Finding the Goldilocks Zone of Mechanical Loading: A Comprehensive Review of Mechanical Loading in the Prevention and Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Knee Osteoarthritis
1.2. Post-Traumatic Osteoarthritis
2. Mechanical Considerations in KOA and PTOA Pathogenesis
2.1. Mechanotransduction
2.2. Mechanical Factors in PTOA
| Study Focus | Author, Year [Source] | Study Type | Number of Patients | Study Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impact of Athletics on Development of PTOA | Hootman et al., 2007 [26] | Epidemiological | 182,000 | Summarizing injury data to identify preventable risk factors for injury prevention strategies |
| Golightly et al., 2009 [27] | Epidemiological | 2528 | Describes prevalence of KOA within retired football players | |
| Drawer et al., 2001 [28] | Epidemiological | 500 | Determines the prevalence of KOA within retired soccer players | |
| Kujala et al., 1995 [31] | Epidemiological | 117 | Analyzing the impact of increased mechanical loading during sport on KOA | |
| Swärd et al., 2010 [32] | Epidemiological | 331 | Compares radiographic structural changes of KOA and PTOA in athletes v non-athletes | |
| Boocock et al., 2009 [72] | Epidemiological | 20 | Investigates the effect of running on cartilage degeneration in athletes | |
| Thelin et al., 2005 [78] | Epidemiological | 825 | Analyzes the risk of KOA development in patients with sports participation and/or injury | |
| Shaw et al., 2004 [89] | Epidemiological | 258 | Evaluates the effect of triathlon training on likelihood of future injury | |
| Koplan et al., 1995 [90] | Epidemiological | 535 | Analyzes the impact of exercise on risk of knee injury and KOA development | |
| Piggot et al., 2009 [91] | Epidemiological | 16 | Analyzes the relationship between training load and injury in football players | |
| Satterthwaite 1999 [92] | Epidemiological | 875 | Investigates the impact of marathon running on prevalence of injuries in athletes | |
| Clausen et al., 2015 [93] | Epidemiological | 326 | Investigates the effect of previous knee injury on risk of future knee injury in soccer players | |
| Mechanical Contributors to OA | Gillquist et al., 1999 [29] | Literature review | - | Summarizes the risk of ligamentous injury for osteoarthritis progression |
| Hunter et al., 2005 [63] | Epidemiological | 162 | Analyzes the effect of malalignment in KOA progression | |
| Timmins et al., 2017 [75] | Systematic review | - | Determines the effect of running on development of KOA | |
| Schueller-Weidekamm et al., 2006 [94] | Epidemiological | 26 | Analyzes the long-term changes of the knee via MRI in former long-distance runners | |
| Bosomworth 2009 [76] | Systematic review | - | Analyzes the effect of exercise on risk of KOA | |
| D’Lima et al., 2008 [67] | Epidemiological | 3 | Investigates the effects of various activities on mechanical loading in the knee joint | |
| D’Lima 2006 [95] | Literature review | - | Synthesizes studies characterizing forces on the knee joint during various exercises | |
| Borelli et al., 2004 [66] | In vivo | - | Investigates the impact of varied loading conditions on knee cartilage in rabbit models | |
| Whittaker et al., 2022 [65] | Systematic review | - | Analyzes the effect of previous knee injury on PTOA progression | |
| Felson et al., 2013 [64] | Epidemiological | 11,006 | Characterizes the effect of malalignment on KOA progression | |
| Aljehani et al., 2022 [96] | Epidemiological | 229 | Investigates biomechanical predictors of KOA progression | |
| Driban et al., 2015 [97] | Epidemiological | 4435 | Analyzes the impact of knee pain or previous injury on the likelihood of future injury | |
| Lieberthal et al., 2015 [61] | Systematic review | - | Compiles evidence for the role of inflammation in joint injury and PTOA | |
| September et al., 2007 [98] | Literature review | - | Discusses risk factors and contributing elements to dysfunction in several joints | |
| He et al., 2020 [51] | In vivo | - | Evaluate effect of lessened mechanical loading on KOA in mouse model | |
| Fang et al., 2020 [52] | Systematic review | - | Summarize the biological underpinnings of the effect mechanical loading on KOA | |
| Schroder et al., 2019 [50] | In vitro * | 5 | Investigates the impact of mechanical loading on gene expression within chondrocytes in OA and non-OA patient samples | |
| Sharma et al., 2001 [69] | Epidemiological | 237 | Investigates the impact of alignment on KOA progression | |
| Tanamas et al., 2009 [70] | Systematic review | - | Analyzes the correlation between malalignment and KOA progression | |
| Neelapala et al., 2020 [99] | Systematic review | - | Summarizes current evidence on the effect of hip muscle weakness in KOA patients | |
| Zhu et al., 2020 [47] | In vivo | - | Analyzes the effect of mechanical loading on subchondral bone, cartilage, and KOA | |
| Robbins et al., 2011 [42] | Epidemiological | 38 | Evaluates the effect of increased mechanical loading of functional scores of KOA patients | |
| Milentijevic 2005 [34] | In vivo | - | Investigates the impact of loading stress on rabbit articular cartilage | |
| Roos et al., 1998 [30] | Epidemiological | 123 | Determining the effect of meniscal surgery/removal on osteoarthritis progression | |
| Therapeutic Potential of Mechanical Loading | Frontera et al., 1988 [56] | Epidemiological | 12 | Analyzing the impact of strength-training regimen on muscle development |
| Nebelung et al., 2012 [58] | In vitro * | 8 | Investigates gene expression of human chondrocytes following total knee replacement | |
| Veugelers et al., 2016 [100] | Epidemiological | 45 | Analyzes the impact of varied training loads on risk of future injury | |
| Baert et al., 2014 [101] | Systematic review | - | Investigates the impact of lateral wedge insoles in patients with KOA | |
| Fantini-Pagani 2011 [102] | Epidemiological | 10 | Analyzes the benefit of knee brace on minimizing force at the knee joint | |
| Robert-Lachaine 2022 [103] | Epidemiological | 10 | Investigates the impact of knee brace and orthoses in KOA treatment | |
| Barrios et al., 2010 [104] | Epidemiological | 8 | Investigates the effect of malalignment on KOA progression | |
| Jan et al., 2008 [105] | Epidemiological | 102 | Compares the effects of high and low load training regimens on KOA functional scores | |
| Kunduracilar 2018 [106] | Epidemiological | 89 | Investigates the effect of water training (low load bearing) on KOA progression | |
| Tagesson et al., 2008 [107] | Epidemiological | 42 | Analyzes the effect of quadriceps strengthening on KOA functional scores | |
| Heywood et al., 2019 [108] | Epidemiological | 41 | Analyzes variance in water v. land conditions while performing various exercises in KOA | |
| Vleck et al., 2010 [109] | Epidemiological | 35 | Investigates the effect of varied training regimens on risk of future injury | |
| Soligard et al., 2016 [110] | Literature review | - | Summarizes the impact of loading conditions on risk of injury, and injury prevention | |
| Quantification of Mechanical Forces in Rehabilitation Exercises | Thambyah et al., 2005 [79] | In vitro * | 5 | Quantifies mechanical forces present at knee joint during walking |
| Wong et al., 2011 [111] | In vitro * | 4 | Analyzes mechanical forces present on knee joint during various malalignment conditions | |
| Sasaki 2010 [112] | Computer model | - | Utilizes walking simulation to determine the muscles involved in walking | |
| Holyoak et al., 2019 [113] | In vivo | - | Quantifies mechanical forces during compression to elucidate beneficial loading range | |
| Glass et al., 2010 [114] | Systematic review | - | Analyzes the mechanical loading force of OKC and CKC exercises at the knee joint | |
| Bini 2017 [115] | Computer models | - | Utilizes computer simulated models to analyze forces on the knee joint during leg extension | |
| Escamilla et al., 1998 [116] | Epidemiological | 10 | Quantifies mechanical force at the knee joint during squat, knee extension, and leg press | |
| Escamilla 2001 [117] | Literature review | - | Discusses the mechanical forces incurred at the knee joint during the squat | |
| Schoenfeld 2020 [118] | Literature review | - | Summarizes the mechanical load incurred during the squat | |
| Perez et al., 2015 [119] | Literature review | - | Summarizes the mechanical load during various rehabilitation exercises | |
| Wallace et al., 2002 [80] | Epidemiological | 15 | Quantifies patellofemoral joint forces during the squat |
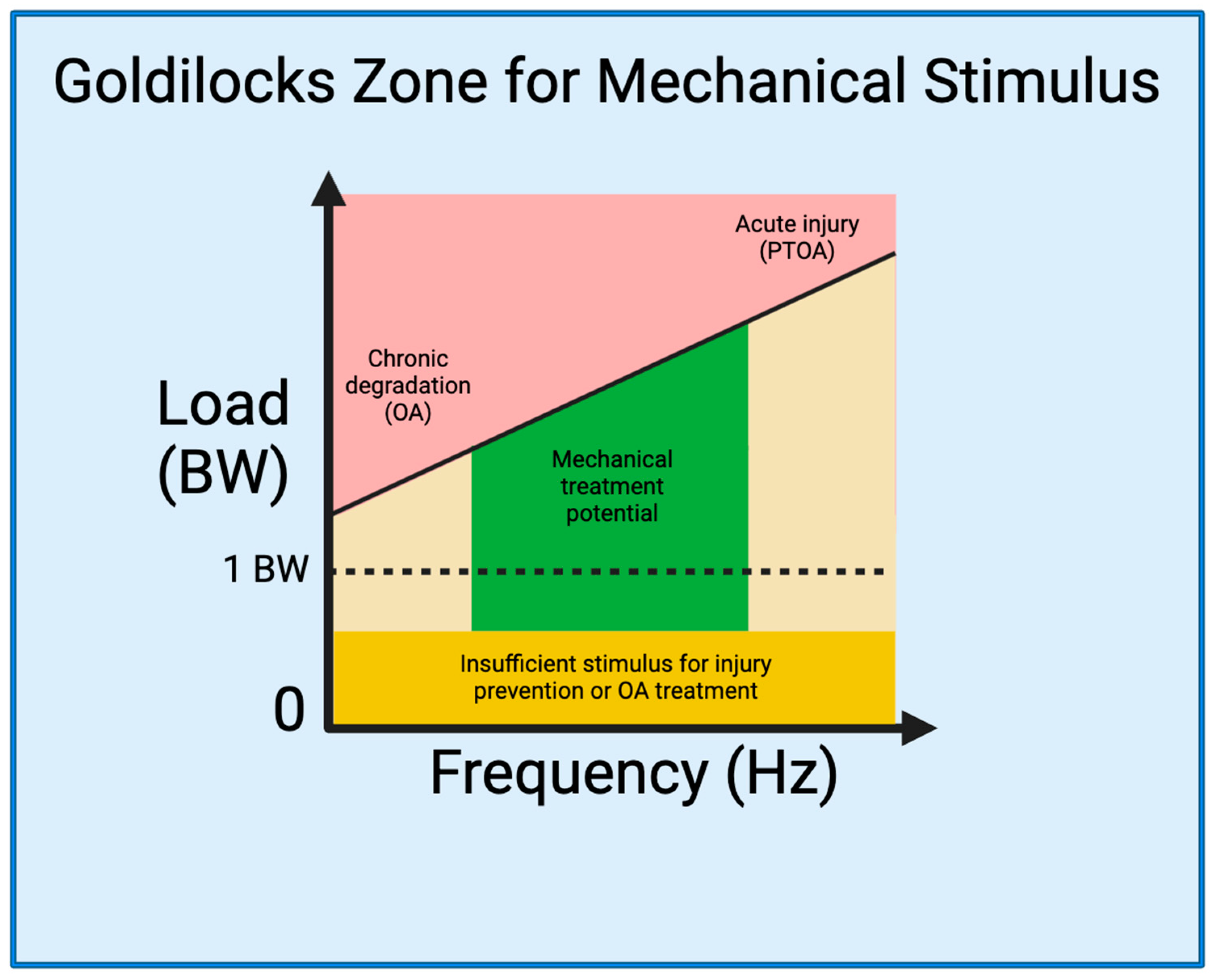
2.3. The Goldilocks Zone
3. Biomechanics of Rehabilitation Exercises
3.1. Rehabilitation Techniques
3.2. Resistance Exercises
3.3. Squat
3.4. Leg Extension
3.5. Comparison
3.6. Aerobic Exercises
| Type | Exercise | Tibiofemoral Force | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| CKC | Squat | 2.44–7.3 BW | [79,80,88,134] |
| Leg press | 3.0–6.32 BW | [67,136] | |
| OKC | Leg extension | 1.0–5.04 BW | [67,136] |
| Aerobic | Walking | 1.0–3.5 BW | [95,140] |
| Elliptical | 3.0–4.0 BW | [67] | |
| Stairmaster | 3.0–4.0 BW | [67] | |
| Jogging/running | 3.0–5.1 BW | [67,140] | |
| Jumping | 6.7–10.4 BW | [138,139] |
3.7. Mechanical Loading as a Therapeutic for KOA
4. Biomechanical Strategies for Prevention and Treatment of KOA and PTOA
4.1. Preventing PTOA Development by Monitoring Joint Loading
4.2. Mitigating OA by Reducing Abnormal Joint Biomechanics
4.3. Treating KOA by Application of Controlled Joint Loading Defined in the Goldilocks Zone
4.4. Future Directions and Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Description |
| ACL | anterior cruciate ligament |
| BW | body weight |
| CKC | closed kinetic chain |
| FFS | forefoot strike |
| IOC | International Olympic Committee |
| KAM | knee adduction movement |
| KOA | knee osteoarthritis |
| MPa | megapascals |
| N | Newtons |
| OA | osteoarthritis |
| OKC | open kinetic chain |
| PCL | posterior cruciate ligament |
| PTOA | post-traumatic osteoarthritis |
| RFS | rearfoot strike |
References
- Yang, G.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Lu, H.; He, L.; Ma, C.; Zhao, Z. Burden of Knee Osteoarthritis in 204 Countries and Territories, 1990–2019: Results From the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Arthritis Care Res. 2023, 75, 2489–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, B.R.; Katz, J.N.; Solomon, D.H.; Yelin, E.H.; Hunter, D.J.; Messier, S.P.; Suter, L.G.; Losina, E. Number of Persons With Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis in the US: Impact of Race and Ethnicity, Age, Sex, and Obesity. Arthritis Care Res. 2016, 68, 1743–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felson, D.T.; Naimark, A.; Anderson, J.; Kazis, L.; Castelli, W.; Meenan, R.F. The prevalence of knee osteoarthritis in the elderly. the framingham osteoarthritis study. Arthritis Rheum. 1987, 30, 914–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudo, A.; Miyamoto, N.; Horikawa, K.; Urawa, M.; Yamakawa, T.; Yamada, T.; Uchida, A. Prevalence and risk factors for knee osteoarthritis in elderly Japanese men and women. J. Orthop. Sci. 2008, 13, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, S.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Zhao, G.; Cai, Y.; Dong, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, S. Prevalence and factors associated with knee osteoarthritis among middle-aged and elderly individuals in rural Tianjin: A population-based cross-sectional study. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2023, 18, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saase, J.L.v.; Romunde, L.K.v.; Cats, A.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; Valkenburg, H.A. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis: Zoetermeer survey. Comparison of radiological osteoarthritis in a Dutch population with that in 10 other populations. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1989, 48, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari, B. Knee osteoarthritis prevalence, risk factors, pathogenesis and features: Part I. Casp. J. Intern. Med. 2011, 2, 205–212. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, D.L.; Kersh, M.E.; Walsh, N.C.; Ackland, D.C.; de Steiger, R.N.; Pandy, M.G. Mechanical properties of normal and osteoarthritic human articular cartilage. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 61, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donell, S. Subchondral bone remodelling in osteoarthritis. EFORT Open Rev. 2019, 4, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Coras, R.; Torres, A.; Lane, N.E.; Guma, M. Synovial inflammation in osteoarthritis progression. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 258–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kean, W.F.; Kean, R.; Buchanan, W.W. Osteoarthritis: Symptoms, signs and source of pain. Inflammo. Pharmacol. 2004, 12, 3–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicuttini, F.M.; Spector, T.D. Genetics of osteoarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1996, 55, 665–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spector, T.D.; MacGregor, A.J. Risk factors for osteoarthritis: Genetics11supported by Procter & Gamble Pharmaceuticals, Mason, OH. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2004, 12, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrezas, I.; Elsner, G.; Bolm-Audorff, U.; Abolmaali, N.; Seidler, A. Case–control study of knee osteoarthritis and lifestyle factors considering their interaction with physical workload. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2010, 83, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiev, T.; Angelov, A.K. Modifiable risk factors in knee osteoarthritis: Treatment implications. Rheumatol. Int. 2019, 39, 1145–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connelly, A.E.; Tucker, A.J.; Kott, L.S.; Wright, A.J.; Duncan, A.M. Modifiable lifestyle factors are associated with lower pain levels in adults with knee osteoarthritis. Pain Res. Manag. 2015, 20, 389084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.N.; Kim, S.H.; Park, K.N. Relationship between objectively measured lifestyle factors and health factors in patients with knee osteoarthritis: The STROBE Study. Medicine 2019, 98, e16060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhon, D.I.; Perez, K.G.; Eskridge, S.L. Risk of post-traumatic knee osteoarthritis after knee injury in military service members. Musculoskelet. Care 2019, 17, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, J.L.; Losciale, J.M.; Juhl, C.B.; Thorlund, J.B.; Lundberg, M.; Truong, L.K.; Miciak, M.; Meer, B.L.v.; Culvenor, A.G.; Crossley, K.M.; et al. Risk factors for knee osteoarthritis after traumatic knee injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials and cohort studies for the OPTIKNEE Consensus. Br. J. Sports Med. 2022, 56, 1406–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakowski, P.; Karpiński, R.; Jojczuk, M.; Nogalska, A.; Jonak, J. Knee MRI Underestimates the Grade of Cartilage Lesions. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakowski, P.; Karpiński, R.; Maciejewski, R.; Jonak, J.; Jurkiewicz, A. Short-Term Effects of Arthroscopic Microfracturation of Knee Chondral Defects in Osteoarthritis. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpiński, R. Knee joint osteoarthritis diagnosis based on selected acoustic signal discriminants using machine learning. Appl. Comput. Sci. 2022, 18, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Fu, P.; Wu, H.; Pei, M. Meniscus, articular cartilage and nucleus pulposus: A comparative review of cartilage-like tissues in anatomy, development and function. Cell Tissue Res. 2017, 370, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, C.; McAlindon, T.; Coggon, D.; Egger, P.; Dieppe, P. Occupational activity and osteoarthritis of the knee. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1994, 53, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.J.; Felson, D.T. Factors Assocciated With Osteoarthritis Of The Knee In The First National Health And Nutrition Examination Survey (HANES I): Evidence For An Association With Overweight, Race, And Physical Demands Of Work. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1988, 128, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hootman, J.M.; Dick, R.; Agel, J. Epidemiology of collegiate injuries for 15 sports: Summary and recommendations for injury prevention initiatives. J. Athl. Train. 2007, 42, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Golightly, Y.M.; Marshall, S.W.; Callahan, L.F.; Guskiewicz, K. Early-onset arthritis in retired National Football League players. J. Phys. Act. Health 2009, 6, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drawer, S.; Fuller, C. Propensity for osteoarthritis and lower limb joint pain in retired professional soccer players. Br. J. Sports Med. 2001, 35, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillquist, J.; Messner, K. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction and the long-term incidence of gonarthrosis. Sports Med. 1999, 27, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, H.; Laurén, M.; Adalberth, T.; Roos, E.M.; Jonsson, K.; Lohmander, L.S. Knee osteoarthritis after meniscectomy: Prevalence of radiographic changes after twenty-one years, compared with matched controls. Arthritis Rheum. 1998, 41, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujala, U.M.; Kettunen, J.; Paananen, H.; Aalto, T.; Battié, M.C.; Impivaara, O.; Videman, T.; Sarna, S. Knee osteoarthritis in former runners, soccer players, weight lifters, and shooters. Arthritis Rheum. Off. J. Am. Coll. Rheumatol. 1995, 38, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swärd, P.; Kostogiannis, I.; Neuman, P.; Von Porat, A.; Boegård, T.; Roos, H. Differences in the radiological characteristics between post-traumatic and non-traumatic knee osteoarthritis. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2010, 20, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.D.; Chubinskaya, S.; Guilak, F.; Martin, J.A.; Oegema, T.R.; Olson, S.A.; Buckwalter, J.A. Post-traumatic osteoarthritis: Improved understanding and opportunities for early intervention. J. Orthop. Res. 2011, 29, 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milentijevic, D.; Rubel, I.F.; Liew, A.S.; Helfet, D.L.; Torzilli, P.A. An in vivo rabbit model for cartilage trauma: A preliminary study of the influence of impact stress magnitude on chondrocyte death and matrix damage. J. Orthop. Trauma 2005, 19, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyvang, J.; Hedström, M.; Gleissman, S.A. It’s not just a knee, but a whole life: A qualitative descriptive study on patients’ experiences of living with knee osteoarthritis and their expectations for knee arthroplasty. Int. J. Qual. Stud. Health Well-Being 2016, 11, 30193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, D.J.; Schofield, D.; Callander, E. The individual and socioeconomic impact of osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2014, 10, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, C.; Wen, L.; Qin, H.; Zhu, B.; Lu, X.; Luo, S. Sotrastaurin, a PKC inhibitor, attenuates RANKL-induced bone resorption and attenuates osteochondral pathologies associated with the development of OA. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 8452–8465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Warburton, C.; Perez, O.F.; Wang, Y.; Ho, L.; Finelli, C.; Ehlen, Q.T.; Wu, C.; Rodriguez, C.D.; Kaplan, L.; et al. Hippo Signaling Modulates the Inflammatory Response of Chondrocytes to Mechanical Compressive Loading. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Kuo, S.J.; Liu, S.C.; Lu, Y.C.; Chen, Y.L.; Wang, S.W.; Tang, C.H. Resistin Enhances VCAM-1 Expression and Monocyte Adhesion in Human Osteoarthritis Synovial Fibroblasts by Inhibiting MiR-381 Expression through the PKC, p38, and JNK Signaling Pathways. Cells 2020, 9, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, H.; Wirth, K.; Klusemann, M. Analysis of the Load on the Knee Joint and Vertebral Column with Changes in Squatting Depth and Weight Load. Sports Med. 2013, 43, 993–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, M.; Creaby, M.W.; Lund, H.; Juhl, C.; Christensen, R. Is there a causal link between knee loading and knee osteoarthritis progression? A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies and randomised trials. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e005368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbins, S.M.; Birmingham, T.B.; Callaghan, J.P.; Jones, G.R.; Chesworth, B.M.; Maly, M.R. Association of pain with frequency and magnitude of knee loading in knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilak, F.; Hung, C.T. Physical regulation of cartilage metabolism. In Basic Orthopaedic Biomechanics; Lippincott-Raven: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005; pp. 259–300. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, T.M.; Guilak, F. The Role of Mechanical Loading in the Onset and Progression of Osteoarthritis. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2005, 33, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldring, S.R.; Goldring, M.B. The role of cytokines in cartilage matrix degeneration in osteoarthritis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2004, 427, S27–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckwalter, J.A.; Anderson, D.D.; Brown, T.D.; Tochigi, Y.; Martin, J.A. The roles of mechanical stresses in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: Implications for treatment of joint injuries. Cartilage 2013, 4, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Xiao, W.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y. Instability and excessive mechanical loading mediate subchondral bone changes to induce osteoarthritis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zheng, J.J.Y.; Li, G.; Yuan, J.; Ebert, J.R.; Li, H.; Papadimitriou, J.; Wang, Q.; Wood, D.; Jones, C.W.; et al. Pathogenesis and clinical management of obesity-related knee osteoarthritis: Impact of mechanical loading. J. Orthop. Transl. 2020, 24, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egloff, C.; Hügle, T.; Valderrabano, V. Biomechanics and pathomechanisms of osteoarthritis. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2012, 142, w13583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, A.; Nazet, U.; Muschter, D.; Grässel, S.; Proff, P.; Kirschneck, C. Impact of mechanical load on the expression profile of synovial fibroblasts from patients with and without osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Nie, P.; Lu, J.; Ling, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, B.; Hu, J.; Liao, J.; Gu, J.; Dai, B.; et al. Less mechanical loading attenuates osteoarthritis by reducing cartilage degeneration, subchondral bone remodelling, secondary inflammation, and activation of NLRP3 inflammasome. Bone Jt. Res. 2020, 9, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Zhou, X.; Jin, M.; Nie, J.; Li, X. Molecular mechanisms of mechanical load-induced osteoarthritis. Int. Orthop. 2021, 45, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, A.E.M.; Kjær, M.; Heinemeier, K.M. The Effect of Aging and Mechanical Loading on the Metabolism of Articular Cartilage. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 44, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, D.J.; Sun, H.B. Mechanical loading: Potential preventive and therapeutic strategy for osteoarthritis. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2014, 22, 465–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, M.T.; Lalley, A.L.; Shearn, J.T. The role of mechanical loading in tendon development, maintenance, injury, and repair. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2013, 95, 1620–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontera, W.R.; Meredith, C.N.; O’Reilly, K.P.; Knuttgen, H.G.; Evans, W.J. Strength conditioning in older men: Skeletal muscle hypertrophy and improved function. J. Appl. Physiol. 1988, 64, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanrenterghem, J.; Nedergaard, N.J.; Robinson, M.A.; Drust, B. Training Load Monitoring in Team Sports: A Novel Framework Separating Physiological and Biomechanical Load-Adaptation Pathways. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 2135–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebelung, S.; Gavenis, K.; Lüring, C.; Zhou, B.; Mueller-Rath, R.; Stoffel, M.; Tingart, M.; Rath, B. Simultaneous anabolic and catabolic responses of human chondrocytes seeded in collagen hydrogels to long-term continuous dynamic compression. Ann. Anat. Anat. Anz. 2012, 194, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.Y.; Chang, Y.H.; Wang, H.Y.; Yang, T.C.; Chiu, T.K.; Huang, S.B.; Wu, M.H. The study of the frequency effect of dynamic compressive loading on primary articular chondrocyte functions using a microcell culture system. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 762570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Adams, J.; Leddy, H.A.; McNulty, A.L.; O’Conor, C.J.; Guilak, F. The mechanobiology of articular cartilage: Bearing the burden of osteoarthritis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2014, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberthal, J.; Sambamurthy, N.; Scanzello, C.R. Inflammation in joint injury and post-traumatic osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2015, 23, 1825–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-J.; Zeng, N.; Yan, Z.-P.; Li, J.-T.; Ni, G.-X. Post-traumatic osteoarthritis following ACL injury. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, D.J.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, J.; Tu, X.; Amin, S.; Goggins, J.; Lavalley, M.; Guermazi, A.; Gale, D.; Felson, D.T. Structural factors associated with malalignment in knee osteoarthritis: The Boston osteoarthritis knee study. J. Rheumatol. 2005, 32, 2192–2199. [Google Scholar]
- Felson, D.T.; Niu, J.; Gross, K.D.; Englund, M.; Sharma, L.; Cooke, T.D.V.; Guermazi, A.; Roemer, F.W.; Segal, N.; Goggins, J.M.; et al. Valgus malalignment is a risk factor for lateral knee osteoarthritis incidence and progression: Findings from the multicenter osteoarthritis study and the osteoarthritis initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, J.L.; Losciale, J.M.; Juhl, C.; Thorlund, J.B.; Lundberg, M.; Troung, L.K.; Miciak, M.; van Meer, B.L.; Culvenor, A.G.; Crossley, K.M. Risk factors for knee osteoarthritis after knee trauma: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials and cohort studies for the optiknee initiative. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2022, 30, S223–S224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, J., Jr.; Zhu, Y.; Burns, M.; Sandell, L.; Silva, M.J. Cartilage tolerates single impact loads of as much as half the joint fracture threshold. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2004, 426, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Lima, D.D.; Steklov, N.; Patil, S.; Colwell Jr, C.W. The Mark Coventry Award: In vivo knee forces during recreation and exercise after knee arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2008, 466, 2605–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Lima, D.D.; Fregly, B.J.; Patil, S.; Steklov, N.; Colwell, C.W. Knee joint forces: Prediction, measurement, and significance. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2012, 226, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, L.; Song, J.; Felson, D.T.; Cahue, S.; Shamiyeh, E.; Dunlop, D.D. The role of knee alignment in disease progression and functional decline in knee osteoarthritis. JAMA 2001, 286, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanamas, S.; Hanna, F.S.; Cicuttini, F.M.; Wluka, A.E.; Berry, P.; Urquhart, D.M. Does knee malalignment increase the risk of development and progression of knee osteoarthritis? A systematic review. Arthritis Care Res. Off. J. Am. Coll. Rheumatol. 2009, 61, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lequesne, M.G.; Dang, N.; Lane, N.E. Sport practice and osteoarthritis of the limbs. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 1997, 5, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boocock, M.; McNair, P.; Cicuttini, F.; Stuart, A.; Sinclair, T. The short-term effects of running on the deformation of knee articular cartilage and its relationship to biomechanical loads at the knee. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2009, 17, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.H.; Grimshaw, P.N. The Biomechanics of the Modern Golf Swing: Implications for Lower Back Injuries. Sports Med. 2016, 46, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.; English, M.; Willick, S.E. Does Running Cause Osteoarthritis in the Hip or Knee? PMR 2012, 4, S117–S121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmins, K.A.; Leech, R.D.; Batt, M.E.; Edwards, K.L. Running and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Am. J. Sports Med. 2017, 45, 1447–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosomworth, N.J. Exercise and knee osteoarthritis: Benefit or hazard? Can. Fam. Physician 2009, 55, 871–878. [Google Scholar]
- James, S.L. Running Injuries to the Knee. JAAOS J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 1995, 3, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thelin, N.; Holmberg, S.; Thelin, A. Knee injuries account for the sports-related increased risk of knee osteoarthritis. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2006, 16, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thambyah, A.; Goh, J.C.; De, S.D. Contact stresses in the knee joint in deep flexion. Med. Eng. Phys. 2005, 27, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, D.A.; Salem, G.J.; Salinas, R.; Powers, C.M. Patellofemoral joint kinetics while squatting with and without an external load. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2002, 32, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtig, M.; Chubinskaya, S.; Dickey, J.; Rueger, D. BMP-7 protects against progression of cartilage degeneration after impact injury. J. Orthop. Res. Off. Publ. Orthop. Res. Soc. 2009, 27, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundell, S.A.; Baars, D.C.; Phillips, D.M.; Haut, R.C. The limitation of acute necrosis in retro-patellar cartilage after a severe blunt impact to the in vivo rabbit patello-femoral joint. J. Orthop. Res. Off. Publ. Orthop. Res. Soc. 2005, 23, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farquhar, T.; Xia, Y.; Mann, K.; Bertram, J.; Burton-Wurster, N.; Jelinski, L.; Lust, G. Swelling and fibronectin accumulation in articular cartilage explants after cyclical impact. J. Orthop. Res. Off. Publ. Orthop. Res. Soc. 1996, 14, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radin, E.L.; Burr, D.B.; Caterson, B.; Fyhrie, D.; Brown, T.D.; Boyd, R.D. Mechanical determinants of osteoarthrosis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 1991, 21, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radin, E.L.; Martin, R.B.; Burr, D.B.; Caterson, B.; Boyd, R.D.; Goodwin, C. Effects of mechanical loading on the tissues of the rabbit knee. J. Orthop. Res. Off. Publ. Orthop. Res. Soc. 1984, 2, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohue, J.M.; Buss, D.; Oegema, T.R., Jr.; Thompson, R.C., Jr. The effects of indirect blunt trauma on adult canine articular cartilage. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 1983, 65, 948–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, E.G.; Baumer, T.G.; Slade, J.M.; Smith, W.E.; Haut, R.C. Tibiofemoral contact pressures and osteochondral microtrauma during anterior cruciate ligament rupture due to excessive compressive loading and internal torque of the human knee. Am. J. Sports Med. 2008, 36, 1966–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, G.J.; Powers, C.M. Patellofemoral joint kinetics during squatting in collegiate women athletes. Clin. Biomech. 2001, 16, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, T.; Howat, P.; Trainor, M.; Maycock, B. Training patterns and sports injuries in triathletes. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2004, 7, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koplan, J.P.; Rothenberg, R.B.; Jones, E.L. The natural history of exercise: A 10-yr follow-up of a cohort of runners. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1995, 27, 1180–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piggott, B. The Relationship between Training Load and Incidence of Injury and Illness over a Pre-Season at an Australian Football League Club. Master’s Thesis, Edith Cowan University, Joondalup, WA, Australia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Satterthwaite, P.; Norton, R.; Larmer, P.; Robinson, E. Risk factors for injuries and other health problems sustained in a marathon. Br. J. Sports Med. 1999, 33, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, M.B.; Tang, L.; Zebis, M.K.; Krustrup, P.; Hölmich, P.; Wedderkopp, N.; Andersen, L.L.; Christensen, K.B.; Møller, M.; Thorborg, K. Self-reported previous knee injury and low knee function increase knee injury risk in adolescent female football. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2016, 26, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schueller-Weidekamm, C.; Schueller, G.; Uffmann, M.; Bader, T. Incidence of chronic knee lesions in long-distance runners based on training level: Findings at MRI. Eur. J. Radiol. 2006, 58, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Lima, D.D.; Patil, S.; Steklov, N.; Slamin, J.E.; Colwell, C.W., Jr. Tibial forces measured in vivo after total knee arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2006, 21, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljehani, M.S.; Christensen, J.C.; Snyder-Mackler, L.; Crenshaw, J.; Brown, A.; Zeni, J.A., Jr. Knee biomechanics and contralateral knee osteoarthritis progression after total knee arthroplasty. Gait Posture 2022, 91, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driban, J.B.; Lo, G.H.; Eaton, C.B.; Price, L.L.; Lu, B.; McAlindon, T.E. Knee pain and a prior injury are associated with increased risk of a new knee injury: Data from the osteoarthritis initiative. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 42, 1463–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- September, A.V.; Schwellnus, M.P.; Collins, M. Tendon and ligament injuries: The genetic component. Br. J. Sports Med. 2007, 41, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghava Neelapala, Y.V.; Bhagat, M.; Shah, P. Hip Muscle Strengthening for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review of Literature. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2020, 43, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veugelers, K.R.; Young, W.B.; Fahrner, B.; Harvey, J.T. Different methods of training load quantification and their relationship to injury and illness in elite Australian football. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2016, 19, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baert, I.A.; Nijs, J.; Meeus, M.; Lluch, E.; Struyf, F. The effect of lateral wedge insoles in patients with medial compartment knee osteoarthritis: Balancing biomechanics with pain neuroscience. Clin. Rheumatol. 2014, 33, 1529–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantini Pagani, C.H.; Hinrichs, M.; Brüggemann, G.P. Kinetic and kinematic changes with the use of valgus knee brace and lateral wedge insoles in patients with medial knee osteoarthritis. J. Orthop. Res. 2012, 30, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert-Lachaine, X.; Dessery, Y.; Belzile, É.L.; Corbeil, P. Knee braces and foot orthoses multimodal treatment of medial knee osteoarthritis. Gait Posture 2022, 96, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios, J.A.; Crossley, K.M.; Davis, I.S. Gait retraining to reduce the knee adduction moment through real-time visual feedback of dynamic knee alignment. J. Biomech. 2010, 43, 2208–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, M.-H.; Lin, J.-J.; Liau, J.-J.; Lin, Y.-F.; Lin, D.-H. Investigation of Clinical Effects of High- and Low-Resistance Training for Patients With Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Phys. Ther. 2008, 88, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunduracilar, Z.; Guvenir Sahin, H.; Sonmezer, E.; Sozay, S. The effects of two different water exercise trainings on pain, functional status and balance in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2018, 31, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagesson, S.; Oberg, B.; Good, L.; Kvist, J. A comprehensive rehabilitation program with quadriceps strengthening in closed versus open kinetic chain exercise in patients with anterior cruciate ligament deficiency: A randomized clinical trial evaluating dynamic tibial translation and muscle function. Am. J. Sports Med. 2008, 36, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heywood, S.; McClelland, J.; Geigle, P.; Rahmann, A.; Villalta, E.; Mentiplay, B.; Clark, R. Force during functional exercises on land and in water in older adults with and without knee osteoarthritis: Implications for rehabilitation. Knee 2019, 26, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vleck, V.E.; Bentley, D.J.; Millet, G.P.; Cochrane, T. Triathlon Event Distance Specialization: Training and Injury Effects. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soligard, T.; Schwellnus, M.; Alonso, J.-M.; Bahr, R.; Clarsen, B.; Dijkstra, H.P.; Gabbett, T.; Gleeson, M.; Hägglund, M.; Hutchinson, M.R. How much is too much?(Part 1) International Olympic Committee consensus statement on load in sport and risk of injury. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 1030–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.; Steklov, N.; Patil, S.; Flores-Hernandez, C.; Kester, M.; Colwell, C.W., Jr.; D’Lima, D.D. Predicting the effect of tray malalignment on risk for bone damage and implant subsidence after total knee arthroplasty. J. Orthop. Res. 2011, 29, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Neptune, R.R. Individual muscle contributions to the axial knee joint contact force during normal walking. J. Biomech. 2010, 43, 2780–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holyoak, D.T.; Chlebek, C.; Kim, M.J.; Wright, T.M.; Otero, M.; van der Meulen, M.C.H. Low-level cyclic tibial compression attenuates early osteoarthritis progression after joint injury in mice. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2019, 27, 1526–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, R.; Waddell, J.; Hoogenboom, B. The Effects of Open versus Closed Kinetic Chain Exercises on Patients with ACL Deficient or Reconstructed Knees: A Systematic Review. N. Am. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2010, 5, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bini, R.R. Patellofemoral and tibiofemoral forces during knee extension: Simulations to strength training and rehabilitation exercises. Fisioter. Em. Mov. 2017, 30, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escamilla, R.F.; Fleisig, G.S.; Zheng, N.; Barrentine, S.W.; Wilk, K.E.; Andrews, J.R. Biomechanics of the knee during closed kinetic chain and open kinetic chain exercises. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1998, 30, 556–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escamilla, R.F. Knee biomechanics of the dynamic squat exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2001, 33, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld, B.J. Squatting kinematics and kinetics and their application to exercise performance. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 3497–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, J.; Kaplan, L.; C Huang, C.-Y. Mechanical Injury of Knee Articular Cartilage in Sports-Related Exercise and Potential Post-Injury Preventative Therapy. Curr. Tissue Eng. (Discontin.) 2015, 4, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokoloff, L. The biology of degenerative joint disease. Perspect. Biol. Med. 1963, 7, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabbett, T.J. The training—Injury prevention paradox: Should athletes be training smarter and harder? Br. J. Sports Med. 2016, 50, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, R.W.; Morton, A.R.; Keast, D. Overtraining in athletes: An update. Sports Med. 1991, 12, 32–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovens, A.; Janssen, G.; Vermeer, H.; Hoeberigs, J.; Janssen, M.; Verstappen, F. Occurrence of running injuries in adults following a supervised training program. Int. J. Sports Med. 1989, 10, S186–S190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Middelkoop, M.; Kolkman, J.; Van Ochten, J.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.; Koes, B.W. Risk factors for lower extremity injuries among male marathon runners. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2008, 18, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orchard, J.W.; Blanch, P.; Paoloni, J.; Kountouris, A.; Sims, K.; Orchard, J.J.; Brukner, P. Cricket fast bowling workload patterns as risk factors for tendon, muscle, bone and joint injuries. Br. J. Sports Med. 2015, 49, 1064–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Xu, T. Effects of body weight-supported treadmill training on cartilage-subchondral bone unit in the rat model of posttraumatic osteoarthritis. J. Orthop. Res. 2021, 39, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazbun, L.; Martinez, J.A.; Best, T.M.; Kaplan, L.; Huang, C.Y. Anti-inflammatory effects of tibial axial loading on knee articular cartilage post traumatic injury. J. Biomech. 2021, 128, 110736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotkin, D.L.; Roberts, M.D.; Haun, C.T.; Schoenfeld, B.J. Muscle Fiber Type Transitions with Exercise Training: Shifting Perspectives. Sports 2021, 9, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrokhi, S.; Voycheck, C.A.; Tashman, S.; Fitzgerald, G.K. A biomechanical perspective on physical therapy management of knee osteoarthritis. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2013, 43, 600–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpiński, R.; Krakowski, P.; Jonak, J.; Machrowska, A.; Maciejewski, M.; Nogalski, A. Diagnostics of Articular Cartilage Damage Based on Generated Acoustic Signals Using ANN-Part II: Patellofemoral Joint. Sensors 2022, 22, 3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karandikar, N.; Vargas, O.O. Kinetic chains: A review of the concept and its clinical applications. Pm. R. 2011, 3, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.V. Length of muscle, and the heat and tension developed in an isometric contraction. J. Physiol. 1925, 60, 237–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutzner, I.; Heinlein, B.; Graichen, F.; Bender, A.; Rohlmann, A.; Halder, A.; Beier, A.; Bergmann, G. Loading of the knee joint during activities of daily living measured in vivo in five subjects. J. Biomech. 2010, 43, 2164–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagura, T.; Matsumoto, H.; Kiriyama, Y.; Chaudhari, A.; Andriacchi, T.P. Tibiofemoral joint contact force in deep knee flexion and its consideration in knee osteoarthritis and joint replacement. J. Appl. Biomech. 2006, 22, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisell, R.; Németh, G.; Ohlsén, H. Joint forces in extension of the knee. Analysis of a mechanical model. Acta. Orthop. Scand. 1986, 57, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilk, K.E.; Escamilla, R.F.; Fleisig, G.S.; Barrentine, S.W.; Andrews, J.R.; Boyd, M.L. A comparison of tibiofemoral joint forces and electromyographic activity during open and closed kinetic chain exercises. Am. J. Sports Med. 1996, 24, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rooney, B.D.; Derrick, T.R. Joint contact loading in forefoot and rearfoot strike patterns during running. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 2201–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleather, D.J.; Goodwin, J.E.; Bull, A.M. Hip and knee joint loading during vertical jumping and push jerking. Clin. Biomech. 2013, 28, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, K.J.; Kanter, L. Jump distance of dance landings influencing internal joint forces: I. Axial forces. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1997, 29, 916–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxby, D.J.; Modenese, L.; Bryant, A.L.; Gerus, P.; Killen, B.; Fortin, K.; Wrigley, T.V.; Bennell, K.L.; Cicuttini, F.M.; Lloyd, D.G. Tibiofemoral contact forces during walking, running and sidestepping. Gait Posture 2016, 49, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torzilli, P.A.; Bhargava, M.; Chen, C.T. Mechanical Loading of Articular Cartilage Reduces IL-1-Induced Enzyme Expression. Cartilage 2011, 2, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, T.T.; Arghandawi, S.; Brand, J.; Akanji, O.O.; Bader, D.L.; Salter, D.M.; Lee, D.A. Dynamic compression counteracts IL-1beta induced inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclo-oxygenase-2 expression in chondrocyte/agarose constructs. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008, 10, R35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernon, L.; Abadin, A.; Wilensky, D.; Huang, C.Y.; Kaplan, L. Subphysiological compressive loading reduces apoptosis following acute impact injury in a porcine cartilage model. Sports Health 2014, 6, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Frank, E.H.; Wang, Y.; Chubinskaya, S.; Huang, H.H.; Grodzinsky, A.J. Moderate dynamic compression inhibits pro-catabolic response of cartilage to mechanical injury, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6, but accentuates degradation above a strain threshold. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2013, 21, 1933–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Pan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, J.; Fu, L.; Cai, H.; Liu, C.; et al. Axial Compressive Loading Attenuates Early Osteoarthritis by Reducing Subchondral Bone Remodeling. Am. J. Sports Med. 2023, 51, 1752–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Liu, D.; Zhai, L.; Wang, X.; Abdurahman, A.; Yokota, H.; Zhang, P. Knee Loading Enhances the Migration of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells to the Osteoarthritic Sites Through the SDF-1/CXCR4 Regulatory Axis. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2022, 111, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Ding, B.; Li, X.; Liu, D.; Yokota, H.; Zhang, P. Knee loading repairs osteoporotic osteoarthritis by relieving abnormal remodeling of subchondral bone via Wnt/β-catenin signaling. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 3399–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, D.; Li, J.; Niu, K.; Feng, S.; Yokota, H.; Zhang, P. Knee loading inhibits osteoclast lineage in a mouse model of osteoarthritis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takacs, J.; Anderson, J.E.; Leiter, J.R.; MacDonald, P.B.; Peeler, J.D. Lower body positive pressure: An emerging technology in the battle against knee osteoarthritis? Clin. Interv. Aging. 2013, 8, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giarmatzis, G.; Zacharaki, E.I.; Moustakas, K. Real-Time Prediction of Joint Forces by Motion Capture and Machine Learning. Sensors 2020, 20, 6933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rane, L.; Ding, Z.; McGregor, A.H.; Bull, A.M.J. Deep Learning for Musculoskeletal Force Prediction. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 47, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, A.; Haghverd, F.; Behbahani, S. Robotic Home-Based Rehabilitation Systems Design: From a Literature Review to a Conceptual Framework for Community-Based Remote Therapy During COVID-19 Pandemic. Front. Robot. AI 2021, 8, 612331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jahn, J.; Ehlen, Q.T.; Huang, C.-Y. Finding the Goldilocks Zone of Mechanical Loading: A Comprehensive Review of Mechanical Loading in the Prevention and Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020110
Jahn J, Ehlen QT, Huang C-Y. Finding the Goldilocks Zone of Mechanical Loading: A Comprehensive Review of Mechanical Loading in the Prevention and Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(2):110. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020110
Chicago/Turabian StyleJahn, Jacob, Quinn T. Ehlen, and Chun-Yuh Huang. 2024. "Finding the Goldilocks Zone of Mechanical Loading: A Comprehensive Review of Mechanical Loading in the Prevention and Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis" Bioengineering 11, no. 2: 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020110
APA StyleJahn, J., Ehlen, Q. T., & Huang, C.-Y. (2024). Finding the Goldilocks Zone of Mechanical Loading: A Comprehensive Review of Mechanical Loading in the Prevention and Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis. Bioengineering, 11(2), 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020110








