Yeast—As Bioremediator of Silver-Containing Synthetic Effluents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Syntethic Effluents
2.3. Biosorbent
2.4. Metal Removal from Silver-Containing Effluents
2.5. Metal Desorption
2.6. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
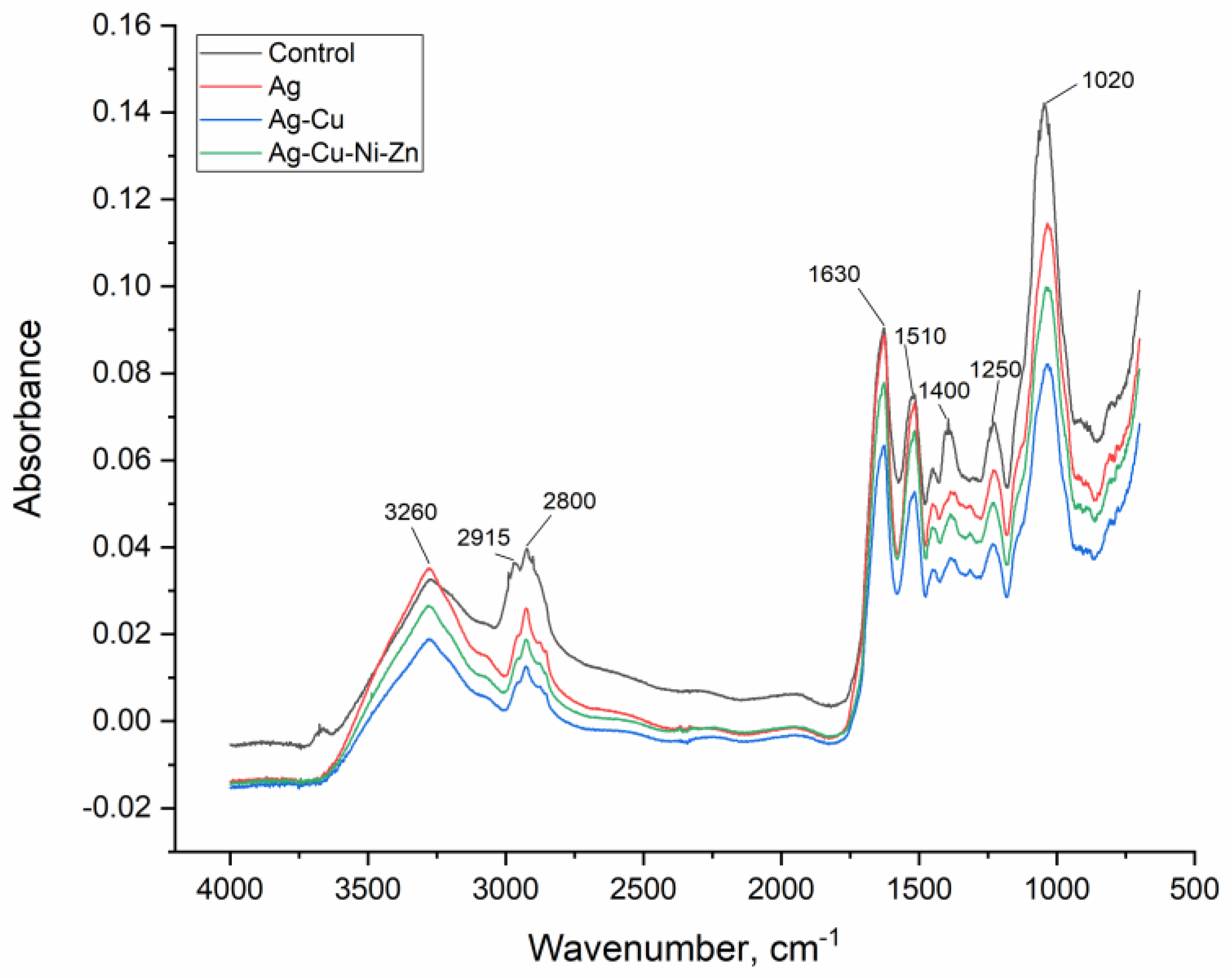
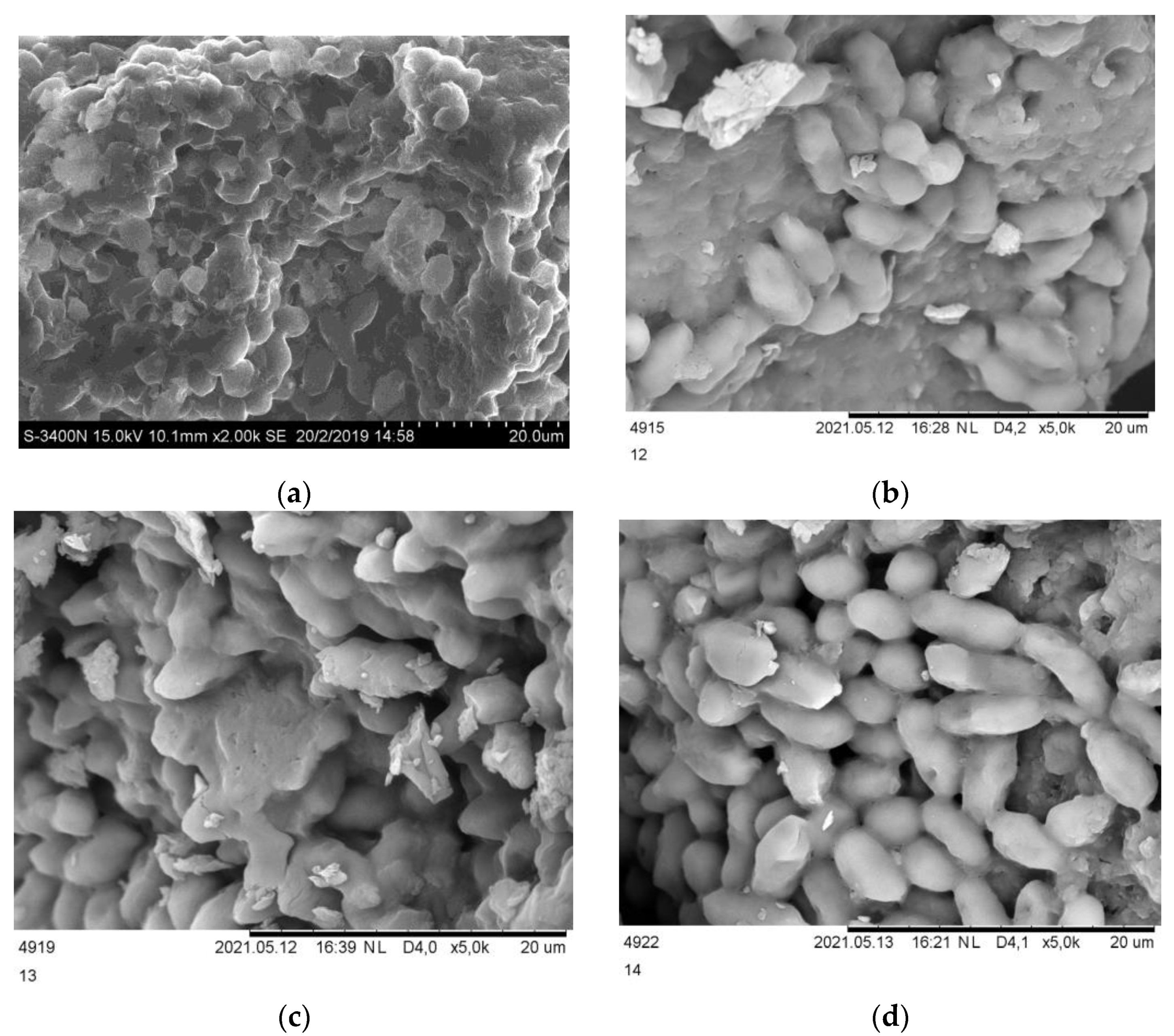
3.1. Biosorbent Characterization
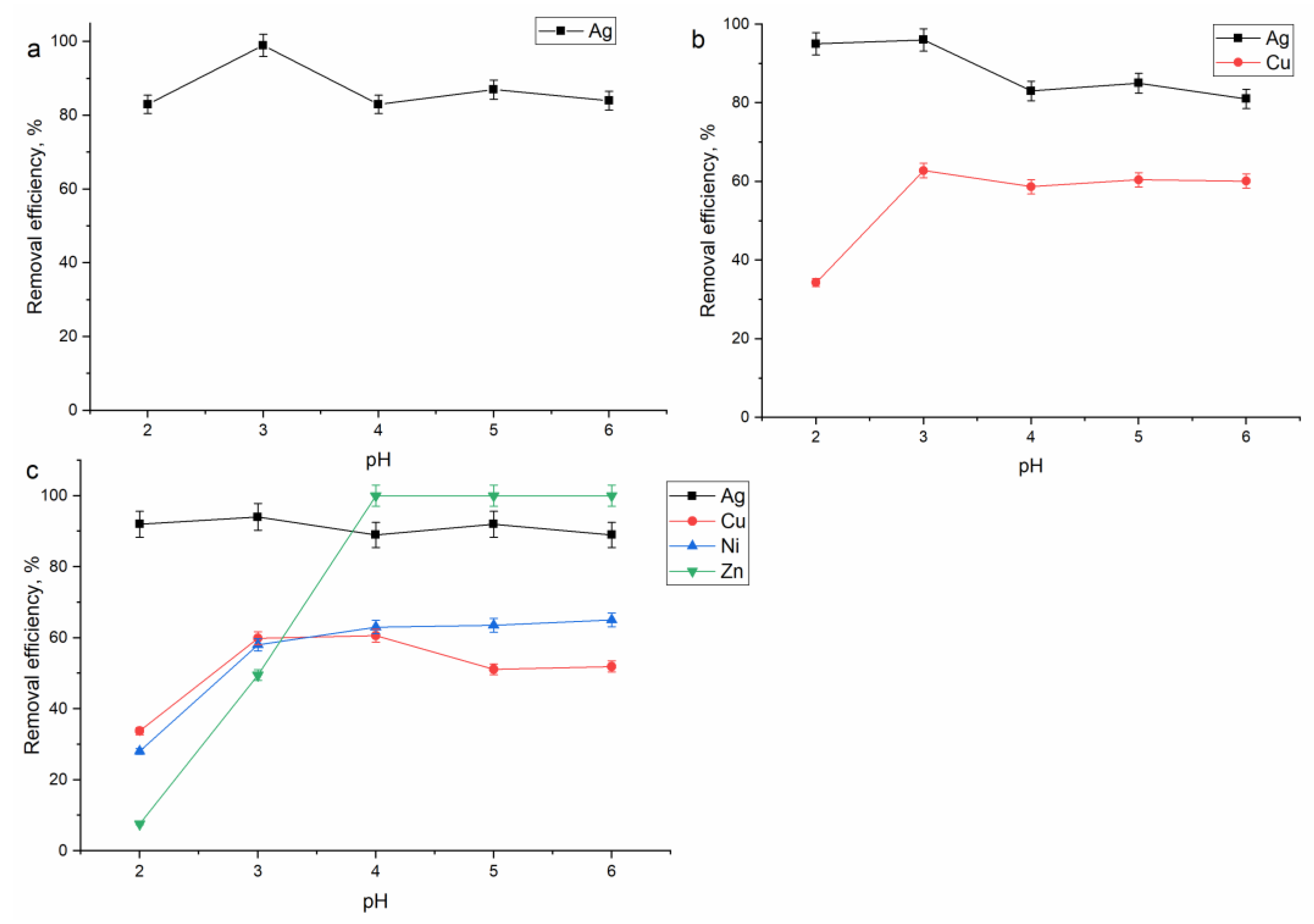
3.2. Effect of pH on Metal Removal from Silver Containing Effluents
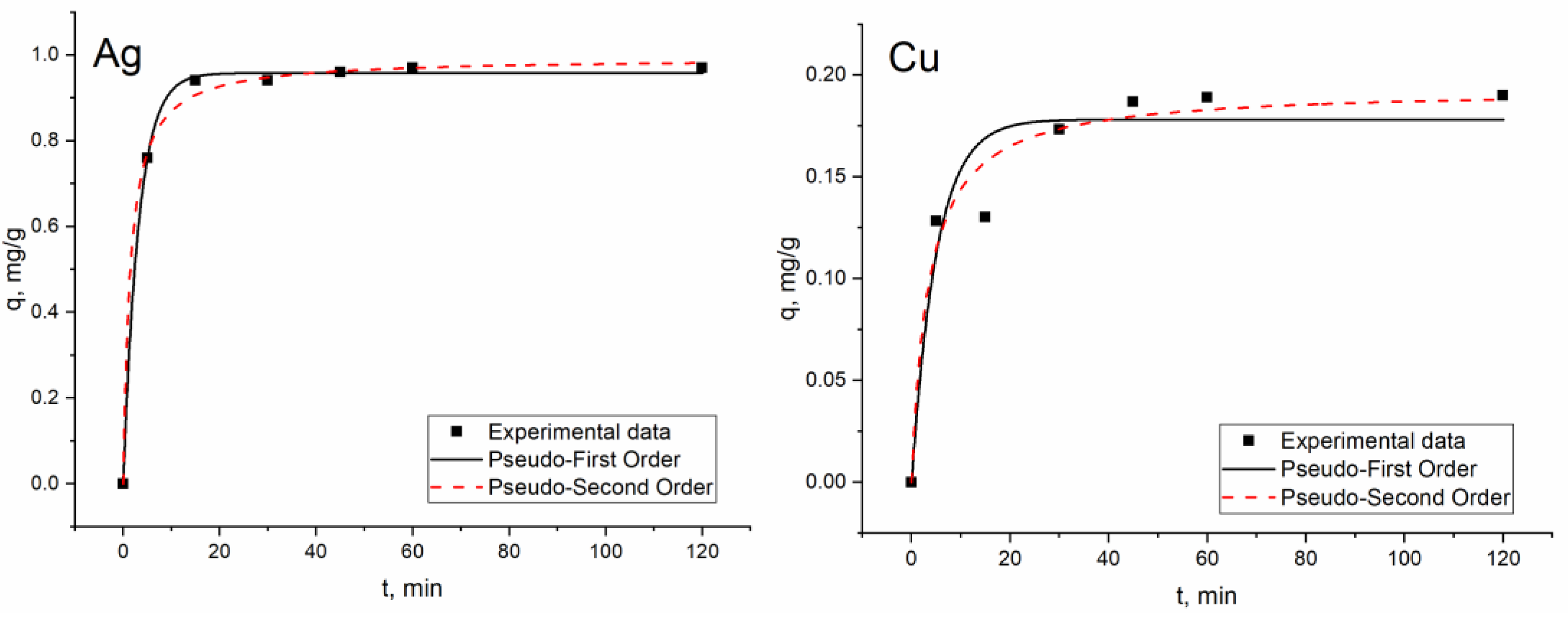
3.3. Effect of Time on Metal Biosorption on S. cerevisiae Biomass and Kinetic Studies
3.4. Effect of Silver Concentration on Metal Ion Biosorption on S. cerevisiae Biomass and Equlibrium Studies
3.5. Effect of Temperature on Metal Ion Biosorption on on S. cerevisiae Biomass and Thermodinamic Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elwakeel, K.Z.; Al-Bogami, A.S.; Guibal, E. 2-Mercaptobenzimidazole derivative of chitosan for silver sorption—Contribution of magnetite incorporation and sonication effects on enhanced metal recovery. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 403, 126265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, K.R.; Bhan, A. Particle size dependence of ethylene epoxidation rates on Ag/α-Al2O3 catalysts: Why particle size distributions matter. J. Catal. 2023, 420, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bi, F.; Wang, Y.; Jia, M.; Tao, X.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, X. MOF-derived CeO2 supported Ag catalysts for toluene oxidation: The effect of synthesis method. Mol. Catal. 2021, 515, 111922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Song, L.; Bi, F.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Cui, L. Catalytic oxidation of toluene using a facile synthesized Ag nanoparticle supported on UiO-66 derivative. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 571, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Long, J.; Xi, Y.; Luo, X. Recovery of Silver from Wastewater Using a New Magnetic Photocatalytic Ion-Imprinted Polymer. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2090–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.; Wang, L.; Waseem, H.; Sharif, H.M.A.; Djellabi, R.; Zhang, C.; Pan, G. Bioelectrochemical recovery of silver from wastewater with sustainable power generation and its reuse for biofouling mitigation. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 235, 1425–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jintakosol, T.; Nitayaphat, W. Adsorption of Silver (I) from Aqueous Solution Using Chitosan/Montmorillonite Composite Beads. Mater. Res. 2016, 19, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Kuang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wu, D. A closed-loop sustainable scheme for silver recovery from water by reusable thiol-grafted graphene oxide. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 305, 127146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sverdrup, H.; Koca, D.; Ragnarsdottir, K.V. Investigating the sustainability of the global silver supply, reserves, stocks in society and market price using different approaches. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 83, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staroń, P.; Chwastowski, J.; Banach, M. Sorption and desorption studies on silver ions from aqueous solution by coconut fiber. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 149, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbar, B.; Alem, A.; Marcotte, S.; Pantet, A.; Ahfir, N.D.; Bizet, L.; Duriatti, D. Experimental investigation on removal of heavy metals (Cu2+, Pb2+, and Zn2+) from aqueous solution by flax fibres. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 109, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Chab, J.C.; Castañeda-Chávez M del, R.; Chan-Bacab, M.J.; Aguila-Ramírez, R.N.; Galaviz-Villa, I.; Bartolo-Pérez, P.; Lango-Reynoso, F.; Tabasco-Novelo, C.; Gaylarde, C.; Ortega-Morales, B.O. Biosorption of cadmium by non-toxic extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) synthesized by bacteria from marine intertidal biofilms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tytłak, A.; Oleszczuk, P.; Dobrowolski, R. Sorption and desorption of Cr (VI) ions from water by biochars in different environmental conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 5985–5994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlinić, S.; Piljac, I. Electrolytic desorption of silver from ion-exchange resins. Water Res. 1998, 32, 2913–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, I.; Roca, A.; Cruells, M.; Patiño, F.; Salinas, E. Study of silver precipitation in thiosulfate solutions using sodium dithionite. Application to an industrial effluent. Hydrometallurgy 2007, 89, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinicovscaia, I.; Yushin, N.; Grozdov, D.; Safonov, A. Application of Shewanella xiamenensis Placed on Zeolite in Treatment of Silver-Containing Effluents. Minerals 2023, 13, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, C. Adsorption and recovery of immobilized coffee ground beads for silver ions from industrial wastewater. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 53, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinicovscaia, I.; Cepoi, L.; Chiriac, T.; Ana Culicov, O.; Frontasyeva, M.; Pavlov, S.; Kirkesali, E.; Akshintsev, A.; Rodlovskaya, E. Spirulina platensis as biosorbent of chromium and nickel from industrial effluents. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 11103–11110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinicovscaia, I.; Yushin, N.; Grozdov, D.; Abdusamadzoda, D.; Safonov, A.; Rodlovskaya, E. Zinc-containing effluent treatment using Shewanella xiamenensis biofilm formed on zeolite. Materials 2021, 14, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhuang, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, G.; Lv, W. Selective removal of heavy metals by Zr-based MOFs in wastewater: New acid and amino functionalization strategy. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 124, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savastru, E.; Bulgariu, D.; Zamfir, C.I.; Bulgariu, L. Application of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in the Biosorption of Co (II), Zn (II) and Cu (II) Ions from Aqueous Media. Water 2022, 14, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinicovscaia, I.; Safonov, A.; Troshkina, I.; Demina, L.; German, K. Biosorption of Re (VII) from Batch Solutions and Industrial Effluents by Cyanobacteria Spirulina platensis. CLEAN—Soil Air Water 2018, 46, 1700576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen Van, P.; Thi Hong Truong, H.; Pham, T.A.; Le Cong, T.; Le, T.; Thi Nguyen, K.C. Removal of Manganese and Copper from Aqueous Solution by Yeast Papiliotrema huenov. Mycobiology 2021, 49, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacHado, M.D.; Janssens, S.; Soares, H.M.V.M.; Soares, E.V. Removal of heavy metals using a brewer’s yeast strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Advantages of using dead biomass. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 106, 1792–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, W.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhong, Z. Investigation of the Adsorption Process of Chromium (VI) Ions from Petrochemical Wastewater Using Nanomagnetic Carbon Materials. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujan, P.; Prell, A.; Šafář, H.; Sobotka, M.; Řezanka, T.; Holler, P. Removal of copper ions from dilute solutions by Streptomyces noursei mycelium. Comparison with yeast biomass. Folia Microbiol. 2005, 50, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschatre, M.; Ghillebaert, F.; Guezennec, J.; Colin, C.S. Sorption of Copper (II) and Silver (I) by four bacterial exopolysaccharides. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 171, 1313–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajenifuja, E.; Ajao, J.A.; Ajayi, E.O.B. Equilibrium adsorption isotherm studies of Cu (II) and Co (II) in high concentration aqueous solutions on Ag-TiO2-modified kaolinite ceramic adsorbents. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2279–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bădescu, I.S.; Bulgariu, D.; Ahmad, I.; Bulgariu, L. Valorisation possibilities of exhausted biosorbents loaded with metal ions—A review. J. Environ. Manage. 2018, 224, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirmahdi, R.S.; Mofid, V.; Zoghi, A.; Khosravi_Darani, K.; Mortazavian, A.M. Risk of low stability Saccharomyces cerevisiae ATCC 9763-heavy metals complex in gastrointestinal simulated conditions. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, C. Biosorption of heavy metals by Saccharomyces cerevisiae: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2006, 24, 427–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davydenko, S.; Meledina, T.; Mittenberg, A.; Shabelnikov, S.; Vonsky, M.; Morozov, A. Proteomics answers which yeast genes are specific for baking, brewing, and ethanol production. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-espeja, P. Next generation winemakers: Genetic engineering in saccharomyces cerevisiae for trendy challenges. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, D.; Xie, H.; Won, S.W.; Cui, L.; Wu, G. Adsorption of Ag (I) from aqueous solution by waste yeast: Kinetic, equilibrium and mechanism studies. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 38, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhan, S.N.; Khadom, A.A. Biosorption of heavy metals from aqueous solutions by Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Int. J. Ind. Chem. 2015, 6, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Rova, U.; Christakopoulos, P.; Matsakas, L. From Yeast to Biotechnology. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, E.V.; De Coninck, G.; Duarte, F.; Soares, H.M.V.M. Use of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for Cu2+ removal from solution: The advantages of using a flocculent strain. Biotechnol. Lett. 2002, 24, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharchenko, Y.; Lastovetska, L.; Maslak, V.; Sidorenko, M.; Vasylenko, V.; Shydlovska, O. Antibacterial Activity of Green Synthesised Silver Nanoparticles on Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korbekandi, H.; Mohseni, S.; Jouneghani, R.M.; Pourhossein, M.; Iravani, S. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.-N.; Liang, J.; Chen, C.; Li, K.; Zhou, W.; Jia, J.; Sun, T. Treatment of real deplating wastewater through an environmental friendly precipitation-electrodeposition-oxidation process: Recovery of silver and copper and reuse of wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 248, 117082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlihor, R.M.; Diaconu, M.; Fertu, D.; Chelaru, C.; Sandu, I.; Tavares, T.; Gavrilescu, M. Bioremediation of Cr (VI) polluted wastewaters by sorption on heat inactivated Saccharomyces cerevisiae biomass. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2013, 7, 581–594. [Google Scholar]
- Zinicovscaia, I.; Yushin, N.; Abdusamadzoda, D.; Grozdov, D.; Shvetsova, M. Efficient removal of metals from synthetic and real galvanic zinc-containing effluents by Brewer’s yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Materials 2020, 13, 3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, L.A.; El-Sesy, M.E.; ElSayed, E.S.E.B.; Zelenakova, M.; Hlinkova, M.; Mohamed, E.S.; Abu-Hashim, M. Simultaneous Removal of Metal Ions from Wastewater by a Greener Approach. Water 2022, 14, 4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinicovscaia, I.; Yushin, N.; Grozdov, D.; Vergel, K.; Ostrovnaya, T.; Rodlovskaya, E. Metal Removal from Complex Copper Containing Effluents by Waste Biomass of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S 2020, 27, 415–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, D.; Glaum, D.; Duncan, J.R. Copper tolerance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1994, 18, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedari, C.S.; Das, S.K.; Ghosh, S. Biosorption of long lived radionuclides using immobilized cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 17, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Lopes, L.P.; Macena, M.; Esteves, B.; Guiné, R.P.F. Ideal pH for the adsorption of metal ions Cr6+, Ni2+, Pb2+ in aqueous solution with different adsorbent materials. Open Agric. 2021, 6, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Ni, J.; Cao, X.; Gao, J.; Yang, L.; Jia, W.; Chen, F.; Feng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, F. Separation and Removal of Radionuclide Cesium from Water by Biodegradable Magnetic Prussian Blue Nanospheres. Processes 2022, 10, 2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha de Freitas, G.; Adeodato Vieira, M.G.; Carlos da Silva, M.G. Characterization and biosorption of silver by biomass waste from the alginate industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 271, 122588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, M.D.; Soares, E.V.; Soares, H.M.V.M. Impact of fluorides on the removal of heavy metals from an electroplating effluent using a flocculent brewer’s yeast strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 2011, 23, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Ling, C.; Yuan, R.; Liu, F.; Li, A. Bridging effects behind the coadsorption of copper and sulfamethoxazole by a polyamine-modified resin. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinicovscaia, I.; Yushin, N.; Grozdov, D.; Boldyrev, K.; Rodlovskaya, E.; Ostrovnaya, T. Removal of metals from synthetic and real galvanic nickel-containing effluents by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Chem. Ecol. 2021, 37, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, M.D.; Soares, E.V.; Soares, H.M.V.M. Removal of heavy metals using a brewer’s yeast strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Chemical speciation as a tool in the prediction and improving of treatment efficiency of real electroplating effluents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 180, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, I.; Simmons, P. Factors affecting silver biosorption by an industrial strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1996, 65, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinicovscaia, I.; Cepoi, L.; Chiriac, T.; Mitina, T.; Grozdov, D.; Yushin, N.; Culicov, O. Application of Arthrospira (Spirulina) platensis biomass for silver removal from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2017, 19, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudzinski, W.; Plazinski, W. Kinetics of solute adsorption at solid/solution interfaces: A theoretical development of the empirical pseudo-first and pseudo-second order kinetic rate equations, based on applying the statistical rate theory of interfacial transport. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 16514–16525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltrėnaitė-Gedienė, E.; Leonavičienė, T.; Baltrėnas, P. Comparison of CU (II), MN (II) and ZN (II) adsorption on biochar using diagnostic and simulation models. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Mishra, R.; Kushwaha, P.; Saha, P. Removal of safranin from aqueous solutions by NaOH-treated rice husk: Thermodynamics, kinetics and isosteric heat of adsorption. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 7, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández Pérez, B.; Ayala Espina, J.; Fernández González, M.d.L.Á. Adsorption of Heavy Metals Ions from Mining Metallurgical Tailings Leachate Using a Shell-Based Adsorbent: Characterization, Kinetics and Isotherm Studies. Materials 2022, 15, 5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, S.; Arora, N.; Gupta, P.; Pruthi, P.A.; Poluri, K.M.; Pruthi, V. Microalgae: An emerging source for mitigation of heavy metals and their potential implications for biodiesel production. In Advanced Biofuels: Applications, Technologies and Environmental Sustainability; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2019; pp. 97–128. ISBN 9780081027912. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.G.; Ma, X.L.; Sun, J.; Huang, M.R. Powerful reactive sorption of Silver(I) and Mercury(Π) onto Poly(o-phenylenediamine) microparticles. Langmuir 2009, 25, 1675–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.G.; Feng, H.; Huang, M.R. Redox sorption and recovery of silver ions as silver nanocrystals on poly(aniline-co-5-sulfo-2-anisidine) nanosorbents. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2010, 16, 10113–10123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escudero, L.B.; Vanni, G.; Duarte, F.A.; Segger, T.; Dotto, G.L. Biosorption of silver from aqueous solutions using wine industry wastes. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2018, 205, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschatre, M.; Ghillebaert, F.; Guezennec, J.; Simon-Colin, C. Study of biosorption of copper and silver by marine bacterial exopolysaccharides. In Water Resources Management VIII; WIT Press: Billerica, MA, USA, 2015; Volume 1, pp. 549–559. [Google Scholar]
- Cantuaria, M.L.; Almeida Neto, A.F.; Vieira, M.G.A. Biosorption of silver by macrophyte salvinia cucullata. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2014, 38, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, H.; Song, Y.; Huang, W.; Pan, J.; Xue, Y.; Yi, C.; Yan, Y. Biosorption of silver ions by paecilomyces lilacinus biomass: Equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2011, 29, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.; Gogate, P.R. Intensified removal of copper from waste water using activated watermelon based biosorbent in the presence of ultrasound. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 30, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condurache, B.C.; Cojocaru, C.; Samoila, P.; Cosmulescu, S.F.; Predeanu, G.; Enache, A.C.; Harabagiu, V. Oxidized Biomass and Its Usage as Adsorbent for Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Aqueous Solutions. Molecules 2022, 27, 6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladipo, B.; Govender-Opitz, E.; Ojumu, T. V Kinetics, Thermodynamics, and Mechanism of Cu (II) Ion Sorption by Biogenic Iron Precipitate: Using the Lens of Wastewater Treatment to Diagnose a Typical Biohydrometallurgical Problem. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 27984–27993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebisike, K.; Elvis Okoronkwo, A.; Kanayo Alaneme, K.; Jeremiah Akinribide, O. Thermodynamic study of the adsorption of Cd2+ and Ni2+ onto chitosan—Silica hybrid aerogel from aqueous solution. Results Chem. 2023, 5, 100730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahmoune, M.N. Evaluation of thermodynamic parameters for adsorption of heavy metals by green adsorbents. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobasherpour, I.; Salahi, E.; Ebrahimi, M. Thermodynamics and kinetics of adsorption of Cu (II) from aqueous solutions onto multi-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2014, 18, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Abraham, J. Desorption of heavy metals from metal loaded sorbents and e-wastes: A review. Biotechnol. Lett. 2019, 41, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, Y.; Yuan, Y. A new adsorbent of Pb (II) ions from aqueous solution synthesized by mechanochemical preparation of sulfonated expanded graphite. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 38350–38359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołodyńska, D.; Krukowska, J.; Thomas, P. Comparison of sorption and desorption studies of heavy metal ions from biochar and commercial active carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropacheva, T.N.; Didik, M.V.; Kornev, V.I. Simulation of the influence of EDTA on the sorption of heavy metals by humic acids. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2015, 48, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Ag | Ag/Cu | Ag/Cu/Ni/Zn | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metal | Ag | Ag | Cu | Ag | Cu | Ni | Zn | |
| qexp | 1.48 ± 0.02 | 0.97 ± 0.004 | 0.19 ± 0.03 | 0.99 ± 0.01 | 0.20 ± 0.003 | 0.13 ± 0.004 | 0.37 ± 0.003 | |
| PFO | qe | 1.44 ± 0.03 | 0.96 ± 0.005 | 0.18 ± 0.09 | 0.96 ± 0.03 | 0.19 ± 0.005 | 0.12 ± 0.005 | 0.26 ± 0.005 |
| k1 | 0.28 ± 0.04 | 0.3 ± 0.01 | 0.2 ± 0.06 | 0.23 ± 0.05 | 0.3 ± 0.06 | 0.40 ± 0.02 | 0.55 ± 0.01 | |
| R2 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.91 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.99 | |
| SSE | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.19 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.91 | 0.18 | |
| PSO | qe | 1.51 ± 0.02 | 0.99 ± 0.01 | 0.19 ± 0.009 | 1.01 ± 0.01 | 0.20 ± 0.004 | 0.13 ± 0.002 | 0.37 ± 0.005 |
| k2 | 0.3 ± 0.06 | 0.7 ± 0.09 | 1.5 ± 0.05 | 0.4 ± 0.09 | 2.7 ± 0.6 | 1.4 ± 0.7 | 5.1 ± 0.5 | |
| R2 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | |
| SSE | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.31 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 1.1 | 0.22 | |
| Ag | Ag/Cu | Ag/Cu/Ni/Zn | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm, mg/g | 51 ± 2.1 | 43.6 ± 2.5 | 108 ± 4 | |
| Langmuir | b, L/mg | 0.002 ± 0.0001 | 0.003 ± 0.0002 | 0.0009 ± 0.0002 |
| RL | 0.8 | 0.8 | 09 | |
| R2 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | |
| Radj2 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 | |
| Freundlich | KF, mg/g | 0.18 ± 0.004 | 0.17 ± 0.06 | 0.11 ± 0.001 |
| n | 1.13 ± 0.07 | 1.15 ± 0.02 | 1.11 ± 0.02 | |
| R2 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | |
| Radj2 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 |
| Sorbent | qmax, mg/g | Concentrations Range, mg/L | pH | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. cerevisiae biomass | 43.6 | 10–100 | 3.0 | Present study |
| Immobilized coffee ground beads | 39.583 | 10–300 | 6.0 | [17] |
| Graphene oxide in different modifications | 11.3–123 | 0–150 | 5.0 | [8] |
| Waste yeast | 18.9–41.8 | 0–750 | 3.0 | [34] |
| Coconut fiber | 65–82 | 5–30 | 3.0 | [10] |
| Poly(o-phenylenediamine) microparticles | 533 | 1–10 mM | 5.0 | [61] |
| Spirulina platensis | 31.6 | 5–30 | 5.0 | [55] |
| Chitosan/montmorillonite | 43.48 | 1–10 | 6.0–7.0 | [7] |
| Aniline–sulfoanisidine copolymer nanosorbent | 2034 | 200–400 | 6.0 | [62] |
| Wine industry wastes (grape peel, seed, and stem) | 41.7–61.4 | 25–300 | 7.0 | [63] |
| Exopolysaccharide produced by marine bacteria | 256 | - | [64] | |
| Salvinia Cucullata | 21.1 | 2–500 | 6.0 | [65] |
| Paecilomyces Lilacinus | 1010 | - | 3.0 | [66] |
| System | Metal | ∆G◦, kJ/mol | ∆H°, kJ/mol | ∆S°, J/mol·K | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 293 K | 303 K | 313 K | 323 K | ||||
| Ag | Ag | −19.0 | −19.1 | −19.2 | −19.4 | −15.3 | 12.3 |
| Ag/Cu | Ag | −15.1 | −16.5 | −17.8 | −19.1 | 23.5 | 132 |
| Cu | −9.9 | −10.3 | −10.7 | −11.1 | 1.6 | 39.0 | |
| Ag/Cu/Ni/Zn | Ag | −16.7 | −16.2 | −15.7 | −15.2 | −31.8 | −51.5 |
| Cu | −11.2 | −11.9 | −12.6 | −13.2 | 8.2 | 66.5 | |
| Ni | −18.1 | −18.7 | −19.4 | −20.1 | 1.1 | 65.6 | |
| Zn | −15.4 | −15.6 | −15.9 | −16.1 | −8.3 | 24.1 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zinicovscaia, I.; Yushin, N.; Grozdov, D.; Rodlovskaya, E.; Khiem, L.H. Yeast—As Bioremediator of Silver-Containing Synthetic Effluents. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10040398
Zinicovscaia I, Yushin N, Grozdov D, Rodlovskaya E, Khiem LH. Yeast—As Bioremediator of Silver-Containing Synthetic Effluents. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(4):398. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10040398
Chicago/Turabian StyleZinicovscaia, Inga, Nikita Yushin, Dmitrii Grozdov, Elena Rodlovskaya, and Le Hong Khiem. 2023. "Yeast—As Bioremediator of Silver-Containing Synthetic Effluents" Bioengineering 10, no. 4: 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10040398
APA StyleZinicovscaia, I., Yushin, N., Grozdov, D., Rodlovskaya, E., & Khiem, L. H. (2023). Yeast—As Bioremediator of Silver-Containing Synthetic Effluents. Bioengineering, 10(4), 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10040398







