Evaluation of Different Procedures for Titanium Dental Implant Surface Decontamination—In Vitro Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
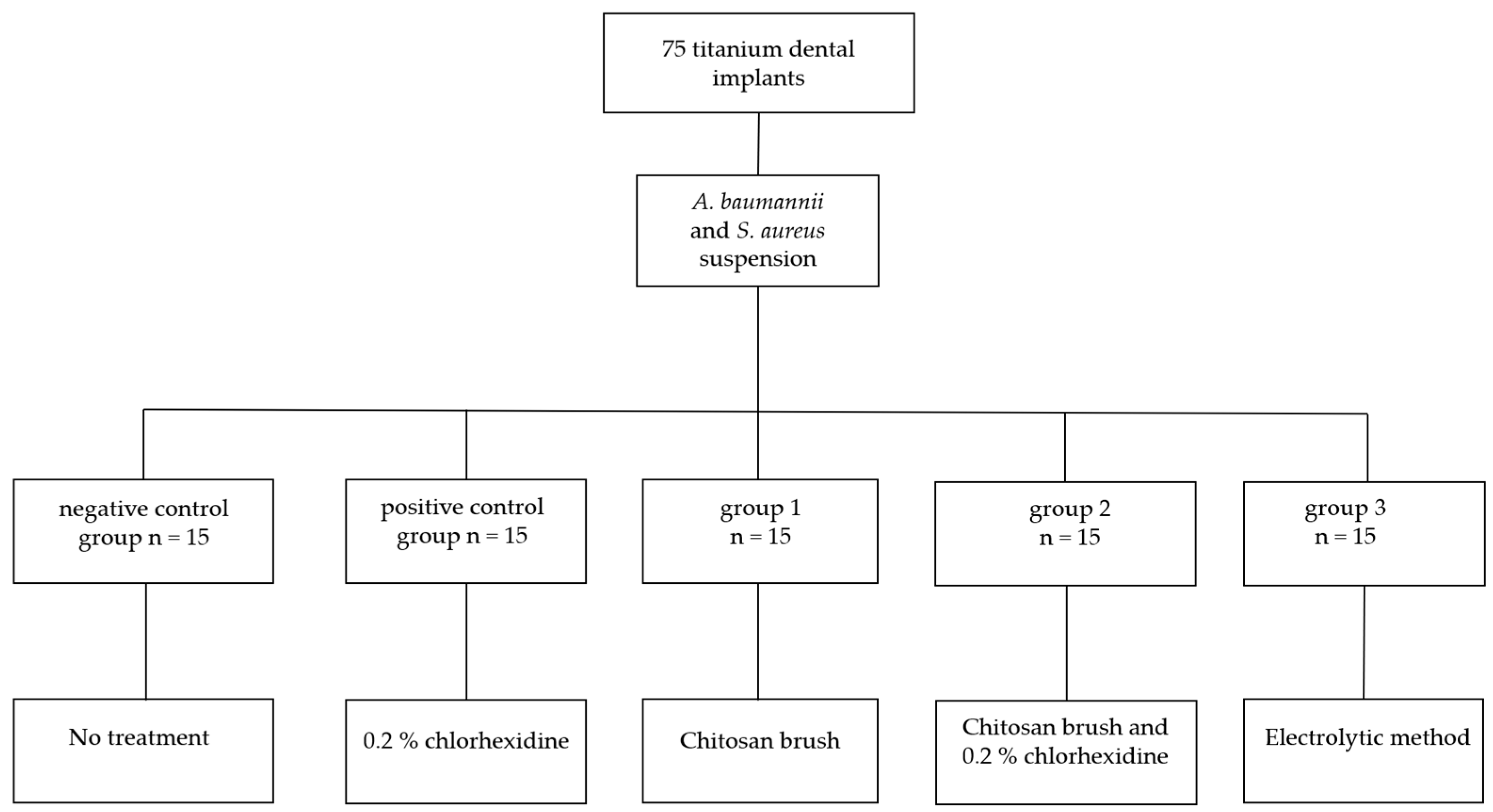
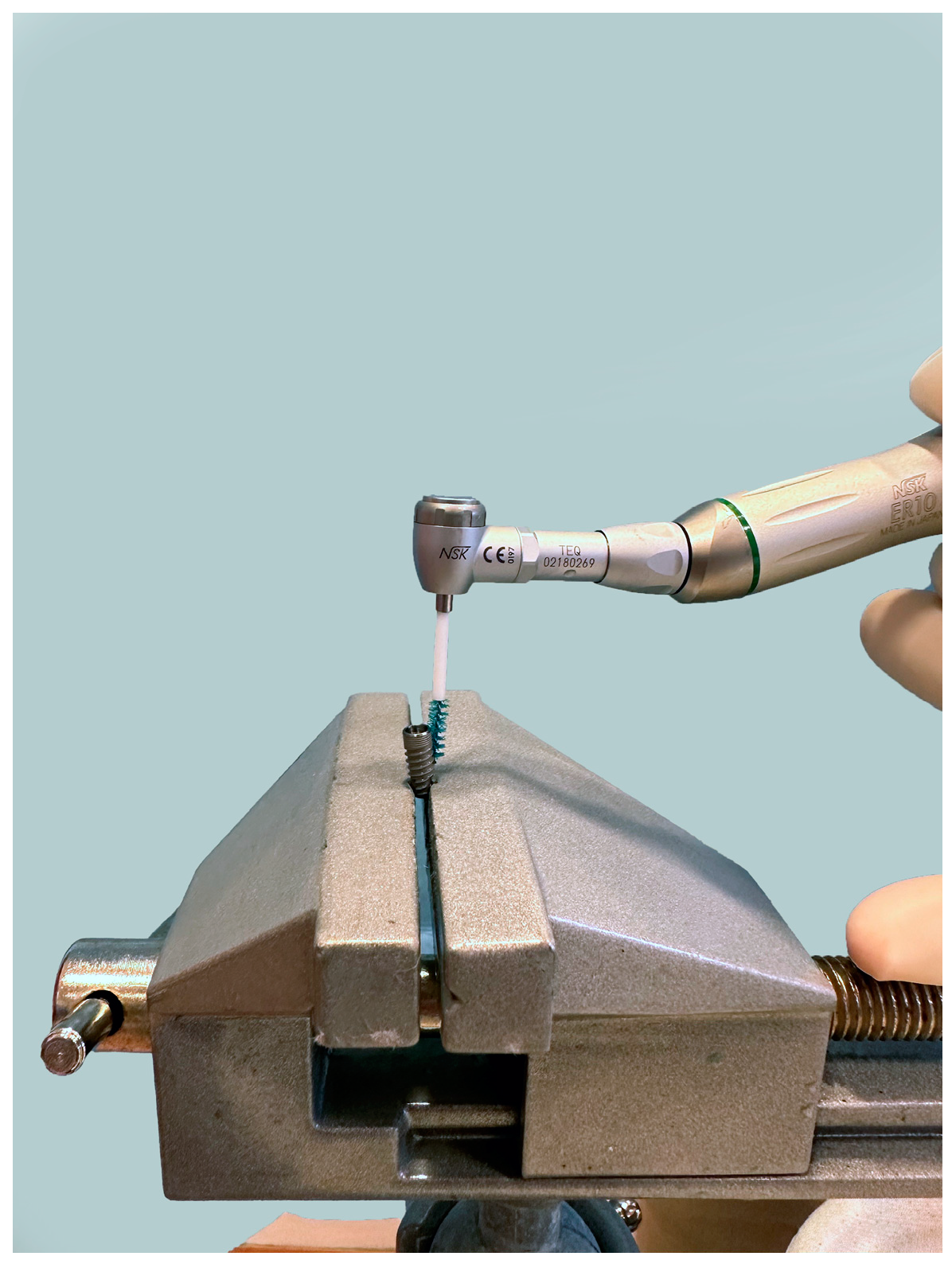
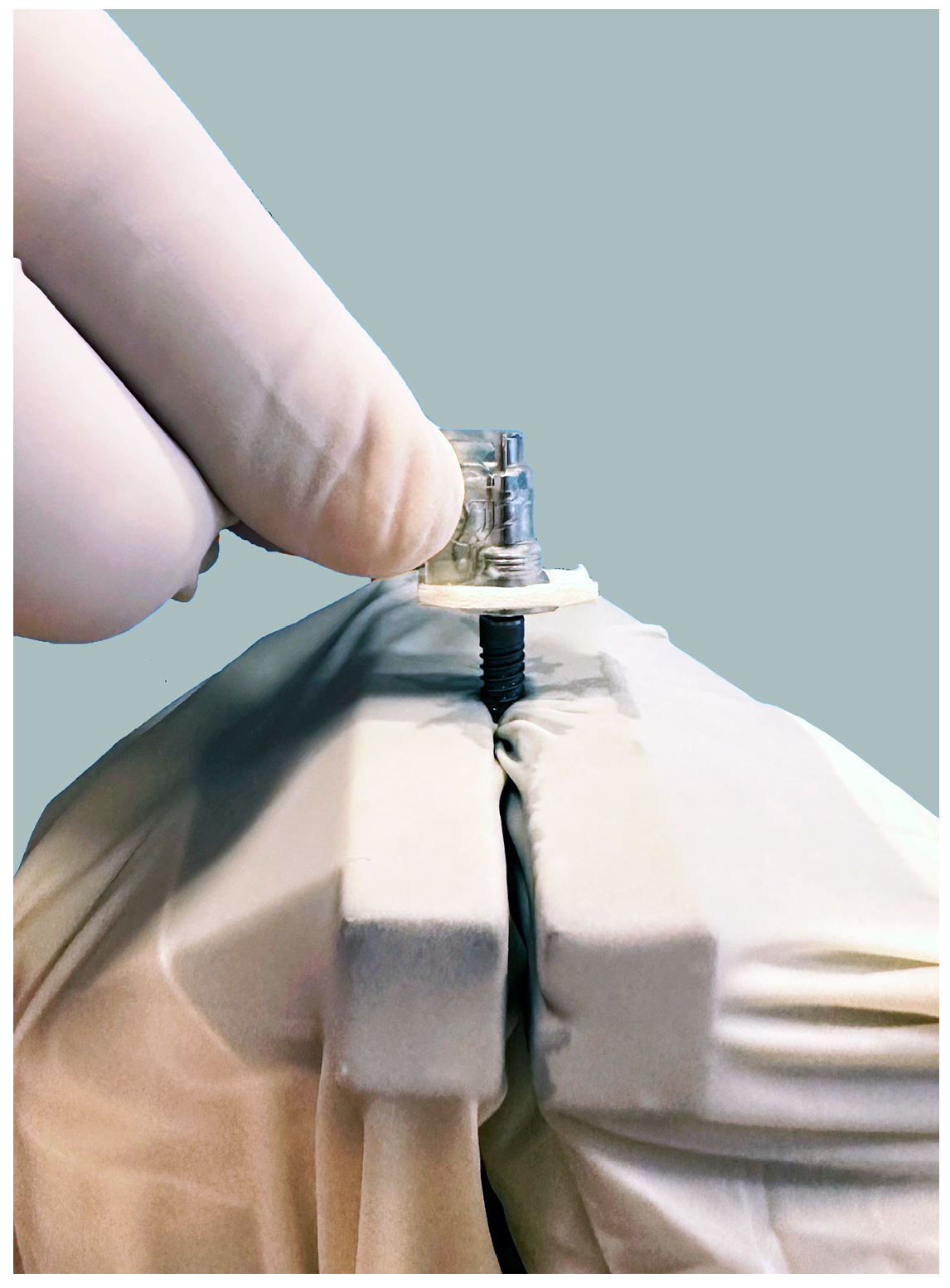
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diaz, P.; Gonzalo, E.; Villagra, L.J.G.; Miegimolle, B.; Suarez, M.J. What is the prevalence of peri-implantitis? A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickenig, H.J.; Terheyden, H.; Reich, R.H.; Kreppel, M.; Linz, C.; Lentzen, M.P. Oral health-related quality of life (OHRQoL) and implant therapy: A prospective multicenter study of preoperative, intermediate, and posttreatment assessment. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2024, 52, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monje, A.; Amerio, E.; Cha, J.K.; Kotsakis, G.; Pons, R.; Renvert, S.; Sanz-Martin, I.; Schwarz, F.; Sculean, A.; Stavropoulos, A.; et al. Strategies for implant surface decontamination in peri-implantitis therapy. Int. J. Oral Implantol. 2022, 15, 213–248. [Google Scholar]
- Sartoretto, S.C.; Shibli, J.A.; Javid, K.; Cotrim, K.; Canabarro, A.; Louro, R.S.; Lowenstein, A.; Mourão, C.F.; Moraschini, V. Comparing the Long-Term Success Rates of Tooth Preservation and Dental Implants: A Critical Review. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.H.; Kang, J. Diagnosis and Treatment of Periimplant Mucositis and Periimplantitis: An Overview and Related Controversial Issues. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2024, 68, 167–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglundh, T.; Armitage, G.; Araujo, M.G.; Avila-Ortiz, G.; Blanco, J.; Camargo, P.M.; Chen, S.; Cochran, D.; Derks, J.; Figuero, E.; et al. Peri-implant diseases and conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 4 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglundh, T.; Mombelli, A.; Schwarz, F.; Derks, J. Etiology, pathogenesis and treatment of peri-implantitis: A European perspective. Periodontology 2000 2024, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahrmann, P.; Gilli, F.; Wiedemeier, D.B.; Attin, T.; Schmidlin, P.R.; Karygianni, L. The Microbiome of Peri-Implantitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banu Raza, F.; Vijayaragavalu, S.; Kandasamy, R.; Krishnaswami, V.; Kumar, V.A. Microbiome and the inflammatory pathway in peri-implant health and disease with an updated review on treatment strategies. J. Oral. Biol. Craniofac. Res. 2023, 13, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butera, A.; Pascadopoli, M.; Pellegrini, M.; Gallo, S.; Zampetti, P.; Scribante, A. Oral Microbiota in Patients with Peri-Implant Disease: A Narrative Review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, H.; Tatro, J.M.; Hausman, B.S.; Hujer, K.M.; Marshall, S.H.; Akkus, O.; Rather, P.N.; Lee, Z.; Bonomo, R.A.; Greenfield, E.M. Staphylococcus aureus and Acinetobacter baumannii Inhibit Osseointegration of Orthopedic Implants. Infect. Immun. 2022, 90, e0066921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlee, M.; Wang, H.-L.; Stumpf, T.; Brodbeck, U.; Bosshardt, D.; Rathe, F. Treatment of Periimplantitis with Electrolytic Cleaning versus Mechanical and Electrolytic Cleaning: 18-Month Results from a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zipprich, H.; Weigl, P.; Di Gianfilippo, R.; Steigmann, L.; Henrich, D.; Wang, H.-L.; Schlee, M.; Ratka, C. Comparison of decontamination efficacy of two electrolyte cleaning methods to diode laser, plasma, and air-abrasive devices. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 4549–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianfreda, F.; Punzo, A.; Pistilli, V.; Bollero, P.; Cervino, G.; D’Amico, C.; Cairo, F.; Cicciù, M. Electrolytic Cleaning and Regenerative Therapy of Peri-implantitis in the Esthetic Area: A Case Report. Eur. J. Dent. 2022, 16, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosshardt, D.D.; Brodbeck, U.R.; Rathe, F.; Stumpf, T.; Imber, J.C.; Weigl, P.; Schlee, M. Evidence of re-osseointegration after electrolytic cleaning and regenerative therapy of peri-implantitis in humans: A case report with four implants. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 3735–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardi, S.; Qorri, E.; Botticelli, G.; Scarano, A.; Marzo, G.; Gatto, R.; Greco Lucchina, A.; Mortellaro, C.; Lupi, E.; Rastelli, C.; et al. Use of electrical field for biofilm implant removal. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 114–121. [Google Scholar]
- Ratka, C.; Weigl, P.; Henrich, D.; Koch, F.; Schlee, M.; Zipprich, H. The Effect of In Vitro Electrolytic Cleaning on Biofilm-Contaminated Implant Surfaces. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batalha, V.C.; Bueno, R.A.; Fronchetti Junior, E.; Mariano, J.R.; Santin, G.C.; Freitas, K.M.S.; Ortiz, M.A.L.; Salmeron, S. Dental Implants Surface in vitro Decontamination Protocols. Eur. J. Dent. 2021, 15, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, J.S.; Abd Rahman, N.A.; Ming, L.C.; Dhaliwal, S.K.S.; Knights, J.; Albuquerque Junior, R.F. Microbial Biofilm Decontamination on Dental Implant Surfaces: A Mini Review. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 736186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/ast_of_bacteria (accessed on 24 November 2023).
- Larsen, O.I.; Enersen, M.; Kristoffersen, A.K.; Wennerberg, A.; Bunæs, D.F.; Lie, S.A.; Leknes, K.N. Antimicrobial Effects of Three Different Treatment Modalities on Dental Implant Surfaces. J. Oral Implantol. 2017, 43, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, V.; Mardas, N.; Spratt, D.; Hassan, I.A.; Walters, N.J.; Beltrán, V.; Donos, N. The Effect of Microcosm Biofilm Decontamination on Surface Topography, Chemistry, and Biocompatibility Dynamics of Implant Titanium Surfaces. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assunção, M.A.; Botelho, J.; Machado, V.; Proença, L.; Matos, A.P.A.; Mendes, J.J.; Bessa, L.J.; Taveira, N.; Santos, A. Dental Implant Surface Decontamination and Surface Change of an Electrolytic Method versus Mechanical Approaches: A Pilot In Vitro Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gedefie, A.; Demsis, W.; Ashagrie, M.; Kassa, Y.; Tesfaye, M.; Tilahun, M.; Bisetegn, H.; Sahle, Z. Acinetobacter baumannii Biofilm Formation and Its Role in Disease Pathogenesis: A Review. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 3711–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Chowdhury, G.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Dutta, S.; Basu, S. Convergence of Biofilm Formation and Antibiotic Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii Infection. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 793615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaatout, N. Presence of non-oral bacteria in the oral cavity. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 2747–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upmanyu, K.; Haq, Q.M.R.; Singh, R. Factors mediating Acinetobacter baumannii biofilm formation: Opportunities for developing therapeutics. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2022, 3, 100131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, V.; Nibali, L.; Spratt, D.; Dopico, J.; Mardas, N.; Petrie, A.; Donos, N. Peri-implant and periodontal microbiome diversity in aggressive periodontitis patients: A pilot study. Clin. Oral. Implants Res. 2017, 28, 558–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharadwaj, A.; Rastogi, A.; Pandey, S.; Gupta, S.; Sohal, J.S. Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria: Their Mechanism of Action and Prophylaxis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 5419874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alagl, A.S.; Madi, M.; Bedi, S.; Al Onaizan, F.; Al-Aql, Z.S. The Effect of Er,Cr:YSGG and Diode Laser Applications on Dental Implant Surfaces Contaminated with Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Materials 2019, 12, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrasiabi, S.; Benedicenti, S.; Signore, A.; Arshad, M.; Chiniforush, N. Simultaneous Dual-Wavelength Laser Irradiation against Implant-Adherent Biofilms of Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Candida albicans for Improved Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citterio, F.; Zanotto, E.; Pellegrini, G.; Annaratore, L.; Barbui, A.M.; Dellavia, C.; Baima, G.; Romano, F.; Aimetti, M. Comparison of Different Chemical and Mechanical Modalities for Implant Surface Decontamination: Activity against Biofilm and Influence on Cellular Regrowth-An In Vitro Study. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 886559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichioka, Y.; Derks, J.; Dahlén, G.; Berglundh, T.; Larsson, L. Mechanical removal of biofilm on titanium discs: An in vitro study. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2022, 110, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toma, S.; Behets, C.; Brecx, M.C.; Lasserre, J.F. In Vitro Comparison of the Efficacy of Peri-Implantitis Treatments on the Removal and Recolonization of Streptococcus gordonii Biofilm on Titanium Disks. Materials 2018, 11, 2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

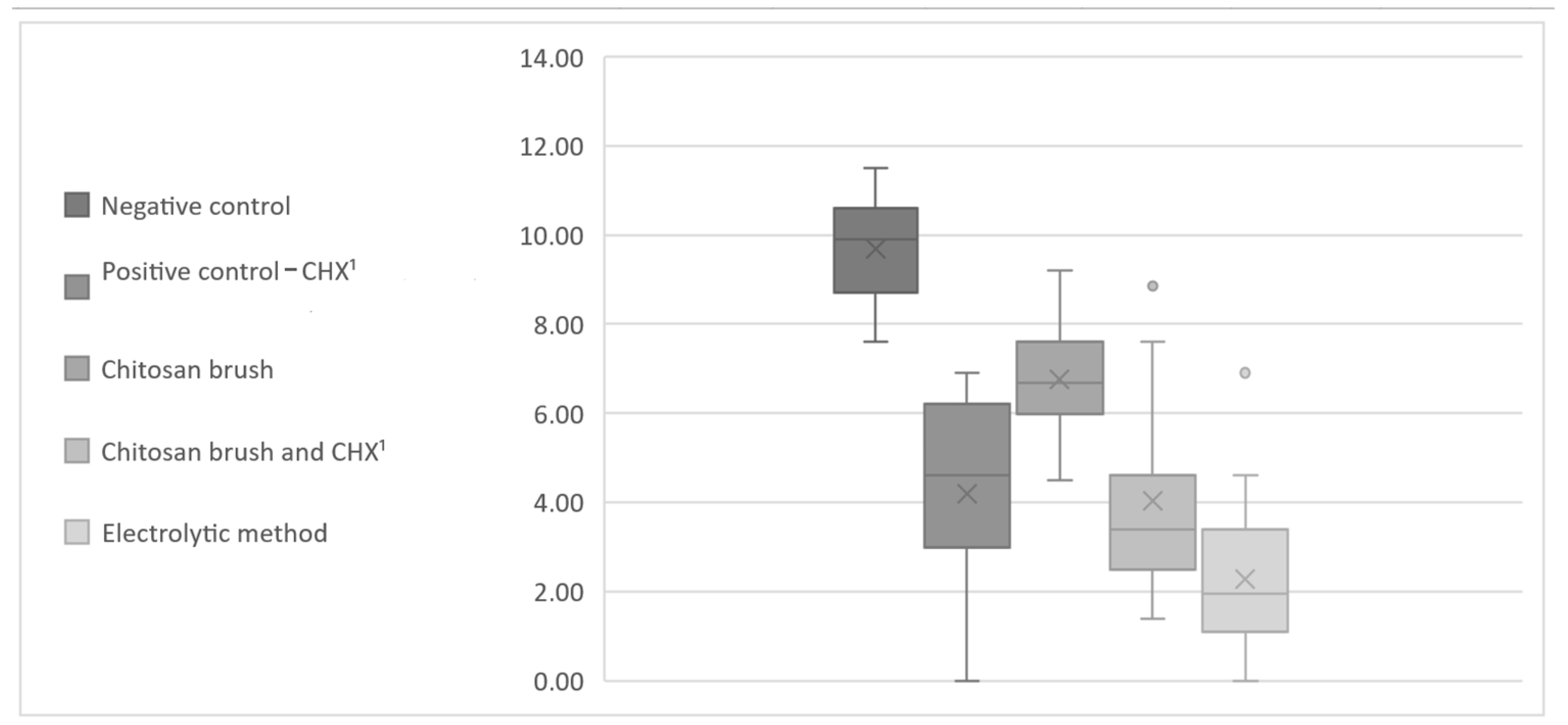
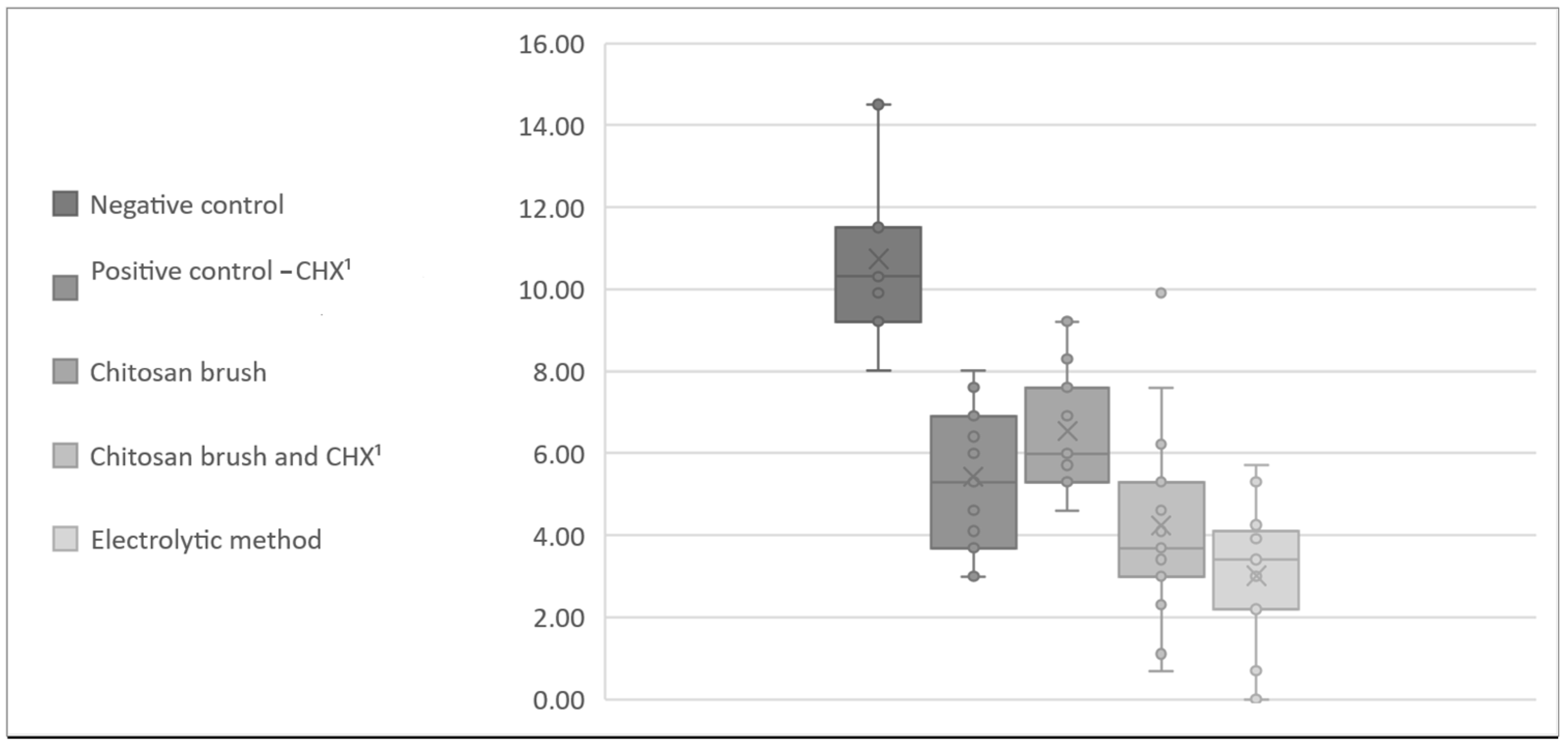
| CFU A. baumannii | Negative Control | Positive Control (CHX 2) | Chitosan Brush | Chitosan Brush and CHX 2 | Electrolytic Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| avg CFU | 30,867 | 276 | 1906 | 645 | 83 |
| min CFU | 2000 | 0 | 90 | 4 | 0 |
| max CFU | 100,000 | 1000 | 10,000 | 7000 | 1000 |
| sd 1 | 33,233 | 361 | 2959 | 1829 | 255 |
| median CFU | 20,000 | 100 | 800 | 30 | 7 |
| CFU S. aureus | Negative Control | Positive Control (CHX 2) | Chitosan Brush | Chitosan Brush and CHX 2 | Electrolytic Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| avg CFU | 303,533 | 705 | 2060 | 1542 | 58 |
| min CFU | 3000 | 20 | 100 | 2 | 0 |
| max CFU | 2,000,000 | 3000 | 10,000 | 20,000 | 300 |
| sd 1 | 689,789 | 931 | 3379 | 5131 | 84 |
| median CFU | 30,000 | 200 | 400 | 40 | 30 |
| SUMMARY | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Groups | Count | Sum | Average | Variance | ||
| Positive control (CHX 1) | 15 | 63.03 | 4.20 | 5.04 | ||
| Chitosan brush | 15 | 101.46 | 6.76 | 1.56 | ||
| Chitosan brush and CHX 1 | 15 | 60.53 | 4.04 | 4.07 | ||
| Electrolytic method | 15 | 34.04 | 2.27 | 3.63 | ||
| ANOVA | ||||||
| Source of Variation | SS 2 | df 3 | MS 4 | F | p-value 5 | F crit |
| Between groups | 154.13 | 3 | 51.378198 | 14.361941 | 4.69 × 10−7 | 2.769431 |
| Within groups | 200.33 | 56 | 3.577385 | |||
| Total | 354.47 | 59 |
| SUMMARY | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Groups | Count | Sum | Average | Variance | ||
| Positive control (CHX 1) | 15 | 81.38 | 5.43 | 3.05 | ||
| Chitosan brush | 15 | 98.24 | 6.55 | 2.18 | ||
| Chitosan brush and CHX 1 | 15 | 63.59 | 4.24 | 5.60 | ||
| Electrolytic methode | 15 | 45.16 | 3.01 | 3.09 | ||
| ANOVA | ||||||
| Source of Variation | SS 2 | df 2 | MS 4 | F | p-value 5 | F crit |
| Between groups | 104.51 | 3 | 34.83733 | 10.00527 | 2.23 × 10−5 | 2.76943 |
| Within groups | 194.99 | 56 | 3.48190 | |||
| Total | 299.50 | 59 |
| ANOVA (p-Values) | Positive Control (CHX 1) | Chitosan Brush | Chitosan Brush and CHX 1 | Electrolytic Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive control (CHX 1) | 0.0006 | 0.8324 | 0.0169 | |
| Chitosan brush | 0.0001 | 2.54 × 10−8 | 0.0322 | |
| Chitosan brush and CHX 1 | 0.0201 | 0.2568 | ||
| Electrolytic method | ||||
| ANOVA (p-Values) | Positive Control (CHX 1) | Chitosan Brush | Chitosan Brush and CHX 1 | Electrolytic Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive control (CHX 1) | 0.0674 | 0.1297 | 0.0008 | |
| Chitosan brush | 0.0033 | 1.98 × 10−6 | ||
| Chitosan brush and CHX 1 | 0.1177 | |||
| Electrolytic method | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jordan, A.; Smojver, I.; Budimir, A.; Gabrić, D.; Vuletić, M. Evaluation of Different Procedures for Titanium Dental Implant Surface Decontamination—In Vitro Study. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11040326
Jordan A, Smojver I, Budimir A, Gabrić D, Vuletić M. Evaluation of Different Procedures for Titanium Dental Implant Surface Decontamination—In Vitro Study. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(4):326. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11040326
Chicago/Turabian StyleJordan, Ante, Igor Smojver, Ana Budimir, Dragana Gabrić, and Marko Vuletić. 2024. "Evaluation of Different Procedures for Titanium Dental Implant Surface Decontamination—In Vitro Study" Bioengineering 11, no. 4: 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11040326
APA StyleJordan, A., Smojver, I., Budimir, A., Gabrić, D., & Vuletić, M. (2024). Evaluation of Different Procedures for Titanium Dental Implant Surface Decontamination—In Vitro Study. Bioengineering, 11(4), 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11040326








