Self-Attention MHDNet: A Novel Deep Learning Model for the Detection of R-Peaks in the Electrocardiogram Signals Corrupted with Magnetohydrodynamic Effect
Abstract
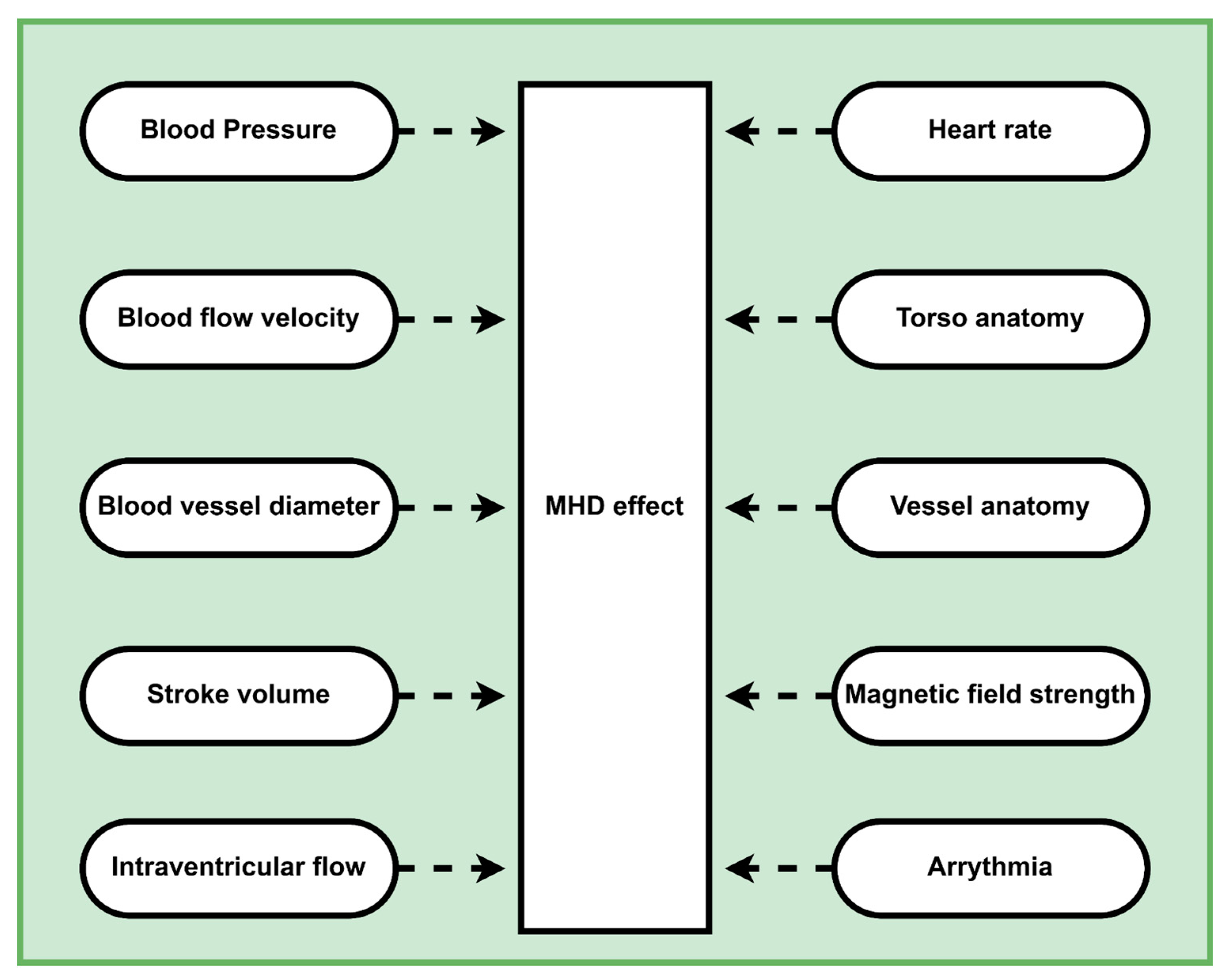
1. Introduction
- Proposing a novel deep learning model, Self-Attention MHDNet, which can accurately detect R-peaks by approaching the problem as a segmentation problem.
- Assessing the performance of the model on ECG data collected from both 3T and 7T MRI machines.
- Pioneering the use of deep learning models for R-peak detection in MHD corrupted ECG signals.
- Demonstrating that three-channel ECG signals are sufficient for detecting R-peaks in multi-channel ECG signals.
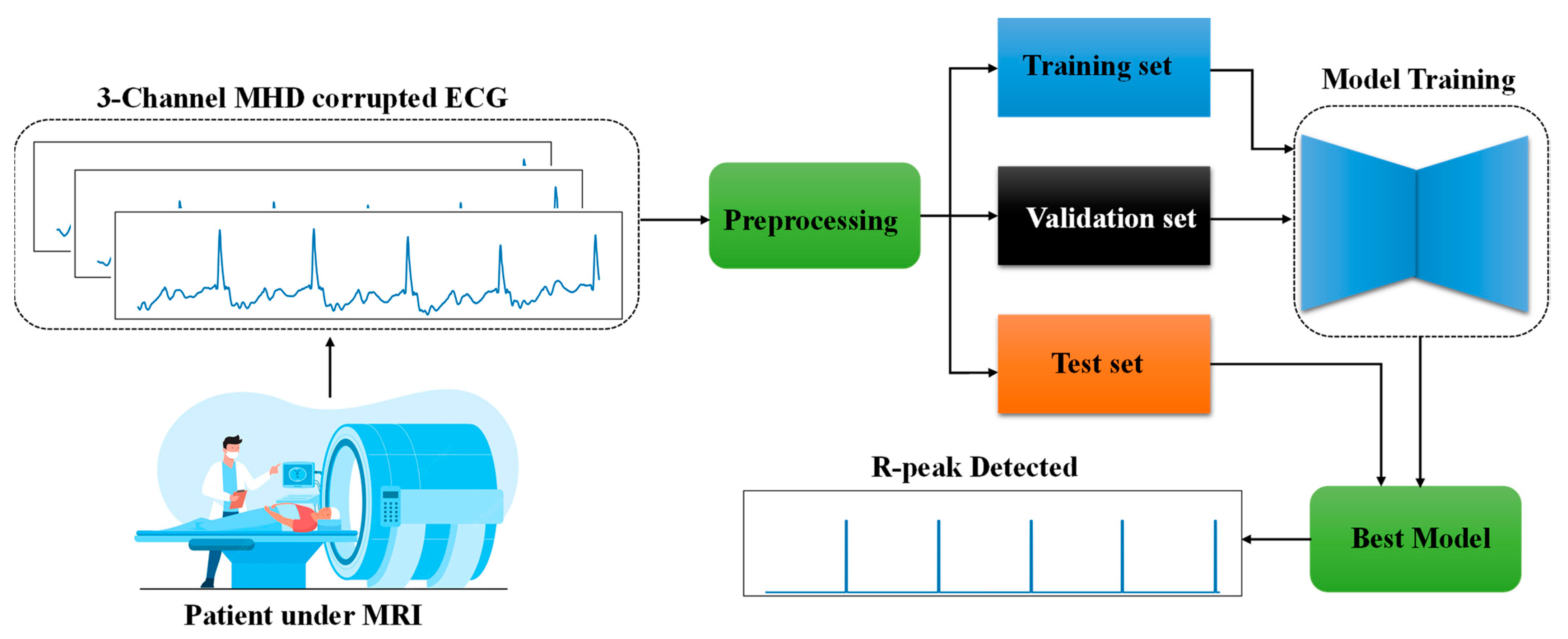
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. R-peak Detection as av Segmentation Problem
2.2. Dataset Description
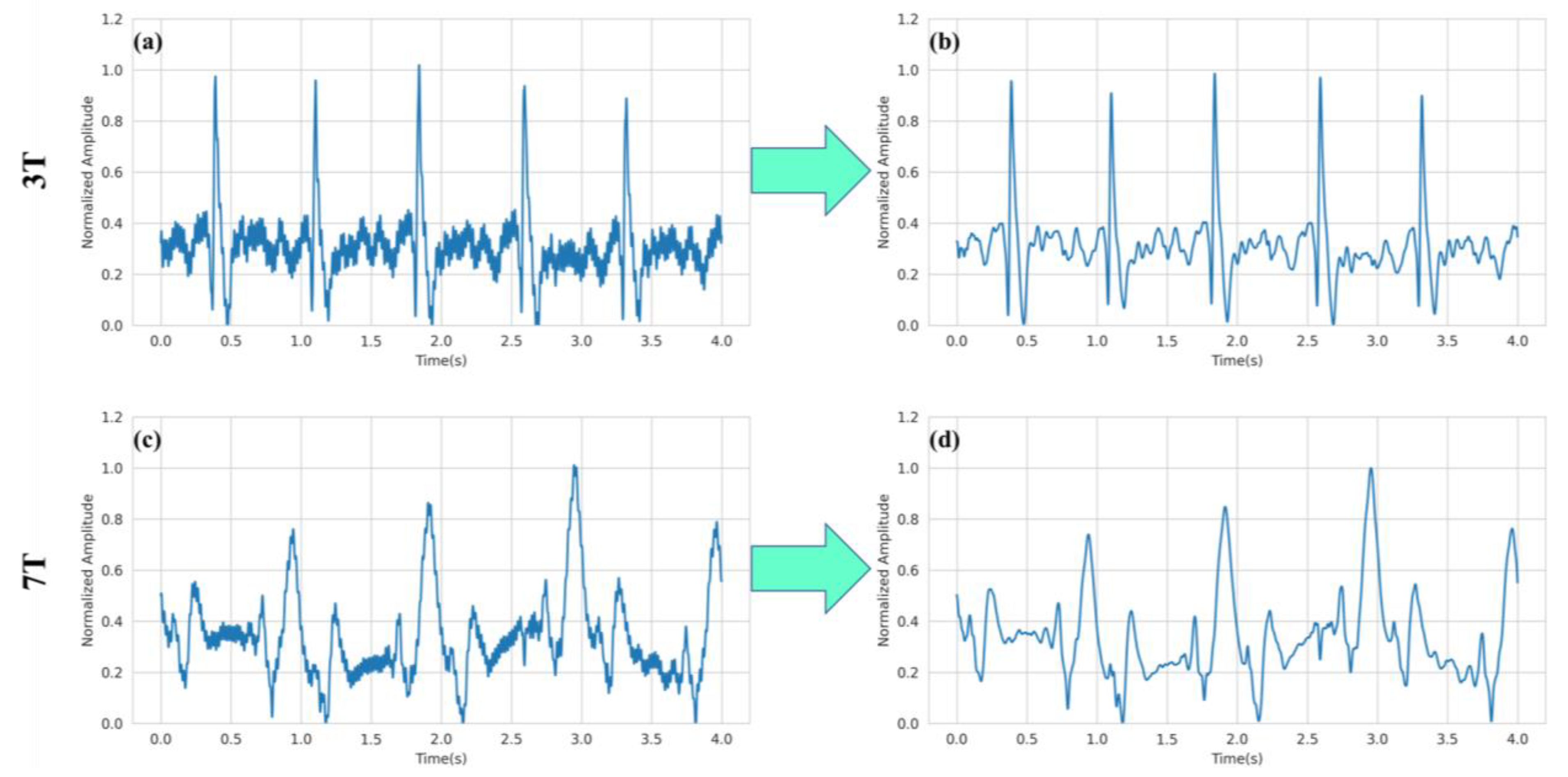
2.3. Preprocessing
2.4. Model Architecture
2.4.1. Self-ONN
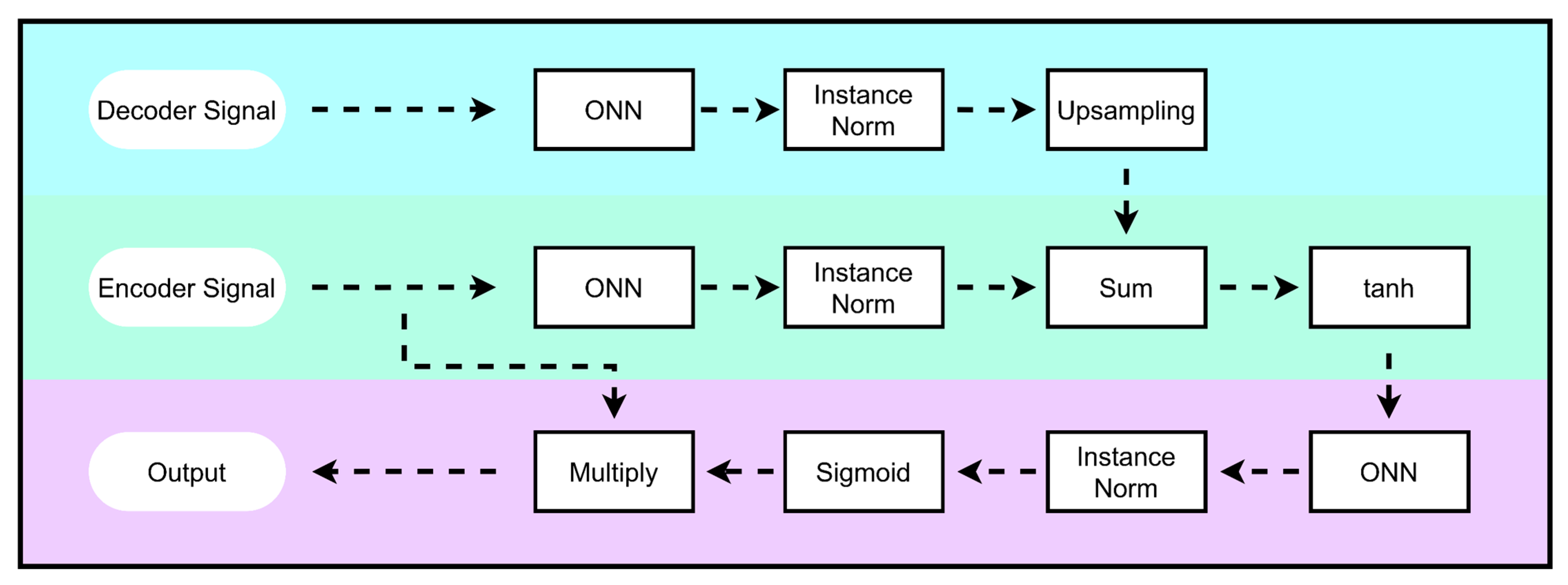
2.4.2. Self-Attention MHDNet
2.4.3. Attention Mechanism
2.5. Training Methodology
2.6. Evaluation Criteria
3. Results and Discussion
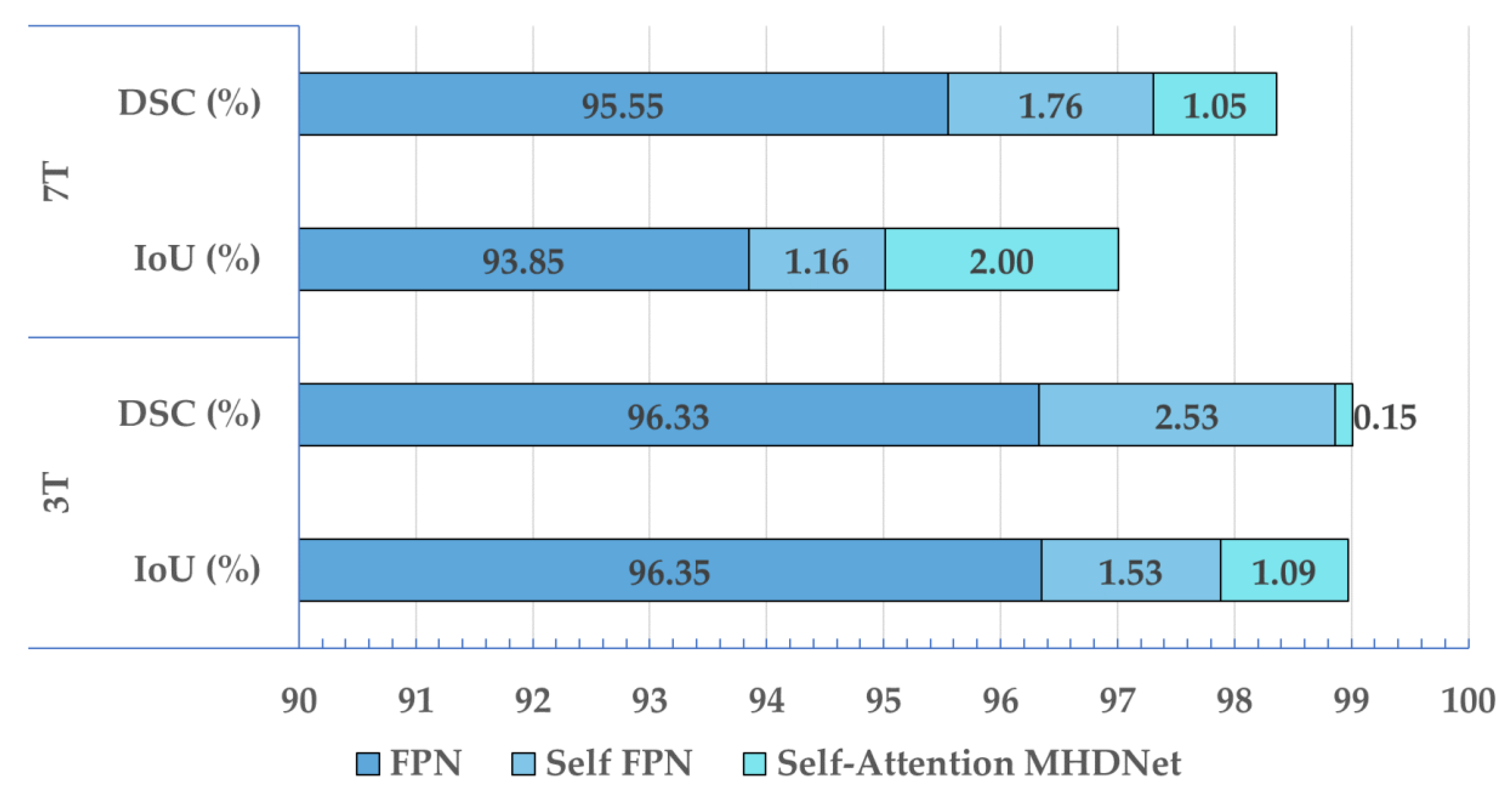
3.1. Ablation Study
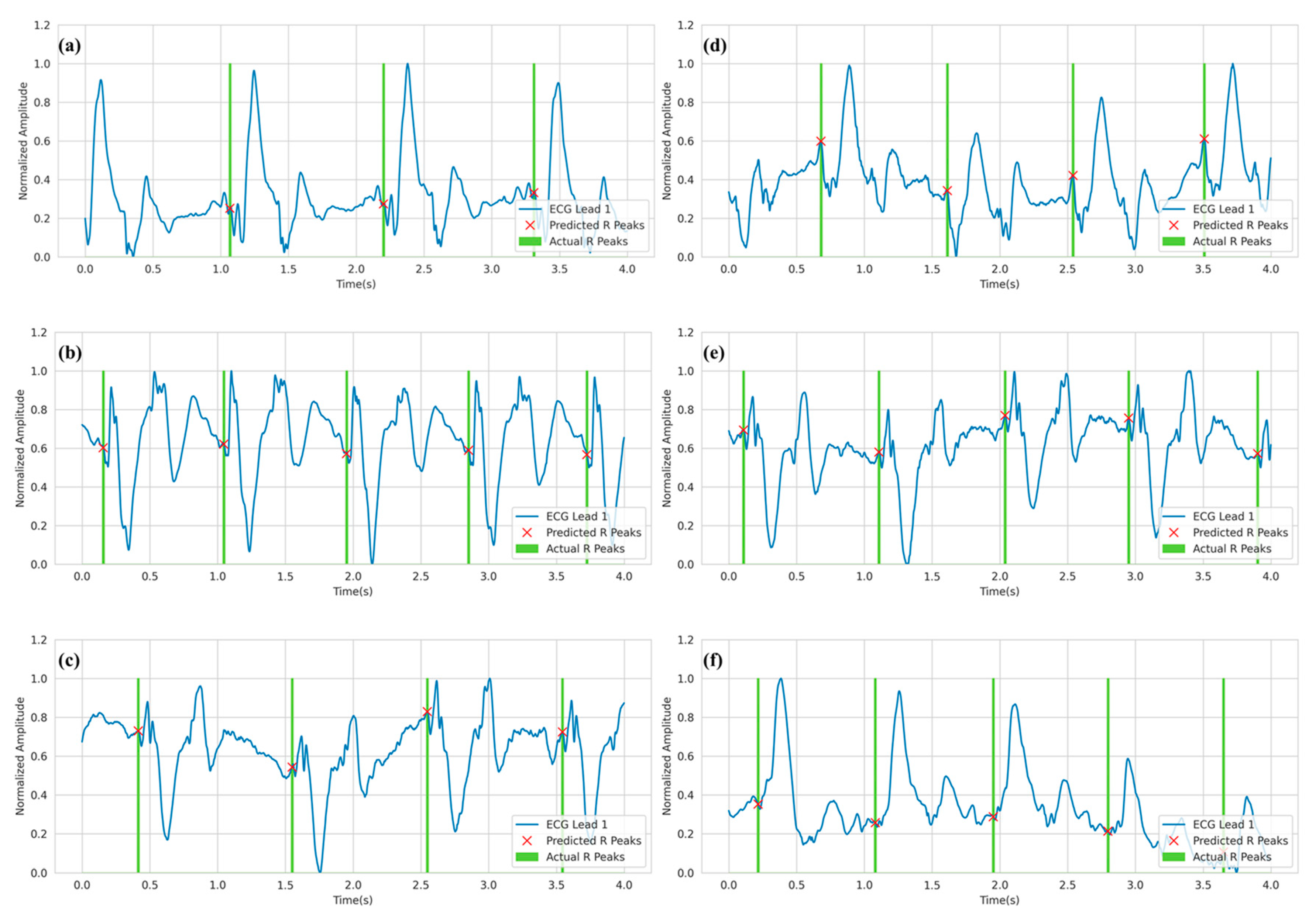
3.2. R-peak Detection Analysis
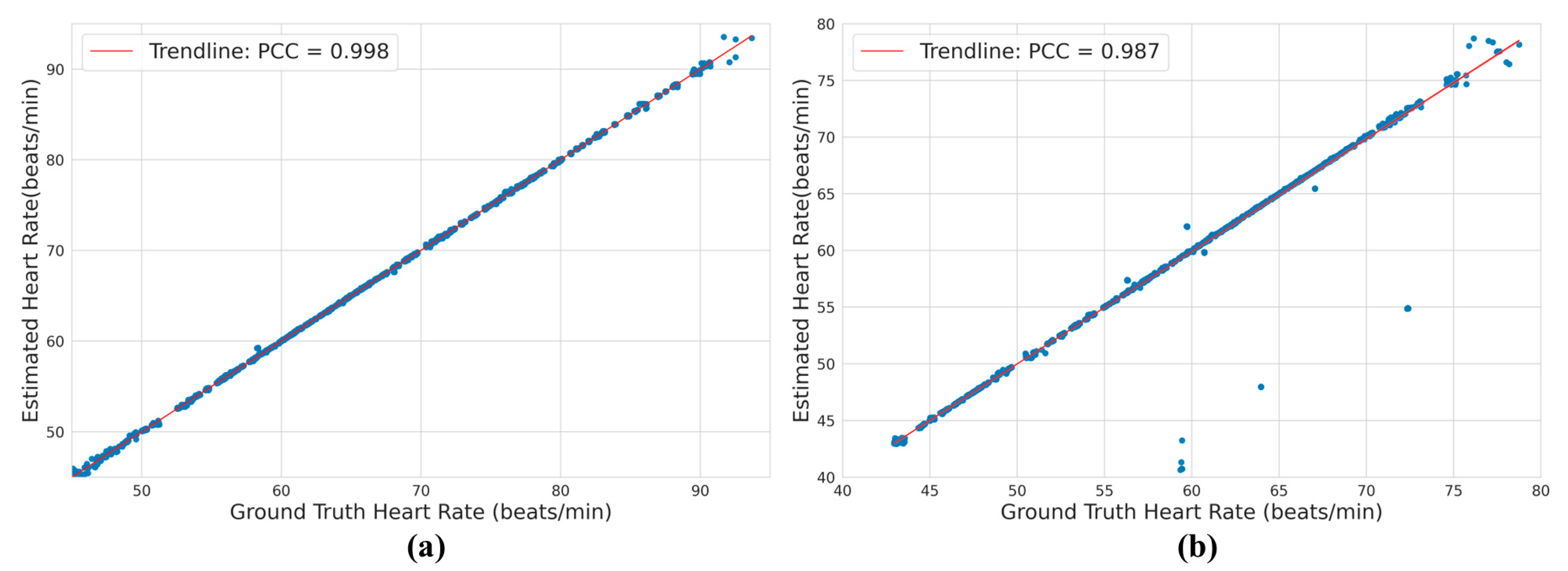
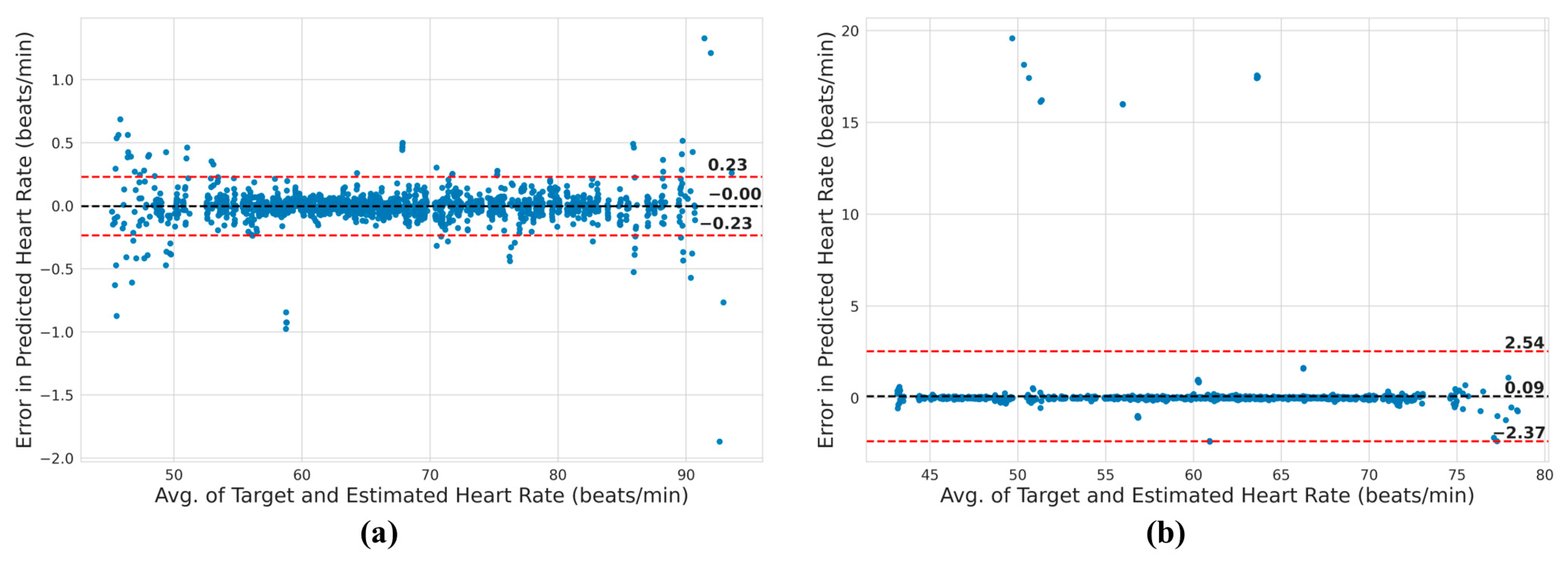
3.3. Heart Rate Analysis
3.4. Comparison with Current Work
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amano, Y.; Yanagisawa, F.; Tachi, M.; Asai, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Hashimoto, H.; Ishihara, K.; Kumita, S. Three-dimensional cardiac MR imaging: Related techniques and clinical applications. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2017, 16, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Knobelsdorff-Brenkenhoff, F.; Pilz, G.; Schulz-Menger, J. Representation of cardiovascular magnetic resonance in the AHA/ACC guidelines. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2017, 19, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, S.E.; Aung, N.; Sanghvi, M.M.; Zemrak, F.; Fung, K.; Paiva, J.M.; Francis, J.M.; Khanji, M.Y.; Lukaschuk, E.; Lee, A.M.; et al. Reference ranges for cardiac structure and function using cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) in Caucasians from the UK Biobank population cohort. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Resonance 2017, 19, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu-Narayan, S.V.; Giannakoulas, G.; Valente, A.M.; Li, W.; Gatzoulis, M.A. Imaging of congenital heart disease in adults. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 1182–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kording, F.; Ruprecht, C.; Schoennagel, B.; Fehrs, K.; Yamamura, J.; Adam, G.; Goebel, J.; Nassenstein, K.; Maderwald, S.; Quick, H.; et al. Doppler ultrasound triggering for cardiac MRI at 7T. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 80, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spicher, N.; Kukuk, M.; Maderwald, S.; Ladd, M.E. Initial evaluation of prospective cardiac triggering using photoplethysmography signals recorded with a video camera compared to pulse oximetry and electrocardiography at 7T MRI. Biomed. Eng. Online 2016, 15, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sablong, R.; Rengle, A.; Ramgolam, A.; Saint-Jalmes, H.; Beuf, O. An optical fiber-based gating device for prospective mouse cardiac MRI. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 61, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abi-Abdallah, D.; Drochon, A.; Robin, V.; Fokapu, O. Cardiac and respiratory MRI gating using combined wavelet sub-band decomposition and adaptive filtering. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 35, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, J.W.; Rose, G.; Clifford, G.; Oster, J. ECG-based gating in ultra high field cardiovascular magnetic resonance using an independent component analysis approach. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2013, 15, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Committee of Standards and Practice Parameters; American Society of Anesthesiologists. Standards for Basic Anesthetic Monitoring. 2012. Available online: https://www.asahq.org/standards-and-guidelines/standards-for-basic-anesthetic-monitoring (accessed on 28 February 2023).
- Bogaert, J.; Dymarkowski, S.; Taylor, A.M.; Muthurangu, V. Clinical Cardiac MRI; Springer Science and Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sommer, P.; Grothoff, M.; Eitel, C.; Gaspar, T.; Piorkowski, C.; Gutberlet, M.; Hindricks, G. Feasibility of real-time magnetic resonance imaging-guided electrophysiology studies in humans. Europace 2013, 15, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, T.S.; Cheng, R.; Tang, G.; Mao, L.; Tse, Z.T.H. The magnetohydrodynamic effect and its associated material designs for biomedical applications: A state-of-the-art review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 3942–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mader, W.; Hoppe, G.; Timmer, J.; Lorenz, R.; Buchenberg, W.B.; Büchert, M.; Menza, M.; Jung, B. In vitro study to simulate the intracardiac magnetohydrodynamic effect. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 74, 850–857. [Google Scholar]
- Abi-Abdallah, D.; Robin, V.; Drochon, A.; Fokapu, O. Alterations in human ECG due to the MagnetoHydroDynamic effect: A method for accurate R peak detection in the presence of high MHD artifacts. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Lyon, France, 22–26 August 2007; pp. 1842–1845. [Google Scholar]
- Krug, J.W.; Rose, G. Magnetohydrodynamic distortions of the ECG in different MR scanner configurations. In Proceedings of the Computing in Cardiology, Hangzhou, China, 18–21 September 2011; pp. 769–772. [Google Scholar]
- Krug, J.W.; Rose, G.H.; Stucht, D.; Clifford, G.D.; Oster, J. Filtering the magnetohydrodynamic effect from 12-lead ECG signals using independent component analysis. In Proceedings of the Computing in Cardiology, Krakow, Poland, 9–12 September 2012; pp. 589–592. [Google Scholar]
- Krug, J.W. Improved Cardiac Gating and Patient Monitoring in High Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging by Means of Electrocardiogram Signal Processing. Ph.D. Dissertation, Magdeburg University, Magdeburg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Passand, J.K.; Rose, G. Progress of MRI-guided EP Interventions is Hampered by a Lack of ECG-based Patient Monitoring-An Engineering Perspective. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Bio-Inspired Systems and Signal Processing, Prague, Czech Republic, 22–24 February 2019; pp. 201–208. [Google Scholar]
- Kinouchi, Y.; Yamaguchi, H.; Tenforde, T. Theoretical analysis of magnetic field interactions with aortic blood flow. Bioelectromagnetics 1996, 17, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, J.; Rose, G.; Stucht, D.; Clifford, G.; Oster, J. Limitations of VCG based gating methods in ultra high field cardiac MRI. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2013, 15, W19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H.; Bin Heyat, B.; Akhtar, F.; Muaad, A.Y.; Ukwuoma, C.C.; Bilal, M.; Miraz, M.H.; Bhuiyan, M.A.S.; Wu, K.; Damaševičius, R.; et al. An Automatic Premature Ventricular Contraction Recognition System Based on Imbalanced Dataset and Pre-Trained Residual Network Using Transfer Learning on ECG Signal. Diagnostics 2022, 13, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, M.T.; Amir, M.; Maqsood, S.; Yousufi, M.; Abdullah, S.; Irfan, M. Modified block compressed sensing for extraction of fetal electrocardiogram from mother electrocardiogram using block compressed sensing based guided focuss and fast-independent component. Inf. Technol. Control. 2021, 50, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Krug, J.W.; Rose, G. Reducing of gradient induced artifacts on the ECG signal during MRI examinations using Wilcoxon filter. Curr. Dir. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 2, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A. Signal Processing of an ECG signal in the Presence of a Strong Static Magnetic Field. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Central Florida, Orlando, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Tompkins, W. A real-time QRS detection algorithm. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1985, BME-32, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aqil, M.; Jbari, A.; Bourouhou, A. Adaptive ECG Wavelet analysis for R-peaks detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Electrical and Information Technologies (ICEIT), Tangiers, Morocco, 4–7 May 2016; pp. 164–167. [Google Scholar]
- Thiamchoo, N.; Phukpattaranont, P. Application of wavelet transform and Shannon energy on R peak detection algorithm. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer, Telecommunications and Information Technology (ECTI-CON), Chiang Mai, Thailand, 28 June–1 July 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, J.; Escalona, O.J.; Kodoth, V.; Manoharan, G.; Bosnjak, A. Denoising and automated R-peak detection in the ECG using Discrete Wavelet Transform. In Proceedings of the Computing in Cardiology Conference (CinC), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 11–14 September 2016; pp. 1045–1048. [Google Scholar]
- Sadhukhan, D.; Mitra, M. R-peak detection algorithm for ECG using double difference and RR interval processing. Procedia Technol. 2012, 4, 873–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.B.; Bashar, S.K.; Walkey, A.J.; McManus, D.D.; Chon, K.H. An accurate QRS complex and P wave detection in ECG signals using complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise approach. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 128869–128880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, S.E.; Wickline, S.A.; Lorenz, C.H. Novel real-time R-wave detection algorithm based on the vectorcardiogram for accurate gated magnetic resonance acquisitions. Magn. Reson. Med. 1999, 42, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, J.M.; Fischer, S.E.; Wickline, S.A.; Lorenz, C.H. Performance of QRS detection for cardiac magnetic resonance imaging with a novel vectorcardiographic triggering method. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2000, 12, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Deursen, C.J.; Vernooy, K.; Dudink, E.; Bergfeldt, L.; Crijns, H.J.G.M.; Prinzen, F.W.; Wecke, L. Vectorcardiographic QRS area as a novel predictor of response to cardiac resynchronization therapy. J. Electrocardiol. 2015, 48, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton-Craig, C.; Stäeb, D.; Al Najjar, A.; O’brien, K.; Crawford, W.; Fletcher, S.; Barth, M.; Galloway, G. 7-Tesla Functional Cardiovascular MR Using Vectorcardiographic Triggering—Overcoming the Magnetohydrodynamic Effect. Tomography 2021, 7, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abi-Abdallah, D.; Chauvet, E.; Bouchet-Fakri, L.; Bataillard, A.; Briguet, A.; Fokapu, O. Reference signal extraction from corrupted ECG using wavelet decomposition for MRI sequence triggering: Application to small animals. Biomed. Eng. Online 2006, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- El B’charri, O.; Latif, R.; Elmansouri, K.; Abenaou, A.; Jenkal, W. ECG signal performance de-noising assessment based on threshold tuning of dual-tree wavelet transform. Biomed. Eng. Online 2017, 16, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Al, Z.M.A.; Thapa, K.; Yang, S.-H. Improving R Peak Detection in ECG Signal Using Dynamic Mode Selected Energy and Adaptive Window Sizing Algorithm with Decision Tree Algorithm. Sensors 2021, 21, 6682. [Google Scholar]
- Asgari, S.; Mehrnia, A.; Moussavi, M. Automatic detection of atrial fibrillation using stationary wavelet transform and support vector machine. Comput. Biol. Med. 2015, 60, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.; Ray, K.C.; Shankar, O. Cardiac arrhythmia beat classification using DOST and PSO tuned SVM. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2016, 136, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayarangan, S.; Vignesh, R.; Murugesan, B.; Preejith, S.; Joseph, J.; Sivaprakasam, M. RPnet: A Deep Learning approach for robust R Peak detection in noisy ECG. In Proceeding of the 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 July 2020; pp. 345–348. [Google Scholar]
- Romdhane, T.F.; Alhichri, H.; Ouni, R.; Atri, M. Electrocardiogram heartbeat classification based on a deep convolutional neural network and focal loss. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 123, 103866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.L.; Ng, E.Y.; Tan, R.S.; Acharya, U.R. Automated beat-wise arrhythmia diagnosis using modified U-net on extended electrocardiographic recordings with heterogeneous arrhythmia types. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 105, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabbouj, M.; Kiranyaz, S.; Malik, J.; Zahid, M.U.; Ince, T.; Chowdhury, M.E.H.; Khandakar, A.; Tahir, A. Robust Peak Detection for Holter ECGs by Self-Organized Operational Neural Networks. In IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks Learning Systems; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, T.; Khandakar, A.; Kadir, M.A.; Islam, K.R.; Islam, K.F.; Mazhar, R.; Hamid, T.; Islam, M.T.; Kashem, S.; Mahbub, Z.B.; et al. Reliable tuberculosis detection using chest X-ray with deep learning, segmentation and visualization. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 191586–191601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Passand, J.W.K. Influence of the MHD Effect on 12-lead and 3-lead ECGs Recorded in 1T to 7T MRI Scanners. Available online: https://physionet.org/content/mhd-effect-ecg-mri/1.0.0/ (accessed on 28 February 2023).
- Goldberger, A.L.; Amaral, L.A.; Glass, L.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Ivanov, P.C.; Mark, R.G.; Mietus, J.E.; Moody, G.B.; Peng, C.K.; Stanley, H.E. PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: Components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation 2000, 101, e215–e220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krug, J.W.; Schmidt, M.; Rose, G.; Friebe, M. A database of electrocardiogram signals acquired in different magnetic resonance imaging scanners. In Proceedings of the Computing in Cardiology (CinC), Rennes, France, 24–27 September 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Keleş, O.; Tekalp, A.M.; Malik, J.; Kιranyaz, S. Self-Organized Residual Blocks For Image Super-Resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Anchorage, AK, USA, 19–22 September 2021; pp. 589–593. [Google Scholar]
- Kiranyaz, S.; Ince, T.; Iosifidis, A.; Gabbouj, M. Operational neural networks. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 6645–6668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiranyaz, S.; Malik, J.; Abdallah, H.B.; Ince, T.; Iosifidis, A.; Gabbouj, M. Self-organized operational neural networks with generative neurons. Neural Netw. 2021, 140, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, J.; Kiranyaz, S.; Yamac, M.; Guldogan, E.; Gabbouj, M. Convolutional versus Self-Organized Operational Neural Networks for Real-World Blind Image Denoising. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.03070. [Google Scholar]
- Yílmaz, M.A.; Kelesş, O.; Güven, H.; Tekalp, A.M.; Malik, J.; Kíranyaz, S. Self-Organized Variational Autoencoders (Self-Vae) For Learned Image Compression. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Anchorage, AK, USA, 19–22 September 2021; pp. 3732–3736. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, J.; Kiranyaz, S.; Gabbouj, M. Self-organized operational neural networks for severe image restoration problems. Neural Netw. 2021, 135, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifford, G.D. Signal Processing Methods for Heart Rate Variability. PhD Thesis, Oxford University, Oxford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]




| 3T | 7T | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Network | IoU (%) | DSC (%) | IoU (%) | DSC (%) |
| FPN | 96.35 | 96.33 | 93.85 | 95.55 |
| Self-FPN | 97.88 | 98.86 | 95.01 | 97.31 |
| Self-Attention MHDNet | 98.97 | 99.01 | 97.01 | 98.36 |
| Network | Magnetic Field Strength | Recall (%) | Precision (%) | F1-Score (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Self-Attention MHDNet | 3T | 99.83 | 99.68 | 99.76 |
| 7T | 99.87 | 99.78 | 99.82 |
| Method | Magnetic Field | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICA of ECG for R-peak detection [9] | 7T | 99.10 | 99.20 | - |
| M1: R-peak detection in a single ECG lead [57] | 7T | 89.40 | 87.10 | - |
| M2: R-peak detection in a single VCG lead [57] | 7T | 91.20 | 88.90 | - |
| M3: 3D VCG-based R-peak detection [32] | 7T | 57.50 | 72.10 | - |
| M5: ICA of the VCG for R-peak detection [57] | 7T | 87.50 | 84.30 | - |
| Self-Attention MHDNet | 7T | 99.87 | 99.78 | 99.82 |
| 3T | 99.83 | 99.68 | 99.76 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chowdhury, M.H.; Chowdhury, M.E.H.; Khan, M.S.; Ullah, M.A.; Mahmud, S.; Khandakar, A.; Hassan, A.; Tahir, A.M.; Hasan, A. Self-Attention MHDNet: A Novel Deep Learning Model for the Detection of R-Peaks in the Electrocardiogram Signals Corrupted with Magnetohydrodynamic Effect. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10050542
Chowdhury MH, Chowdhury MEH, Khan MS, Ullah MA, Mahmud S, Khandakar A, Hassan A, Tahir AM, Hasan A. Self-Attention MHDNet: A Novel Deep Learning Model for the Detection of R-Peaks in the Electrocardiogram Signals Corrupted with Magnetohydrodynamic Effect. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(5):542. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10050542
Chicago/Turabian StyleChowdhury, Moajjem Hossain, Muhammad E. H. Chowdhury, Muhammad Salman Khan, Md Asad Ullah, Sakib Mahmud, Amith Khandakar, Alvee Hassan, Anas M. Tahir, and Anwarul Hasan. 2023. "Self-Attention MHDNet: A Novel Deep Learning Model for the Detection of R-Peaks in the Electrocardiogram Signals Corrupted with Magnetohydrodynamic Effect" Bioengineering 10, no. 5: 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10050542
APA StyleChowdhury, M. H., Chowdhury, M. E. H., Khan, M. S., Ullah, M. A., Mahmud, S., Khandakar, A., Hassan, A., Tahir, A. M., & Hasan, A. (2023). Self-Attention MHDNet: A Novel Deep Learning Model for the Detection of R-Peaks in the Electrocardiogram Signals Corrupted with Magnetohydrodynamic Effect. Bioengineering, 10(5), 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10050542










