Safety and Effectiveness of Triple-Antenna Hepatic Microwave Ablation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Theoretical Background
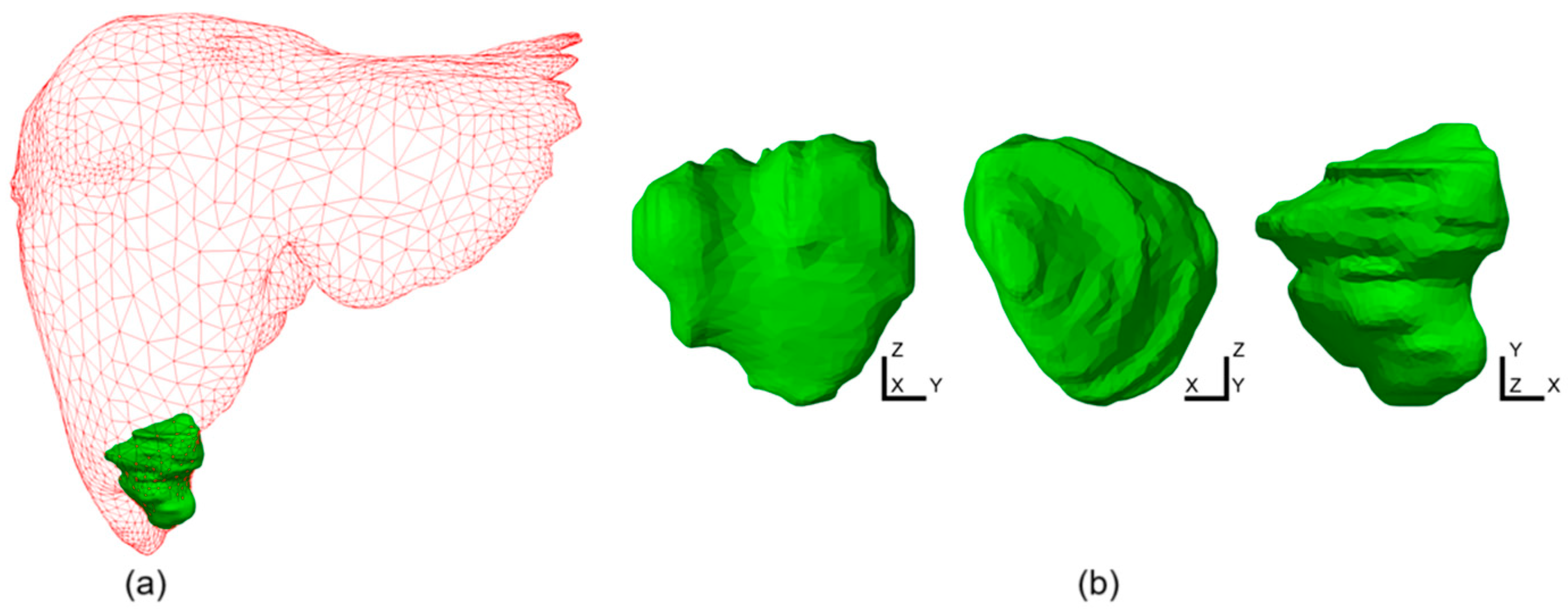
2.2. Simulation Conditions
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ong, S.L.; Gravante, G.; Metcalfe, M.S.; Strickland, A.D.; Dennison, A.R.; Lloyd, D.M. Efficacy and safety of microwave ablation for primary and secondary liver malignancies: A systematic review. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 21, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brace, C.L. Microwave ablation technology: What every user should know. Curr. Probl. Diagn. Radiol. 2009, 38, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzo, F.; Granata, V.; Grassi, R.; Fusco, R.; Palaia, R.; Delrio, P.; Carrafiello, G.; Azoulay, D.; Petrillo, A.; Curley, S.A. Radiofrequency Ablation and Microwave Ablation in Liver Tumors: An Update. Oncologist 2019, 24, e990–e1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobascio, F.; Di Modugno, R.; Fiore, M.; Di Modugno, N.; Bruno, C.; De Nicolo, T.; Barberis, R.V.; Cabiale, K.; Radoiu, M. Microwave and Radiofrequency Ablation: A Comparative Study between Technologies in Ex Vivo Tissues. Drugs Drug Candidates 2024, 3, 550–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.J.; Zhu, X.D.; Zhou, L.M.; Zhang, L.L.; Liu, N.N.; Chen, M.; Wang, J.Y.; Hu, S.J. Short-term efficacy of microwave ablation in the treatment of liver cancer and its effect on immune function. World J. Clin. Cases 2024, 12, 3395–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogl, T.J.; Nour-Eldin, N.A.A.; Hammerstingl, R.M.; Panahi, B.; Naguib, N.N.N. Microwave Ablation (MWA): Basics, Technique and Results in Primary and Metastatic Liver Neoplasms—Review Article. Fortschr. Röntgenstr. 2017, 89, 1055–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachetta, A.; Cheung, S.; Moore, E.R.; Nguyen, D.; Kiely, M.J.; Whiteley, M.S. Defining the Parameters for Endovenous Microwave Ablation to Achieve Equivalence with Endovenous Laser Ablation, Using the Porcine Liver Model. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2024, 58, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, A.S.; Asran, M.; Fotiadis, D.I. Optimal Power for Microwave Slotted Probes in Ablating Different Hepatocellular Carcinoma Sizes. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 127, 104101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, T.; Brace, C.L.; Hinshaw, J.L.; Quek, L.H.H.; Huang, I.K.H.; Kwan, J.; Lim, G.H.T.; Lee, F.T., Jr.; Pua, U. Microwave ablation of the liver in a live porcine model: The impact of power, time and total energy on ablation zone size and shape. Int. J. Hyperth. 2020, 37, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzato, R.L.; De Marini, P.; Leclerc, L.; Dalili, D.; Koch, G.; Rao, P.; Auloge, P.; Garnon, J.; Gangi, A. Large nearly spherical ablation zones are achieved with simultaneous multi-antenna microwave ablation applied to treat liver tumours. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 971–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnon, J.; Delmas, L.; De Marini, P.; Leclerc, L.; Dalili, D.; Koch, G.; Auloge, P.; Cazzato, R.L.; Gangi, A. Triple-Antenna Microwave Ablation with Repositioning for the Creation of a Reliable 6-cm Ablation Zone in the Liver. Cardiovasc. Intervent Radiol. 2021, 44, 1291–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keangin, P.; Rattanadecho, P.; Wessapan, T. An analysis of heat transfer in liver tissue during microwave ablation using single and double slot antenna. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 38, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wu, M.; Qian, Y. Efficacy and safety of single- and multiple-antenna microwave ablation for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma and liver metastases: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Medicine 2022, 101, e32304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andresciani, F.; Pacella, G.; Vertulli, D.; Altomare, C.; Bitonti, M.T.; Bruno, A.; Cea, L.; Faiella, E.; Beomonte Zobel, B.; Grasso, R.F. Microwave ablation using two simultaneous antennas for thetreatment of liver malignant lesions: A 3 year single-Centre experience. Int. J. Hyperth. 2023, 40, 2163309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.Q.; Huang, S.M.; Gu, Y.K.; Jiang, X.Y.; Huang, Z.M.; Deng, H.X.; Huang, J.H. Sequential and Simultaneous 4-Antenna Microwave Ablation in an Ex Vivo Bovine Liver Model. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 42, 1466–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, A.S.; Lee, F.T., Jr.; Mahvi, D.M. Hepatic microwave ablation with multiple antennae results in synergistically larger zones of coagulation necrosis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2003, 10, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahi, H.; Prakash, P. Antenna designs for microwave tissue ablation. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 46, 495–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, L.; Moser, M.A.J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, B. A review of antenna designs for percutaneous microwave ablation. Phys. Med. 2021, 84, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Jiang, H.; Huang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhi, D.; Zhao, G.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Qiu, B. A multi-slot coaxial microwave antenna for liver tumor ablation. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 175011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjenović, B.; Sabo, M.; Šoltes, L.; Prnova, M.; Čičak, P.; Radmilović-Radjenović, M. On Efficacy of Microwave Ablation in the Thermal Treatment of an Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harari, C.M.; Magagna, M.; Bedoya, M.; Lee, F.T., Jr.; Lubner, M.G.; Hinshaw, J.L.; Ziemlewicz, T.; Brace, C.L. Microwave Ablation: Comparison of Simultaneous and Sequential Activation of Multiple Antennas in Liver Model Systems. Radiology 2016, 278, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selmi, M.; Bin Dukhyil, A.A.; Belmabrouk, H. Numerical Analysis of Human Cancer Therapy Using Microwave Ablation. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, M.H.H.; Soltani, M.; Kashkooli, F.M.; Raahemifar, K. Use of microwave ablation for thermal treatment of solid tumors with different shapes and sizes—A computational approach. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, S.; Gao, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, S. Computer Simulations of Dual-Antenna Microwave Ablation and Comparison to Experimental Measurements. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafarchio, A.; Iasiello, M.; Brunese, M.C.; Francica, G.; Rocca, A.; Andreozzi, A. Emprint Microwave Thermoablation System: Bridging Thermal Ablation Efficacy between Human Patients and Porcine Models through Mathematical Correlation. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bošković, N.; Radmilović-Radjenović, M.; Radjenović, B. Finite Element Analysis of Microwave Tumor Ablation Based on Open-Source Software Components. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bošković, N.; Radjenović, B.; Nikolić, S.; Radmilović-Radjenović, M. Effectiveness of microwave ablation using two simultaneous antennas for liver malignancy treatment. Open Phys. 2024, 22, 20240079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, I. Finite Element Analysis of Hepatic Radiofrequency Ablation Probes using Temperature-Dependent Electrical Conductivity. Biomed. Eng. OnLine 2003, 2, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phasukkit, P.; Tungjitkusolmun, S.; Sangworasil, M. Finite element analysis and in vitro experiments of placement configurations using triple antennas in microwave hepatic ablation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 56, 2564–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangadhara, B.; Mariappan, P. A vector finite element approach to temperature dependent parameters of microwave ablation for liver cancer. Int. J. Numer. Method. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 39, e3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, L.; Hostettler, A.; Agnus, V.; Charnoz, A.; Fasquel, J.B.; Moreau, J.; Osswald, A.-B.; Bouhadjar, M.; Marescaux, J. 3D image reconstruction for comparison of algorithm database: A patient-specific anatomical and medical image database. IRCAD, Strasbourg, France. Tech. Rep. 2010, 1, 1. Available online: https://www.ircad.fr/research/data-sets/liver-segmentation-3d-ircadb-01/ (accessed on 15 September 2024).
- Rossmann, C.; Haemmerich, D. Review of temperature dependence of thermal properties, dielectric properties, and perfusion of biological tissues at hyperthermic and ablation temperatures. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 42, 467–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Rourke, A.P.; Lazebnik, M.; Bertram, J.M.; Converse, M.C.; Hagness, S.C.; Webster, J.G.; Mahvi, D.M. Dielectric properties of human normal, malignant and cirrhotic liver tissue: In vivo and ex vivo measurements from 0.5 to 20 GHz using a precision open-ended coaxial probe. Phys. Med. Biol. 2007, 52, 4707–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.; Brace, C.L. Expanded modeling of temperature-dependent dielectric properties for microwave thermal ablation. Phys. Med. Biol. 2011, 56, 5249–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radmilović-Radjenović, M.; Bošković, N.; Radjenović, B. Computational modeling of microwave tumor ablation. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennes, H.H. Analysis of tissue and arterial blood temperatures in the resting human forearm. J. Appl. Physiol. 1998, 85, 5–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diller, K.R.; Pearce, J.A. Issues in modeling thermal alterations in tissues. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1999, 888, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Moser, M.A.; Zhang, E.M.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W. Study of the relationship between the target tissue necrosis volume and the target tissue size in liver tumours using two-compartment finite element RFA modelling. Int. J. Hyperth. 2014, 30, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuchehrabadi, N.; Zhu, L. Development of a computational simulation tool to design a protocol for treating prostate tumours using transurethral laser photothermal therapy. Int. J. Hyperth. 2014, 30, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliqab, K.; Nadeem, I.; Khan, S.R. A Comprehensive Review of In-Body Biomedical Antennas: Design, Challenges and Applications. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Configuration | VD | DT |
|---|---|---|
| Single antenna (40 W) | 452.3% | 3.4% |
| Two antennas (15 mm separation and 20 W per probe) | 213.1% | 1.6% |
| Three antennas (15 mm separation and 15 W per probe) | 194.6% | 1.4% |
| Three antennas (10 mm separation and 15 W per probe) | 161.6% | 1.2% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bošković, N.; Nikolić, S.; Radjenović, B.; Radmilović-Radjenović, M. Safety and Effectiveness of Triple-Antenna Hepatic Microwave Ablation. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11111133
Bošković N, Nikolić S, Radjenović B, Radmilović-Radjenović M. Safety and Effectiveness of Triple-Antenna Hepatic Microwave Ablation. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(11):1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11111133
Chicago/Turabian StyleBošković, Nikola, Srdjan Nikolić, Branislav Radjenović, and Marija Radmilović-Radjenović. 2024. "Safety and Effectiveness of Triple-Antenna Hepatic Microwave Ablation" Bioengineering 11, no. 11: 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11111133
APA StyleBošković, N., Nikolić, S., Radjenović, B., & Radmilović-Radjenović, M. (2024). Safety and Effectiveness of Triple-Antenna Hepatic Microwave Ablation. Bioengineering, 11(11), 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11111133






