Design of a Multiparametric Perfusion Bioreactor System for Evaluating Sub-Normothermic Preservation of Rat Abdominal Wall Vascularized Composite Allografts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. VCA Procurement Surgery
2.2. Cold Storage
2.3. Transplantation
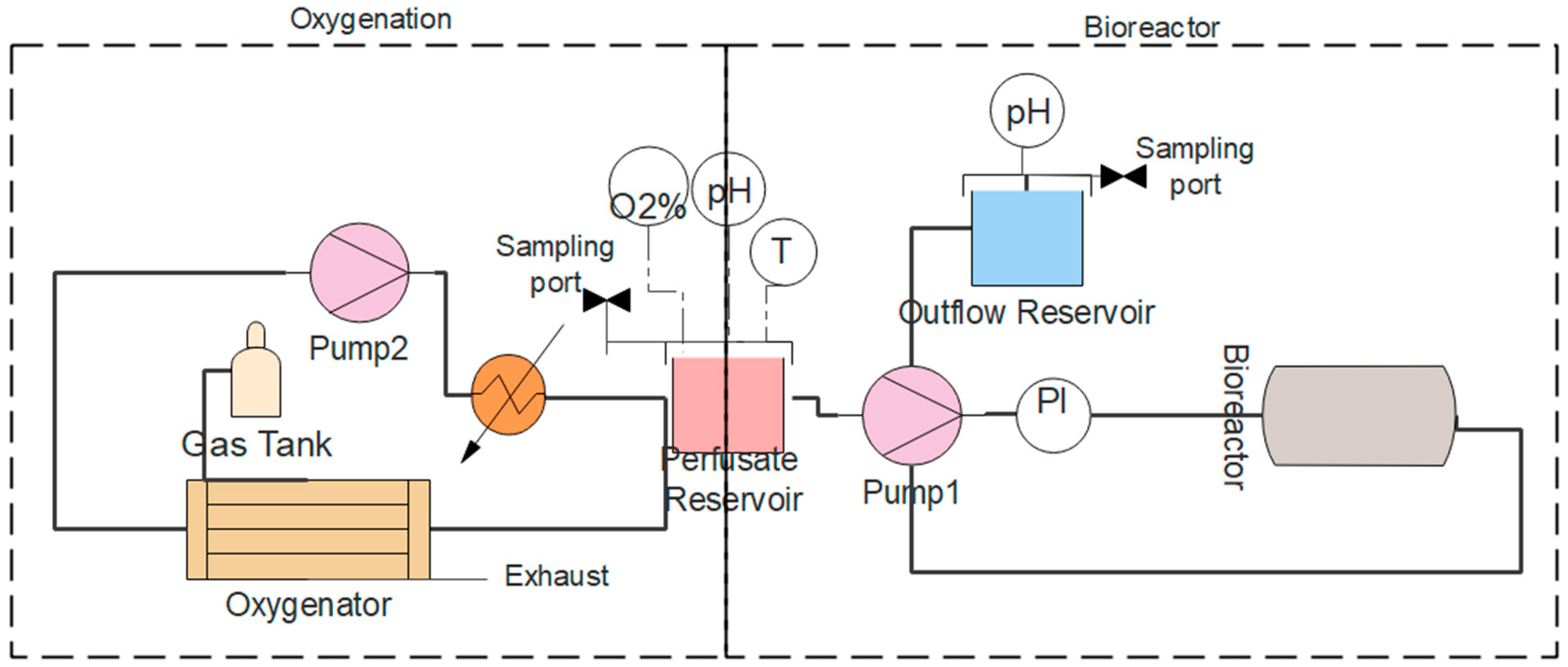
2.4. Machine Perfusion System
2.5. Histology
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
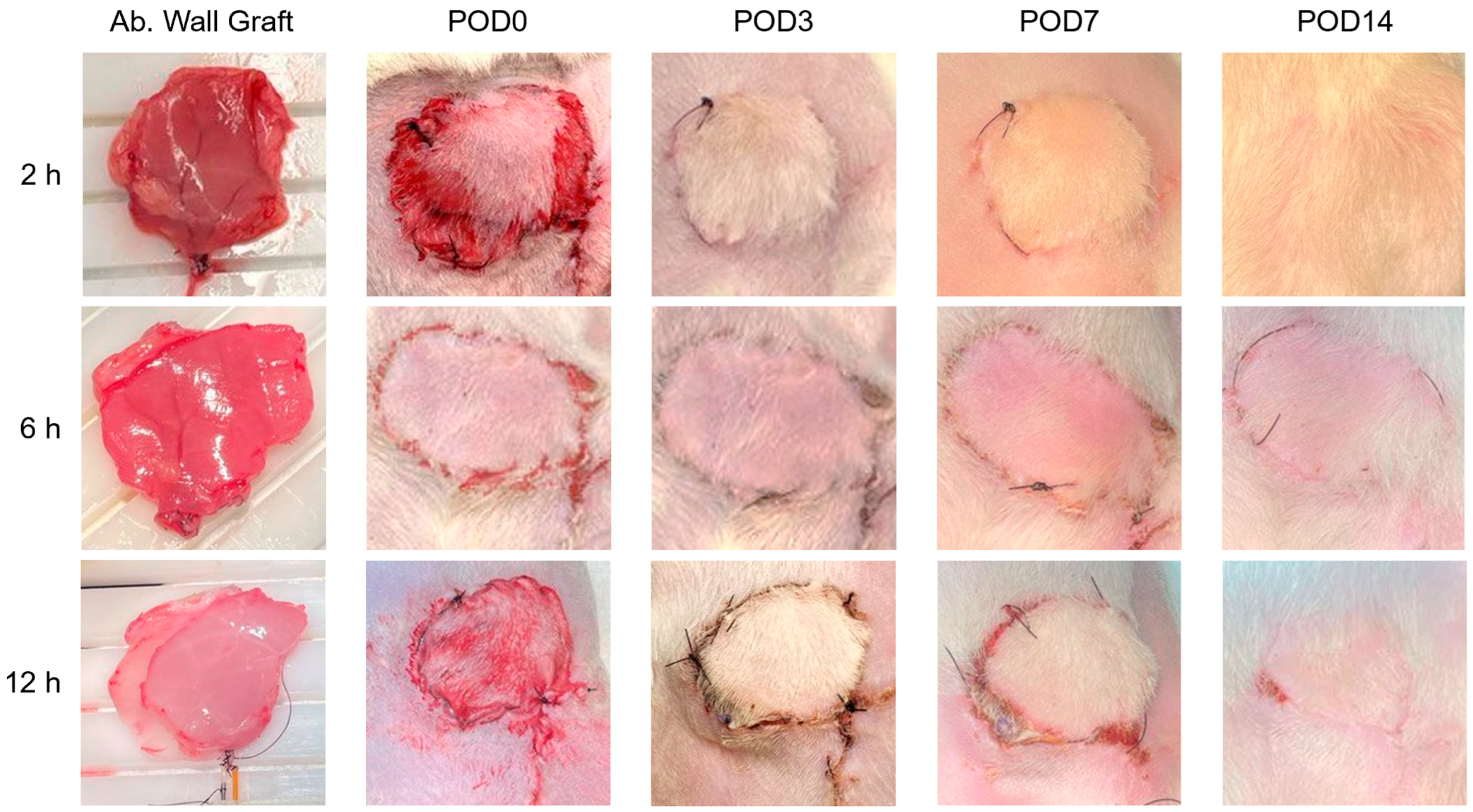
3.1. Quantitative Metrics of Necrosis Were Established to Study the Correlation between Ischemic Damage and Graft Survival in a Transplantation Model of Rat Abdominal Wall VCA Grafts
3.2. Custom-Designed Bioreactor Housing Unit for Rat Abdominal Wall VCA Grafts
3.3. Electrical Stimulation of Rat Abdominal Wall VCA Grafts
3.4. Machine Perfusion Circuit
3.5. Pressure-Controlled Perfusion and Modified Perfadex Composition Minimized Perfusion-Induced Damage in the Abdominal Wall VCA
3.6. Evaluation of Physical, Biomolecular, and Histological Metrics during and after Perfusion of Rat Abdominal Wall Grafts
3.7. Successful Transplantation and Integration of Perfused Abdominal Wall Grafts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Milek, D.; Reed, L.T.; Echternacht, S.R.; Shanmugarajah, K.; Cetrulo, C.L., Jr.; Lellouch, A.G.; Leckenby, J.I. A systematic review of the reported complications related to facial and upper extremity vascularized composite allotransplantation. J. Surg. Res. 2023, 281, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriani, R.; Contedini, F.; Gelati, C.; Miralles, M.E.; Zanfi, C.; Pinna, A.D.; Cescon, M. Abdominal wall transplantation with microsurgical technique. In Reconstructive Transplantation; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 311–320. [Google Scholar]
- Redett, R.J., III; Etra, J.W.; Brandacher, G.; Burnett, A.L.; Tuffaha, S.H.; Sacks, J.M.; Shores, J.T.; Bivalacqua, T.J.; Bonawitz, S.; Cooney, C.M.; et al. Total penis, scrotum, and lower abdominal wall transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1876–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Siso, J.R.; Borab, Z.M.; Plana, N.M.; Parent, B.; Stranix, J.T.; Rodriguez, E.D. Vascularized Composite Allotransplantation: Alternatives and Catch-22s. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 142, 1320–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlage, L.C.; Tessier, S.N.; Etra, J.W.; Uygun, K.; Brandacher, G. Advances in machine perfusion, organ preservation, and cryobiology: Potential impact on vascularized composite allotransplantation. Curr. Opin. Organ Transpl. 2018, 23, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kueckelhaus, M.; Dermietzel, A.; Alhefzi, M.; Aycart, M.A.; Fischer, S.; Krezdorn, N.; Wo, L.; Maarouf, O.H.; Riella, L.V.; Abdi, R.; et al. Acellular Hypothermic Extracorporeal Perfusion Extends Allowable Ischemia Time in a Porcine Whole Limb Replantation Model. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 139, 922e–932e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Figueroa, B.; Orfahli, L.M.; Ordenana, C.; Brunengraber, H.; Dasarathy, S.; Rampazzo, A.; Bassiri Gharb, B. Composite Vascularized Allograft Machine Preservation: State of the Art. Curr. Transplant. Rep. 2019, 6, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belzer, F.O.; Southard, J.H. Principles of solid-organ preservation by cold storage. Transplantation 1988, 45, 673–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Jernryd, V.; Sjoberg, T.; Steen, S.; Nilsson, J. Machine Perfusion for Human Heart Preservation: A Systematic Review. Transpl. Int. 2022, 35, 10258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Nie, Y.; Li, J.; Xie, H.; Zhou, L.; Yu, J.; Zheng, S.S. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Machine Perfusion vs. Static Cold Storage of Liver Allografts on Liver Transplantation Outcomes: The Future Direction of Graft Preservation. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, K.; Rojas-Pena, A.; Mendias, C.L.; Bryner, B.S.; Toomasian, C.; Bartlett, R.H. The effect of ex situ perfusion in a swine limb vascularized composite tissue allograft on survival up to 24 hours. J. Hand Surg. 2016, 41, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RM3 Kidney Perfusion System. Available online: https://wtrs.com/rm3-kidney-perfusion-system/ (accessed on 5 January 2014).
- Krezdorn, N.; Macleod, F.; Tasigiorgos, S.; Turk, M.D.M.; Wo, L.; Kiwanuka, B.A.H.; Lopdrup, B.I.D.R.; Kollar, B.; Edelman, E.R.; Pomahac, B. Twenty-Four-Hour Ex Vivo Perfusion with Acellular Solution Enables Successful Replantation of Porcine Forelimbs. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 144, 608e–618e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, K.R.; Stone, J.P.; Kerr, J.; Geraghty, A.; Joseph, L.; Montero-Fernandez, A.; Wong, J.K.; Fildes, J.E. Randomized preclinical study of machine perfusion in vascularized composite allografts. Br. J. Surg. 2021, 108, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahradyan, V.; Said, S.A.; Ordenana, C.; Dalla Pozza, E.; Frautschi, R.; Duraes, E.F.R.; Madajka-Niemeyer, M.; Papay, F.A.; Rampazzo, A.; Bassiri Gharb, B. Extended ex vivo normothermic perfusion for preservation of vascularized composite allografts. Artif. Organs. 2020, 44, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenzel, N.; Blasczyk, R.; Figueiredo, C. Animal Models in Allogenic Solid Organ Transplantation. Transplantology 2021, 2, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broyles, J.M.; Sarhane, K.A.; Tuffaha, S.H.; Cooney, D.S.; Lee, W.A.; Brandacher, G.; Sacks, J.M. Reconstruction of large abdominal wall defects using neurotized vascular composite allografts. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 136, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrant, A.B.; Wang, Z.; Anderson, J.B.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Johnson, A.C.; Washington, K.; Navarro-Alvarez, N.; Farkash, E.A.; Huang, C.A. Rat hind limb transplant model to assess vascularized composite allograft (VCA) ischemic reperfusion injury and inflammation. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open. 2020, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruit, A.S.; Winters, H.; van Luijk, J.; Schreinemachers, M.J.M.; Ulrich, D.J.O. Current insights into extracorporeal perfusion of free tissue flaps and extremities: A systematic review and data synthesis. J. Surg. Res. 2018, 227, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciorati, C.; Rigamonti, E.; Manfredi, A.A.; Rovere-Querini, P. Cell death, clearance and immunity in the skeletal muscle. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.H.; Banuelos, K.; Ward, S.R.; Lieber, R.L. Architectural and morphological assessment of rat abdominal wall muscles: Comparison for use as a human model. J. Anat. 2010, 217, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, S.A.; Ordenana, C.X.; Rezaei, M.; Figueroa, B.A.; Dasarathy, S.; Brunengraber, H.; Rampazzo, A.; Gharb, B.B. Ex-Vivo Normothermic Limb Perfusion With a Hemoglobin-Based Oxygen Carrier Perfusate. Mil. Med. 2020, 185, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, V.; Kollar, B.; Endo, Y.; Kadakia, N.; Veeramani, A.; Kauke, M.; Tchiloemba, B.; Klasek, R.; Pomahac, B. Comparison of Acellular Solutions for Ex-situ Perfusion of Amputated Limbs. Mil. Med. 2020, 185, e2004–e2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenbergen, C.H.; Deleeuw, G.; Rich, T.E.; Williamson, J.R. Effects of acidosis and ischemia on contractility and intracellular pH of rat heart. Circ. Res. 1977, 41, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, O.; Carmel, N.; Sela, M.; Abu Jabal, A.; Inbal, A.; Ben Hamou, M.; Krelin, Y.; Gur, E.; Shani, N. Immunological and inflammatory mapping of vascularized composite allograft rejection processes in a rat model. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fichter, A.M.; Ritschl, L.M.; Borgmann, A.; Humbs, M.; Luppa, P.B.; Wolff, K.D.; Mucke, T. Development of an Extracorporeal Perfusion Device for Small Animal Free Flaps. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gok, E.; Alghanem, F.; Moon, R.; Guy, E.; Rojas-Pena, A.; Bartlett, R.H.; Ozer, K. Development of an Ex-Situ Limb Perfusion System for a Rodent Model. ASAIO J. 2019, 65, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, M.; Moreira, C.; Mendonça Eusébio, T.; de Pinho, M.N.; Brogueira, P.; Semião, V. Oxygen mass transfer in a gas/membrane/liquid system surrogate of membrane blood oxygenators. AIChE J. 2018, 64, 3756–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfgang Boettcher, E.; Frank Merkle, E.C.C.P.; Heinz-Hermann Weitkemper, E.C.C.P. History of Extracorporeal Circulation: The Conceptional and Developmental Period. J. Extra-Corpor. Technol. 2003, 35, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, V.; Kollar, B.; Tasigiorgos, S.; Endo, Y.; Kauke, M.; Safi, A.F.; Veeramani, A.; Abdulrazzak, O.; Bausk, B.; Walt, D.; et al. Hypothermic ex situ perfusion of human limbs with acellular solution for 24 hours. Transplantation 2020, 104, e260–e270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruit, A.S.; Schreinemachers, M.J.M.; Koers, E.J.; Zegers, H.J.H.; Hummelink, S.; Ulrich, D.J.O. Successful Long-term Extracorporeal Perfusion of Free Musculocutaneous Flaps in a Porcine Model. J. Surg. Res. 2019, 235, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taeger, C.D.; Friedrich, O.; Dragu, A.; Weigand, A.; Hobe, F.; Drechsler, C.; Geppert, C.I.; Arkudas, A.; Munch, F.; Buchholz, R.; et al. Assessing viability of extracorporeal preserved muscle transplants using external field stimulation: A novel tool to improve methods prolonging bridge-to-transplantation time. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortimer, J.T.; Bhadra, N. Peripheral nerve and muscle stimulation. In Neuroprosthetics: Theory and Practice; World Scientific Publishing Company: London, UK, 2004; pp. 638–682. [Google Scholar]
- Bennie, S.D.; Petrofsky, J.S.; Nisperos, J.; Tsurudome, M.; Laymon, M. Toward the optimal waveform for electrical stimulation of human muscle. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 88, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russ, D.W.; Elliott, M.A.; Vandenborne, K.; Walter, G.A.; Binder-Macleod, S.A. Metabolic costs of isometric force generation and maintenance of human skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 282, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manekeller, S.; Leuvenink, H.; Sitzia, M.; Minor, T. Oxygenated machine perfusion preservation of predamaged kidneys with HTK and Belzer machine perfusion solution: An experimental study in pigs. Transpl. Proc. 2005, 37, 3274–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobert, M.; Peltz, M.; West, L.; Jessen, M.E. 174: Maintenance of Human Heart Oxidative Metabolism after 12 Hour Perfusion Preservation. J. Heart Lung Transpl. 2009, 28, S126–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latchana, N.; Peck, J.R.; Whitson, B.; Black, S.M. Preservation solutions for cardiac and pulmonary donor grafts: A review of the current literature. J Thorac Dis 2014, 6, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stig Steen, M.; Ingemansson, R.; Budrikis, A.; Bolys, R.; Roscher, R.; Sjöberg, T. Successful Transplantation of Lungs Topically Cooled in the Non–Heart-Beating Donor for 6 Hours. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 1997, 63, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, L.; Yao, L.; Zhao, M.; Peng, L.P.; Liu, M. Organ preservation: From the past to the future. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 845–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahas, G.G. The Clinical Pharmacology of Tham (Tris(Hydroxymethyl)Aminomethane). Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1963, 4, 784–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutafchieva, D.; Popova, D.; Dimitrova, M.; Tchaoushev, S. Experimental Determination of TheVolumetric Mass Transfer Coefficient. Tchaoushev. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2013, 48, 351–356. [Google Scholar]
- Jamnongwong, M.; Loubiere, K.; Dietrich, N.; Hébrard, G. Experimental study ofoxygen diffusion coefficients in clean water containing salt, glucose or surfactant: Consequences on the liquid-side mass transfer coefficients. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 165, 758–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salehi, S.; Lippert Lozano, E.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, R.; Tran, K.; Messner, F.; Brandacher, G.; Grayson, W.L. Design of a Multiparametric Perfusion Bioreactor System for Evaluating Sub-Normothermic Preservation of Rat Abdominal Wall Vascularized Composite Allografts. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11040307
Salehi S, Lippert Lozano E, Zhang Y, Guo Y, Liu R, Tran K, Messner F, Brandacher G, Grayson WL. Design of a Multiparametric Perfusion Bioreactor System for Evaluating Sub-Normothermic Preservation of Rat Abdominal Wall Vascularized Composite Allografts. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(4):307. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11040307
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalehi, Sara, Ernesto Lippert Lozano, Yichuan Zhang, Yinan Guo, Renee Liu, Kenny Tran, Franka Messner, Gerald Brandacher, and Warren L. Grayson. 2024. "Design of a Multiparametric Perfusion Bioreactor System for Evaluating Sub-Normothermic Preservation of Rat Abdominal Wall Vascularized Composite Allografts" Bioengineering 11, no. 4: 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11040307
APA StyleSalehi, S., Lippert Lozano, E., Zhang, Y., Guo, Y., Liu, R., Tran, K., Messner, F., Brandacher, G., & Grayson, W. L. (2024). Design of a Multiparametric Perfusion Bioreactor System for Evaluating Sub-Normothermic Preservation of Rat Abdominal Wall Vascularized Composite Allografts. Bioengineering, 11(4), 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11040307






