N.M.; Lamin, M.; Ayipeh, C.S. Multidimensional CNN-Based Deep Segmentation Method for Tumor Identification. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 5061112. [Google Scholar]
- Azizi, S.; Bayat, S.; Yan, P.; Tahmasebi, A.; Kwak, J.T.; Xu, S.; Turkbey, B.; Choyke, P.; Pinto, P.; Wood, B. Deep Recurrent Neural Networks for Prostate Cancer Detection: Analysis of Temporal Enhanced Ultrasound. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 2695–2703. [Google Scholar]
- Güler, İ.; Übeyli, E.D. A Recurrent Neural Network Classifier for Doppler Ultrasound Blood Flow Signals. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2006, 27, 1560–1571. [Google Scholar]
- Chlap, P.; Min, H.; Vandenberg, N.; Dowling, J.; Holloway, L.; Haworth, A. A Review of Medical Image Data Augmentation Techniques for Deep Learning Applications. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 65, 545–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikołajczyk, A.; Grochowski, M. Data Augmentation for Improving Deep Learning in Image Classification Problem. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Interdisciplinary PhD Workshop (IIPhDW), Swinoujscie, Poland, 9–12 May 2018; pp. 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Amezcua, K.-L.; Collier, J.; Lopez, M.; Hernandez Torres, S.I.; Ruiz, A.; Gathright, R.; Snider, E.J. Design and Testing of Ultrasound Probe Adapters for a Robotic Imaging Platform. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5102. [Google Scholar]
- Abolmaesumi, P.; Salcudean, S.E.; Zhu, W.H.; DiMaio, S.P.; Sirouspour, M.R. A User Interface for Robot-Assisted Diagnostic Ultrasound. In Proceedings of the 2001 ICRA—IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No.01CH37164), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 21–26 May 2001; Volume 2, pp. 1549–1554. [Google Scholar]
- Farshad-Amacker, N.A.; Bay, T.; Rosskopf, A.B.; Spirig, J.M.; Wanivenhaus, F.; Pfirrmann, C.W.A.; Farshad, M. Ultrasound-Guided Interventions with Augmented Reality in Situ Visualisation: A Proof-of-Mechanism Phantom Study. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2020, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
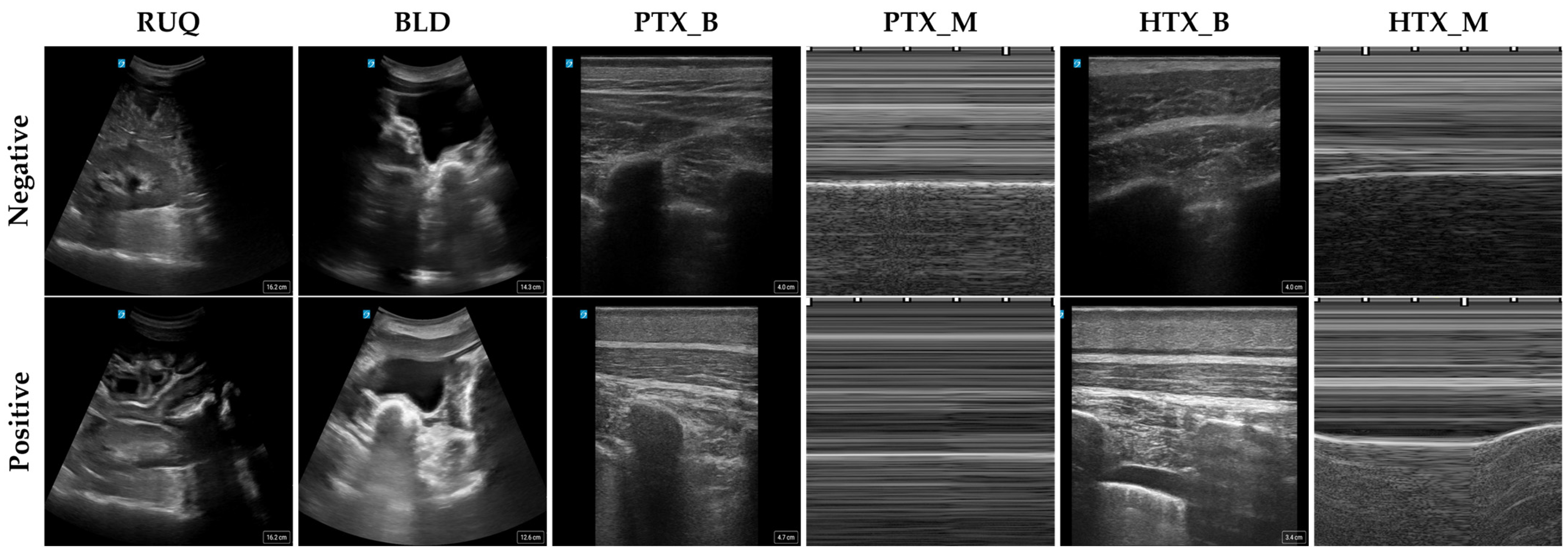



| Scan Point | RUQ | BLD | PTX_B | PTX_M | HTX_B | HTX_M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive Images | 30,000 | 20,845 | 34,957 | 4525 | 76,431 | 9368 |
| Negative Images | 31,396 | 22,049 | 54,420 | 6425 | 54,420 | 6425 |
| Total Number of Images | 61,396 | 42,894 | 89,377 | 10,950 | 130,851 | 15,793 |
| Subjects | 25 | 21 | 22 | 20 | 25 | 25 |
| Batch Size | Optimizer | Learning Rate | Activator | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUQ | 16 | RMSprop | 0.0001 | softmax |
| BLD | 16 | RMSprop | 0.001 | softplus |
| PTX_B | 16 | ADAM | 0.001 | softmax |
| PTX_M | 16 | ADAM | 0.0001 | softmax |
| HTX_B | 64 | RMSprop | 0.0001 | softmax |
| HTX_M | 16 | ADAM | 0.0001 | softmax |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernandez Torres, S.I.; Ruiz, A.; Holland, L.; Ortiz, R.; Snider, E.J. Evaluation of Deep Learning Model Architectures for Point-of-Care Ultrasound Diagnostics. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11040392
Hernandez Torres SI, Ruiz A, Holland L, Ortiz R, Snider EJ. Evaluation of Deep Learning Model Architectures for Point-of-Care Ultrasound Diagnostics. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(4):392. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11040392
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernandez Torres, Sofia I., Austin Ruiz, Lawrence Holland, Ryan Ortiz, and Eric J. Snider. 2024. "Evaluation of Deep Learning Model Architectures for Point-of-Care Ultrasound Diagnostics" Bioengineering 11, no. 4: 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11040392
APA StyleHernandez Torres, S. I., Ruiz, A., Holland, L., Ortiz, R., & Snider, E. J. (2024). Evaluation of Deep Learning Model Architectures for Point-of-Care Ultrasound Diagnostics. Bioengineering, 11(4), 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11040392








