Assessment of the Influence of 5-Fluorouracil on SMAD4 and TGFB1 Gene Expression, Apoptosis Induction and DNA Damage in Human Cell Lines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Cell Culture
2.2.2. Assessment of Cell Viability by MTT (3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-Diphenyltetrazolium Bromide) Assay
2.2.3. Assessment of Cell Death by MUSE Test Kit
2.2.4. Assessment of DNA Damage by MUSE Test Kit
2.2.5. Assessment of SMAD4 and TGFB1 Gene Expression in CACO-2, SW480 and SW620 Cells Treated with 5-FU
Exposure of Cells to 5-FU
RNA Isolation from 5-FU-Treated Cells
Reverse Transcription Reaction
Real-Time PCR
2.2.6. Bioinformatic Analysis of SMAD4 Gene Expression
2.2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
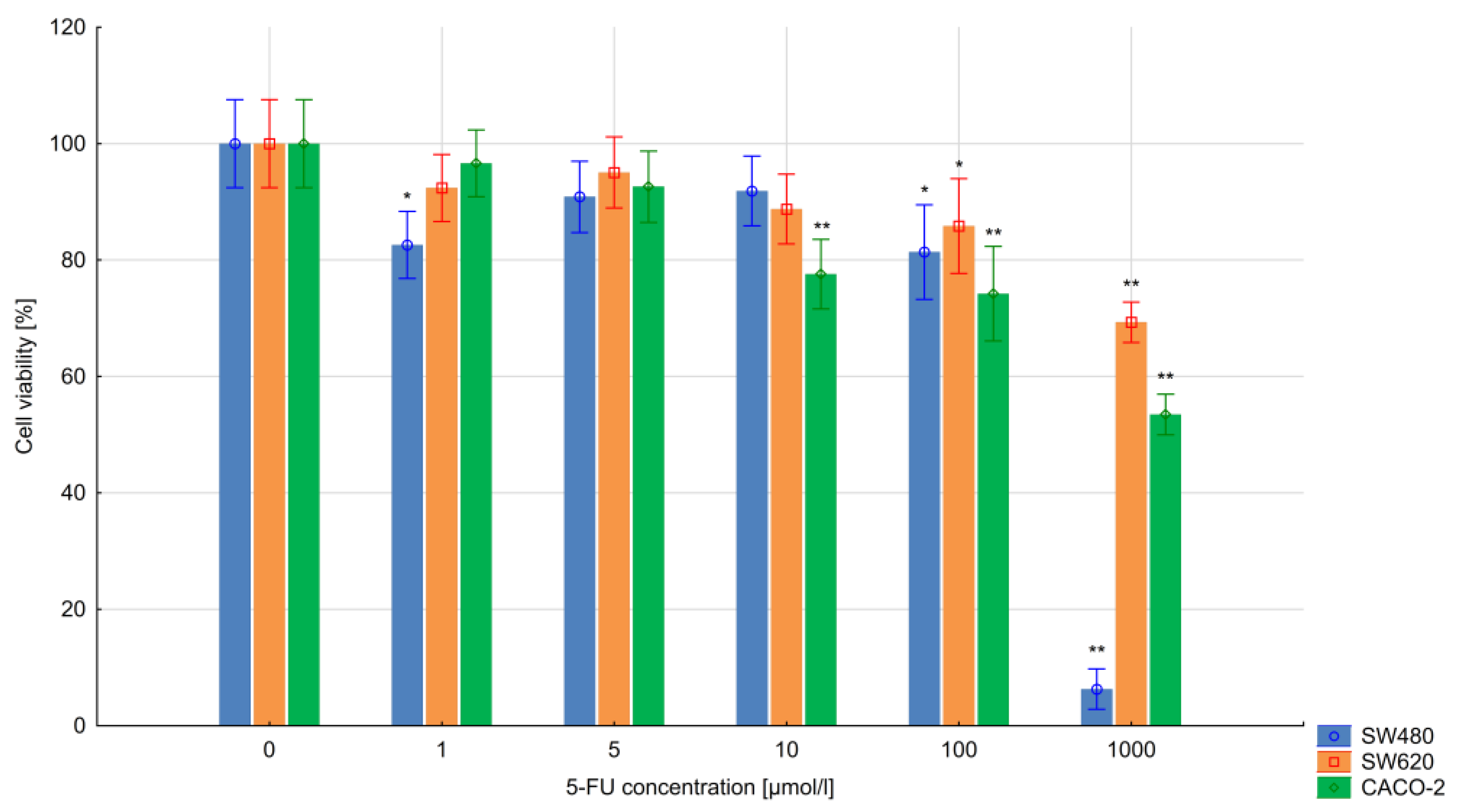
3.1. The Results of the MTT Assay
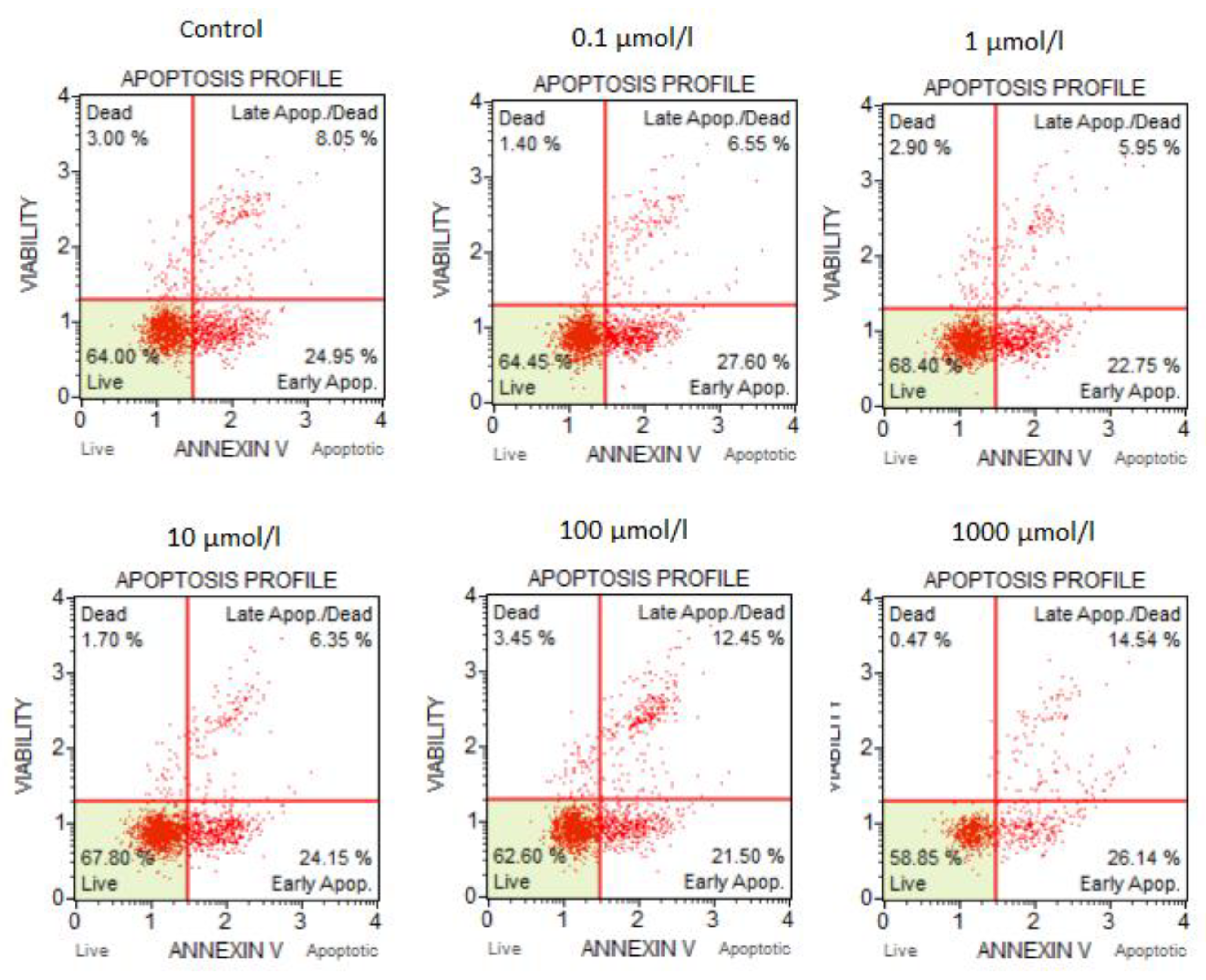
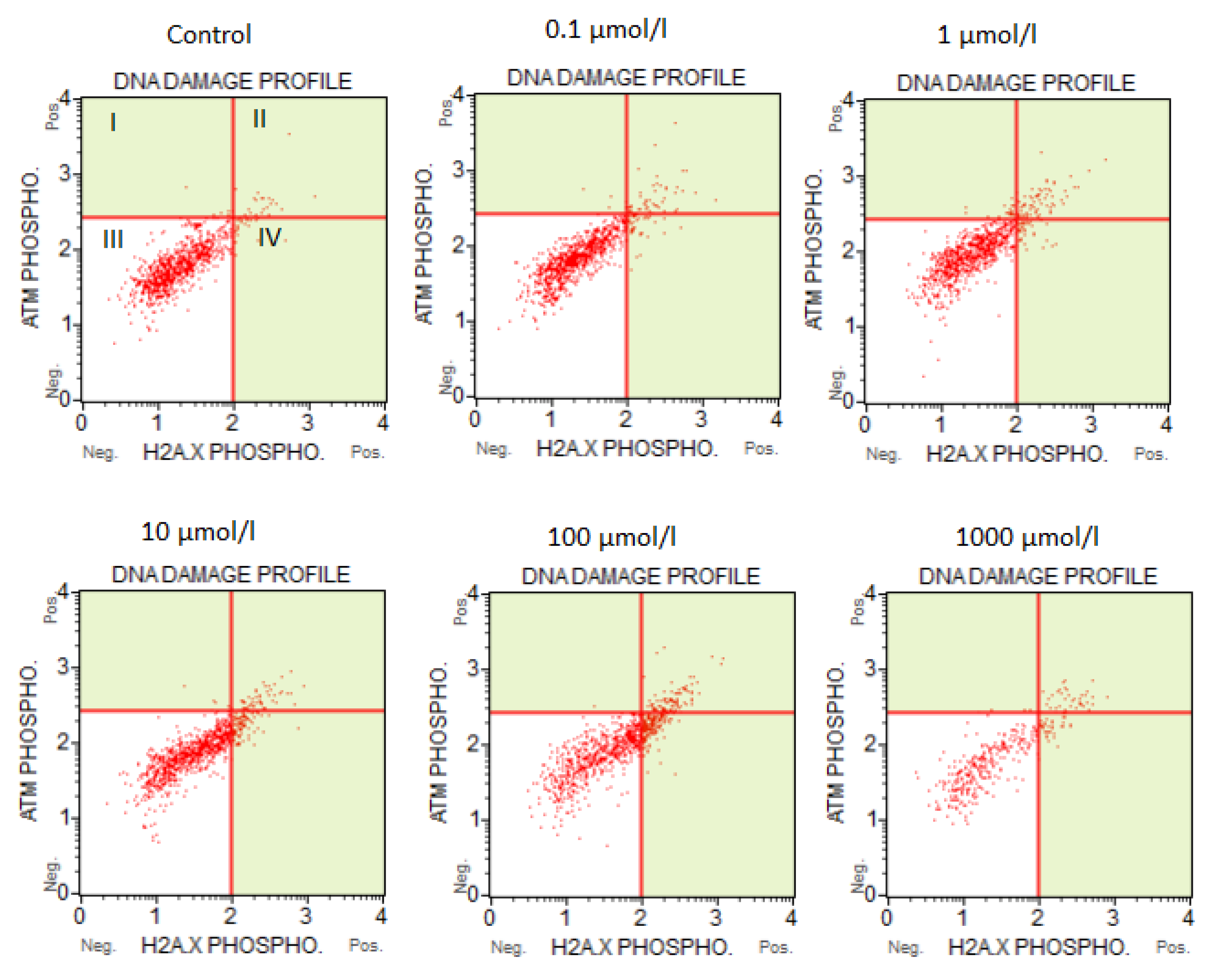
3.2. The Results of the Flow Cytometry Assays
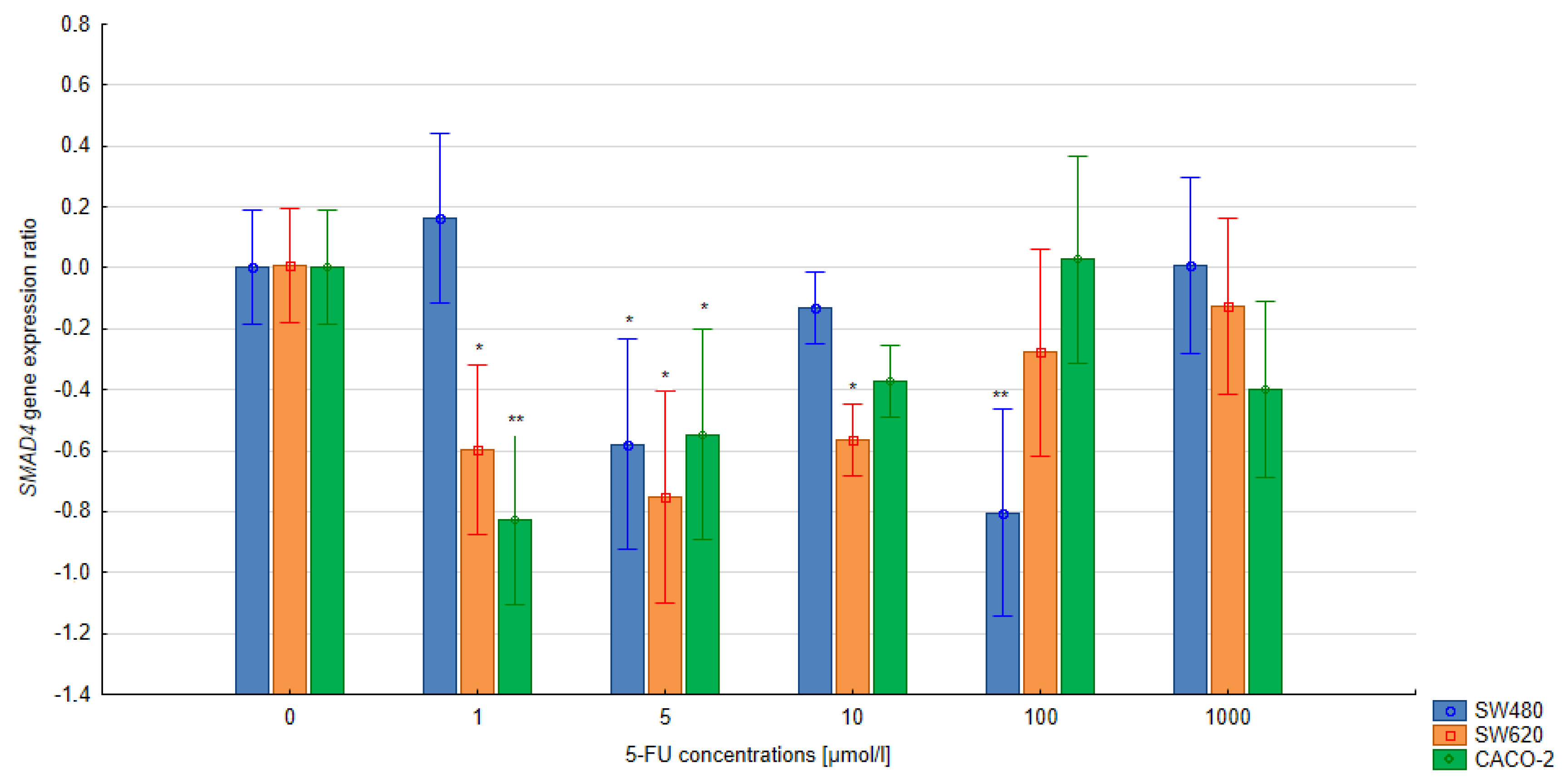
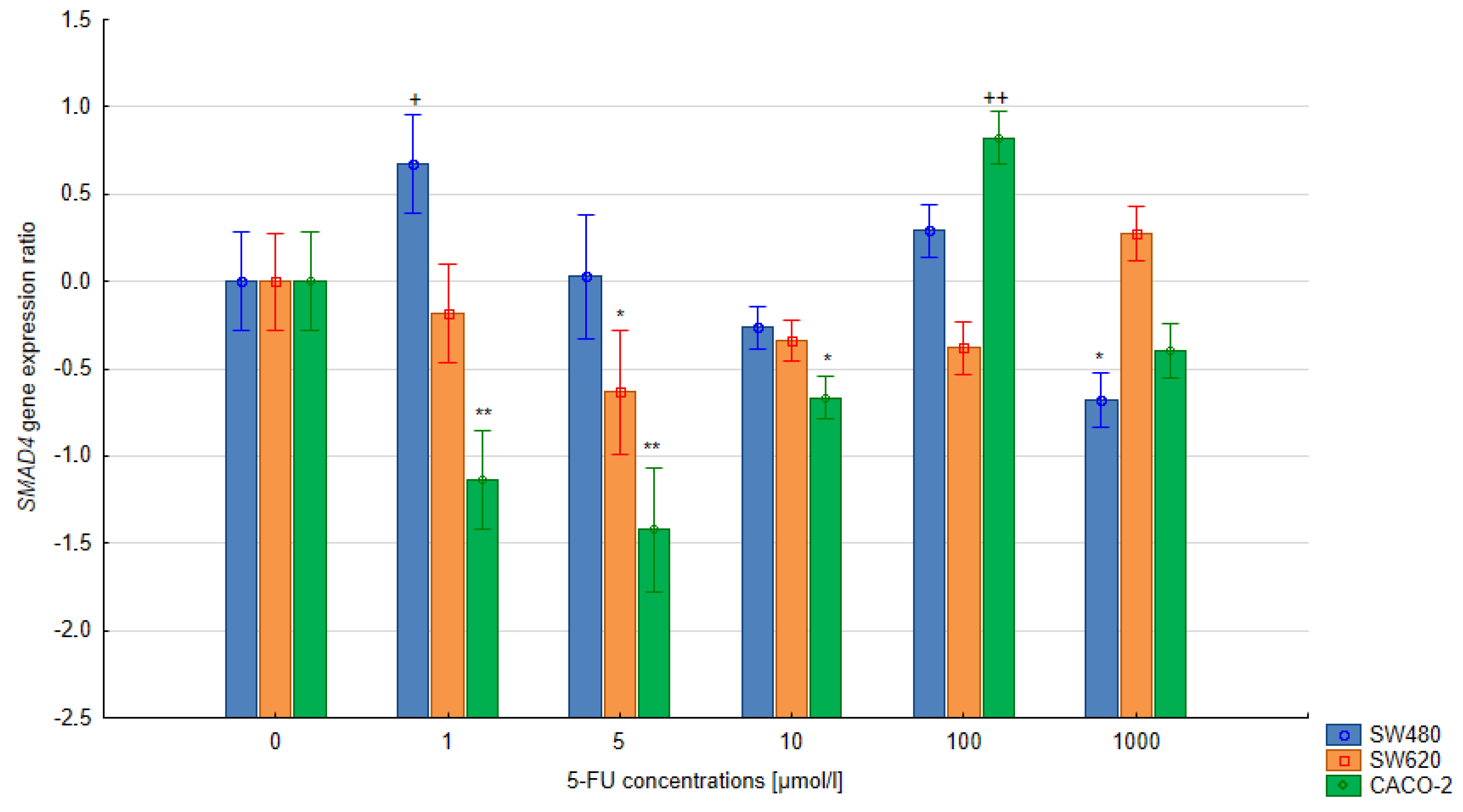
3.3. The Relative Expression of the SMAD4 and TGFB1 Gene in Colorectal Cells Treated with 5-FU
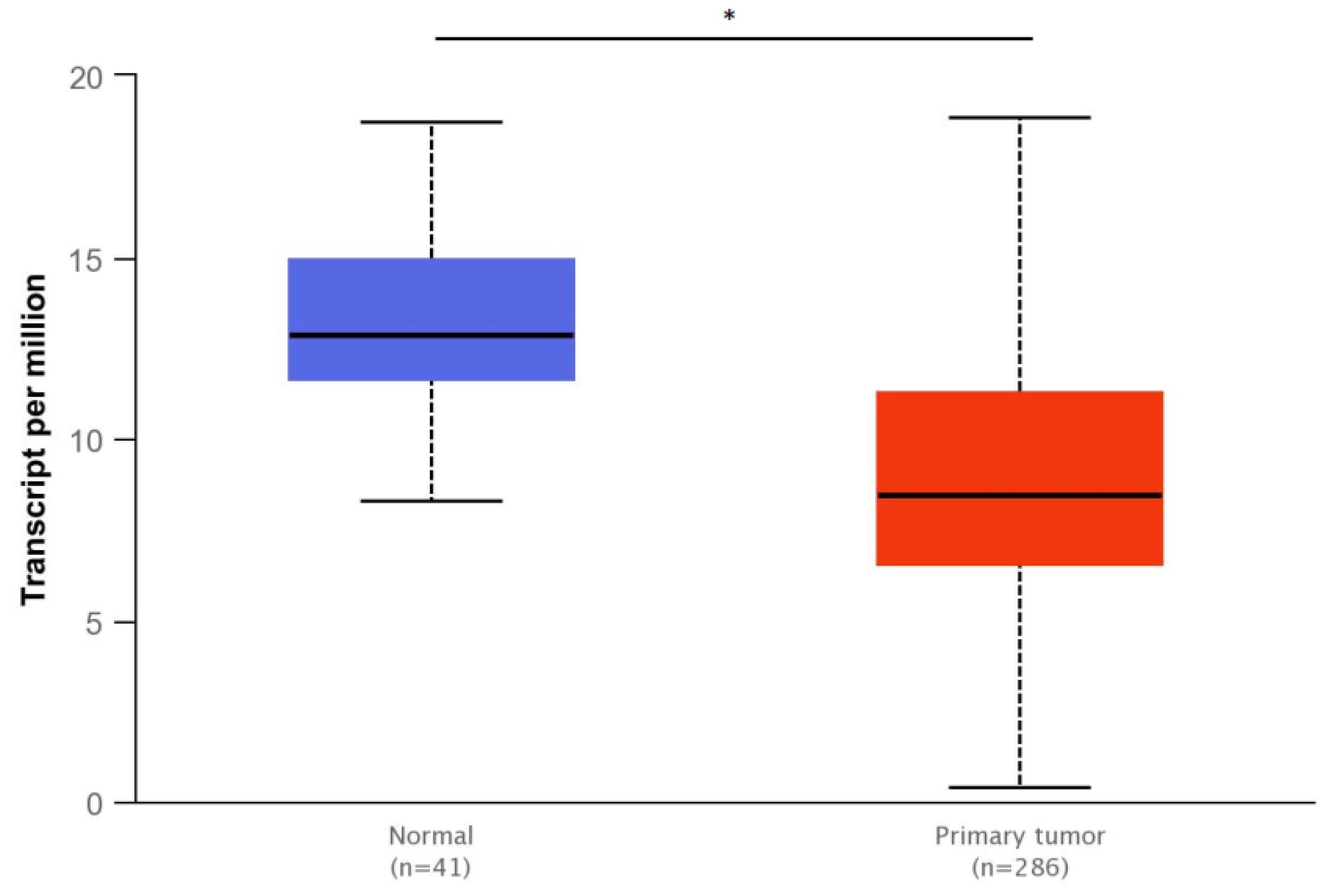
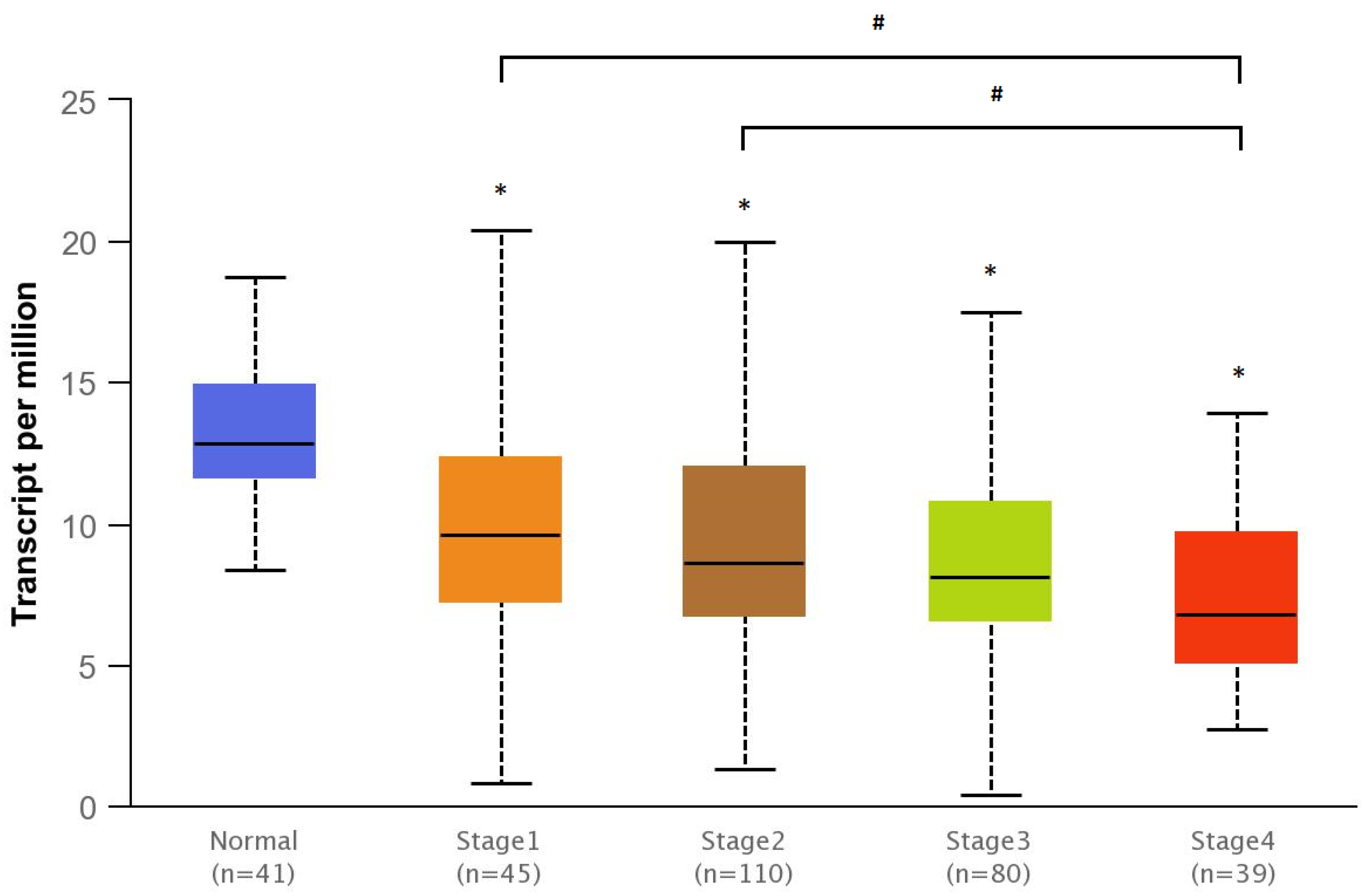
3.4. Bioinformatics Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Isaksson-Mettävainio, M.; Palmqvist, R.; Forssell, J.; Stenling, R.; Oberg, A. SMAD4/DPC4 expression and prognosis in human colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2006, 26, 507–510. [Google Scholar]
- Lanza, G.; Matteuzzi, M.; Gafá, R.; Orvieto, E.; Maestri, I.; Santini, A.; del Senno, L. Chromosome 18q allelic loss and prognosis in stage II and III colon cancer. Int. J. Cancer 1998, 79, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derynck, R.; Zhang, Y.E. Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in TGF-β family signalling. Nature 2003, 425, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurokowa, M.; Lynch, K.; Podolsky, D.K. Effects of growth factors on an intestinal epithelial cell line: Transforming growth factor β inhibits proliferation and stimulates differentiation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1987, 142, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, X.; Bishop, A.E.; Wallace, M.; Wang, H.; Willcocks, T.C.; Maclouf, J.; Polak, J.M.; Knight, S.; Talbot, I.C. Early expression of cyclo-oxygenase-2 during sporadic colorectal carcinogenesis. J. Pathol. 1999, 187, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itatani, Y.; Kawada, K.; Sakai, Y. Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling Pathway in Colorectal Cancer and Its Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maitra, A.; Molberg, K.; Albores-Saavedra, J.; Lindberg, G. Loss of Dpc4 Expression in Colonic Adenocarcinomas Correlates with the Presence of Metastatic Disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaki, M.; Iijima, T.; Konishi, M.; Sakai, K.; Ishii, A.; Yasuno, M.; Hishima, T.; Koike, M.; Shitara, N.; Iwama, T.; et al. Higher frequency of Smad4 gene mutation in human colorectal cancer with distant metastasis. Oncogene 1999, 18, 3098–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, I.; Lee, L.H.; Ogino, S.; Marco, M.R.; Wu, C.; Chen, X.; Datta, J.; Sadot, E.; Szeglin, B.; Guillem, J.G.; et al. SMAD4 Loss in Colorectal Cancer Patients Correlates with Recurrence, Loss of Immune Infiltrate, and Chemoresistance. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 1948–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Klingbiel, D.; Saridaki, Z.; Ceppa, P.; Curto, M.; McKee, T.A.; Roth, A.; Tejpar, S.; Delorenzi, M.; Bosman, F.T.; et al. Reduced Expression of SMAD4 Is Associated with Poor Survival in Colon Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 3037–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhopuro, P.; Alazzouzi, H.; Sammalkorpi, H.; Dávalos, V.; Salovaara, R.; Hemminki, A.; Järvinen, H.; Mecklin, J.-P.; Schwartz, S.; Aaltonen, L.A.; et al. SMAD4 Levels and Response to 5-Fluorouracil in Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 6311–6316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrag, D.K.; Sabri, N.A.; Tawfik, A.S.; Shaheen, S.M. Evaluation of the clinical effect of pharmacist intervention: Results of patient education about breast cancer. Eur. J. Oncol. Pharm. 2020, 3, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, H.E.; Sabri, N.A.; Saad, A.S. Prediction of chemotherapy prescribing errors for oncology patients. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2016, 7, 3274. [Google Scholar]
- De Gramont, A.; Figer, A.; Seymour, M.; Homerin, M.; Hmissi, A.; Cassidy, J.; Boni, C.; Cortes-Funes, H.; Cervantes, A.; Freyer, G.; et al. Leucovorin and Fluorouracil With or Without Oxaliplatin as First-Line Treatment in Advanced Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 2938–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanciullino, R.; Giacometti, S.; Mercier, C.; Aubert, C.; Blanquicett, C.; Piccerelle, P.; Ciccolini, J. In vitro and in vivo reversal of resistance to 5-fluorouracil in colorectal cancer cells with a novel stealth double-liposomal formulation. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 97, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Cho, J.-M.; Sai, S.; Oh, J.Y.; Park, J.-A.; Oh, S.J.; Park, M.; Kwon, J.; Shin, U.S.; Baek, J.-H.; et al. 5-Fluorouracil as a Tumor-Treating Field-Sensitizer in Colon Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2019, 11, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, M.M.; von Eyben, R.; Pai, J.; Vossler, S.R.; Limaye, M.; Jayachandran, P.; Anderson, E.M.; Shaffer, J.L.; Longacre, T.; Pai, R.K.; et al. Smad4 inactivation predicts for worse prognosis and response to fluorouracil-based treatment in colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Pathol. 2015, 68, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Wu, T.-T.; Catalano, P.J.; Ueki, T.; Satriano, R.; Haller, D.G.; Benson, A.B.; Hamilton, S.R. Molecular Predictors of Survival after Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Colon Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1196–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, B.K.; Jang, S.-H.; Paik, S.S.; Lee, K.H. Smad4 May Help to Identify a Subset of Colorectal Cancer Patients with Early Recurrence after Curative Therapy. Hepato-Gastroenterology 2011, 58, 1933–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Preet, R.; Mohapatra, P.; Satapathy, S.R.; Siddharth, S.; Tamir, T.; Jain, V.; Bharatam, P.V.; Wyatt, M.D.; Kundu, C.N. 5-Fluorouracil mediated anti-cancer activity in colon cancer cells is through the induction of Adenomatous Polyposis Coli: Implication of the long-patch base excision repair pathway. DNA Repair 2014, 24, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracht, K.; Nicholls, A.M.; Liu, Y.; Bodmer, W.F. 5-Fluorouracil response in a large panel of colorectal cancer cell lines is associated with mismatch repair deficiency. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulay, J.-L.; Mild, G.; Lowy, A.M.; Reuter, J.; Lagrange, M.; Terracciano, L.; Laffer, U.; Herrmann, R.G.; Rochlitz, C. SMAD4 is a predictive marker for 5-fluorouracil-based chemotherapy in patients with colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 87, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alazzouzi, H.; Alhopuro, P.; Salovaara, R.; Sammalkorpi, H.; Järvinen, H.; Mecklin, J.-P.; Hemminki, A.; Schwartz, S.; Aaltonen, L.A.; Arango, D. SMAD4 as a Prognostic Marker in Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 2606–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touil, Y.; Igoudjil, W.; Corvaisier, M.; Dessein, A.-F.; Vandomme, J.; Monté, D.; Stechly, L.; Skrypek, N.; Langlois, C.; Grard, G.; et al. Colon Cancer Cells Escape 5FU Chemotherapy-Induced Cell Death by Entering Stemness and Quiescence Associated with the c-Yes/YAP Axis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Marsh, S.; Cassidy, J.; McLeod, H.L. Pharmacogenomic dissection of resistance to thymidylate synthase inhibitors. Cancer Res 2001, 61, 5505–5510. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Leng, C.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Dou, L.; Luo, X.; Zhang, B.; Chen, X. Smad4 sensitizes colorectal cancer to 5-fluorouracil through cell cycle arrest by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/CDC2/survivin cascade. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 35, 1807–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, X.; Bae, S.; Singh, K.K.; Washington, M.K.; Datta, P.K. Loss of Smad4 in colorectal cancer induces resistance to 5-fluorouracil through activating Akt pathway. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 946–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Di, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Yan, J.; Xu, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, H.; et al. Transforming growth factor β signaling pathway: A promising therapeutic target for cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 1903–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, G.; Santi, L.; Bianco, M.R.; Giuffrè, M.R.; Pettinato, M.; Bugarin, C.; Garanzini, C.; Savarese, L.; Leoni, S.; Cerrito, M.G.; et al. The TGF-β pathway is activated by 5-fluorouracil treatment in drug resistant colorectal carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 22077–22091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Fowlis, D.J.; Bryson, S.; Duffie, E.; Ireland, H.; Balmain, A.; Akhurst, R.J. TGFβ1 inhibits the formation of benign skin tumors, but enhances progression to invasive spindle carcinomas in transgenic mice. Cell 1996, 86, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shemi, A.; Kensara, O.; Mohamed, A.; Refaat, B.; Idris, S.; Ahmad, J. Thymoquinone subdues tumor growth and potentiates the chemopreventive effect of 5-fluorouracil on the early stages of colorectal carcinogenesis in rats. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, ume 10, 2239–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondy, S.; David, V.; Verdier, M.; Mathonnet, M.; Perraud, A.; Christou, N. 5-Fluorouracil resistance mechanisms in colorectal cancer: From classical pathways to promising processes. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 3142–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amerizadeh, F.; Rezaei, N.; Rahmani, F.; Hassanian, S.M.; Moradi-Marjaneh, R.; Fiuji, H.; Boroumand, N.; Nosrati-Tirkani, A.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; Ferns, G.A.; et al. Crocin synergistically enhances the antiproliferative activity of 5-flurouracil through Wnt/PI3K pathway in a mouse model of colitis-associated colorectal cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 10250–10261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wosiak, A.; Szmajda-Krygier, D.; Pietrzak, J.; Boncela, J.; Balcerczak, E. Assessment of the Influence of 5-Fluorouracil on SMAD4 and TGFB1 Gene Expression, Apoptosis Induction and DNA Damage in Human Cell Lines. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10050570
Wosiak A, Szmajda-Krygier D, Pietrzak J, Boncela J, Balcerczak E. Assessment of the Influence of 5-Fluorouracil on SMAD4 and TGFB1 Gene Expression, Apoptosis Induction and DNA Damage in Human Cell Lines. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(5):570. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10050570
Chicago/Turabian StyleWosiak, Agnieszka, Dagmara Szmajda-Krygier, Jacek Pietrzak, Joanna Boncela, and Ewa Balcerczak. 2023. "Assessment of the Influence of 5-Fluorouracil on SMAD4 and TGFB1 Gene Expression, Apoptosis Induction and DNA Damage in Human Cell Lines" Bioengineering 10, no. 5: 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10050570
APA StyleWosiak, A., Szmajda-Krygier, D., Pietrzak, J., Boncela, J., & Balcerczak, E. (2023). Assessment of the Influence of 5-Fluorouracil on SMAD4 and TGFB1 Gene Expression, Apoptosis Induction and DNA Damage in Human Cell Lines. Bioengineering, 10(5), 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10050570




