Applying a Deep Learning Model for Total Kidney Volume Measurement in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Data Collection and Specifications
- Patients with polycystic kidney disease who are at least 20 years old;
- High-quality MRI images as determined by a radiologist.
2.2. Data Pre-Processing
2.3. Data Augmentation
2.4. Data Labeling and Management
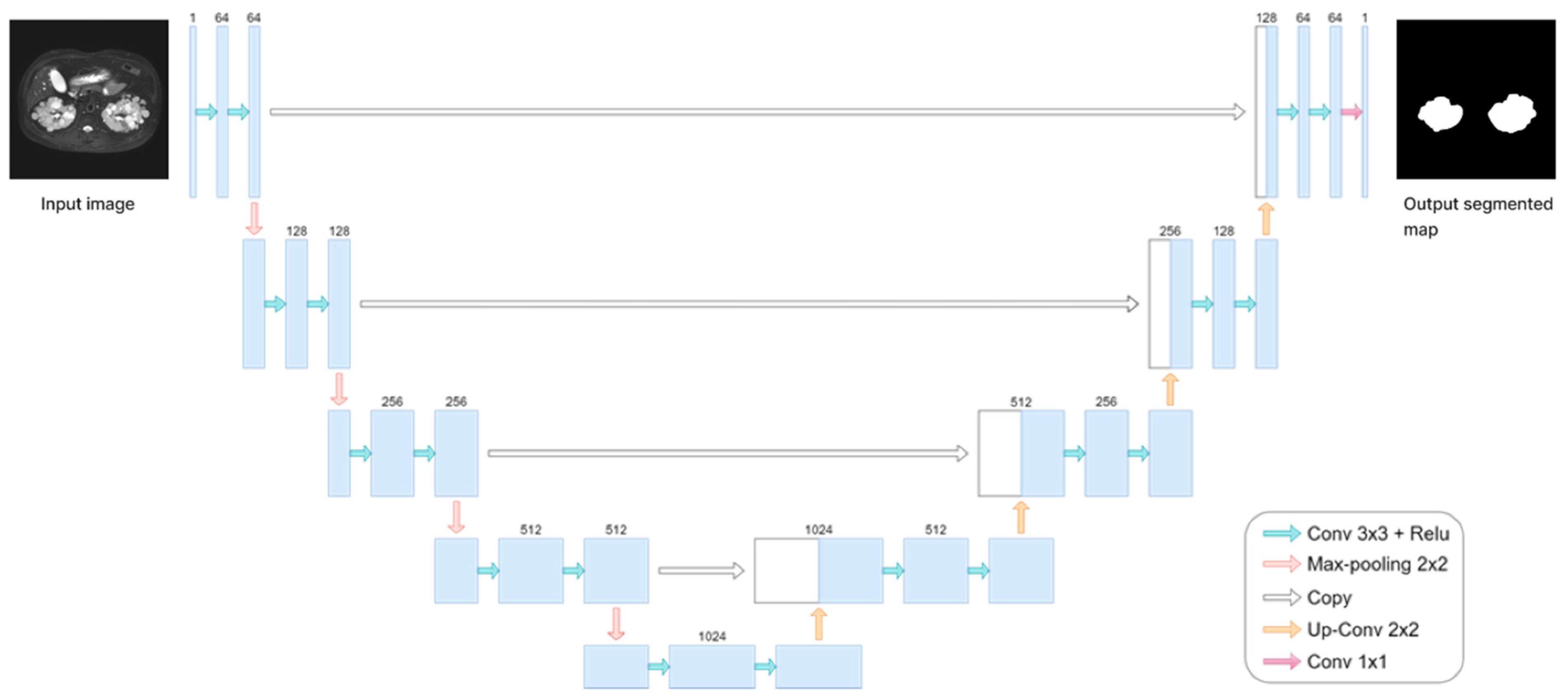
2.5. Deep Learning Model
U-Net
2.6. Loss Function
2.7. Optimizer
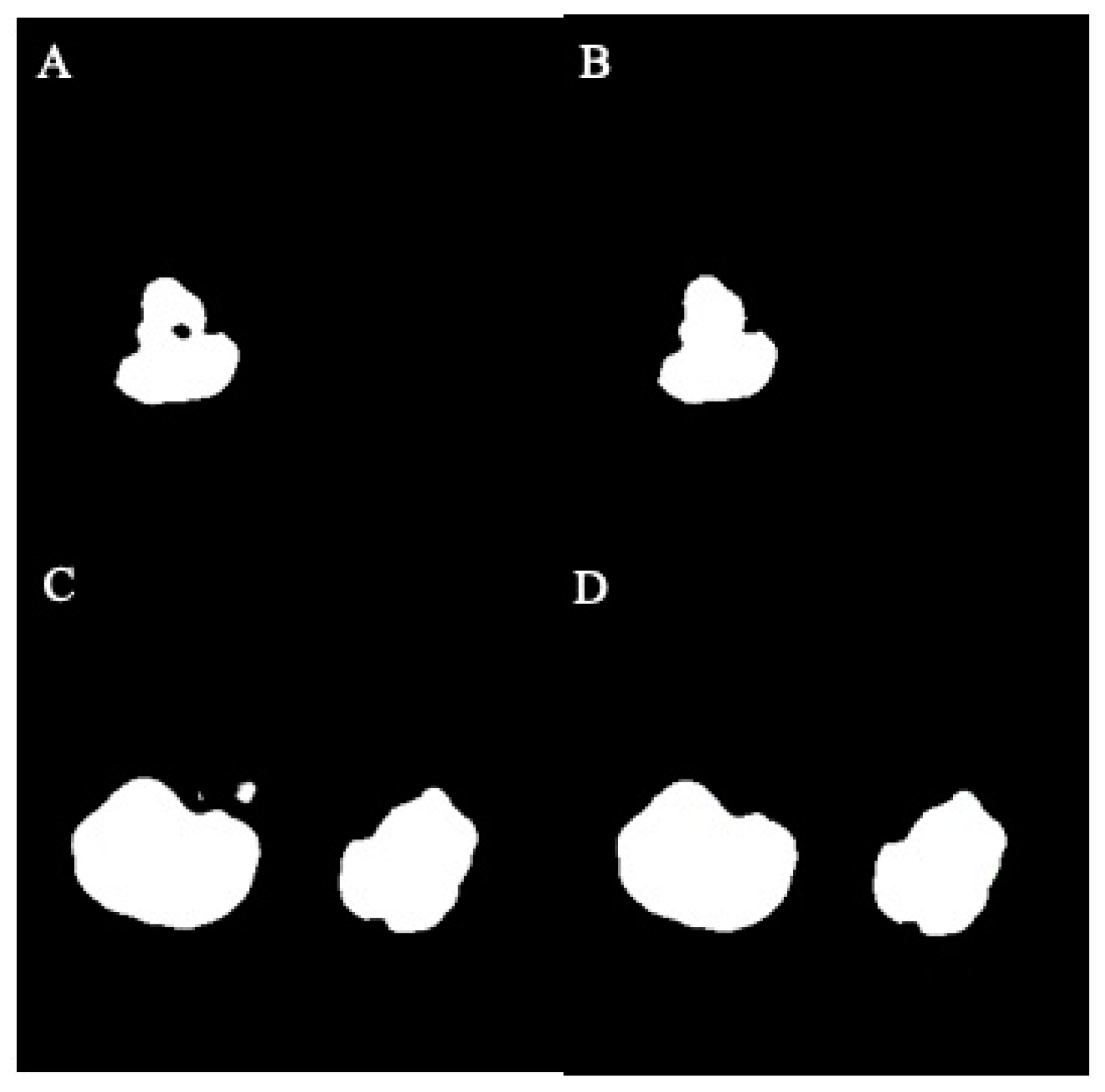
2.8. Data Post-Processing: Inpainting and Volume Calculation
2.9. Experiment Environment
2.10. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Images Collection
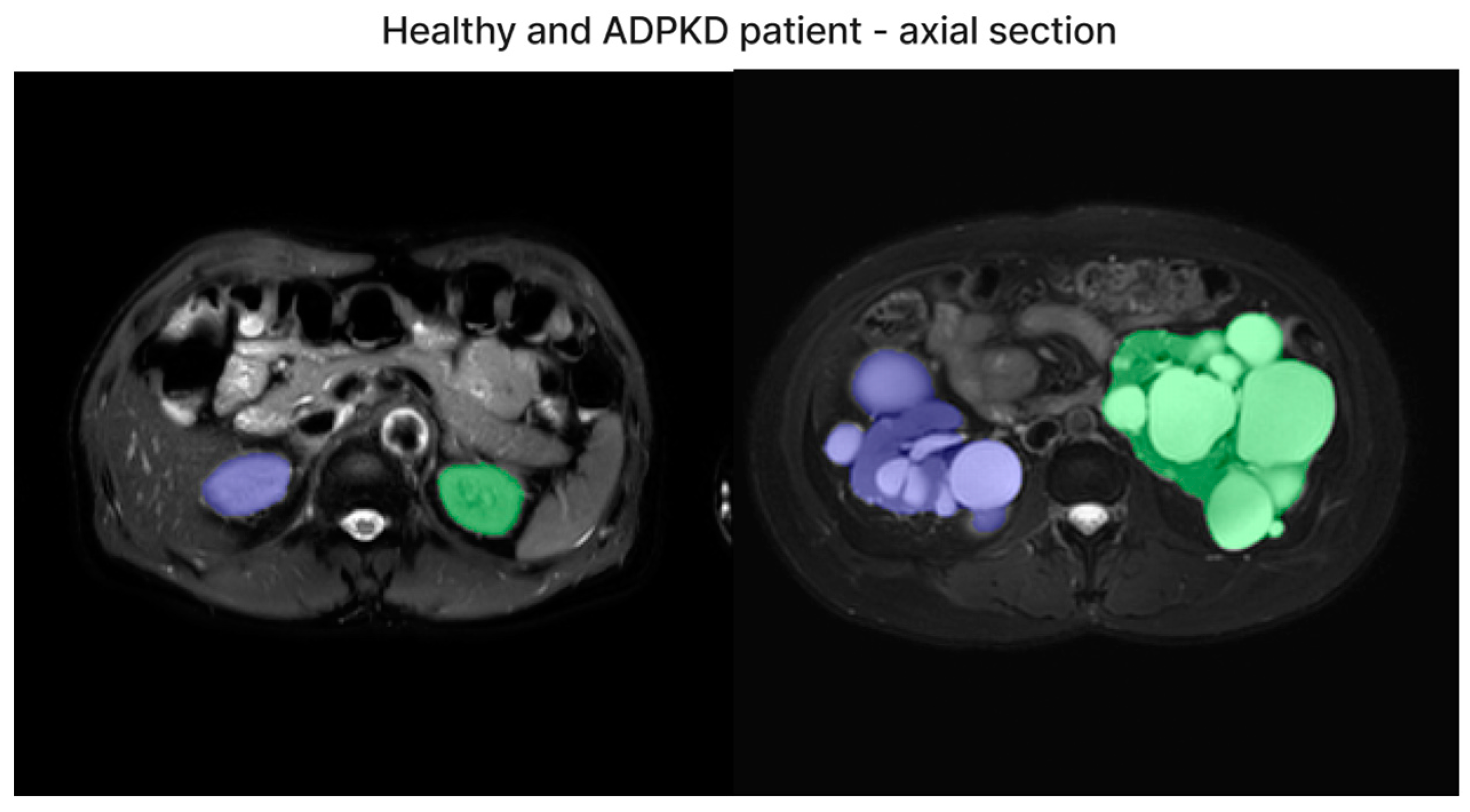
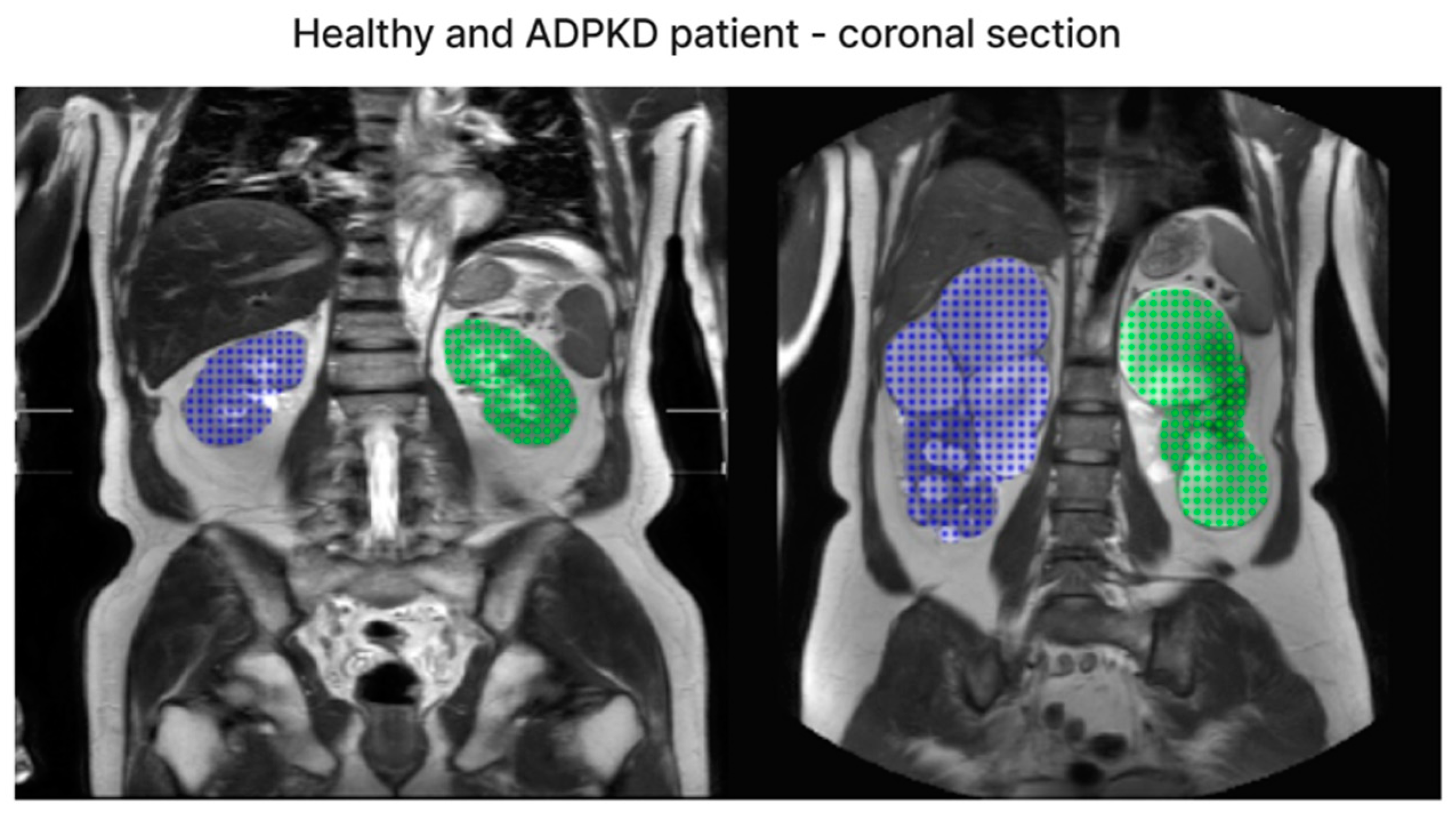
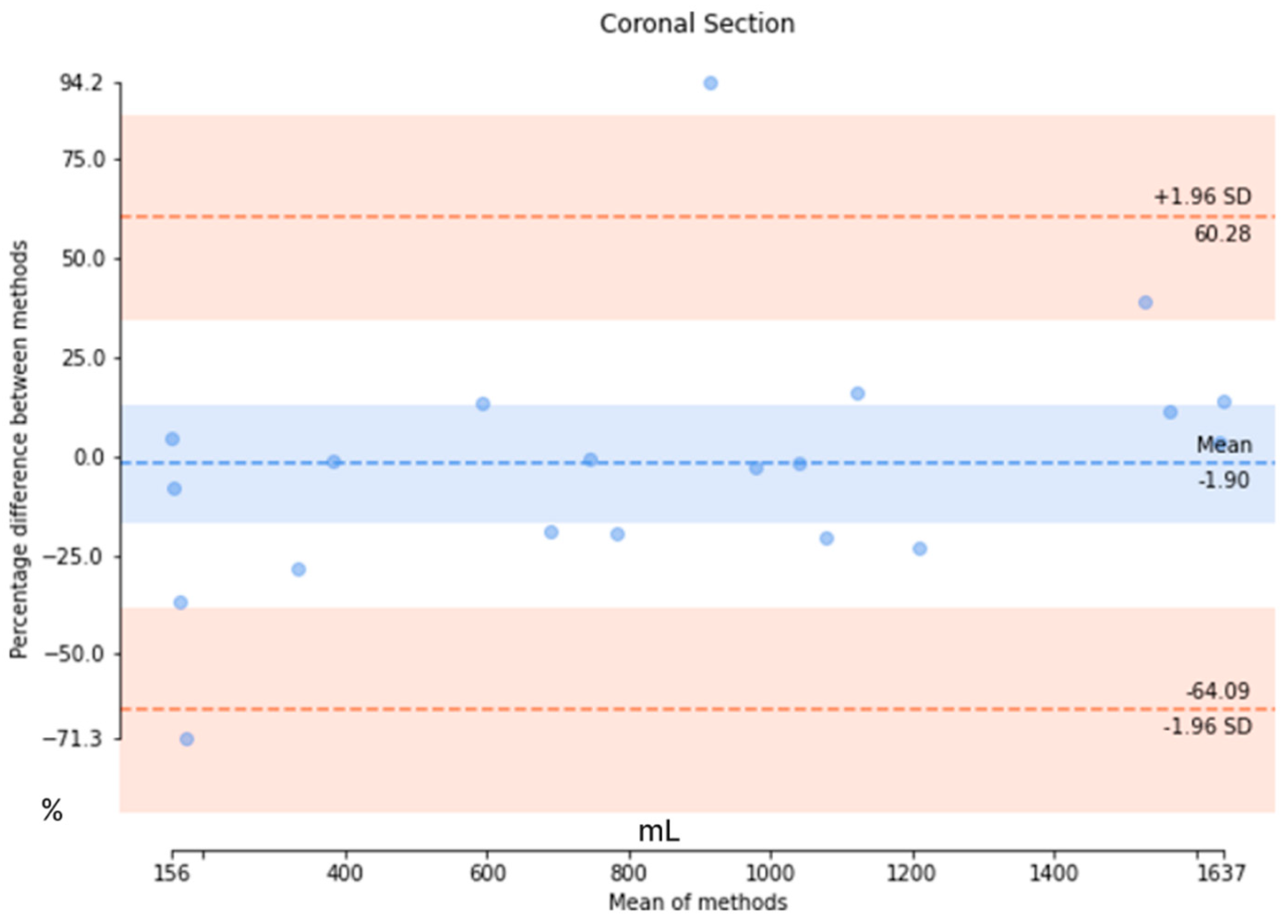
3.2. Validation and Results Comparison
3.3. Accuracy of Segmentation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iglesias, C.G.; Torres, V.E.; Offord, K.P.; Holley, K.E.; Beard, C.M.; Kurland, L.T. Epidemiology of adult polycystic kidney disease, olmsted county, minnesota: 1935–1980. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 1983, 2, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, C.; Guay-Woodford, L.M.; Harris, P.C.; Horie, S.; Peters, D.J.M.; Torres, V.E. Polycystic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solazzo, A.; Testa, F.; Giovanella, S.; Busutti, M.; Furci, L.; Carrera, P.; Ferrari, M.; Ligabue, G.; Mori, G.; Leonelli, M.; et al. The prevalence of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (adpkd): A meta-analysis of european literature and prevalence evaluation in the italian province of modena suggest that adpkd is a rare and underdiagnosed condition. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grantham, J.J.; Chapman, A.B.; Torres, V.E. Volume progression in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: The major factor determining clinical outcomes. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2006, 1, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grantham, J.J. Clinical practice. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1477–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, V.E.; Chapman, A.B.; Devuyst, O.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Perrone, R.D.; Koch, G.; Ouyang, J.; McQuade, R.D.; Blais, J.D.; Czerwiec, F.S.; et al. Tolvaptan in later-stage autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1930–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, V.E.; Chapman, A.B.; Devuyst, O.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Grantham, J.J.; Higashihara, E.; Perrone, R.D.; Krasa, H.B.; Ouyang, J.; Czerwiec, F.S.; et al. Tolvaptan in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 2407–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick-Brosnahan, G.M.; Belz, M.M.; McFann, K.K.; Johnson, A.M.; Schrier, R.W. Relationship between renal volume growth and renal function in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: A longitudinal study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2002, 39, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magistroni, R.; Corsi, C.; Marti, T.; Torra, R. A review of the imaging techniques for measuring kidney and cyst volume in establishing autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease progression. Am. J. Nephrol. 2018, 48, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, V.E.; King, B.F.; Chapman, A.B.; Brummer, M.E.; Bae, K.T.; Glockner, J.F.; Arya, K.; Risk, D.; Felmlee, J.P.; Grantham, J.J.; et al. Magnetic resonance measurements of renal blood flow and disease progression in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2007, 2, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grantham, J.J. Crisp: Opening a new frontier in the diagnosis and treatment of pkd. Nephrol. News Issues 2006, 20, 29–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kistler, A.D.; Poster, D.; Krauer, F.; Weishaupt, D.; Raina, S.; Senn, O.; Binet, I.; Spanaus, K.; Wuthrich, R.P.; Serra, A.L. Increases in kidney volume in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease can be detected within 6 months. Kidney Int. 2009, 75, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bae, K.T.; Commean, P.K.; Lee, J. Volumetric measurement of renal cysts and parenchyma using mri: Phantoms and patients with polycystic kidney disease. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2000, 24, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, K.T.; Tao, C.; Wang, J.; Kaya, D.; Wu, Z.; Bae, J.T.; Chapman, A.B.; Torres, V.E.; Grantham, J.J.; Mrug, M.; et al. Novel approach to estimate kidney and cyst volumes using mid-slice magnetic resonance images in polycystic kidney disease. Am. J. Nephrol. 2013, 38, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashihara, E.; Nutahara, K.; Okegawa, T.; Tanbo, M.; Hara, H.; Miyazaki, I.; Kobayasi, K.; Nitatori, T. Kidney volume estimations with ellipsoid equations by magnetic resonance imaging in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Nephron 2015, 129, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demoulin, N.; Nicola, V.; Michoux, N.; Gillion, V.; Ho, T.A.; Clerckx, C.; Pirson, Y.; Annet, L. Limited performance of estimated total kidney volume for follow-up of adpkd. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 2821–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turco, D.; Severi, S.; Mignani, R.; Aiello, V.; Magistroni, R.; Corsi, C. Reliability of total renal volume computation in polycystic kidney disease from magnetic resonance imaging. Acad. Radiol. 2015, 22, 1376–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, K.; Park, B.; Sun, H.; Wang, J.; Tao, C.; Chapman, A.B.; Torres, V.E.; Grantham, J.J.; Mrug, M.; Bennett, W.M.; et al. Segmentation of individual renal cysts from mr images in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2013, 8, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Ge, Y.; Tao, C.; Zhu, J.; Chapman, A.B.; Torres, V.E.; Yu, A.S.; Mrug, M.; Bennett, W.M.; Flessner, M.F.; et al. Automated segmentation of kidneys from mr images in patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2016, 11, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, T.L.; Edwards, M.E.; Korfiatis, P.; Akkus, Z.; Torres, V.E.; Erickson, B.J. Semiautomated segmentation of polycystic kidneys in t2-weighted mr images. AJR. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2016, 207, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignani, R.; Corsi, C.; De Marco, M.; Caiani, E.G.; Santucci, G.; Cavagna, E.; Severi, S.; Cagnoli, L. Assessment of kidney volume in polycystic kidney disease using magnetic resonance imaging without contrast medium. Am. J. Nephrol. 2011, 33, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Isla, C.; Campello, V.M.; Izquierdo, C.; Raisi-Estabragh, Z.; Baessler, B.; Petersen, S.E.; Lekadir, K. Image-based cardiac diagnosis with machine learning: A review. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montazeri, M.; ZahediNasab, R.; Farahani, A.; Mohseni, H.; Ghasemian, F. Machine learning models for image-based diagnosis and prognosis of COVID-19: Systematic review. JMIR Med. Inf. 2021, 9, e25181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seuss, H.; Janka, R.; Prummer, M.; Cavallaro, A.; Hammon, R.; Theis, R.; Sandmair, M.; Amann, K.; Bauerle, T.; Uder, M.; et al. Development and evaluation of a semi-automated segmentation tool and a modified ellipsoid formula for volumetric analysis of the kidney in non-contrast t2-weighted mr images. J. Digit. Imaging 2017, 30, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simms, R.J.; Doshi, T.; Metherall, P.; Ryan, D.; Wright, P.; Gruel, N.; van Gastel, M.D.A.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Tindale, W.; Ong, A.C.M. A rapid high-performance semi-automated tool to measure total kidney volume from mri in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 4188–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazgir, O.; Barck, K.; Carano, R.A.; Weimer, R.M.; Xie, L. Kidney segmentation using 3d u-net localized with expectation maximization. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Southwest Symposium on Image Analysis and Interpretation (SSIAI), Albuquerque, NM, USA, 29–31 March 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, A.J.; Buchanan, C.E.; Allcock, T.; Scerri, D.; Cox, E.F.; Prestwich, B.L.; Francis, S.T. Automated renal segmentation in healthy and chronic kidney disease subjects using a convolutional neural network. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021, 86, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Rupprecht, C.; Caroli, A.; Aparicio, M.C.; Remuzzi, A.; Baust, M.; Navab, N. Automatic segmentation of kidneys using deep learning for total kidney volume quantification in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilacqua, V.; Brunetti, A.; Cascarano, G.D.; Palmieri, F.; Guerriero, A.; Moschetta, M. A deep learning approach for the automatic detection and segmentation in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease based on magnetic resonance images. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Computing Theories and Application: 14th International Conference, ICIC 2018, Wuhan, China, 15–18 August 2018; Proceedings, Part II 14. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 643–649. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III 18. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1026–1034. [Google Scholar]
- Jagtap, J.M.; Gregory, A.V.; Homes, H.L.; Wright, D.E.; Edwards, M.E.; Akkus, Z.; Erickson, B.J.; Kline, T.L. Automated measurement of total kidney volume from 3d ultrasound images of patients affected by polycystic kidney disease and comparison to mr measurements. Abdom. Radiol. 2022, 47, 2408–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, A.; Tollens, F.; Hansen, L.; Golla, A.K.; Schad, L.R.; Norenberg, D.; Zollner, F.G. Deep learning-based total kidney volume segmentation in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease using attention, cosine loss, and sharpness aware minimization. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.; Thomas, R.; Metherall, P.; Ong, A.; Simms, R. Mo012: Development of an accurate automated segmentation algorithm to measure total kidney volume in adpkd suitable for clinical application (the cystvas study). Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2022, 37, gfac061-007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, A.; Shih, G.; Riyahi, S.; Jeph, S.; Dev, H.; Hu, R.; Romano, D.; Teichman, K.; Blumenfeld, J.D.; Barash, I.; et al. Deployed deep learning kidney segmentation for polycystic kidney disease mri. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2022, 4, e210205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kline, T.L.; Korfiatis, P.; Edwards, M.E.; Blais, J.D.; Czerwiec, F.S.; Harris, P.C.; King, B.F.; Torres, V.E.; Erickson, B.J. Performance of an artificial multi-observer deep neural network for fully automated segmentation of polycystic kidneys. J. Digit. Imaging 2017, 30, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Gastel, M.D.A.; Edwards, M.E.; Torres, V.E.; Erickson, B.J.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Kline, T.L. Automatic measurement of kidney and liver volumes from mr images of patients affected by autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2019, 30, 1514–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milletari, F.; Navab, N.; Ahmadi, S.-A. V-net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Stanford, CA, USA, 25–28 October 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 565–571. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Gupta, R.K.; Sharma, A. Review and potential for artificial intelligence in healthcare. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 2022, 13, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, C.-H.; Tsai, M.-C.; Lin, F.Y.-S.; Lin, P.-C.; Yang, F.-J.; Yang, S.-Y.; Wang, S.-Y.; Liu, P.-R.; Huang, Y. Automatic kidney volume estimation system using transfer learning techniques. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications, Toronto, ON, Canada, 12–14 May 2021; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 370–381. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, K. Consortium for Radiologic Imaging Studies of Polycystic Kidney Disease (V9) [Dataset]. NIDDK Cent. Repos. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Dataset | ADPKD (n) | Non-ADPKD (n) | Total (n) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Training set | 21 | 9 | 30 |
| Testing set | 9 | 1 | 10 |
| Total (n) | 30 | 10 |
| Participant (n) | Axial-Section Images (n) | Coronal-Section Images (n) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ADPKD | 30 | 1572 | 1265 |
| Non-ADPKD | 10 | 437 | 271 |
| Dataset | Total Images Axial/Coronal (n) | ADPKD Images Axial/Coronal (n) | Non-ADPKD Images Axial/Coronal (n) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Training set | 1483/1127 | 1094/883 | 389/244 |
| Testing set | 526/409 | 478/382 | 48/27 |
| Total images axial/coronal (n) | 2009/1536 | 1572/1265 | 437/271 |
| Participants | Ground Truth (mL) | Our Method (mL) | Diff. (mL) | Diff. (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participant 1 | 2992.23 | 3004.72 | 12.49 | 0.42 |
| Participant 2 | 1078.51 | 1117.47 | 38.96 | 3.61 |
| Participant 3 | 1121.51 | 1195.16 | 73.65 | 6.57 |
| Participant 4 | 2169.31 | 2162.39 | 6.92 | 0.32 |
| Participant 5 | 1740.32 | 1763.23 | 22.91 | 1.32 |
| Participant 6 (Non-ADPKD) | 316.14 | 324.86 | 8.72 | 2.76 |
| Participant 7 | 310.54 | 346.36 | 35.82 | 11.53 |
| Participant 8 | 2836.07 | 2794.3 | 41.77 | 1.47 |
| Participant 9 | 1770.83 | 1970.3 | 199.47 | 11.26 |
| Participant 10 | 682.89 | 684.51 | 1.62 | 0.24 |
| Mean ± SD | 1501.8 ± 965.8 | 1536.3 ± 958.7 | 44.2 ± 58.7 | 3.95 ± 4.14 |
| Participants | Ground Truth (mL) | Our Method (mL) | Diff. (mL) | Diff. (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participant 1 | 3573.87 | 2753.84 | 820.03 | 22.95 |
| Participant 2 | 1328.97 | 1614.76 | 285.79 | 21.5 |
| Participant 3 | 1374.44 | 1303.08 | 71.36 | 5.19 |
| Participant 4 | 2557.89 | 1515.7 | 1042.19 | 40.74 |
| Participant 5 | 1995.45 | 2039.09 | 43.64 | 2.19 |
| Participant 6 (Non-ADPKD) | 248.8 | 434.7 | 185.9 | 74.72 |
| Participant 7 | 312.48 | 317.74 | 5.26 | 1.68 |
| Participant 8 | 3310.56 | 3078.19 | 232.37 | 7.02 |
| Participant 9 | 2034.05 | 2540.41 | 506.36 | 24.89 |
| Participant 10 | 666.63 | 764.95 | 98.32 | 14.75 |
| Mean ± SD | 1740.3 ± 1172.2 | 1636.2 ± 964.7 | 329.1 ± 352.6 | 21.6 ± 22.4 |
| Study | Modality | Method | No. of Patients | Dice Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jagtap [32] | 3D-Ultra sound | 2D U-Net | 22 | 0.80 |
| Sharma [28] | CT | 2D VGG-16 FCN | 125 | 0.86 |
| Raj [33] | MRI-Coronal | 2D Attention U-Net | 100 | 0.922 |
| Taylor [34] | MRI | 3D U-Net | 227 | 0.96 |
| Goel [35] | MRI Axial T2 | 2D U-Net + EfficientNet encoder | 173 | Test set 0.95 |
| Kline [36] | MRI Coronal T2 +/− fatsat | 2D U-Net + ResNet-like encoder | 60 | 1st Reader: 0.86 2nd Reader: 0.84 |
| Van Gastel [37] | MRI Coronal T2 fatsat | 2D U-Net | 145 | 0.96 |
| Our Method | MRI Axial + Coronal T2 | 2D U-Net | 40 | 0.89/0.82 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, J.-L.; Singaravelan, A.; Lai, C.-Y.; Li, Z.-L.; Lin, C.-N.; Wu, W.-S.; Kao, T.-W.; Chu, P.-L. Applying a Deep Learning Model for Total Kidney Volume Measurement in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11100963
Hsu J-L, Singaravelan A, Lai C-Y, Li Z-L, Lin C-N, Wu W-S, Kao T-W, Chu P-L. Applying a Deep Learning Model for Total Kidney Volume Measurement in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(10):963. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11100963
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Jia-Lien, Anandakumar Singaravelan, Chih-Yun Lai, Zhi-Lin Li, Chia-Nan Lin, Wen-Shuo Wu, Tze-Wah Kao, and Pei-Lun Chu. 2024. "Applying a Deep Learning Model for Total Kidney Volume Measurement in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease" Bioengineering 11, no. 10: 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11100963
APA StyleHsu, J.-L., Singaravelan, A., Lai, C.-Y., Li, Z.-L., Lin, C.-N., Wu, W.-S., Kao, T.-W., & Chu, P.-L. (2024). Applying a Deep Learning Model for Total Kidney Volume Measurement in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease. Bioengineering, 11(10), 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11100963








