The Role of Treatment-Related Parameters and Brain Morphology in the Lesion Volume of Magnetic-Resonance-Guided Focused Ultrasound Thalamotomy in Patients with Tremor-Dominant Neurological Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials & Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. CT Protocol
2.3. MRI Scanning Protocols
2.4. MRgFUS Treatment
2.5. Clinical Measures
2.6. Brain Volumetric Quantification
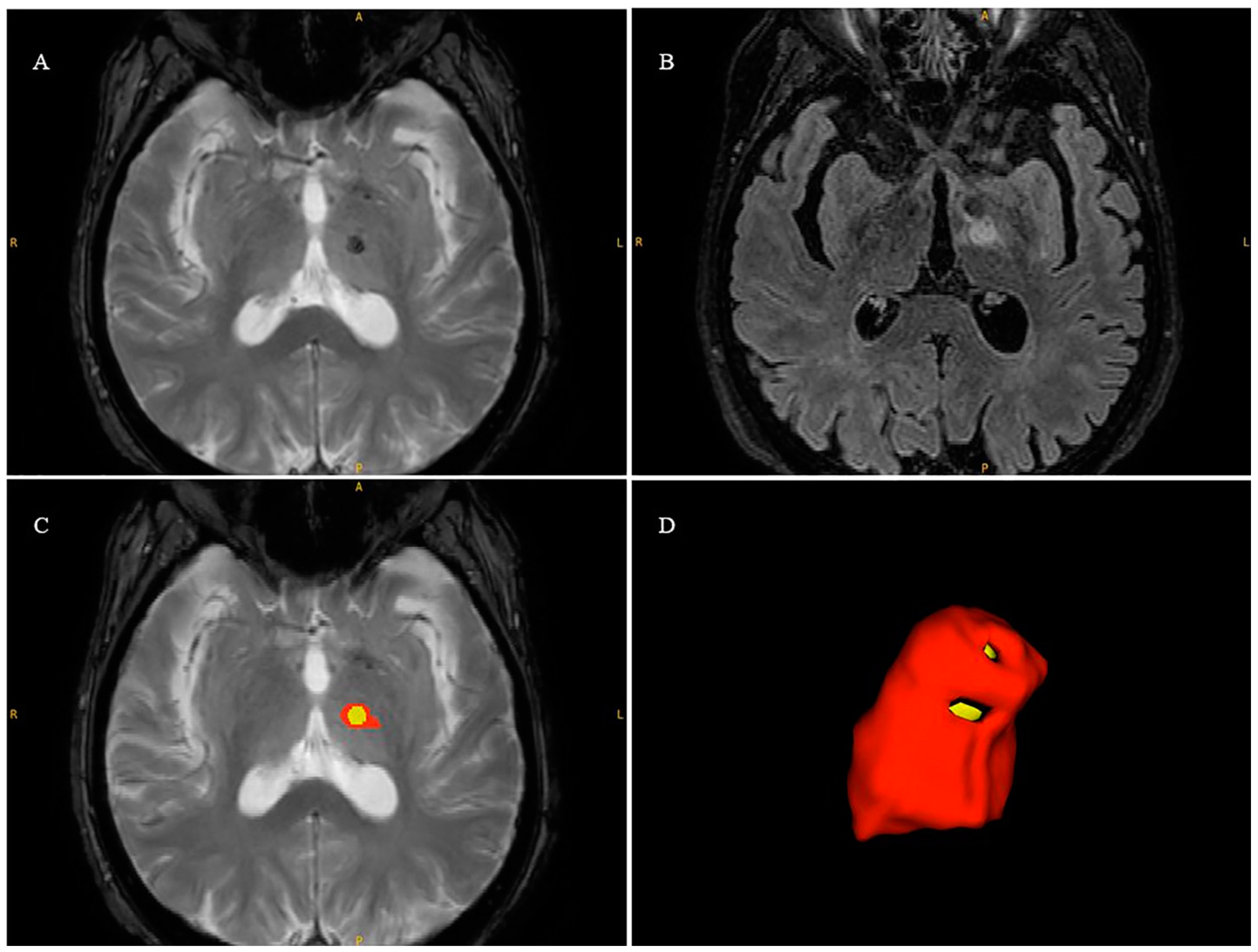
2.7. Lesion Volume Segmentation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Brain Structural and Radiological Data
3.2. Clinical Data
3.3. Regression Analyses
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heusinkveld, L.E.; Hacker, M.L.; Turchan, M.; Davis, T.L.; Charles, D. Impact of Tremor on Patients with Early Stage Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, W.J.; Lipsman, N.; Ondo, W.G.; Ghanouni, P.; Kim, Y.G.; Lee, W.; Schwartz, M.; Hynynen, K.; Lozano, A.M.; Shah, B.B.; et al. A Randomized Trial of Focused Ultrasound Thalamotomy for Essential Tremor. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDannold, N.J.; King, R.L.; Jolesz, F.A.; Hynynen, K.H. Usefulness of MR Imaging-Derived Thermometry and Dosimetry in Determining the Threshold for Tissue Damage Induced by Thermal Surgery in Rabbits. Radiology 2000, 216, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuurman, P.R.; Bosch, D.A.; Merkus, M.P.; Speelman, J.D. Long-term follow-up of thalamic stimulation versus thalamotomy for tremor suppression. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsman, N.; Schwartz, M.L.; Huang, Y.; Lee, L.; Sankar, T.; Chapman, M.; Hynynen, K.; Lozano, A.M. MR-guided focused ultrasound thalamotomy for essential tremor: A proof-of-concept study. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.S.; Jung, H.H.; Zadicario, E.; Rachmilevitch, I.; Tlusty, T.; Vitek, S.; Chang, J.W. Factors associated with successful magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound treatment: Efficiency of acoustic energy delivery through the skull. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 124, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagliardo, C.; Cannella, R.; Filorizzo, G.; Toia, P.; Salvaggio, G.; Collura, G.; Pignolo, A.; Maugeri, R.; Napoli, A.; D’Amelio, M.; et al. Preoperative imaging findings in patients undergoing transcranial magnetic resonance imaging-guided focused ultrasound thalamotomy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.W.; Park, Y.-S.; Chang, J.W. Skull Factors Affecting Outcomes of Magnetic Resonance-Guided Focused Ultrasound for Patients with Essential Tremor. Yonsei Med. J. 2019, 60, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’souza, M.; Chen, K.S.; Rosenberg, J.; Elias, W.J.; Eisenberg, H.M.; Gwinn, R.; Taira, T.; Chang, J.W.; Lipsman, N.; Krishna, V.; et al. Impact of skull density ratio on efficacy and safety of magnetic resonance–guided focused ultrasound treatment of essential tremor. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 132, 1392–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinai, A.; Nassar, M.; Eran, A.; Constantinescu, M.; Zaaroor, M.; Sprecher, E.; Schlesinger, I. Magnetic resonance–guided focused ultrasound thalamotomy for essential tremor: A 5-year single-center experience. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 133, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, F.; Tommasino, E.; Pertici, L.; Pagliei, V.; Gagliardi, A.; Catalucci, A.; Arrigoni, F.; Palumbo, P.; Sucapane, P.; Pistoia, F.; et al. MRgFUS thalamotomy for the treatment of tremor: Evaluation of learning curve and operator’s experience impact on the procedural and clinical outcome. Acta Neurochir. 2023, 165, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, K.; Ito, H.; Fukutake, S.; Odo, T.; Kamei, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Taira, T. Factors Associated with Heating Efficiency in Transcranial Focused Ultrasound Therapy. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2020, 60, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Lipsman, N.; Schwartz, M.L.; Krishna, V.; Sammartino, F.; Lozano, A.M.; Hynynen, K. Predicting lesion size by accumulated thermal dose in MR-guided focused ultrasound for essential tremor. Med. Phys. 2018, 45, 4704–4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond, A.E.; Elias, W.J. Predicting lesion size during focused ultrasound thalamotomy: A review of 63 lesions over 3 clinical trials. Neurosurg. Focus 2018, 44, E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, K.P.; Bain, P.; Bajaj, N.; Elble, R.J.; Hallett, M.; Louis, E.D.; Raethjen, J.; Stamelou, M.; Testa, C.M.; Deuschl, G.; et al. Consensus Statement on the classification of tremors. from the task force on tremor of the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defer, G.L.; Widner, H.; Marié, R.M.; Rémy, P.; Levivier, M. Core assessment program for surgical interventional therapies in Parkinson’s disease (CAPSIT-PD). Mov. Disord. 1999, 14, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, J.; Goyal, A.; Kaufmann, T.J.; Jackson, L.M.; Miller, K.J.; Klassen, B.T.; Dhawan, N.; Lee, K.H.; Lehman, V.T. Comparison of the impact of skull density ratio with alternative skull metrics on magnetic resonance–guided focused ultrasound thalamotomy for tremor. J. Neurosurg. 2022, 138, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, A. Stereotactic Atlas of the Human Thalamus and Basal Ganglia; Informa Healthcare: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Moser, D.; Zadicario, E.; Schiff, G.; Jeanmonod, D. Measurement of targeting accuracy in focused ultrasound functional neurosurgery. Neurosurg. Focus 2012, 32, E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoehn, M.M.; Yahr, M.D. Parkinsonism onset, progression, and mortality. Neurology 1967, 17, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahn, S.; Tolosa, E.; Conceppcion, M. Clinical rating scale for tremor. In Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders; Jankovic, J., Tolosa, E., Eds.; Williams and Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1993; pp. 271–280. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, J.H.; Jolly, A.; De Simoni, S.; Bourke, N.; Patel, M.C.; Scott, G.; Sharp, D.J. Spatial patterns of progressive brain volume loss after moderate-severe traumatic brain injury. Brain 2018, 141, 822–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahnke, R.; Yotter, R.A.; Gaser, C. Cortical thickness and central surface estimation. NeuroImage 2013, 65, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yotter, R.A.; Dahnke, R.; Thompson, P.M.; Gaser, C. Topological correction of brain surface meshes using spherical harmonics. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2011, 32, 1109–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazekas, F.; Chawluk, J.B.; Alavi, A.; Hurtig, H.I.; Zimmerman, R.A. MR signal abnormalities at 1.5 T in Alzheimer’s dementia and normal aging. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1987, 149, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yushkevich, P.A.; Pashchinskiy, A.; Oguz, I.; Mohan, S.; Schmitt, J.E.; Stein, J.M.; Zukić, D.; Vicory, J.; McCormick, M.; Yushkevich, N.; et al. User-Guided Segmentation of Multi-modality Medical Imaging Datasets with ITK-SNAP. Neuroinformatics 2019, 17, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dempster, A.P.; Laird, N.M.; Rubin, D.B. Maximum Likelihood from Incomplete Data Via the EM Algorithm. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1977, 39, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, G.R.; Lipsman, N.; Lozano, A.M.; Chang, J.W.; Halpern, C.; Ghanouni, P.; Eisenberg, H.; Fishman, P.; Taira, T.; Schwartz, M.L.; et al. Magnetic resonance imaging-guided focused ultrasound thalamotomy for essential tremor: 5-year follow-up results. J. Neurosurg. 2022, 138, 1028–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapareto, S.A.; Dewey, W.C. Thermal dose determination in cancer therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1984, 10, 787–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, M.; Garg, K.; Samala, R.; Rajan, R.; Naik, V.; Singh, M. Outcome and Complications of MR Guided Focused Ultrasound for Essential Tremor: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 654711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda-Pardo, J.A.; Urso, D.; Martínez-Fernández, R.; Rodríguez-Rojas, R.; Del-Alamo, M.; Millar Vernetti, P.; Máñez-Miró, J.U.; Hernández-Fernández, F.; de Luis-Pastor, E.; Vela-Desojo, L.; et al. Transcranial Magnetic Resonance-Guided Focused Ultrasound Thalamotomy in Essential Tremor: A Comprehensive Lesion Characterization. Neurosurgery 2020, 87, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutet, A.; Ranjan, M.; Zhong, J.; Germann, J.; Xu, D.; Schwartz, M.L.; Lipsman, N.; Hynynen, K.; Devenyi, G.A.; Chakravarty, M.; et al. Focused ultrasound thalamotomy location determines clinical benefits in patients with essential tremor. Brain 2018, 141, 3405–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.I.; Chaibainou, H.; Wang, S.; Hitti, F.L.; McShane, B.J.; Tilden, D.; Korn, M.; Blanke, A.; Dayan, M.; Wolf, R.L.; et al. Focused Ultrasound Thalamotomy for Essential Tremor in the Setting of a Ventricular Shunt: Technical Report. Neurosurgery 2019, 17, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.M.; Kamps, S.; Huang, Y.; Scantlebury, N.; Lipsman, N.; Schwartz, M.L.; Hynynen, K. Accumulated thermal dose in MRI-guided focused ultrasound for essential tremor: Repeated sonications with low focal temperatures. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 132, 1802–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Fernández, R.; Pineda-Pardo, J.A. Magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound for movement disorders: Clinical and neuroimaging advances. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2020, 33, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaeijo, S.M.; Hashemi, B.; Mofid, B.; Bakhshandeh, M.; Mahdavi, A.; Hashemi, M.S. The feasibility of a dose painting procedure to treat prostate cancer based on mpMR images and hierarchical clustering. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 16, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanfari, H.; Mehranfar, S.; Cheki, M.; Sadr, M.M.; Moniri, S.; Heydarheydari, S.; Rezaeijo, S.M. Exploring the efficacy of multi-flavored feature extraction with radiomics and deep features for prostate cancer grading on mpMRI. BMC Med. Imaging 2023, 23, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Tremor-Dominant Patients (N°36) | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|
| Normalized GM Volume (cm3) | 326.3 ± 35.3 |
| Normalized WM Volume (cm3) | 292.8 ± 41.3 |
| Normalized CSF Volume (cm3) | 377.5 ± 49.6 |
| Normalized Brain Volume (GM + WM) (cm3) | 619.1 ± 48.4 |
| Total Cortical Thickness (mm) | 2.61 ± 0.2 |
| Fazekas Scale | 3 [0–7] |
| Tremor-Dominant Patients (N°36) | Mean ± SD Values |
|---|---|
| SDR | 0.49 ± 0.12 |
| Skull Area (cm) | 338.6 ± 31.3 |
| N° of Transducer Elements | 906.6 ± 66.2 |
| N° of Sonications | 6.9 ± 2.1 |
| Maximal Watt | 896.3 ± 139.5 |
| Maximal Joule | 17673.6 ± 7413.7 |
| Maximal Temperature (T°C_max) | 57.4 ± 3.4 |
| Maximal Sonication Time (s) | 22.9 ± 7.5 |
| ATD | 56 ± 2.9 |
| I° Rater | II° Rater | ICC | Mean Dice | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Edema Volume (cm3) | 1607.24 ± 705.5 | 2042.76 ± 895.92 | 0.81 | 0.74 ± 0.13 |
| Necrosis Volume (cm3) | 179.31 ± 135.72 | 153.35 ± 118.56 | 0.88 | 0.70 ± 0.11 |
| Predictors for Necrosis Volume | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N° Model | R | R2 | Variable | Standardized β Coefficients | t-Value | p-Value |
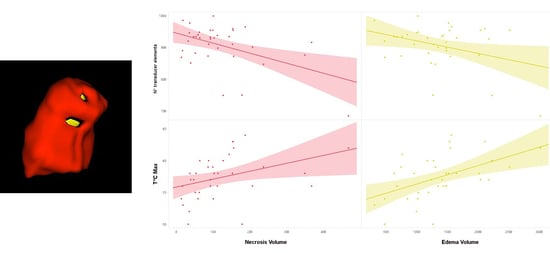
| Model 1 | 0.484 | 0.234 | N° transducer elements | −0.484 | −3.22 | 0.003 |
| Model 2 | 0.595 | 0.354 | N° transducer elements | −0.466 | −3.32 | 0.002 |
| T°C_max | 0.346 | 2.47 | 0.02 | |||
| Model 3 | 0.664 | 0.44 | N° transducer elements | −0.441 | −3.32 | 0.002 |
| T°C_max | 0.345 | 2.61 | 0.01 | |||
| Normalized WM Volume | 0.295 | 2.23 | 0.03 | |||
| Predictors for Edema Volume | ||||||
| Model 1 | 0.508 | 0.258 | T°C_max | 0.508 | 3.44 | 0.002 |
| Model 2 | 0.606 | 0.368 | T°C_max | 0.491 | 3.54 | 0.001 |
| N° transducer elements | −0.331 | −2.39 | 0.023 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morabito, R.; Cammaroto, S.; Militi, A.; Smorto, C.; Anfuso, C.; Lavano, A.; Tomasello, F.; Di Lorenzo, G.; Brigandì, A.; Sorbera, C.; et al. The Role of Treatment-Related Parameters and Brain Morphology in the Lesion Volume of Magnetic-Resonance-Guided Focused Ultrasound Thalamotomy in Patients with Tremor-Dominant Neurological Conditions. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11040373
Morabito R, Cammaroto S, Militi A, Smorto C, Anfuso C, Lavano A, Tomasello F, Di Lorenzo G, Brigandì A, Sorbera C, et al. The Role of Treatment-Related Parameters and Brain Morphology in the Lesion Volume of Magnetic-Resonance-Guided Focused Ultrasound Thalamotomy in Patients with Tremor-Dominant Neurological Conditions. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(4):373. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11040373
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorabito, Rosa, Simona Cammaroto, Annalisa Militi, Chiara Smorto, Carmelo Anfuso, Angelo Lavano, Francesco Tomasello, Giuseppe Di Lorenzo, Amelia Brigandì, Chiara Sorbera, and et al. 2024. "The Role of Treatment-Related Parameters and Brain Morphology in the Lesion Volume of Magnetic-Resonance-Guided Focused Ultrasound Thalamotomy in Patients with Tremor-Dominant Neurological Conditions" Bioengineering 11, no. 4: 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11040373
APA StyleMorabito, R., Cammaroto, S., Militi, A., Smorto, C., Anfuso, C., Lavano, A., Tomasello, F., Di Lorenzo, G., Brigandì, A., Sorbera, C., Bonanno, L., Ielo, A., Vatrano, M., Marino, S., Cacciola, A., Cerasa, A., & Quartarone, A. (2024). The Role of Treatment-Related Parameters and Brain Morphology in the Lesion Volume of Magnetic-Resonance-Guided Focused Ultrasound Thalamotomy in Patients with Tremor-Dominant Neurological Conditions. Bioengineering, 11(4), 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11040373