ClearF++: Improved Supervised Feature Scoring Using Feature Clustering in Class-Wise Embedding and Reconstruction
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Algorithm 1 Algorithm ClearF++: Supervised feature scoring method using feature clustering in the class-wise embedding and reconstruction method. |
|
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. ClearF-One: Simplifying Bottleneck Layer Selection
2.2. ClearF++: Advanced Feature Selection via Feature-Wise Clustering
3. Results
3.1. Datasets
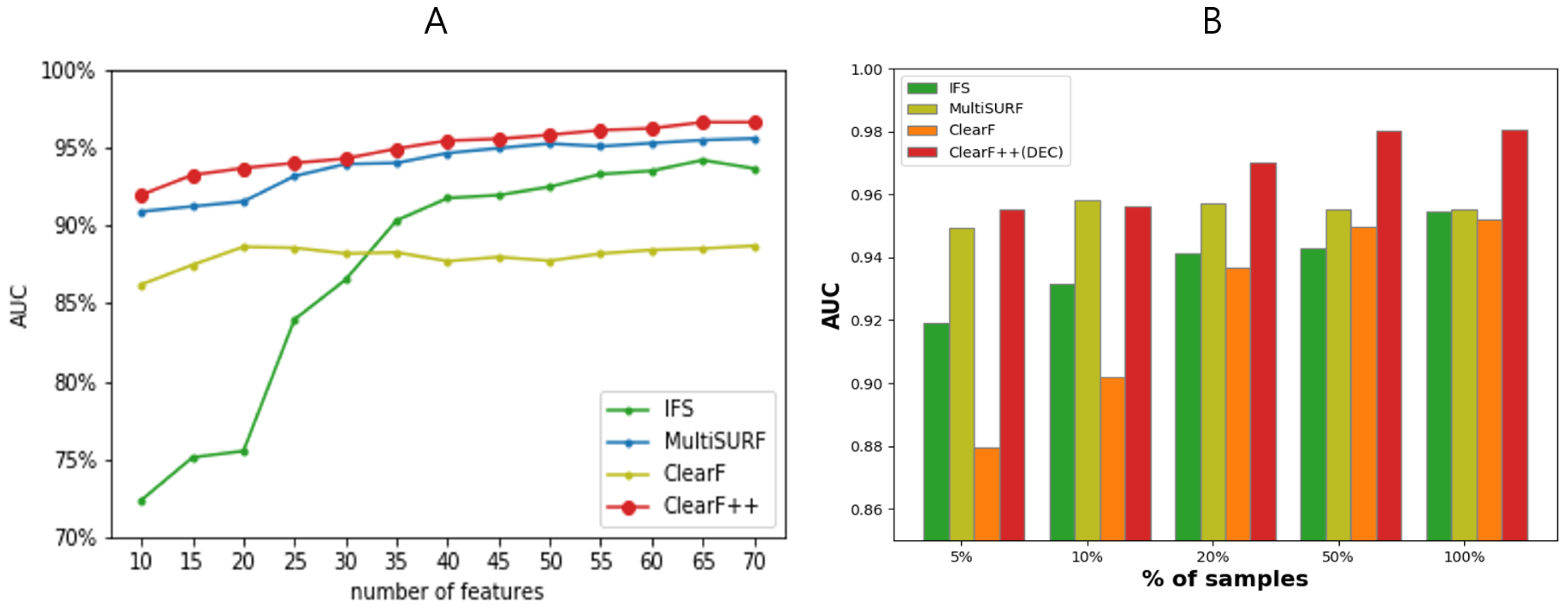
3.2. Performance Evaluation on Multiple Benchmark Datasets
3.3. Performance Evaluation across Varying Feature and Sample Sizes
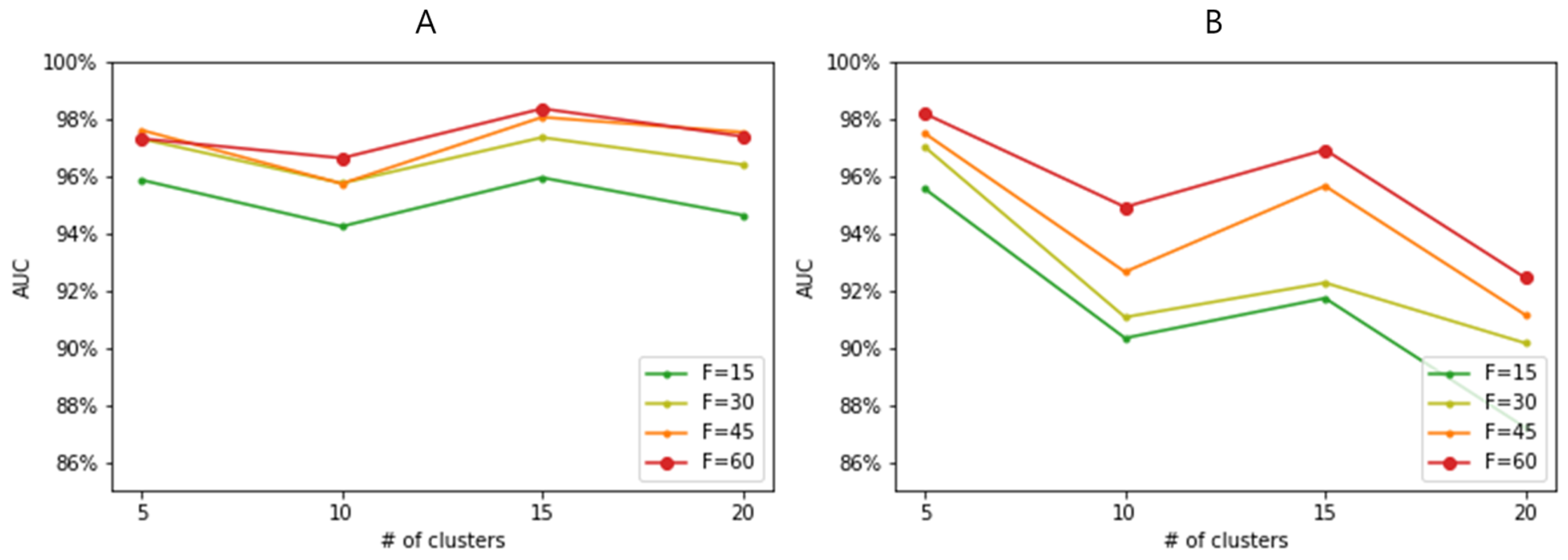
3.4. Effect of Feature-Wise Clustering Algorithms
3.5. Computational Cost Validation
3.6. Functional Enrichment Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Group, B.D.W.; Atkinson, A.J., Jr.; Colburn, W.A.; DeGruttola, V.G.; DeMets, D.L.; Downing, G.J.; Hoth, D.F.; Oates, J.A.; Peck, C.C.; Schooley, R.T.; et al. Biomarkers and surrogate endpoints: Preferred definitions and conceptual framework. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 69, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.H.; Lushington, G.H.; Visvanathan, M. A filter-based feature selection approach for identifying potential biomarkers for lung cancer. J. Clin. Bioinfor. 2011, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeel, T.; Helleputte, T.; Van de Peer, Y.; Dupont, P.; Saeys, Y. Robust biomarker identification for cancer diagnosis with ensemble feature selection methods. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.T.; Blackwood, N.O.; Taroni, J.N.; Fu, W.; Breitenstein, M.K. Integrated machine learning pipeline for aberrant biomarker enrichment (i-mAB): Characterizing clusters of differentiation within a compendium of systemic lupus erythematosus patients. AMIA Annu. Symp. Proc. 2018, 2018, 1358–1367. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Yu, W. Stable feature selection for biomarker discovery. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2010, 34, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemphill, E.; Lindsay, J.; Lee, C.; Măndoiu, I.I.; Nelson, C.E. Feature selection and classifier performance on diverse bio- logical datasets. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15 (Suppl. S13), S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cheng, K.; Wang, S.; Morstatter, F.; Trevino, R.P.; Tang, J.; Liu, H. Feature Selection: A Data Perspective. ACM Comput. Surv. 2017, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.C. Statistics and Data Analysis in Geology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, M.A. Correlation-Based Feature Selection for Machine Learning. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Waikato, Hamilton, New Zeland, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Robnik-Šikonja, M.; Kononenko, I. Theoretical and Empirical Analysis of ReliefF and RReliefF. Mach. Learn. 2003, 53, 23–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanowicz, R.J.; Olson, R.S.; Schmitt, P.; Meeker, M.; Moore, J.H. Benchmarking relief-based feature selection methods for bioinformatics data mining. J. Biomed. Inform. 2018, 85, 168–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Long, F.; Ding, C. Feature selection based on mutual information criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2005, 27, 1226–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleuret, F. Fast Binary Feature Selection with Conditional Mutual Information. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2004, 5, 1531–1555. [Google Scholar]
- Leem, S.; Hwan Jeong, H.; Lee, J.; Wee, K.; Sohn, K.A. Fast detection of high-order epistatic interactions in genome-wide association studies using information theoretic measure. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2014, 50, 19–28, Advances in Bioinformatics: Twelfth Asia Pacific Bioinformatics Conference (APBC2014). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, R. Feature selection based on mutual information with correlation coefficient. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 5457–5474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sarem, M.; Saeed, F.; Alkhammash, E.H.; Alghamdi, N.S. An aggregated mutual information based feature selection with machine learning methods for enhancing iot botnet attack detection. Sensors 2022, 22, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Sun, J.; Yao, K.; Xu, M.; Cao, Y. A variable selection method based on mutual information and variance inflation factor. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 268, 120652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Gao, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, P.; Gao, W. Feature-specific mutual information variation for multi-label feature selection. Inf. Sci. 2022, 593, 449–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohyr-Nielsen, M. Loss of Information by Discretizing Hydrologic Series; Colorado State University Hydrology Papers; Colorado State University: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Jeong, H.H.; Sohn, K.A. ClearF: A supervised feature scoring method to find biomarkers using class-wise embedding and reconstruction. BMC Med. Genom. 2019, 12, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. Unsupervised Deep Embedding for Clustering Analysis. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning–ICML’16, New York, NY, USA, 19–24 June 2016; Volume 48, pp. 478–487. [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann, A.; Torre, D.; Keenan, A.B.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lee, H.J.; Wang, L.; Silverstein, M.C.; Ma’ayan, A. Massive mining of publicly available RNA-seq data from human and mouse. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobel, B.; Klein, H.; Leparc, G.; Stierstorfer, B.E.; Gantner, F.; Kreuz, S. Time and phenotype-dependent transcriptome analysis in AAV-TGFβ1 and Bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis models. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Oskotsky, B.; Butte, A.J.; Hu, Z. Systematic identification of ACE2 expression modulators reveals cardiomyopathy as a risk factor for mortality in COVID-19 patients. Genome Biol. 2022, 23, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golub, T.R.; Slonim, D.K.; Tamayo, P.; Huard, C.; Gaasenbeek, M.; Mesirov, J.P.; Coller, H.; Loh, M.L.; Downing, J.R.; Caligiuri, M.A.; et al. Molecular classification of cancer: Class discovery and class prediction by gene expression monitoring. Science 1999, 286, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alon, U.; Barkai, N.; Notterman, D.A.; Gish, K.; Ybarra, S.; Mack, D.; Levine, A.J. Broad patterns of gene expression revealed by clustering analysis of tumor and normal colon tissues probed by oligonucleotide arrays. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 6745–6750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roffo, G.; Melzi, S.; Castellani, U.; Vinciarelli, A.; Cristani, M. Infinite Feature Selection: A Graph-based Feature Filtering Approach. IEEE Trans. Pattern. Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 4396–4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Bardes, E.E.; Aronow, B.J.; Jegga, A.G. ToppGene Suite for gene list enrichment analysis and candidate gene prioritization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W305–W311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Hu, M.; Huang, K.; Lin, S.; Du, H. Roles of Proteoglycans and Glycosaminoglycans in Cancer Development and Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morla, S. Glycosaminoglycans and Glycosaminoglycan Mimetics in Cancer and Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Osada, T.; Wang, Y.; Yu, L.; Sakakura, K.; Katayama, A.; McCarthy, J.B.; Brufsky, A.; Chivukula, M.; Khoury, T.; et al. CSPG4 protein as a new target for the antibody-based immunotherapy of triple-negative breast cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2010, 102, 1496–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arokiasamy, S.; Balderstone, M.J.M.; De Rossi, G.; Whiteford, J.R. Syndecan-3 in Inflammation and Angiogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Wang, C.; Xiao, Y.; Sheng, N.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Mo, W.; Jing, N.; Hu, G. NDST1-dependent heparan sulfate regulates BMP signaling and internalization in lung development. J. Cell. Sci. 2009, 122, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, C.; Reis, C.A.; Vivès, R.R.; Magalhães, A. Heparan Sulfate Biosynthesis and Sulfation Profiles as Modulators of Cancer Signalling and Progression. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 778752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, Y.; Amatya, V.J.; Kushitani, K.; Kambara, T.; Suzuki, R.; Fujii, Y.; Tsutani, Y.; Miyata, Y.; Okada, M.; Takeshima, Y. Glypican-1 is a novel immunohistochemical marker to differentiate poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma from solid predominant adenocarcinoma of the lung. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karna, E.; Surazynski, A.; Palka, J. Collagen metabolism disturbances are accompanied by an increase in prolidase activity in lung carcinoma planoepitheliale. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2000, 81, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eni-Aganga, I.; Lanaghan, Z.M.; Balasubramaniam, M.; Dash, C.; Pandhare, J. PROLIDASE: A Review from Discovery to its Role in Health and Disease. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 723003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballester, B.; Milara, J.; Cortijo, J. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer: Mechanisms and Molecular Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galicka, A.; Wolczyñski, S.; Anchim, T.; Surazyñski, A.; Lesniewicz, R.; Palka, J. Defects of type I procollagen metabolism correlated with decrease of prolidase activity in a case of lethal osteogenesis imperfecta. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 2172–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galicka, A.; Wołczyński, S.; Gindzieński, A.; Surazyński, A.; Pałka, J. Gly511 to Ser substitution in the COL1A1 gene in osteogenesis imperfecta type III patient with increased turnover of collagen. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2003, 248, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Xu, T.; Bao, L.; Hu, X.; Jin, T.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Qian, Y.; Lu, X.; Li, L.; et al. CREB3L1 promotes tumor growth and metastasis of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma by remodeling the tumor microenvironment. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.Y.J.; Kuay, K.T.; Tan, T.Z.; Asad, M.; Tang, H.M.; Ng, A.H.C.; Ye, J.; Chung, V.Y.; Thiery, J.P. Functional relevance of a six mesenchymal gene signature in epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) reversal by the triple angiokinase inhibitor, nintedanib (BIBF1120). Oncotarget 2015, 6, 22098–22113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor López, A.; Mazariegos, M.S.; Capuano, A.; Ximénez-Embún, P.; Hergueta-Redondo, M.; Recio, J.Á.; Muñoz, E.; Al-Shahrour, F.; Muñoz, J.; Megías, D.; et al. Inactivation of EMILIN-1 by Proteolysis and Secretion in Small Extracellular Vesicles Favors Melanoma Progression and Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Lin, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, M. Collagen type 1 alpha 1 chain is a novel predictive biomarker of poor progression-free survival and chemoresistance in metastatic lung cancer. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 5723–5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagita, K.; Nagashio, R.; Jiang, S.X.; Kuchitsu, Y.; Hachimura, K.; Ichinoe, M.; Igawa, S.; Fukuda, E.; Goshima, N.; Satoh, Y.; et al. Cytoskeleton-Associated Protein 4 Is a Novel Serodiagnostic Marker for Lung Cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188, 1328–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.K.; Srinivasan, N.; Godbole, R.; More, S.K.; Budnar, S.; Gude, R.P.; Kalraiya, R.D. Role of tumor cell surface lysosome-associated membrane protein-1 (LAMP1) and its associated carbohydrates in lung metastasis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 141, 1563–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Kapoor, V.; Thotala, D.; Hallahan, D.E. TAF15 contributes to the radiation-inducible stress response in cancer. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 2647–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehme, E.; Rahal, Z.; Sinjab, A.; Khalil, A.; Chami, H.; Nemer, G.; Kadara, H. Epigenetic Suppression of the T-box Subfamily 2 (TBX2) in Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| n 1 | Colon | ALL/AML | ARCHS4 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MultiSURF | IFS | ClearF | ClearF++ | MultiSURF | IFS | ClearF | ClearF++ | MultiSURF | IFS | ClearF | ClearF++ | |
| 15 | 0.648 | 0.749 | 0.707 | 0.805 | 0.906 | 0.913 | 0.912 | 0.947 | 0.925 | 0.927 | 0.949 | 0.959 |
| 30 | 0.711 | 0.672 | 0.765 | 0.773 | 0.927 | 0.926 | 0.921 | 0.940 | 0.944 | 0.953 | 0.943 | 0.973 |
| 45 | 0.703 | 0.658 | 0.801 | 0.751 | 0.938 | 0.915 | 0.927 | 0.949 | 0.955 | 0.955 | 0.952 | 0.980 |
| 60 | 0.723 | 0.761 | 0.815 | 0.826 | 0.927 | 0.915 | 0.949 | 0.949 | 0.969 | 0.949 | 0.951 | 0.983 |
| Methods | IFS | MultiSURF | ClearF | ClearF++ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPU times (s) | 398.91 ± 17.22 | 78,515.59 ± 346.53 | 132.68 ± 6.51 | 166.85 ± 10.77 |
| Category | ID | Name | p-Value | q-Value 1 | q-Value 2 | HC 3 | HCG 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BP | GO:0032963 | collagen metabolic process | 7 | 144 | |||
| BP | GO:0030042 | actin filament depolymerization | 5 | 71 | |||
| BP | GO:0032964 | collagen biosynthetic process | 5 | 75 | |||
| MF | GO:0044877 | protein-containing complex binding | 16 | 1726 | |||
| BP | GO:0001568 | blood vessel development | 13 | 1152 | |||
| BP | GO:0035904 | aorta development | 5 | 88 | |||
| BP | GO:0001944 | vasculature development | 13 | 1239 | |||
| BP | GO:0030198 | extracellular matrix organization | 8 | 394 | |||
| BP | GO:0043062 | extracellular structure organization | 8 | 395 | |||
| BP | GO:0045229 | external encapsulating structure organization | 8 | 398 | |||
| Disease | C0268362 | Osteogenesis imperfecta type III (disorder) | 3 | 11 | |||
| Pathway | 1269980 | Heparan sulfate/heparin (HS-GAG) metabolism | 4 | 54 | |||
| Pathway | 1309217 | Defective B3GALT6 causes EDSP2 and SEMDJL1 | 3 | 19 | |||
| Pathway | 1269015 | Defective B3GAT3 causes JDSSDHD | 3 | 19 | |||
| Pathway | 1269014 | Defective B4GALT7 causes EDS, progeroid type | 3 | 19 | |||
| Pathway | 1269981 | A tetrasaccharide linker sequence is required for GAG synthesis | 3 | 26 | |||
| Pathway | 1269011 | Diseases associated with glycosaminoglycan metabolism | 3 | 26 | |||
| Pathway | 1269982 | HS-GAG biosynthesis | 3 | 31 | |||
| Pathway | M39870 | Type I collagen synthesis in the context of osteogenesis imperfecta | 3 | 33 | |||
| Pathway | 1268756 | Unfolded Protein Response (UPR) | 4 | 92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Sohn, K.-A. ClearF++: Improved Supervised Feature Scoring Using Feature Clustering in Class-Wise Embedding and Reconstruction. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070824
Wang S, Kim SY, Sohn K-A. ClearF++: Improved Supervised Feature Scoring Using Feature Clustering in Class-Wise Embedding and Reconstruction. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(7):824. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070824
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Sehee, So Yeon Kim, and Kyung-Ah Sohn. 2023. "ClearF++: Improved Supervised Feature Scoring Using Feature Clustering in Class-Wise Embedding and Reconstruction" Bioengineering 10, no. 7: 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070824
APA StyleWang, S., Kim, S. Y., & Sohn, K.-A. (2023). ClearF++: Improved Supervised Feature Scoring Using Feature Clustering in Class-Wise Embedding and Reconstruction. Bioengineering, 10(7), 824. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10070824






