Enhancing Diagnostic Images to Improve the Performance of the Segment Anything Model in Medical Image Segmentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
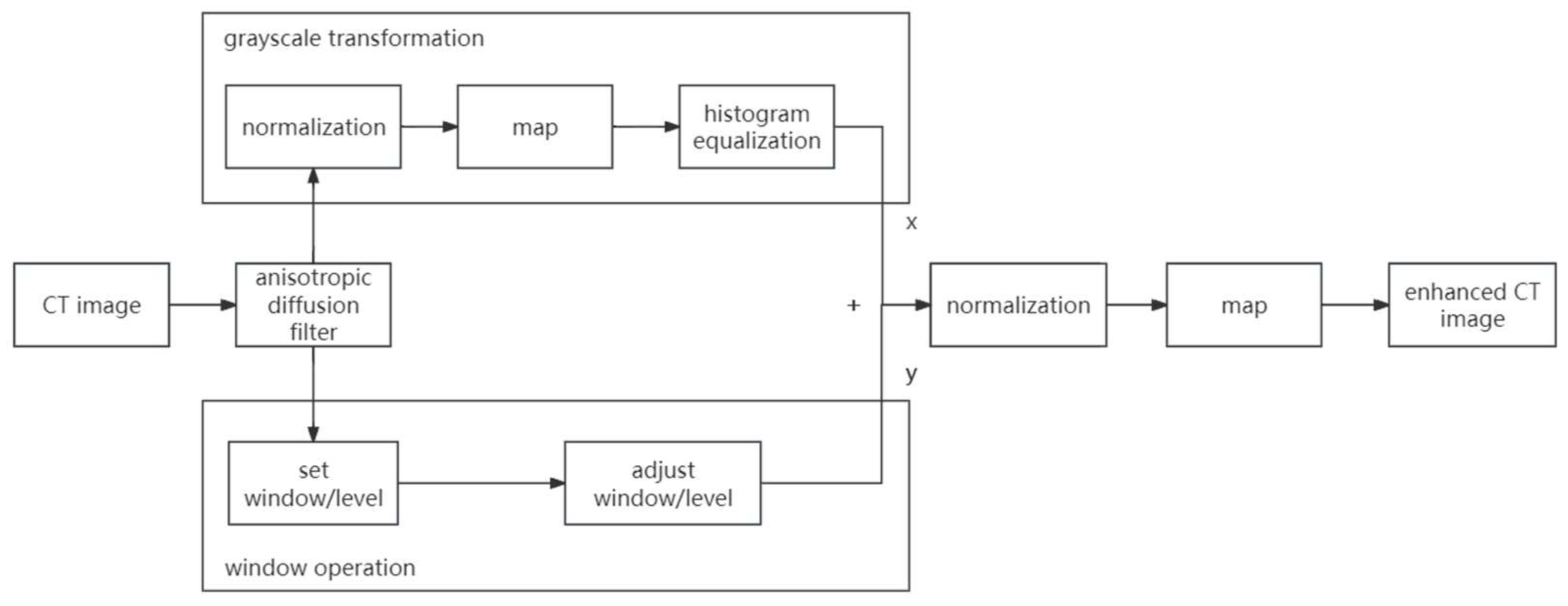
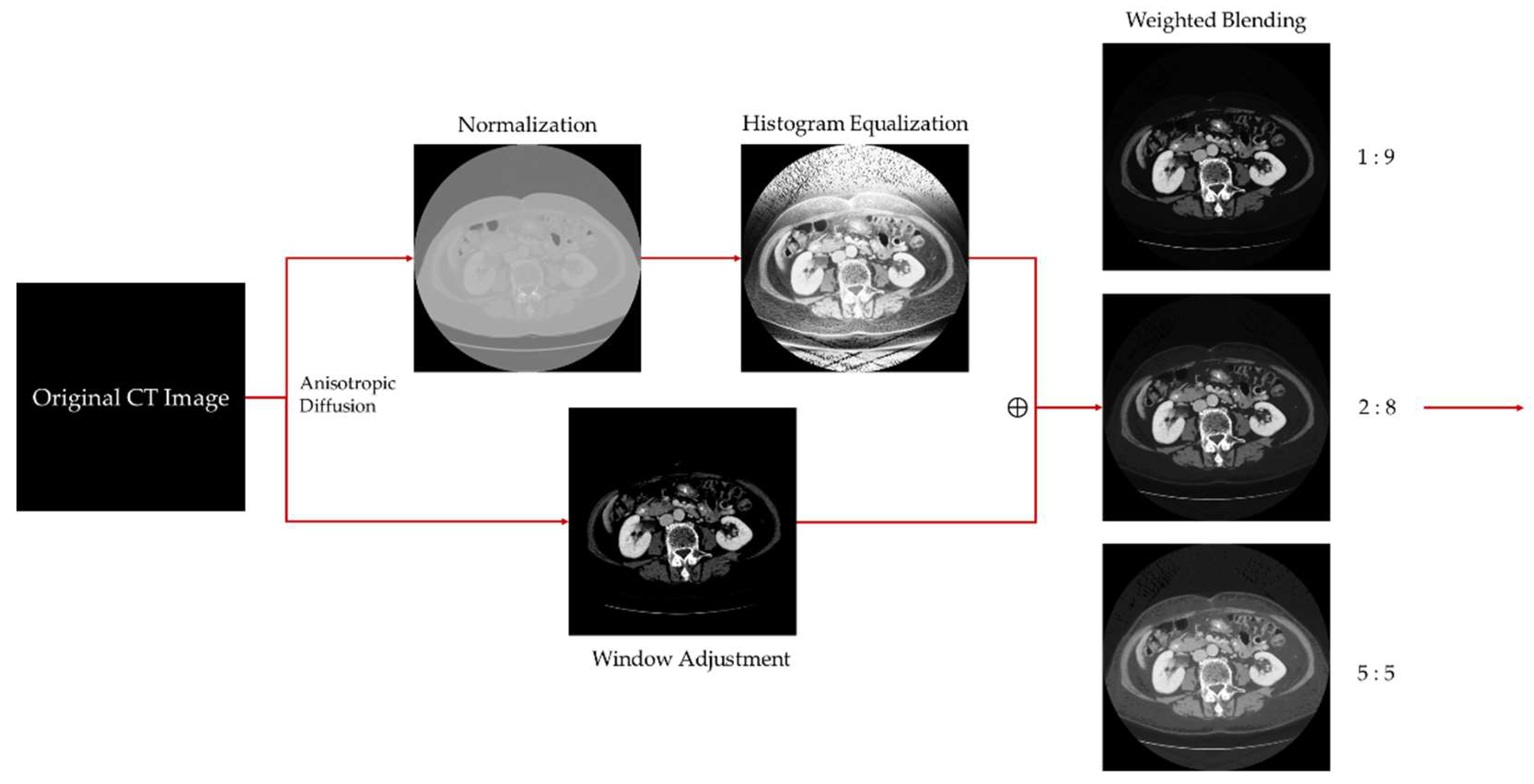
- Digital image enhancement strategies for medical image features: Medical images often contain a high level of noise and details hidden in low-intensity regions. To address this, anisotropic diffusion filters are used for denoising, and histogram equalization is employed to enhance the texture and details of medical images globally. Additionally, the fusion of window level and window width adjustment techniques specific to medical images is applied to target the regions of interest within the image. These strategies aim to achieve global enhancement of medical images while highlighting the desired targets.
- Exploring the root causes of low accuracy in medical image segmentation and addressing them: The main reasons for the low accuracy in medical image segmentation are the limited quantity and low quality of medical image datasets. The Data Engine in the Segment Anything Model provides a continuous stream of data, thereby addressing the issue of scarce medical image data. This article attempts to use image-enhancement techniques to provide high-quality data to the model and, thus, improve its accuracy.
2. Related Works
2.1. Image Enhancement
2.2. Image Segmentation
3. Methodology
3.1. Medical Image Enhancement Scheme—Procedure and Structure
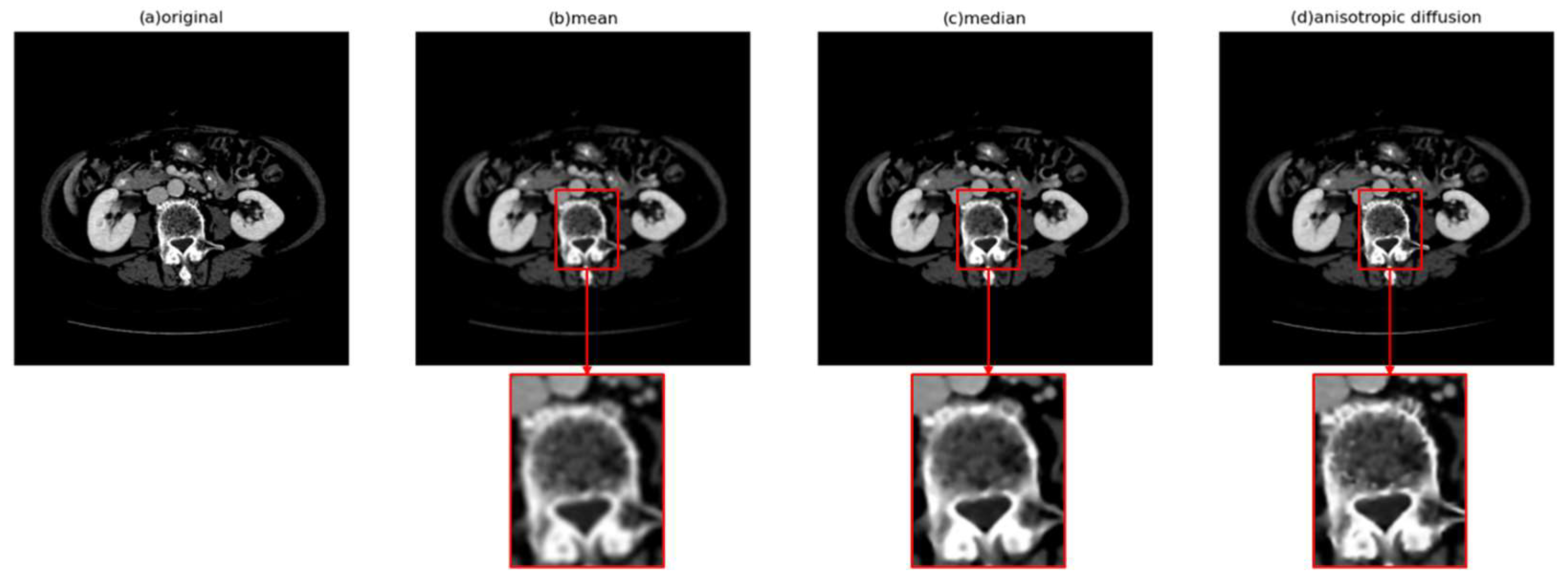
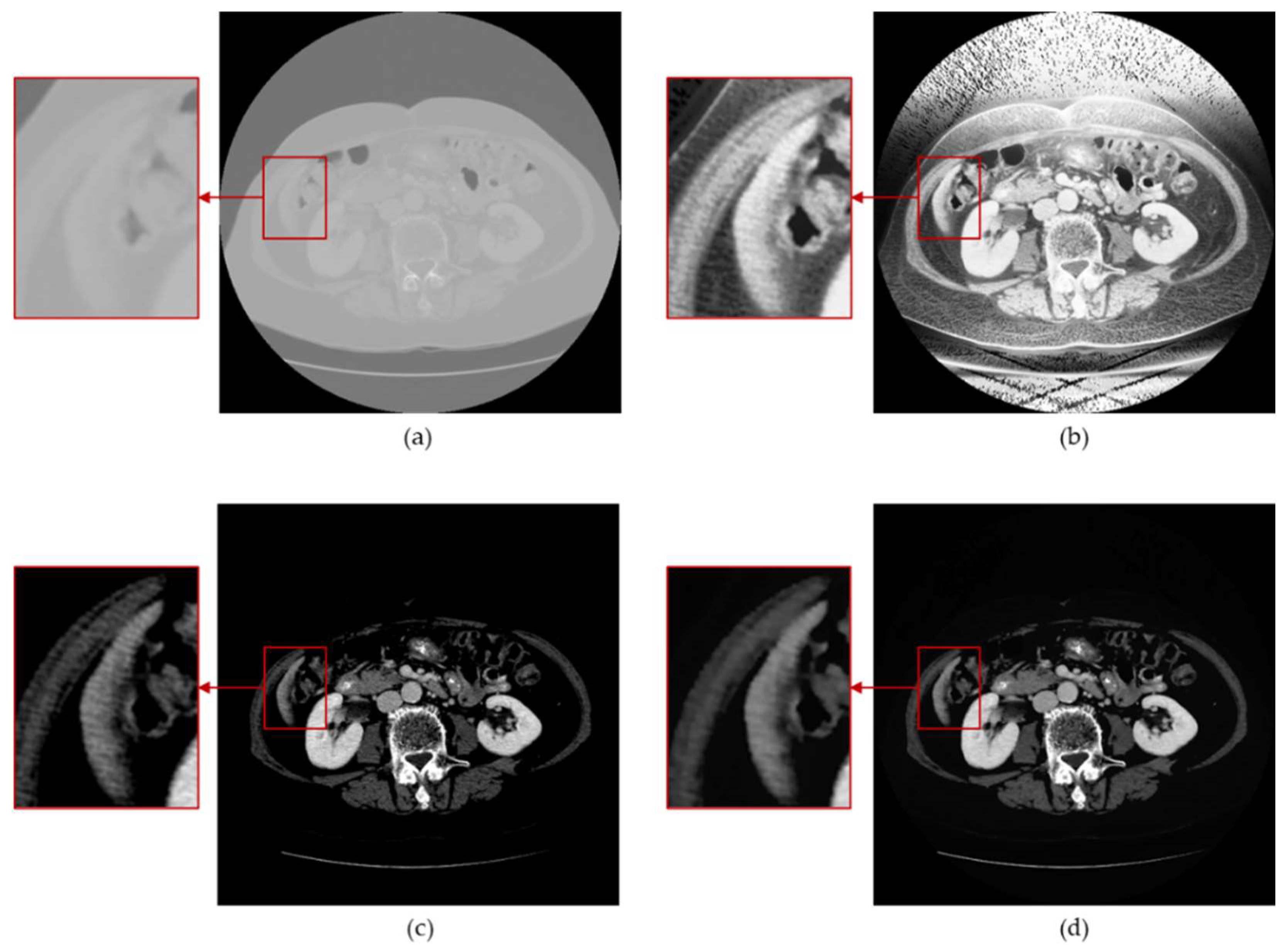
3.2. Anisotropic Diffusion
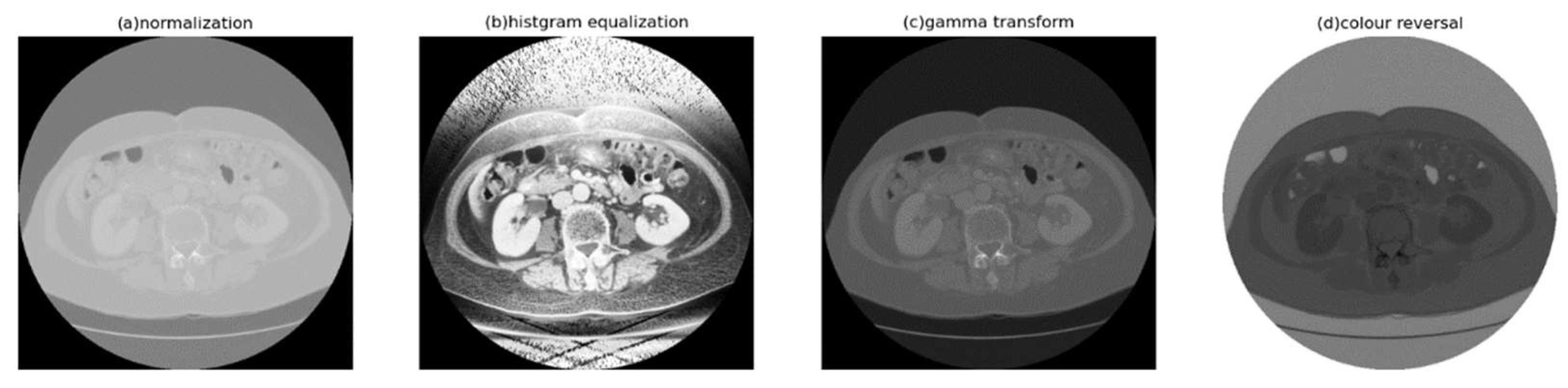
3.3. Histogram Equalization
3.4. Window Adjustment
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Server Information
4.2. Model Selection
4.3. Dataset
4.4. Evaluation Metrics
4.5. Time Complexity Analysis
- Anisotropic diffusion
- 2.
- Histogram Equalization
- 3.
- Window Adjustment
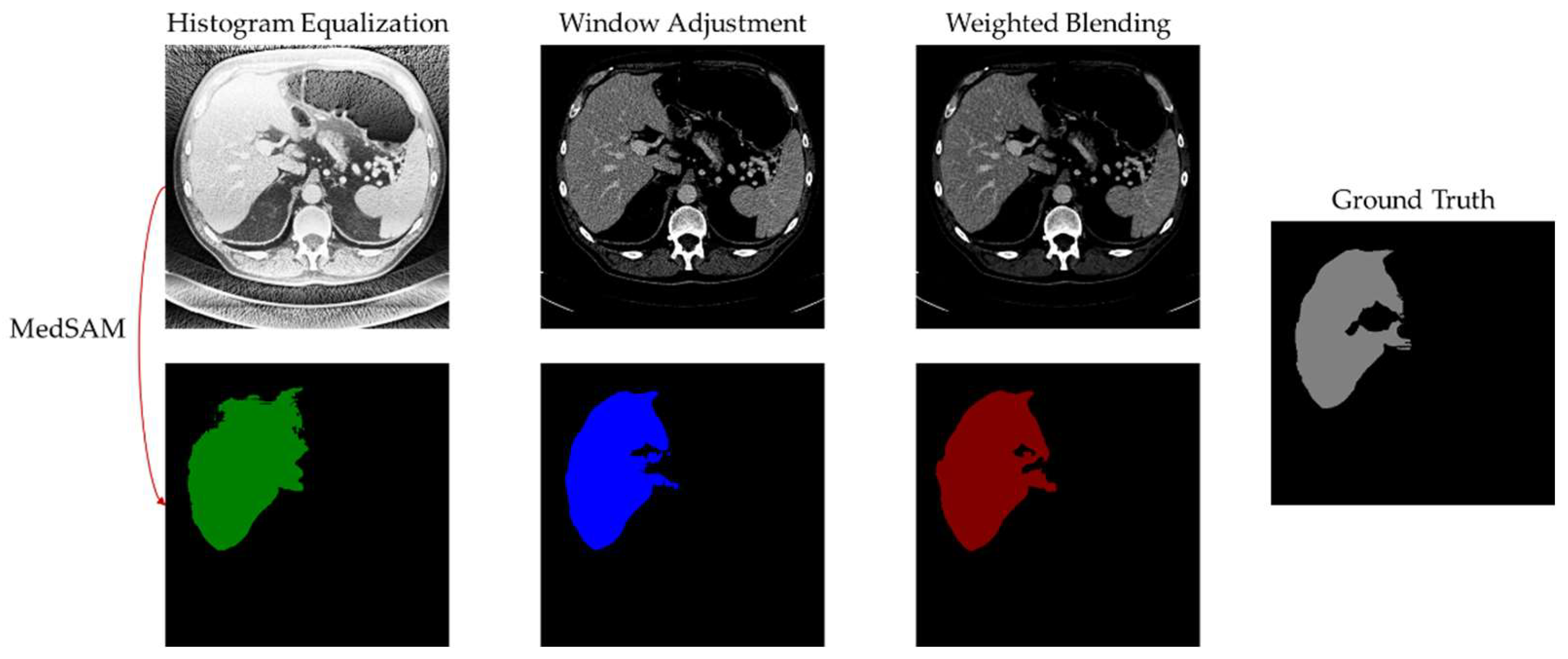
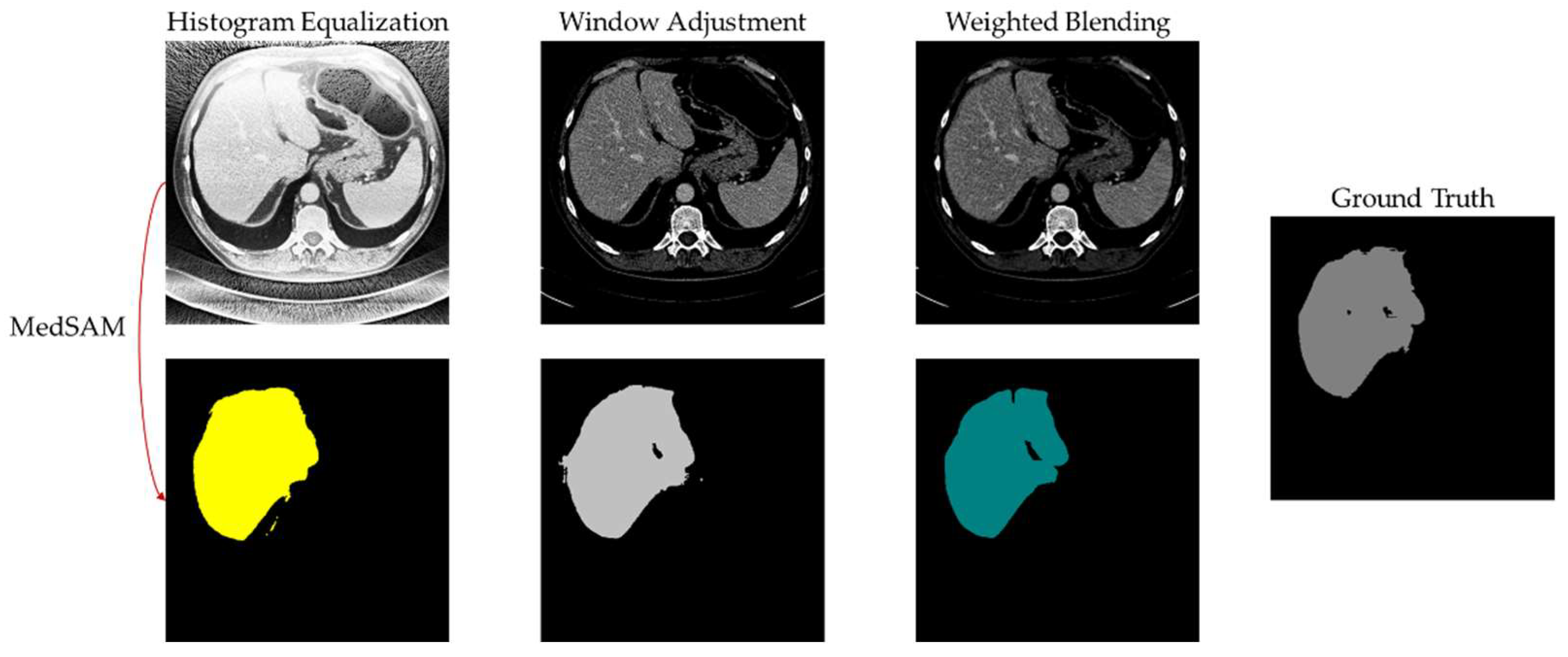
4.6. Experimental Results and Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
7. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brenner, D.J.; Hall, E.J. Computed Tomography—An Increasing Source of Radiation Exposure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2277–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, A.; Silver, E.; Korja, R.; Lehtola, S.J.; Merisaari, H.; Saukko, E.; Sinisalo, S.; Saunavaara, J.; Lähdesmäki, T.; Parkkola, R.; et al. Infant and Child MRI: A Review of Scanning Procedures. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 666020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, A.; Vongkovit, T.; Linguraru, M.G. Adversarial Approach to Diagnostic Quality Volumetric Image Enhancement. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018), 4–7 April 2018; pp. 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.C.F.; Wong, C.Y.; Jiang, G.; Rahman, M.A.; Ren, T.R.; Kwok, N.; Shi, H.; Yu, Y.-H.; Wu, T. Intensity and Edge Based Adaptive Unsharp Masking Filter for Color Image Enhancement. Optik 2016, 127, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Joo, I.; Lee, D.H.; Bae, J.S.; Yoo, J.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, J.M. Diagnostic Performance of LI-RADS Treatment Response Algorithm for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Adding Ancillary Features to MRI Compared with Enhancement Patterns at CT and MRI. Radiology 2020, 296, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otazo, R.; Lambin, P.; Pignol, J.-P.; Ladd, M.E.; Schlemmer, H.-P.; Baumann, M.; Hricak, H. MRI-Guided Radiation Therapy: An Emerging Paradigm in Adaptive Radiation Oncology. Radiology 2021, 298, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Lei, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhou, J.; Roper, J.; Lin, L.; McDonald, M.W.; Bradley, J.D.; Curran, W.J.; Liu, T.; et al. Synthetic Dual-Energy CT for MRI-Only Based Proton Therapy Treatment Planning Using Label-GAN. Phys. Med. Biol. 2021, 66, 065014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, G.; Mittal, A. Various Image Enhancement Techniques—A Critical Review. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Res. 2014, 10, 267–274. [Google Scholar]
- Woods, E.; Gonzalez, R.; Gonzalez, R.C. Digital Image Processing, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, D.-C.; Wu, W.-R. Image Contrast Enhancement Based on a Histogram Transformation of Local Standard Deviation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1998, 17, 518–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, S.; Raju, A.B.K.; Mathivanan, S.K.; Jayagopal, P.; Babu, J.C.; Sahu, A.K. Local-Ternary-Pattern-Based Associated Histogram Equalization Technique for Cervical Cancer Detection. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, R.; Kumar, S.N. 8—Fast Bilateral Filter with Unsharp Masking for the Preprocessing of Optical Coherence Tomography Images—An Aid for Segmentation and Classification. Computational Methods and Deep Learning for Ophthalmology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panetta, K.; Grigoryan, A. Transform-Based Image Enhancement Algorithms with Performance Measure. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2001, 10, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoryan, A.M.; Jenkinson, J.; Agaian, S.S. Quaternion Fourier Transform Based Alpha-Rooting Method Color Image Meas. Enhancement. Signal Process. 2015, 109, 269–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wu, H.; Jin, Z. FourLLIE: Boosting Low-Light Image Enhancement by Fourier Frequency Information. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 29 October–3 November 2023; pp. 7459–7469. [Google Scholar]
- Samani, A.; Panetta, K.; Agaian, S. Contrast Enhancement for Color Images Using Discrete Cosine Transform Coefficient Scaling. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Symposium on Technologies for Homeland Security (HST), Waltham, MA, USA, 10–11 May 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, R.K.; Chouhan, R.; Aizawa, K.; Biswas, P.K. Dark Low-Contrast Image Enhanc. Using Dyn. Stoch. Reson. Discret. Cosine Transform Domain. APSIPA Trans. Signal Inf. Process. 2013, 2, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low-Contrast Satellite Images Enhancement Using Discrete Cosine Transform Pyramid and Singular Value Decomposi-Tion—Atta—2013—IET Image Processing—Wiley Online Library. Available online: https://ietresearch.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1049/iet-ipr.2013.0083 (accessed on 26 February 2024).
- Sengar, P.S.; Rawat, T.K.; Parthasarathy, H. Color Image Enhancement by Scaling the Discrete Wavelet Transform Coefficients. In Proceedings of the 2013 Annual International Conference on Emerging Research Areas and 2013 International Conference on Microelectronics, Communications and Renewable Energy, Kanjirapally, India, 4–6 June 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, H.; Anbarjafari, G. Discrete Wavelet Transform-Based Satellite Image Resolution Enhancement. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 1997–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Yao, J.; Fu, X.; Bi, H.; Hong, D. An Enhanced 3-D Discrete Wavelet Transform for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 18, 1104–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidong, H.; Wei, Z.; Jun, W.; Zebin, S. Combination of Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalisation and Discrete Wavelet Transform for Image Enhancement. IET Image Process. 2015, 9, 908–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, G.; Sanghvi, R. Fusesharp: A multi-image focus fusion method using discrete wavelet transform and unsharp masking. J. Appl. Math. Inform. 2023, 41, 1115–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. SegNet: A Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çiçek, Ö.; Abdulkadir, A.; Lienkamp, S.S.; Brox, T.; Ronneberger, O. 3D U-Net: Learning Dense Volumetric Segmentation from Sparse Annotation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2016; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Lian, S.; Luo, Z.; Li, S. Weighted Res-UNet for High-Quality Retina Vessel Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2018 9th International Conference on Information Technology in Medicine and Education (ITME), Hangzhou, China, 19–21 October 2018; pp. 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Khan, A.A.; Sikdar, S.; Chitnis, P.V. Fully Dense UNet for 2-D Sparse Photoacoustic Tomography Artifact Removal. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 24, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, D.; Smedsrud, P.H.; Riegler, M.A.; Johansen, D.; Lange, T.D.; Halvorsen, P.; Johansen, H.D. ResUNet++: An Advanced Architecture for Medical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Multimedia (ISM), San Diego, CA, USA, 9–11 December 2019; pp. 225–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Luo, X.; Adeli, E.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Yuille, A.L.; Zhou, Y. TransUNet: Transformers Make Strong Encoders for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirillov, A.; Mintun, E.; Ravi, N.; Mao, H.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; Xiao, T.; Whitehead, S.; Berg, A.C.; Lo, W.-Y.; et al. Segment Anything. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Cui, C.; Liu, Q.; Yao, T.; Remedios, L.W.; Bao, S.; Landman, B.A.; Wheless, L.E.; Coburn, L.A.; Wilson, K.T.; et al. Segment Anything Model (SAM) for Digital Pathology: Assess Zero-Shot Segmentation on Whole Slide Imaging. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; He, Y.; Li, F.; Han, L.; You, C.; Wang, B. Segment Anything in Medical Images. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ji, W.; Liu, Y.; Fu, H.; Xu, M.; Xu, Y.; Jin, Y. Medical SAM Adapter: Adapting Segment Anything Model for Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Ye, J.; Deng, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, T.; Wang, H.; Su, Y.; Huang, Z.; Chen, J.; Jiang, L.; et al. SAM-Med2D. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhu, L.; Ding, C.; Cao, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Sun, L.; Mao, P.; Zang, Y. SAM Fails to Segment Anything?—SAM-Adapter: Adapting SAM in Underperformed Scenes: Camouflage, Shadow, Medical Image Segmentation, and More. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perona, P.; Malik, J. Scale-Space and Edge Detection Using Anisotropic Diffusion. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1990, 12, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilic, P.; Christ, P.; Li, H.B.; Vorontsov, E.; Ben-Cohen, A.; Kaissis, G.; Szeskin, A.; Jacobs, C.; Mamani, G.E.H.; Chartrand, G.; et al. The Liver Tumor Segmentation Benchmark (LiTS). Med. Image Anal. 2023, 84, 102680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Guo, J.; Porikli, F.; Pang, Y. LightenNet: A Convolutional Neural Network for Weakly Illuminated Image Enhancement. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2018, 104, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Dong, S.; Chen, L.; Ren, Q. Image Enhancement Method for Low-Light Pipeline Weld X-Ray Radiographs Based on Weakly Supervised Deep Learning. NDT E Int. 2024, 143, 103049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Server configuration and Environment | |
|---|---|
| OS | Ubuntu 22.04.3 LTS |
| CPU | 32 13th Gen Intel(R) Core(TM) i9-13900K |
| GPU | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090 × 2 |
| RAM | 32 GB DDR5 × 4 |
| Evaluation Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| IoU | Intersection over Union, which measures the overlap between the predicted and ground truth regions. |
| Dice Coefficient | Measures the similarity between the predicted and ground truth regions. |
| Accuracy | Measures the overall correctness of the segmentation. |
| Precision | Measures the proportion of correctly predicted positive pixels among all the predicted positive pixels. |
| Recall | Measures the proportion of correctly predicted positive pixels among all the ground truth positive pixels. |
| Sensitivity | Measures the ability to correctly identify positive pixels. |
| F1 | Combines precision and recall to provide a balanced measure of segmentation accuracy. |
| Specificity | Measures the ability to correctly identify negative pixels. |
| Proposed Method | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IoU | dice | accuracy | precision | recall | sensitivity | f1 | specificity | |
| 1 | 0.9635 | 0.9814 | 0.9970 | 0.9948 | 0.9683 | 0.9683 | 0.9814 | 0.9996 |
| 2 | 0.9164 | 0.9564 | 0.9902 | 0.9978 | 0.9182 | 0.9182 | 0.9564 | 0.9997 |
| 3 | 0.7682 | 0.8689 | 0.9988 | 0.8284 | 0.9135 | 0.9135 | 0.8689 | 0.9992 |
| 4 | 0.7752 | 0.8734 | 0.9923 | 0.8915 | 0.8559 | 0.8559 | 0.8734 | 0.9967 |
| 5 | 0.9009 | 0.9479 | 0.9854 | 0.9207 | 0.9766 | 0.9766 | 0.9479 | 0.9867 |
| 6 | 0.8816 | 0.9371 | 0.9846 | 0.9137 | 0.9616 | 0.9616 | 0.9371 | 0.9878 |
| 7 | 0.9367 | 0.9673 | 0.9920 | 0.9894 | 0.9462 | 0.9462 | 0.9673 | 0.9986 |
| 8 | 0.9428 | 0.9706 | 0.9908 | 0.9926 | 0.9495 | 0.9495 | 0.9706 | 0.9987 |
| 9 | 0.9577 | 0.9784 | 0.9976 | 0.9894 | 0.9676 | 0.9676 | 0.9784 | 0.9994 |
| 10 | 0.9594 | 0.9793 | 0.9933 | 0.9804 | 0.9782 | 0.9782 | 0.9793 | 0.9962 |
| 0.9002 | 0.9460 | 0.9922 | 0.9499 | 0.9436 | 0.9436 | 0.9460 | 0.9962 | |
| Normalization | ||||||||
| IoU | dice | accuracy | precision | recall | sensitivity | f1 | specificity | |
| 1 | 0.9576 | 0.9784 | 0.9965 | 0.986 | 0.9709 | 0.9709 | 0.9784 | 0.9988 |
| 2 | 0.8668 | 0.9286 | 0.9828 | 0.9053 | 0.9532 | 0.9532 | 0.9286 | 0.9867 |
| 3 | 0.6667 | 0.8000 | 0.9979 | 0.6732 | 0.9856 | 0.9856 | 0.8000 | 0.998 |
| 4 | 0.5641 | 0.7213 | 0.9767 | 0.5744 | 0.9693 | 0.9693 | 0.7213 | 0.9769 |
| 5 | 0.7928 | 0.8844 | 0.9661 | 0.8265 | 0.9511 | 0.9511 | 0.8844 | 0.9685 |
| 6 | 0.8652 | 0.9278 | 0.9816 | 0.8703 | 0.9933 | 0.9933 | 0.9278 | 0.9800 |
| 7 | 0.8661 | 0.9283 | 0.9821 | 0.9309 | 0.9256 | 0.9256 | 0.9283 | 0.9902 |
| 8 | 0.9315 | 0.9646 | 0.9885 | 0.9474 | 0.9824 | 0.9824 | 0.9646 | 0.9896 |
| 9 | 0.7801 | 0.8765 | 0.9854 | 0.8307 | 0.9276 | 0.9276 | 0.8765 | 0.9888 |
| 10 | 0.9010 | 0.9479 | 0.9826 | 0.9217 | 0.9758 | 0.9758 | 0.9479 | 0.9840 |
| 0.8192 | 0.8958 | 0.984 | 0.8466 | 0.9635 | 0.9635 | 0.8958 | 0.9862 | |
| Window Adjustment | ||||||||
| IoU | dice | accuracy | precision | recall | sensitivity | f1 | specificity | |
| 1 | 0.9605 | 0.9798 | 0.9968 | 0.9946 | 0.9655 | 0.9655 | 0.9798 | 0.9995 |
| 2 | 0.8886 | 0.9410 | 0.9869 | 0.9964 | 0.8914 | 0.8914 | 0.941 | 0.9996 |
| 3 | 0.7224 | 0.8389 | 0.9986 | 0.8454 | 0.8324 | 0.8324 | 0.8389 | 0.9994 |
| 4 | 0.5290 | 0.6919 | 0.9725 | 0.5314 | 0.9914 | 0.9914 | 0.6919 | 0.9719 |
| 5 | 0.8988 | 0.9467 | 0.9855 | 0.9506 | 0.9429 | 0.9429 | 0.9467 | 0.9923 |
| 6 | 0.8887 | 0.9411 | 0.9857 | 0.9246 | 0.9581 | 0.9581 | 0.9411 | 0.9895 |
| 7 | 0.9352 | 0.9665 | 0.9918 | 0.9902 | 0.9440 | 0.9440 | 0.9665 | 0.9987 |
| 8 | 0.9347 | 0.9662 | 0.9891 | 0.9515 | 0.9814 | 0.9814 | 0.9662 | 0.9905 |
| 9 | 0.9526 | 0.9757 | 0.9973 | 0.9939 | 0.9582 | 0.9582 | 0.9757 | 0.9997 |
| 10 | 0.9463 | 0.9724 | 0.9910 | 0.9657 | 0.9792 | 0.9792 | 0.9724 | 0.9933 |
| 0.8657 | 0.922 | 0.9895 | 0.9144 | 0.9445 | 0.9445 | 0.9220 | 0.9934 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, L.; Huang, M.; Zhang, L.; Chan, L.W.C. Enhancing Diagnostic Images to Improve the Performance of the Segment Anything Model in Medical Image Segmentation. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11030270
Kong L, Huang M, Zhang L, Chan LWC. Enhancing Diagnostic Images to Improve the Performance of the Segment Anything Model in Medical Image Segmentation. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(3):270. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11030270
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Luoyi, Mohan Huang, Lingfeng Zhang, and Lawrence Wing Chi Chan. 2024. "Enhancing Diagnostic Images to Improve the Performance of the Segment Anything Model in Medical Image Segmentation" Bioengineering 11, no. 3: 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11030270
APA StyleKong, L., Huang, M., Zhang, L., & Chan, L. W. C. (2024). Enhancing Diagnostic Images to Improve the Performance of the Segment Anything Model in Medical Image Segmentation. Bioengineering, 11(3), 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11030270