A Study of the Associated Risk Factors for Early Failure and the Effect of Photofunctionalisation in Full-Arch Immediate Loading Treatment Based on the All-on-Four Concept
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Patients over the age of 18 of both sexes and Japanese;
- Severe atrophy of the maxilla or mandible in the posterior regions;
- Prior to treatment, a decision towards an immediately loaded implant and supported fixed complete dental prostheses had to be made;
- Patients had to be physically and psychologically able to tolerate conventional surgical and restorative procedures.
- Patients who did not undergo follow-up at the private clinic;
- Patients with zygomatic implants;
- Immunosuppression;
- Active treatment of malignancy;
- Intravenous bisphosphonate therapy;
- Uncontrolled systemic diseases (e.g., diabetes).
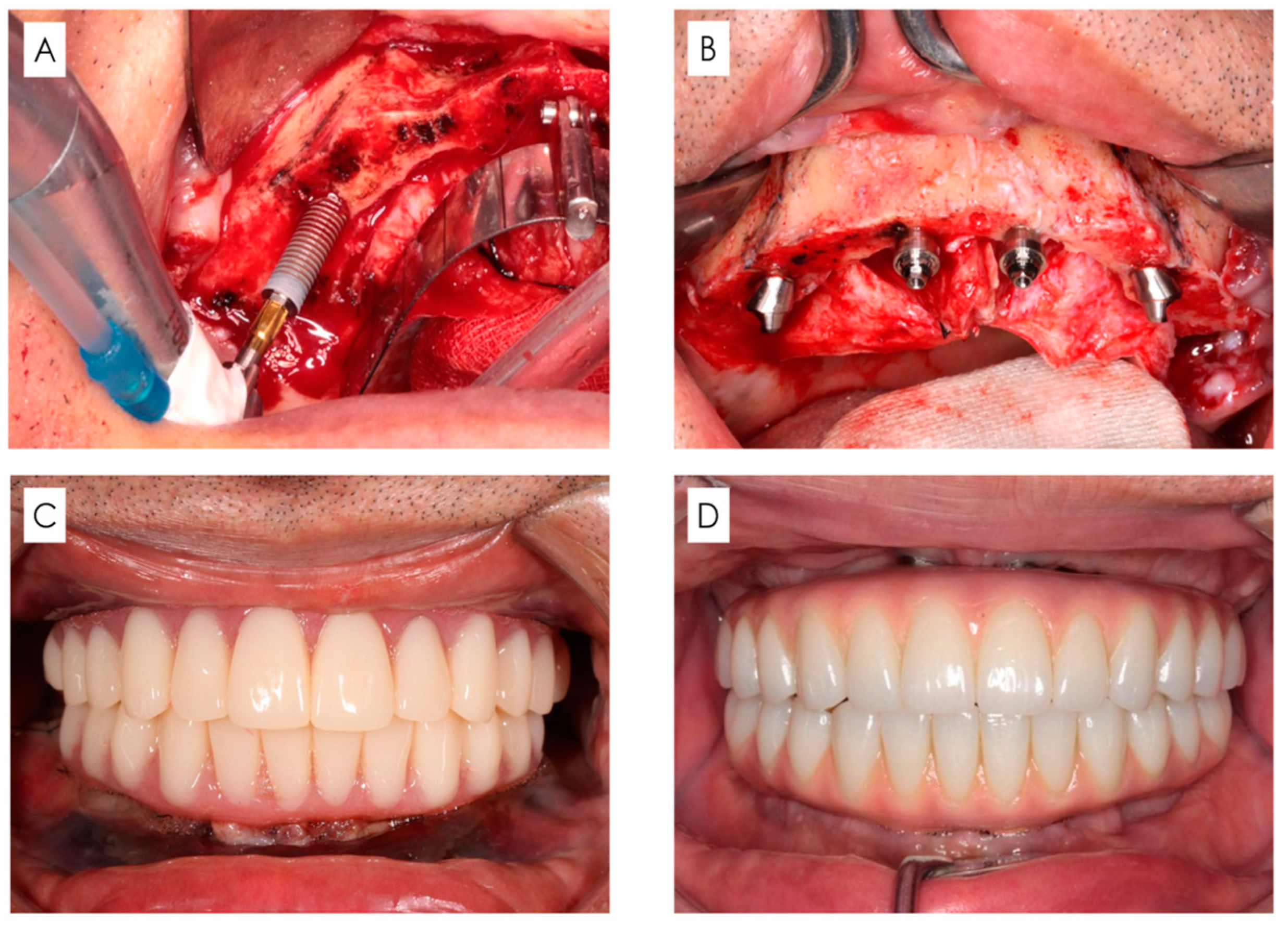
2.1. Surgical Protocol
- Regarding patients with remaining teeth, these teeth were extracted.
- A longitudinal incision was made on the mucosa distal to the first molars on both sides, and a transverse incision was made on the mucosa on the alveolar crest slightly on the lingual/palatal side to form a mucoperiosteal flap.
- If necessary, shaping of the alveolar bone and jawbone was performed to secure the clearance required for prosthetic device fabrication and base surface levelling.
- For the maxillary sinus, a portion of the anterior wall of the maxillary sinus was excised using a round burr tip, and a probe was used to explore the same area to confirm the morphology of the anterior maxillary sinus. With respect to the mandible, the mental foramen was clearly indicated, and a probe was inserted in the mesial direction along the bone surface and used to confirm the nerve running morphology.
- Implants (with diameter ≥ 4.0 mm) were inserted from the posterior end on both sides. The implantation position and tilt angle were determined using a standardised surgical guide (All-on-four Guide, Nobel Biocare AG, Kloten, Switzerland).
- The leading tip of the implant embedded in the posterior slope was placed in the mouth region equivalent to the canines while being careful to avoid causing interference. The anterior implant (with diameter ≥ 3.3 mm) was placed in the area corresponding to the middle and lateral incisors.
- In principle, four implant bodies were inserted. However, if it was not possible to place an implant with a length ≥ 10 mm, or if an initial fixation of ≥35 Ncm could not be obtained, additional implants should be placed nearby if necessary and possible.
- When inserting the implant, a straight or 17° and 30° angled abutment were attached anteriorly and posteriorly, respectively, and sutured.
2.2. Prosthetic Protocol
2.3. Follow-Up and Maintenance Protocol
2.4. Clinical Outcome
- Early failure within 1 year of implantation:
- 2.
- Examination of risk factors affecting early failure:
- Implant-related factors (photofunctionalisation, tilt, implant length, diameter, and initial fixation value);
- Patient-related factors (sex, smoking history (number of cigarettes: 10 cigarettes/day or more), and systemic diseases (diabetes, osteoporosis, cardiovascular diseases));
- Risk factors for survival rate multivariate analysis.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Survival Rate (Early Failure Rate) 1 Year after Implantation (Table 1)
3.2. Examination of Risk Factors Affecting Early Failure
Implant-Related Factors (Table 2 and Table 3)
- Photofunctionalisation.
| Photofunctionalisation | Patient-Level | Implant-Level | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maxilla | Yes | 2.4% (3/126 cases) |  | 0.6% (3/486 implants) |  |
| No | 3.2% (7/219 cases) | 1.3% (12/890 implants) | |||
| Mandible | Yes | 1.2% (1/85 cases) | 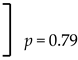 | 0.3% (1/333 implants) | 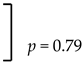 |
| No | 1.6% (184/187 cases) | 0.4% (741/744 implants) | |||
| Total (n = 2453) | Failure (n = 19) | Rate (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Photofunctionalisation | ||||
| Yes | 819 | 4 | 0.5 | 0.25 |
| No | 1634 | 15 | 0.9 | |
| Implant angulation | ||||
| Straight | 1229 | 7 | 0.6 | |
| Tilted | 1224 | 12 | 1 | 0.24 |
| Implant length (mm) | ||||
| <10 | 46 | 0 | 0 | ― |
| 10≤, <15 | 651 | 7 | 1.1 | 0.47 |
| 15≤, <18 | 712 | 5 | 0.7 | 0.57 |
| 18≤ | 1044 | 7 | 0.7 | 0.58 |
| Implant diameter (mm) | ||||
| 3.3 | 135 | 1 | 0.7 | ― |
| 4.0 | 2291 | 18 | 0.8 | 0.95 |
| 5.0≤ | 27 | 0 | 0 | 0.65 |
| Primary stability (N·cm) | ||||
| <35 | 143 | 0 | 0 | ― |
| 35≤, <50 | 630 | 10 | 1.6 | 0.13 |
| 50≤ | 1680 | 9 | 0.5 | 0.38 |
- 2.
- Patient-related factors (Table 4).
- Sex:
- Smoking:
- Systemic disease:
- 3.
- Risk factors for survival rate after multivariate analysis (Table 5).
4. Discussion
4.1. Factors Related to Early Failure
4.1.1. Implant-Related Factors
4.1.2. Patient-Related Factors
5. Conclusions
- The survival rate after 1 year of implantation was high for both the maxilla and mandible. However, at the implant level, the maxilla showed a significantly lower survival rate compared to the mandible.
- Among the implant-related factors, significantly higher early failure rates were seen in the maxilla.
- Among the patient-related factors, smoking significantly increased the risk of early failure (OR: 2.52, p = 0.03).
- Photofunctionalisation did not show the effect on early failure with an odds ratio of 0.51; however, statistical significance was not found.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, L.-C. Risk factors associated with early failure of maxillary versus mandibular implants: A retrospective study. Int. J. Oral Implantol. 2020, 13, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Jemt, T.; Nilsson, M.; Olsson, M.; Stenport, V.F. Associations between early implant failure, patient age, and patient mortality: A 15-year follow-up study on 2566 patients treated with implant-supported prostheses in the edentulous jaw. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2017, 30, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoun, H.; Karouni, M.; Abitbol, J.; Zouiten, O.; Jemt, T. A retrospective study on 1592 consecutively performed operations in one private referral clinic. Part I: Early inflammation and early implant failures. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2017, 19, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borba, M.; Deluiz, D.; Lourenço, E.J.V.; Oliveira, L.; Tannure, P.N. Risk factors for implant failure: A retrospective study in an educational institution using GEE analyses. Braz. Oral Res. 2017, 31, e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tattan, M.; Puranam, M.; Conmick, C.; McBrearty, C.; Xie, X.J.; Caplan, D.J.; Avila-Ortiz, G.; Elangovan, S. Surgery start time and early implant failure: A case-control study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2021, 32, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Shi, Q.; Huang, Y.; Chang, P.; Huo, N.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, J. Failure risk of short dental implants under immediate loading: A meta-analysis. J. Prosthodont. 2021, 30, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malm, M.O.; Jemt, T.; Stenport, V. Early implant failures in edentulous patients: A multivariable regression analysis of 4615 consecutively treated jaws. A Retrospective Study. J. Prosthodont. 2018, 27, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedo-Gaya, M.V.; Manzano-Moreno, F.J.; Cañaveral-Cavero, E.; Castillo, J.D.L.; Vallecillo-Capilla, M. Risk factors associated with early implant failure: A 5-year retrospective clinical study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2016, 115, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hu, H.; Zeng, M.; Chu, H.; Gan, Z.; Duan, J.; Rong, M. The survival rates and risk factors of implants in the early stage: A retrospective study. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrcanovic, B.R.; Kisch, J.; Albreketsson, T.; Wennerberg, T. Factors influencing early dental implant failures. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 95, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grisar, K.; Sinha, D.; Schoenaers, J.; Dormaar, T.; Politis, C. Retrospective analysis of dental implants placed between 2012 and 2014: Indications, risk factors, and early survival. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2017, 32, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaadi, G.; Quirynen, M.; Komárek, A.; van Steenberghe, D. Impact of local and systemic factors on the incidence of oral implant failures, up to abutment connection. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2007, 34, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, F.; Papi, P.; Mencio, F.; Rosella, D.; Di Carlo, S.; Pompa, G. Implant survival and success rates in patients with risk factors: Results from a long-term retrospective study with a 10 to 18 years follow-up. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Camps-Font, O.; Martín-Fatás, P.; Clé-Ovejero, A.; Figueiredo, R.; Gay-Escoda, C.; Valmaseda-Castellón, E. Postoperative infections after dental implant placement: Variables associated with increased risk of failure. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maló, P.; Nobre, M.A.; Lopes, A.; Ferro, A.; Nunes, M. The All-on-4 concept for full-arch rehabilitation of the edentulous maxillae: A longitudinal study with 5–13 years of follow-up. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2019, 21, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maló, P.; Nobre, M.A.; Lopes, A.; Ferro, A.; Botto, J. The All-on-4 treatment concept for the rehabilitation of the completely edentulous mandible: A longitudinal study with 10 to 18 years of follow-up. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2019, 21, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.Y.; Davies, J.E. Red blood cell and platelet interactions with titanium implant surfaces. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2000, 11, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, J.E. Understanding peri-implant endosseous healing. J. Dent. Educ. 2003, 67, 932–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, D.; Schenk, R.K.; Steinemann, S.; Fiorellini, J.P.; Fox, C.H.; Stich, H. Influence of surface characteristics on bone integration of titanium implants. A histomorphometric study in miniature pigs. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1991, 25, 899–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericsson, I.; Johansson, C.B.; Bystedt, H.; Norton, M.R. A histomorphometric evaluation of bone-to-implant contact on machine-prepared and roughened titanium dental implants. A pilot study in the dog. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1994, 5, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzara, R.J.; Testori, T.; Trisi, P.; Porter, S.S.; Weinstein, R.L. A human histologic analysis of osseotite and machined surfaces using implants with 2 opposing surfaces. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 1999, 19, 117–129. [Google Scholar]
- Del Fabbro, M.; Testori, T.; Francetti, L.; Taschieri, S.; Weinstein, R. Systematic review of survival rates for immediately loaded dental implants. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2006, 26, 249–263. [Google Scholar]
- Papaspyridakos, P.; Chen, C.-J.; Chuang, S.-K.; Weber, H.-P. Implant loading protocols for edentulous patients with fixed prostheses: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implant. 2014, 29, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aita, H.; Hori, N.; Takeuchi, M.; Suzuki, T.; Yamada, M.; Anpo, M.; Ogawa, T. The effect of ultraviolet functionalization of titanium on integration with bone. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T. Ultraviolet photofunctionalization of titanium implants. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2014, 29, e95–e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawase, T.; Jimbo, R.; Baba, K.; Shibata, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Atsuta, M. Photo-induced hydrophilicity enhances initial cell behavior and early bone apposition. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2008, 19, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, I.-S.L. Modifications of dental implant surfaces at the micro- and nano-level for enhanced osseointegration. Materials 2019, 13, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuna, T.; Wein, M.; Swain, M.; Fischer, J.; Att, W. Influence of ultraviolet photofunctionalization on the surface characteristics of zirconia-based dental implant materials. Dent. Mater. 2015, 31, e14–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasa, F.; Tsukimura, N.; Sugita, Y.; Kanuru, R.K.; Kubo, K.; Hasnain, H.; Att, W.; Ogawa, T. TiO2 micro-nano-hybrid surface to alleviate biological aging of UV-photofunctionalized titanium. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 1327–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Yamada, M.; Ueda, T.; Sakurai, K. Reduction of biofilm formation on titanium surface with ultraviolet-C preirradiation. J. BioMater. Appl. 2014, 29, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Avila, E.D.; Lima, B.P.; Sekiya, T.; Torii, Y.; Ogawa, T.; Shi, W.; Lux, R. Effect of UV-photofunctionalization on oral bacterial attachment and biofilm formation to titanium implant material. Biomaterials 2015, 67, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirota, M.; Ozawa, T.; Iwai, T.; Ogawa, T.; Tohnai, I. Effect of photofunctionalization on early implant failure. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2018, 33, 1098–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uesugi, T.; Shimoo, Y.; Munakata, M.; Sato, D.; Yamaguchi, K.; Fujimaka, M.; Nakayama, K.; Watanabe, T.; Malo, P. The All-on-four concept for fixed full-arch rehabilitation of the edentulous maxilla and mandible: A longitudinal study in Japanese patients with 3–17-year follow-up and analysis of risk factors for survival rate. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2023, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.H.; Nudell, Y.A. All-on-4 concept update. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 65, 211–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derks, J.; Håkansson, J.; Wennström, J.L.; Tomasi, C.; Larsson, M.; Berglundh, T. Effectiveness of implant therapy analysed in a Swedish population: Early and late implant loss. J. Dent. Res. 2015, 94, 44S–51S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.; Ye, S.; Liu, F.; He, F. A retrospective study of 30,959 implants: Risk factors associated with early and late implant loss. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maló, P.; de Araújo, N.M.; Lopes, A.; Francischone, C.; Rigolizzo, M. “All-on-4” immediate-function concept for completely edentulous maxillae: A clinical report on the medium (3 years) and long-term (5 years) outcomes. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2012, 14, e139–e150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baqain, Z.H.; Moqbel, W.Y.; Sawair, F.A. Early dental implant failure: Risk factors. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 50, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennerberg, A.; Albrektsson, T. Effects of titanium surface topography on bone integration: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2009, 20, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagirkaya, E.; Kucukekenci, A.S.; Karasoy, D.; Akca, K.; Eckert, S.; Çehreli, M.C. Comparative assessments, meta-analysis, and recommended guidelines for reporting studies on histomorphometric bone-implant contact in humans. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2013, 28, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar]
- Funato, A.; Yamada, M.; Ogawa, T. Success rate, healing time, and implant stability of photofunctionalized dental implants. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2013, 28, 1261–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Ogawa, T. Implant stability change and osseointegration speed of immediately loaded photofunctionalized implants. Implant. Dent. 2013, 22, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, P.; Lin, Y.; Li, J.-H.; Luo, J.; Xiu, L.-X.; Chen, B.; Cui, H.-Y. The All-on-Four implant therapy protocol in the management of edentulous Chinese patients. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2013, 26, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maló, P.; Nobre, M.A.; Gonçalves, Y.; Lopes, A. Long-term outcome of implant rehabilitations in patients with systemic disorders and smoking habits: A retrospective clinical study. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2016, 18, 64965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Patient-Level | Implant-Level | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maxilla | 2.9% (10/345 cases) | 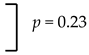 | 1.1% (15/1376 implants) | 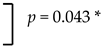 |
| Mandible | 1.5% (4/272 cases) | 0.4% (4/1077 implants) | ||
| Total (n = 617) | Failure (n = 14) | Rate (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 320 | 11 | 3.4 | 0.043 * |
| Female | 297 | 3 | 1 | |
| Age (years; mean ± SD) | 56.8 ± 10.8 | |||
| Smoking | ||||
| Yes | 220 | 9 | 4.1 | 0.023 * |
| No | 397 | 5 | 1.3 | |
| Systemic disease | ||||
| Healthy | ||||
| Yes | 348 | 7 | 2 | |
| No | 269 | 7 | 2.6 | 0.625 |
| Diabetes | ||||
| Yes | 38 | 2 | 5.3 | |
| No | 579 | 12 | 2.1 | 0.2 |
| Osteoporosis | ||||
| Yes | 8 | 1 | 12.5 | |
| No | 609 | 13 | 2.1 | 0.051 |
| Cardiovascular diseases | ||||
| Yes | 130 | 3 | 2.3 | |
| No | 487 | 11 | 2.3 | 0.97 |
| Risk Factor | Odds Ratio | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Implant-related factors for implant level | |||
| Photofunctionalisation | Yes | 0.51 | 0.237 > 0.05 |
| Treatment area | Maxilla | 3.12 | 0.0444 < 0.05 * |
| Patient-related factors for patient level | |||
| Sex | Male | 1.25 | 0.649 > 0.05 |
| Smoker | Smoking | 2.92 | 0.0296 < 0.05 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uesugi, T.; Shimoo, Y.; Munakata, M.; Kataoka, Y.; Sato, D.; Yamaguchi, K.; Sanda, M.; Fujimaki, M.; Nakayama, K.; Watanabe, T.; et al. A Study of the Associated Risk Factors for Early Failure and the Effect of Photofunctionalisation in Full-Arch Immediate Loading Treatment Based on the All-on-Four Concept. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11030223
Uesugi T, Shimoo Y, Munakata M, Kataoka Y, Sato D, Yamaguchi K, Sanda M, Fujimaki M, Nakayama K, Watanabe T, et al. A Study of the Associated Risk Factors for Early Failure and the Effect of Photofunctionalisation in Full-Arch Immediate Loading Treatment Based on the All-on-Four Concept. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(3):223. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11030223
Chicago/Turabian StyleUesugi, Takashi, Yoshiaki Shimoo, Motohiro Munakata, Yu Kataoka, Daisuke Sato, Kikue Yamaguchi, Minoru Sanda, Michiya Fujimaki, Kazuhisa Nakayama, Tae Watanabe, and et al. 2024. "A Study of the Associated Risk Factors for Early Failure and the Effect of Photofunctionalisation in Full-Arch Immediate Loading Treatment Based on the All-on-Four Concept" Bioengineering 11, no. 3: 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11030223
APA StyleUesugi, T., Shimoo, Y., Munakata, M., Kataoka, Y., Sato, D., Yamaguchi, K., Sanda, M., Fujimaki, M., Nakayama, K., Watanabe, T., & Malo, P. (2024). A Study of the Associated Risk Factors for Early Failure and the Effect of Photofunctionalisation in Full-Arch Immediate Loading Treatment Based on the All-on-Four Concept. Bioengineering, 11(3), 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11030223








