Breakage of Tapered Junctions of Modular Stems in Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty—High Incidence in a Consecutive Series of a Single Institution
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Rationale
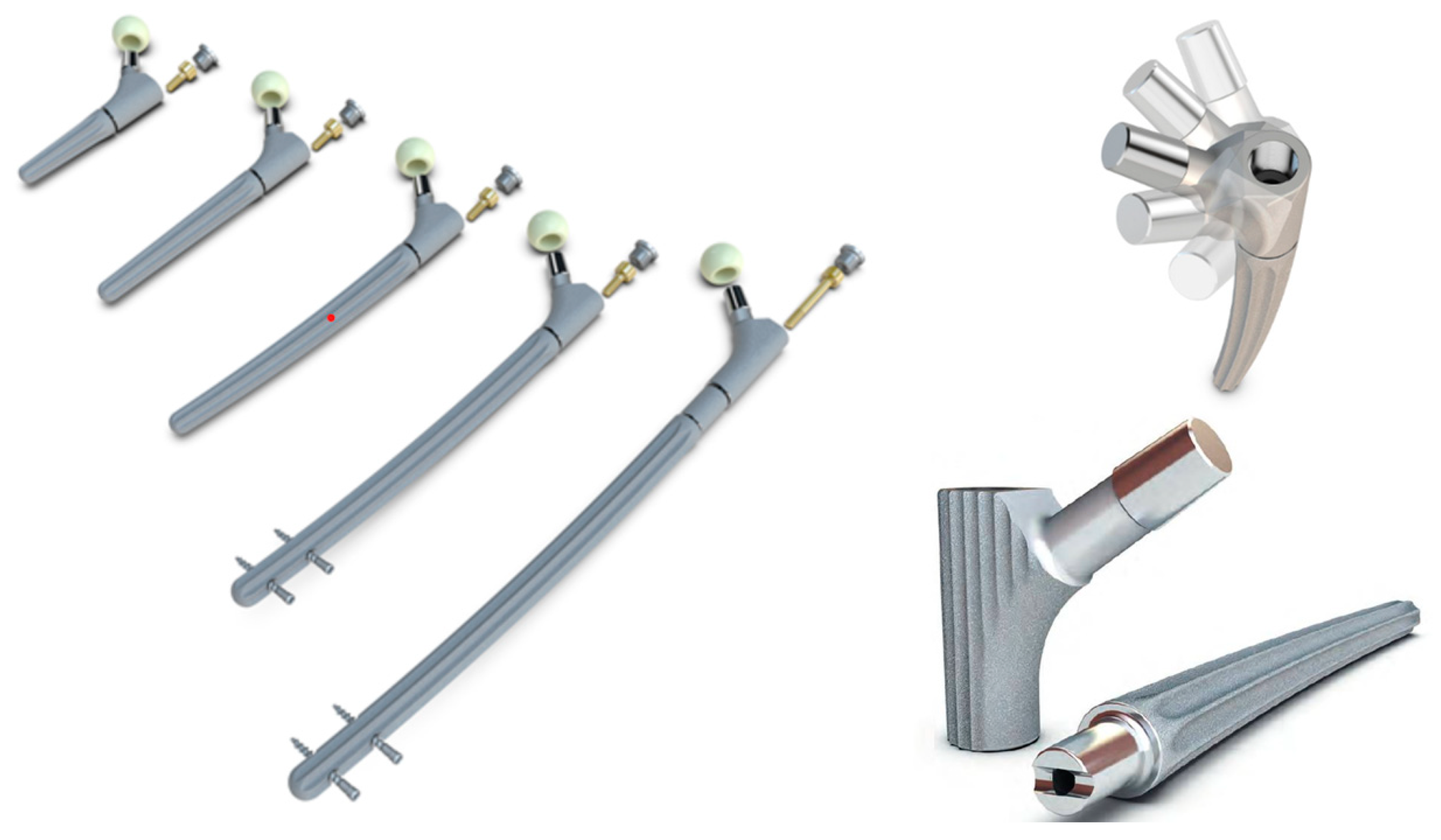
2. Materials and Methods
Surgical Technique
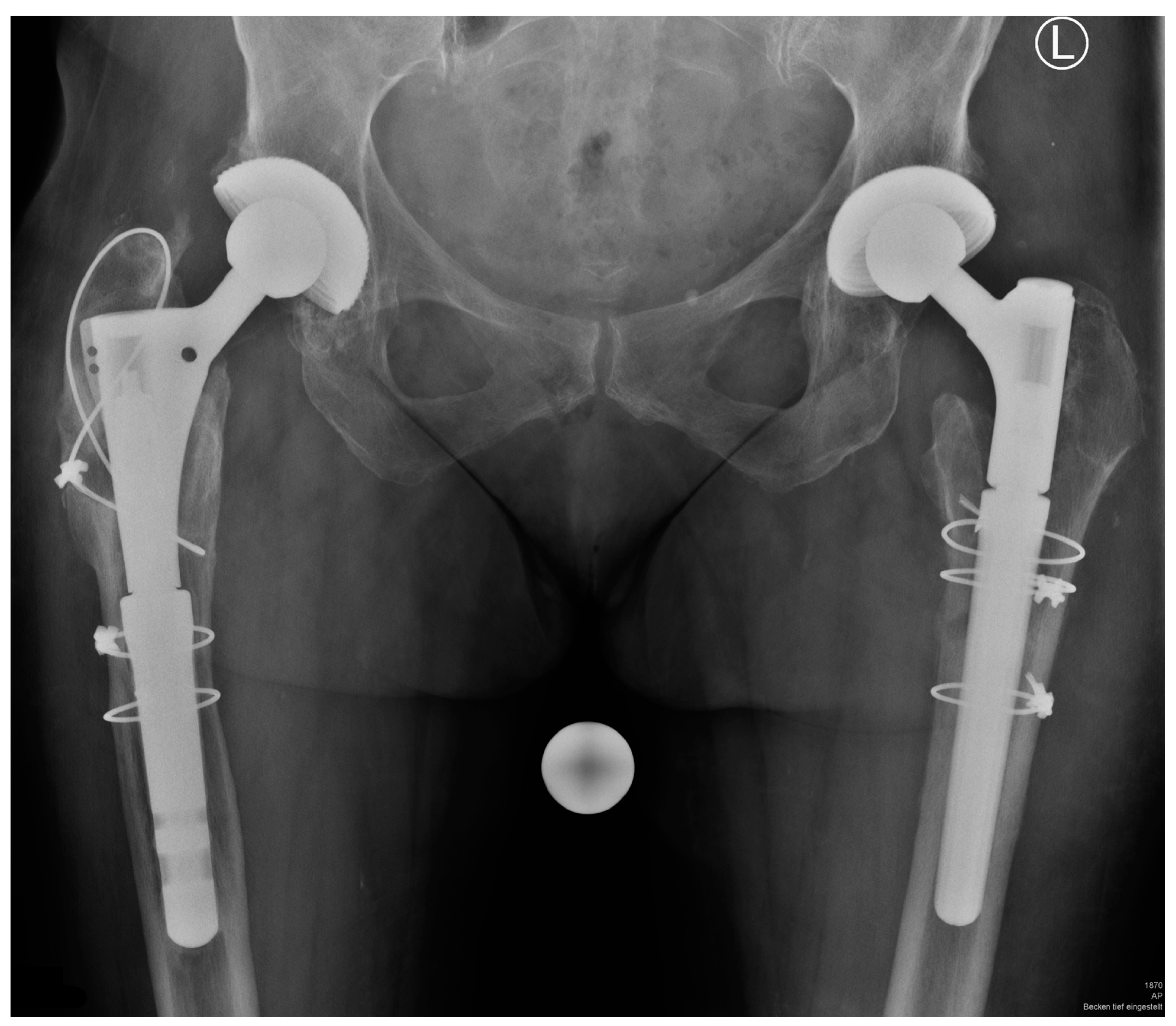
3. Results
3.1. Complications
3.2. Risk Factors for Breakage of the Taper Junction
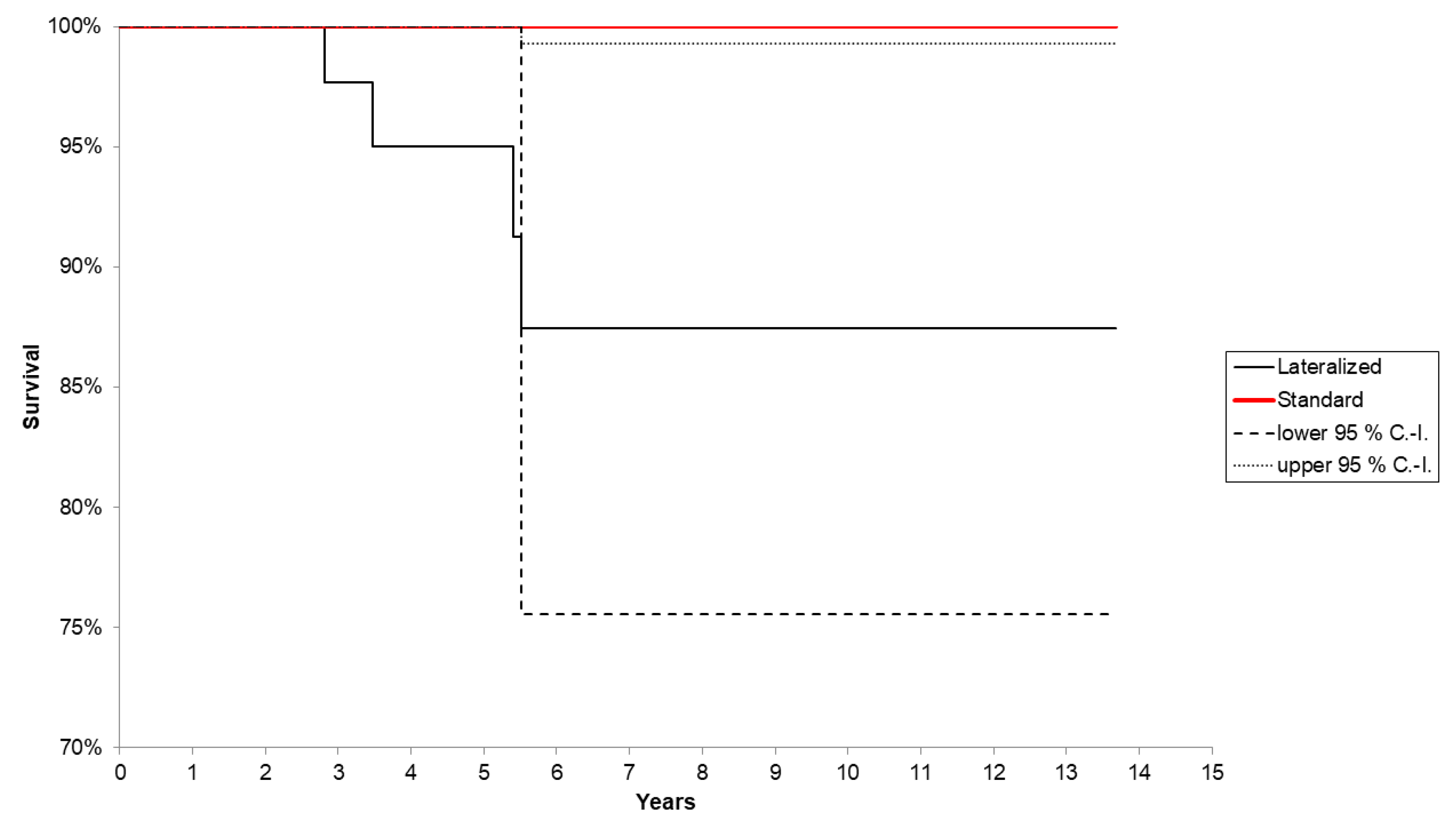
3.3. Survival Analysis
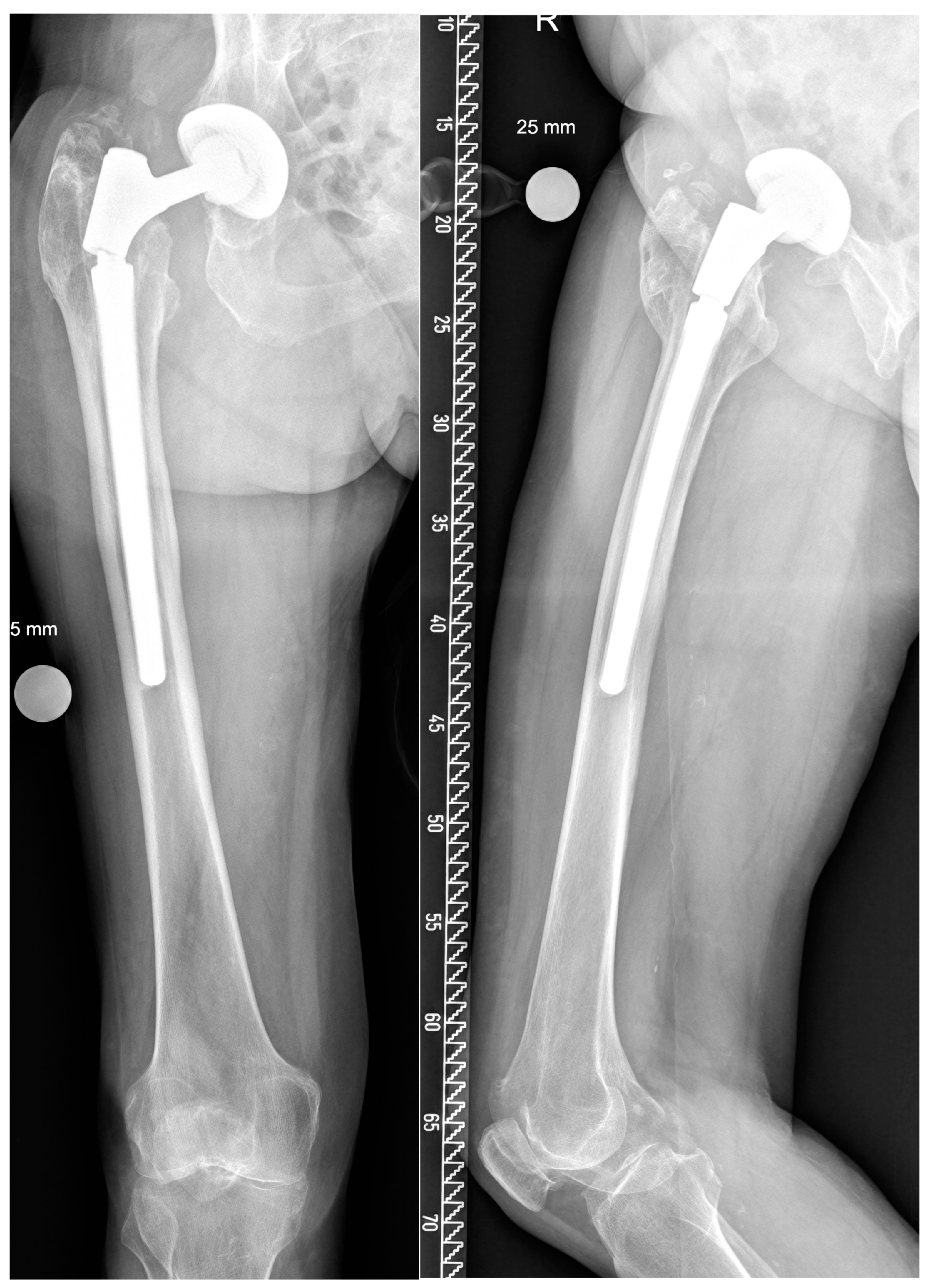
3.4. Retrieval Analysis of Coupling
4. Discussion
4.1. Background and Rationale
4.2. Cumulative Risk of Stem Breakage
4.3. Lateralized Neck and Obesity As a Risk Factor
4.4. Further Factors Influencing Risk of Breakage and Technical Considerations
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bedair, H.T.M.; Choi, H.R.; Mayle, R.; Bashyal, R.; Abbot, D.; Eberhardt, J.; Sporer, S.; Della Valle, C. A comparison of modular tapered versus modular cylindrical stems for complex femoral revisions. J. Arthroplast. 2013, 28, 71–73. [Google Scholar]
- Bohm, P.; Bischel, O. The use of tapered stems for femoral revision surgery. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2004, 420, 148–159. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, C.J.; Duncan, C.P.; Masri, B.A.; Garbuz, D.S. Femoral revision hip arthroplasty: A comparison of two stem designs. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010, 468, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakstein, D.; Backstein, D.; Safir, O.; Kosashvili, Y.; Gross, A.E. Revision total hip arthroplasty with a porous-coated modular stem: 5 to 10 years follow-up. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010, 468, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jibodh, S.R.; Schwarzkopf, R.; Anthony, S.G.; Malchau, H.; Dempsey, K.E.; Estok, D.M., 2nd. Revision hip arthroplasty with a modular cementless stem: Mid-term follow up. J. Arthroplast. 2013, 28, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kop, A.M.; Keogh, C.; Swarts, E. Proximal component modularity in THA--at what cost? An implant retrieval study. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2012, 470, 1885–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouzelis, A.; Georgiou, C.S.; Megas, P. Dissociation of modular total hip arthroplasty at the neck-stem interface without dislocation. J. Orthop. Traumatol. Off. J. Ital. Soc. Orthop. Traumatol. 2012, 13, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehran, N.; North, T.; Laker, M. Failure of a modular hip implant at the stem-sleeve interface. Orthopedics 2013, 36, e978–e981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, D.R.; Guenther, K.-P.; Deml, M.C.; Perka, C. Mechanical failure of 113 uncemented modular revision femoral components. Bone Jt. J. 2020, 102-B, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, B. What can the surgeon do to reduce the risk of junction breakage in modular revision stems? Arthroplast. Today 2018, 4, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakstein, D.; Eliaz, N.; Levi, O.; Backstein, D.; Kosashvili, Y.; Safir, O.; Gross, A.E. Fracture of cementless femoral stems at the mid-stem junction in modular revision hip arthroplasty systems. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2011, 93, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, G.; Morlock, M.M. Which length should the neck segment of modular revision stems have? Clin. Biomech. 2022, 94, 105286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, D.A.; Fernando, N.D. Classifications In Brief: The Paprosky Classification of Femoral Bone Loss. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2017, 475, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.M.; Tetreault, M.; Cipriano, C.A.; Della Valle, C.J.; Paprosky, W.; Sporer, S. Modular Tapered Implants for Severe Femoral Bone Loss in THA: Reliable Osseointegration but Frequent Complications. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2015, 473, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, G.; McCaul, J.; Jones, B.; Ingram, R.; Stark, A. Outcome after femoral revision using the restoration cone/conical femoral revision stem. Orthopedics 2011, 34, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restrepo, C.; Mashadi, M.; Parvizi, J.; Austin, M.S.; Hozack, W.J. Modular femoral stems for revision total hip arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2011, 469, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelt, C.E.; Madsen, W.; Erickson, J.A.; Gililland, J.M.; Anderson, M.B.; Peters, C.L. Revision total hip arthroplasty with a modular cementless femoral stem. J. Arthroplast. 2014, 29, 1803–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omlor, G.W.; Kretzer, J.P.; Reinders, J.; Streit, M.R.; Bruckner, T.; Gotterbarm, T.; Aldinger, P.R.; Merle, C. In vivo serum titanium ion levels following modular neck total hip arthroplasty--10 year results in 67 patients. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 6278–6282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, D.A.; Urban, R.M.; Jacobs, J.J.; Gilbert, J.L.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Cooper, H.J. Modern Trunnions Are More Flexible: A Mechanical Analysis of THA Taper Designs. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2014, 472, 3963–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vundelinckx, B.J.; Verhelst, L.A.; De Schepper, J. Taper corrosion in modular hip prostheses: Analysis of serum metal ions in 19 patients. J. Arthroplast. 2013, 28, 1218–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, T.; Burroughs, B.; Kwon, Y.M. Modular hip implant fracture at the stem-sleeve interface. Orthopedics 2015, 38, e234–e239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, J.T.; Garbuz, D.S.; Masri, B.A.; Duncan, C.P. Role and results of tapered fluted modular titanium stems in revision total hip arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. Vol. 2012, 94, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, J.A.; Deshmukh, A.J.; Robinson, J.; Cornell, C.N.; Rasquinha, V.J.; Ranawat, A.S.; Ranawat, C.S. Reproducible fixation with a tapered, fluted, modular, titanium stem in revision hip arthroplasty at 8–15 years follow-up. J. Arthroplast. 2014, 29, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtz, D.C.; Gravius, S.; Ascherl, R.; Thorweihe, M.; Forst, R.; Noeth, U.; Maus, U.M.; Wimmer, M.D.; Zeiler, G.; Deml, M.C. Uncemented femoral revision arthroplasty using a modular tapered, fluted titanium stem: 5- to 16-year results of 163 cases. Acta Orthop. 2014, 85, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Yang, Y.; An, B.; Yang, Y.; Shi, L.; Han, X.; Gao, S. Risk factors for dislocation after revision total hip arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2017, 38, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetters, N.G.; Murray, T.G.; Moric, M.; Sporer, S.M.; Paprosky, W.G.; Della Valle, C.J. Risk factors for dislocation after revision total hip arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2013, 471, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regis, D.; Sandri, A.; Bartolozzi, P. Stem modularity alone is not effective in reducing dislocation rate in hip revision surgery. J. Orthop. Traumatol. Off. J. Ital. Soc. Orthop. Traumatol. 2009, 10, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duwelius, P.J.; Burkhart, B.; Carnahan, C.; Branam, G.; Ko, L.M.; Wu, Y.; Froemke, C.; Wang, L.; Grunkemeier, G. Modular versus nonmodular neck femoral implants in primary total hip arthroplasty: Which is better? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2014, 472, 1240–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, D.J.; Berend, K.R.; Morris, M.J.; Adams, J.B.; Lombardi, A.V., Jr. Results of a Modular Femoral Revision System Before and After Taper Roller Hardening in Total Hip Arthroplasty. Surg. Technol. Int. 2017, 30, 336–340. [Google Scholar]
- Huddleston, J.I., 3rd; Tetreault, M.W.; Yu, M.; Bedair, H.; Hansen, V.J.; Choi, H.R.; Goodman, S.B.; Sporer, S.M.; Della Valle, C.J. Is There a Benefit to Modularity in ‘Simpler’ Femoral Revisions? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2016, 474, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konan, S.; Garbuz, D.S.; Masri, B.A.; Duncan, C.P. Modular tapered titanium stems in revision arthroplasty of the hip: The Risk and Causes of Stem Fracture. Bone Jt. J. 2016, 98-B, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Patients Sex, Age (Year) | Indication # | Stem Configuration * | BMI | Bone Defect | Breakage Po. (Year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m., 82 | ppf | c, 21, 200, lat, long, m | 27 | 3A | 2.8 |
| f., 55 | al | s, 16, 140, lat, short, s | 33 | 2 | 5.4 |
| m., 58 § | al | s, 30, 200, lat, short, s | 44 | 3A | 3.5 |
| m., 47 | ts | c, 16, 200, lat, short, s | 45 | 2 | 5.5 |
| Paprosky | 2 | 3A | 3B | 4 |
| No. of Cases | 32 | 18 | 31 | 8 |
| Group | Survival |
|---|---|
| Overall | 94.2 (95% CI: 88.6–100%) after 13.7 years |
| Lateralized (L) vs. standard neck (S) (log rank test p = 0.0283) | L: 87.4 (95% CI: 75.6–100%) after 13.7 years (n = 4) S: 100% after 13.5 years |
| BMI: overweight > 30 kg/m2 (O) vs. normal weight (N) (log rank test p = 0.0327) | O: 82.9 (95% CI: 64.9–100%) after 11.6 years (3 out of 26) N: 98.4% (95% CI: 95.3–100%) after 13.7 years (1 out of 63) |
| BMI: overweight > 40 kg/m2 (O) vs. normal weight (N) (log rank test p < 0.001) | O: 50.0 (95% CI: 1.0–99.0%) after 8.9 years (2 out of 4) N: 97.0% (95% CI: 92.8–100%) after 13.7 years (2 out of 85) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bischel, O.E.; Suda, A.J.; Böhm, P.M.; Bormann, T.; Jäger, S.; Seeger, J.B. Breakage of Tapered Junctions of Modular Stems in Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty—High Incidence in a Consecutive Series of a Single Institution. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10030341
Bischel OE, Suda AJ, Böhm PM, Bormann T, Jäger S, Seeger JB. Breakage of Tapered Junctions of Modular Stems in Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty—High Incidence in a Consecutive Series of a Single Institution. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(3):341. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10030341
Chicago/Turabian StyleBischel, Oliver E., Arnold J. Suda, Paul M. Böhm, Therese Bormann, Sebastian Jäger, and Jörn B. Seeger. 2023. "Breakage of Tapered Junctions of Modular Stems in Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty—High Incidence in a Consecutive Series of a Single Institution" Bioengineering 10, no. 3: 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10030341
APA StyleBischel, O. E., Suda, A. J., Böhm, P. M., Bormann, T., Jäger, S., & Seeger, J. B. (2023). Breakage of Tapered Junctions of Modular Stems in Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty—High Incidence in a Consecutive Series of a Single Institution. Bioengineering, 10(3), 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10030341







