A Novel and Noninvasive Risk Assessment Score and Its Child-to-Adult Trajectories to Screen Subclinical Renal Damage in Middle Age
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cohorts and Participants
2.2. Anthropometric Measurements
2.3. Blood Pressure Measurements
2.4. Biochemical Parameter Measurements
2.5. Definitions
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
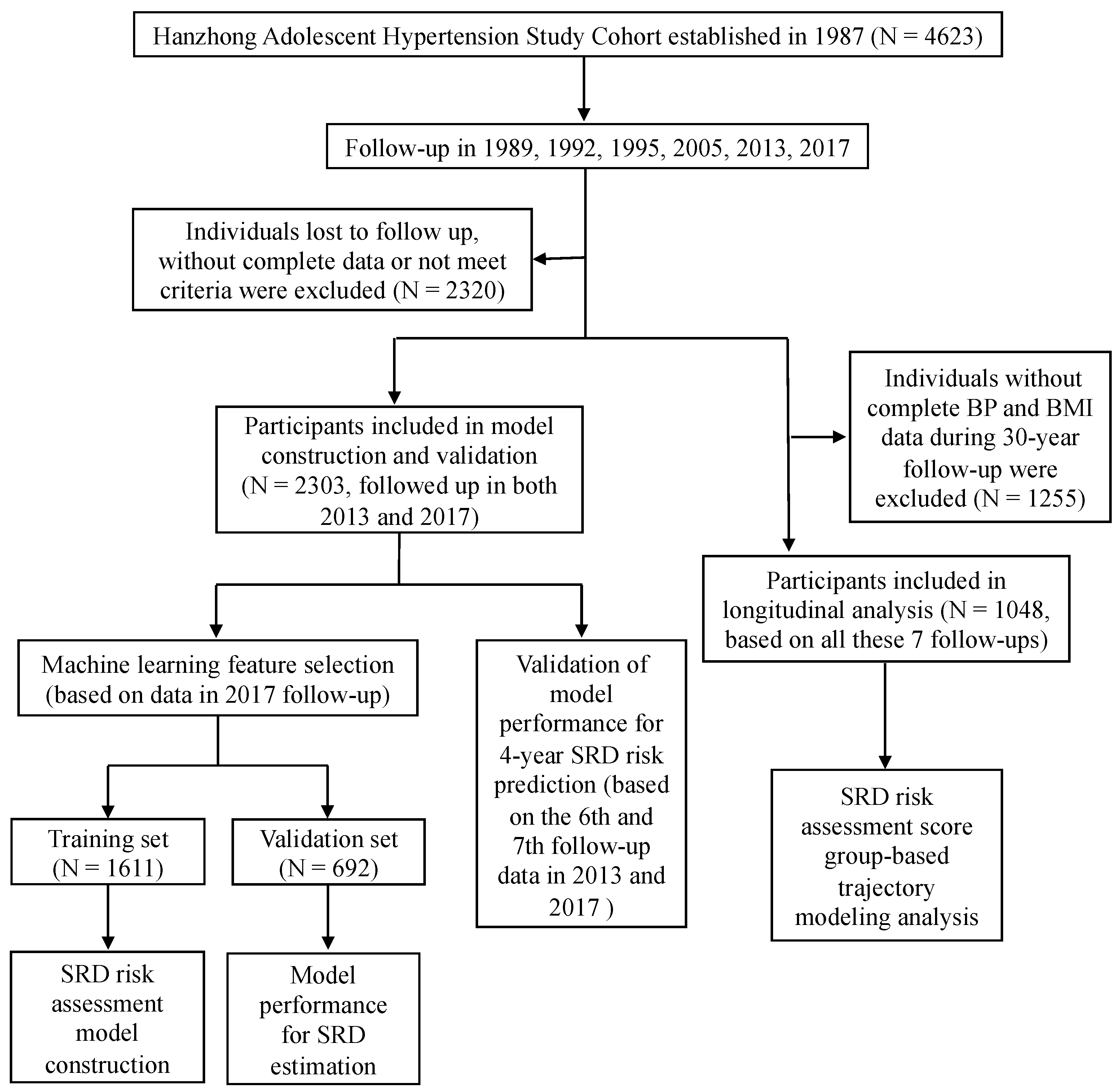
3.1. Study Population
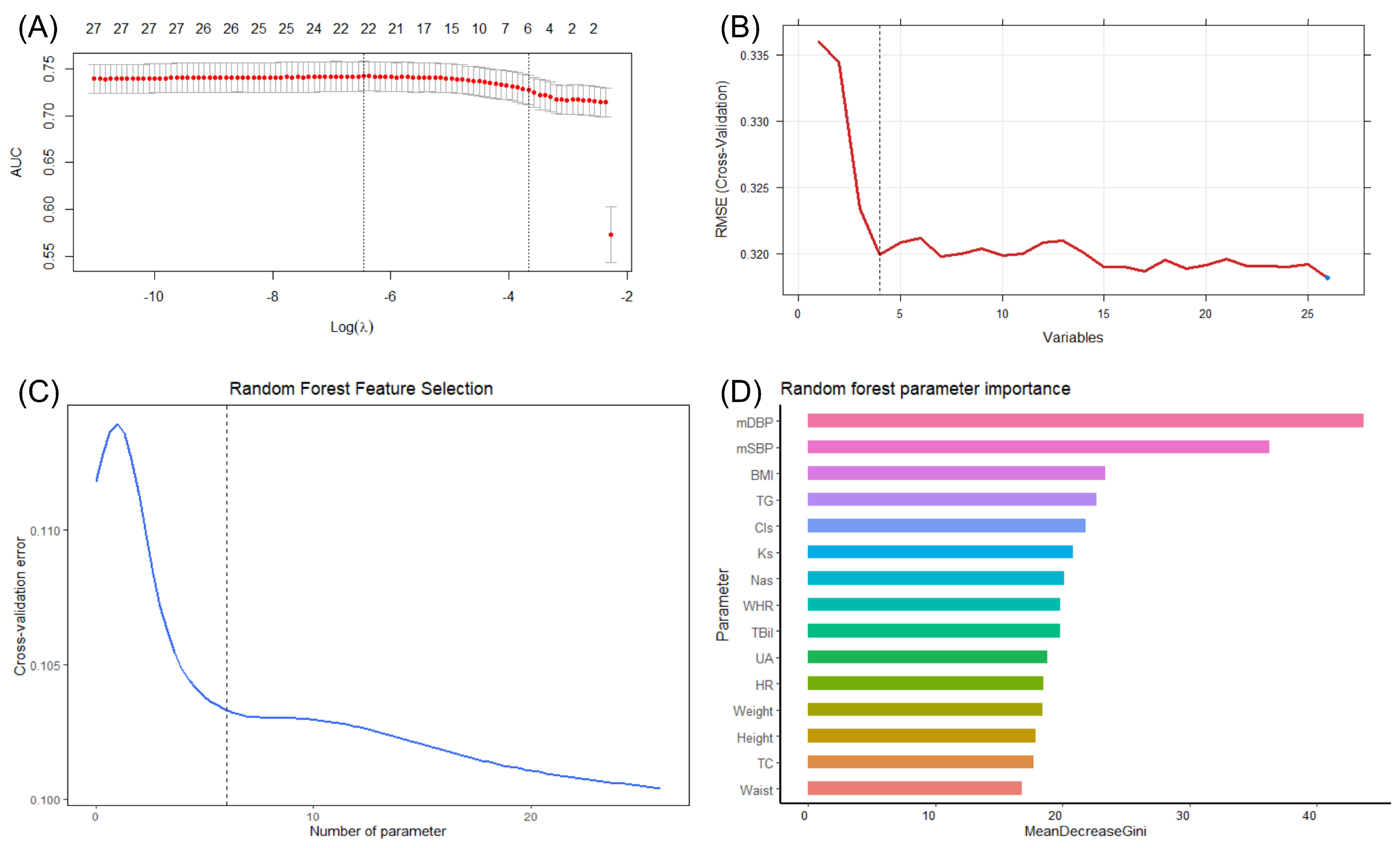
3.2. Feature Selection
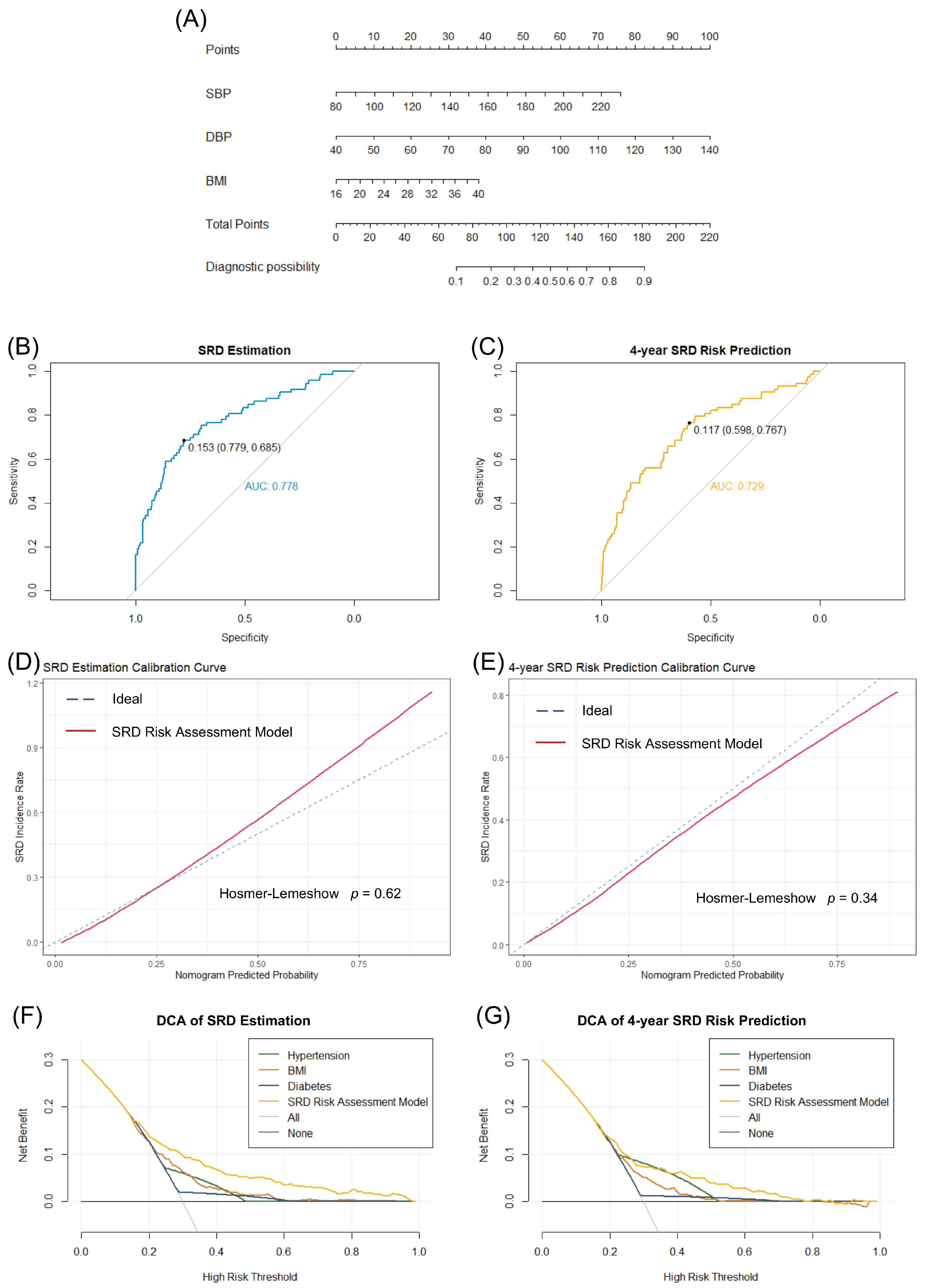
3.3. Construction and Validation of the SRD Risk Assessment Model
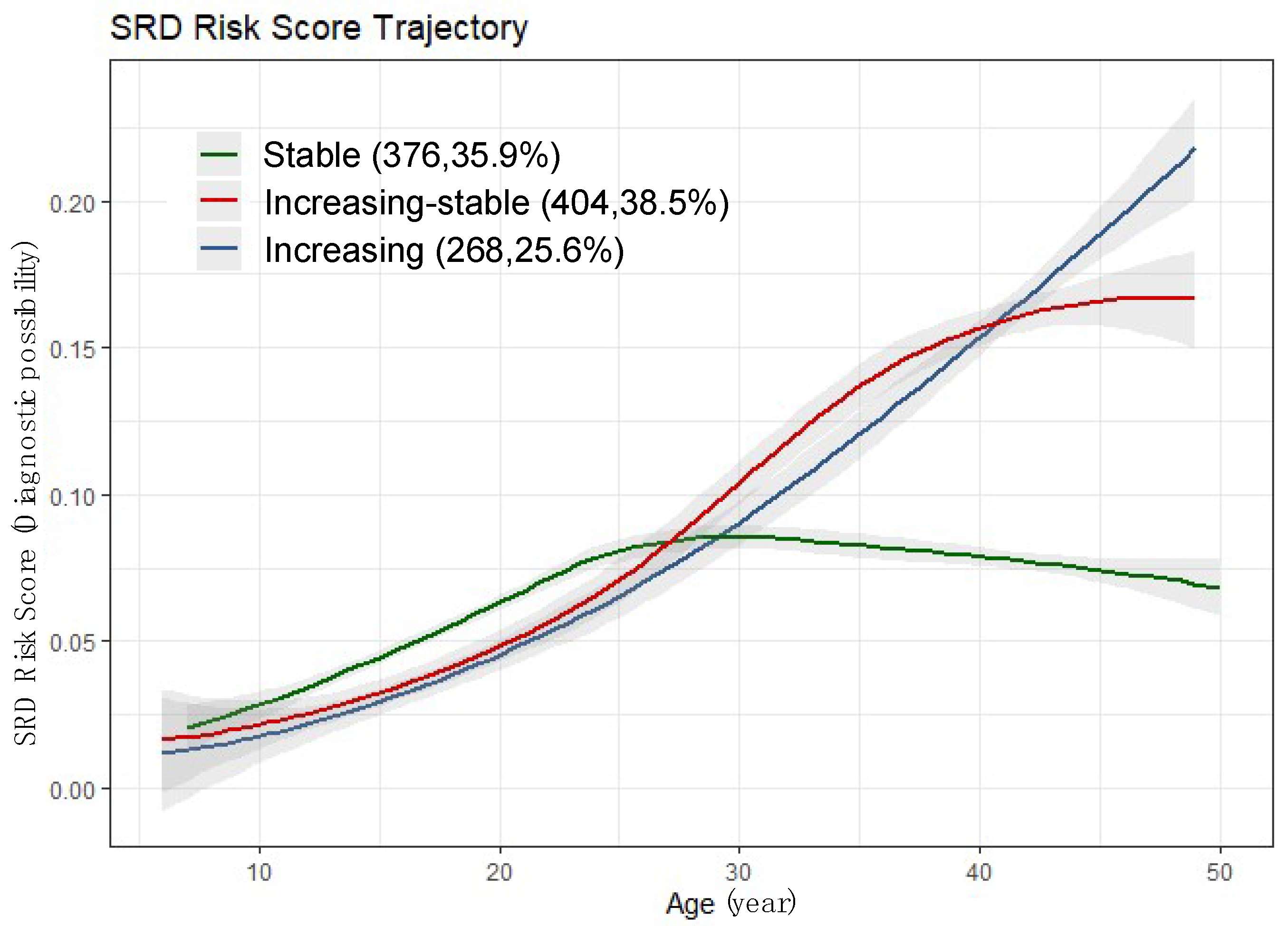
3.4. SRD Risk Score Trajectory
3.5. Cardiovascular Risk Factors for SRD Risk Score Trajectory Groups
3.6. Association between Novel SRD Risk Score Trajectories and Subclinical Renal Damage
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Findings
4.2. Prior Studies and the Focus of our Investigation
4.3. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Inker, L.A.; Astor, B.C.; Fox, C.H.; Isakova, T.; Lash, J.P.; Peralta, C.A.; Kurella Tamura, M.; Feldman, H.I. KDOQI US Commentary on the 2012 KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 63, 713–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; de Jong, P.E.; Coresh, J.; El Nahas, M.; Astor, B.C.; Matsushita, K.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Kasiske, B.L.; Eckardt, K.-U. The definition, classification, and prognosis of chronic kidney disease: A KDIGO Controversies Conference report. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couser, W.G.; Remuzzi, G.; Mendis, S.; Tonelli, M. The contribution of chronic kidney disease to the global burden of major noncommunicable diseases. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1789–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liyanage, T.; Toyama, T.; Hockham, C.; Ninomiya, T.; Perkovic, V.; Woodward, M.; Fukagawa, M.; Matsushita, K.; Praditpornsilpa, K.; Hooi, L.S.; et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in Asia: A systematic review and analysis. BMJ Glob. Health 2022, 7, e007525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, A.C.; Nagler, E.V.; Morton, R.L.; Masson, P. Chronic Kidney Disease. Lancet 2017, 389, 1238–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiss, A.B.; Miyawaki, N.; Moon, J.; Kasselman, L.J.; Voloshyna, I.; D’Avino, R., Jr.; De Leon, J. CKD, arterial calcification, atherosclerosis and bone health: Inter–relationships and controversies. Atherosclerosis 2018, 278, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrador, G.T.; Levin, A. CKD Hotspots: Challenges and Areas of Opportunity. Semin. Nephrol. 2019, 39, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drawz, P.; Rahman, M. Chronic kidney disease. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, ITC1-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballew, S.; Matsushita, K. Cardiovascular Risk Prediction in CKD. Semin. Nephrol. 2018, 38, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaitonde, D.Y.; Cook, D.L.; Rivera, I.M. Chronic Kidney Disease: Detection and Evaluation. Am. Fam. Physician 2017, 96, 776–783. [Google Scholar]
- Mulè, G.; Calcaterra, I.; Costanzo, M.; Geraci, G.; Guarino, L.; Foraci, A.C.; Vario, M.G.; Cerasola, G.; Cottone, S. Relationship Between Short-Term Blood Pressure Variability and Subclinical Renal Damage in Essential Hypertensive Patients. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2015, 17, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zheng, W.; Ma, Q.; Chu, C.; Hu, J.; Wang, K.; Liao, Y.; Chen, C.; Yuan, Y.; Lv, Y.; et al. Child-to-adult body mass index trajectories and the risk of subclinical renal damage in middle age. Int. J. Obes. 2021, 45, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Du, M.-F.; Gao, W.-H.; Fu, B.-W.; Ma, Q.; Yan, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Chu, C.; Chen, C.; Liao, Y.-Y.; et al. Risk factors for subclinical renal damage and its progression: Hanzhong Adolescent Hypertension Study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 75, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Mu, J.; Chu, C.; Hu, J.; Yan, Y.; Ma, Q.; Lv, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; et al. Association of Blood Pressure Trajectories in Early Life with Subclinical Renal Damage in Middle Age. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 2835–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, V.A. Screening for chronic kidney disease: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2012, 157, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.; Stevens, P.E. Early detection of CKD: The benefits, limitations and effects on prognosis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2011, 7, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, P.E.; Levin, A. Evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease: Synopsis of the kidney disease: Improving global outcomes 2012 clinical practice guideline. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Atkins, E.; Lv, J.; Bennett, A.; Neal, B.; Ninomiya, T.; Woodward, M.; MacMahon, S.; Turnbull, F.; Hillis, G.S.; et al. Effects of intensive blood pressure lowering on cardiovascular and renal outcomes: Updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2016, 387, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, H.; Luke, A.; Bidani, A.; Cao, G.; Cooper, R.; McGee, D. Obesity and Prevalent and Incident CKD: The Hypertension Detection and Follow-Up Program. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2005, 46, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivante, A.; Golan, E.; Tzur, D.; Leiba, A.; Tirosh, A.; Skorecki, K.; Calderon-Margalit, R. Body mass index in 1.2 million adolescents and risk for end–stage renal disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 2012, 172, 1644–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, R.G.; Grams, M.E.; Ballew, S.H.; Sang, Y.; Azizi, F.; Chadban, S.J.; Chaker, L.; Dunning, S.C.; Fox, C.; Hirakawa, Y.; et al. Development of Risk Prediction Equations for Incident Chronic Kidney Disease. JAMA 2019, 322, 2104–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, K.-L.; Lin, H.-J.; Lee, B.-C.; Hsu, H.-C.; Lee, Y.-T.; Chen, M.-F. A Prediction Model for the Risk of Incident Chronic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Med. 2010, 123, 836–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerner, B.; Desrochers, S.; Tangri, N. Risk Prediction Models in CKD. Semin. Nephrol. 2017, 37, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagin, D.S.; Jones, B.L.; Passos, V.L.; Tremblay, R.E. Group–based multi–trajectory modeling. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2018, 27, 2015–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Ma, Q.; Liao, Y.; Chen, C.; Hu, J.; Zheng, W.; Chu, C.; Wang, K.; Sun, Y.; Zou, T.; et al. Blood pressure and long-term subclinical cardiovascular outcomes in low-risk young adults: Insights from Hanzhong adolescent hypertension cohort. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2021, 23, 1020–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.; Dai, Y.; Mu, J.; Yang, R.; Wang, M.; Yang, J.; Ren, Y.; Xie, B.; Dong, Z.; Yang, F.; et al. Associations of risk factors in childhood with arterial stiffness 26 years later: The Hanzhong adolescent hypertension cohort. J. Hypertens. 2017, 35 (Suppl. 1), S10–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.-C.; Zuo, L.; Chen, J.-H.; Luo, Q.; Yu, X.-Q.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.-S.; Huang, S.-M.; Wang, L.-N.; Huang, W.; et al. Modified Glomerular Filtration Rate Estimating Equation for Chinese Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 2937–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiffman, S.; Tindle, H.; Li, X.; Scholl, S.; Dunbar, M.; Mitchell-Miland, C. Characteristics and smoking patterns of intermittent smokers. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2012, 20, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, L.X.; Xu, H.X.; Liu, X.Y.; Yang, J.J.; Zhang, P.J.; Zhang, Y.H. Effects of smoking and alcohol consumption on lipid profile in male adults in northwest rural China. Public Health 2018, 157, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.H.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Regularization Paths for Generalized Linear Models via Coordinate Descent. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 33, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, X.; Turck, N.; Hainard, A.; Tiberti, N.; Lisacek, F.; Sanchez, J.-C.; Müller, M. pROC: An open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, M.H.; Sundaram, R.; Robinson, S.L.; Lin, T.C.; Bell, E.M.; Ghassabian, A.; Yeung, E.H. Association of Trajectory and Covariates of Children’s Screen Media Time. JAMA Pediatr. 2020, 174, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.K.; Knicely, D.H.; Grams, M.E. Chronic Kidney Disease Diagnosis and Management: A Review. JAMA 2019, 322, 1294–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teasdale, E.J.; Leydon, G.; Fraser, S.; Roderick, P.; Taal, M.W.; Tonkin-Crine, S. Patients’ Experiences After CKD Diagnosis: A Meta-ethnographic Study and Systematic Review. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 70, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClellan, W.M.; Ramirez, S.P.B.; Jurkovitz, C. Screening for Chronic Kidney Disease: Unresolved Issues. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, S81–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, M.A.; Griffith, D.M.; Thorpe, R.J.J. Stress and the kidney. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2015, 22, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronenberg, F. Emerging risk factors and markers of chronic kidney disease progression. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2009, 5, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallan, S.; de Mutsert, R.; Carlsen, S.; Dekker, F.W.; Aasarød, K.; Holmen, J. Obesity, smoking, and physical inactivity as risk factors for CKD: Are men more vulnerable? Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2006, 47, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson, M.; Maher, G.; Boland, F.; Fitzgerald, A.P.; Murray, D.M.; Biesma, R. Group-based trajectory modelling for BMI trajectories in childhood: A systematic review. Obes. Rev. 2019, 20, 998–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagin, D.S.; Odgers, C.L. Group-Based Trajectory Modeling in Clinical Research. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2010, 6, 109–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagura, J.; Adair, L.S.; Munthali, R.J.; Pettifor, J.M.; Norris, S. Association Between Early Life Growth and Blood Pressure Trajectories in Black South African Children. Hypertension 2016, 68, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Total | Training Set | Internal Validation Set | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBP (mmHg) | 121.3 (112.7–131.3) | 121.7 (113.0–131.3) | 120.8 (112.0–131.3) | 0.363 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 76.0 (69.3–84.3) | 76.3 (70.0–84.3) | 75.3 (68.3–84.7) | 0.096 |
| BMI (kg/cm2) | 23.8 (21.9–26.0) | 23.8 (21.9–26.2) | 23.8 (21.9–25.6) | 0.397 |
| eGFR (mL/min per 1.73 m2) | 96.9 (87.1–106.1) | 96.5 (86.8–105.8) | 98.2 (88.0–106.6) | 0.096 |
| uACR (mg/mmol) | 0.95 (0.62–1.68) | 0.95 (0.62–1.69) | 0.96 (0.63–1.65) | 0.939 |
| SRD (n, %) | 276 (13.2) | 203 (13.9) | 73 (11.7) | 0.177 |
| Total | Stable | Increasing-Stable | Increasing | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male (%) | 583 | 169 (45.1) | 258 (63.7) | 156 (58.2) | <0.001 |
| Age (years) | 43.0 (41.0–46.0) | 43.0 (41.0–46.0) | 43.0 (40.0–45.0) | 43.0 (41.0–45.0) | 0.049 |
| Occupation (%) | 1011 | 0.383 | |||
| Farmer | 408 | 146 (40.1) | 157 (40.3) | 105 (40.9) | |
| Worker | 194 | 63 (17.3) | 82 (21.0) | 49 (19.1) | |
| Business | 81 | 35 (9.6) | 30 (7.7) | 16 (6.2) | |
| Governor | 21 | 5 (1.4) | 13 (3.4) | 3 (1.2) | |
| Other | 307 | 115 (31.6) | 108 (27.7) | 84 (32.7) | |
| Marital status (%) | 1041 | 0.064 | |||
| Unmarried or other | 15 | 4 (1.1) | 8 (2.1) | 3 (1.2) | |
| Married | 1015 | 365 (97.1) | 387 (97.0) | 263 (98.9) | |
| Divorced | 11 | 7 (1.9) | 4 (1.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Education (%) | 1016 | 0.553 | |||
| Primary school or less | 73 | 24 (6.6) | 27 (6.9) | 22 (18.7) | |
| Middle school | 628 | 221 (60.5) | 240 (61.2) | 167 (64.5) | |
| High school | 226 | 82 (22.5) | 92 (23.5) | 52 (20.1) | |
| College or more | 89 | 38 (10.4) | 33 (8.4) | 18 (6.9) | |
| Current smoking (%) | 450 | 126 (34.8) | 200 (51.9) | 124 (49.2) | <0.001 |
| Alcohol consumption (%) | 321 | 96 (26.5) | 141 (36.6) | 84 (33.3) | 0.011 |
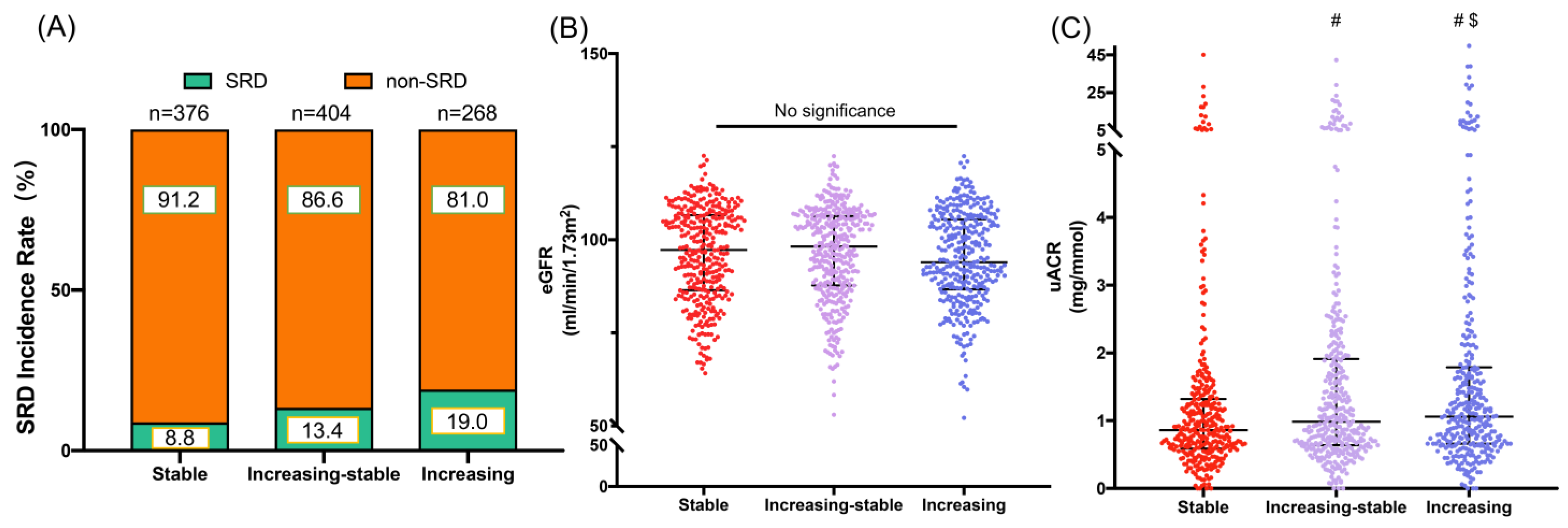
| SRD (%) | 138 | 33 (8.8) | 54 (13.4) | 51 (19.0) | 0.001 |
| AS (%) | 139 | 48 (12.9) | 55 (13.9) | 36 (13.7) | 0.922 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 424 | 119 (31.6) | 170 (42.1) | 135 (50.4) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 172 | 10 (2.7) | 65 (16.1) | 97 (36.2) | <0.001 |
| Heart rate 1987 (beats/min) | 78.0 (72.0–84.0) | 78.0 (72.0–84.0) | 78.0 (72.0–84.0) | 78.0 (72.0–84.0) | 0.983 |
| Heart rate 2017 (beats/min) | 73.0 (66.0–80.0) | 72.5 (66.0–79.0) | 73.0 (66.0–80.0) | 75.0 (69.0–82.0) | 0.072 |
| Waist (cm) | 84.8 (78.2–92.2) | 80.8 (75.5–87.2) | 87.0 (79.7–94.3) | 89.4 (82.4–95.5) | <0.001 |
| Hips (cm) | 92.2 (88.8–95.9) | 90.7 (87.7–93.4) | 93.4 (89.5–97.0) | 93.7 (90.4–97.0) | <0.001 |
| TC (mmol/L) | 4.48 (4.03–5.00) | 4.40 (3.92–4.87) | 4.49 (4.02–5.08) | 4.58 (4.17–5.18) | 0.001 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 1.39 (1.01–2.01) | 1.20 (0.89–1.66) | 1.44 (1.08–2.03) | 1.64 (1.13–2.44) | <0.001 |
| LDL–C (mmol/L) | 2.49 (2.11–2.88) | 2.44 (2.05–2.78) | 2.48 (2.13–2.95) | 2.55 (2.22–3.00) | 0.006 |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 1.13 (0.99–1.33) | 1.20 (1.02–1.42) | 1.12 (0.98–1.29) | 1.09 (0.95–1.29) | <0.001 |
| Serum uric acid (μmol/L) | 283.2 (226.2–338.8) | 264.9 (212.5–316.8) | 300.7 (239.7–352.6) | 293.8 (243.3–352.2) | <0.001 |
| Urine uric acid (μmol/L) | 1298.5 (914.8–1984.5) | 1291.5 (897.5–1994.5) | 1317.0 (981.5–1951.0) | 1283.0 (889.0–2090.0) | 0.268 |
| Serum creatinine (μmol/L) | 76.3 (66.7–86.8) | 73.7 (65.3–82.9) | 78.8 (68.6–88.8) | 77.0 (69.7–88.0) | <0.001 |
| Urine albumin (mg/L) | 8.0 (4.1–13.7) | 6.4 (3.1–11.1) | 9.0 (4.8–14.2) | 9.2 (5.2–22.5) | <0.001 |
| eGFR (mL/min per 1.73 m2) | 97.2 (87.0–106.3) | 97.2 (86.2–107.0) | 97.7 (87.1–106.3) | 94.3 (85.9–106.0) | 0.260 |
| uACR (mg/mmol) | 0.98 (0.64–1.72) | 0.85 (0.57–1.33) | 0.99 (0.64–1.96) | 1.25 (0.74–2.34) | <0.001 |
| Trajectory Groups | No. of Subjects with SRD in 2017 | Unadjusted | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stable | 33 (8.8) | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Increasing-stable | 54 (13.4) | 1.60 (1.01–2.54) | 1.53 (0.96–2.43) | 1.25 (0.77–2.05) | 1.24 (0.76–2.03) |
| Increasing | 51 (19.0) | 2.44 (1.53–3.91) | 2.39 (1.49–3.84) | 1.75 (1.05–2.91) | 1.73 (1.04–2.89) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.; Liu, G.; Chu, C.; Zheng, W.; Ma, Q.; Liao, Y.; Yan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, D.; Mu, J. A Novel and Noninvasive Risk Assessment Score and Its Child-to-Adult Trajectories to Screen Subclinical Renal Damage in Middle Age. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10020257
Chen C, Liu G, Chu C, Zheng W, Ma Q, Liao Y, Yan Y, Sun Y, Wang D, Mu J. A Novel and Noninvasive Risk Assessment Score and Its Child-to-Adult Trajectories to Screen Subclinical Renal Damage in Middle Age. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(2):257. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10020257
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Chen, Guanzhi Liu, Chao Chu, Wenling Zheng, Qiong Ma, Yueyuan Liao, Yu Yan, Yue Sun, Dan Wang, and Jianjun Mu. 2023. "A Novel and Noninvasive Risk Assessment Score and Its Child-to-Adult Trajectories to Screen Subclinical Renal Damage in Middle Age" Bioengineering 10, no. 2: 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10020257
APA StyleChen, C., Liu, G., Chu, C., Zheng, W., Ma, Q., Liao, Y., Yan, Y., Sun, Y., Wang, D., & Mu, J. (2023). A Novel and Noninvasive Risk Assessment Score and Its Child-to-Adult Trajectories to Screen Subclinical Renal Damage in Middle Age. Bioengineering, 10(2), 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10020257








