Development of an Eye Irritation Test Method Using an In-House Fabrication of a Reconstructed Human Cornea-like Epithelium Model for Eye Hazard Identification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Substances
2.2. Development of iHCE-NY1 Model
2.2.1. Cells and Culture Conditions
2.2.2. Construction
2.2.3. Viability
2.2.4. Morphology
2.3. Test Protocol and Cell Viability in Tested iHCE-NY1 Models
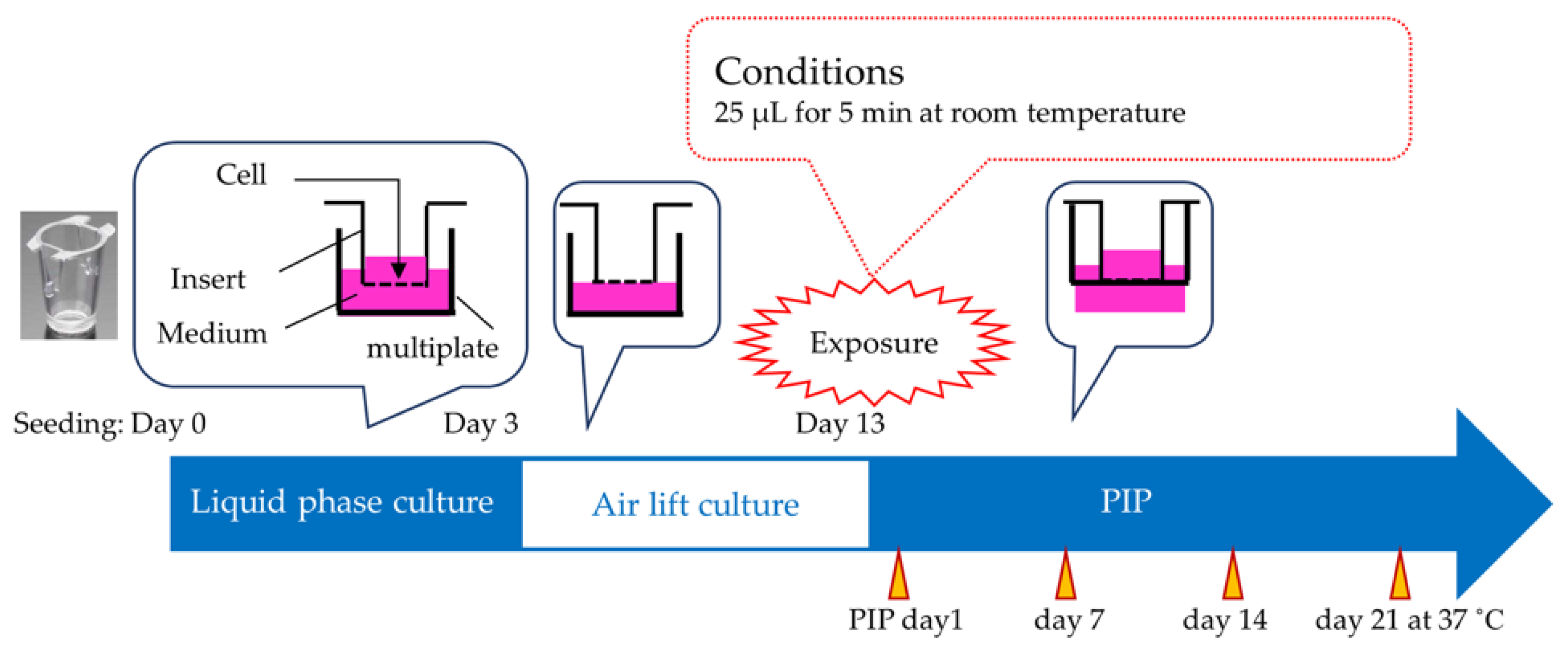
2.3.1. Test Protocol
2.3.2. Cell Viability in Tested iHCE-NY1 Models
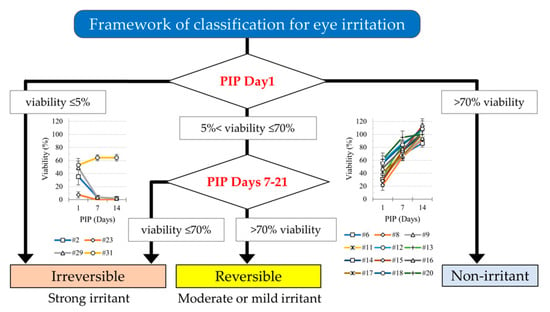
2.4. Predictive Capacity and Recovery in iHCE-NY1 Models
3. Results
3.1. Predictive Capacity with a PIP of 1 Day
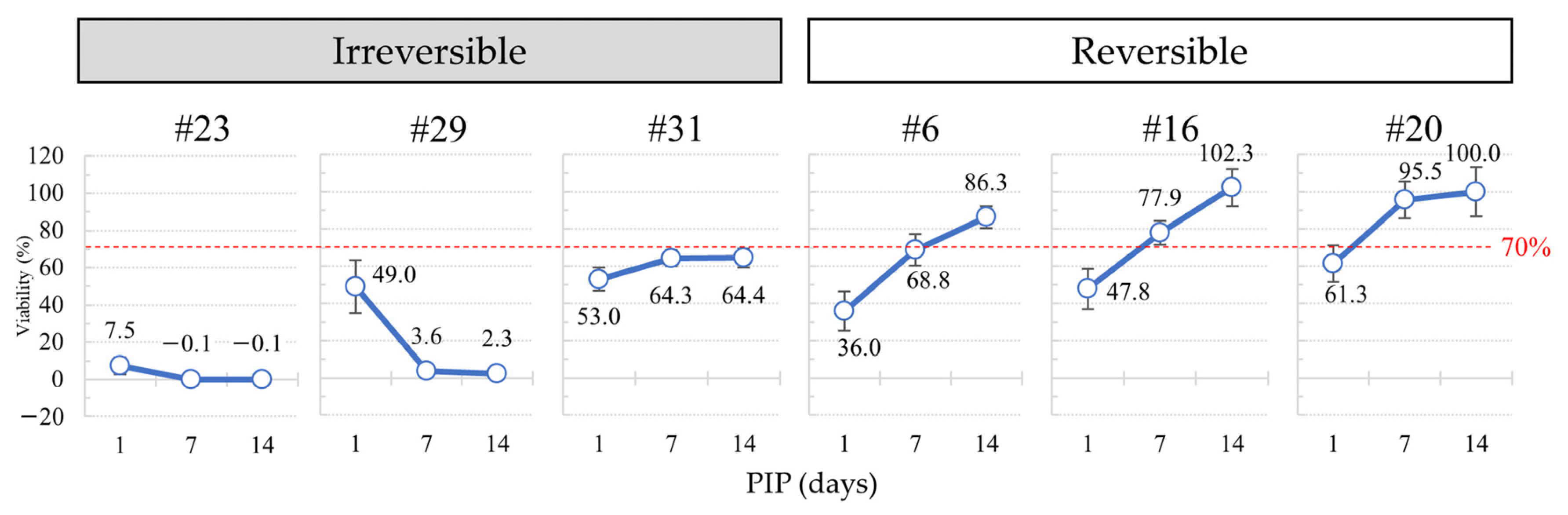
3.2. Effect of PIPs 7 to 21 Days on Cell Recovery
3.2.1. Recovery of Cell Viability
3.2.2. Histopathological Findings
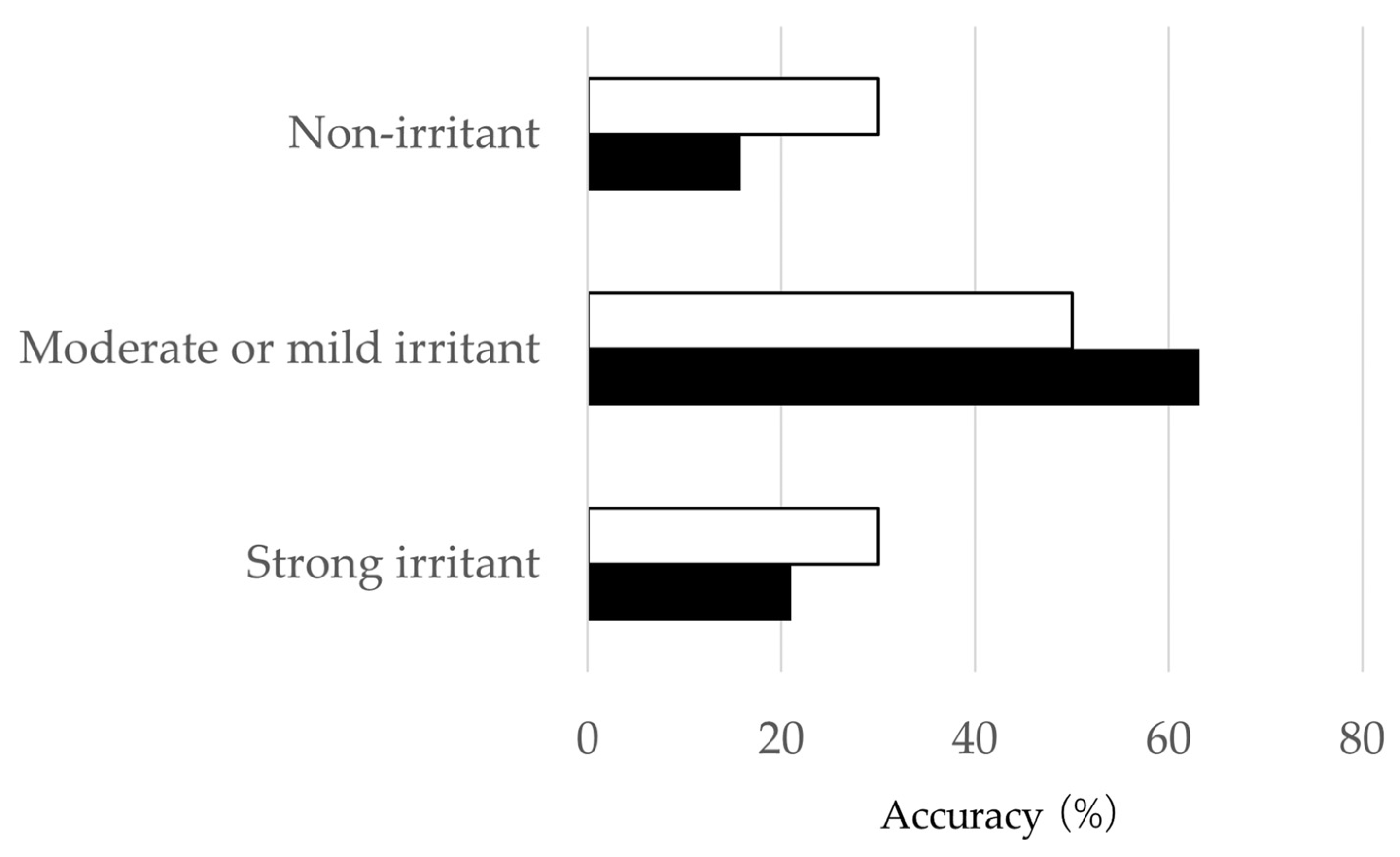
3.2.3. Table (3 × 3) by PIPs 7 to 14 Days
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS), 5th revised ed.; ST/SG/AC.10/30; United Nations: New York, NY, USA; Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Series on Testing and Assessment No. 263: Guidance Document No 263 on Integrated Approaches to Testing and Assessment (IATA) for Serious Eye Damage and Eye Irritation; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, L.; Eskes, C.; Hoffmann, S.; Adriaens, E.; Alepee, N.; Bufo, M.; Clothier, R.; Facchini, D.; Faller, C.; Guest, R.; et al. A proposed eye irritation testing strategy to reduce and replace in vivo studies using Bottom-Up and Top-Down approaches. Toxicol. In Vitro 2010, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Series on Testing and Assessment No. 216: Performance Standards for the Assessment of Proposed Similar or Modified In Vitro Reconstructed Human Cornea-like Epithelium (RhCE) Test Methods for Identifying Chemicals Not Requiring Classification and Labelling for Eye Irritation or Serious Eye Damage; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Test No. 492: Reconstructed Human Cornea-like Epithelium (RhCE) Test Method for Identifying Chemicals Not Requiring Classification and Labelling for Eye Irritation or Serious Eye Damage; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Alepee, N.; Leblanc, V.; Adriaens, E.; Grandidier, M.H.; Lelievre, D.; Meloni, M.; Nardelli, L.; Roper, C.S.; Santirocco, E.; Toner, F.; et al. Multi-laboratory validation of SkinEthic HCE test method for testing serious eye damage/eye irritation using liquid chemicals. Toxicol. In Vitro 2016, 31, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alepee, N.; Adriaens, E.; Grandidier, M.H.; Meloni, M.; Nardelli, L.; Vinall, C.J.; Toner, F.; Roper, C.S.; Van Rompay, A.R.; Leblanc, V.; et al. Multi-laboratory evaluation of SkinEthic HCE test method for testing serious eye damage/eye irritation using solid chemicals and overall performance of the test method with regard to solid and liquid chemicals testing. Toxicol. In Vitro 2016, 34, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Test No. 492B: Reconstructed Human Cornea-like Epithelium (RHCE) Test Method for Eye Hazard Identification, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 4: Health Effects. OECD iLibrary. 2022. Available online: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/environment/test-no-492b-reconstructed-human-cornea-like-epithelium-rhce-test-method-for-eye-hazard-identification_0d603916-en (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- Kato, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Hiramatsu, N.; Sato, A.; Kojima, H. Inhouse fabrication of a reconstructed human corneal epithelium model for use in testing for eye irritation potential. Appl. In Vitro Toxicol. 2020, 6, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, N.; Hirano, K.; Kojima, H.; Sumitomo, M.; Yamashita, H.; Ayaki, M.; Taniguchi, K.; Tanikawa, A.; Horiguchi, M. Cultured human corneal epithelial stem/progenitor cells derived from the corneal limbus. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2010, 46, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, N.; Kato, Y.; Sato, A.; Hiramatsu, N.; Yamashita, H.; Ohkuma, M.; Miyachi, E.; Horiguchi, M.; Hirano, K.; Kojima, H. Establishment of a new immortalized human corneal epithelial cell line (iHCE-NY1) for use in evaluating eye irritancy by in vitro test methods. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2016, 52, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Revised Performance Standard for the Assessment of Proposed Similar of Modified In Vitro Reconstructed Human Cornea-like Epithelium (RhCE) Test Method for Eye Hazard; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki, K.; Kawasaki, S.; Young, R.D.; Fukuoka, H.; Tanioka, H.; Nakatsukasa, M.; Quantock, A.J.; Kinoshita, S. Genomic aberrations and cellular heterogeneity in SV40-immortalized human corneal epithelial cells. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kim, C.W.; Go, R.E.; Lee, G.A.; Kim, C.D.; Chun, Y.J.; Choi, K.C. Immortalization of human corneal epithelial cells using simian virus 40 large T antigen and cell characterization. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2016, 78, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barroso, J.; Pfannenbecker, U.; Adriaens, E.; Alepee, N.; Cluzel, M.; De Smedt, A.; Hibatallah, J.; Klaric, M.; Mewes, K.R.; Millet, M.; et al. Cosmetics Europe compilation of historical serious eye damage/eye irritation in vivo data analysed by drivers of classification to support the selection of chemicals for development and evaluation of alternative methods/strategies: The Draize eye test Reference Database (DRD). Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 521–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adriaens, E.; Verstraelen, S.; Alepee, N.; Kandarova, H.; Drzewiecka, A.; Gruszka, K.; Guest, R.; Willoughby, J.A., Sr.; Van Rompay, A.R. CON4EI: Development of testing strategies for hazard identification and labelling for serious eye damage and eye irritation of chemicals. Toxicol. In Vitro 2018, 49, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiyama, M.; Shiga, M.; Sasamoto, K.; Mizoguchi, M.; He, P.G. A new sulfonated tetrazolium salt that produces a highly water-soluble formazan dye. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1993, 41, 1118–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, H.; Ishiyama, M.; Ohseto, F.; Sasamoto, K.; Hamamoto, T.; Suzuki, K.; Watanabe, M. A water-soluble tetrazolium salt useful for colorimetric cell viability assay. Anal. Commun. 1999, 36, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakahara, S.; Kojima, H.; Omori, T.; Yamashita, A.; Endo, M.; Satake, M.; Nishiura, H.; Shinoda, S.; Hagiwara, S.; Kasahara, T.; et al. A validation study of a new in vitro eye irritation test using the reconstructed human corneal epithelial tissue, LabCyte CORNEA-MODEL24. AATEX 2019, 24, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Report of the Validation Study on the MCTT Human Corneal-like Epithelium Eye Irritation Test Model and Report of the Validation Pee-Review, ENV/JM/MONO(2019)16. 28 August 2019. Available online: https://one.oecd.org/document/ENV/JM/MONO(2019)16/En/pdf (accessed on 28 February 2024).
- ECETOC. Eye Irritation: Reference Chemicals Data Bank, 2nd ed.; Technical Report No. 48 (2); ECETOC: Brussels, Belgium, 1998; Available online: https://www.ecetoc.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/ECETOC-TR-0481.pdf (accessed on 28 February 2024).


| No. | CAS RN | Chemical Name | Supplier | OECD | In Vivo Category | In Vitro Prediction | Judgment: Recoverability | In Vitro Prediction with PIP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original TG492PS | (UN GHS) | |||||||
| 1 | 1760-24-3 | (Ethylenediamine-propyl)-trimethoxysilane | Sigma-Aldrich | 〇 | 1 | Irritant | NT | Strong |
| 2 | 2365-48-2 | Methylthioglycolate | Sigma-Aldrich | 〇 | 1 | Irritant | Irreversible | Strong |
| 3 | 818-61-1 | Hydroxyethyl acrylate | FUJIFILM Wako | 〇 | 1 | Irritant | NT | Strong |
| 4 | 17831-71-9 | Tetraethylene glycol diacrylate | Sigma-Aldrich | 1 | Irritant | NT | Strong | |
| 5 | 18472-51-0 | 2,4,11,13-Tetraazatetradecane-diimidamide, N,N″-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-3,12-diimino-, di-D-gluconate (20%, aqueous) | Sigma-Aldrich | 〇 | 2A | Irritant | NT | Strong |
| 6 | 96-48-0 | γ-Butyrolactone | Sigma-Aldrich | 〇 | 2A | Irritant | Reversible | Moderate or mild |
| 7 | 104-76-7 | 2-Ethyl-1-hexanol | FUJIFILM Wako | 2A | Irritant | NT | Strong | |
| 8 | 67-64-1 | Acetone | Sigma-Aldrich | 2A | Irritant | Reversible | Moderate or mild | |
| 9 | 67-63-0 | Isopropyl alcohol | FUJIFILM Wako | 2A | Irritant | Reversible | Moderate or mild | |
| 10 | 105-34-0 | Methyl cyanoacetate | Sigma-Aldrich | 2A | Non-irritant | NT | Non-irritant | |
| 11 | 78-93-3 | Methyl ethyl ketone (2-butanone) | TCI | 2A | Irritant | Reversible | Moderate or mild | |
| 12 | 111-27-3 | n-Hexanol | Sigma-Aldrich | 2A | Irritant | Reversible | Moderate or mild | |
| 13 | 96-41-3 | Cyclopentanol | Sigma-Aldrich | 2A | Irritant | Reversible | Moderate or mild | |
| 14 | 1569-01-3 | Propylene glycol propyl ether | Sigma-Aldrich | 2A | Irritant | Reversible | Moderate or mild | |
| 15 | 9002-93-1 | Triton X-100 (5%) | Sigma-Aldrich | 2A | Irritant | Reversible | Moderate or mild | |
| 16 | 105-30-6 | 2-Methyl-1-pentanol | Sigma-Aldrich | 〇 | 2B | Irritant | Reversible | Moderate or mild |
| 17 | 134-62-3 | Diethyl toluamide | Sigma-Aldrich | 〇 | 2B | Irritant | Reversible | Moderate or mild |
| 18 | 29911-27-1 | 1-(2-Propoxy-1-methylethoxy)-2-propanol | Sigma-Aldrich | 2B | Irritant | Reversible | Moderate or mild | |
| 19 | 542-76-7 | 3-Chloropropionitrile | FUJIFILM Wako | 2B | Non-irritant | NT | Non-irritant | |
| 20 | 609-14-3 | Ethyl-2-methylacetoacetate | Sigma-Aldrich | 2B | Irritant | Reversible | Moderate or mild | |
| 21 | 78-84-2 | Isobutyraldehyde | Sigma-Aldrich | 2B | Irritant | NT | Strong | |
| 22 | 542-08-5 | Isopropyl acetoacetate | FUJIFILM Wako | 2B | Non-irritant | NT | Non-irritant | |
| 23 | 123-72-8 | n-Butanal | FUJIFILM Wako | 2B | Irritant | Irreversible | Strong | |
| 24 | 342573-75-5 | 1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium ethylsulfate | Sigma-Aldrich | 〇 | NC | Non-irritant | NT | Non-irritant |
| 25 | 2370-63-0 | 2-Ethoxyethyl methacrylate | Sigma-Aldrich | 〇 | NC | Non-irritant | NT | Non-irritant |
| 26 | 13826-35-2 | 3-Phenoxybenzyl alcohol | Sigma-Aldrich | 〇 | NC | Irritant | NT | Strong |
| 27 | 3446-89-7 | 4-(Methylthio)-benzaldehyde | Sigma-Aldrich | 〇 | NC | Non-irritant | NT | Non-irritant |
| 28 | 629-19-6 | Dipropyl disulfide | Sigma-Aldrich | 〇 | NC | Non-irritant | NT | Non-irritant |
| 29 | 623-51-8 | Ethyl thioglycolate | Sigma-Aldrich | 〇 | NC | Irritant | Irreversible | Strong |
| 30 | 51-03-6 | Piperonyl butoxide | Sigma-Aldrich | 〇 | NC | Non-irritant | NT | Non-irritant |
| 31 | 61788-85-0 | Polyethylene glycol (PEG-40) hydrogenated castor oil | FUJIFILM Wako | 〇 | NC | Irritant | Irreversible | Strong |
| Liquid Chemicals | In Vivo Category (UN GHS) | Number of Chemicals | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category 1, 2A and 2B | No Category | |||
| In vitro prediction | Irritant (viability ≤ 70%) | 20 | 3 | 23 |
| Non-irritant (viability > 70%) | 3 | 5 | 8 | |
| Number of chemicals | 23 | 8 | 31 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamamoto, N.; Hiramatsu, N.; Kato, Y.; Sato, A.; Kojima, H. Development of an Eye Irritation Test Method Using an In-House Fabrication of a Reconstructed Human Cornea-like Epithelium Model for Eye Hazard Identification. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11040302
Yamamoto N, Hiramatsu N, Kato Y, Sato A, Kojima H. Development of an Eye Irritation Test Method Using an In-House Fabrication of a Reconstructed Human Cornea-like Epithelium Model for Eye Hazard Identification. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(4):302. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11040302
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamamoto, Naoki, Noriko Hiramatsu, Yoshinao Kato, Atsushi Sato, and Hajime Kojima. 2024. "Development of an Eye Irritation Test Method Using an In-House Fabrication of a Reconstructed Human Cornea-like Epithelium Model for Eye Hazard Identification" Bioengineering 11, no. 4: 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11040302
APA StyleYamamoto, N., Hiramatsu, N., Kato, Y., Sato, A., & Kojima, H. (2024). Development of an Eye Irritation Test Method Using an In-House Fabrication of a Reconstructed Human Cornea-like Epithelium Model for Eye Hazard Identification. Bioengineering, 11(4), 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11040302