Multiphysics Interaction Analysis of the Therapeutic Effects of the Sigmoid Sinus Wall Reconstruction in Patients with Venous Pulsatile Tinnitus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients’ Data
2.2. Multiphysics Interaction Geometry Models
2.3. Meshing Generation
2.4. Multiphysics Interaction Governing Equations
2.5. Boundary Condition and Calculation Setting
3. Results
3.1. Blood Flow Velocity
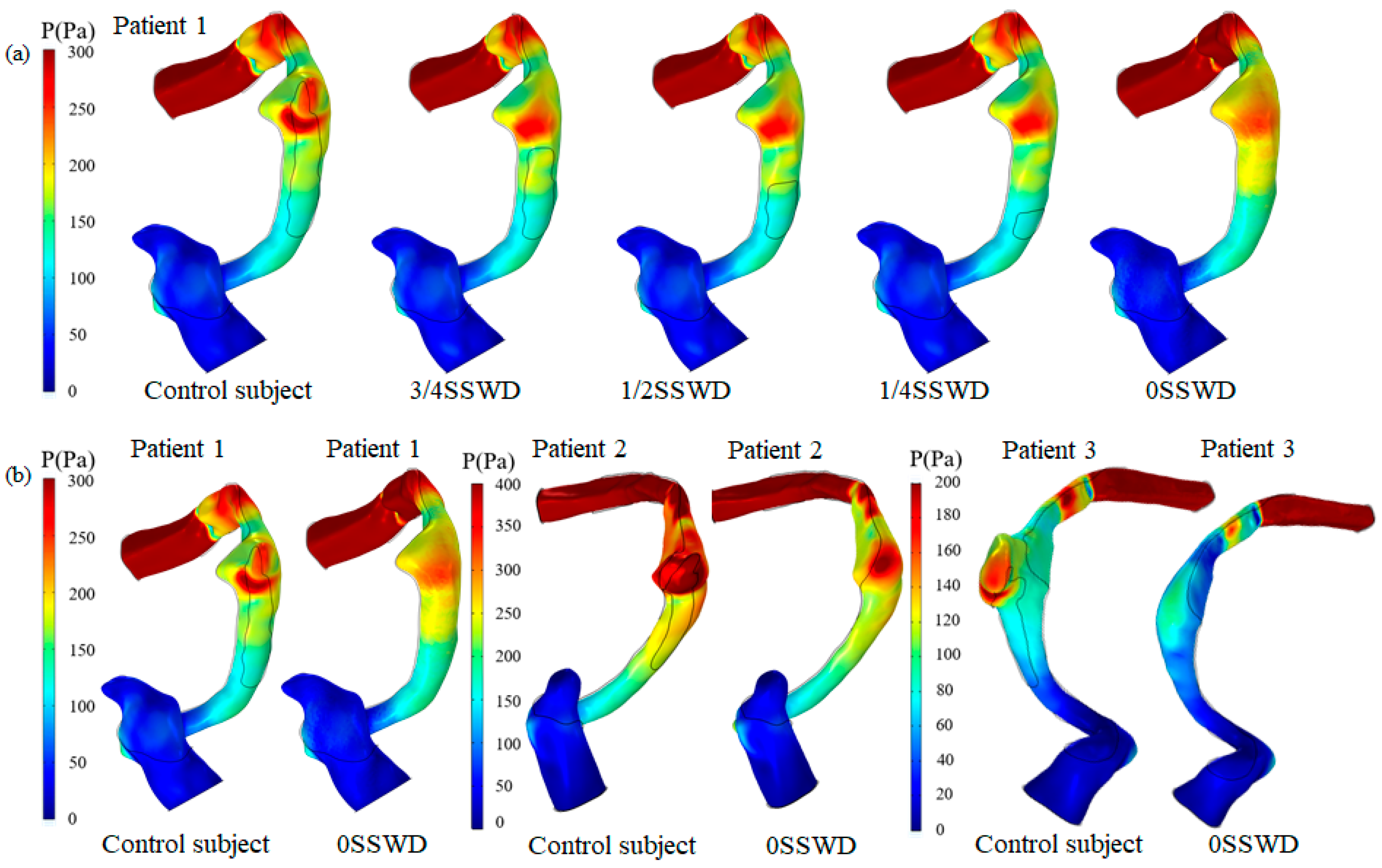
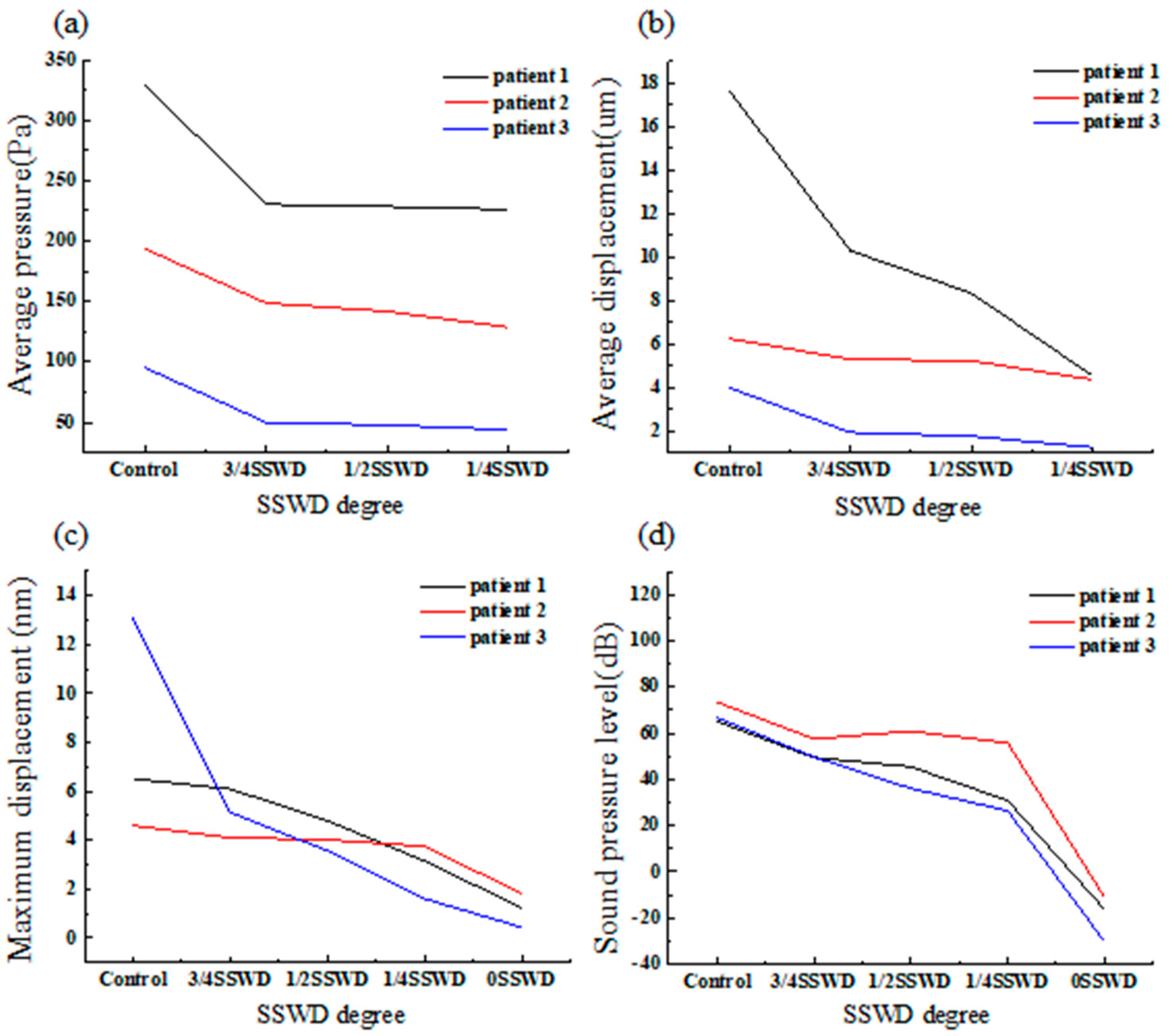
3.2. Blood Wall Pressure
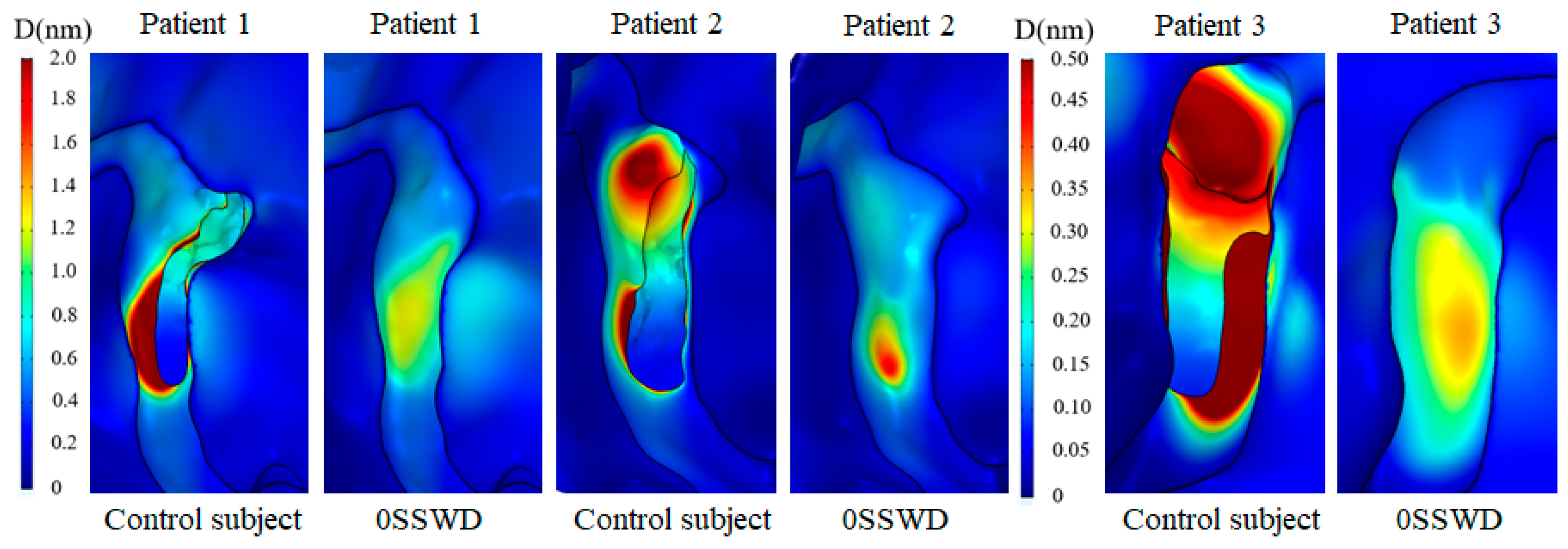
3.3. Average Displacement of the Venous Vessel
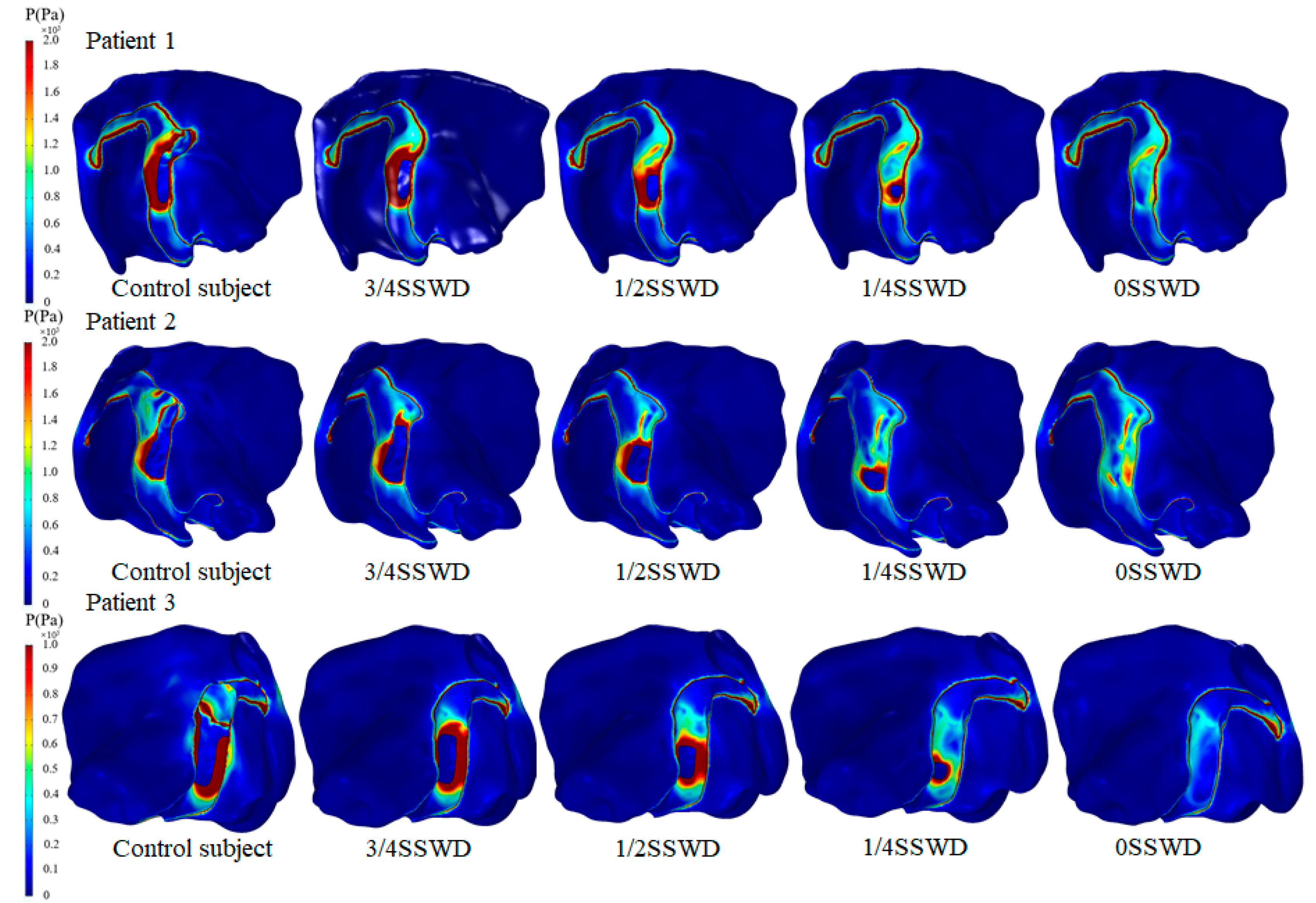
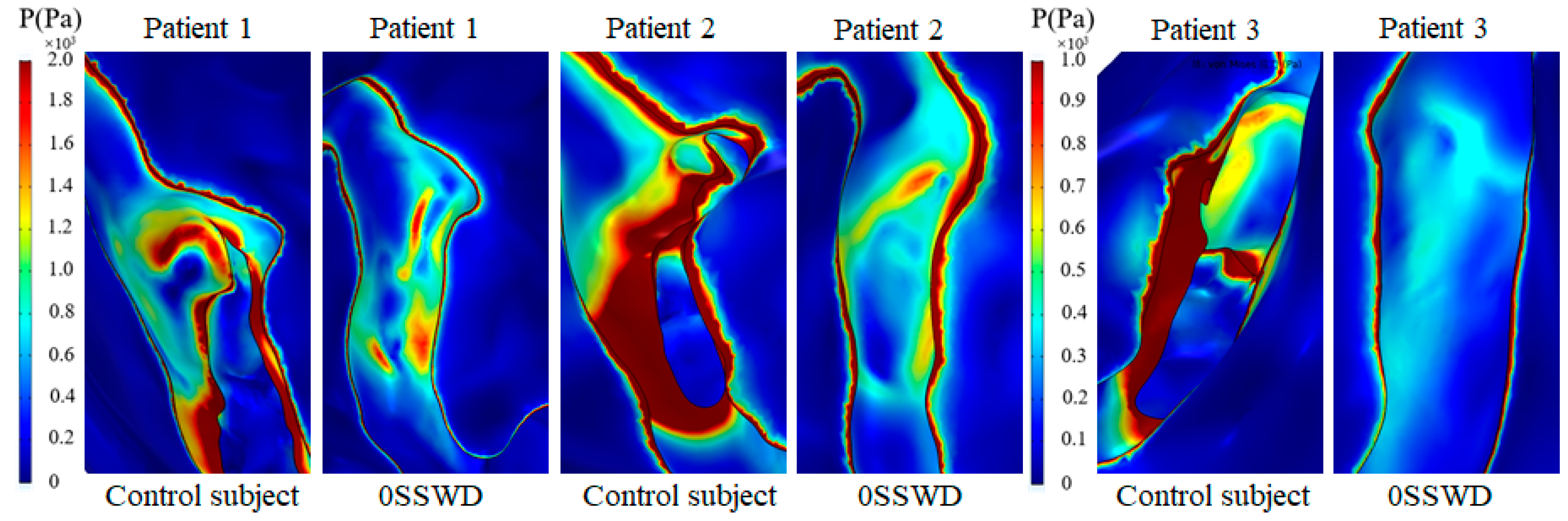
3.4. Von Mises Stress of the Temporal Bone
3.5. Displacement Distribution of the Temporal Bone
3.6. Sound Pressure Level
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| VPT | venous pulsatile tinnitus |
| SS | sigmoid sinus |
| TS | transverse sinus |
| SSD | sigmoid sinus diverticulum |
| SSWD | sigmoid sinus wall dehiscence |
| SSWR | sigmoid sinus wall reconstruction |
| TBAC | temporal bone air cell |
References
- Zhao, P.; Ding, H.; Lv, H.; Li, X.; Qiu, X.; Zeng, R.; Wang, G.; Wei, J.; Jin, L.; Yang, Z.; et al. CT venography correlate of transverse sinus stenosis and venous transstenotic pressure gradient in unilateral pulsatile tinnitus patients with sigmoid sinus wall anomalies. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 2896–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baguley, D.; McFerran, D.; Hall, D. Tinnitus. Lancet 2013, 382, 1600–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lv, H.; Zhao, P.; Liu, Z.; Chen, W.; Gong, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, J.M. Neuroanatomical Alterations in Patients with Early Stage of Unilateral Pulsatile Tinnitus: A Voxel-Based Morphometry Study. Neural Plast. 2018, 2018, 4756471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Zhao, P.-F.; Yang, J.-G.; Liu, Z.-H.; Wang, Z.-C. Incidence of vascular anomalies and variants associated with unilateral venous pulsatile tinnitus in 242 patients based on dual-phase contrast-enhanced computed tomography. Chin. Med. J. 2015, 128, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, S.; Wang, L.; Yang, J.; Mao, R.; Liu, Z.; Fan, Y. Sigmoid sinus cortical plate dehiscence induces pulsatile tinnitus through amplifying sigmoid sinus venous sound. J. Biomech. 2017, 52, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Z.; Li, X.; Zhao, D.; Qiu, X.; Dai, C.; Meng, X.; Huang, S.; Gao, B.; Lv, H.; Li, S.; et al. Hemodynamics study on the relationship between the sigmoid sinus wall dehiscence and the blood flow pattern of the transverse sinus and sigmoid sinus junction. J. Biomech. 2022, 135, 111022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Lv, H.; Dong, C.; Niu, Y.; Xian, J.; Wang, Z. CT evaluation of sigmoid plate dehiscence causing pulsatile tinnitus. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Su, Y.; Dai, J.; Zhang, C.; Wu, J.; Wang, W.; Han, D. Treatment of venous pulsatile tinnitus by compression reconstruction of sigmoid sinus. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2021, 141, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.P.; Zeng, R.; Ma, X.B.; Liu, Z.H.; Wang, Z.C.; Gong, S.S. Surgical treatment of pulsatile tinnitus caused by the sigmoid sinus diverticulum: A preliminary study. Medicine 2015, 94, e882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhao, P.; Lv, H.; Liu, X.; Zeng, R.; Wang, G.; Gong, S.; Wang, Z. Temporal bone contrast-enhanced high-resolution CT evaluation of pulsatile tinnitus after sigmoid sinus wall reconstruction. Acta Radiol. 2019, 60, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Xia, J.; Jin, L.; Qiao, A.; Su, T.; Li, Z.; Xiong, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z. Computational fluid dynamics study of the effect of transverse sinus stenosis on the blood flow pattern in the ipsilateral superior curve of the sigmoid sinus. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 6286–6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliano, A.F.; Ginat, D.T.; Moonis, G. Imaging Review of the Temporal Bone: Part II. Traumatic, Postoperative, and Noninflammatory Nonneoplastic Conditions. Radiology 2015, 276, 655–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Yang, Q.; Yang, Z.; Xia, J.; Su, T.; Yu, J.; Jin, L.; Qiao, A. Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulation of Hemodynamic Alterations in Sigmoid Sinus Diverticulum and Ipsilateral Upstream Sinus Stenosis After Stent Implantation in Patients with Pulsatile Tinnitus. World Neurosurg. 2017, 106, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.Y.; Zhao, P.F.; Ding, H.Y.; Li, X.S.; Lv, H.; Yang, Z.H.; Gong, S.S.; Jin, L.; Wang, Z.C. Bone remodeling in sigmoid sinus diverticulum after stenting for transverse sinus stenosis in pulsatile tinnitus: A case report. World J. Clin. Cases 2021, 9, 2320–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Z.; Liu, L.; Sun, Y.; Gao, B.; Lv, H.; Zhao, P.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z. Multiphysics coupling numerical simulation of flow-diverting stents in the treatment of patients with pulsatile tinnitus. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 2021, 37, e3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessonov, N.; Sequeira, A.; Simakov, S.; Vassilevskii, Y.; Volpert, V. Methods of Blood Flow Modelling. Math. Model. Nat. Phenom. 2015, 11, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Oertel, H.; Schenkel, T. Fluid-structure coupled CFD simulation of the left ventricular flow during filling phase. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 33, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Qiu, X.; Gao, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, P.; Wang, Z. Multiphysics coupling study on the effect of blood flow pulsation in patients with pulsatile tinnitus. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 41, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.W.; Kim, S.W.; Sung, M.H.; Ro, K.C.; Ryou, H.S. Fluid-structure interaction analysis on the effects of vessel material properties on blood flow characteristics in stenosed arteries under axial rotation. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 2011, 23, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofink, P.; Müller, W. Numerical Modeling of Fluid-Structure Interaction of Blood in a Vein by Simulating Conservation of Mass and Linear Momentum with the Finite Element Method in FEniCS. PAMM 2013, 13, 209–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.F.; Mo, Z.J.; Tian, S.; Wang, L.Z.; Fan, J.; Liu, S.Y.; Fan, Y.B. Biomechanical investigation of thoracolumbar spine in different postures during ejection using a combined finite element and multi-body approach. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 2014, 30, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Fan, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L. A study on relationship between pulsatile tinnitus and temporal bone pneumatization grade. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 22, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudde, H.; Engel, A. Measuring and modeling basic properties of the human middle ear and ear canal. Part III: Eardrum impedances, transfer functions and model calculations. Acta Acust. United Acust. 1998, 84, 1091–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Hudde, H.; Engel, A. Measuring and Modeling Basic Properties of the Human Middle Ear and Ear Canal. Part II: Ear Canal, Middle Ear Cavities, Eardrum, and Ossicles. Acta Acust. United Acust. 1998, 84, 894–913. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Wang, G.; Zeng, R.; Li, W.; Chen, N.; Zhao, P.; Wang, Z.; Gong, S. Analysis of Revision Surgery following Surgical Reconstruction of the Sigmoid Sinus Wall in Patients with Pulsatile Tinnitus. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2022, 18, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Z.; Feng, X. The Characteristic and Short-Term Prognosis of Tinnitus Associated with Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Neural Plast. 2018, 2018, 6059697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.L.; Xu, X.; Hsieh, Y.D.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Wang, D.; Guo, P.; Wang, W. Hydroacoustic analysis and extraluminal compression surgical insights of venous pulsatile tinnitus. Auris Nasus Larynx 2021, 48, 852–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newberry, I.; Highland, J.; DeTorres, A.; Gurgel, R. Transmastoid Hydroxyapatite Resurfacing for Sigmoid Sinus Wall Anomalies Causing Pulsatile Tinnitus. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2021, 130, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.; Wang, G.P.; Liu, Z.H.; Liang, X.H.; Zhao, P.F.; Wang, Z.C.; Gong, S.S. Sigmoid Sinus Wall Reconstruction for Pulsatile Tinnitus Caused by Sigmoid Sinus Wall Dehiscence: A Single-Center Experience. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, H.; He, L.; Cao, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, S.; Li, R.; Yuan, C. Hemodynamic assessments of venous pulsatile tinnitus using 4D-flow MRI. Neurology 2018, 91, E586–E593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; An, G.S.; Choi, I.; Koo, J.W.; Lee, K.; Song, J.J. Pre-Treatment Objective Diagnosis and Post-Treatment Outcome Evaluation in Patients with Vascular Pulsatile Tinnitus Using Transcanal Recording and Spectro-Temporal Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Patients | Age | Gender | Duration (Years) | Side | Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| patient 1 | 38 | female | 6 | left | SSWD + SSD + HJB |
| patient 2 | 41 | female | 4 | left | SSWD + SSD + HJB |
| patient 3 | 55 | female | 5 | right | SSWD + SSD |
| Patients | Inlet Area (mm2) | Outlet Area (mm2) | SSWD Area (mm2) | Longest Horizontal Diameter of SSWD (mm) | Longest Longitudinal Diameter of SSWD (mm) | TBAC Volume (mm3) | Tympanum Area (mm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| patient 1 | 31.95 | 63.26 | 131.68 | 5.04 | 27.46 | 6834.90 | 18.56 |
| patient 2 | 40.83 | 60.73 | 159.45 | 5.49 | 28.46 | 5814.80 | 16.14 |
| patient 3 | 22.80 | 56.78 | 179.72 | 7.86 | 30.35 | 8763.30 | 16.31 |
| Name | Density (g/cm3) | Viscosity (Pa∙s) | Elastic Module (MP) | Poisson’s Ratio | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Venous blood | 1.05 | 0.0035 | - | - | Mu et al. [18] |
| Venous vessel | 1.05 | - | 1.26 | 0.3 | Cho et al. [19] and Lofink et al. [20] |
| Temporal bone | 2.00 | - | 12,000 | 0.3 | Du et al. [21] |
| Parameters | Control Subject | 3/4SSWD | 1/2SSWD | 1/4SSWD | 0SSWD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average wall pressure (Pa) | 206.39 ± 117.79 | 33.70 ± 12.53% | 35.86 ± 12.39% | 39.70 ± 12.45% | - |
| Average displacement (μm) | 9.31 ± 7.32 | 35.8 ± 18.66% | 41.66 ± 21.97% | 58.12 ± 23.49% | - |
| Maximum displacement (nm) | 8.06 ± 4.44 | 25.91 ± 30.20% | 37.20 ± 31.47% | 52.60 ± 34.66% | 79.35 ± 18.13% |
| Sound pressure level (dB) | 68.49 ± 4.44 | 23.72 ± 1.91% | 31.03 ± 14.40% | 45.62 ± 19.11% | 128.46 ± 15.46% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mu, Z.; Zhuang, L.; Zhao, P.; Gao, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, S.; Wang, X. Multiphysics Interaction Analysis of the Therapeutic Effects of the Sigmoid Sinus Wall Reconstruction in Patients with Venous Pulsatile Tinnitus. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10060715
Mu Z, Zhuang L, Zhao P, Gao B, Liu Y, Wang Z, Yang S, Wang X. Multiphysics Interaction Analysis of the Therapeutic Effects of the Sigmoid Sinus Wall Reconstruction in Patients with Venous Pulsatile Tinnitus. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(6):715. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10060715
Chicago/Turabian StyleMu, Zhenxia, Lihui Zhuang, Pengfei Zhao, Bin Gao, Youjun Liu, Zhenchang Wang, Shifeng Yang, and Ximing Wang. 2023. "Multiphysics Interaction Analysis of the Therapeutic Effects of the Sigmoid Sinus Wall Reconstruction in Patients with Venous Pulsatile Tinnitus" Bioengineering 10, no. 6: 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10060715
APA StyleMu, Z., Zhuang, L., Zhao, P., Gao, B., Liu, Y., Wang, Z., Yang, S., & Wang, X. (2023). Multiphysics Interaction Analysis of the Therapeutic Effects of the Sigmoid Sinus Wall Reconstruction in Patients with Venous Pulsatile Tinnitus. Bioengineering, 10(6), 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10060715






