Digitalized 3D Spinal Decompression and Correction Device Improved Initial Brace Corrections and Patients’ Comfort Among Adolescents with Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Single-Centre, Single-Blinded Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
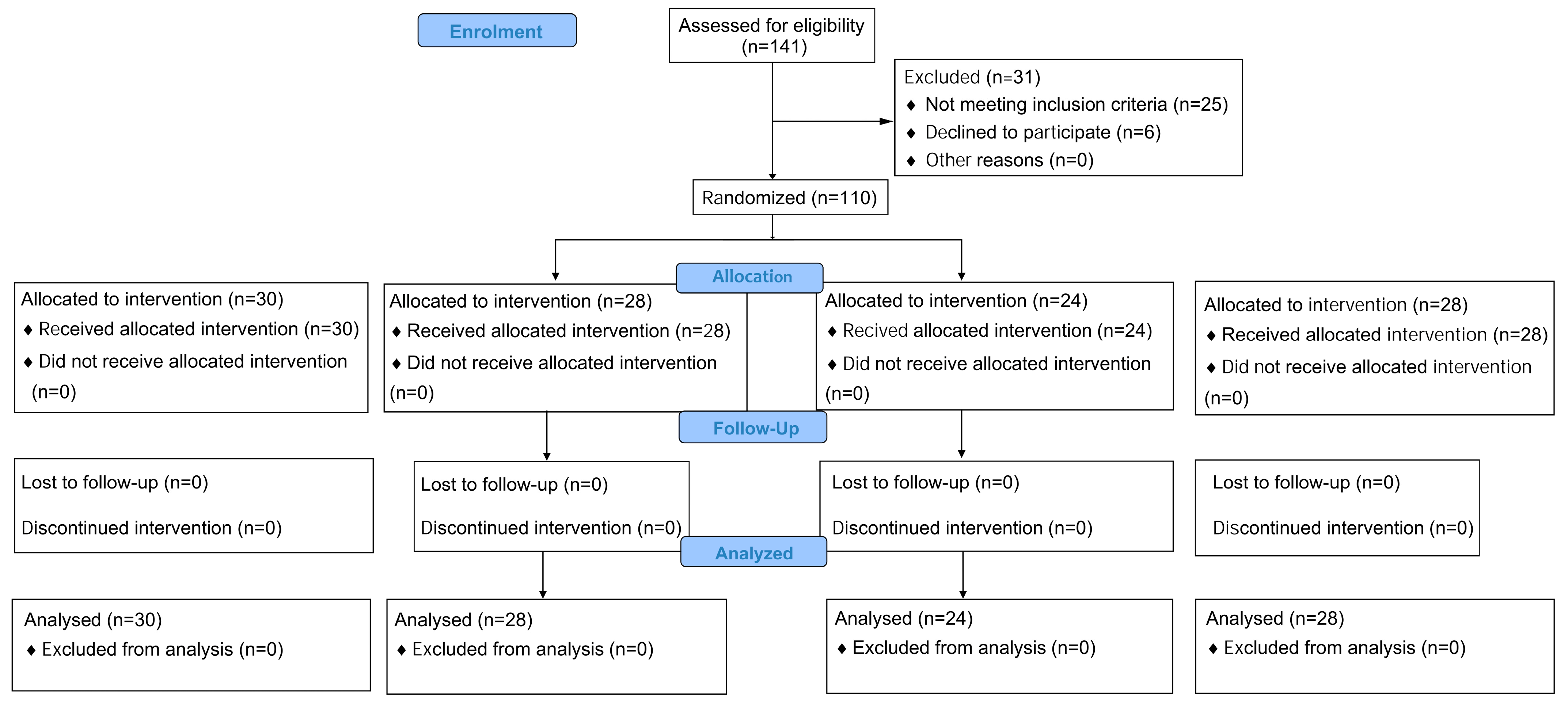
2.3. Randomization and Blinding
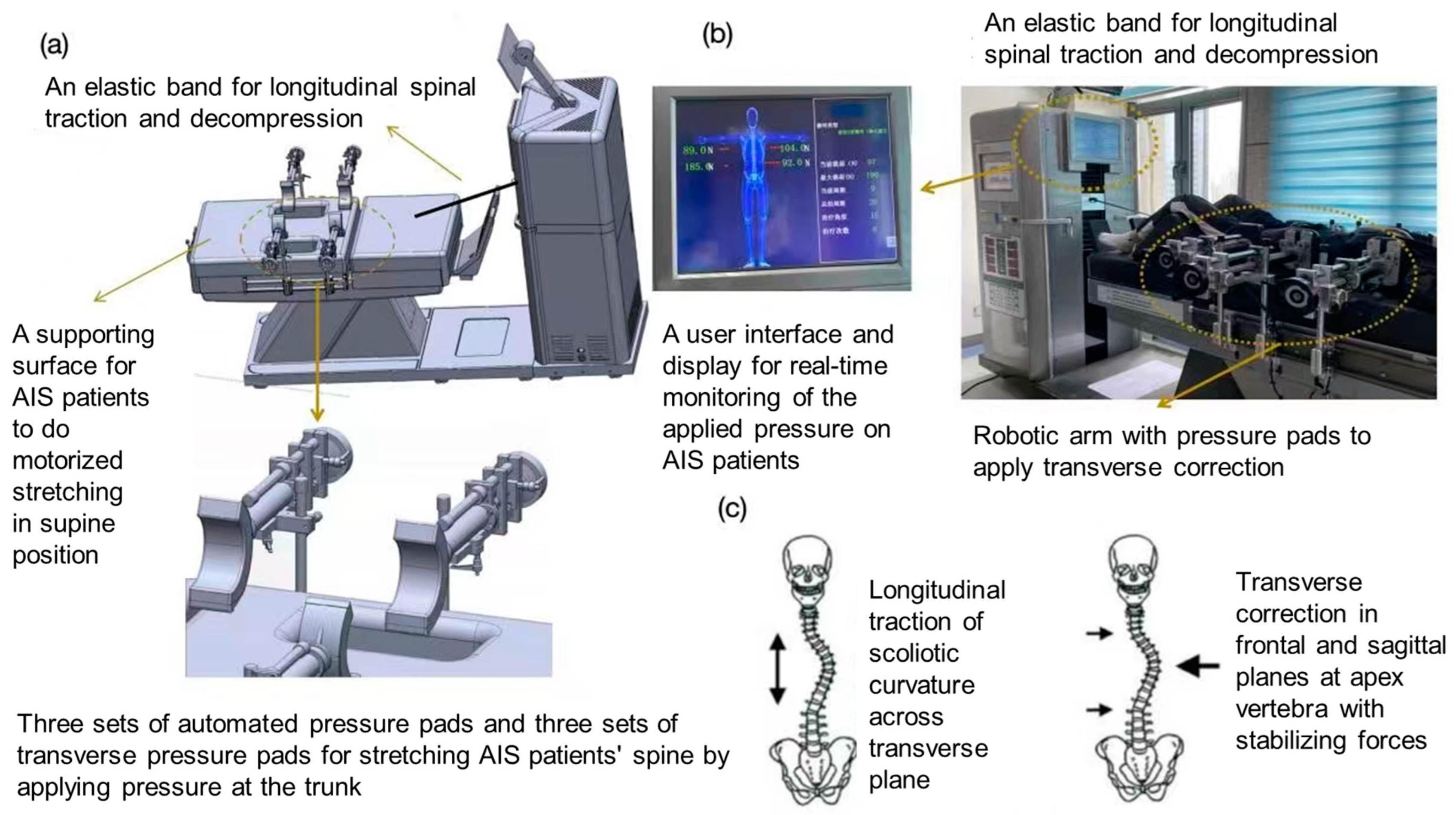
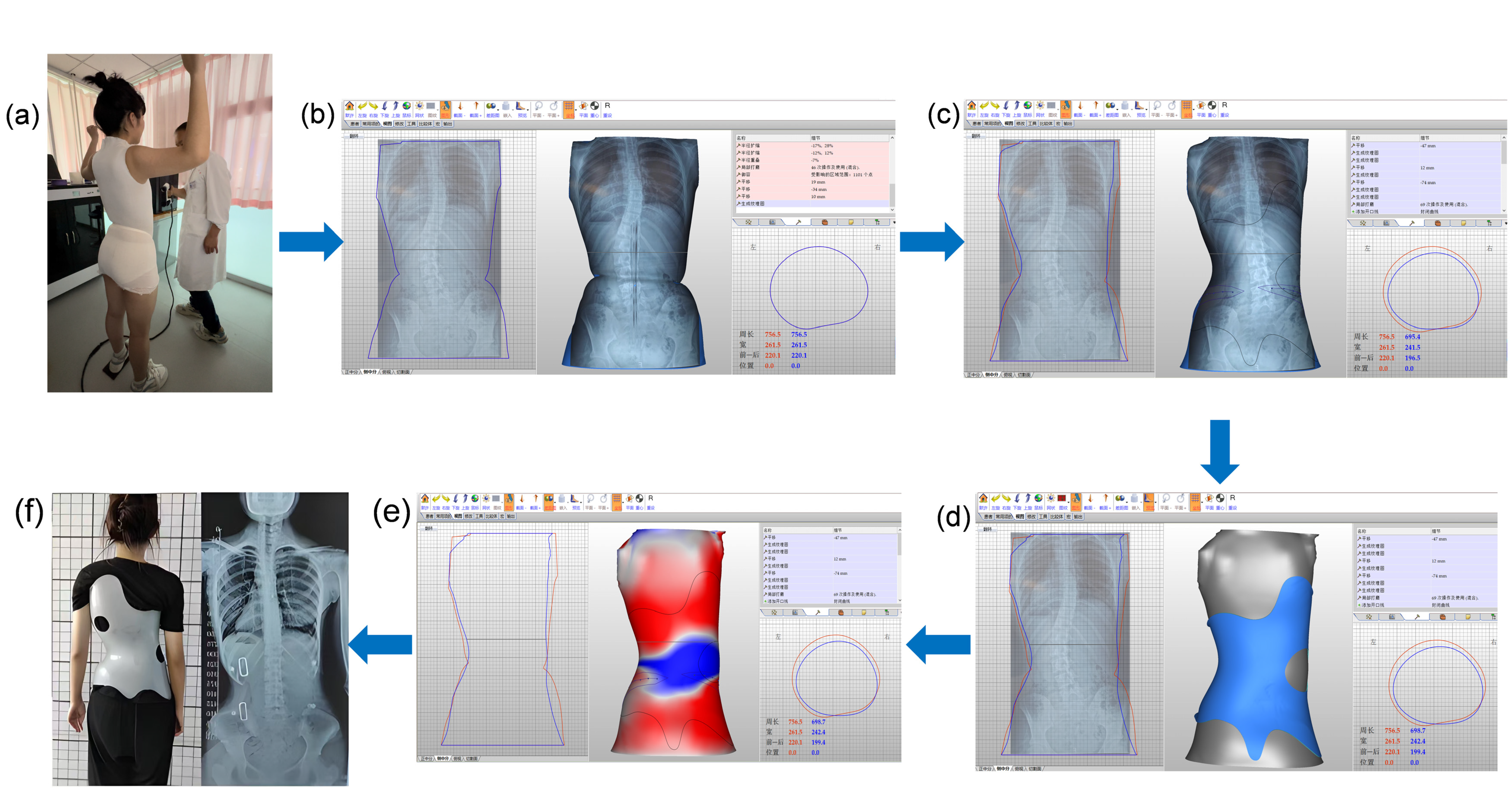
2.4. Intervention
2.5. Outcome Measures
2.5.1. Primary Outcomes
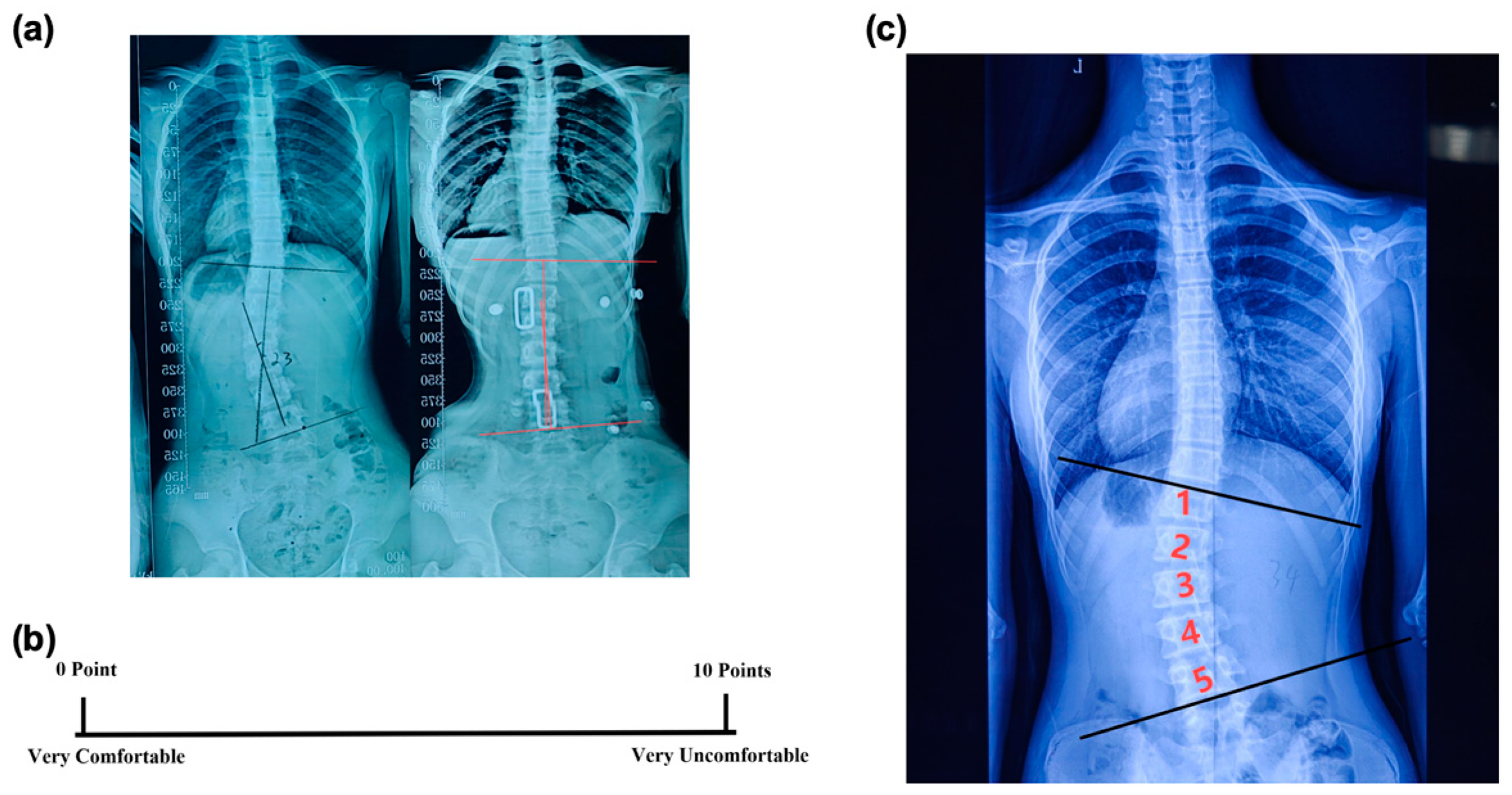
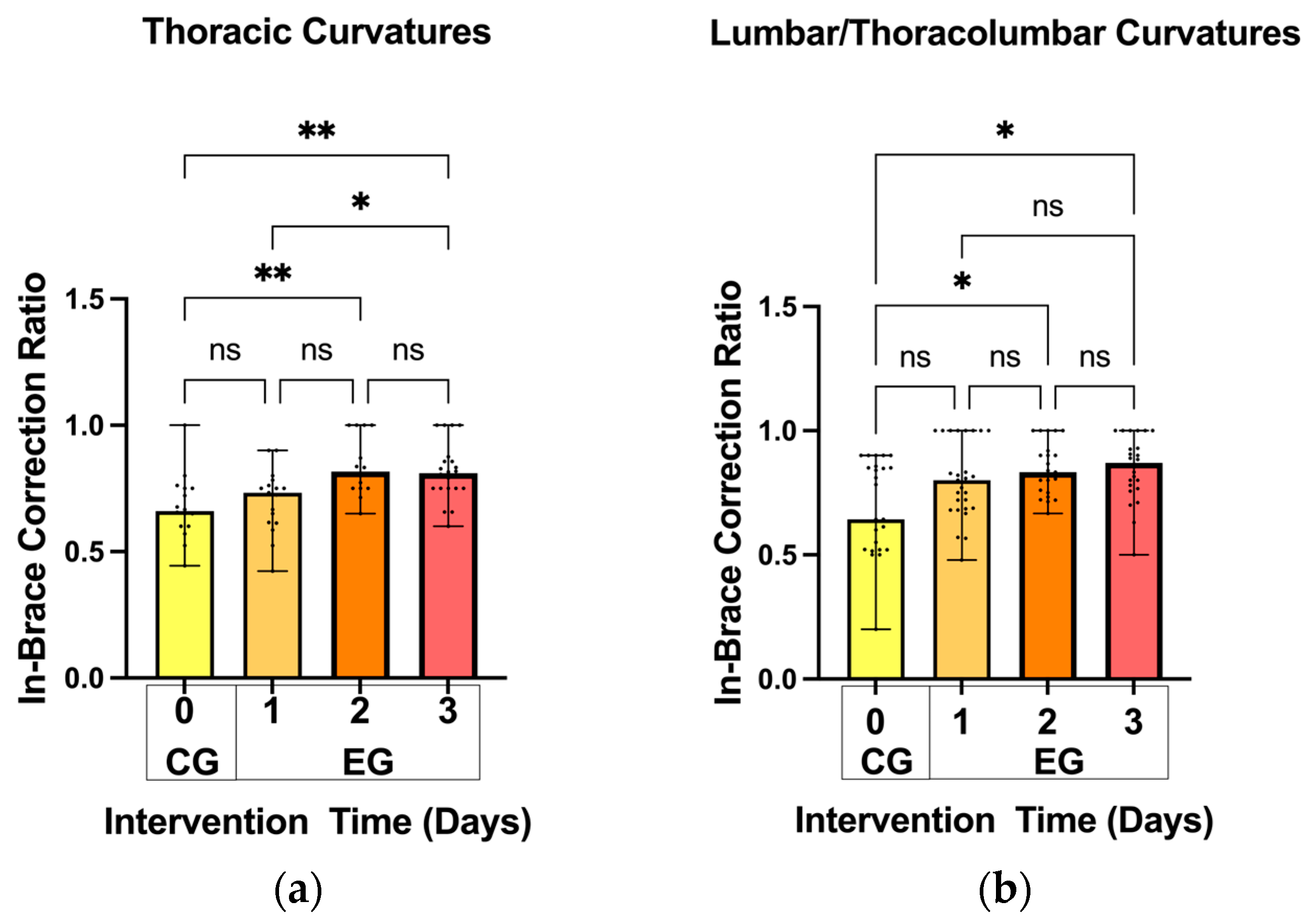
- In-brace Correction Ratio: Immediately after the patients wore the spinal braces, an X-ray examination was conducted to measure the in-brace Cobb angle (Figure 3a). The in-brace correction ratio was calculated using the following equation:
- 2.
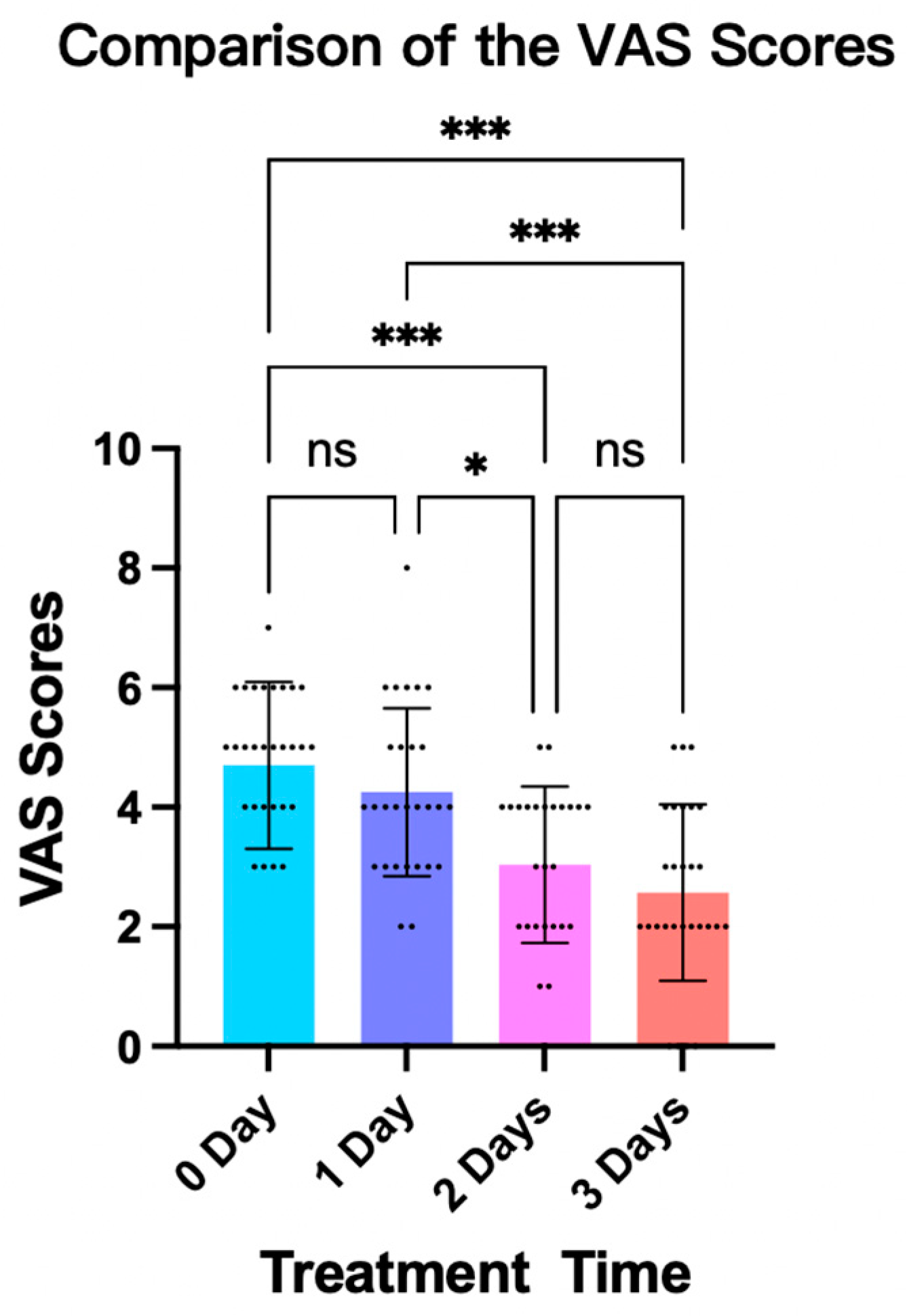
- Visual Analogue Scale (VAS): After fitting the brace, the VAS was used to assess a subject’s comfort level [20]. The scale ranged from 0 to 10, with 0 meaning very comfortable and 10 meaning very uncomfortable (Figure 3b). This rating was given independently by the patient to ensure an unbiased assessment of their comfort level while wearing the brace.
2.5.2. Secondary Outcomes
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. In-Brace Correction Ratios
3.3. Patient Comfort Level While Wearing the Fitted Brace
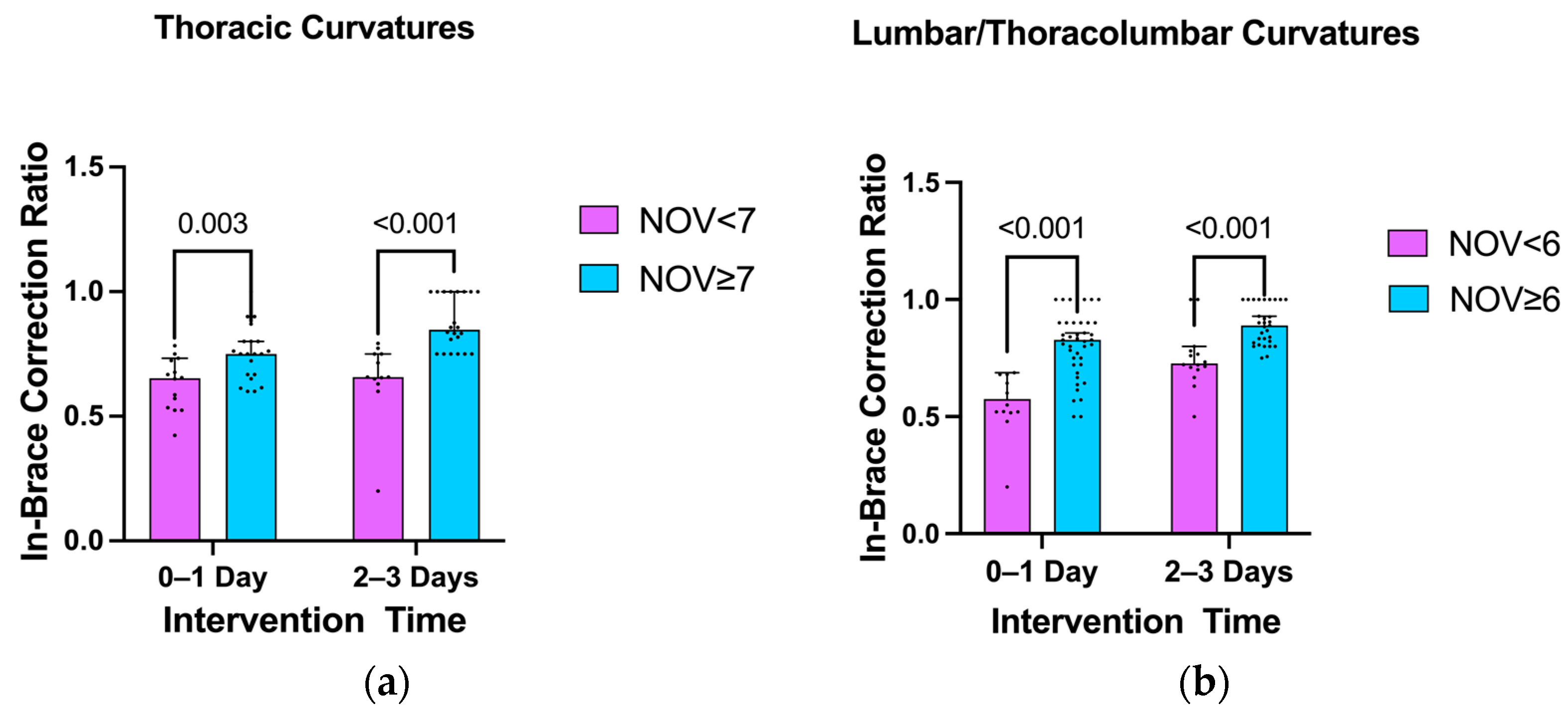
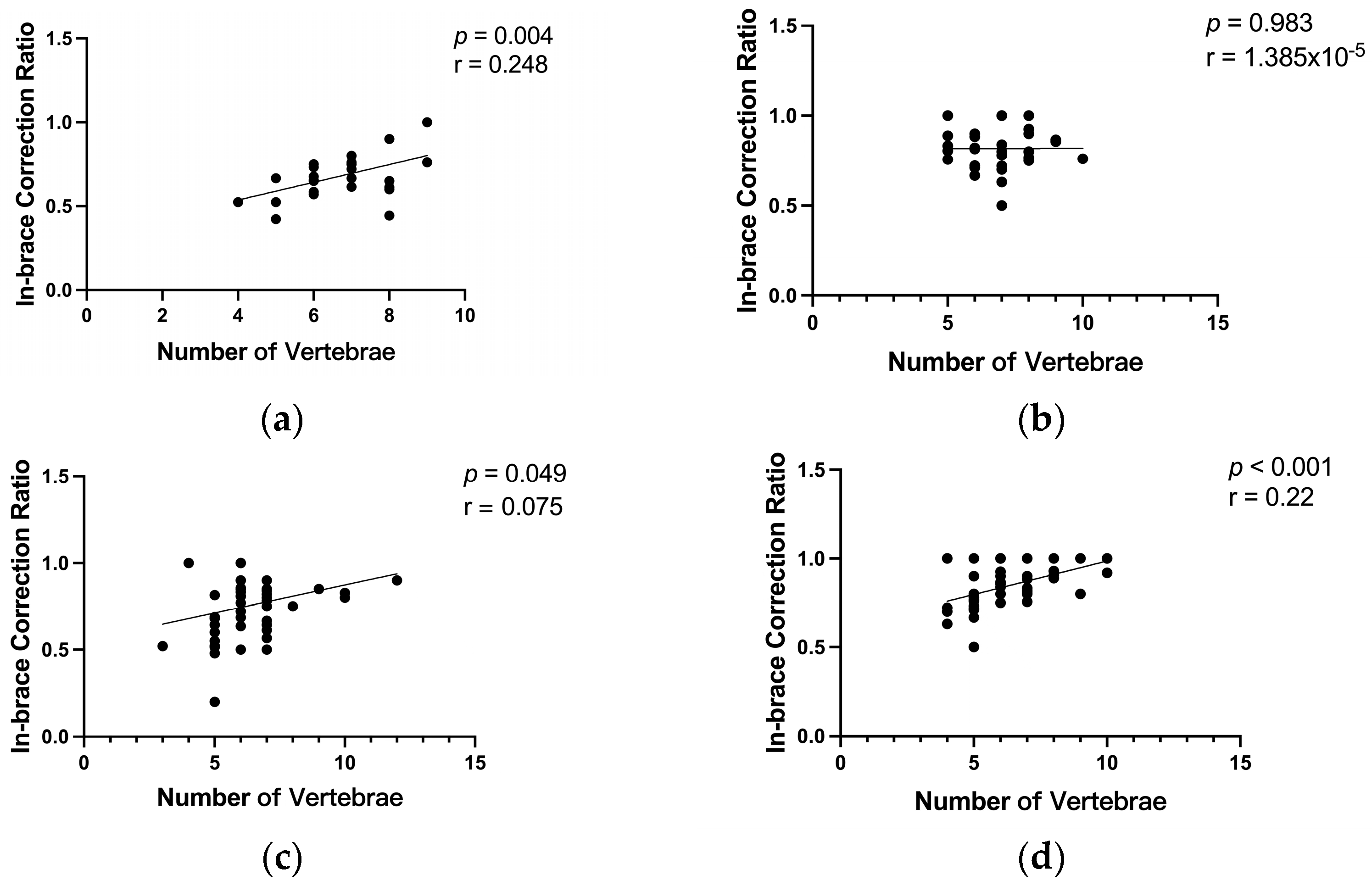
3.4. Impact of the Number of Vertebrae Involved in Scoliosis Curvature on the In-Brace Correction’s Effectiveness
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gorman, K.F.; Julien, C.; Moreau, A. The genetic epidemiology of idiopathic scoliosis. Eur. Spine J. 2012, 21, 1905–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, S.L.; Dolan, L.A.; Cheng, J.C.; Danielsson, A. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Lancet 2008, 371, 1527–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savvides, P.; Gerdhem, P.; Grauers, A.; Danielsson, A.; Diarbakerli, E. Self-Experienced Trunk Appearance in Individuals with and Without Idiopathic Scoliosis. Spine 2020, 45, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koumbourlis, A.C. Scoliosis and the respiratory system. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2006, 7, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, C.; Wang, R.; Chen, Z.; He, S.; Zou, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhu, X. Incidence and Risk Factors of Cardiac Abnormalities in Patients with Idiopathic Scoliosis. World Neurosurg. 2019, 125, e824–e828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, S.L.; Dolan, L.A.; Wright, J.G.; Dobbs, M.B. Effects of Bracing in Adolescents with Idiopathic Scoliosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1512–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrini, S.; Minozzi, S.; Bettany-Saltikov, J.; Chockalingam, N.; Grivas, T.B.; Kotwicki, T.; Maruyama, T.; Romano, M.; Zaina, F. Braces for idiopathic scoliosis in adolescents. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, CD006850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivas, T.B.; Wade, M.H.; Negrini, S.; O’Brien, J.P.; Maruyama, T.; Hawes, M.C.; Rigo, M.; Weiss, H.R.; Kotwicki, T.; Vasiliadis, E.S.; et al. SOSORT consensus paper: School screening for scoliosis. Where are we today? Scoliosis 2007, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, J.A.; Katz, D.E.; Browne, R.H.; Kelly, D.M.; Birch, J.G. Brace wear control of curve progression in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2010, 92, 1343–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, S.; Kiaghadi, A.; Fallahian, N. Effective factors on brace compliance in idiopathic scoliosis: A literature review. Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2020, 15, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hawary, R.; Zaaroor-Regev, D.; Floman, Y.; Lonner, B.S. Brace treatment in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: Risk factors for failure—A literature review. Spine J. 2019, 19, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.M.; Hubbard, E.W.; Jo, C.-H.; Virostek, D.; Karol, L.A. Brace Success Is Related to Curve Type in Patients with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2017, 99, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Ho, L.Y.; Beygi, B.H.; Wong, M.S. Effectiveness of Orthotic Treatment on Clinical Outcomes of the Patients with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Under Different Wearing Compliance Levels: A Systematic Review. JBJS Rev. 2023, 11, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karol, L.A.; Virostek, D.; Felton, K.; Wheeler, L. Effect of Compliance Counseling on Brace Use and Success in Patients with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2016, 98, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogaart, M.v.D.; van Royen, B.J.; Haanstra, T.M.; de Kleuver, M.; Faraj, S.S.A. Predictive factors for brace treatment outcome in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A best-evidence synthesis. Eur. Spine J. 2019, 28, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulisa, A.G.; Galli, M.; Giordano, M.; Falciglia, F.; Careri, S.; Toniolo, R.M. Initial In-Brace Correction: Can the Evaluation of Cobb Angle Be the Only Parameter Predictive of the Outcome of Brace Treatment in Patients with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis? Children 2022, 9, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Zayat, A.R.; Gomah, W.; Aldesouky, A.H. Spinal decompression therapy as an alternative modality for management of low back pain and radicular pain caused by lumbar disc herniation or protrusion. Egypt. Rheumatol. Rehabil. 2019, 46, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergolizzi, J.V., Jr.; Clair, D.F. 2 Prospective Evaluation of the Efficacy of Spinal Decompression via the DRX9000 for Chronic Low Back Pain. J. Pain Pract. 2008, 2–8. [Google Scholar]
- Karam, J.A.; Eid, R.; Kreichati, G.; Abiad, R.; Kharrat, K.; Ghanem, I.B. Optimizing the vertical position of the brace thoracic pad: Apical rib or apical vertebra? Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2019, 105, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, E.J.M. Comfort and its measurement—A literature review. Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2009, 4, 301–31020094301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; To, M.K.-T.; Cheung, J.P.-Y.; Cheung, K.M.-C.; Chan, C.-K.; Jiang, W.-W.; Zhou, G.-Q.; Lai, K.K.-L.; Zheng, Y.-P.; Wong, M.-S. An effective assessment method of spinal flexibility to predict the initial in-orthosis correction on the patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0190141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jie, Y.; Ma, W.M.; Zhang, M. The Usefulness of a Dual-period System with Distraction and Lateral Force Application for Spinal Correction and Flexibility in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis; The International Research Society of Spinal Deformities (IRSSD): Hong Kong, China, 2024; p. 94. [Google Scholar]
- Peeters, C.M.; van Hasselt, A.J.; Wapstra, F.H.; Jutte, P.C.; Kempen, D.H.; Faber, C. Predictive Factors on Initial in-brace Correction in Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Systematic Review. Spine 2022, 47, E353–E361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Lee, T.; Lai, K.; Wong, Y.; Wong, L.; Yang, J.; Lam, T.; Castelein, R.; Cheng, J.; Zheng, Y. A novel classification method for mild adolescent idiopathic scoliosis using 3D ultrasound imaging. Med. Nov. Technol. Devices 2021, 11, 100075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Lee, T.T.-Y.; Lai, K.K.-L.; Lam, T.-P.; Chu, W.C.-W.; Castelein, R.M.; Cheng, J.C.-Y.; Zheng, Y.-P. Semi-automatic ultrasound curve angle measurement for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine Deform. 2022, 10, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xia, N.; Wang, C.; Zheng, Q.; Ma, C.Z.; Youssef, A.S.A.; Zhang, C.; Deng, Y.; Zhu, G.; Huang, X. Optimized scheme for paired transverse corrective forces in S-shaped scoliosis via ultrasound and application in Cheneau brace: A pilot study. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2022, 46, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Xie, L.; Xu, J.; Xia, N.; Ma, C.Z. A feasibility study of applying two-dimensional photogrammetry for screening and monitoring of patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in clinical practice. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanti, C.; Panizzolo, A.; Turone, L.; A Guccione, A.; Violante, F.S.; Pillastrini, P.; Bertozzi, L. Effectiveness of Mechanical Traction for Lumbar Radiculopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Phys. Ther. 2021, 101, pzaa231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Rabczuk, T.; Luthfi, M.; Pourabbas, B.; Esrafilian, A. An evaluation of the efficiency of endpoint control on the correction of scoliotic curve with brace: A case study. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2019, 21, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, T.; Bowen, J.R.; Takemitsu, M.; Scott, C. The Association Between Brace Compliance and Outcome for Patients with Idiopathic Scoliosis. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2005, 25, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, C.; Huang, Z.; Zou, Q.; Sui, W.; Deng, Y.; Yang, J. Coronal deformity angular ratio may serve as a valuable parameter to predict in-brace correction in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine J. 2019, 19, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Subject Demographics | 0-Day Control (n = 30) | 1-Day Intervention (n = 28) | 2-Day Intervention (n = 24) | 3-Day Intervention (n = 28) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (ANOVA) | |||||
| Age (years), Mean (SD) | 13.97 (2.03) | 14.14 (1.60) | 14.79 (2.65) | 14.71 (1.60) | 0.325 |
| Gender, n (%) | |||||
| Female | 20 (18.20%) | 23 (20.90%) | 17 (15.50%) | 23 (20.90%) | |
| Male | 10 (9.09%) | 5 (4.55%) | 7 (6.36%) | 5 (4.55%) | |
| Curve type, n (%) | |||||
| STC | 3 (2.73%) | 2 (1.82%) | 6 (5.45%) | 5 (4.55%) | |
| SL/TLC | 12 (10.91%) | 9 (8.18%) | 8 (7.27%) | 5 (4.55%) | |
| DC | 15 (13.64%) | 17 (15.45%) | 10 (9.09%) | 18 (16.36%) | |
| Risser Sign, Mean (SD) | 2.60 (1.16) | 2.71 (1.08) | 2.81 (1.17) | 2.79 (0.96) | 0.940 |
| Cobb angle, Mean (SD) | |||||
| T Cobb angle | 24.78 (7.22) | 25.89 (7.08) | 28.58 (9.16) | 29.36 (6.89) | 0.091 |
| L/TL Cobb angle | 25.52 (7.24) | 27.27 (7.95) | 28.39 (7.18) | 30.74 (7.32) | 0.104 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jie, Y.; Li, M.; Dong, A.; Luo, Y.-Y.; Luo, C.-L.; Li, J.; Zheng, P.; Zhang, X.; Wong, M.S.; Ma, C.Z.-H.; et al. Digitalized 3D Spinal Decompression and Correction Device Improved Initial Brace Corrections and Patients’ Comfort Among Adolescents with Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Single-Centre, Single-Blinded Randomized Controlled Trial. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11121246
Jie Y, Li M, Dong A, Luo Y-Y, Luo C-L, Li J, Zheng P, Zhang X, Wong MS, Ma CZ-H, et al. Digitalized 3D Spinal Decompression and Correction Device Improved Initial Brace Corrections and Patients’ Comfort Among Adolescents with Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Single-Centre, Single-Blinded Randomized Controlled Trial. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(12):1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11121246
Chicago/Turabian StyleJie, Yi, Mengyao Li, Anqin Dong, Yu-Yan Luo, Chang-Liang Luo, Jing Li, Pengyuan Zheng, Xinmin Zhang, Man Sang Wong, Christina Zong-Hao Ma, and et al. 2024. "Digitalized 3D Spinal Decompression and Correction Device Improved Initial Brace Corrections and Patients’ Comfort Among Adolescents with Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Single-Centre, Single-Blinded Randomized Controlled Trial" Bioengineering 11, no. 12: 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11121246
APA StyleJie, Y., Li, M., Dong, A., Luo, Y.-Y., Luo, C.-L., Li, J., Zheng, P., Zhang, X., Wong, M. S., Ma, C. Z.-H., & Zhang, M. (2024). Digitalized 3D Spinal Decompression and Correction Device Improved Initial Brace Corrections and Patients’ Comfort Among Adolescents with Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Single-Centre, Single-Blinded Randomized Controlled Trial. Bioengineering, 11(12), 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11121246









