Neural Networks for the Detection of COVID-19 and Other Diseases: Prospects and Challenges
Abstract
1. Introduction
- First, we present a critical review of state-of-the-art ANN models that have contributed to the detection and diagnosis of various diseases, including skin diseases, retinal diseases, and COVID-19. While numerous studies are available on using ANNs in the medical field, a comprehensive review of these techniques is crucial to understand their current and future potential clearly. Therefore, this paper aims to offer a comprehensive and concise overview of recent advancements in ANNs for medical applications.
- Second, our work focuses explicitly on detecting and diagnosing COVID-19 using convolutional neural network (CNN) models. We provide an in-depth analysis of existing CNN models designed for COVID-19 detection, discussing their contributions and limitations.
- Then, we propose a novel deep learning model called ConXNet, which has been trained and tested using different datasets to improve the accuracy of COVID-19 detection by up to 98%. This contribution is significant as it offers an innovative approach to enhance the detection capabilities of AI-based models in the context of a global health crisis.
- Finally, we highlight the gaps that require attention in the future to improve ANN-based disease diagnosis and treatment. These future research challenges include algorithm complexity, inadequate available data, security and privacy concerns, and biosensing integration with ANNs.
2. Background and Related work
3. Review of Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs)
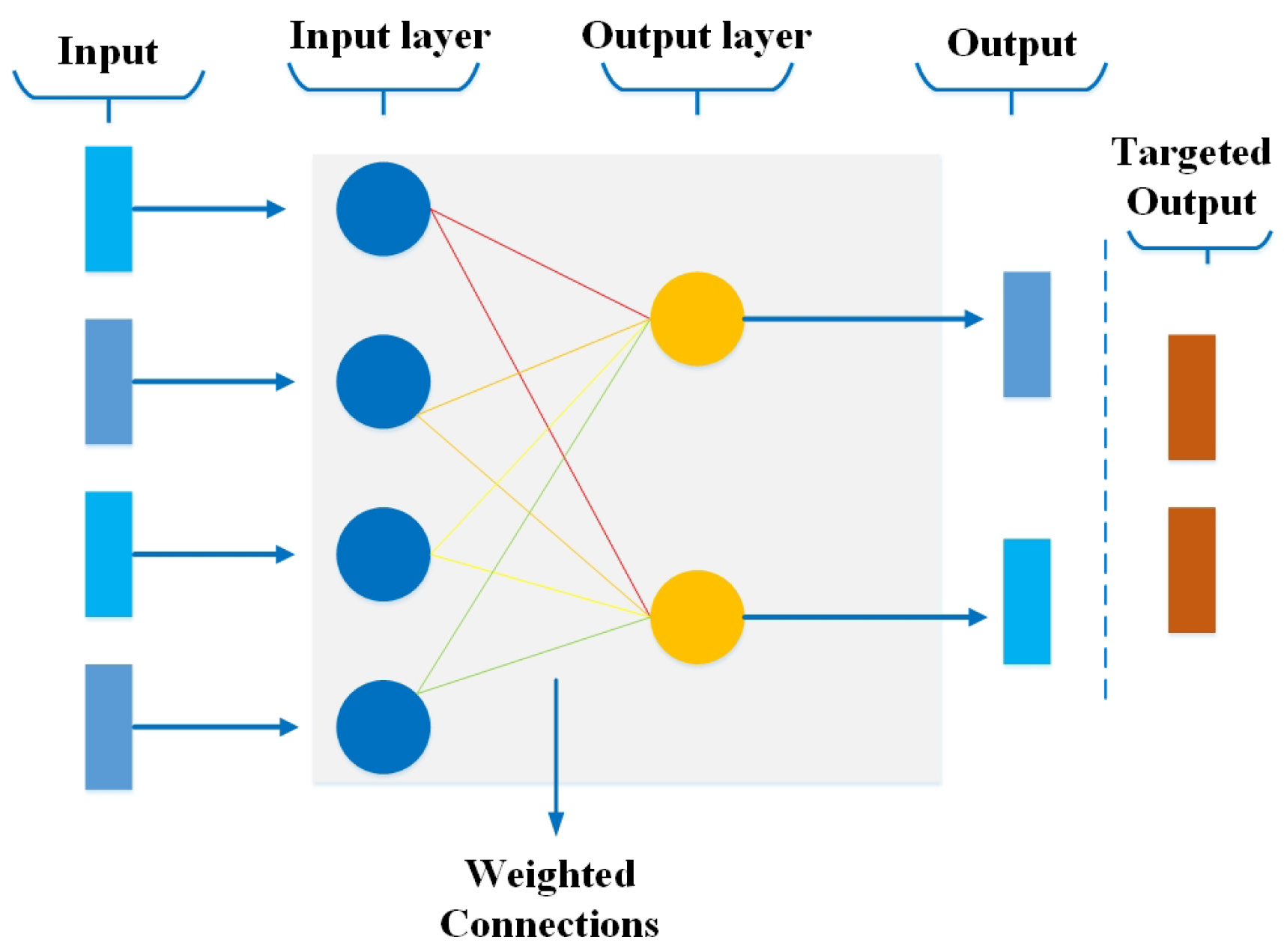
3.1. Perceptron
3.2. Multilayer Perceptron
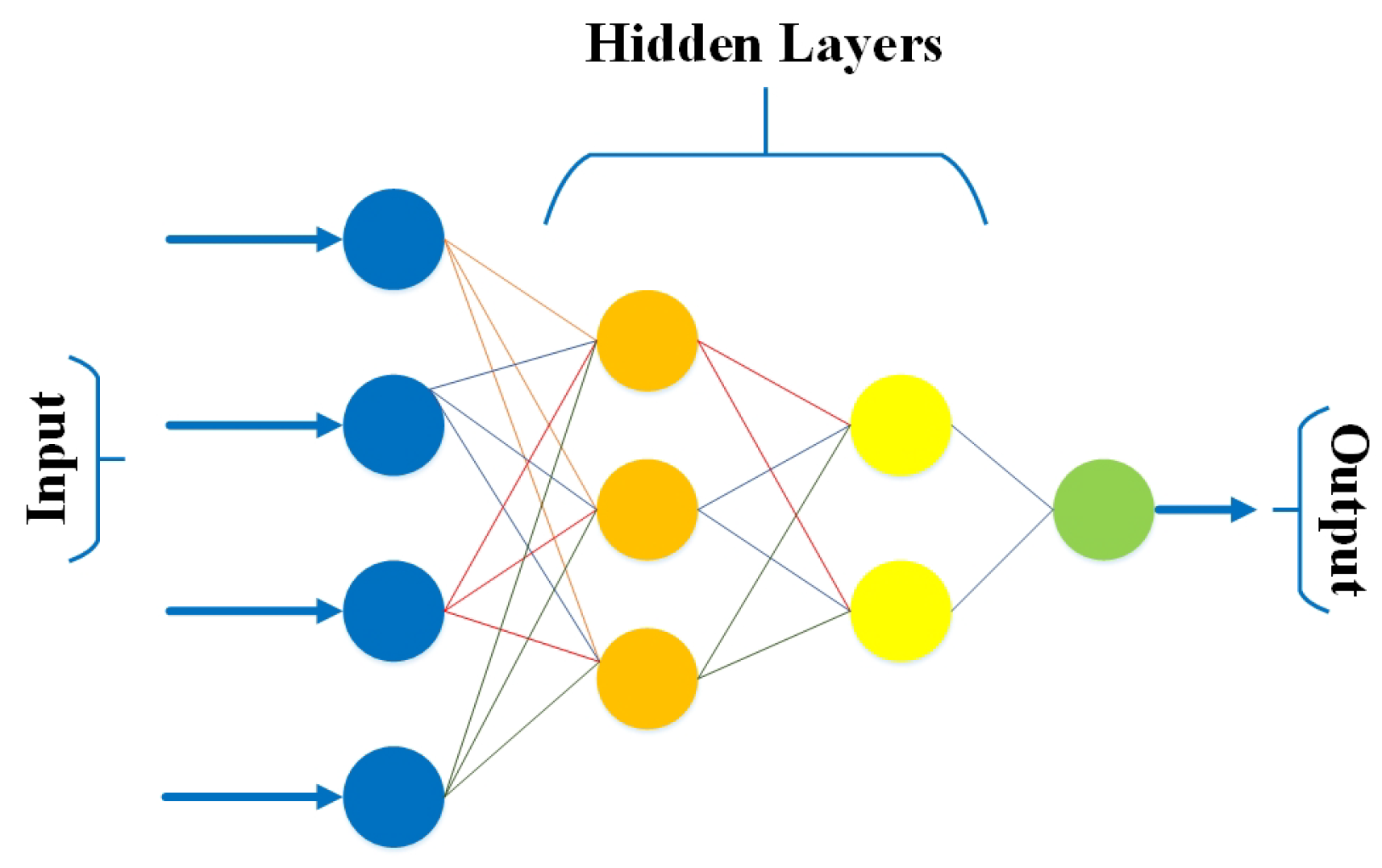
3.3. Feed-Forward Neural Network (FFNN)
3.4. Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
3.5. Radial Basis Function Neural Networks
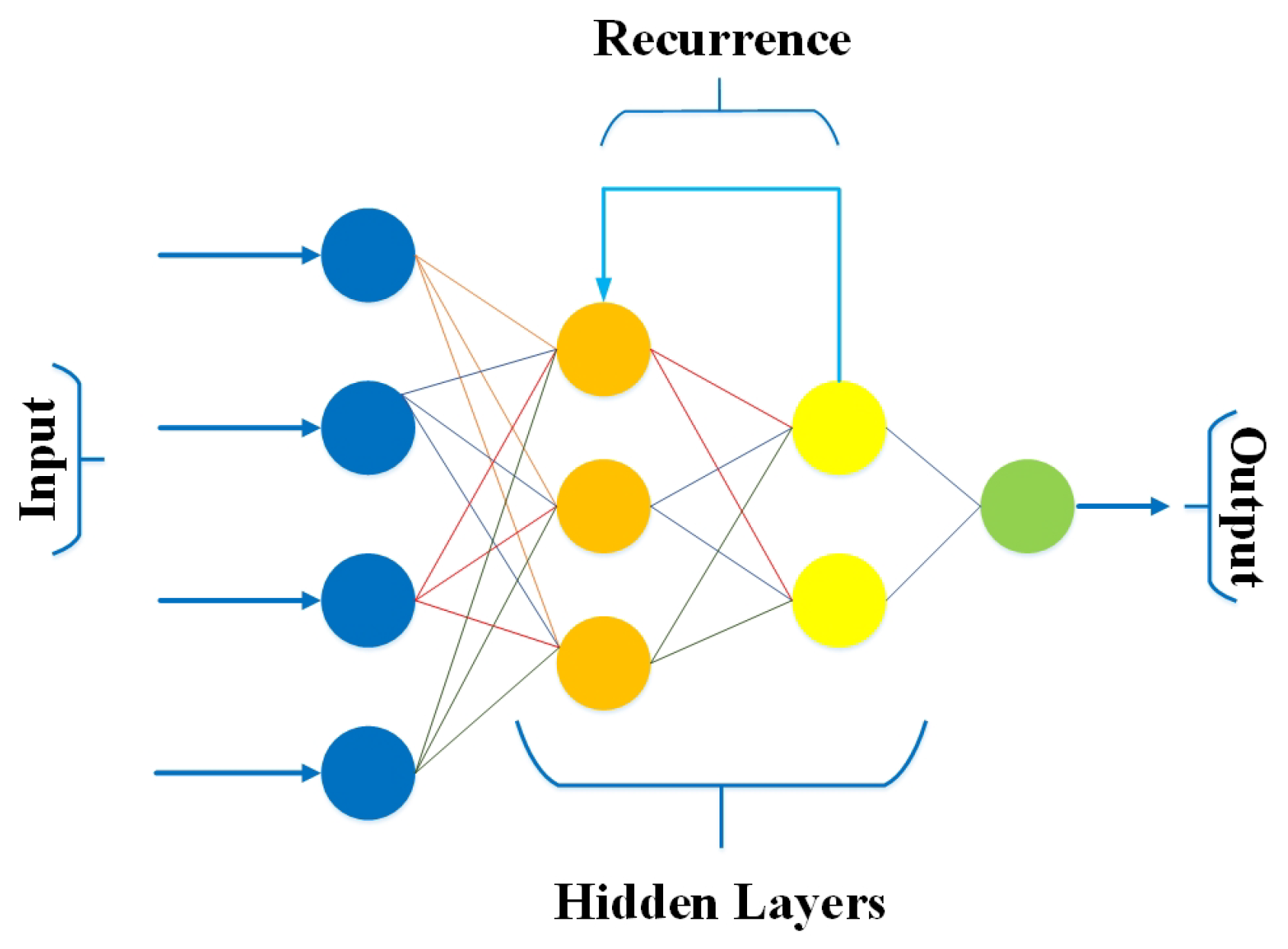
3.6. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
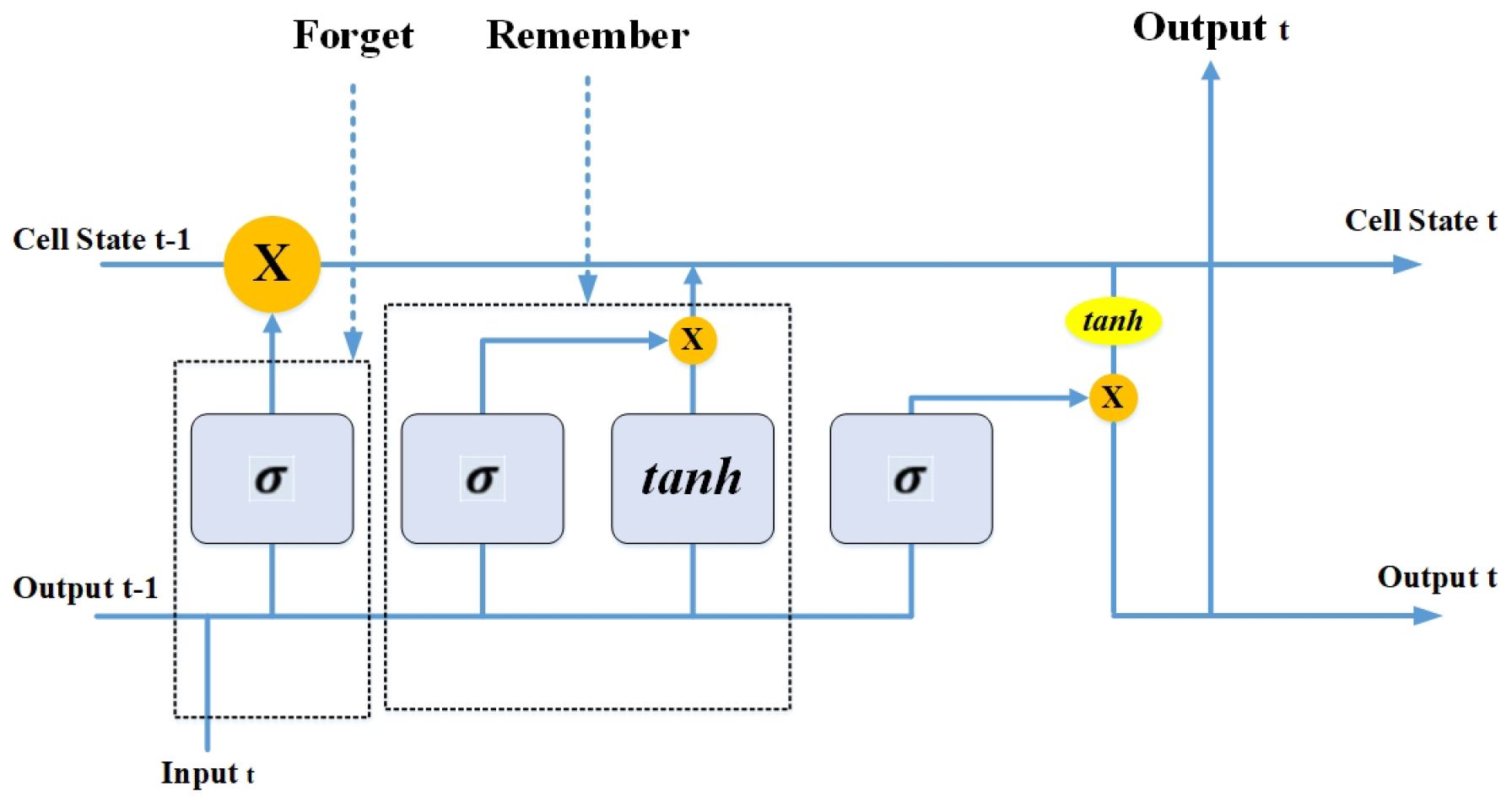
3.6.1. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Networks
3.6.2. Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) Networks
3.7. Sequence-to-Sequence Models
3.8. Modular Neural Network
4. CNN Models for COVID-19 Detection
4.1. Decompose, Transfer, and Compose (DeTraC)
4.2. COVID-Net
4.3. Coro-Net
4.4. OptCoNet
4.5. COVID-MTNet
4.6. CovNet30
4.7. COVIDPEN
4.8. PDCOVIDNet
4.9. U-Net
4.10. CapsNet
| Ref. | Model | Dataset | Image Type | Accuracy | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [66] | DeTraC deep convolutional neural network | 80 negative 105 positive | Chest X-ray images | 93.1% | This model produces a significant performance on chest radiography images. However, dataset samples are too small to make perception for its performance over a large dataset in an ideal condition. |
| [74] | Coro-Net deep neural network | 310 negative 330 positive | Chest X-ray images | 90% | The number of samples is not up to the mark to judge the model performance in a real-time environment. Although accuracy seems good, there are many chances of model overfitting in this case. |
| [75] | OptCoNet optimized convolutional neural network | 1800 negative 900 positive | Chest X-ray images | 97.78% | This model achieved significant accuracy. However, the dataset is average in size and cannot be considered ideal for complying the model for real-time analysis and set as an example. |
| [76] | COVID MTNet deep learning model | 1341 negative 3875 positive | Chest X-ray and CT images | 84.76% | The number of positive samples is relatively higher than the negative, , which may lead to an unusual behaviour model. Moreover, the model achieved an average accuracy, which may have high chances for underfitting of the model. |
| [79] | PDCOVIDNet parallel-dilated CNN | 1341 negative 1564 Positive | Chest X-ray images | 96.58% | The model achieved good accuracy on an average size of the dataset. |
| [80] | U-Net a novel deep learning model | 552 negative 448 positive | Chest X-ray images | 94.10% | This model acquires high accuracy on a small dataset, which needs to be better for a reliable model, and results may mislead in critical situations. |
| [81] | CapsNet a novel ANN model | 1050 negative 231 positive | Chest X-ray images | 97.24% | Again the model achieved higher accuracy on a small dataset. Consequently, model overfitting can be expected. |
| [82] | COVID-Net deep convolutional neural network | 13,604 negative 2972 positive | Chest X-ray images | 92.4% | This model seems quite promising with good accuracy results and a significant number of samples. However, a large set of negative samples can influence the results. |
| [83] | CovNet30 30-layered CNN model | 1139 negative 1625 Positive | Chest X-ray images | 92.74% | The model achieves good accuracy, but the number of samples is smaller compared with the performance of other state-of-the-art models trained on a large number of samples. |
| [84] | COVIDPEN pruned efficiently net-based model | 180 negative 566 positive | Chest X-ray and CT images | 96% | Due to the significantly small dataset size, despite achieving high accuracy, the reliability of the results is compromised. |
| [85] | EMCNet CNN and ensemble of machine learning classifiers | 2300 negative 2300 positive | Chest X-ray images | 98.91% | The model performed significantly well on a balanced dataset and produced high-accuracy results. However, increasing the data size may lead to a slight performance decrease. |
| [86] | Four-layered CNN model for analyzing CT images | 3250 negative 5776 positive | Chest X-ray and CT images | 97.8% | The model performed significantly well on a relatively large dataset. However, time and space complexity may vary over time, and several training hyperparameters are also high, which may cause the slow performance of a model in the future with more large datasets. |
| ConXNet proposed CNN model | 10,192 negative 3616 Positive | Chest X-ray images | 97.8% | A proposed model in the paper acquires a significantly good accuracy on a relatively large dataset as compared with other models. Some of the models also achieved good results close to the proposed model. However, this model is trained on a fewer number of hyperparameters by using different techniques, such as batch processing and dropout layers, to overcome overfitting of the model as well. Therefore, the results of the model are reliable but can be improved in the future with more samples. |
5. Proposed ConXNet Model for COVID-19 Detection
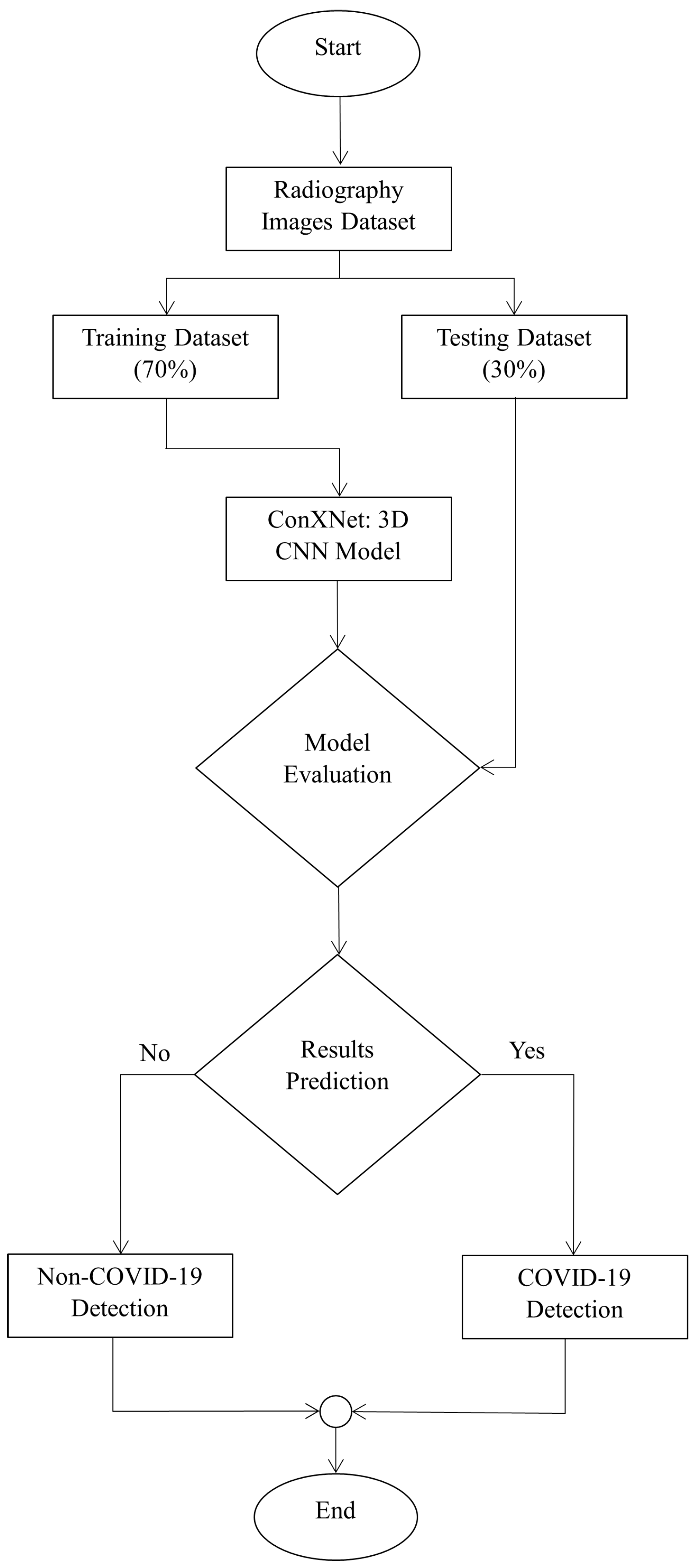
5.1. Dataset
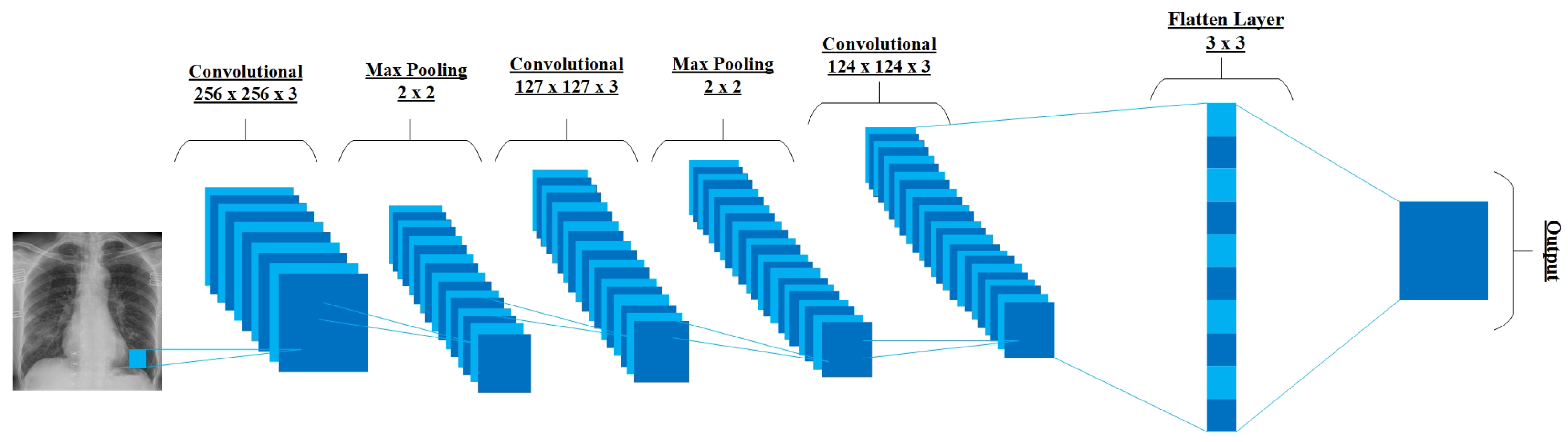
5.2. ConXNet Architecture
5.3. Experimental Results
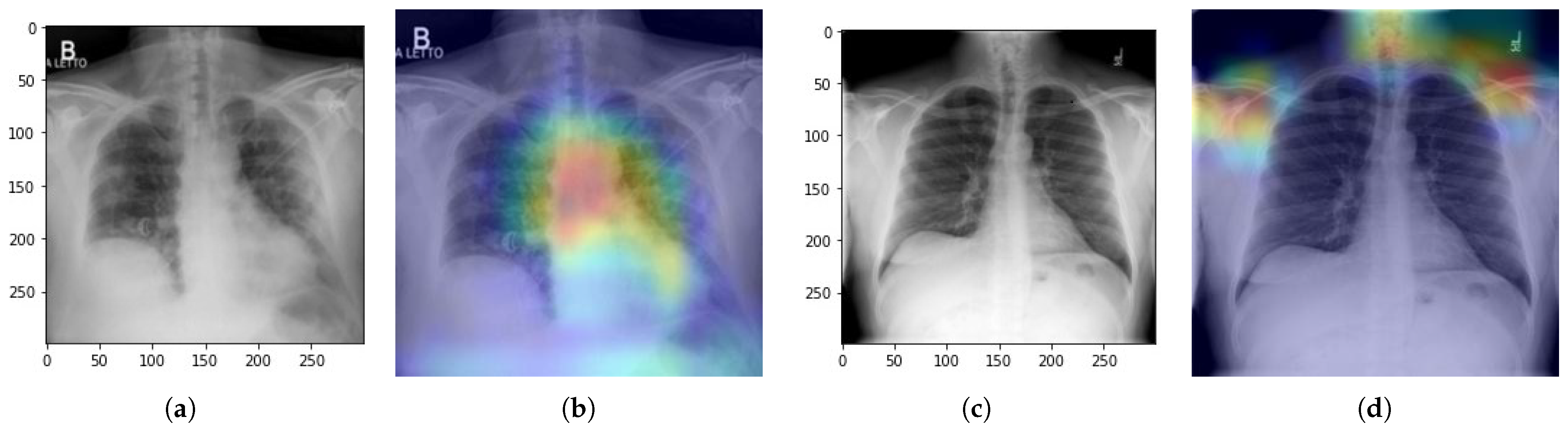
5.3.1. Obtained Results for “COVID-19_Radiography_Dataset”
5.3.2. Testing of the Proposed Scheme
6. CNN Models for Detection of Other Diseases
6.1. Alzheimer’s Disease Detection
6.2. Cancer Detection
6.3. Retinal Disease Detection
7. Discussion, Opportunities, and Open Issues
7.1. Discussion
7.2. Opportunities
7.2.1. Integration of AI with Internet of Healthcare Things (IoHT)
7.2.2. Federated Learning for Privacy-Preserving Analysis
7.2.3. Integration of AI in Telemedicine Platforms
7.3. Open Issues
7.3.1. Standardization of Evaluation Metrics and Benchmark Datasets
7.3.2. Addressing the Challenges of Model Interpretability and Explainability
7.3.3. Ethical Considerations in AI deployment
7.3.4. Integration of AI Models into Clinical Workflows
8. Future Research Directions
8.1. Complexity
8.2. Algorithm Selection
8.3. Deficient Training Data
8.4. Privacy and Security
8.5. Integration of Biosensing and ANN
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 1D | one (1) dimensional |
| 2D | two (2) dimensional |
| 3D | three (3) dimensional |
| AI | artificial intelligence |
| ANN | artificial neural network |
| CART | classification and regression tree |
| CNN | convolutional neural network |
| CT | computed tomography |
| DBNN | deep belief neural networks |
| DeTraC | Decompose, Transfer, and Compose |
| DT | decision tree |
| FNN | feed-forward neural network |
| GRU | gated recurrent unit |
| KNN | k-nearest neighbor |
| LSTM | long short-term memory |
| ML | machine learning |
| MLP | multilayer perceptron |
| NB | naïve Bayes |
| NN | neural network |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| PNN | probabilistic neural networks |
| RBF | radial basis function |
| ReLU | rectified linear unit |
| RF | random forest |
| RRCNN | recurrent, residual neural network |
| ROI | region of interest |
| RNN | recurrent neural network |
| SVM | support vector machine |
References
- Baloni, D.; Verma, S.K. Detection of hydrocephalus using deep convolutional neural network in medical science. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 16171–16193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itchhaporia, D. Artificial intelligence in cardiology. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 32, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, Z.; Key, S.; Habib, A.R.; Wong, E.; Aweidah, L.; Kumar, A.; Sacks, R.; Singh, N. Convolutional neural networks in ENT Radiology: Systematic review of the literature. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2023, 132, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehranian, A.; Wollenweber, S.D.; Walker, M.D.; Bradley, K.M.; Fielding, P.A.; Su, K.H.; Johnsen, R.; Kotasidis, F.; Jansen, F.P.; McGowan, D.R. Image enhancement of whole-body oncology [18F]-FDG PET scans using deep neural networks to reduce noise. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrowski, D.A.; Logan, J.R.; Antony, M.; Broms, R.; Weiss, D.A.; Van Batavia, J.; Long, C.J.; Smith, A.L.; Zderic, S.A.; Edwins, R.C.; et al. Automated Society of Fetal Urology (SFU) grading of hydronephrosis on ultrasound imaging using a convolutional neural network. J. Pediatr. Urol. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.I.; Franco-Gonçalo, P.; Leite, P.; Ribeiro, A.; Alves-Pimenta, M.S.; Colaço, B.; Loureiro, C.; Gonçalves, L.; Filipe, V.; Ginja, M. Artificial Intelligence in Veterinary Imaging: An Overview. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurani, A.; Doshi, P.; Vakharia, A.; Shah, M. A comprehensive comparative study of artificial neural network (ANN) and support vector machines (SVM) on stock forecasting. Ann. Data Sci. 2023, 10, 183–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosan, M.A.; Karacan, H.; Urgen, B.A. Predicting personality traits with semantic structures and LSTM-based neural networks. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 8007–8025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Zhang, Q. Evaluation of rural financial, ecological environment based on machine learning and improved neural networks. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 9335–9352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N. Benefit evaluation of human resource management in agricultural enterprises based on convolutional neural network. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2023, 60, 217–227. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, J.; Jan, T.; Khalil, R.; Altalbe, A. Hybrid source prior based independent vector analysis for blind separation of speech signals. IEEE Access. 2020, 8, 132871–132881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Ji, Y.; Huang, H.H. Illuminati: Towards explaining graph neural networks for cybersecurity analysis. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 7th European Symposium on Security and Privacy (EuroS&P), Genoa, Italy, 6–10 June 2022; pp. 74–89. [Google Scholar]
- Ananya, S.; Bharamagoudra, M.R.; Bharath, K.; Pujari, R.R.; Hanamanal, V.A. Glaucoma Detection using HOG and Feed-forward Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Integrated Circuits and Communication Systems (ICICACS), Raichur, India, 24–25 February 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Pilarz, J.; Polishuk, I.; Chorążewski, M. Prediction of sound velocity for selected ionic liquids using a multilayer feed-forward neural network. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 347, 118376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Tahir, G.A.; Masuyama, N.; Kakudi, H.A.; Fu, Z.; Pasupa, K. Error-output recurrent multi-layer Kernel Reservoir Network for electricity load time series forecasting. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 117, 105611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Li, Z.; He, Y.; Guo, Q.; Lu, Y.; Gu, S.; Wu, H. Potential use of artificial intelligence in infectious disease: Take ChatGPT as an example. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 51, 1130–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Kumar, R.; Tiwari, S.K.; Ranjan, P. Machine learning approaches in the diagnosis of infectious diseases: A review. Bull. Electr. Eng. Inform. 2022, 11, 3509–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, M.; Monneret, A.; Hammon, H.; Post, C.; Müller, U.; Frieten, D.; Gerbert, C.; Dusel, G.; Koch, C. Deep convolutional neural networks for the detection of diarrhea and respiratory disease in preweaning dairy calves using data from automated milk feeders. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 9882–9895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.; Peng, K.; Yang, X.; Huang, P.; Luo, Y.; Feng, P.; Wei, B. E-TBNet: Light Deep Neural Network for automatic detection of tuberculosis with X-ray DR Imaging. Sensors 2022, 22, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panja, M.; Chakraborty, T.; Nadim, S.S.; Ghosh, I.; Kumar, U.; Liu, N. An ensemble neural network approach to forecast Dengue outbreak based on climatic condition. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2023, 167, 113124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, S.H.; Zhang, Y.D. EDNC: Ensemble deep neural network for COVID-19 recognition. Tomography 2022, 8, 869–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, D.M.S.; Khalil, R.A.; Saeed, N.; Nam, H. Detection and Spatial Correlation Analysis of infectious Diseases using wireless body area network under Imperfect wireless channel. Big Data 2022, 10, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Luo, Z.; Xu, M.; Liang, Z.; Fan, X.; Lu, X. Automated detection for Retinopathy of Prematurity with knowledge distilling from multi-stream fusion network. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2023, 269, 110461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiodun, K.M.; Awotunde, J.B.; Aremu, D.R.; Adeniyi, E.A. Explainable AI for fighting COVID-19 pandemic: Opportunities, challenges, and future prospects. In Computational Intelligence for COVID-19 and Future Pandemics: Emerging Applications and Strategies; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 315–332. [Google Scholar]
- Ghrabli, S.; Elgendi, M.; Menon, C. Challenges and opportunities of deep learning for cough-based COVID-19 diagnosis: A scoping review. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MV, M.K.; Atalla, S.; Almuraqab, N.; Moonesar, I.A. Detection of COVID-19 using deep learning techniques and cost-effectiveness evaluation: A survey. Front. Artif. Intell. 2022, 5, 912022. [Google Scholar]
- Khattab, R.; Abdelmaksoud, I.R.; Abdelrazek, S. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Detecting COVID-19 Using Medical Images: A Survey. New Gener. Comput. 2023, 41, 343–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malo, D.C.; Rahman, M.M.; Mahbub, J.; Khan, M.M. Skin Cancer Detection using Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 12th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26–29 January 2022; pp. 169–176. [Google Scholar]
- Thaseen, M.; UmaMaheswaran, S.; Naik, D.A.; Aware, M.S.; Pundhir, P.; Pant, B. A Review of Using CNN Approach for Lung Cancer Detection Through Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 2nd International Conference on Advance Computing and Innovative Technologies in Engineering (ICACITE), Greater Noida, India, 28–29 April 2022; pp. 1236–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizaz, Z.; Khare, K.; Khursheed, A.; Tirmizi, A. Pix2Pix Generative adversarial Networks (GAN) for breast cancer detection. In Proceedings of the 2022 5th International Conference on Multimedia, Signal Processing and Communication Technologies (IMPACT), Aligarh, India, 26–27 November 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.M.T.; Rahman, Z.; Shaikh, R.; Hossain, S.I. Malaria Parasite Detection Using CNN-Based Ensemble Technique on Blood Smear Images. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Communication Engineering (ECCE), Chittagong, Bangladesh, 23–25 February 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Y.P.; Lobiyal, D.K. Brain Tumor Classification Using Deep Transfer Learning CNN Models. In Proceedings of the 2022 4th International Conference on Inventive Research in Computing Applications (ICIRCA), Coimbatore, India, 21–23 September 2022; pp. 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Y.; Koul, A.; Singla, R.; Ijaz, M.F. Artificial intelligence in disease diagnosis: A systematic literature review, synthesizing framework and future research agenda. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2022, 14, 8459–8486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Khan, M.; Khan, W.; Khan, M.Z.; Srivastava, N.K. A Comparative Study on Data Mining Approach Using Machine Learning Techniques: Prediction Perspective. In Pervasive Healthcare: A Compendium of Critical Factors for Success; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 153–165. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Singh, H. Antenna Array Pattern Synthesis Using Nature-Inspired Computational Techniques: A Review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2023, 30, 3235–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kumar, V. Application of genetic algorithms in healthcare: A review. In Next Generation Healthcare Informatics; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, A.; Zhao, D.; Yu, F.; Heidari, A.A.; Wu, Z.; Cai, Z.; Alenezi, F.; Mansour, R.F.; Chen, H.; Chen, M. Directional mutation and crossover boosted ant colony optimization with application to COVID-19 X-ray image segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 148, 105810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shami, T.M.; El-Saleh, A.A.; Alswaitti, M.; Al-Tashi, Q.; Summakieh, M.A.; Mirjalili, S. Particle swarm optimization: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 10031–10061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, E.; Gorkemli, B.; Akay, B.; Karaboga, D. A review on the studies employing artificial bee colony algorithm to solve combinatorial optimization problems. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 115, 105311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, M.; Oluwasanmi, A.; Yimen, N.; Qinxiu, Z.; Ukwuoma, C.C.; Ezurike, B.; Bamisile, O. Development and comparison of two novel hybrid neural network models for hourly solar radiation prediction. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Changsheng, Z.; Liu, J.; Rong, Y. Application of neural-network hybrid models in estimating the infection functions of nonlinear epidemic models. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.05018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floresta, G.; Zagni, C.; Gentile, D.; Patamia, V.; Rescifina, A. Artificial intelligence technologies for COVID-19 de novo drug design. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zeng, N.; Wu, P.; Clawson, K. Cov-Net: A computer-aided diagnosis method for recognizing COVID-19 from chest X-ray images via machine vision. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 207, 118029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, J.; Alsubai, S. A Hybrid Deep Fused Learning Approach to Segregate Infectious Diseases. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2023, 74, 4239–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, X.; Jia, L.; Wei, Y.; Li, X.A.; Chen, F. Epi-DNNs: Epidemiological priors informed deep neural networks for modeling COVID-19 dynamics. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 158, 106693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathamuthu, N.D.; Subramaniam, S.; Le, Q.H.; Muthusamy, S.; Panchal, H.; Sundararajan, S.C.M.; Alrubaie, A.J.; Zahra, M.M.A. A deep transfer learning-based convolution neural network model for COVID-19 detection using computed tomography scan images for medical applications. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2023, 175, 103317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol Doğan, G.; Uzbaş, B. Diagnosis of COVID-19 from blood parameters using convolutional neural network. Soft Comput. 2023, 27, 10555–10570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.R.; Murray, T.J.; Chen, C. Predicting sun spots using a layered perceptron neural network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1996, 7, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, M.S.; Goni, S.; Tasneem, P.; Vintha, K.; Kumar, D.S. Unipolar and Bipolar Mathematical Inference of Weight Adjustment Mode of Single Layer Perceptron on AND Logic Gate. In Proceedings of the 2023 Third International Conference on Advances in Electrical, Computing, Communication and Sustainable Technologies (ICAECT), Bhilai, India, 5–6 January 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sivasankari, S.; Surendiran, J.; Yuvaraj, N.; Ramkumar, M.; Ravi, C.; Vidhya, R. Classification of diabetes using multilayer perceptron. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Distributed Computing and Electrical Circuits and Electronics (ICDCECE), Ballari, India, 23–24 April 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Tong, Y.; Neri, F. An ensemble of differential evolution and Adam for training feed-forward neural networks. Inf. Sci. 2022, 608, 453–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Sun, W.; Jha, S.K. A Lightweight CNN Based on Transfer Learning for COVID-19 Diagnosis. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 72, 1123–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, R.; Jones, E.; Babar, M.; Jan, T.; Zafar, M.; Alhussain, T. Speech emotion recognition using deep learning techniques: A review. IEEE Access. 2019, 7, 117327–117345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, A.; Navimipour, N.J.; Unal, M. A Secure Intrusion Detection Platform Using Blockchain and Radial Basis Function Neural Networks for Internet of Drones. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 8445–8454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olabanjo, O.A.; Wusu, A.S.; Manuel, M. A machine learning prediction of academic performance of secondary school students using radial basis function neural network. Trends Neurosci. Educ. 2022, 29, 100190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Gales, M.J.; Woodland, P.C. Efficient lattice rescoring using recurrent neural network language models. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Florence, Italy, 4–9 May 2014; pp. 4908–4912. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Jiang, Q.; Shen, Y.; Qian, C.; Xu, F.; Zhu, Q. Application of recurrent neural network to mechanical fault diagnosis: A review. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2022, 36, 527–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Wei, C.; Wang, B.; Yang, J.; Xu, X.; Wu, S.; Huang, S. Well performance prediction based on Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) neural network. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 208, 109686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Tang, L.; Gu, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, L. Displacement prediction of Jiuxianping landslide using gated recurrent unit (GRU) networks. Acta Geotech. 2022, 17, 1367–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Li, M.; Feng, J.; Wu, Z.; Kong, L. Diffuseq: Sequence to sequence text generation with diffusion models. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.08933. [Google Scholar]
- Varela-Santos, S.; Melin, P. A new modular neural network approach with fuzzy response integration for lung disease classification based on multiple objective feature optimization in chest X-ray images. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 168, 114361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahouda, M.K.; Joe, I. Neural architecture search net-based feature extraction with modular neural network for image classification of copper/cobalt raw minerals. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 72253–72262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Sarkar, A.; Roy, S.; Singh, P.K.; Sarkar, R. COVID-19 chest X-ray detection through blending ensemble of CNN snapshots. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2022, 78, 104000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollias, D.; Arsenos, A.; Kollias, S. Ai-mia: COVID-19 detection and severity analysis through medical imaging. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 677–690. [Google Scholar]
- Kogilavani, S.V.; Prabhu, J.; Sandhiya, R.; Kumar, M.S.; Subramaniam, U.; Karthick, A.; Muhibbullah, M.; Imam, S.B.S. COVID-19 detection based on lung CT scan using deep learning techniques. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 7672196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Abdelsamea, M.M.; Gaber, M.M. Classification of COVID-19 in chest X-ray images using DeTraC deep convolutional neural network. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, M.; Siłka, J.; Woźniak, M. Neural network powered COVID-19 spread forecasting model. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 140, 110203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videla, L.S.; Harita, U.; Chippada, N.; Santhi, C.; Gupta, A.S.G. Convolution Neural Networks based COVID-19 Detection using X-ray Images of Human Chest. In Proceedings of the 2022 8th International Conference on Smart Structures and Systems (ICSSS), Chennai, India, 21–22 April 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, F.; Mao, S.; Huang, Z.; Zeng, T. Detachable image decomposition and illumination mapping search for low-light image enhancement. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2023, 436, 115435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Itbi, A.S.; Alwahhab, A.B.A.; Sahan, A.M. X-ray Covid-19 Detection Based on Scatter Wavelet Transform and Dense Deep Neural Network. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2022, 41, 1255–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, K.J.; Whitaker, M.; Anglin, O.; Milucky, J.; Patel, K.; Pham, H.; Chai, S.J.; Kirley, P.D.; Armistead, I.; McLafferty, S.; et al. Hospitalizations of children and adolescents with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19—COVID-NET, 14 states, July 2021–January 2022. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2022, 71, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; He, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xie, P. COVID-CT-dataset: A CT scan dataset about COVID-19. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.13865. [Google Scholar]
- Theckedath, D.; Sedamkar, R. Detecting affect states using VGG16, ResNet50 and SE-ResNet50 networks. SN Comput. Sci. 2020, 1, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.I.; Shah, J.L.; Bhat, M.M. CoroNet: A deep neural network for detection and diagnosis of COVID-19 from chest X-ray images. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 196, 105581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, T.; Murugan, R.; Mirjalili, S.; Chakrabartty, D.K. OptCoNet: An optimized convolutional neural network for an automatic diagnosis of COVID-19. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 1351–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alom, M.Z.; Rahman, M.; Nasrin, M.S.; Taha, T.M.; Asari, V.K. COVID_MTNet: COVID-19 detection with multi-task deep learning approaches. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.03747. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, R.; Sarkar, H.; Prasad, A.O.; Sahoo, A.K.; Vidyarthi, A.; Barik, R.K. Exploration of Deep Neural Networks and Effect of Optimizer for Pulmonary Disease Diagnosis. SN Comput. Sci. 2023, 4, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhu, F.; Lu, K.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Chen, P.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Z. COVID-19 Classification from Chest X-rays Based on Attention and Knowledge Distillation. In International Conference on Intelligent Computing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 787–798. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, N.K.; Rahman, M.M.; Kabir, M.A. PDCOVIDNet: A parallel-dilated convolutional neural network architecture for detecting COVID-19 from chest X-ray images. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2020, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalane, P.; Patil, S.; Patil, B.; Sharma, D.P. Automatic detection of COVID-19 disease using U-Net architecture based fully convolutional network. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2021, 67, 102518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toraman, S.; Alakus, T.B.; Turkoglu, I. Convolutional capsnet: A novel artificial neural network approach to detect COVID-19 disease from X-ray images using capsule networks. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 140, 110122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lin, Z.Q.; Wong, A. Covid-net: A tailored deep convolutional neural network design for detection of COVID-19 cases from chest X-ray images. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gour, M.; Jain, S. Stacked convolutional neural network for diagnosis of COVID-19 disease from X-ray images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.13817. [Google Scholar]
- Jaiswal, A.K.; Tiwari, P.; Rathi, V.K.; Qian, J.; Pandey, H.M.; Albuquerque, V.H.C. Covidpen: A novel covid-19 detection model using chest x-rays and ct scans. Medrxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, P.; Sadi, M.S.; Islam, M.M. EMCNet: Automated COVID-19 diagnosis from X-ray images using convolutional neural network and ensemble of machine learning classifiers. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2021, 22, 100505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, M.; Javaid, S.; Fahim, H.; Saeed, N. AI for Good: CNN for COVID-19 Detection, Diagnosis, and Personalized Treatment. IEEE Smart Cities Newsletter. 2021. Available online: https://smartcities.ieee.org/newsletter/july-2021/ai-for-good-cnn-for-covid-19-detection-diagnosis-and-personalized-treatment (accessed on 28 June 2023).
- Kaggle. COVID-19 Radiography Database; Kaggle: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- BIMCV-COVID19. Available online: https://bimcv.cipf.es/bimcv-projects/bimcv-covid19/#1590858128006-9e640421-6711 (accessed on 29 December 2021).
- COVID-19-Image. Available online: https://github.com/ml-workgroup/covid-19-image-repository/tree/master/png (accessed on 1 January 2021).
- COVID-19 DATABASE-SIRM. Available online: https://sirm.org/category/senza-categoria/covid-19/ (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Covi19 Image. Available online: https://eurorad.org (accessed on 1 January 2021).
- Covid Chest X-ray Dataset. Available online: https://github.com/ieee8023/covid-chestxray-dataset (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- COVID-19 Chest X-ray Image. 2021. Available online: https://figshare.com/articles/COVID-19_Chest_X-Ray_Image_Repository/12580328 (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- COVID-CXNet. Available online: https://github.com/armiro/COVID-CXNet (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Chui, K.T.; Gupta, B.B.; Alhalabi, W.; Alzahrani, F.S. An MRI scans-based Alzheimer’s disease detection via convolutional neural network and transfer learning. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, V.; Madgi, M.; Kiran, A. Early prediction of Alzheimer’s disease using convolutional neural network: A review. Egypt. J. Neurol. Psychiatry Neurosurg. 2022, 58, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lu, H.; Pan, X.; Xu, M.; Lan, R.; Luo, X. Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease via an attention-based multi-scale convolutional neural network. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 238, 107942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houria, L.; Belkhamsa, N.; Cherfa, A.; Cherfa, Y. Multi-modality MRI for Alzheimer’s disease detection using deep learning. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2022, 45, 1043–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, A.; Luo, S.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Convolutional neural networks for Alzheimer’s disease detection on MRI images. J. Med. Imaging 2021, 8, 024503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, D.; El-Khatib, M.; El-Khatib, H.; Ichim, L. New trends in melanoma detection using neural networks: A systematic review. Sensors 2022, 22, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunjan, V.K.; Singh, N.; Shaik, F.; Roy, S. Detection of lung cancer in CT scans using grey wolf optimization algorithm and recurrent neural network. Health Technol. 2022, 12, 1197–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamrani, D.; Cherradi, B.; El Gannour, O.; Bouqentar, M.A.; Bahatti, L. Brain tumor detection using mri images and convolutional neural network. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2022, 13, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, A.I.; Aly, W.; Aly, S. MBTFCN: A novel modular fully convolutional network for MRI brain tumor multi-classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 212, 118776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinyelu, A.A.; Zaccagna, F.; Grist, J.T.; Castelli, M.; Rundo, L. Brain tumor diagnosis using machine learning, convolutional neural networks, capsule neural networks and vision transformers, applied to MRI: A survey. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, P.; Pant, B.; Elarabawy, M.M.; Abd-Elnaby, M.; Mohd, N.; Dhiman, G.; Sharma, S. Cnn based multiclass brain tumor detection using medical imaging. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 1830010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vankdothu, R.; Hameed, M.A.; Fatima, H. A brain tumor identification and classification using deep learning based on CNN-LSTM method. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 101, 107960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Maitra, M. MRI-based brain tumour image detection using CNN based deep learning method. Neurosci. Inform. 2022, 2, 100060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, S.; Rezayi, S.; Keshavarz, H.; R Niakan Kalhori, S. MRI-based brain tumor detection using convolutional deep learning methods and chosen machine learning techniques. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2023, 23, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puneet; Kumar, R.; Gupta, M. Optical coherence tomography image-based eye disease detection using deep convolutional neural network. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2022, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarki, R.; Ahmed, K.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, K. Convolutional neural network for multi-class classification of diabetic eye disease. EAI Endorsed Trans. Scalable Inf. Syst. 2022, 9, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akil, M.; Elloumi, Y.; Kachouri, R. Detection of retinal abnormalities in fundus image using CNN deep learning networks. In State of the Art in Neural Networks and Their Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 19–61. [Google Scholar]
- Tayal, A.; Gupta, J.; Solanki, A.; Bisht, K.; Nayyar, A.; Masud, M. DL-CNN-based approach with image processing techniques for diagnosis of retinal diseases. Multimed. Syst. 2022, 28, 1417–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, P.; Bhatnaghar, C. Retinal Disease Classification Using Convolutional Neural Networks Algorithm. Turk. J. Comput. Math. Educ. (TURCOMAT) 2021, 12, 5681–5689. [Google Scholar]
- Vu, T.D.; Ho, N.H.; Yang, H.J.; Kim, J.; Song, H.C. Non-white matter tissue extraction and deep convolutional neural network for Alzheimer’s disease detection. Soft Comput. 2018, 22, 6825–6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, J.; Zhang, Y. An ensemble of deep convolutional neural networks for Alzheimer’s disease detection and classification. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1712.01675. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, J.; Thibeau-Sutre, E.; Diaz-Melo, M.; Samper-González, J.; Routier, A.; Bottani, S.; Dormont, D.; Durrleman, S.; Burgos, N.; Colliot, O.; et al. Convolutional neural networks for classification of Alzheimer’s disease: Overview and reproducible evaluation. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 63, 101694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, A.; Anwar, S.; Awais, M.; Rehman, S. A deep CNN based multi-class classification of Alzheimer’s disease using MRI. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Imaging systems and techniques (IST), Beijing, China, 18–20 October 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Wang, H.; Jiang, H.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xin, J. Breast cancer detection using extreme learning machine based on feature fusion with CNN deep features. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 105146–105158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alakwaa, W.; Nassef, M.; Badr, A. Lung cancer detection and classification with 3D convolutional neural network (3D-CNN). Lung Cancer 2017, 8, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.; Gujrathi, I.; Haider, M.A.; Khalvati, F. Prostate cancer detection using deep convolutional neural networks. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Cohen, A.; Diamant, I.; Klang, E.; Amitai, M.; Greenspan, H. Fully convolutional network for liver segmentation and lesions detection. In Deep Learning and Data Labeling for Medical Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Abiwinanda, N.; Hanif, M.; Hesaputra, S.T.; Handayani, A.; Mengko, T.R. Brain tumor classification using convolutional neural network. In World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering 2018; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Seetha, J.; Raja, S.S. Brain tumor classification using convolutional neural networks. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2018, 11, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaldera, H.; Gunasekara, S.R.; Dissanayake, M.B. Brain tumor classification and segmentation using faster R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2019 Advances in Science and Engineering Technology International Conferences (ASET), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 26 March–10 April 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sarhan, A.M. Brain tumor classification in magnetic resonance images using deep learning and wavelet transform. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 2020, 13, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaiselvi, T.; Padmapriya, S.; Sriramakrishnan, P.; Somasundaram, K. Deriving tumor detection models using convolutional neural networks from MRI of human brain scans. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 2020, 12, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, N.; Narasimhan, V.; Vinjimoor, S.K.; Aiyer, J. Deep CNN framework for retinal disease diagnosis using optical coherence tomography images. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2021, 12, 7569–7580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnour, M.; Himeur, Y.; Fadli, F.; Mohammedsherif, H.; Meskin, N.; Ahmad, A.M.; Petri, I.; Rezgui, Y.; Hodorog, A. Neural network-based model predictive control system for optimizing building automation and management systems of sports facilities. Appl. Energy 2022, 318, 119153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, J.; Sim, D. Low-complexity CNN with 1D and 2D filters for super-resolution. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2020, 17, 2065–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharana, K.; Mondal, S.; Nemade, B. A review: Data pre-processing and data augmentation techniques. Glob. Transitions Proc. 2022, 3, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blind, K.; von Laer, M. Paving the path: Drivers of standardization participation at ISO. J. Technol. Transf. 2022, 47, 1115–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stergiopoulos, V.; Vassilakopoulos, M.; Tousidou, E.; Corral, A. An Application of ANN Hyper-Parameters Tuning in the Field of Recommender Systems; Technical Report; Data Structuring & Engineering Laboratory, University of Thessaly: Volos, Greece, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, A.; Han, X.; Cohn, T.; Baldwin, T.; Frermann, L. Optimising equal opportunity fairness in model training. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.02393. [Google Scholar]
- Gulzar, Y. Fruit image classification model based on MobileNetV2 with deep transfer learning technique. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xu, S.; Li, J.; Guo, A.J. Group-based network pruning via nonlinear relationship between convolution filters. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 9274–9288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okey, O.D.; Melgarejo, D.C.; Saadi, M.; Rosa, R.L.; Kleinschmidt, J.H.; Rodríguez, D.Z. Transfer learning approach to IDS on cloud IoT devices using optimized CNN. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 1023–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, V.G.; Pedreira, C.E. Recent advances in decision trees: An updated survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 4765–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, L. Fine tuning attribute weighted naive Bayes. Neurocomputing 2022, 488, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, M.; Goyal, A.; Choudhary, A. A comparative analysis of K-nearest neighbor, genetic, support vector machine, decision tree, and long short term memory algorithms in machine learning. Decis. Anal. J. 2022, 3, 100071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balyan, A.K.; Ahuja, S.; Lilhore, U.K.; Sharma, S.K.; Manoharan, P.; Algarni, A.D.; Elmannai, H.; Raahemifar, K. A hybrid intrusion detection model using ega-pso and improved random forest method. Sensors 2022, 22, 5986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikotun, A.M.; Ezugwu, A.E.; Abualigah, L.; Abuhaija, B.; Heming, J. K-means clustering algorithms: A comprehensive review, variants analysis, and advances in the era of big data. Inf. Sci. 2022, 622, 178–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, R.A.; Saeed, N.; Masood, M.; Fard, Y.M.; Alouini, M.S.; Al-Naffouri, T.Y. Deep Learning in the Industrial Internet of Things: Potentials, Challenges and Emerging Applications. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 11016–11040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Duan, X.; Tang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y. Non-interactive and privacy-preserving neural network learning using functional encryption. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2023, 145, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubab, S.; Khan, M.M.; Uddin, F.; Abbas Bangash, Y.; Taqvi, S.A.A. A Study on AI-based Waste Management Strategies for the COVID-19 Pandemic. ChemBioEng Rev. 2022, 9, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaysha, S.; Moreb, M.; Zolait, A. Detecting Network Traffic-based Attacks Using ANNs. Int. J. Comput. Digit. Syst. 2023, 13, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsalan, M.; Di Matteo, D.; Imtiaz, S.; Abbas, Z.; Vlassov, V.; Issakov, V. Energy-Efficient Privacy-Preserving Time-Series Forecasting on User Health Data Streams. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications (TrustCom), Wuhan, China, 9–11 December 2022; pp. 541–546. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Shqeerat, K.H.A. Securing a Question-Based Multi-factor Authentication System Using LSB Steganography Technique. In International Conference on Business and Technology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 1118–1128. [Google Scholar]
- Kalam, S.; Yousuf, U.; Abu-Khamsin, S.A.; Waheed, U.B.; Khan, R.A. An ANN model to predict oil recovery from a 5-spot waterflood of a heterogeneous reservoir. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 210, 110012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krichen, M.; Ammi, M.; Mihoub, A.; Almutiq, M. Blockchain for modern applications: A survey. Sensors 2022, 22, 5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharany, S.; Sharma, S.; Khalaf, O.I.; Abdulsahib, G.M.; Al Humaimeedy, A.S.; Aldhyani, T.H.; Maashi, M.; Alkahtani, H. A systematic survey on energy-efficient techniques in sustainable cloud computing. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-juboori, A.M.; Alsaeedi, A.H.; Nuiaa, R.R.; Alyasseri, Z.A.A.; Sani, N.S.; Hadi, S.M.; Mohammed, H.J.; Musawi, B.A.; Amin, M.M. A hybrid cracked tiers detection system based on adaptive correlation features selection and deep belief neural networks. Symmetry 2023, 15, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, S.; Wu, Z.; Hamid, Z.; Zeadally, S.; Fahim, H. Temperature-aware routing protocol for Intrabody Nanonetworks. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2021, 183, 103057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, N.; Loukil, M.H.; Sarieddeen, H.; Al-Naffouri, T.Y.; Alouini, M.S. Body-Centric Terahertz Networks: Prospects and Challenges. IEEE Trans. Mol. Biol. Multi-Scale Commun. 2022, 8, 138–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahim, H.; Javaid, S.; Li, W.; Mabrouk, I.B.; Al Hasan, M.; Rasheed, M.B.B. An efficient routing scheme for intrabody nanonetworks using artificial bee colony algorithm. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 98946–98957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, S.; Wu, Z.; Fahim, H.; Mabrouk, I.B.; Al-Hasan, M.; Rasheed, M.B. Feedforward Neural Network-Based Data Aggregation Scheme for Intrabody Area Nanonetworks. IEEE Syst. J. 2020, 16, 1796–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahim, H.; Li, W.; Javaid, S.; Sadiq Fareed, M.M.; Ahmed, G.; Khattak, M.K. Fuzzy logic and bio-inspired firefly algorithm based routing scheme in intrabody nanonetworks. Sensors 2019, 19, 5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, F.; Yue, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, H.S. Advancing biosensors with machine learning. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 3346–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Epochs | Accuracy | Precision | F1-Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 97.8% | 97.93% | 97.92% |
| Diseases | Ref. | Model | Dataset | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alzheimer | [114] | Deep CNN for Alzheimer’s disease detection | Total 615 MRI scan images | 94.48% |
| [115] | An ensemble of deep CNN | OASIS dataset comprises 416 MRI scan images | 93.18% | |
| [116] | CNN for classification of Alzheimer’s disease | ADNI dataset comprises a total of 1455 MRI scan images | 96% | |
| [117] | A Deep CNN based multiclass classification of Alzheimer’s disease | Dataset comprises of total 355 MRI scans images | 98.8% | |
| Cancer | [118] | Breast cancer detection using extreme learning machine based on feature fusion with CNN deep features | Total 400 mammography images | 81.75% |
| [119] | Lung cancer detection and class- ification with 3D CNN | Kaggle Data Science Bowl (DSB) comprises a total of 1397 MRI scan images | 86.6% | |
| [120] | Prostate cancer detection using deep CNN | Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging dataset comprises a total of 427 images | 84% | |
| [121] | Fully CNN for liver segmentation and lesions detection | Dataset comprises of total 88 CT scan images | 86% | |
| [122] | Brain tumor classification using CNN | Radiopaedia and brain tumor image segmentation benchmark 2015 datasets are used | 97.5% | |
| [123] | Brain tumor detection using CNN | BRATS dataset comprises 217 MRI images | 97.87% | |
| [124] | Brain tumor classification and segmentation using faster R-CNN | A total of 218 MRI images are used | 94.6% | |
| [125] | Brain tumor classification in magnetic resonance images using deep learning and wavelet transform | MRI image dataset | 96% | |
| [126] | Deriving tumor detection models using CNN from MRI of human brain scans | BraTS2013 dataset and WBA dataset are used | 96-99% | |
| Retinal | [127] | Deep CNN framework for retinal disease diagnosis | OCT image dataset containing a total of 12,000 images | 95.7% |
| [111] | Detection of retinal abnormalities using CNN | Dataset comprises a total of 1110 fundus images | 95.8% | |
| [112] | DL-CNN-based approach diagnosis of retinal diseases | OCT image dataset comprises a total of 84,495 images | 96.5% | |
| [113] | Retinal disease classification using CNN algorithm | OCT image dataset comprises a total of 108,312 images | 98.73% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azeem, M.; Javaid, S.; Khalil, R.A.; Fahim, H.; Althobaiti, T.; Alsharif, N.; Saeed, N. Neural Networks for the Detection of COVID-19 and Other Diseases: Prospects and Challenges. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 850. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070850
Azeem M, Javaid S, Khalil RA, Fahim H, Althobaiti T, Alsharif N, Saeed N. Neural Networks for the Detection of COVID-19 and Other Diseases: Prospects and Challenges. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(7):850. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070850
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzeem, Muhammad, Shumaila Javaid, Ruhul Amin Khalil, Hamza Fahim, Turke Althobaiti, Nasser Alsharif, and Nasir Saeed. 2023. "Neural Networks for the Detection of COVID-19 and Other Diseases: Prospects and Challenges" Bioengineering 10, no. 7: 850. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070850
APA StyleAzeem, M., Javaid, S., Khalil, R. A., Fahim, H., Althobaiti, T., Alsharif, N., & Saeed, N. (2023). Neural Networks for the Detection of COVID-19 and Other Diseases: Prospects and Challenges. Bioengineering, 10(7), 850. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070850









