FEA-Based Stress–Strain Barometers as Forecasters for Corneal Refractive Power Change in Orthokeratology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Contact Lens Design and Manufacturing
2.2. Subject Data Collection and Processing
2.3. Contact Lens Fitting Protocol and Follow-Up
2.4. Tangential Refractive Power Change (RPC)
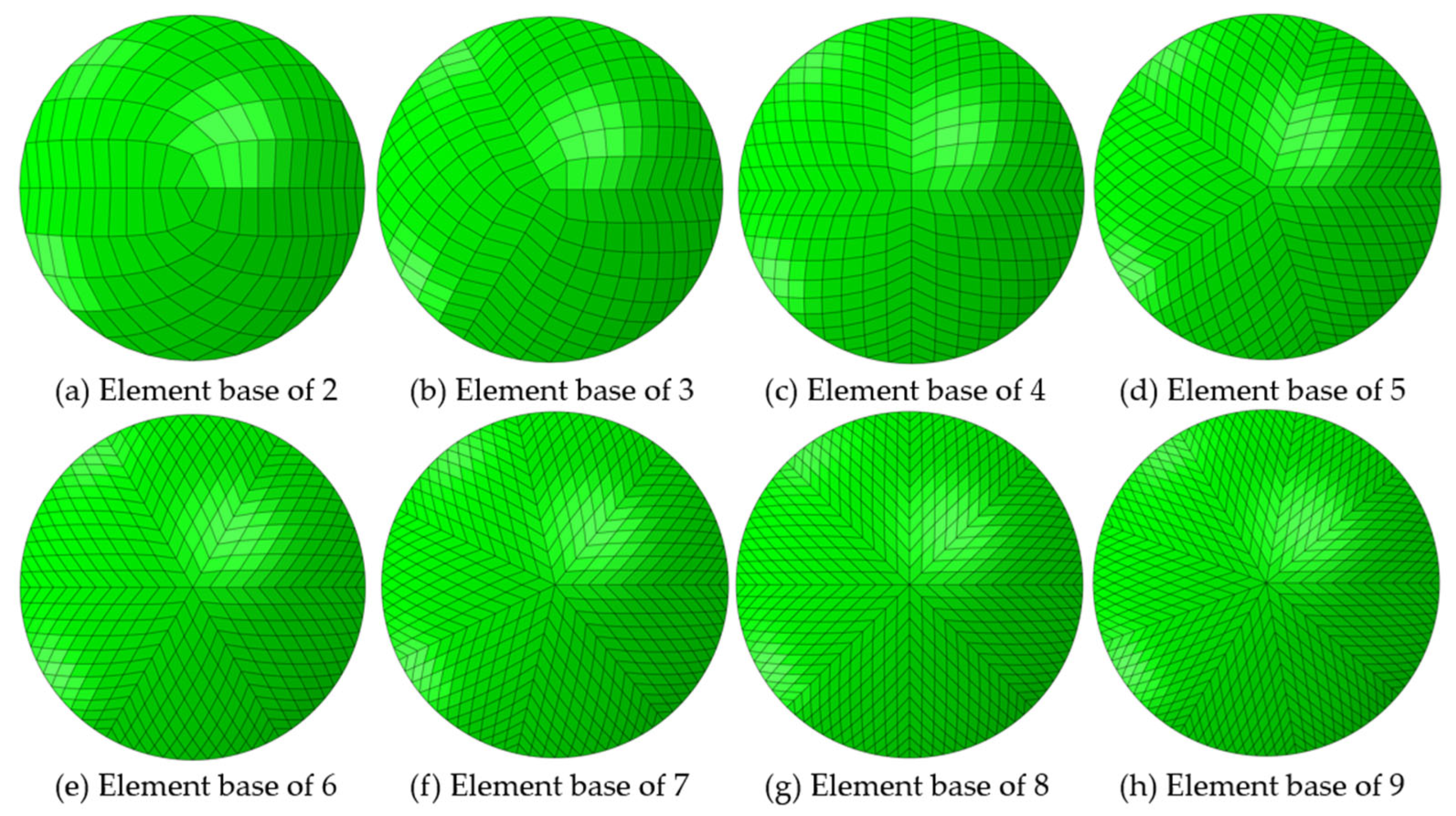
2.5. Finite Element Modelling
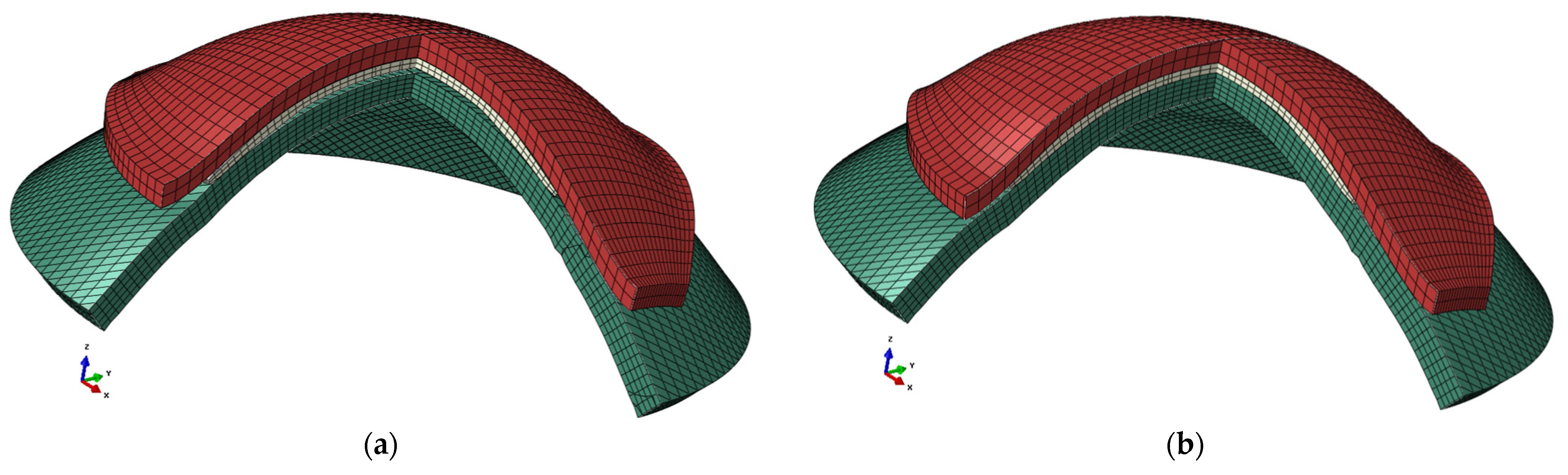
2.6. Anterior Eye Model
2.7. Eyelid Edge Detection and Modelling
2.8. Contact Lens Model
2.9. Modelling Results Exportation Methodology
2.10. Statistical Analysis
2.11. Two-Dimension (2D) Normalised Cross-Correlation
2.12. Structural Similarity (SSIM) Index
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carney, L.G. The basis for corneal shape change during contact lens wear. Optom. Vis. Sci. 1975, 52, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, S.J.; Cho, P.; Chan, K.Y.; Fadel, D.; Ghorbani-Mojarrad, N.; González-Méijome, J.M.; Johnson, L.; Kang, P.; Michaud, L.; Simard, P.; et al. BCLA CLEAR—Orthokeratology. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2021, 44, 240–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullimore, M.A.; Johnson, L.A. Overnight orthokeratology. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2020, 43, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria-Ribeiro, M.; Belsue, R.N.; Lopez-Gil, N.; Gonzalez-Meijome, J.M. Morphology, topography, and optics of the orthokeratology cornea. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 75011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carracedo, G.; Espinosa-Vidal, T.M.; Martinez-Alberquilla, I.; Batres, L. The Topographical Effect of Optical Zone Diameter in Orthokeratology Contact Lenses in High Myopes. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 2019, 1082472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, P.; Cheung, S.W. Retardation of myopia in Orthokeratology (ROMIO) study: A 2-year randomized clinical trial. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 7077–7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wen, D.; Wang, Q.; McAlinden, C.; Flitcroft, I.; Chen, H.; Saw, S.M.; Chen, H.; Bao, F.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Efficacy Comparison of 16 Interventions for Myopia Control in Children: A Network Meta-analysis. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robboy, M.W.; Hilmantel, G.; Tarver, M.E.; Eydelman, M.B. Assessment of Clinical Trials for Devices Intended to Control Myopia Progression in Children. Eye Contact Lens 2018, 44, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarbrick, H.A. Orthokeratology review and update. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2006, 89, 124–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Li, F.; Wang, T. Redistribution of the corneal epithelium after overnight wear of orthokeratology contact lenses for myopia reduction. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2020, 43, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charman, W.N.; Mountford, J.; Atchison, D.A.; Markwell, E.L. Peripheral Refraction in Orthokeratology Patients. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2006, 83, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gifford, P.; Tran, M.; Priestley, C.; Maseedupally, V.; Kang, P. Reducing treatment zone diameter in orthokeratology and its effect on peripheral ocular refraction. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2020, 43, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.; Lopes, B.T.; Eliasy, A.; Geraghty, B.; Wu, R.; White, L.; Elsheikh, A.; Abass, A. Simulation of the Effect of Material Properties on Soft Contact Lens On-Eye Power. Bioengineering 2019, 6, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abass, A.; Stuart, S.; Lopes, B.T.; Zhou, D.; Geraghty, B.; Wu, R.; Jones, S.; Flux, I.; Stortelder, R.; Snepvangers, A.; et al. Simulated optical performance of soft contact lenses on the eye. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, T.; Moore, J.; Shihab, A.H.; Lopes, B.T.; Eliasy, A.; Maklad, O.; Wu, R.; White, L.; Jones, S.; Elsheikh, A.; et al. Which feature influences on-eye power change of soft toric contact lenses: Design or corneal shape? PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.-P.; Zhai, H.-T.; Xiang, H.-Z.; Wu, L.-M.; Chen, Q.-O.; Chen, C.; Zhou, M. Biomechanical study of cornea response under orthokeratology lens therapy: A finite element analysis. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 2023, 39, e3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraya, M.; Moore, J.; Lopes, B.T.; Wu, R.; Bao, F.; Zheng, X.; Consejo, A.; Abass, A. Limitations of Reconstructing Pentacam Rabbit Corneal Tomography by Zernike Polynomials. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Simpson, T.; Sorbara, L.; Fonn, D. The relationship between the treatment zone diameter and visual, optical and subjective performance in Corneal Refractive Therapy lens wearers. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2007, 27, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.-Y.; Gomes Esporcatte, L.P.; Li, W.-K.; Lin, W.-P.; Wu, R.; White, L.; Salomão, M.Q.; Lopes, B.T.; Ambrósio, R., Jr.; Abass, A. Investigation of the relationship between contact lens design parameters and refractive changes in Ortho-K. Heliyon 2022, 8, E11699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, T. On the calculation of power from curvature of the cornea. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1986, 70, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.-D.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Tsai, R.J.-F.; Kuo, L.-L.; Tsai, I.L.; Liou, S.-W. Validity of the keratometric index: Evaluation by the Pentacam rotating Scheimpflug camera. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2008, 34, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, G.; Atchison, D.A. The Eye and Visual Optical Instruments; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Vojnikovi, B.o.; Tamajo, E. Gullstrand’s Optical Schematic System of the Eye Modified by Vojnikovi & Tamajo. Coll. Antropol. 2013, 37, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, D. Robust smoothing of gridded data in one and higher dimensions with missing values. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2010, 54, 1167–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abass, A.; Lopes, B.T.; Eliasy, A.; Salomao, M.; Wu, R.; White, L.; Jones, S.; Clamp, J.; Ambrósio, R., Jr.; Elsheikh, A. Artefact-free topography based scleral-asymmetry. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shihab, A.H.; Eliasy, A.; Lopes, B.T.; Wu, R.; White, L.; Jones, S.; Geraghty, B.; Joda, A.; Elsheikh, A.; Abass, A. Compressive behaviour of soft contact lenses and its effect on refractive power on the eye and handling off the eye. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towler, J.; Consejo, A.; Zhou, D.; Romano, V.; Levis, H.; Boote, C.; Elsheikh, A.; Geraghty, B.; Abass, A. Typical localised element-specific finite element anterior eye model. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikh, A.; Whitford, C.; Hamarashid, R.; Kassem, W.; Joda, A.; Buchler, P. Stress free configuration of the human eye. Med. Eng. Phys. 2013, 35, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Xu, L.; Wei, W.B.; Jonas, J.B. Intraocular pressure and its normal range adjusted for ocular and systemic parameters. The Beijing Eye Study 2011. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.J.; Collins, M.J.; Davis, B.A.; Carney, L.G. Eyelid pressure and contact with the ocular surface. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 1911–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, K.-A.; Shipley, R.J.; Edirisinghe, M.; Ezra, D.G.; Rose, G.; Best, S.M.; Cameron, R.E. High-speed camera characterization of voluntary eye blinking kinematics. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10, 20130227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Wollmer, P. Surface activity of tear fluid. Acta Ophthalmol. Scand. 1998, 76, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, L.A.; Young, G.; Wolffsohn, J.S.; Riley, C. The influence of corneoscleral topography on soft contact lens fit. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 6801–6806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Pasricha, N.D.; Kuo, A.N.; Vann, R.R. Influence of corneal diameter on surgically induced astigmatism in small-incision cataract surgery. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 54, 556–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.; Shu, X.; Lopes, B.T.; Wu, R.; Abass, A. Limbus misrepresentation in parametric eye models. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pye, D.C. A clinical method for estimating the modulus of elasticity of the human cornea in vivo. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0224824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinciguerra, R.; Rehman, S.; Vallabh, N.A.; Batterbury, M.; Czanner, G.; Choudhary, A.; Cheeseman, R.; Elsheikh, A.; Willoughby, C.E. Corneal biomechanics and biomechanically corrected intraocular pressure in primary open-angle glaucoma, ocular hypertension and controls. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 104, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, F.; Chen, H.; Yu, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhou, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Elsheikh, A. Evaluation of the shape symmetry of bilateral normal corneas in a Chinese population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, R.; Rozema, J.J.; Tassignon, M.J. Optical changes of the human cornea as a function of age. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2013, 90, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vurgese, S.; Panda-Jonas, S.; Jonas, J.B. Scleral thickness in human eyes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, R.; Rozema, J.J.; Tassignon, M.J. Orientation changes of the main corneal axes as a function of age. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2013, 90, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprioli, J.; Coleman, A.L. Intraocular pressure fluctuation a risk factor for visual field progression at low intraocular pressures in the advanced glaucoma intervention study. Ophthalmology 2008, 115, 1123–1129.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glozman, T.; Azhari, H. A Method for Characterization of Tissue Elastic Properties Combining Ultrasonic Computed Tomography With Elastography. J. Ultrasound Med. 2010, 29, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox Cartwright, N.E.; Tyrer, J.R.; Marshall, J. Age-Related Differences in the Elasticity of the Human Cornea. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 4324–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessing, S.V. A New Division of the Conjunctiva on the Basis of X-ray Examination. Acta Ophthalmol. 1967, 45, 680–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beenakker, J.-W.M.; Wezel, J.; Groen, J.; Webb, A.G.; Börnert, P. Silent volumetric multi-contrast 7 Tesla MRI of ocular tumors using Zero Echo Time imaging. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.; Wei, S.; Ou, Y.; Liu, F.; Li, H.; Jiang, W.; Li, W.; Lei, Y.; Guo, W.; Luo, S. Reduced Global-Brain Functional Connectivity of the Cerebello-Thalamo-Cortical Network in Patients With Dry Eye Disease. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 572693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Hwang, K. Skin thickness of Korean adults. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2002, 24, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, K. Surgical anatomy of the upper eyelid relating to upper blepharoplasty or blepharoptosis surgery. Anat. Cell Biol. 2013, 46, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.T.; Pham, D.T.; O’Connor, A.J.; Wood, J.; Casson, R.; Selva, D.; Costi, J.J. The Biomechanics of eyelid tarsus tissue. J. Biomech. 2015, 48, 3455–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, T.; Klyce, S.D.; Zheng, X.; Maeda, N.; Kuroda, T.; Ide, C. Gender- and age-related differences in corneal topography. Cornea 2001, 20, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consejo, A.; Fathy, A.; Lopes, B.T.; Ambrósio, R.; Abass, A. Effect of Corneal Tilt on the Determination of Asphericity. Sensors 2021, 21, 7636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, O.; Aeschlimann, R.; Zürcher, S.; Osborn Lorenz, K.; Kakkassery, J.; Spencer, N.D.; Tosatti, S.G.P. Friction Measurements on Contact Lenses in a Physiologically Relevant Environment: Effect of Testing Conditions on Friction. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 5383–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsaglia, G.; Tsang, W.W.; Wang, J. Evaluating Kolmogorov’s Distribution. J. Stat. Softw. 2003, 8, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everitt, B.S.; Skrondal, A. The Cambridge Dictionary of Statistics, 4th ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, J.P. Fast Normalized Cross-Correlation. Ind. Light Magic 2001, 10, 819–843. [Google Scholar]
- Haralick, R.M.; Shapiro, L.G. Computer and Robot Vision; Addison-Wesley Longman Publishing Co., Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, M.G.; Stuart, A. The Advanced Theory of Statistics; Inference and Relationsship; Griffin: London, UK, 1973; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, P.B.; Efron, N.; Woods, C.A.; Santodomingo-Rubido, J. International survey of orthokeratology contact lens fitting. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2019, 42, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, P.; Tan, Q. Myopia and orthokeratology for myopia control. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2019, 102, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queirós, A.; González-Méijome, J.M.; Jorge, J.; Villa-Collar, C.; Gutiérrez, A.R. Peripheral refraction in myopic patients after orthokeratology. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2010, 87, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, P.; Swarbrick, H. Peripheral refraction in myopic children wearing orthokeratology and gas-permeable lenses. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2011, 88, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, H.; Allen, P.M.; Calver, R.I.; Theagarayan, B.; Price, H.; Rae, S.; Sailoganathan, A.; O’Leary, D.J. Peripheral Refractive Changes Associated with Myopia Progression. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchison, D.A.; Pritchard, N.; Schmid, K.L. Peripheral refraction along the horizontal and vertical visual fields in myopia. Vis. Res. 2006, 46, 1450–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.; Shen, M.; Jiang, J.; Mao, X.; Lu, P.; Zhu, D.; Chen, Q.; Wang, J.; Lu, F. Vertical and horizontal thickness profiles of the corneal epithelium and Bowman’s layer after orthokeratology. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinstein, D.Z.; Gobbe, M.; Archer, T.J.; Couch, D.; Bloom, B. Epithelial, Stromal and Corneal Pachmetry Changes during Orthokeratology. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2009, 86, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, A.; Swarbrick, H.A. The effects of overnight orthokeratology lens wear on corneal thickness. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 2518–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Z.; Moore, J.; Jiang, F.; Guo, H.; Eliasy, A.; Lopes, B.T.; Bao, F.; Jiang, J.; Abass, A.; Elsheikh, A. A new approach for quantifying epithelial and stromal thickness changes after orthokeratology contact lens wear. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2021, 8, 211108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, S.W.; Cho, P.; Chui, W.S.; Woo, G.C. Refractive error and visual acuity changes in orthokeratology patients. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2007, 84, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-C.; Hsu, M.-Y.; Hsiao, W.-T.; Shum, P.J.-T. Finite Element Modeling of an Elderly Person’s Cornea and Rigid Gas Permeable Contact Lenses for Presbyopic Patients. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Time of Wear (Days) | Number of Eyes | Age in Years (m ± std) | IOP (mmHg) | CCT (µm) | Pre Simulated Keratometry (Sim-K) (D) | Post Simulated Keratometry (Sim-K) (D) | Pre-Wear Asphericity | Post-Wear Asphericity | Eye | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flat (m ± std) | Steep (m ± std) | Flat (m ± std) | Steep (m ± std) | Flat (m ± std) | Steep (m ± std) | Flat (m ± std) | Steep (m ± std) | Right | Left | |||||
| 10 to 100 | 249 | 14.1 ± 4 | 15 ± 3 | 554 ± 33 | 42.6 ± 1.3 | 44 ± 1.3 | 41 ± 1.3 | 42.7 ± 1.5 | 0.66 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.18 | 0.34 ± 0.14 | 0.43 ± 0.17 | 132 | 117 |
| Model | Step | Description | Integration Scheme | Loading Condition | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eye | 1 | Stress-free iterations [28] | Implicit | Static | Normalised increments (0:1) |
| 2 | Inflation by patient-specific IOP [29] | Implicit | Static | Normalised increments (0:1) | |
| Lens between eye and eyelid | 3 | Eyelid blinking pressure 8.0 mmHg [30] | Implicit | Dynamic | 0.6 s, see [31] |
| 4 | Surface tension 43.6 mPa [32] | Implicit | Static | Normalised increments (0:1) | |
| 5 | Eyelid closer pressure 8.0 mmHg [30] | Implicit | Static | Normalised increments (0:1) |
| (m ± std) | (m ± std) | (m ± std) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right eyes | Upper eyelid | −0.0832 ± 0.0197 | −0.0262 ± 0.0445 | 3.5809 ± 0.4375 |
| Lower eyelid | 0.0842 ± 0.0197 | 0.0163 ± 0.0445 | −3.9734 ± 0.4375 | |
| Left eyes | Upper eyelid | −0.0864 ± 0.0187 | 0.0256 ± 0.0463 | 3.6564 ± 0.3865 |
| Lower eyelid | 0.0868 ± 0.0187 | −0.0206 ± 0.0463 | −3.9902 ± 0.3865 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, L.-Y.; Lin, W.-P.; Wu, R.; White, L.; Abass, A. FEA-Based Stress–Strain Barometers as Forecasters for Corneal Refractive Power Change in Orthokeratology. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020166
Wu L-Y, Lin W-P, Wu R, White L, Abass A. FEA-Based Stress–Strain Barometers as Forecasters for Corneal Refractive Power Change in Orthokeratology. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(2):166. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020166
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Lo-Yu, Wen-Pin Lin, Richard Wu, Lynn White, and Ahmed Abass. 2024. "FEA-Based Stress–Strain Barometers as Forecasters for Corneal Refractive Power Change in Orthokeratology" Bioengineering 11, no. 2: 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020166
APA StyleWu, L.-Y., Lin, W.-P., Wu, R., White, L., & Abass, A. (2024). FEA-Based Stress–Strain Barometers as Forecasters for Corneal Refractive Power Change in Orthokeratology. Bioengineering, 11(2), 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020166









