Deciphering Membrane Proteins Through Deep Learning Models by Revealing Their Locale Within the Cell
Abstract
1. Introduction
- DL has been applied to the membrane proteins database of the MemLoci Approach.
- The indulgence of pseudo amino acid composition in the auto-retrieval feature selection of DL has been completed for MP in the study. This feature extraction technique constructs the hydrophobicity and hydrophilicity of MP, thus granting explicit local information.
- A comparison of RNN and LSTM has been proposed for membrane proteins excerpted from amino acid sequences, which is also a peculiar aspect of this research.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Feature Extraction
2.3. Experiments and Evaluation
2.3.1. Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) Architecture
2.3.2. LSTM Architecture
2.4. Layout of the Approach
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hung, M.-C.; Link, W. Protein localization in disease and therapy. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 3381–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liimatainen, K.; Huttunen, R.; Latonen, L.; Ruusuvuori, P. Convolutional neural network-based artificial intelligence for classification of protein localization patterns. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neupert, W.; Herrmann, J.M. Translocation of proteins into mitochondria. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2007, 76, 723–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickner, W.; Schekman, R. Protein translocation across biological membranes. Science 2005, 310, 1452–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnell, D.J.; Hebert, D.N. Protein translocons. Cell 2003, 112, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, L.; Knölker, H.-J.; Simons, K. Subcellular targeting strategies for drug design and Delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Sirkis, D.W.; Schekman, R. Protein sorting at the trans-golgi network. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 169–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niaraki, M.J. Membrane proteins: Structure, function and motion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, A.E. Membrane protein engineering to the rescue. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2018, 46, 1541–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierleoni, A.; Martelli, P.L.; Casadio, R. MEMLOCI: Predicting subcellular localiza-tion of membrane proteins in eukaryotes. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1224–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nor, A.; Mohamad, K.; Abu Bakar, A.; Zainudin, S. Classification of Human Membrane Protein Types Using Optimal Local Discriminant Bases Feature Extraction Method. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2018, 96, 767–771. [Google Scholar]
- Rey, S.; Gardy, J.L.; Brinkman, F.S. Assessing the Precision of High-Throughput Computational and Laboratory Approaches for the Genome-Wide Identification of Protein Subcellular Localization in Bacteria. BMC Genom. 2005, 6, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faiz, M.; Khan, S.J.; Azim, F.; Ejaz, N. Disclosing the locale of transmembrane proteins within cellular alcove by Machine Learning Approach: Systematic Review and Meta Analysis. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Ding, Y.; Tang, J.; Zou, Q.; Guo, F. Critical evaluation of web-based prediction tools for human protein subcellular localization. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 21, 1628–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Sønderby, C.K.; Sønderby, S.K.; Nielsen, H.; Winther, O. DeepLoc: Prediction of protein subcellular localization using Deep Learning. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3387–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Wong, K.C.; Li, X. iDeepSubMito: Identification of Protein Submitochondrial Localization with Deep Learning. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbab288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savojardo, C.; Bruciaferri, N.; Tartari, G.; Martelli, P.L.; Casadio, R. DeepMito: Accurate prediction of protein sub-mitochondrial localization using convolutional neural networks. Bioinformatics 2019, 36, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thumuluri, V.; Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Johansen, A.R.; Nielsen, H.; Winther, O. DeepLoc 2.0: Multi-Label Subcellular Localization Prediction Using Protein Language Models. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W228–W234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Pan, G.; Sun, C.; Tang, J. Predicting Subcellular Location of Protein with Evolution Information and Sequence-Based Deep Learning. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22 (Suppl. S10), 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillani, M.; Pollastri, G. Protein Subcellular Localization Prediction Tools. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2024, 23, 1796–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleel, M.; Ellinger, L.; Lalor, C.; Pollastri, G.; Mooney, C. sclpred-mem: Subcellular localization prediction of membrane proteins by deep n-to-1 Convolutional Neural Networks. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2021, 89, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamm, L.; Righetto, R.D.; Wietrzynski, W.; Pöge, M.; Martinez-Sanchez, A.; Peng, T.; Engel, B.D. MemBrain: A deep learning-aided pipeline for detection of membrane proteins in cryo-electron tomograms. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 224, 106990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Lu, L.; Cai, Y.D. Predicting Protein Subcellular Location with Network Embedding and Enrichment Features. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Proteins Proteom. 2020, 1868, 140477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.M.; Taju, S.W.; Dlamini, B.B.; Ou, Y.-Y. Deepsirt: A deep neural network for identification of sirtuin targets and their subcellular localizations. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2021, 93, 107514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.-B.; Chou, K.-C. PseAAC: A flexible web-server for generating various kinds of protein pseudo amino acid composition. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 373, 386–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jin, S.; Gao, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Zhou, W.; Yu, B. Predicting the multi-label protein subcellular localization through multi-information fusion and MLSI dimensionality reduction based on MLFE classifier. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Authors | Database | Deep Learning Algorithm | Performance Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Almagro Armenteros et al. [15] | UniProt database | RNN | 92% (membrane-protein) |
| Hou et al. [16] | SM424-18 dataset | CNN | Not reported |
| Savojardo et al. [17] | SM424-18 dataset | CNN | Not reported |
| Thumuluri et al. [18] | UniProt database release 2021_03, Human Protein Atlas | protein transformer language model | Not reported |
| Liao et al. [19] | D3106, D4802 | BLSTM | Not reported |
| Kaleel et al. [21] | UniProtKB release 2019_05 | Ensemble of Deep N-to-1 Convolution Neural Network | 81.25% |
| Lamm et al. [22] | cryo-electron tomograms | Convolution Neural Network | Not reported |
| Pan et al. [23] | SwissProt | RNN | 86.9 |
| Shah et al. [24] | NCBI protein database | 1D-CNN | In the range of 93.24–97.30%, for SIRT1 to SIRT7 |
| RNN | LSTM | |
|---|---|---|
| DL Model Layers | 3 | 3 |
| No. of Dense Layers | 2 | 3 |
| No. of Dropout Layers | 4 | 5 |
| Loss Function | Cross-Entropy | Cross-Entropy |
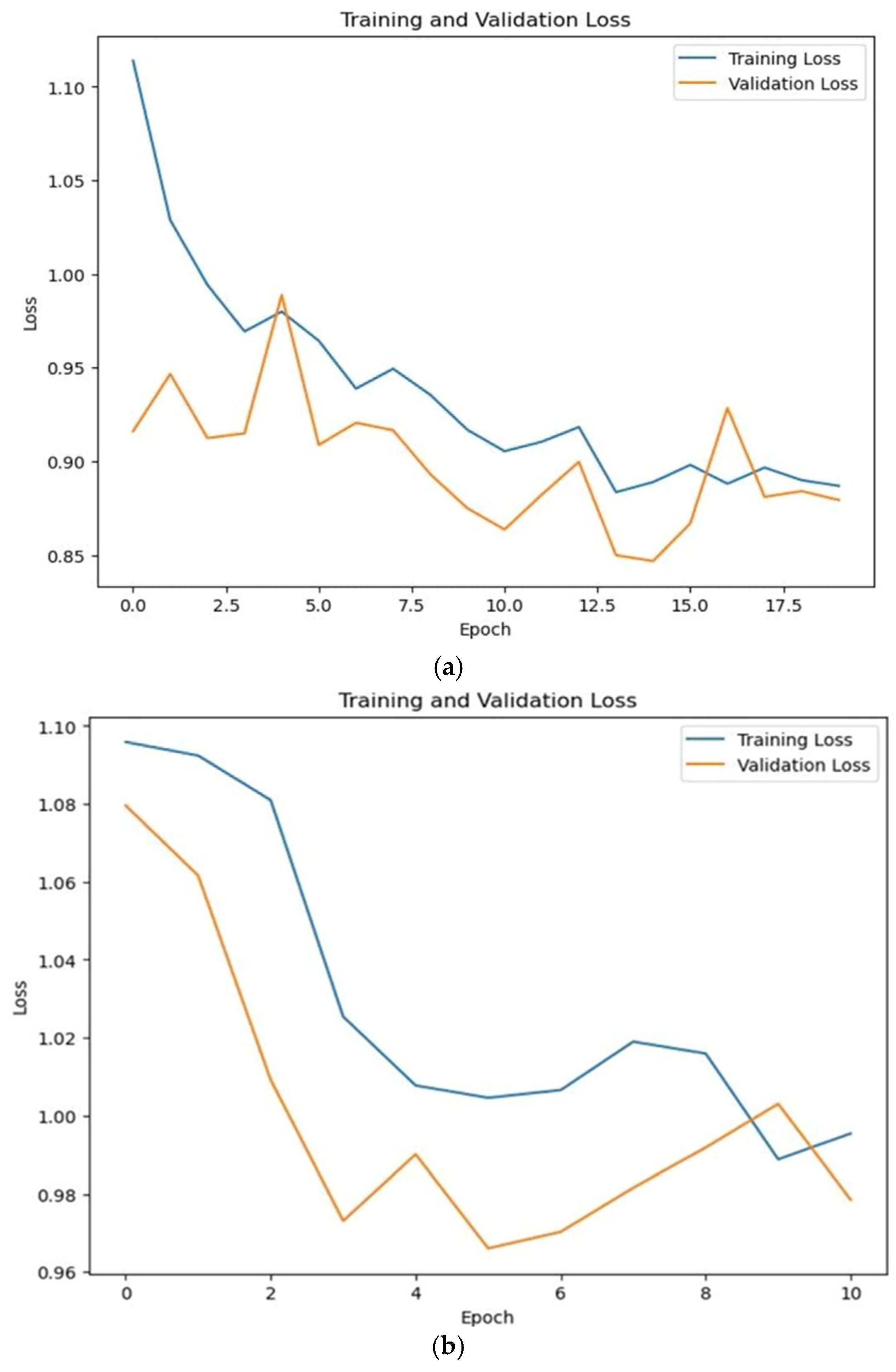
| Training Loss | 0.56 | 0.70 |
| Validation Loss | 0.60 | 0.66 |
| Testing Loss | 0.66 | 0.76 |
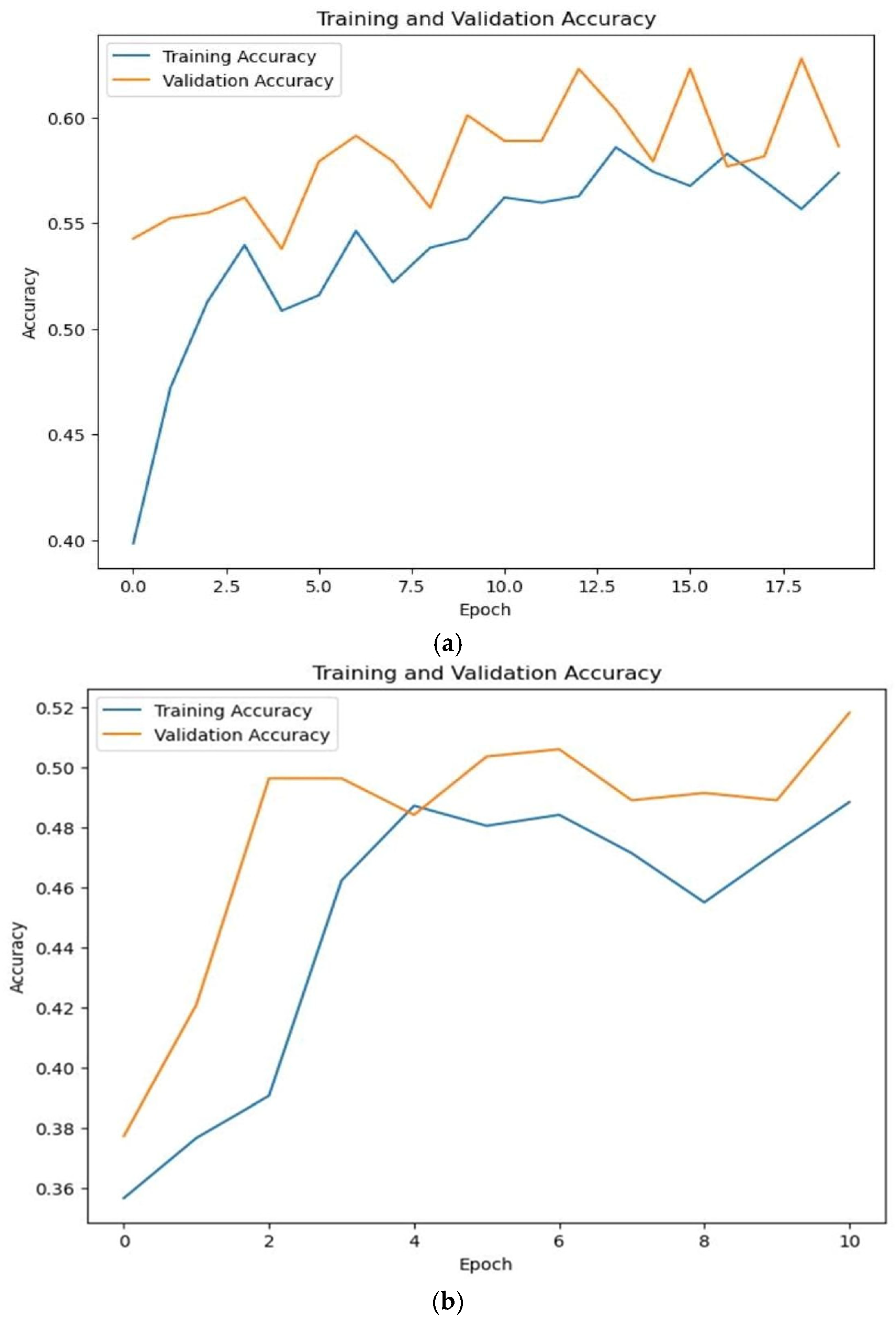
| Training Accuracy | 0.841 | 0.81 |
| Validation Accuracy | 0.852 | 0.800 |
| Testing Accuracy | 0.832 | 0.80 |
| Implemented Models | Accuracy |
|---|---|
| LSTM | 83.4% |
| RNN | 80.5% |
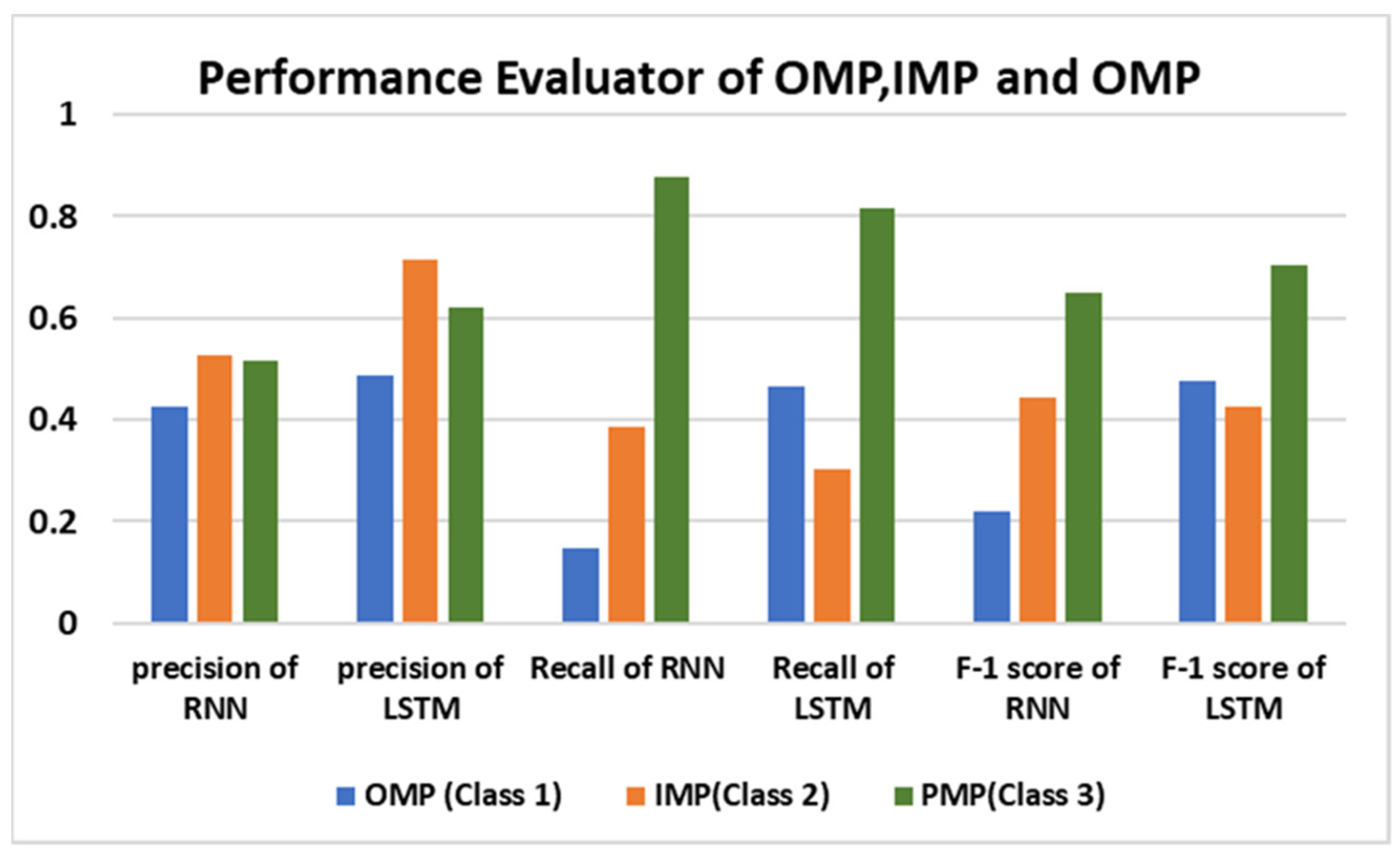
| Precision (%) | NPV (%) | FPR (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Accuracy (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | 71.4 | 84.5 | 3 | 30.12 | 96.9 | 83.4 |
| RNN | 52.4 | 85.4 | 8.8 | 38.5 | 91.1 | 80.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faiz, M.; Khan, S.J.; Azim, F.; Ejaz, N.; Shamim, F. Deciphering Membrane Proteins Through Deep Learning Models by Revealing Their Locale Within the Cell. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11111150
Faiz M, Khan SJ, Azim F, Ejaz N, Shamim F. Deciphering Membrane Proteins Through Deep Learning Models by Revealing Their Locale Within the Cell. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(11):1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11111150
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaiz, Mehwish, Saad Jawaid Khan, Fahad Azim, Nazia Ejaz, and Fahad Shamim. 2024. "Deciphering Membrane Proteins Through Deep Learning Models by Revealing Their Locale Within the Cell" Bioengineering 11, no. 11: 1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11111150
APA StyleFaiz, M., Khan, S. J., Azim, F., Ejaz, N., & Shamim, F. (2024). Deciphering Membrane Proteins Through Deep Learning Models by Revealing Their Locale Within the Cell. Bioengineering, 11(11), 1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11111150








