Three-Dimensional Preoperative Planning Software for Hip Resurfacing Arthroplasty
Abstract
1. Introduction
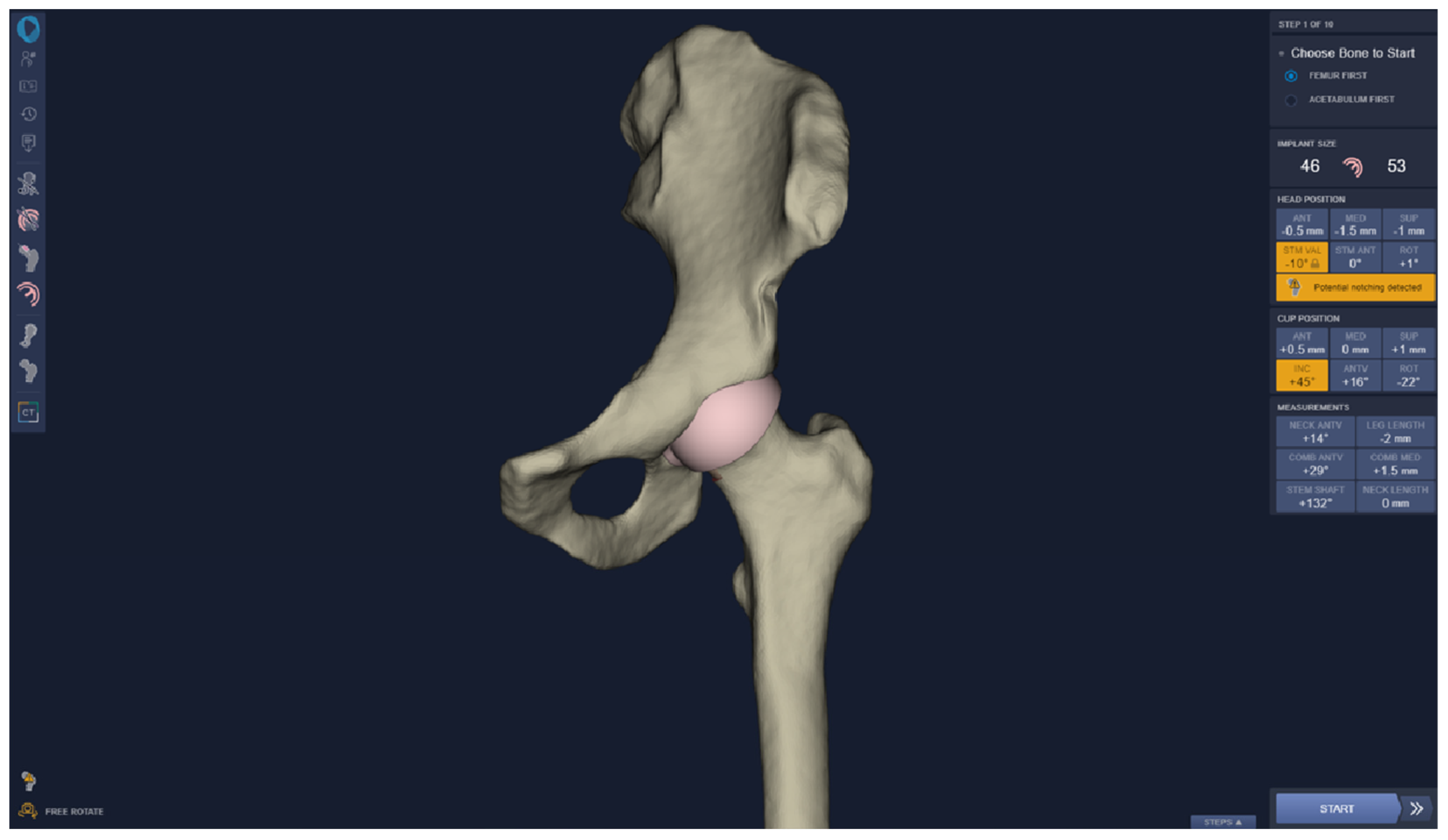
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Comparison of Techniques (3D vs. 2D)
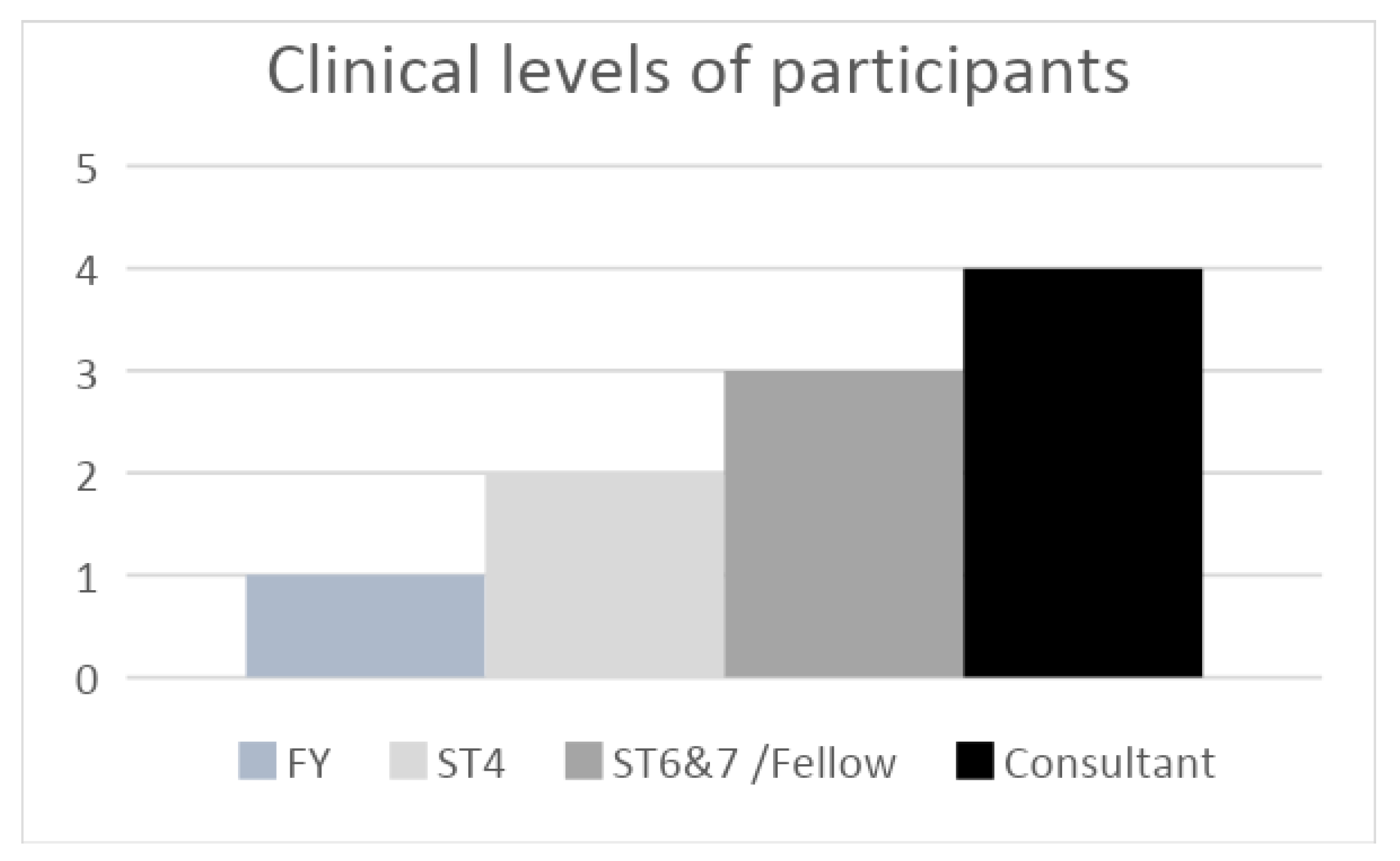
2.2. Usability
3. Results
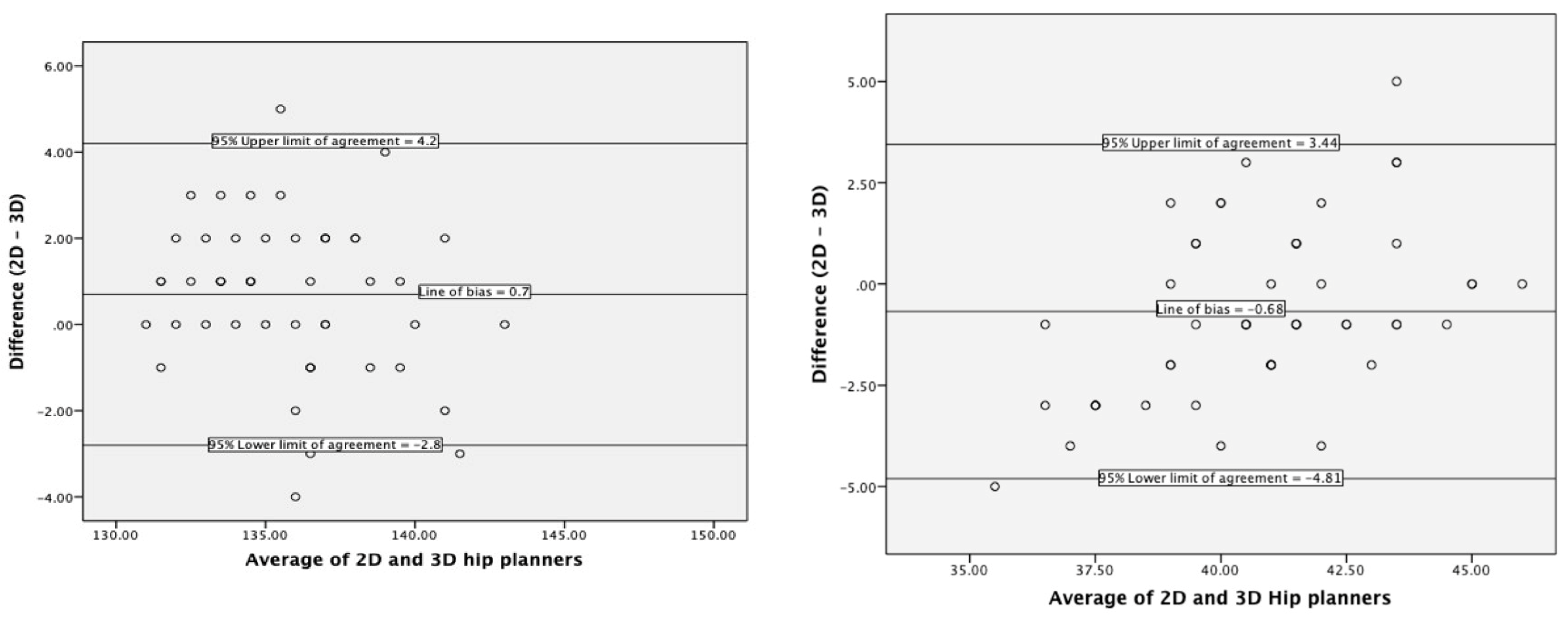
3.1. Agreement with Current Practice
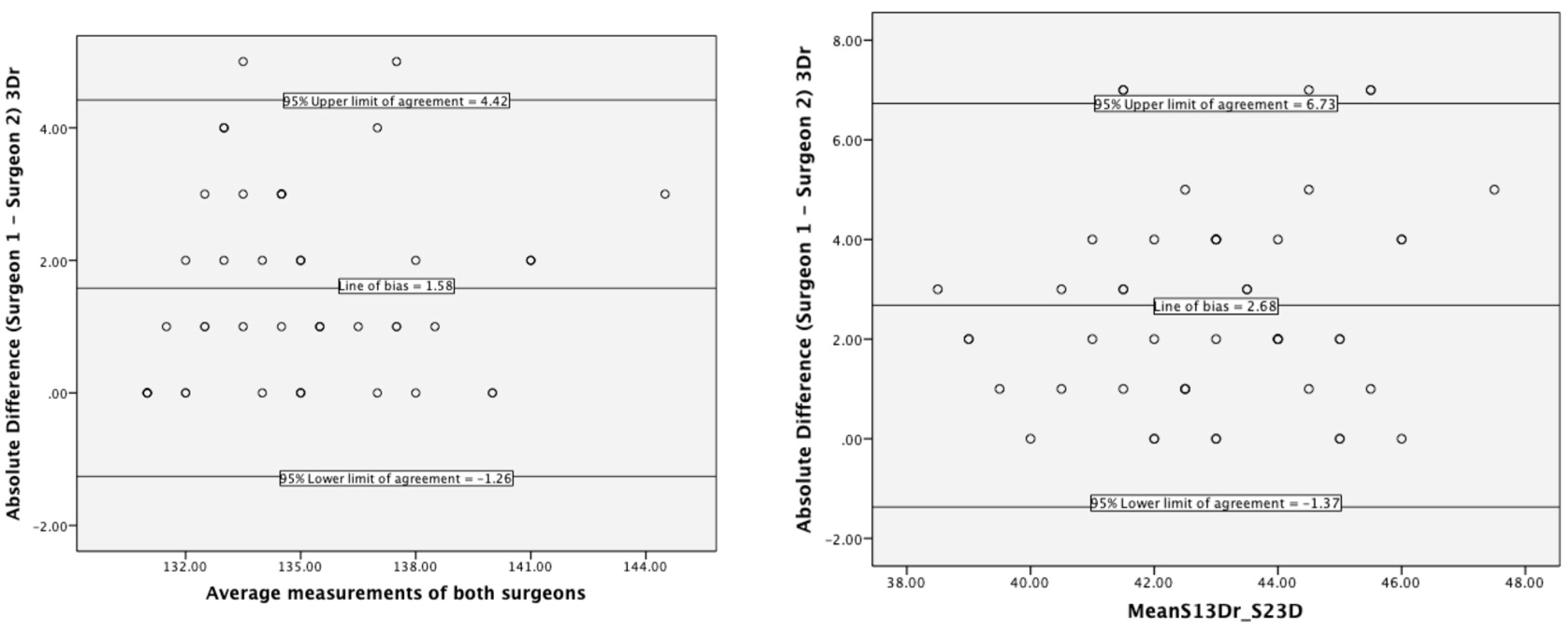
3.2. Interrater Reliability
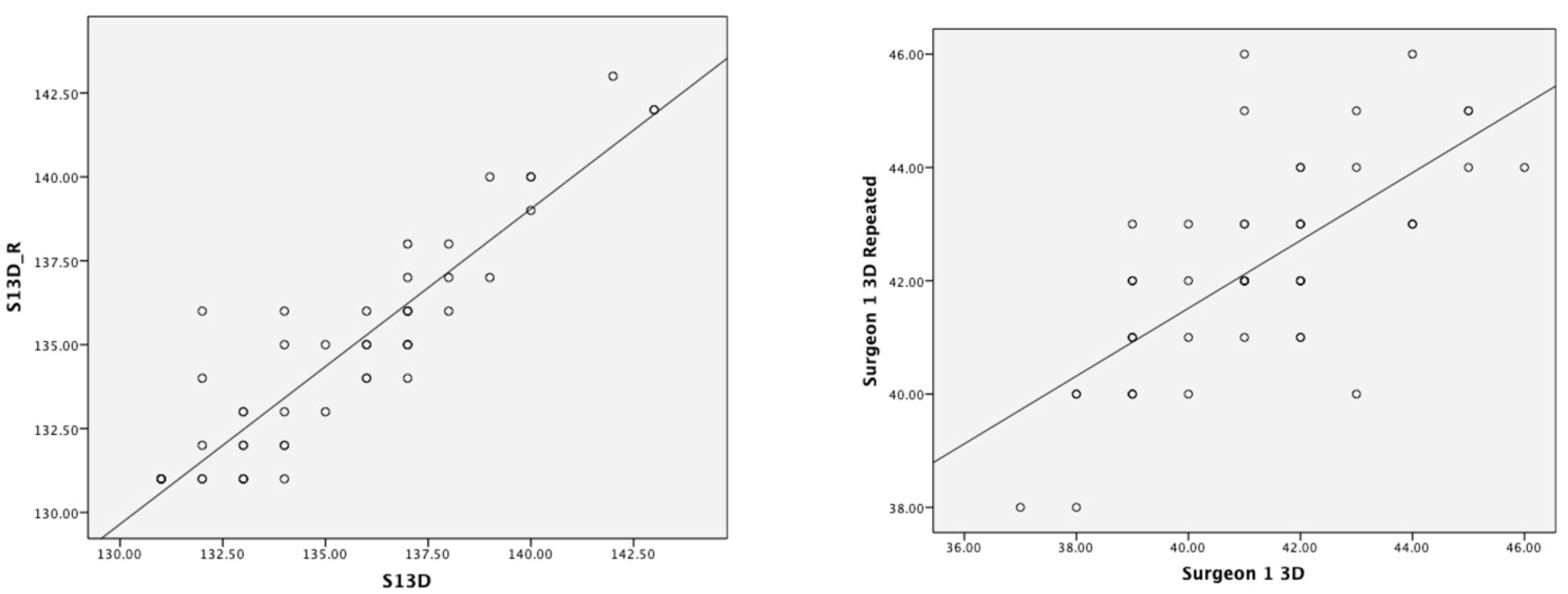
3.3. D Test–Retest Reliability
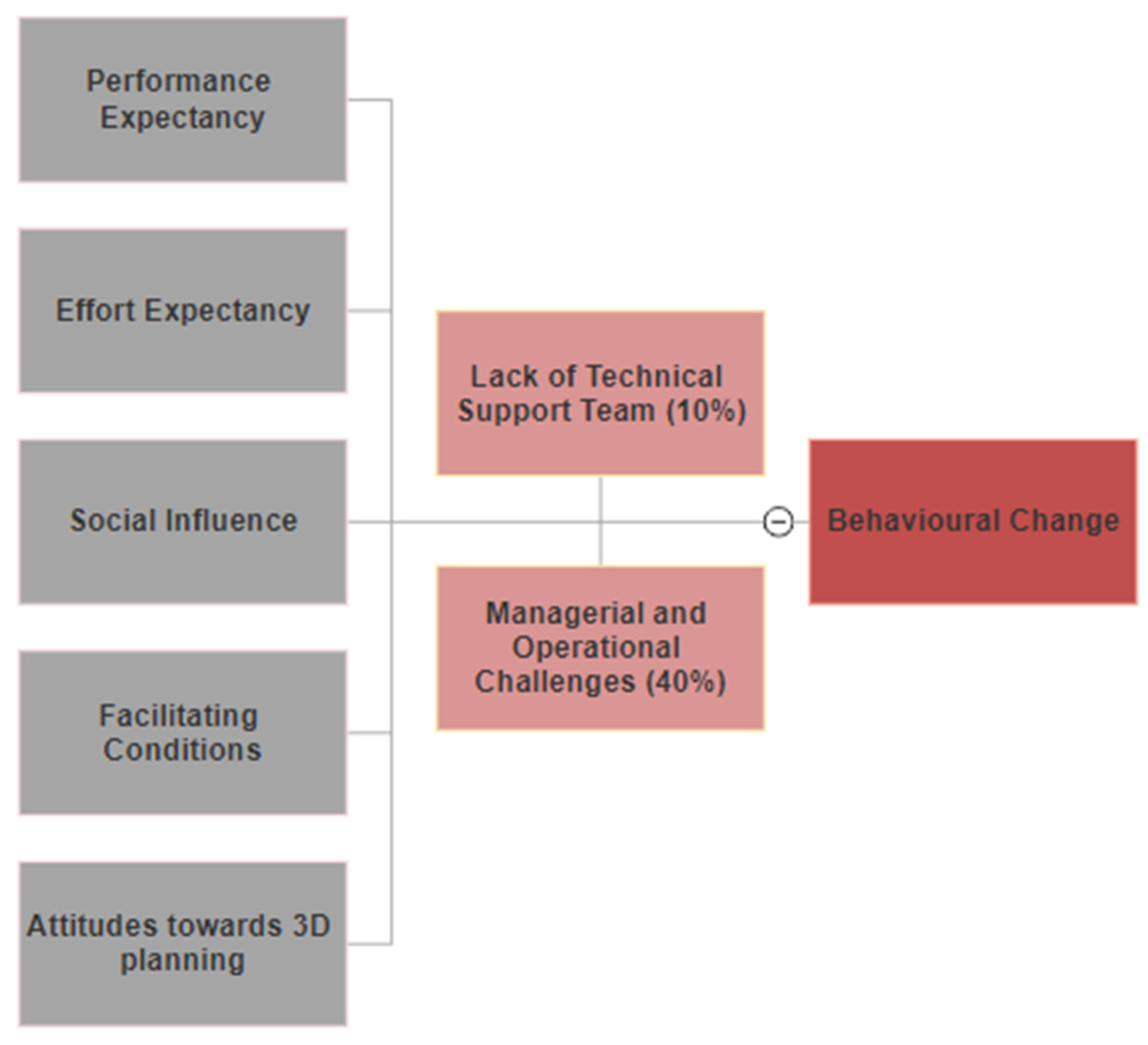
3.4. Usability
4. Discussion
4.1. Agreement with Current Practice
4.2. Interrater Reliability of 3D Hip Planner
4.3. Test–Retest Reliability of 3D Hip Planner
4.4. Usability of 3D Hip Planner
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shimmin, A.; Beaulé, P.E.; Campbell, P. Metal-on-Metal Hip Resurfacing Arthroplasty. JBJS 2008, 90, 637–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amstutz, H.C.; Duff, M.J.L. Effects of physical activity on long-term survivorship after metal-on-metal hip resurfacing arthroplasty. Bone Jt. J. 2019, 101-B, 1186–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhardt, D.; Mors, T.G.T.; Hannink, G.; Van Susante, J.L.C. Resurfacing hip arthroplasty better preserves a normal gait pattern at increasing walking speeds compared to total hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2019, 90, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Girard, J.; De Smet, K. Reproducing the Proximal Femur Anatomy Using Hip Resurfacing Implants. In Personalized Hip and Knee Joint Replacement; Rivière, C., Vendittoli, P.-A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Kendal, A.R.; Prieto-Alhambra, D.; Arden, N.K.; Carr, A.; Judge, A. Mortality rates at 10 years after metal-on-metal hip resurfacing compared with total hip replacement in England: Retrospective cohort analysis of hospital episode statistics. BMJ 2013, 347, f6549. [Google Scholar]
- Penny, J.O.; Brixen, K.; Varmarken, J.E.; Ovesen, O.; Overgaard, S. Changes in bone mineral density of the acetabulum, femoral neck and femoral shaft, after hip resurfacing and total hip replacement: Two-year results from a randomised study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2012, 94, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar]
- Savarino, L.; Cadossi, M.; Chiarello, E.; Baldini, N.; Giannini, S. Do ion levels in metal-on-metal hip resurfacing differ from those in metal-on-metal THA at long-term followup? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2013, 471, 2964–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellon, S.J.; Grammatopoulos, G.; Andersen, M.S.; Pegg, E.C.; Pandit, H.G.; Murray, D.W.; Gill, H.S. Individual motion patterns during gait and sit-to-stand contribute to edge-loading risk in metal-on-metal hip resurfacing. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H 2013, 227, 799–810. [Google Scholar]
- Prosser, G.H.; Yates, P.J.; Wood, D.J.; Graves, S.E.; de Steiger, R.N.; Miller, L.N. Outcome of primary resurfacing hip replacement: Evaluation of risk factors for early revision. Acta Orthop. 2010, 81, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Knight, J.L.; Atwater, R.D. Preoperative planning for total hip arthroplasty. Quantitating its utility and precision. J. Arthroplast. 1992, 7, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slover, J.; Wetter, E.; Malchau, H. Computer Templating of Hip Resurfacing Arthroplasty. In Modern Hip Resurfacing; McMinn, D.J.W., Ed.; Springer: London, UK, 2009; pp. 185–188. [Google Scholar]
- Di Martino, A.; Rossomando, V.; Brunello, M.; D’Agostino, C.; Pederiva, D.; Frugiuele, J.; Pilla, F.; Faldini, C. How to perform correct templating in total hip replacement. Musculoskelet Surg. 2023, 107, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishi, H.; Smith, J.B.; Asopa, V.; Field, R.E.; Sochart, D.H.; Wang, C. Comparison of the accuracy of 2D and 3D templating methods for planning primary total hip replacement: A systematic review and meta-analysis. EFORT Open Rev. 2022, 7, 70–83. [Google Scholar]
- Hassani, H.; Cherix, S.; Ek, E.T.; Rüdiger, H.A. Comparisons of preoperative three-dimensional planning and surgical reconstruction in primary cementless total hip arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2014, 29, 1273–1277. [Google Scholar]
- Sariali, E.; Catonne, Y.; Pascal-Moussellard, H. Three-dimensional planning-guided total hip arthroplasty through a minimally invasive direct anterior approach. Clinical outcomes at five years’ follow-up. Int. Orthop. 2017, 41, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Knafo, Y.; Houfani, F.; Zaharia, B.; Egrise, F.; Clerc-Urmès, I.; Mainard, D. Value of 3D Preoperative Planning for Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty Based on Biplanar Weightbearing Radiographs. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 1932191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moralidou, M.; Di Laura, A.; Henckel, J.; Hothi, H.; Hart, A.J. Three-dimensional pre-operative planning of primary hip arthroplasty: A systematic literature review. EFORT Open Rev. 2020, 5, 845–855. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, E.F.; Richardson, M.D.; Nestel, D. Mental imagery and learning: A qualitative study in orthopaedic trauma surgery. Med. Educ. 2015, 49, 888–900. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, C.R. Preoperative planning for fracture management. Am. J. Orthop. 2012, 41, E128–E129. [Google Scholar]
- Colombi, A.; Schena, D.; Castelli, C.C. Total hip arthroplasty planning. EFORT Open Rev. 2019, 4, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainard, D.; Barbier, O.; Knafo, Y.; Belleville, R.; Mainard-Simard, L.; Gross, J.B. Accuracy and reproducibility of preoperative three-dimensional planning for total hip arthroplasty using biplanar low-dose radiographs: A pilot study. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2017, 103, 531–536. [Google Scholar]
- Steen, A.; Widegren, M. (Eds.) 3D Visualization of Pre-operative Planning for Orthopedic Surgery; SIGRAD: Norrköping, Sweden, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pour, A.E.; Green, J.H.; Christensen, T.H.; Muthusamy, N.; Schwarzkopf, R. Is It Necessary to Obtain Lateral Pelvic Radiographs in Flexed Seated Position for Preoperative Total Hip Arthroplasty Planning? Arthroplast. Today 2023, 17, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Savov, P.; Budde, S.; Tsamassiotis, S.; Windhagen, H.; Klintschar, M.; Ettinger, M. Three-dimensional templating in hip arthroplasty: The basis for template-directed instrumentation? Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2020, 140, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treacy, R.B.C.; Holland, J.P.; Daniel, J.; Ziaee, H.; McMinn, D.J.W. Preliminary report of clinical experience with metal-on-highly-crosslinked-polyethylene hip resurfacing. Bone Jt. Res. 2019, 8, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altman, B. Practical statistics for medical research. Douglas G. Altman, Chapman and Hall, London, 1991. No. of pages: 611. Stat. Med. 1991, 10, 1635–1636. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh, V.; Morris, M.G.; Davis, G.B.; Davis, F.D. User Acceptance of Information Technology: Toward a Unified View. MIS Q. 2003, 27, 425–478. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, M.; Gamble, P.; Chiu, M.; Tumia, N.; Boyle, R.A.; Schemitsch, E.H. Assessment of accuracy and reliability in preoperative templating for hip resurfacing arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2010, 25, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.K.; Geller, J.A.; Wang, W.; Nyce, J.D.; Macaulay, W. The accuracy and reliability of preoperative templating for metal-on-metal hip resurfacing. J. Arthroplast. 2011, 26, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.K.; Son, S.M.; Kim, T.W.; Shin, W.C.; Lee, J.S.; Suh, K.T. Accuracy and Reliability of Preoperative On-screen Templating Using Digital Radiographs for Total Hip Arthroplasty. Hip Pelvis 2016, 28, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westacott, D.J.; McArthur, J.; King, R.J.; Foguet, P. Assessment of cup orientation in hip resurfacing: A comparison of TraumaCad and computed tomography. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2013, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmani, F.A.; Thakkar, S.; Ramme, A.; Elbuluk, A.; Wojack, P.; Vigdorchik, J.M. Variance in predicted cup size by 2-dimensional vs 3-dimensional computerized tomography-based templating in primary total hip arthroplasty. Arthroplast. Today 2017, 3, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wako, Y.; Nakamura, J.; Miura, M.; Kawarai, Y.; Sugano, M.; Nawata, K. Interobserver and Intraobserver Reliability of Three-Dimensional Preoperative Planning Software in Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.M.; Peacock, J. Statistical Questions in Evidence-Based Medicine; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Vaz, S.; Falkmer, T.; Passmore, A.E.; Parsons, R.; Andreou, P. The Case for Using the Repeatability Coefficient When Calculating Test–Retest Reliability. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73990. [Google Scholar]
- Guyatt, G.; Walter, S.; Norman, G. Measuring change over time: Assessing the usefulness of evaluative instruments. J. Chronic Dis. 1987, 40, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huppertz, A.; Radmer, S.; Asbach, P.; Juran, R.; Schwenke, C.; Diederichs, G.; Hamm, B.; Sparmann, M. Computed tomography for preoperative planning in minimal-invasive total hip arthroplasty: Radiation exposure and cost analysis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2011, 78, 406–413. [Google Scholar]
- Huppertz, A.; Radmer, S.; Wagner, M.; Roessler, T.; Hamm, B.; Sparmann, M. Computed tomography for preoperative planning in total hip arthroplasty: What radiologists need to know. Skeletal Radiol. 2014, 43, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kyo, T.; Nakahara, I.; Kuroda, Y.; Miki, H. Effects of coordinate-system construction methods on postoperative computed tomography evaluation of implant orientation after total hip arthroplasty. Comput. Aided Surg. 2015, 20, 52–60. [Google Scholar]
- Kearney, R.; Shaikh, A.H.; O’Byrne, J.M. The accuracy and inter-observer reliability of acetate templating in total hip arthroplasty. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 182, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alagha, M.A.; Logishetty, K.; O’Hanlon, C.; Liddle, A.D.; Cobb, J. Three-Dimensional Preoperative Planning Software for Hip Resurfacing Arthroplasty. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10080939
Alagha MA, Logishetty K, O’Hanlon C, Liddle AD, Cobb J. Three-Dimensional Preoperative Planning Software for Hip Resurfacing Arthroplasty. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(8):939. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10080939
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlagha, M. Abdulhadi, Kartik Logishetty, Ciaran O’Hanlon, Alexander D. Liddle, and Justin Cobb. 2023. "Three-Dimensional Preoperative Planning Software for Hip Resurfacing Arthroplasty" Bioengineering 10, no. 8: 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10080939
APA StyleAlagha, M. A., Logishetty, K., O’Hanlon, C., Liddle, A. D., & Cobb, J. (2023). Three-Dimensional Preoperative Planning Software for Hip Resurfacing Arthroplasty. Bioengineering, 10(8), 939. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10080939





