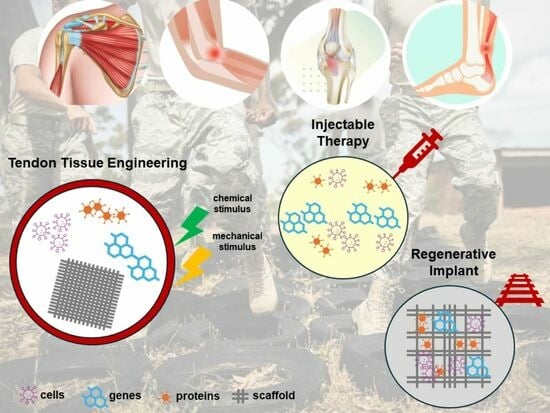
Treatment of Tendon Injuries in the Servicemember Population across the Spectrum of Pathology: From Exosomes to Bioinductive Scaffolds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Burden of Disease among Servicemembers
3. Implications on Operational Readiness and Injury Prevention
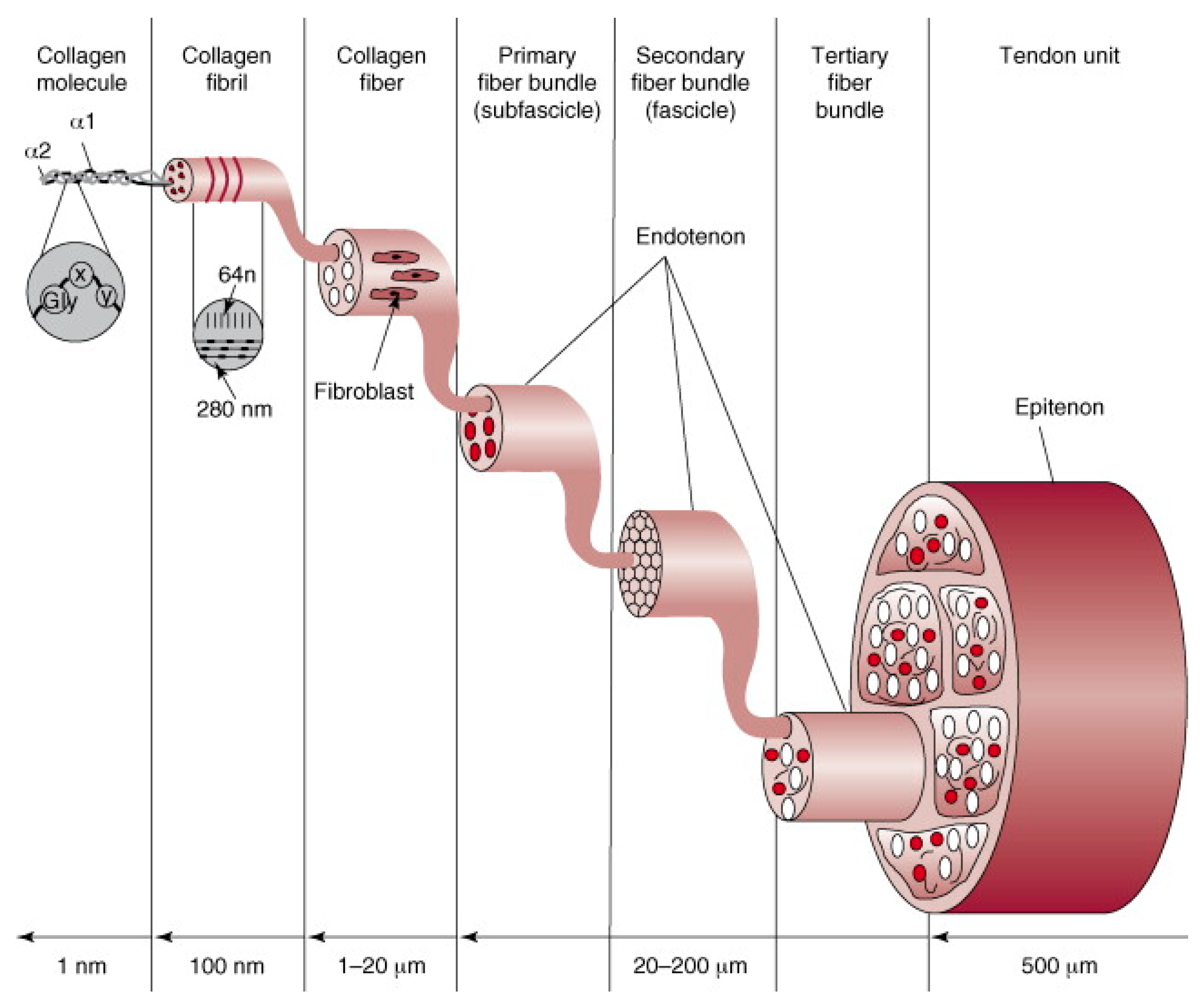
4. Review of Basic Tendon Structure
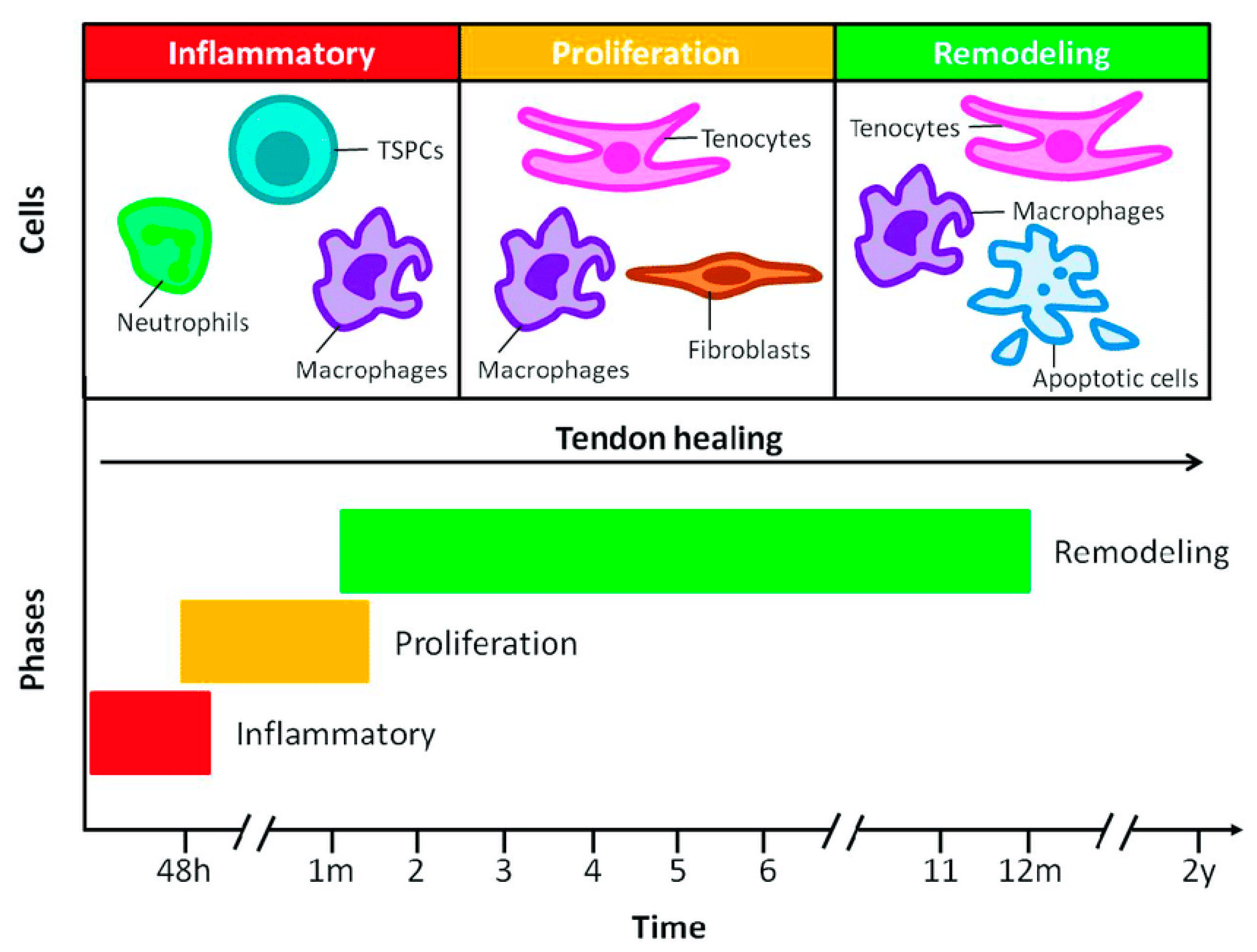
5. Principles of Tendon Healing
| Phase | Time | Predominant Cell Types | Cytokines | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inflammatory | 0 to 48 h | Neutrophils, macrophages, TSPCs | IL-1, TNF-, IL-6 |
|
| Proliferative | 2 days to 6 weeks | Tenocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts | IL-6, IL-8, IL-10 |
|
| Remodeling | 6 weeks to 12 months | Tenocytes, macrophages, apoptotic cells | BMPs, TGF-, IFG-1 |
|
6. Signaling Pathways to Stimulate Tendon Repair
6.1. Chemical Stimulation in Tendon Tissue Engineering
6.2. Mechanical Stimulation in Tendon Tissue Engineering
7. Novel Therapeutic Approaches in Tendon Tissue Engineering
7.1. Cell-Based Therapy
7.2. Exosome-Based Therapy
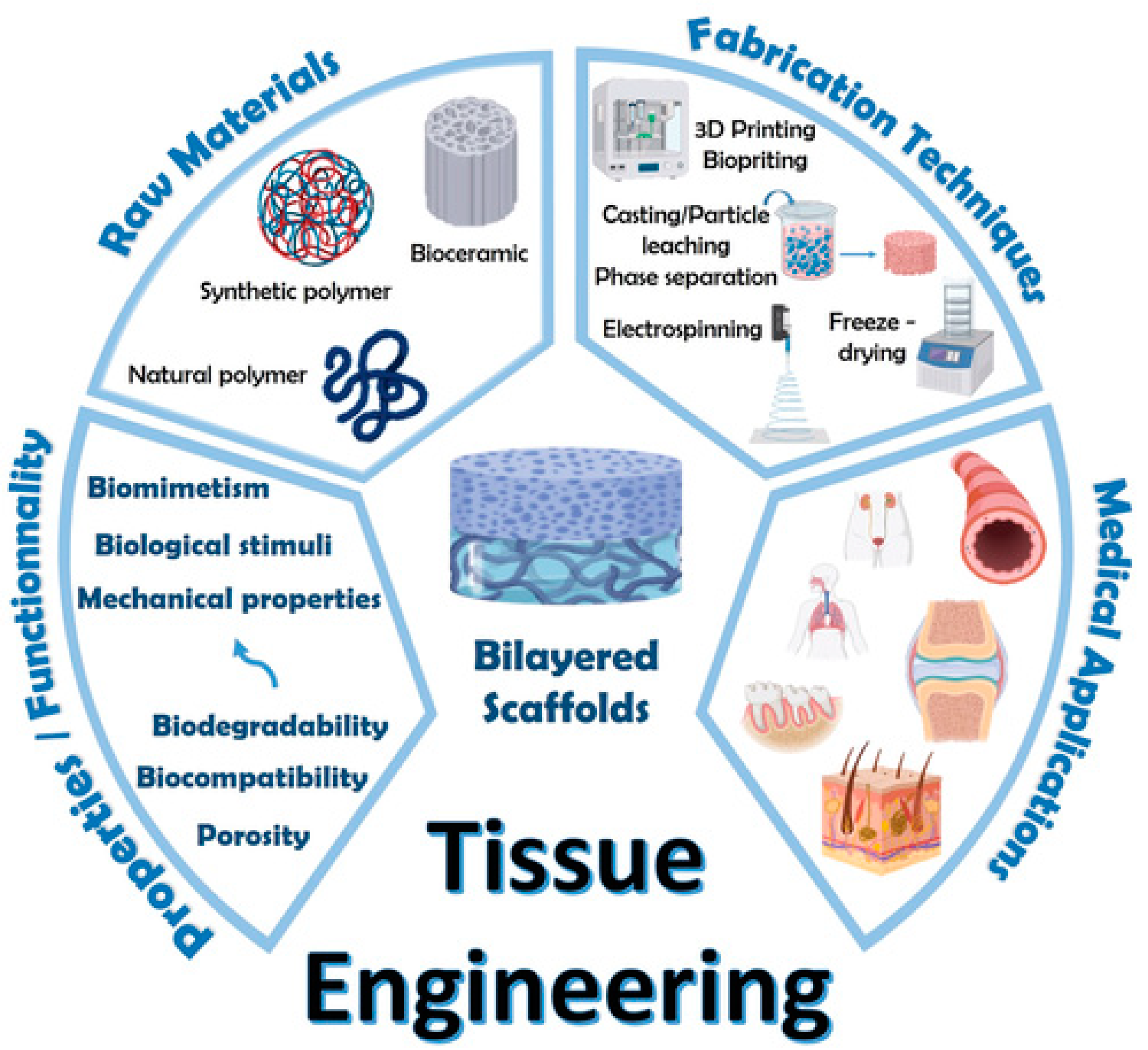
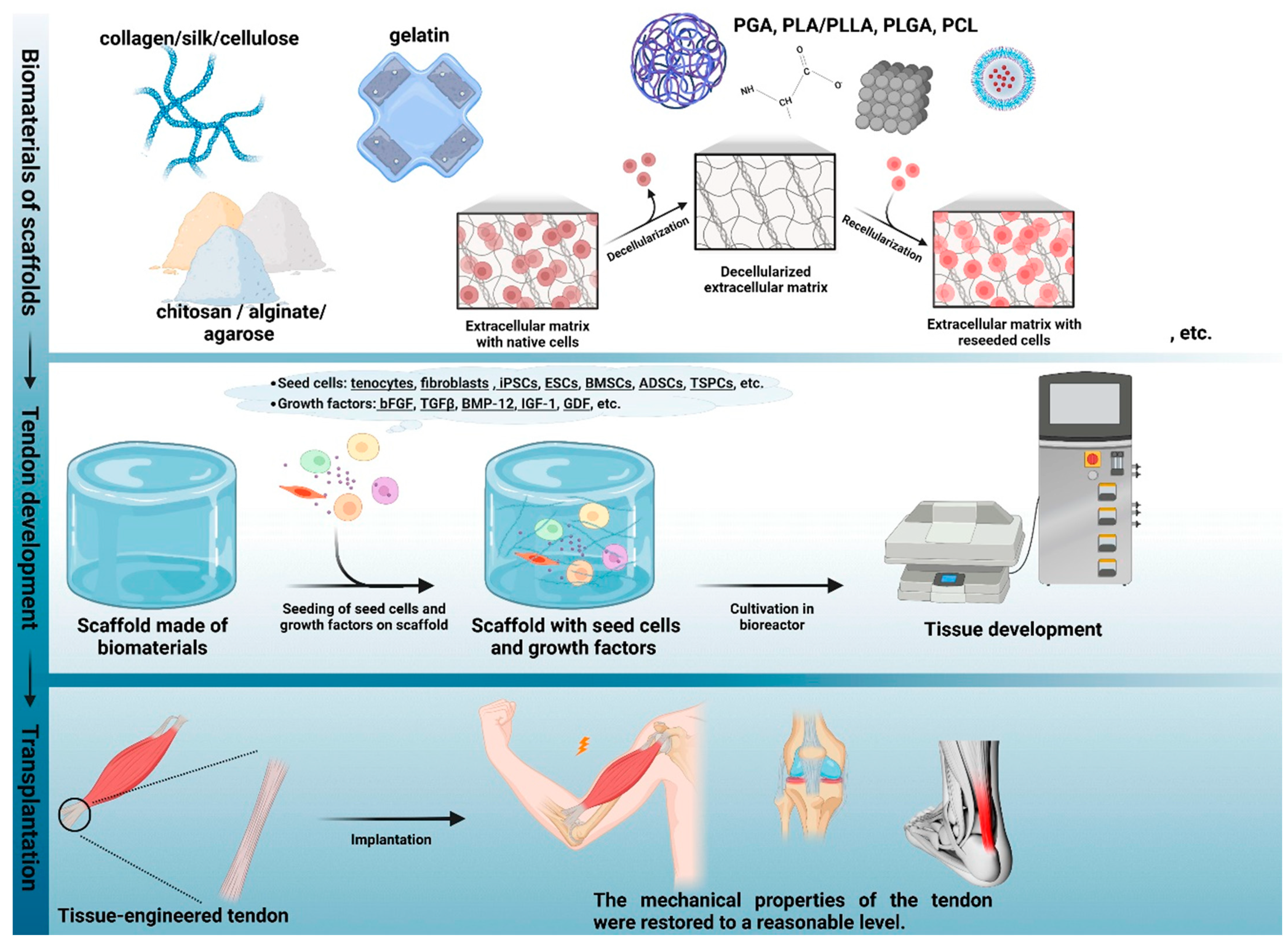
7.3. Scaffolds for Tendon Repair
7.3.1. Biological Scaffolds
7.3.2. Synthetic Scaffolds
7.3.3. Composite Scaffolds
8. Future Directions with Novel Advancements
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teyhen, D.S.; Goffar, S.L.; Shaffer, S.W.; Kiesel, K.; Butler, R.J.; Tedaldi, A.-M.; Prye, J.C.; Rhon, D.I.; Plisky, P.J. Incidence of Musculoskeletal Injury in US Army Unit Types: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2018, 48, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molloy, J.M.; Pendergrass, T.L.; Lee, I.E.; Chervak, M.C.; Hauret, K.G.; Rhon, D.I. Musculoskeletal Injuries and United States Army Readiness Part I: Overview of Injuries and their Strategic Impact. Mil. Med. 2020, 185, e1461–e1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.O.; Sawadkar, P.; Mudera, V. A review on the use of cell therapy in the treatment of tendon disease and injuries. J. Tissue Eng. 2014, 5, 2041731414549678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, B.D.; Wolf, J.M.; Seelig, A.D.; Jacobson, I.G.; Boyko, E.J.; Smith, B.; Ryan, M.A.; Gackstetter, G.D.; Smith, T.C.; Bagnell, M.; et al. Risk Factors for Lower Extremity Tendinopathies in Military Personnel. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2013, 1, 2325967113492707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nindl, B.C.; Williams, T.J.; Deuster, P.A.; Butler, N.L.; Jones, B.H. Strategies for optimizing military physical readiness and preventing musculoskeletal injuries in the 21st century. US Army Med. Dep. J. 2013, 20, 5–23. [Google Scholar]
- Sheean, A.J.; Dickens, J.F.; Provencher, M.T. Extremity War Injury Symposium XV: Sports and Readiness Symposium Summary. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2022, 30, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredericks, D.R.; Slaven, S.E.; McCarthy, C.F.; Dingle, M.E.; Brooks, D.I.; Steelman, T.J.; Donohue, M.A.; Griffin, D.W.; Giuliani, J.R.; Dickens, J.F. Incidence and Risk Factors of Acute Patellar Tendon Rupture, Repair Failure, and Return to Activity in the Active-Duty Military Population. Am. J. Sports Med. 2021, 49, 2916–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, D.W.; Wenke, J.C.; Mosely, D.S.; Mountcastle, S.B.; Basamania, C.J. Incidence of major tendon ruptures and anterior cruciate ligament tears in US Army soldiers. Am. J. Sports Med. 2007, 35, 1308–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lause, G.; Egbert, R.; Anderson, C.; Ryan, P. Outcomes of Insertional Achilles Tendinopathy in Active Duty Military Population. Foot Ankle Orthop. 2018, 3, 2473011418S2473000304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antosh, I.J.; Grassbaugh, J.A.; Parada, S.A.; Arrington, E.D. Pectoralis major tendon repairs in the active-duty population. Am. J. Orthop. 2009, 38, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Balazs, G.C.; Brelin, A.M.; Donohue, M.A.; Dworak, T.C.; Rue, J.-P.H.; Giuliani, J.R.; Dickens, J.F. Incidence Rate and Results of the Surgical Treatment of Pectoralis Major Tendon Ruptures in Active-Duty Military Personnel. Am. J. Sports Med. 2016, 44, 1837–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, P.D.; Mauntel, T.C.; Potter, B.K. Combat and Noncombat Musculoskeletal Injuries in the US Military. Sports Med. Arthrosc. Rev. 2019, 27, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molloy, J.M.; Pendergrass, T.L.; Lee, I.E.; Hauret, K.G.; Chervak, M.C.; Rhon, D.I. Musculoskeletal Injuries and United States Army Readiness. Part II: Management Challenges and Risk Mitigation Initiatives. Mil. Med. 2020, 185, e1472–e1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, I.G.; Dijksma, I.; van Etten-Jamaludin, F.S.; Lucas, C.; Stuiver, M.M. Nonexercise Interventions for Prevention of Musculoskeletal Injuries in Armed Forces: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2021, 60, e73–e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijksma, I.; Sharma, J.; Gabbett, T.J. Training Load Monitoring and Injury Prevention in Military Recruits: Considerations for Preparing Soldiers to Fight Sustainably. Strength. Cond. J. 2021, 43, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, C.T.; Screen, H.R. Tendon Structure and Composition. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 920, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.H. Mechanobiology of tendon. J. Biomech. 2006, 39, 1563–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chartier, C.; ElHawary, H.; Baradaran, A.; Vorstenbosch, J.; Xu, L.; Efanov, J.I. Tendon: Principles of Healing and Repair. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2021, 35, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannus, P. Structure of the tendon connective tissue. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2000, 10, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasiliadis, A.V.; Katakalos, K. The Role of Scaffolds in Tendon Tissue Engineering. J. Funct. Biomater. 2020, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Liu, T.; Lyu, K.; Chen, Y.; Lu, J.; Wang, X.; Long, L.; Li, S. Inflammation-related signaling pathways in tendinopathy. Open Life Sci. 2023, 18, 20220729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, C.K.; Janney, C.F.; Fraser, J.J. Burden and risk factors for Achilles tendinopathy in the military population from 2006 to 2015. A retrospective cohort study. medRxiv 2023. medRxiv:2023:2023-02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, R.; Jiang, Y.; Backman, L.J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J. The Application of Mechanical Stimulations in Tendon Tissue Engineering. Stem Cells Int. 2020, 2020, 8824783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.M.; Liu, X. Advancing biomaterials of human origin for tissue engineering. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 53, 86–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riehl, B.D.; Park, J.H.; Kwon, I.K.; Lim, J.Y. Mechanical stretching for tissue engineering: Two-dimensional and three-dimensional constructs. Tissue Eng. Part. B Rev. 2012, 18, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engebretson, B.; Mussett, Z.R.; Sikavitsas, V.I. The effects of varying frequency and duration of mechanical stimulation on a tissue-engineered tendon construct. Connect. Tissue Res. 2018, 59, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimondi, M.T.; Laganà, M.; Conci, C.; Crestani, M.; Di Giancamillo, A.; Gervaso, F.; Deponti, D.; Boschetti, F.; Nava, M.M.; Scandone, C.; et al. Development and biological validation of a cyclic stretch culture system for the ex vivo engineering of tendons. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2018, 41, 400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamplot, J.D.; Rodeo, S.A.; Brophy, R.H. A Practical Guide for the Current Use of Biologic Therapies in Sports Medicine. Am. J. Sports Med. 2020, 48, 488–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thankam, F.G.; Chandra, I.; Diaz, C.; Dilisio, M.F.; Fleegel, J.; Gross, R.M.; Agrawal, D.K. Matrix regeneration proteins in the hypoxia-triggered exosomes of shoulder tenocytes and adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2020, 465, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, R.; Hussain, A.; Behfar, A.; Moran, S.L.; Zhao, C. The Therapeutic Potential of Exosomes in Soft Tissue Repair and Regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, D.; Spanoudes, K.; Holladay, C.; Pandit, A.; Zeugolis, D. Progress in cell-based therapies for tendon repair. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 84, 240–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandonà, M.; Di Pietro, L.; Esposito, F.; Ventura, A.; Silini, A.R.; Parolini, O.; Saccone, V. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Their Secretome: New Therapeutic Perspectives for Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 652970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H.J. Advances in mesenchymal stem cell exosomes: A review. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, K.; Liu, T.; Chen, Y.; Lu, J.; Jiang, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Li, S. A “cell-free treatment” for tendon injuries: Adipose stem cell-derived exosomes. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2022, 27, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodas, G.; Soler-Rich, R.; Rius-Tarruella, J.; Alomar, X.; Balius, R.; Orozco, L.; Masci, L.; Maffulli, N. Effect of Autologous Expanded Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells or Leukocyte-Poor Platelet-Rich Plasma in Chronic Patellar Tendinopathy (With Gap >3 mm): Preliminary Outcomes After 6 Months of a Double-Blind, Randomized, Prospective Study. Am. J. Sports Med. 2021, 49, 1492–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Fan, H.; Li, Y.; Yun, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Q. Effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma injections for the treatment of acute Achilles tendon rupture: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2021, 100, e27526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.H. PRP Treatment Efficacy for Tendinopathy: A Review of Basic Science Studies. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 9103792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droppelmann, G.; Saavedra, A.; Apablaza, F.; Macedo, A. The effect of regenerative therapy in functional outcome in the treatment of patellar and Achilles tendinopathy: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials. Princ. Pract. Clin. Res. 2021, 7, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhi, M.I.; Yausep, O.E.; Khamdan, K.; Trigkilidas, D. The use of PRP in treatment of Achilles Tendinopathy: A systematic review of literature. Study design: Systematic review of literature. Ann. Med. Surg. 2020, 55, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, A.; LaPrade, R.F.; Harmon, K.G.; Filardo, G.; Kon, E.; Della Villa, S.; Bahr, R.; Moksnes, H.; Torgalsen, T.; Lee, J.; et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma for Patellar Tendinopathy: A Randomized Controlled Trial of Leukocyte-Rich PRP or Leukocyte-Poor PRP Versus Saline. Am. J. Sports Med. 2019, 47, 1654–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desouza, C.; Dubey, R.; Shetty, V. Platelet-rich plasma in chronic Achilles tendinopathy. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2023, 33, 3255–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsousou, J.; Keene, D.; Harrison, P.; Hulley, P.; Wagland, S.; Thompson, J.Y.; Parsons, S.R.; Byrne, C.; Schlüssel, M.M.; O’connor, H.M.; et al. Platelet-rich plasma injection for adults with acute Achilles tendon rupture: The PATH-2 RCT. Effic. Mech. Eval. 2019, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keene, D.J.; Alsousou, J.; Harrison, P.; O’connor, H.M.; Wagland, S.; Dutton, S.J.; Hulley, P.; Lamb, S.E.; Willett, K.; on behalf of the PATH-2 Trial group. Platelet-rich plasma injection for acute Achilles tendon rupture. Bone Jt. J. 2022, 104, 1256–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthur Vithran, D.T.; Xie, W.; Opoku, M.; Essien, A.E.; He, M.; Li, Y. The Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection Therapy in the Treatment of Patients with Achilles Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearney, R.S.; Ji, C.; Warwick, J.; Parsons, N.; Brown, J.; Harrison, P.; Young, J.; Costa, M.L.; ATM Trial Collaborators. Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection vs Sham Injection on Tendon Dysfunction in Patients With Chronic Midportion Achilles Tendinopathy: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 326, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boesen, A.P.; Boesen, M.I.; Hansen, R.; Barfod, K.W.; Lenskjold, A.; Malliaras, P.; Langberg, H. Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Nonsurgically Treated Acute Achilles Tendon Ruptures: A Randomized, Double-Blinded Prospective Study. Am. J. Sports Med. 2020, 48, 2268–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, A.; Sinha, M.K.; Sahoo, J.; Jena, D.; Patel, V.; Patel, S.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Baral, D. Platelet-rich plasma injection in the treatment of patellar tendinopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Knee Surg. Relat. Res. 2022, 34, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuhmani, S.; Ahsan, M.; Bari, M.A.; Malhotra, D.; Al Muslem, W.H.; Alsaadi, S.M.; Muaidi, Q.I. Patellar Tendinopathy-Does Injection Therapy Have a Role? A Systematic Review of Randomised Control Trials. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.C.; Wu, K.T.; Chou, W.Y.; Huang, Y.C.; Wang, L.Y.; Yang, T.H.; Siu, K.-K.; Tu, Y.-K. Comparative Effectiveness of Different Nonsurgical Treatments for Patellar Tendinopathy: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. Arthroscopy 2019, 35, 3117–3131.e3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriolo, L.; Altamura, S.A.; Reale, D.; Candrian, C.; Zaffagnini, S.; Filardo, G. Nonsurgical Treatments of Patellar Tendinopathy: Multiple Injections of Platelet-Rich Plasma Are a Suitable Option: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Am. J. Sports Med. 2019, 47, 1001–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Yan, W.; Leng, X.; Wang, J.; Hu, X.; Cheng, J.; Ao, Y. Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Placebo in the Treatment of Tendinopathy: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2023, 33, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.R.Y.; Toth, E.; Rajesparan, K.; Rashid, A. The use of platelet-rich plasma therapy in treating tennis elbow: A critical review of randomised control trials. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma 2022, 32, 101965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, A.; Morgan, B.; Birch, A.; Nuttall, D.; Trail, I. Comparing leukocyte-rich platelet-rich plasma injection with surgical intervention for the management of refractory tennis elbow. A prospective randomised trial. Shoulder Elb. 2020, 12, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandil, M.I.; Ahmed, A.A.; Eldesouky, R.S.; Eltregy, S. Allogeneic platelet-derived growth factors local injection in treatment of tennis elbow: A prospective randomized controlled study. Int. Orthop. 2022, 46, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simental-Mendía, M.; Vilchez-Cavazos, F.; Álvarez-Villalobos, N.; Blázquez-Saldaña, J.; Peña-Martínez, V.; Villarreal-Villarreal, G.; Acosta-Olivo, C. Clinical efficacy of platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of lateral epicondylitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled clinical trials. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 2255–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthu, S.; Patel, S.; Gobbur, A.; Patil, S.C.; Ks, K.H.; Yadav, V.; Jeyaraman, M. Platelet-rich plasma therapy ensures pain reduction in the management of lateral epicondylitis—A PRISMA-compliant network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2022, 22, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudelaar, B.W.; Huis In‘t Veld, R.; Ooms, E.M.; Schepers-Bok, R.; Nelissen, R.G.H.H.; Vochteloo, A.J.H. Efficacy of Adjuvant Application of Platelet-Rich Plasma After Needle Aspiration of Calcific Deposits for the Treatment of Rotator Cuff Calcific Tendinitis: A Double-Blinded, Randomized Controlled Trial With 2-Year Follow-up. Am. J. Sports Med. 2021, 49, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prodromos, C.C.; Finkle, S.; Prodromos, A.; Chen, J.L.; Schwartz, A.; Wathen, L. Treatment of Rotator Cuff Tears with platelet rich plasma: A prospective study with 2 year follow-up. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jones, I.A.; Togashi, R.; Park, C.; Vangsness, C.T. Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Improvement of Pain and Function in Rotator Cuff Tears: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis With Bias Assessment. Am. J. Sports Med. 2020, 48, 2028–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, E.T.; Lim Fat, D.; Moran, C.J.; Mullett, H. The Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Am. J. Sports Med. 2019, 47, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.N.; Deng, J.; Liu, Y.; Yu, X.; Cheng, B.; He, H.C. Conservative treatment of partial-thickness rotator cuff tears and tendinopathy with platelet-rich plasma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Rehabil. 2021, 35, 1661–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godek, P.; Szczepanowska-Wolowiec, B.; Golicki, D. Collagen and platelet-rich plasma in partial-thickness rotator cuff injuries. Friends or only indifferent neighbours? Randomised controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pas, H.; Moen, M.H.; Haisma, H.J.; Winters, M. No evidence for the use of stem cell therapy for tendon disorders: A systematic review. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilaltdinov, A.W.; Gong, Y.; Leong, D.J.; Gruson, K.I.; Zheng, D.; Fung, D.T.; Sun, L.; Sun, H.B. Advances in the development of gene therapy, noncoding RNA, and exosome-based treatments for tendinopathy. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2021, 1490, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Chen, Z.Y.; Lin, Y.H.; Chen, S.H.; Chou, P.Y.; Kao, H.K.; Lin, F.H. Extracellular Vesicles of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Promote the Healing of Traumatized Achilles Tendons. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjørge, I.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Mano, J.F.; Kalionis, B.; Chrzanowski, W. Extracellular vesicles, exosomes and shedding vesicles in regenerative medicine—A new paradigm for tissue repair. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 6, 60–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, H.; Cui, Q.; Han, P.; Yang, S.; Shi, M.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z. Tendon stem cell-derived exosomes regulate inflammation and promote the high-quality healing of injured tendon. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henson, F.; Getgood, A. The use of scaffolds in musculoskeletal tissue engineering. Open Orthop. J. 2011, 5 (Suppl. S2), 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Laurent, C.; Liu, X.; De Isla, N.; Wang, X.; Rahouadj, R. Defining a scaffold for ligament tissue engineering: What has been done, and what still needs to be done. J. Cell. Immunother. 2018, 4, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, C.N.; Schwartz, A.G.; Liu, W.; Xie, J.; Havlioglu, N.; Sakiyama-Elbert, S.; Silva, M.; Xia, Y.; Gelberman, R.; Thomopoulos, S. Controlled delivery of mesenchymal stem cells and growth factors using a nanofiber scaffold for tendon repair. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 6905–6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertsch, C.; Maréchal, H.; Gribova, V.; Lévy, B.; Debry, C.; Lavalle, P.; Fath, L. Biomimetic Bilayered Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering: From Current Design Strategies to Medical Applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2203115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Chen, L.; Chen, H.; Wang, M.; Jin, L.; Zhou, S.; Gao, L.; Li, R.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; et al. Biomimetic Scaffolds for Tendon Tissue Regeneration. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, T.; Zhang, T.; Ju, W.; Chen, X.; Heng, B.C.; Shen, W.; Yin, Z. Biomimetic strategies for tendon/ligament-to-bone interface regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 2491–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Han, S.C.; Jeong, H.J.; Rhee, S.M.; Kim, Y.S.; Jin, Y.J.; Park, S.-H.; Oh, J.H. Recombinant Human Parathyroid Hormone Biocomposite Promotes Bone-to-Tendon Interface Healing by Enhancing Tenogenesis, Chondrogenesis, Osteogenesis in a Rabbit Model of Chronic Rotator Cuff Tears. Arthroscopy 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Rhee, S.M.; Kim, Y.W.; Park, S.H.; Oh, J.H. Three-dimensionally printed recombinant human parathyroid hormone-soaked nanofiber sheet accelerates tendon-to-bone healing in a rabbit model of chronic rotator cuff tear. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2022, 31, 1628–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stace, E.T.; Nagra, N.S.; Tiberwel, S.; Khan, W.; Carr, A.J. The Use of Electrospun Scaffolds in Musculoskeletal Tissue Engineering: A Focus on Tendon and the Rotator Cuff. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 13, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchman, K.R.; Goetz, J.E.; Uribe, B.U.; Amendola, A.M.; Barber, J.A.; Malandra, A.E.; Fredericks, D.C.; Hettrich, C.M. Delayed administration of recombinant human parathyroid hormone improves early biomechanical strength in a rat rotator cuff repair model. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2016, 25, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás, A.R.; Gonçalves, A.I.; Paz, E.; Freitas, P.; Domingues, R.M.A.; Gomes, M.E. Magneto-mechanical actuation of magnetic responsive fibrous scaffolds boosts tenogenesis of human adipose stem cells. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 18255–18271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesqueira, T.; Costa-Almeida, R.; Gomes, M.E. Uncovering the effect of low-frequency static magnetic field on tendon-derived cells: From mechanosensing to tenogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.I.; Rotherham, M.; Markides, H.; Rodrigues, M.; Reis, R.; Gomes, M.; El Haj, A. Triggering the activation of Activin A type II receptor in human adipose stem cells towards tenogenic commitment using mechanomagnetic stimulation. Nanomedicine 2018, 14, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, S.; Zhou, C.; Cheng, L.; Gao, X.; Xie, X.; Sun, J.; Wang, H.; Weir, M.D.; Reynolds, M.A.; et al. Advanced smart biomaterials and constructs for hard tissue engineering and regeneration. Bone Res. 2018, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citro, V.; Clerici, M.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Della Porta, G.; Maffulli, N.; Forsyth, N.R. Tendon tissue engineering: An overview of biologics to promote tendon healing and repair. J. Tissue Eng. 2023, 14, 20417314231196275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Principle of Load Management | Components for Injury Prevention |
|---|---|
| Establish a moderate chronic load |
|
| Lessen abrupt weekly changes |
|
| Avoid the safety workload ceiling |
|
| Enforce a standard minimum training requirement |
|
| Avoid inconsistent “boom-bust” workloads |
|
| Establish consistent training schedules proportionate to workload demands |
|
| Monitor servicemembers throughout the maintenance phase |
|
| Growth Factor | Abbreviation | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Insulin-like growth factor-1 | IGF-1 | Tendon fibrinogenesis, stimulates cell proliferation and matrix synthesis |
| Transforming growth factor-beta | TGF- | Tendon remodeling, promotes production of collagen and ECM components |
| Platelet-derived growth factor | PDGF | Recruitment and activation, stimulates proliferation and synthesis of collagen |
| Vascular endothelial growth factor | VEGF | Angiogenesis, facilitates adequate blood supply to deliver nutrients and oxygen for healing |
| Interleukins | IL-1, IL-6 | Pro-inflammatory mediation, controls inflammatory response to clear necrotic tissue and initiates repair |
| Connective tissue growth factor | CTGF | Tissue remodeling and scar formation, contributes to synthesis of ECM proteins and collagen |
| Growth Factor | Abbreviation | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Nuclear factor-kappa B | NF-κB |
|
| NOD-like receptor family, pyrin domain-containing 3 | NLRP3 |
|
| Mitogen-activated protein kinase | p38/MAPK |
|
| Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 | STAT3 |
|
| Reference | Year | Sample Size | Study Design | Study Group | Study Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Droppelmann [38] | 2022 | 318 | Metanalysis (8 RCTs) | Achilles tendinopathy/patellar tendinopathy |
|
| Madhi [39] | 2020 | 230 | Systematic review | Achilles tendinopathy |
|
| Scott [40] | 2019 | 57 | RCT | Patellar tendinopathy |
|
| Desouza [41] | 2023 | NR | Metanalysis (5 RCTs) | Achilles tendinopathy |
|
| Alsousou [42]/Keene [43] | 2019/2022 | 230 | RCT | Achilles tendon rupture |
|
| Wang [36] | 2021 | 363 | Systematic review (5 RCTs) | Achilles tendon rupture |
|
| Vithran [44] | 2023 | 526 | Metanalysis (8 RCTs) | Achilles tendinopathy |
|
| Kearney [45] | 2021 | 240 | RCT | Achilles tendinopathy |
|
| Boesen [46] | 2020 | 40 | RCT | Achilles tendon rupture |
|
| Rodas [35] | 2021 | 20 | RCT | Patellar tendinopathy |
|
| Barman [47] | 2022 | 123 | Metanalysis (5 RCTs) | Patellar tendinopathy |
|
| Nuhmani [48] | 2022 | 338 | Metanalysis (9 RCTs) | Patellar tendinopathy |
|
| Chen [49] | 2019 | 430 | Metanalysis | Patellar tendinopathy |
|
| Andriolo [50] | 2018 | 2530 | Metanalysis | Patellar tendinopathy |
|
| Dai [51] | 2023 | 576 | Metanalysis (13 RCTs) | Lateral epicondylitis, rotator cuff tendinopathy, patellar tendinopathy |
|
| Wong [52] | 2022 | 1520 | Systematic review (20 RCTs) | Lateral epicondylitis |
|
| Watts [53] | 2018 | 81 | RCT | Lateral epicondylitis |
|
| Kandil [54] | 2022 | 120 | RCT | Lateral epicondylitis |
|
| Simental-Mendía [55] | 2020 | 276 | Metanalysis (5 RCTs) | Lateral epicondylitis |
|
| Muthu [56] | 2022 | 2040 | Metanalysis (25 RCTs) | Lateral epicondylitis |
|
| Oudelaar [57] | 2021 | 80 | RCT | Rotator cuff tears and tendonitis |
|
| Prodromos [58] | 2021 | 71 | Prospective cohort study | Rotator cuff tears and tendonitis |
|
| Chen [59] | 2019 | 1116 | Metanalysis (18 RCTs) | Rotator cuff tears and tendonitis |
|
| Hurley [60] | 2019 | 1147 | Metanalysis (18 RCTs) | Rotator cuff tears (undergoing arthroscopic repair) |
|
| Xiang [61] | 2021 | 629 | Metanalysis (9 RCTs) | Rotator cuff tears and tendonitis |
|
| Godek [62] | 2022 | 90 | RCT | Rotator cuff tears, partial thickness |
|
| Type | Tissue Source | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biological | Decellularized matrix Collagen tissue |
|
|
| Synthetic | Polyesters Polyurethanes |
|
|
| Composite | Collagen-PLGA Hybrid tissue |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
DeFoor, M.T.; Cognetti, D.J.; Yuan, T.T.; Sheean, A.J. Treatment of Tendon Injuries in the Servicemember Population across the Spectrum of Pathology: From Exosomes to Bioinductive Scaffolds. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020158
DeFoor MT, Cognetti DJ, Yuan TT, Sheean AJ. Treatment of Tendon Injuries in the Servicemember Population across the Spectrum of Pathology: From Exosomes to Bioinductive Scaffolds. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(2):158. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020158
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeFoor, Mikalyn T., Daniel J. Cognetti, Tony T. Yuan, and Andrew J. Sheean. 2024. "Treatment of Tendon Injuries in the Servicemember Population across the Spectrum of Pathology: From Exosomes to Bioinductive Scaffolds" Bioengineering 11, no. 2: 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020158
APA StyleDeFoor, M. T., Cognetti, D. J., Yuan, T. T., & Sheean, A. J. (2024). Treatment of Tendon Injuries in the Servicemember Population across the Spectrum of Pathology: From Exosomes to Bioinductive Scaffolds. Bioengineering, 11(2), 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020158