Simultaneous Quantitative SARS-CoV-2 Antigen and Host Antibody Detection and Pre-Screening Strategy at the Point of Care
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Data
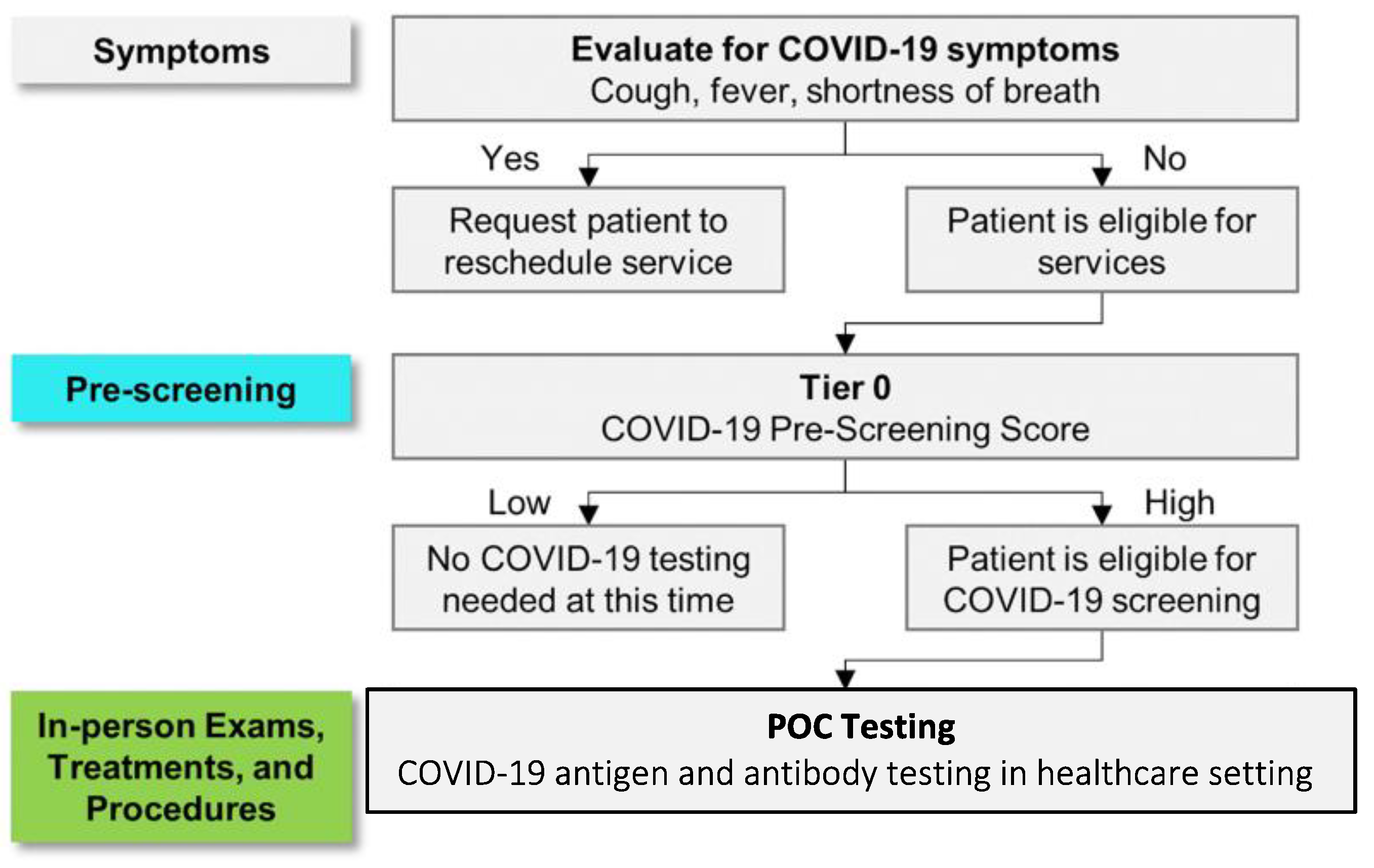
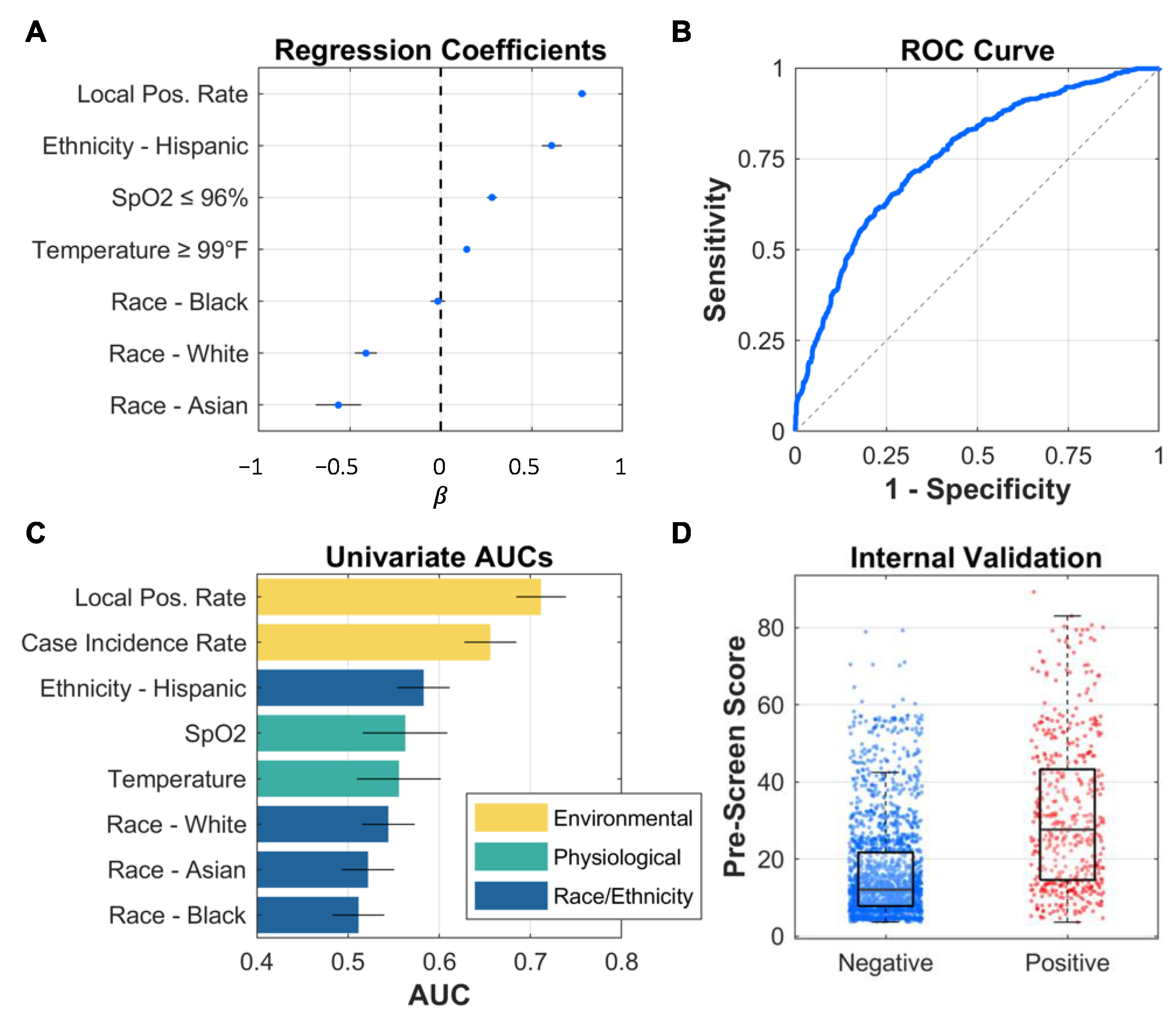
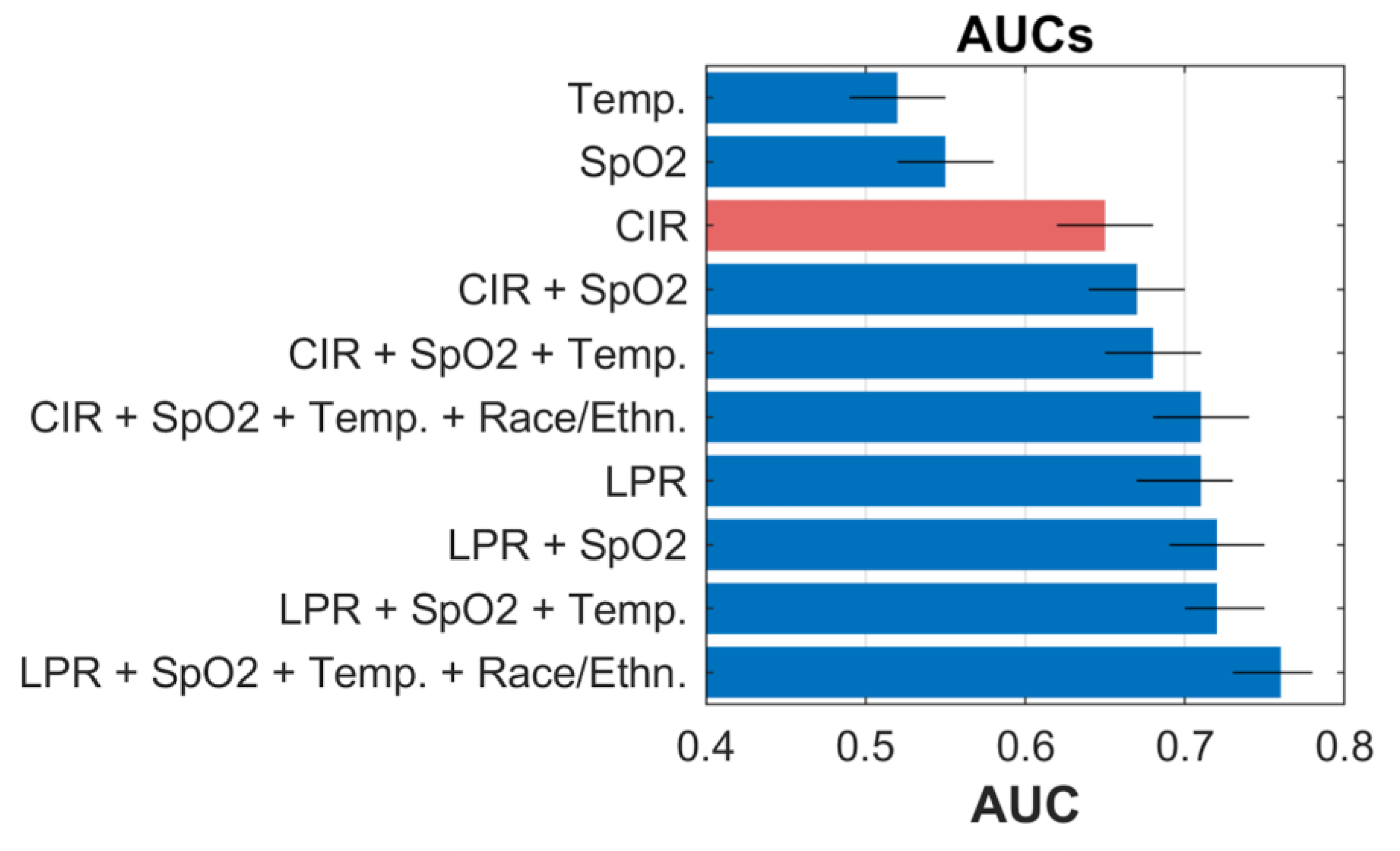
2.2. Model Development and Statistical Analysis
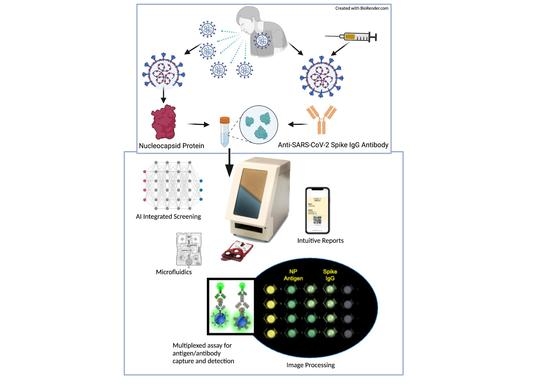
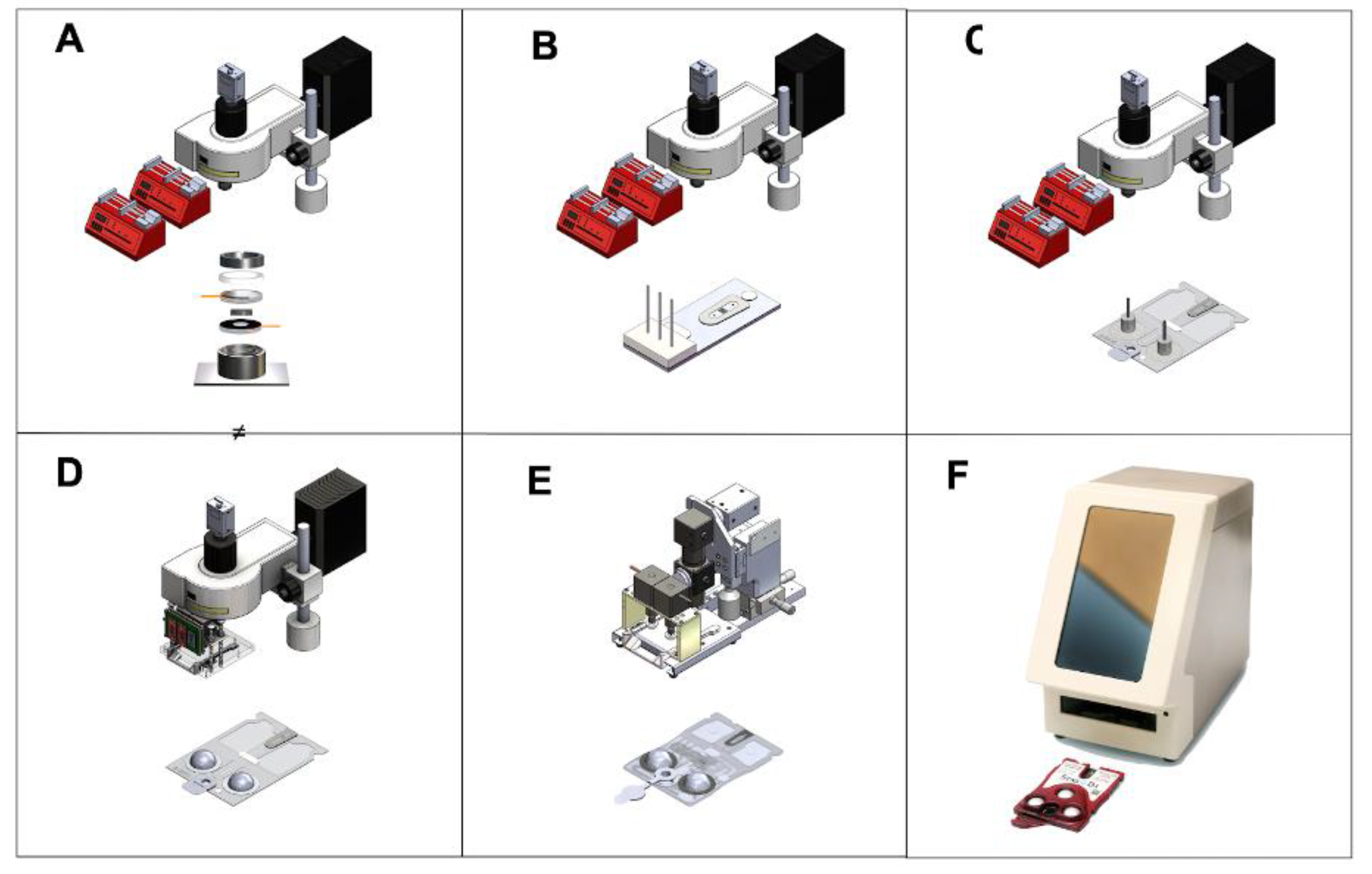
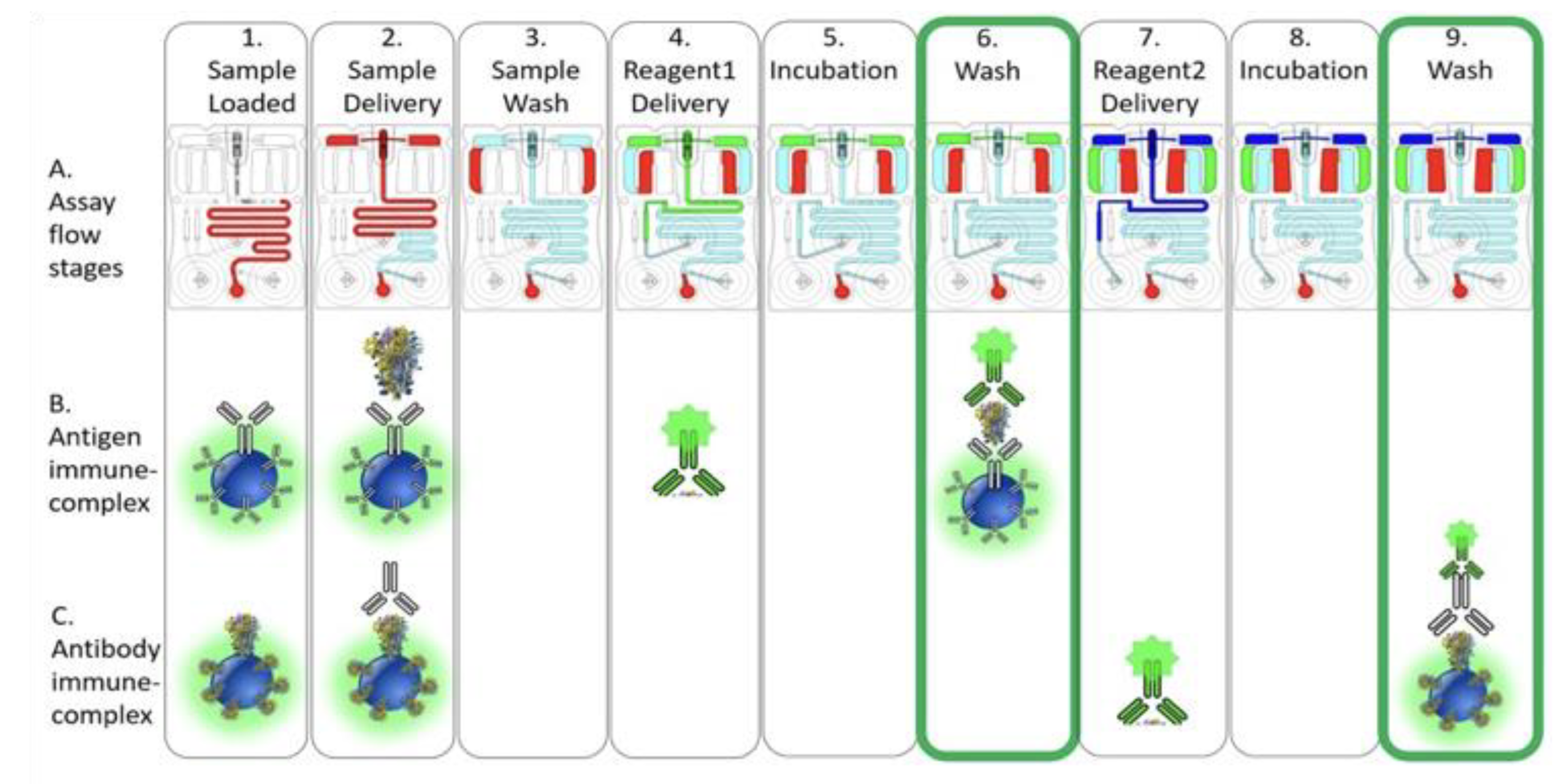
2.3. COVID-19 Antigen/Antibody Assay Development
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Bergman, P.; Blennow, O.; Hansson, L.; Mielke, S.; Nowak, P.; Chen, P.; Söderdahl, G.; Österborg, A.; Smith, C.I.E.; Wullimann, D.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the MRNA BNT162b2 Vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 in Five Groups of Immunocompromised Patients and Healthy Controls in a Prospective Open-Label Clinical Trial. eBioMedicine 2021, 74, 103705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feikin, D.R.; Higdon, M.M.; Abu-Raddad, L.J.; Andrews, N.; Araos, R.; Goldberg, Y.; Groome, M.J.; Huppert, A.; O’Brien, K.L.; Smith, P.G.; et al. Duration of Effectiveness of Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Disease: Results of a Systematic Review and Meta-Regression. Lancet 2022, 399, 924–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC SARS-CoV-2 Variant Classifications and Definitions. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/variants/variant-classifications.html (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Zhang, X.; Wu, S.; Wu, B.; Yang, Q.; Chen, A.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, T.; Zhang, H.; He, X. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Strain Exhibits Potent Capabilities for Immune Evasion and Viral Entrance. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurhade, C.; Zou, J.; Xia, H.; Liu, M.; Chang, H.C.; Ren, P.; Xie, X.; Shi, P.-Y. Low Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2.75.2, BQ.1.1 and XBB.1 by Parental mRNA Vaccine or a BA.5 Bivalent Booster. Nat. Med. 2022, 430, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC Underlying Medical Conditions—COVID Data Tracker. Available online: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Xue, L.; Jing, S.; Zhang, K.; Milne, R.; Wang, H. Infectivity versus Fatality of SARS-CoV-2 Mutations and Influenza. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 121, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalkias, S.; Harper, C.; Vrbicky, K.; Walsh, S.R.; Essink, B.; Brosz, A.; McGhee, N.; Tomassini, J.E.; Chen, X.; Chang, Y.; et al. A Bivalent Omicron-Containing Booster Vaccine against COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1279–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalkias, S.; Whatley, J.; Eder, F.; Essink, B.; Khetan, S.; Bradley, P.; Brosz, A.; McGhee, N.; Tomassini, J.E.; Chen, X.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of Omicron BA.4/BA.5 Bivalent Vaccine Against COVID-19. medRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC COVID-19 Vaccinations in the United States. Available online: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#vaccinations_vacc-people-booster-percent-pop5 (accessed on 3 March 2023).
- CDC Updates and Shortens Recommended Isolation and Quarantine Period for General Population. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2021/s1227-isolation-quarantine-guidance.html (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Viana, R.; Moyo, S.; Amoako, D.G.; Tegally, H.; Scheepers, C.; Althaus, C.L.; Anyaneji, U.J.; Bester, P.A.; Boni, M.F.; Chand, M.; et al. Rapid Epidemic Expansion of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant in Southern Africa. Nature 2022, 603, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senefeld, J.W.; Franchini, M.; Mengoli, C.; Cruciani, M.; Zani, M.; Gorman, E.K.; Focosi, D.; Casadevall, A.; Joyner, M.J. COVID-19 Convalescent Plasma for the Treatment of Immunocompromised Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2250647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almadhi, M.A.; Abdulrahman, A.; Sharaf, S.A.; AlSaad, D.; Stevenson, N.J.; Atkin, S.L.; AlQahtani, M.M. The High Prevalence of Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection Reveals the Silent Spread of COVID-19. Int. J. Infect. Dis. IJID Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Infect. Dis. 2021, 105, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, M.; Yokoe, D.S.; Havlir, D.V. Asymptomatic Transmission, the Achilles’ Heel of Current Strategies to Control COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2158–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ra, S.H.; Lim, J.S.; Kim, G.; Kim, M.J.; Jung, J.; Kim, S.-H. Upper Respiratory Viral Load in Asymptomatic Individuals and Mildly Symptomatic Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Thorax 2021, 76, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeling, R.W.; Sia, S.K. Lessons from COVID-19 for Improving Diagnostic Access in Future Pandemics. Lab. Chip. 2023, 23, 1376–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wölfel, R.; Corman, V.M.; Guggemos, W.; Seilmaier, M.; Zange, S.; Müller, M.A.; Niemeyer, D.; Jones, T.C.; Vollmar, P.; Rothe, C.; et al. Virological Assessment of Hospitalized Patients with COVID-2019. Nature 2020, 581, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yang, P.; Poon, L.L.M.; Wang, Q. Viral Load of SARS-CoV-2 in Clinical Samples. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 411–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; He, Y.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, J. Recent advances of functional nucleic acid-based sensors for point-of-care detection of SARS-CoV-2. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaebler, C.; Wang, Z.; Lorenzi, J.C.C.; Muecksch, F.; Finkin, S.; Tokuyama, M.; Cho, A.; Jankovic, M.; Schaefer-Babajew, D.; Oliveira, T.Y.; et al. Evolution of Antibody Immunity to SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2021, 591, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudbjartsson, D.F.; Norddahl, G.L.; Melsted, P.; Gunnarsdottir, K.; Holm, H.; Eythorsson, E.; Arnthorsson, A.O.; Helgason, D.; Bjarnadottir, K.; Ingvarsson, R.F.; et al. Humoral Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 in Iceland. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1724–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, P.B.; Montefiori, D.C.; McDermott, A.B.; Fong, Y.; Benkeser, D.; Deng, W.; Zhou, H.; Houchens, C.R.; Martins, K.; Jayashankar, L.; et al. Immune Correlates Analysis of the MRNA-1273 COVID-19 Vaccine Efficacy Clinical Trial. Science 2022, 375, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenwick, C.; Croxatto, A.; Coste, A.T.; Pojer, F.; André, C.; Pellaton, C.; Farina, A.; Campos, J.; Hacker, D.; Lau, K.; et al. Changes in SARS-CoV-2 Spike versus Nucleoprotein Antibody Responses Impact the Estimates of Infections in Population-Based Seroprevalence Studies. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e01828-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dispinseri, S.; Secchi, M.; Pirillo, M.F.; Tolazzi, M.; Borghi, M.; Brigatti, C.; De Angelis, M.L.; Baratella, M.; Bazzigaluppi, E.; Venturi, G.; et al. Neutralizing Antibody Responses to SARS-CoV-2 in Symptomatic COVID-19 Is Persistent and Critical for Survival. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, A.B.; Keskinocak, P.; Yildirim, I. Significance of SARS-CoV-2 Specific Antibody Testing during COVID-19 Vaccine Allocation. Vaccine 2021, 39, 5055–5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, N.; Stowe, J.; Kirsebom, F.; Toffa, S.; Rickeard, T.; Gallagher, E.; Gower, C.; Kall, M.; Groves, N.; O’Connell, A.-M.; et al. COVID-19 Vaccine Effectiveness against the Omicron (B.1.1.529) Variant. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1532–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajsri, K.S.; Singh, M.; Rao, M. Efficacy of COVID-19 Vaccines Against the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2. 2023. Available online: https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202303.0097/v1 (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Liu, R.; Liu, X.; Yuan, L.; Han, H.; Shereen, M.A.; Zhen, J.; Niu, Z.; Li, D.; Liu, F.; Wu, K.; et al. Analysis of Adjunctive Serological Detection to Nucleic Acid Test for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Infection Diagnosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 86, 106746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Ren, L.; Yang, S.; Xiao, M.; Chang, D.; Yang, F.; Dela Cruz, C.S.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Profiling Early Humoral Response to Diagnose Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2020, 71, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McRae, M.P.; Simmons, G.; Wong, J.; McDevitt, J.T. Programmable Bio-Nanochip Platform: A Point-of-Care Biosensor System with the Capacity To Learn. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 1359–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajsri, K.S.; McRae, M.P.; Simmons, G.W.; Christodoulides, N.J.; Matz, H.; Dooley, H.; Koide, A.; Koide, S.; McDevitt, J.T. A Rapid and Sensitive Microfluidics-Based Tool for Seroprevalence Immunity Assessment of COVID-19 and Vaccination-Induced Humoral Antibody Response at the Point of Care. Biosensors 2022, 12, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, M.P.; Modak, S.S.; Simmons, G.W.; Trochesset, D.A.; Kerr, A.R.; Thornhill, M.H.; Redding, S.W.; Vigneswaran, N.; Kang, S.K.; Christodoulides, N.J.; et al. Point-of-care Oral Cytology Tool for the Screening and Assessment of Potentially Malignant Oral Lesions. Cancer Cytopathol. 2020, 128, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, M.P.; Bozkurt, B.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Sanchez, X.; Christodoulides, N.; Simmons, G.; Nambi, V.; Misra, A.; Miller, C.S.; Ebersole, J.L.; et al. Cardiac ScoreCard: A Diagnostic Multivariate Index Assay System for Predicting a Spectrum of Cardiovascular Disease. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 54, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, P.M.; Issac, P.D.; Sharif, I.; Anderman, J.; Fenyo, D.; Sinokrot, O.; Stella, K.K.; Christodoulides, C.; Vurmaz, D.; Simmons, W.G.; et al. Managing COVID-19 With a Clinical Decision Support Tool in a Community Health Network: Algorithm Development and Validation. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, M.P.; Simmons, G.W.; Christodoulides, N.J.; Lu, Z.; Kang, S.K.; Fenyo, D.; Alcorn, T.; Dapkins, I.P.; Sharif, I.; Vurmaz, D.; et al. Clinical Decision Support Tool and Rapid Point-of-Care Platform for Determining Disease Severity in Patients with COVID-19. Lab. Chip 2020, 20, 2075–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Buuren, S.; Groothuis-Oudshoorn, K. Mice: Multivariate Imputation by Chained Equations in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2011, 45, 1–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, I. Chi-Squared and Fisher–Irwin Tests of Two-by-Two Tables with Small Sample Recommendations. Stat. Med. 2007, 26, 3661–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, J.T.E. The Analysis of 2 × 2 Contingency Tables—Yet Again. Stat. Med. 2011, 30, 890, author reply 891–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadlbauer, D.; Amanat, F.; Chromikova, V.; Jiang, K.; Strohmeier, S.; Arunkumar, G.A.; Tan, J.; Bhavsar, D.; Capuano, C.; Kirkpatrick, E.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Seroconversion in Humans: A Detailed Protocol for a Serological Assay, Antigen Production, and Test Setup. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2020, 57, e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.T.; Sehlin, D.; Lannfelt, L.; Syvänen, S.; Hultqvist, G. Efficient and Inexpensive Transient Expression of Multispecific Multivalent Antibodies in Expi293 Cells. Biol. Proced. Online 2017, 19, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, M.P.; Simmons, G.W.; Wong, J.; Shadfan, B.; Gopalkrishnan, S.; Christodoulides, N.; McDevitt, J.T. Programmable Bio-Nano-Chip System: A Flexible Point-of-Care Platform for Bioscience and Clinical Measurements. Lab. Chip. 2015, 15, 4020–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, D.A.; Eisenstein, L.G.; Jones, D.S. Hidden in Plain Sight—Reconsidering the Use of Race Correction in Clinical Algorithms. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, X.-Y.; Hao, W.; Wang, Y.; Di, B.; Yin, K.; Xu, Y.-C.; Feng, C.-S.; Wan, Z.-Y.; Cheng, V.C.C.; Yuen, K.-Y. Nucleocapsid Protein as Early Diagnostic Marker for SARS. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 1947–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Du, N.; Lei, Y.; Dorje, S.; Qi, J.; Luo, T.; Gao, G.F.; Song, H. Structures of the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid and Their Perspectives for Drug Design. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e105938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Yang, M.; Hong, Z.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Z.; Chen, X.; He, S.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, Q.; et al. Crystal Structure of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein RNA Binding Domain Reveals Potential Unique Drug Targeting Sites. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2020, 10, 1228–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.; Hou, M.-H.; Chang, C.-F.; Hsiao, C.-D.; Huang, T. The SARS Coronavirus Nucleocapsid Protein—Forms and Functions. Antivir. Res. 2014, 103, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC Science Brief: SARS-CoV-2 Infection-Induced and Vaccine-Induced Immunity—Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/science/science-briefs/vaccine-induced-immunity.html (accessed on 4 March 2023).
- Dörschug, A.; Frickmann, H.; Schwanbeck, J.; Yilmaz, E.; Mese, K.; Hahn, A.; Groß, U.; Zautner, A.E. Comparative Assessment of Sera from Individuals after S-Gene RNA-Based SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination with Spike-Protein-Based and Nucleocapsid-Based Serological Assays. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najjar, D.; Rainbow, J.; Sharma Timilsina, S.; Jolly, P.; de Puig, H.; Yafia, M.; Durr, N.; Sallum, H.; Alter, G.; Li, J.Z.; et al. A Lab-on-a-Chip for the Concurrent Electrochemical Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA and Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Saliva and Plasma. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 6, 968–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyllie, A.L.; Fournier, J.; Casanovas-Massana, A.; Campbell, M.; Tokuyama, M.; Vijayakumar, P.; Warren, J.L.; Geng, B.; Muenker, M.C.; Moore, A.J.; et al. Saliva or Nasopharyngeal Swab Specimens for Detection of SARS-CoV-2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1283–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, N.; Turner, F.; Slepnev, V.; Bacelar, A.; Deming, L.; Kodeboyina, S.; Klausner, J.D. Self-Collected Oral Fluid and Nasal Swabs Demonstrate Comparable Sensitivity to Clinician Collected Nasopharyngeal Swabs for Coronavirus Disease 2019 Detection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e3106–e3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| RT-PCR Negative | RT-PCR Positive | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient-level | |||
| No. of patients | 770 | 304 | |
| Encounters per patient | 1.3 ± 0.6 | 1.2 ± 0.5 | 0.015 |
| Age | 48 ± 17 | 47 ± 17 | 0.443 |
| Gender (no. of males) | 280 (36.4) | 112 (36.8) | 0.883 |
| Body mass index | 29.3 ± 7.9 | 27.9 ± 5.3 | 0.130 |
| Race | |||
| White | 298 (38.7) | 90 (29.6) | 0.005 |
| Black | 137 (17.8) | 44 (14.5) | 0.191 |
| Asian | 77 (10.0) | 17 (5.6) | 0.021 |
| Other | 258 (33.5) | 153 (50.3) | <0.001 |
| Ethnicity—Hispanic | 298 (38.7) | 172 (56.6) | <0.001 |
| Cardiac comorbidities | 218 (28.3) | 73 (24.0) | 0.154 |
| Hypertension | 186 (24.2) | 70 (23.0) | 0.696 |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 83 (10.8) | 23 (7.6) | 0.112 |
| Heart failure | 38 (4.9) | 11 (3.6) | 0.352 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 30 (3.9) | 14 (4.6) | 0.598 |
| Myocardial infarction | 21 (2.7) | 8 (2.6) | 0.931 |
| Ischemic heart disease | 8 (1.0) | 6 (2.0) | 0.224 |
| Asthma | 81 (10.5) | 24 (7.9) | 0.192 |
| Cancer | 49 (6.4) | 18 (5.9) | 0.787 |
| COPD | 104 (13.5) | 30 (9.9) | 0.104 |
| Diabetes | 116 (15.1) | 49 (16.1) | 0.666 |
| HIV/AIDS | 4 (0.5) | 3 (1.0) | 0.391 |
| Liver disease | 30 (3.9) | 12 (3.9) | 0.969 |
| Renal disease | 35 (4.5) | 13 (4.3) | 0.848 |
| Encounter level | |||
| No. of encounters | 2059 | 494 | |
| Systolic blood pressure < 120 mmHg | 270 (13.1) | 141 (28.5) | <0.001 |
| Diastolic blood pressure < 80 mmHg | 426 (20.7) | 186 (37.7) | <0.001 |
| Temperature ≥ 99 °F | 47 (2.3) | 29 (5.9) | <0.001 |
| Pulse < 80 bpm | 251 (12.2) | 87 (17.6) | 0.001 |
| SpO2 ≤ 96% | 105 (5.1) | 74 (15.0) | <0.001 |
| Local Positivity Rate (%) | 17.7 ± 17.6 | 32.8 ± 20.1 | <0.001 |
| Local Case Incidence Rate (cases per 100,000) | 21.4 ± 15.8 | 30.1 ± 16.2 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Srinivasan Rajsri, K.; McRae, M.P.; Christodoulides, N.J.; Dapkins, I.; Simmons, G.W.; Matz, H.; Dooley, H.; Fenyö, D.; McDevitt, J.T. Simultaneous Quantitative SARS-CoV-2 Antigen and Host Antibody Detection and Pre-Screening Strategy at the Point of Care. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10060670
Srinivasan Rajsri K, McRae MP, Christodoulides NJ, Dapkins I, Simmons GW, Matz H, Dooley H, Fenyö D, McDevitt JT. Simultaneous Quantitative SARS-CoV-2 Antigen and Host Antibody Detection and Pre-Screening Strategy at the Point of Care. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(6):670. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10060670
Chicago/Turabian StyleSrinivasan Rajsri, Kritika, Michael P. McRae, Nicolaos J. Christodoulides, Isaac Dapkins, Glennon W. Simmons, Hanover Matz, Helen Dooley, David Fenyö, and John T. McDevitt. 2023. "Simultaneous Quantitative SARS-CoV-2 Antigen and Host Antibody Detection and Pre-Screening Strategy at the Point of Care" Bioengineering 10, no. 6: 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10060670
APA StyleSrinivasan Rajsri, K., McRae, M. P., Christodoulides, N. J., Dapkins, I., Simmons, G. W., Matz, H., Dooley, H., Fenyö, D., & McDevitt, J. T. (2023). Simultaneous Quantitative SARS-CoV-2 Antigen and Host Antibody Detection and Pre-Screening Strategy at the Point of Care. Bioengineering, 10(6), 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10060670